Showing 45 items
matching live%20performance, themes: 'a diverse state','built environment','immigrants and emigrants','local stories'
-

The Palais Theatre
... live music venues... their first date there. Ask them about the Palais and watch them smile. The theatre is underwent restoration in 2016-17, which preserved the heritage value of the site and ensured the Palais remains a live performance venue and cultural icon in St Kilda ...It’s impossible for Melburnians to think about the St Kilda Esplanade without visualising the Palais Theatre standing majestically against Port Phillip Bay. Its grand Art Deco façade is as iconic to St Kilda as the Pavilion on the nearby pier, Acland Street or the theatre’s "just for fun" neighbour, Luna Park.
It’s surprising to discover, then, that the Palais wasn’t always regarded with such affection. When the original building – a dance hall called the Palais de Danse – was being constructed in 1913, over 800 locals attended a public meeting to protest it being given a license. They voiced fears that it would lower the tone of St Kilda, “have a demoralising effect on young people", and be "common with a big C”. The battle was won by the building owners, the three Phillips brothers (American immigrants who also built Luna Park), and an entertainment venue has stood on the site ever since.
The Palais Theatre is a magical place for Melburnians. It’s where generations of us have danced cheek to cheek, watched movies in the darkness, screamed lustily at the Rolling Stones, thrown roses at the feet of Margot Fonteyn and Rudolph Nureyev, and given standing ovations to Dame Joan Hammond’s awe-inspiring soprano. Your grandparents probably had their first date there. Ask them about the Palais and watch them smile.
The theatre is underwent restoration in 2016-17, which preserved the heritage value of the site and ensured the Palais remains a live performance venue and cultural icon in St Kilda for many generations to come. The restoration was funded by the State Government of Victoria and the City of Port Phillip.
-

Sound in Space
... live performance... to relate its narratives. In 2006 the reading room was used as an intimate performing space for the mixture of visual and auditory, western and non-western, electronic and live materials of painter-composer Catherine Schieve. For 30 years, the concerts... the concert at the Special Exhibitions Gallery, Scienceworks, Spotswood on Saturday November 7, 1992. Astra in association with the La Trobe University Music Department: with invented percussion, live electronics, voices. Performers including: Michael Hewes ...Music always interacts with the architecture in which it is heard.
Melbourne has some wonderful acoustic environments. Often, these spaces were built for other purposes – for example the splendid public and ecclesiastical buildings from the first 100 years of the city’s history, and more recent industrial constructions.
Exploiting ‘non-customized’ spaces for musical performance celebrates and explores our architectural heritage.
For 30 years, the concerts of Astra Chamber Music Society have ranged around Melbourne’s architectural environment. Each concert has had a site-specific design that takes advantage of the marvellous visual qualities, spatial possibilities, and acoustic personality of each building.
The music, in turn, contributes a new quality to the perception of the buildings, now experienced by audiences as a sounding space - an area where cultural issues from music’s history are traversed, and new ideas in Australian composition are explored.
In this story take a tour of some of Melbourne’s intimate, hidden spaces and listen to the music that has filled their walls.
For further information about Astra Chamber Music Society click here.
-

Victorian Jazz Stories
... Live music ...Victoria has always had a thriving jazz scene. For the best part of a century, jazz musicians young and old have enthralled audiences and pushed their artistic practice to the limits in Victoria and beyond.
What is it that makes Victoria a jazz hub and who are the people that have contributed to it over the years, from Georgia Lee to Graeme Bell's Czechoslovak Journey to Julia Messenger?
The Australian Jazz Museum has the largest collection of Australian jazz related materials in the country. Through the objects in this vast collection and the organisation's connection to the jazz scene both past and present, audiences are transported into the cool, humble and underground world of Victorian jazz.
-

