Showing 9 items matching "sampling"
-
 Jary Nemo and Lucinda Horrocks
Jary Nemo and Lucinda HorrocksCollections & Climate Change
... Photograph: Sample of mössbauerite taken from Yanga Lake, New South Wales...PLANT COLLECTIONS Dried samples are stored in a special archive called a herbarium. It is similar to a library, but the information is stored in biological form rather than in book form. The first herbarium was established in Kassel, Germany in 1569 ...The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before.
Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans, is having an impact on a global scale. In particular, human activity has altered the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the world’s climate to change.
Already in the state of Victoria we are seeing evidence of this change around us. In the natural world, coastal waters are warming and bringing tropical marine species to our bays. Desert animals are migrating to Victoria. Alpine winters are changing, potentially putting plants and animals at risk of starvation and pushing species closer to the margins. In the world of humans, island and coastal dwellers deal with the tangible and intangible impacts of loss as sea levels rise, bush dwellers live with an increased risk of life-threatening fires, farmers cope with the new normal of longer droughts, and we all face extreme weather events and the impacts of social and economic change.
This Collections and Climate Change digital story explores how Victoria’s scientific and cultural collections help us understand climate change. It focuses on three Victorian institutions - Museums Victoria, the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria and Parks Victoria. It looks at how the information gathered and maintained by a dedicated community of researchers, curators, scientists, specialists and volunteers can help us understand and prepare for a hotter, drier, more inundated world.
The story is made up of a short documentary film and twenty-one examples highlighting how botanical records, geological and biological specimens and living flora and fauna provide a crucial resource for scientists striving to map continuity, variability and change in the natural world. And it helps us rethink the significance of some of Victoria’s cultural collections in the face of a changing climate.
-
 Museums Victoria
Museums VictoriaTime Flies in Museum Collections: Ornithology in Victoria
... contains more than 70,000 specimens of mounted birds, dried study skins, tissue samples, skeletons, eggs, and specimens preserved in alcohol. One of the largest Australian collections, primarily of Australian species and with a strong Victorian emphasis...Natural science collections are vast treasure troves of biological data which inform current research and conservation. Alongside bird skins, nests, eggs and DNA samples sits a magnificent collection of rare books, illustrations and images which ...Natural science collections are vast treasure troves of biological data which inform current research and conservation.
Alongside bird skins, nests, eggs and DNA samples sits a magnificent collection of rare books, illustrations and images which charts the history of amateur and professional ornithology in Victoria.
Whilst the big names such as John Gould (1804–1881), are represented, the very local, independent bird observers such as John Cotton (1801-1849) and Archibald James Campbell (1853–1929) made some of the most enduring contributions.
The collections also document the bird observers themselves; their work in the field, building collections, their efforts to publish and the growth of their ornithological networks. Captured within records are changes in ornithological methods, particularly the way data is captured and published.
However the data itself remains as relevant today as it did when first recorded, 160 years of collecting gives us a long-term picture of birdlife in Victoria through space and time.
-
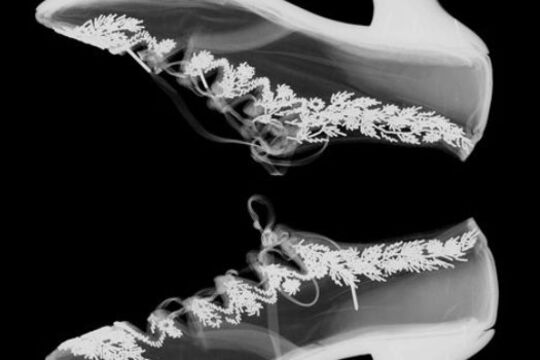
The Fashion Detective
... the prevalence of arsenic was voiced in British news articles, medical pamphlets and books. Less fatal poisonings were soon linked to the wearing of arsenical garments: a London physician identified green muslins as especially hazardous after analysing a sample...The dyes present in four nineteenth-century purple dresses were analysed in an effort to identify aniline dyes in the NGV collection. Fibre samples from each dress were analysed by chemist Dr Jeff Church from CSIRO. Thin-layer chromatography ...The NGV’s fashion archive contains countless works about which we know little.
We don’t know who made them, who wore them, when or why, or indeed, what happened in them! For the curator, such works are endlessly intriguing; a form of ‘material evidence’ to examine and explicate.
In 2014, the NGV’s Fashion Detective exhibition took a selection of unattributed nineteenth century garments and accessories from the Australian fashion and textiles collection as the starting point for a series of investigations. Using forensics and fiction as alternate interpretative methods, the exhibition considered the detective work that curators and conservators do and where this can lead, as well as the role of storytelling in making visible the social life of clothes.
From fakes and forgeries to poisonous dyes, concealed clues and mysterious marks to missing persons, Fashion Detective was a series of ‘cases’ that each followed a different path of analysis.
Some relied on empirical study and science to reach conclusions, others were purposefully speculative - the inspired hypothesis of leading crime writers Garry Disher, Kerry Greenwood, Sulari Gentill and Lili Wilkinson.
A playful exhibition about modes of enquiry, Fashion Detective considered the different ways in which we can decode objects in order to reveal what is normally concealed, and challenged the visitor to reappraise what they see and what they know.
-

