Showing 200 items
matching themes: 'a diverse state','aboriginal culture','creative life','family histories','immigrants and emigrants','kelly country','land and ecology','service and sacrifice'
-

ManStyle: Men + Fashion
Charting a course between absolute restraint and ostentatious display ManStyle explores the extremes of masculine style and some of the most influential ideas that have pervaded menswear over the past three centuries.
ManStyle presents a broad survey of menswear from around 1740 to the present using examples from the NGV collection. Beginning in the eighteenth century with exquisite brocade and embroidered silk coats, the exhibition explores the evolution of the modern suit via the elegantly honed lines of the nineteenth century dandy, examining the rise of tailoring with its focus on perfect cut and fit.
In contemporary menswear design, new and traditional modes of dressing are continually merging to create new definitions of masculinity. From tradition to transformation: changes in proportion, shape and detail as well as material, colour and pattern, including the more radical influence of sportswear, sub-cultural attire and street wear; all have affected men’s fashion.
A range of men discuss their own personal fashion and style. Their responses were often frank, considered, funny or surprising, as each reflected on what they wear and the influences, experiences and observations that have shaped their clothing choices.
-
 Danielle Whitfield
Danielle WhitfieldGetting it Right
There is a great deal of effort that goes into preparing a museum garment for display which the public never sees. This is especially true for historical items.
Most obviously, there is the core work that our textile conservators do examining and treating works so that they are safe to exhibit. Equally vital is the task of creating the appropriate underpinnings and padded supports which ensure a garment has a historically accurate silhouette, and that the fragile fabrics are supported during display.
During the nineteenth century a lot went on beneath women’s gowns. Victorian fashion relied on a variety of contrivances to generate form; corsets compressed the waist, petticoats, crinolines and later cage-crinolines made skirts wider and fuller, while bustles produced a cantilevered behind. Working in tandem with the garment, these structures performed both functional and aesthetic roles.
-

Burke and Wills: Have Camels Will Travel
Dromedary camels were introduced to Australia in 1840. The first significant shipment, however, was made to service the Burke and Wills expedition, which was the first exploring party to use camels, as well as horses, for transporting supplies.
In 1858, George Landells, who had worked as a horse trader in India, wrote to the Victorian Government explaining how the camel was ideally suited to the Australian landscape. He offered to travel to India and purchase camels on behalf of the Victorian government for use in exploration, and as the basis of a breeding stud. The government’s Board of Science and Zoological Gardens Committee agreed that the camel would be useful on the Australian continent, and Landells was authorised to borrow money from the Indian Government and make the purchase.
Landells traveled through India, Pakistan and Afghanistan to source the animals, engaging eight camel drivers to assist him on the journey from Karachi to Melbourne in December 1859, arriving mid-June 1860.
He was hailed for his travels through the ‘very unsettled’ lands by the English Scindian Newspaper, and similarly lauded in Melbourne where the ‘exotic’ animals caused a sensation, as did their handlers, identified variously as Indians, Sepoys, and Malays.
Partly in response to his fame, Landells was appointed second in command of the Burke and Wills expedition. He was also appointed officer in charge of the camels.
Landells recruited John Drakeford and John King, who had helped him bring the animals from Karachi to Melbourne, and four of the eight handlers: Samla (described by Becker as a Hindu), Dost Mahomet (or Botan), from Guznee; Esau Khan (or Hissand or Isaah), Belooch, who came from Mahadpoor in the Punjab, and another man from Kelat.
The expedition party departed Melbourne with 26 camels. As the expedition progressed, Landells and Burke disagreed over their treatment and Landells resigned in Menindee.
Four of the 26 camels were left at Menindee. Dost Mahomet stayed with 16 at the Coopers Creek depot. Burke and Wills took six animals with them on their trek to the Gulf and John King, travelled with them, to care for. Some of the animals strayed or were lost, others were abandoned. Burke, Wills, Charlie Gray and John King ate the last of them, as they struggled back from the Gulf of Carpentaria.
However the Burke and Wills Expedition was not the end of the story. Camels had proved their worth in negotiating the harsh and dry Australian interior and camels became an increasingly important form of transport in the Australian inland. Between 1870 and 1900, over 15,000 camels and 2000 cameleers were brought to Australia. The cameleers were commonly known as “Afghans” although small in number, they made a vital contribution to Australia’s exploration and development.
Feral camels now roam across outback Australia. In response, markets for live camels and camel meat have developed. It is more than likely that the descendents of Landells’ camels are among those that now roam the Australian continent.
-
 Kate Luciano
Kate LucianoSchool Days: Education in Victoria
The exhibition, School Days, developed by Public Record Office Victoria and launched at Old Treasury Building in March 2015, is a history of more than 150 years of schooling in Victoria.
It is a history of the 1872 Education Act - the most significant education reform in Victoria, and a world first! It is a history of early schooling, migrant schooling, Aboriginal schools, women in education, rural education and, of course, education during war time (1914-1918).
This online exhibition is based on the physical exhibition School Days originally displayed at Old Treasury Building, 20 Spring Street, Melbourne, www.oldtreasurybuilding.org.au and curated by Kate Luciano in collaboration with Public Record Office Victoria.
-
 Rachael Cottle
Rachael CottleStories of Support
The 2016 Museums Australia (Victoria) Conference held at Phillip Island in October, was the inspiration for this story. A drive around the Island on arrival unearthed a surprise in Newhaven - the former Boys Home standing silent and abandoned, looming over the ocean.
Care homes were once an essential part of Victorian life. The gold rush and population increase in Victoria created a need for charitable organisations to provide care to those who could not care for themselves, most notably children. Providers of care have also included societies for people with special needs including the 'Deaf and Dumb', and the asylums and hospitals of Victoria. This continued until the late 20th century when reform was prompted by revelations of abuse in the institutional system. The care model has since shifted towards kinship and foster services.
Victoria’s former institutions of care are an important part of our history. Whilst many of the buildings—often architecturally brilliant— no longer exist, they are remembered through the photographs and artefacts held by collecting organisations across the state and catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-