Kylie's Costumes
... Costume: Intimate and Live tour [Australia and London], 1998 (1) ...From Neighbours character, Charlene, to international pop sensation, Kylie Minogue’s costumes chart her rise, her style, and her creative energy.
The Kylie Costume Collection at the Arts Centre, Melbourne, shows the range and development of Kylie's persona through costume, and her collaborations with international and national designers.
As Kylie donates her costumes to the Arts Centre directly, curators are able to keep an extensive, chronological and very complete material record of Kylie's career, across her tours, album cover shoots, music videos, and red carpet and special events.
-
 Jary Nemo and Lucinda Horrocks
Jary Nemo and Lucinda HorrocksCollections & Climate Change
... Victoria has a wealth of living collections that not only showcase the unique geology and biodiversity of the state but act as live indicators of the shifts we are seeing with climate change.... of habitats (i.e. a common species). This is important because almost all native plants growing in Australia’s mountain regions are endemic, meaning they aren’t found elsewhere. Many live in highly specialised habitats such as sphagnum bogs, tussock grassland...The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before. Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans ...The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before.
Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans, is having an impact on a global scale. In particular, human activity has altered the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the world’s climate to change.
Already in the state of Victoria we are seeing evidence of this change around us. In the natural world, coastal waters are warming and bringing tropical marine species to our bays. Desert animals are migrating to Victoria. Alpine winters are changing, potentially putting plants and animals at risk of starvation and pushing species closer to the margins. In the world of humans, island and coastal dwellers deal with the tangible and intangible impacts of loss as sea levels rise, bush dwellers live with an increased risk of life-threatening fires, farmers cope with the new normal of longer droughts, and we all face extreme weather events and the impacts of social and economic change.
This Collections and Climate Change digital story explores how Victoria’s scientific and cultural collections help us understand climate change. It focuses on three Victorian institutions - Museums Victoria, the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria and Parks Victoria. It looks at how the information gathered and maintained by a dedicated community of researchers, curators, scientists, specialists and volunteers can help us understand and prepare for a hotter, drier, more inundated world.
The story is made up of a short documentary film and twenty-one examples highlighting how botanical records, geological and biological specimens and living flora and fauna provide a crucial resource for scientists striving to map continuity, variability and change in the natural world. And it helps us rethink the significance of some of Victoria’s cultural collections in the face of a changing climate.
-

Chinese Australian Families
... of Chinese lived in a city or a town, there would be one or more shops run by members of each of the clans. They sold Chinese goods imported from canton or Hong Kong, and were patronised by the other members of the clan. There was usually room for a few... sojourning, a small proportion of Chinese men in nineteenth-century Australia brought their wives and children to live with them, or married here. As Australian-born children of these families grew to adulthood, their parents would seek brides and grooms ...Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history
From the 1840s onwards, Chinese people have come to Australia inspired by dreams of happiness, longevity and prosperity - of 'jade and gold' in a new and strange land. For most of that time, Chinese people in Australia have been predominantly male. Most of them were temporary sojourners who came to earn money for their families back in the village - most did not intend to settle in Australia.
Despite the predominance of male sojourning, a small proportion of Chinese men in nineteenth-century Australia brought their wives and children to live with them, or married here. As Australian-born children of these families grew to adulthood, their parents would seek brides and grooms on their behalf amongst other Chinese families in Australia.
The majority of post-1905 Chinese brides of Chinese-Australian sons were never able to settle here. Some children were born in China or Hong Kong. Some were born in Australia. Families like this were split for decades, until immigration laws were relaxed.
In the nineteenth century, many of the Chinese men who wanted wives in Australia married or lived de facto with non-Chinese women. At least 500 European-Chinese partnerships are estimated to have occurred before 1900.
Despite repeated waves of racism and official discrimination from the 1840s to the 1970s, a sizeable number of families of Chinese background have put down roots in this country.
In 1973 the Whitlam government abolished racist provisions in immigration laws. Since then, the number of ethnic Chinese migrants has increased dramatically. They have come primarily as family groups - not as sojourners, but as permanent immigrants. They come not only from China and Hong Kong, but also from Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Cambodia and Indonesia, as well as from further afield. The Chinese are now a highly visible and generally accepted part of the Australian community of cultures.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay 'Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history' written by Paul Macgregor for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The full text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Melbourne's Homes
... These house plans from the late 19th and early 20th Centuries, give us an indication of how those with the means to build larger houses lived. Servant's quarters, groom's rooms, sculleries, stables, parlours and children's areas give us clues ...These house plans from the late 19th and early 20th Centuries, give us an indication of how those with the means to build larger houses lived.
Servant's quarters, groom's rooms, sculleries, stables, parlours and children's areas give us clues to social attitudes, relationships to children and employees, social mores and living conditions.
-