The Apinis Loom
... This cloth was woven in the traditional colours and patterns of the Nica region on the west coast of Latvia. It was produced on a four shaft table loom using satin weave and an inlay pattern. It was copied from a sample seen in the Displaced Persons ...When Latvian refugees Anna and Ervins Apinis arrived in Australia in 1950 they brought with them a loom built of wood salvaged from bombed out German ruins, along with Anna's precious notebooks full of traditional fabric designs.
Anna Strauss was born in 1913 in Latvia. She attended weaving lessons in Leipaja from 1930 to 1933 and spent hours at the nearby Ethnographic Museum recording traditional fabric designs in her notebooks.
She married Ervins Apinis, an engineer, in 1938 and they had a son but soon World War II changed their lives. Ervins was conscripted into the German army while Anna fled Latvia, finally ending up in Memmingen Displaced Persons camp in Germany in 1945. There, they were finally reunited, remaining in the camp for five years until they migrated to Australia in 1950.
When they arrived at Parkes Holding Centre in New South Wales, they were so exhausted from their long journey, they slept on a huge wooden crate containing the traditional Latvian loom they had brought with them, built of wood scavenged from bombed German ruins. This loom is now at the Immigration Museum in Melbourne.
Anna continued her weaving traditions, passing her knowledge to her daughter Anita.
-

Dame Nellie Melba
... In this section is a selection of audio samples from some of the operas Dame Nellie Melba performed. ...“...the voice, pure and limpid, with an adorable timbre and perfect accuracy, emerges with the greatest ease.” Arthur Pougin, in Le Ménestral (Paris), May 12, 1889.
Dame Nellie Melba (1861 – 1931), was Australia’s opera superstar, performing in the great opera houses of the world - the Paris Opera, La Scala, the Metropolitan Opera House, and the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden, where she became prima donna, returning season after season.
The extensive Melba Collection at the Victorian Arts Centre includes costumes, records, accessories, letters, programs, photographs, opera scores and other personal effects. Other holdings of interest include 78rpm disks at the State Library of Victoria.
-

Language, A Key to Survival: Cantonese-English Phrasebooks in Australia
... of names of people and occupations and some sample documents (addressed envelope, invoice/receipt, cheque etc). There are advertisements at the beginning and scattered throughout the volume. This phrasebook is part of the founding David Scott Mitchell ...Most international travellers today are familiar with phrasebooks. These books provide a guide to pronunciation, useful vocabulary, but most importantly lists of useful phrases to help travellers negotiate their way around a country where they don't speak the language.
Anyone who has tried to communicate across the language divide without such a tool knows how valuable they are.
This web story explores how Chinese from the gold rush period onwards have used phrasebooks to help them find their way in Australia. You can compare examples of Cantonese-English phrasebooks from different eras; watch Museum volunteers Nick and David speak English using a gold-rush era phrasebook; learn a little about the lives of some of the people who owned these phrasebooks; and hear Mr Ng and Mr Leong discuss their experiences learning English in Australia and China in the early to mid-twentieth century.
This project is supported through funding from the Australian Government's Your Community Heritage Program.
-
 History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of Victoria
History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of VictoriaMacRobertson's Confectionery Factory
... One of the more unusual items in the Royal Historical Society of Victoria collection is this draw full of MacRobertson sample sweets. ...MacRobertson Steam Confectionery Works was a confectionery company founded in 1880 by Macpherson Robertson and operated by his family in Fitzroy, Melbourne until 1967 when it was sold to Cadbury.
This story accompanies the 'Nail Can to Knighthood: the life of Sir Macpherson Robertson KBE' exhibition which took place at the Royal Historical Society of Victoria in 2015.
-