Eureka Stories
What is Eureka and what happened there?
In the early hours of 3 December 1854 a force of police and other troops charged a reinforced camp constructed by miners on the Eureka gold diggings. About 150 diggers were inside the stockade at the time of the attack. In the fighting, 4 soldiers and about 30 other people were killed, and another 120 people taken prisoner. Thirteen people from the stockade were charged with treason – these men were either tried and found not guilty, or charges against them were dropped.
Many people think of the Eureka Stockade as a battle between the diggers (rebellious Irish fighting for democracy) and the police and colonial militia (the forces of the British Crown in the Colony). It’s nice to have a single story to make sense of everything. Eureka, however, is not a single simple narrative. Several stories intertwine and involve many of the same people and places. Let’s look at some of them.
The Hated Gold Licences
In 1854, people mining for gold around Victoria had to pay a monthly fee of 30 shillings for the right to mine, regardless of how much gold they found. Someone who had been looking for gold unsuccessfully for months still had to pay the same fee as someone who was pulling out gold by the pound. Diggers argued that it was an unfair tax, imposed on them without their consent, as they did not have the right to vote. (After the Goldfields Royal Commission the licensing fee was changed to a tax on gold when it was being exported.)
Not only did the diggers resent the licence fee, they were angry at the way the goldfields police went about checking that miners had licences. Diggers claimed that police were beating people up or chaining them to trees if they could not produce a licence, and undertaking unnecessary inspections on people they didn’t like. Resentment of the licence fee and the conduct of police in their “licence hunts” was expressed across the Victorian goldfields.
The Unfair Treatment of Diggers by the Police and Justice System
People around the Victorian goldfields were also unhappy with the lack of thoroughness with which police had investigated a number of goldfields crimes. They were concerned about what they thought was the unfair and secretive way people were charged and convicted of crimes. There were claims by people living on the goldfields that it was necessary to bribe police and government officials in order to do business and stay safe. As the goldfields populations increased, tensions between the goldfields communities and police and other government officials rose.
In Ballarat a series of events (a murder, an arrest and a hotel burning) in late 1854 involving police and Ballarat locals led to the arrests of three men for burning down the Eureka Hotel. These arrests caused enormous disquiet in the area, adding weight to calls by the Ballarat Reform League and other organisations around the goldfields for a fundamental change to the system of government in the Colony – the next element in our Eureka story.
Demands for a Democratic Political System
Since the early 1850s people had been calling for the government to abandon the gold licensing system, remove the gold commissioners, and provide the Colony with a better policing and justice system. Despite an investigation by the Victorian parliament into the goldfields in 1853 (a Legislative Council Select Committee) the government did not make significant changes. By November 1854 an organisation called the Ballarat Reform League had formed in response to official inaction and had written a Charter of democratic rights. They organised a "monster meeting" in Ballarat on 11 November 1854, to have it accepted, and met with Governor Hotham on 27 November 1854, to demand his acceptance of the Charter, and the release of the three prisoners charged with burning down the Eureka Hotel.
Population Explosion
The people calling for these changes to taxes, justice and political participation came from many different parts of the world, such as the United States, Canada, England, Ireland, Scotland, Italy, Germany. This corner of South-Eastern Australia was rapidly changing as thousands and thousands of people arrived to search for gold. Many of these people were educated and from middle-class or merchant backgrounds. The domination of squatters running sheep on large land holdings was being challenged by dense populations of people in goldrush regions generating enormous wealth in the colony, and a desire from these recent arrivals to take up land, and have a say in the making of laws.
We have looked at some parts of the Eureka story; at what unfolded around the colony as a result of this mix of people, events and system of government. There are many other stories about Eureka. To find out more, you can explore the stories through original documents at Eureka on Trial.
-