William Buckley
... to be a reincarnation of a Wathaurang leader, who was also very tall. Over the next 32 years Buckley lived with the Wathaurang, learnt their language and customs, married and had a daughter. When Batman’s colonising party arrived in 1835, Buckley finally emerged... for weeks before he was befriended by the Wathaurang people. Over the next 32 years Buckley lived with the Wathaurang, learnt their language and customs, married and had a daughter. In 1835 he finally emerged to meet Batman’s colonising party and tried ...After convict William Buckley’s escape from a Victorian settlement he was discovered by the Wathaurang people who thought this pale, 198cm giant carrying a spear was the ghost of one of their leaders.
Buckley had arrived at Port Phillip from England in 1803 with about 300 soldiers, settlers and convicts after being sentenced to transportation for life. Before the Port Phillip and Sullivan Bay (Victoria’s first official European settlement) settlement was abandoned, Buckley escaped. He wandered alone for weeks before he was befriended by the Wathaurang people.
Over the next 32 years Buckley lived with the Wathaurang, learnt their language and customs, married and had a daughter. In 1835 he finally emerged to meet Batman’s colonising party and tried to work as an intermediary between settlers and aborigines, but felt he wasn’t trusted by either.
His name lives on in Australian slang with the ironic saying “you’ve got Buckley’s chance” or “Buckley’s hope”.
Further material can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site:-
William Buckley's Escape
Buckley and the Aborigines
Buckley's return to European life
-

A Sensory Experience
... and unremarkable to see deaf people with hearing aids and cochlear implants. This sounds as if hearing people and deaf people are exclusive and separate from each other. However, there is and always has been co-mingling. Deaf people live, work and socialise... their lived experiences. Finally, the story contains an education kit for secondary students, which allows for a deeper study and understanding. ...The mainstream understanding of deaf and blind people has shifted over time. When once it was thought that blind people should be taken care of and sheltered, or deaf people taught to hear and speak, a deeper awareness of distinct culture and experience has emerged.
'A Sensory Experience' explores the world through the eyes and ears of the deaf and blind communities in Victoria and seeks to demystify some of the stereotypes and preconceptions that survive to this day.
The four films that make up part of this story highlight Victoria’s Deaf and blind communities within an historical framework, fostering new insights and provoking thought about the way we understand these communities today. Each film is an open invitation to share the experience of the world from another perspective.
The accompanying images complement the films, giving further understanding to the rich history held within the two groups. In addition, two contemporary essays by prominent writers offer the unique opportunity to share their lived experiences. Finally, the story contains an education kit for secondary students, which allows for a deeper study and understanding.
-

Digital Stories of the Land
... provide a way for understanding place on its own terms and often those terms can be challenging; drought bushfires and isolation for those who live on the land. People across Victoria have shared stories as part of this ACMI collection capturing ...Stories of the Land is a collection produced as part of the Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) digital storytelling program.
These stories explore the land as a thread that connects people to their surroundings. The personal narratives provide a way for understanding place on its own terms and often those terms can be challenging; drought bushfires and isolation for those who live on the land.
People across Victoria have shared stories as part of this ACMI collection capturing the essence of the land as a setting to their lives inextricably linked to the experiences and events that have shaped them.
-

