Showing 8 items
matching conservation, themes: 'built environment','creative life','gold rush','immigrants and emigrants'
-
Viewbank: Unearthing a Colonial Homestead
... conservation...Audio: 1697 Coin - Conservation...This selection of audio interviews with an archaeologist, an historian and a conservator, discusses the Viewbank excavation in some detail, including the artefacts found there and the conservation process at the Heritage Victoria conservation...Heritage Victoria’s Conservator Susanna Collis explains the archaeological and conservation processes involved in conserving the dinnerware unearthed at Viewbank Homestead.... and a conservator. They discuss the Viewbank excavation, describe the artefacts found there and explain the process of their conservation at the Heritage Victoria conservation laboratory. The Viewbank Homestead is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. For more ...Viewbank Homestead was one of the first grand homesteads built on the outskirts of Melbourne. Built around 1840, Viewbank was located near the junction of the Yarra and Plenty Rivers in Heidelberg.
The homestead was built in two phases. Originally a four room house, it was renovated and expanded in the 1850s and 1860s after it was acquired by wealthy squatter Dr Robert Martin.
Viewbank was destroyed by a professional demolition team in the early 1920s, long after the Martin family moved away from the area. By then, the house had fallen into disrepair and locals believed that it was haunted. For most of the 20th century, cattle grazed over the ruins and knowledge of the former grand homestead slipped from public knowledge until archaeologists returned to the site to unlock its secrets.
Between 1996 and 1999, Heritage Victoria conducted three excavations at the site with help from archaeologists from Melbourne, La Trobe and Flinders Universities, and more than 140 archaeology students and community members.
The archaeologists uncovered the stone foundations of the house and remnants of hand-made brick walls, fireplaces and other features. A range of artefacts were found during the excavation including children’s toys, coins, gaming tokens, thimbles and pins. A network of servant’s bells, fragments of marble fireplaces, and pieces of richly decorated plaster cornices reflect the affluence of the Martin family.
This story is made up of audio interviews with an archaeologist, an historian and a conservator. They discuss the Viewbank excavation, describe the artefacts found there and explain the process of their conservation at the Heritage Victoria conservation laboratory.
The Viewbank Homestead is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. For more information on the Viewbank or other heritage sites visit The Victorian Heritage Database.
-

Hubcaps to Creative Hubs
... conservation... conservation”, working with the buildings’ industrial patina and fine-grained details. The mill now hosts a creative community that draws uniquely from the large spaces and mazy corners, with secrets waiting to be unearthed. Watch the trailer for a quick taste ...The project aims to tell the stories of Geelong’s industrial sites undergoing transformation, pointing to a new creative and maker culture that connects the past with the present.
The Returned Soldier & Sailors Woollen and Worsted Mills in Rutland Street Newtown, the Federal Woollen Mills in North Geelong and the Old Paper Mills in Fyansford are all in the process of becoming new creative spaces.
Part One explores how a once-overlooked industrial site the Returned Soldiers and Serviceman’s Mills (RS&S) has become the hub for a remarkable network of artists and creative makers...and if you listen closely, you might hear sounds of the past reverberating in the building’s walls.
Part Two tells the story of the recent reinvention of the Federal Woollen Mills into a tech and creative start-up hub which marks Geelong’s 21st century pivot from industrial decline to rising creative city.
Part Three explores the Fyansford Paper Mills’ salvage and restoration, a remarkable process of “creative conservation”, working with the buildings’ industrial patina and fine-grained details. The mill now hosts a creative community that draws uniquely from the large spaces and mazy corners, with secrets waiting to be unearthed.
Watch the trailer for a quick taste of the project or enjoy the full three part documentary to learn about the transformation of these places. You can also read about how these films were supported by community grants and the people and businesses of Geelong.
‘Hubcaps to Creative Hubs’ is a creative research project by Dr Fiona Gray from Deakin University, Dr Cristina Garduño Freeman from the Australian Centre for Architectural History and Cultural Heritage at the University of Melbourne, in collaboration with industry partners Jennifer Cromarty and Helen Kostiuk of Creative Geelong Inc. The films have been made by documentary producer Nicholas Searle.
-
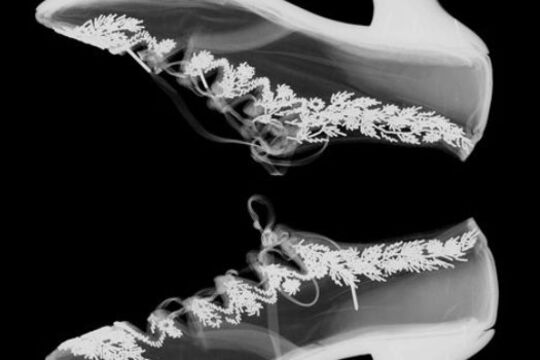
The Fashion Detective
... conservation... and material composition, and condition. Using x-ray techniques can help confirm how an object was made and what it is made of, evidence that is highly valuable in determining an object’s age as well as its current or future conservation needs. ...The NGV’s fashion archive contains countless works about which we know little.
We don’t know who made them, who wore them, when or why, or indeed, what happened in them! For the curator, such works are endlessly intriguing; a form of ‘material evidence’ to examine and explicate.
In 2014, the NGV’s Fashion Detective exhibition took a selection of unattributed nineteenth century garments and accessories from the Australian fashion and textiles collection as the starting point for a series of investigations. Using forensics and fiction as alternate interpretative methods, the exhibition considered the detective work that curators and conservators do and where this can lead, as well as the role of storytelling in making visible the social life of clothes.
From fakes and forgeries to poisonous dyes, concealed clues and mysterious marks to missing persons, Fashion Detective was a series of ‘cases’ that each followed a different path of analysis.
Some relied on empirical study and science to reach conclusions, others were purposefully speculative - the inspired hypothesis of leading crime writers Garry Disher, Kerry Greenwood, Sulari Gentill and Lili Wilkinson.
A playful exhibition about modes of enquiry, Fashion Detective considered the different ways in which we can decode objects in order to reveal what is normally concealed, and challenged the visitor to reappraise what they see and what they know.
-