Geelong Voices
Stories of World War 1, World War 2 and the Vietnam War as told by Geelong residents.
During World War 1 and World War 2 Geelong residents - whether joining the Armed Forces as soldiers, nurses, pilots, or helping out at home on projects such as the Australian Women’s Land Army - were swept up in the action. Motivated by youthful enthusiasm, the desire for adventure, and intense feelings of patriotism, they joined in hordes. For many, however, the war was not what they expected.
The Geelong Voices Oral History Project was established in 2001. The project collected recordings of diverse programs broadcast by a range of groups - including multicultural groups, women’s groups, trade unions, Aboriginal groups, youth groups and Senior Citizen’s groups - on 3YYR, Geelong Community Radio from 1988 to 2000.
Keeping in Touch and Koori Hour were two such programs. Keeping In Touch was a nostalgic program hosted by Gwlad McLachlan. Gwlad conducted interviews delving into historical aspects of Geelong and Geelong West, including world scale events such as WW1 and WW2, that shaped both the city and its people.
Koori Hour was a Wathaurong Aboriginal Co-operative Radio Program hosted by a range of people including Richard Fry and Gwenda Black, and consisted of talk about community activities, messages to friends and family, music and discussions about current events. One such event was the launch of “Forgotten Heroes” a book about the overlooked contribution of Aboriginal people to the Australian Armed Forces.
Over 200 of these interviews were recorded off the radio by Gwlad’s neighbour and her husband, Colin. Many of these recordings have been preserved and are available to listen to in digital format at the State Library of Victoria and the Geelong Heritage Centre.
-

Cuc Lam
Cuc Lam left her whole family behind when she fled from Vietnam in 1978 with her husband Minh.
They escaped in a fruit and vegetable boat down the Mekong Delta, disguised as fishermen. Cuc was able to take very few belongings with her: a watch from her sister, her wedding ring, her mother's earrings.
After 8 days at sea, they were finally picked up by a Malaysian ship. It was whilst in a Malaysian refugee camp that she heard she had been accepted into Australia, and sold her wedding ring to buy a red vinyl suitcase, so that she would not arrive in her new country empty handed. Cuc and Minh stayed in a Maribyrnong hostel in Melbourne until 1979, when Cuc had her first baby.
A former Maribyrnong City councillor, Cuc now works at Centrelink and continues supporting her family in Vietnam.
-
 Jane Routley and Elizabeth Downes
Jane Routley and Elizabeth DownesDegraves Street Subway & Campbell Arcade: The underground artspace
When you first come down the stairs, the Degraves Street Subway seems a bit daunting.
The long, pale pink tiled corridor with its blocked-off doorways and blotched asphalt, seems the perfect place for a mugging. A mysterious blind alley, which used to be an opening into the Mutual Store (and the earliest bowling alley in the CBD), leads off to your right. But stick with this corridor. It’s safe and is actually the route into the Campbell Arcade - a little slice of indie fringe artist-land which I think is a fine place to be.
-

Nyabana Riek
Nyabana Riek left Nasir, southern Sudan, to escape civil war when she was only 9 years old.
With her older sister Mary, she travelled to a refugee camp in Itang, Ethiopia in 1986. But after years in various camps, the sisters made a dangerous trek at night across the mountains between Ethiopia and Kenya. The 12-hour journey was steep, sharp rocks tore their shoes and soldiers patrolled both sides of the border. They managed to cross the border into Kenya and then spent 3 years in a Kenyan refugee camp.
Finally, in 1995, Nyabana reached Australia. When she arrived, Melbourne's Sudanese community was small; she was the first teenager from the Nuer language group and spoke little English. But things are different now - more family members have come to Melbourne, Nyabana completed a Bachelor of Business Management, and the Sudanese community and support networks are growing.
-