Como House and the Armytage Family
... interested when he found out that it would be a mortgagee's auction. He and his wife Caroline lived with their eight children at Fulham Station, a large sheep holding just outside Geelong. The combination of their hard work in the country and Charles.... Their daughters Leila, Constance, and Laura lived on at Como and left an indelible impression there. The last surviving children of Charles and Caroline - Constance and Leila - sold Como to The National Trust of (Vic) in 1959. Como was the first house acquired ...The Armytage family owned Como House in South Yarra for nearly 95 years. The property was managed by the women of the family for more than seventy years from 1876 to 1959. The history of the Armytage family, and the families who worked for them, provides an insight into almost a century of life on a large estate.
Como was purchased in 1864 by Charles Henry Armytage and it became the home of Charles, his wife Caroline, and their ten children. Charles died in 1876 and Caroline in 1909. Their daughters Leila, Constance, and Laura lived on at Como and left an indelible impression there.
The last surviving children of Charles and Caroline - Constance and Leila - sold Como to The National Trust of (Vic) in 1959. Como was the first house acquired by the Trust. One of the most significant aspects of this purchase was the acquisition of the complete contents of the house. The Armytage sisters realized that if Como was to survive as an expression of their family and its lifestyle, it must remain intact as a home. They also left an extensive archive of diaries, letters, journals and photographs.
Boasting one of Melbourne’s finest gardens, an inspiring historic mansion, and an impressive collection of antique furniture, the property provides a glimpse into the privileged lifestyle of its former owners; one of Australia’s wealthiest pioneer families.
Life can be seen to contain two major elements: the animate and the inanimate. While the inanimate bricks and mortar, objects and pathways, help in our understanding of this family, it is the animate, the social history, which makes Como come alive.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay The Armytage Family of Como written by Adrea Fox for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-
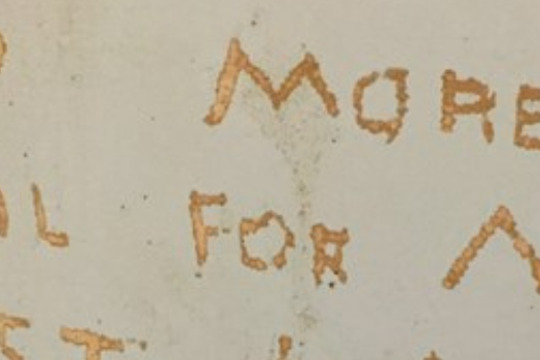 Mark Brandi
Mark BrandiPortable Justice: The old Bacchus Marsh police lock-up
... Scratched into the timber wall of the old Bacchus Marsh police lock–up, these crudely formed words might be a prisoner’s repentance before finally going straight. Or perhaps their regret was short-lived, soon returning to a life of crime. We ...Scratched into the timber wall of the old Bacchus Marsh police lock–up, these crudely formed words might be a prisoner’s repentance before finally going straight. Or perhaps their regret was short-lived, soon returning to a life of crime.
We will never know if they remained faithful to their promise, but the pledge gives life to the bitter solitude of this place, and others like it.
Prior to the widespread construction of police lock-ups, suspected criminals were subject to primitive forms of detention. In some towns, alleged culprits were tied to trees while awaiting trial, and were often subject to threats of lynching.
-