Rippon Lea Estate
... conservation... conservation history as a property saved specifically for its historic gardens. Single-handedly, Louisa Jones fought the full might of the Commonwealth government, after it had compulsorily purchased 4.1 acres to extend the broadcasting facilities of the ABC ..."Do you remember the garden in which you grew up, or the part the backyard played in your family life? Imagine if you had actually grown up in one of Australia's finest gardens.
Created in the English-landscape tradition which traces its roots back to Capability Brown and Humphry Repton, Rippon Lea is one of Australia's most important historic homes, exemplifying the lifestyle of wealthy families living in 19th and 20th century Australian cities. Although its architecture and that of its outbuildings is impressive, it is the mansion’s gardens, which are truly remarkable, both for their landscape qualities and because they have survived many threats and changes in the past 130 years.
Today, the amenities offered by a typical garden are still greatly valued: a safe place for children to play, somewhere to dry the washing, a plot for vegetables and a flower garden that adds colour and produces blooms for the home. Today as then, the scale differs but the experience of owning a garden - with its balance of utility and ornament - is essentially the same.
The National Trust of Australia (Victoria) now runs Rippon Lea as a museum, conserving the architecture and the landscape, and presenting the social history of the owners and their servants. Visitors to Rippon Lea enter a mansion preserved as the Jones family lived in it after their 1938 modernisation. In the pleasure garden the Sargood era is evoked by the staging of a range of performing arts events including opera, theatre, chamber music and outdoor activities."
The text above has been abstracted from an essay Solid Joys and Lasting Treasure: families and gardens written by Richard Heathcote for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Restoring "Shearing the Rams"
... conservation ...John Payne and Michael Varcoe-Cocks, conservators at the National Gallery of Victoria, explain how the restoration process for 'Shearing the Rams' by Tom Roberts began, with an x-ray of the iconic painting.
-
 Danielle Whitfield
Danielle WhitfieldGetting it Right
... conservation ...There is a great deal of effort that goes into preparing a museum garment for display which the public never sees. This is especially true for historical items.
Most obviously, there is the core work that our textile conservators do examining and treating works so that they are safe to exhibit. Equally vital is the task of creating the appropriate underpinnings and padded supports which ensure a garment has a historically accurate silhouette, and that the fragile fabrics are supported during display.
During the nineteenth century a lot went on beneath women’s gowns. Victorian fashion relied on a variety of contrivances to generate form; corsets compressed the waist, petticoats, crinolines and later cage-crinolines made skirts wider and fuller, while bustles produced a cantilevered behind. Working in tandem with the garment, these structures performed both functional and aesthetic roles.
-

Collingwood Technical School
... art conservation ...For over 140 years, the site of the former Collingwood Technical School on Johnston Street, Melbourne, has played an integral role in the well being of the local community.
It has been a civic hub, including courthouse (1853), Council Chambers (1860) and the Collingwood Artisans’ School of Design (1871). The school opened in 1912 when its first principal, Matthew Richmond, rang a bell on the street to attract new students. Collingwood was a poor and industrial suburb, and as a trade school, young boys were offered the opportunity to gain industrial employment skills.
Throughout the twentieth century, Collingwood Technical School supported the local and broader community. From training schemes for ex-servicemen who were suffering from post traumatic stress following World War I (1914-1918), to extra classes during the Great Depression, and the development of chrome and electroplating for machine parts for the Australian Army and Air Force during World War II (1939-1945).
The precinct between Johnston, Perry and Wellington Streets has transformed over time, including expansion with new buildings and school departments, and the change in the demographic of students as Collingwood evolved from an industrial centre to eventual gentrification. And in 1984, New York street artist, Keith Haring (1958-1990), painted a large mural onsite.
Collingwood Technical College closed in 1987 when it amalgamated with the Preston TAFE (Technical and Further Education) campus. Education classes continued until 2005 and the site sat empty for more than a decade, before a section was redeveloped for Circus Oz in 2013.
The former school now has a new identity as Collingwood Arts Precinct, and is being developed into an independent space for small and medium creative organisations. The heritage buildings will house the next generation of thinkers and makers, and will become a permanent home to the arts in Collingwood. -
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