Punching the Bundy
In 1888, Williard LeGrand Bundy patented the first employee time clock. A year later, he and his brother founded the Bundy Manufacturing Company, which was to become part of the computing giant International Business Machines, or IBM.
The early Bundy clocks were mechanical, and employees in early industrial history used cards that were punched by the machine to record their working hours, or to 'bundy' on.
But in the Interknit hosiery factory in Clunes the expression used was 'punching the bundy'.
The Clunes mill was established in the 1920s, in a decommissioned state school building. In 1939, it was bought by Ballarat company Interknit, and became the Clunes Interknit Mill.
The Interknit Hosiery Company employed many locals. Initially a socks manufacturer, and commonly known as 'Interknit Sox', by 1981 Interknit had begun to manufacture jumpers.
Representing a time when industry was more local to its markets, Interknit supplied socks to Victorian Football League, and then the Australian Football League, teams and later jumpers well. Interknit also supplied socks to cricket teams and the Australian armed forces.
The Bundy clock held at the Clunes Museum was the original time clock from the Interknit factory.
In this story, former workers recall working at the Interknit mill, and especially using the time clock or 'Punching the Bundy'.
-
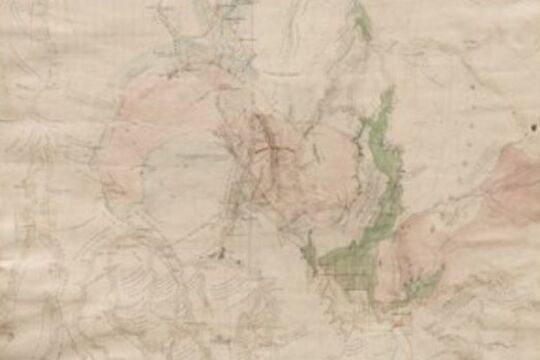
Mapping Great Change
This series of films and stories is centred on a beautiful and complex map with the ungainly name: Plan of the General Survey from the Town of Malmsbury to the Porcupine Inn, from the sources of Forest Creek to Golden Point, shewing the Alexandrian Range, also Sawpit Gully, Bendigo and Bullock Creeks.
In many ways, the map is a mirror of our times: the map is a record of the 'critical years' between 1835 and 1852 in which the dispossession of Aboriginal people of Victoria was allowed to occur; we contemporary people are in the "critical decade" for making the changes necessary to avoid catastrophic climate change.
If we fail to act effectively in this decade, it will be as loaded with moral and practical consequences for coming generations as the moral and policy failures of our colonial ancestors was for the Traditional Owners of the land.
-

The Koorie Heritage Trust Collections and History
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
The Koorie Heritage Trust was established in 1985 with a commitment to protect, preserve and promote the living culture of the Indigenous people of south-east Australia.
Today the Trust boasts extensive collections of artefacts, paintings, photographs, oral history recordings and library materials.
Further information on Tommy McRae can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site
-

Paintings Porcelain and Photography
Geelong Gallery was established in 1896 by twelve passionate citizens who believed Victoria's second largest and fastest growing city deserved an art institution befitting an aspiring metropolis. Since then, Geelong Gallery has established a collection of some 6,000 items – significant amongst these items are their holdings of paintings, porcelain and photography.
The gallery’s collection of Australian painting tells the history of the region from colonial times to the early twentieth century. Eugene von Guerard’s View of Geelong provides a sweeping panorama of Geelong seen from a vantage point near the village of Ceres in the nearby Barrabool Hills in 1856. While Arthur Streeton’s painting Ocean blue, Lorne, one of the gallery’s most recent acquisitions, depicts a shimmering summery sky, a view through slender young gum trees and down to the pristine sand and aquamarine ocean below in the 1920’s.
Geelong Gallery has a large and specialised collection of British painted porcelain spanning 1750 – 1850. It is one of the most significant holdings in Australia and is part of a bequest by well-known local citizen Dorothy McAllister. A fine example is the 'Buckingham Palace' card tray by renowned manufacturer Worcester dating to the 1840’s.
The gallery’s photographic collection is very much of the twentieth century, but not without references to earlier times and other works in the collection. Polixeni Papapetrou’s photograph In the Wimmera 1864 #1 created in 2006 examines the narrative of the ‘lost child’ and refers to Frederick McCubbin’s late nineteenth century paintings of children ‘lost’ or at least wandering absent-mindedly through the Australian bush.
-

Eugene von Guérard
Eugene von Guérard was born in Vienna in 1811. He was the son of the court painter to Emperor Franz Joseph 1 of Austria, Bernard von Guérard, and became a painter himself, studying under Johann Schirmer at the Academy in Düsseldorf.
He came to Australia to try his luck on the goldfields. Unsuccessful, he resumed his painting career in Melbourne in 1854, and by 1870 was appointed First Master of Painting at the National Gallery School, Melbourne and Curator of the National Gallery of Victoria. He returned to Europe in 1882.
His landscapes, remarkable for their detail, are much valued for the depiction of Australian and particularly, Victorian, landscapes of the mid-1800s.
-

Family Stories
From the nuclear to the extended family, from groups of close friends, communities and neighbourhoods, to one on one relationships: family means many different things to different people.
Family describes our most cherished, and sometimes most difficult, relationships. In this collection of digital stories and videos, Victorians share their family stories.
Family stories include stories of immigration; disadvantage and survival, indigenous life, stories of sickness and health; life and death; childhood and old age.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that some of the videos in this story may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