Seeing the Land from an Aboriginal Canoe
... and Rick discuss the life of 'King Tommy', an Aboriginal man who lived close by, never far from the Loddon River, in the 19th century.... rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim ...This project explores the significant contribution Aboriginal people made in colonial times by guiding people and stock across the river systems of Victoria.
Before European colonisation Aboriginal people managed the place we now know as Victoria for millennia. Waterways were a big part of that management. Rivers and waterholes were part of the spiritual landscape, they were valuable sources of food and resources, and rivers were a useful way to travel. Skills such as swimming, fishing, canoe building and navigation were an important aspect of Aboriginal Victorian life.
European explorers and colonists arrived in Victoria from the 1830s onwards. The newcomers dispossessed the Aboriginal people of their land, moving swiftly to the best sites which tended to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped the newcomers understand and survive in their new environment. And Victoria’s river system was a significant part of that new environment.
To understand this world we need to cast ourselves back into the 19th century to a time before bridges and cars, where rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim. So there was a real dilemma for the newcomers settling in Victoria – how to safely cross the rivers and use the rivers to transport stock and goods.
The newcomers benefited greatly from Aboriginal navigational skills and the Aboriginal bark canoe.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-
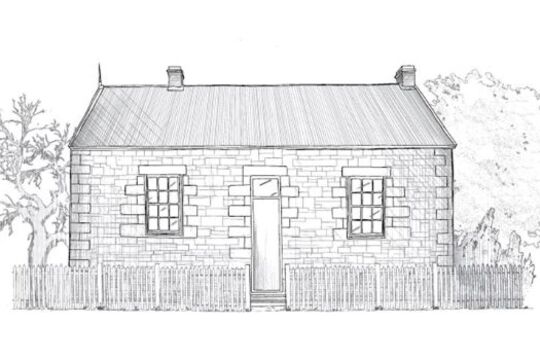
What House Is That?
... of the people who built and lived in them. What house is that? is an exploration of the social and architectural history of Victoria’s housing styles. From our earliest Victorian cottages through to the light filled, open plan houses of the Modern era, we look ...More than just bricks and mortar, our homes are prisms, reflecting the society of the time they were built. Through them, we can understand the changing context of social, economic and architectural history, and the values and assumptions of the people who built and lived in them.
What house is that? is an exploration of the social and architectural history of Victoria’s housing styles. From our earliest Victorian cottages through to the light filled, open plan houses of the Modern era, we look at the houses Victorians call home.
The nine images and text give an overview of each of the main housing styles of Victoria’s history from the 1840s onwards. The 15 videos feature interviews with architects, historians and residents and explore the styles in more detail. This collection of images, text and videos comes from an interactive website created by Heritage Victoria.
-

Bull Allen
... Guinea. He walked alone into a live battlefield and carried twelve wounded American soldiers out on his shoulders. Bull’s heroism was documented in a famous photograph by war correspondent Gordon Short. Bull was decorated by the US Government and awarded ...Leslie ‘Bull’ Allen was a stretcher-bearer in the Middle East and New Guinea in the Second World War who displayed great bravery in rescuing the wounded.
His most celebrated act of heroism took place on the 30th July 1943 on Mount Tambu in New Guinea. He walked alone into a live battlefield and carried twelve wounded American soldiers out on his shoulders. Bull’s heroism was documented in a famous photograph by war correspondent Gordon Short. Bull was decorated by the US Government and awarded a US Silver Star for bravery, but his action on Tambu was never recognised by the Australian Government.
Born in Ballarat in 1916, Allen came from a background of hardship and poverty. He survived the war, returning home to Ballarat and raising a family, but suffered significant post-traumatic stress from his war experience. He died in 1982.
-

From Riches to Rags and Back Again
... to live – its density makes it vibrant, exciting, close to the beach and the bay and it has plenty of parks – and it's within easy reach of the city. Waves of residents have washed through St Kilda, attracted in the boom times by its exclusivity and status ...This story tells of St Kilda’s changing fortunes through its diverse housing styles.
St Kilda’s changing social status over time is visible in the different block sizes and the variety of homes, often sitting cheek-by-jowl.
St Kilda is a great place to live – its density makes it vibrant, exciting, close to the beach and the bay and it has plenty of parks – and it's within easy reach of the city. Waves of residents have washed through St Kilda, attracted in the boom times by its exclusivity and status, and in periods when the suburb was more down at heel, by cheap rents and low priced land.
The story is also an audio tour. Download the audio files and the map from the Heritage Victoria website, and head to St Kilda to see the houses for yourself.
The tour begins at Cleve Gardens, on the corner of Fitzroy Street and Beaconsfield Parade.
From the audio tour From Riches to Rags and Back Again, created by Heritage Victoria.