The Ross Sea Party
... Page 53 "Mentioned a little time ago that I was waxing poetical - here is a sample after the R.W.Service style - The Lone South land Land of the Great White Silence, grim land of the polar night; Land of the blighting blizzard, ice fields ...As Shackleton’s ambitious 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition' of 1914 foundered, the Ross Sea party, responsible for laying down crucial supplies, continued unaware, making epic sledging journeys across Antarctica, to lay stores for an expedition that would never arrive.
In 1914 Ernest Shackleton advertised for men to join the Ross Sea Party which would lay supply deposits for his 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition'. Three Victorians were selected for the ten-man shore party: Andrew Keith Jack (a physicist), Richard Walter Richards (a physics teacher from Bendigo), and Irvine Owen Gaze (a friend of Jack’s).
The Ross Sea party commenced laying supplies in 1915 unaware that Shackleton’s boat Endurance had been frozen in ice and subsequently torn apart on the opposite side of the continent (leading to Shackleton’s remarkable crossing of South Georgia in order to save his men). Thinking that Shackleton’s life depended on them, the Ross Sea Party continued their treacherous work, with three of the men perishing in the process. The seven survivors (including Jack, Richards and Gaze) were eventually rescued in 1917 by Shackleton and John King Davis.
In total, the party’s sledging journeys encompassed 169 days, greater than any journey by Shackleton, Robert Scott, or Roald Amundsen – an extraordinary achievement.
Jack, Gaze and others in the party took striking photographs during their stay. Jack later compiled the hand coloured glass lantern slides, which along with his diaries, are housed at the State Library of Victoria.
-

Collingwood Technical School
... was presented to the school by the British United Shoe Machinery Company, and every phase of boot and shoe manufacture, with the exception of stitching, which [was] generally done by girls, [was] taught. The display of samples of the work of the boys ...For over 140 years, the site of the former Collingwood Technical School on Johnston Street, Melbourne, has played an integral role in the well being of the local community.
It has been a civic hub, including courthouse (1853), Council Chambers (1860) and the Collingwood Artisans’ School of Design (1871). The school opened in 1912 when its first principal, Matthew Richmond, rang a bell on the street to attract new students. Collingwood was a poor and industrial suburb, and as a trade school, young boys were offered the opportunity to gain industrial employment skills.
Throughout the twentieth century, Collingwood Technical School supported the local and broader community. From training schemes for ex-servicemen who were suffering from post traumatic stress following World War I (1914-1918), to extra classes during the Great Depression, and the development of chrome and electroplating for machine parts for the Australian Army and Air Force during World War II (1939-1945).
The precinct between Johnston, Perry and Wellington Streets has transformed over time, including expansion with new buildings and school departments, and the change in the demographic of students as Collingwood evolved from an industrial centre to eventual gentrification. And in 1984, New York street artist, Keith Haring (1958-1990), painted a large mural onsite.
Collingwood Technical College closed in 1987 when it amalgamated with the Preston TAFE (Technical and Further Education) campus. Education classes continued until 2005 and the site sat empty for more than a decade, before a section was redeveloped for Circus Oz in 2013.
The former school now has a new identity as Collingwood Arts Precinct, and is being developed into an independent space for small and medium creative organisations. The heritage buildings will house the next generation of thinkers and makers, and will become a permanent home to the arts in Collingwood.
