Showing 45 items with the theme 'Built Environment'
-

The Palais Theatre
It’s impossible for Melburnians to think about the St Kilda Esplanade without visualising the Palais Theatre standing majestically against Port Phillip Bay. Its grand Art Deco façade is as iconic to St Kilda as the Pavilion on the nearby pier, Acland Street or the theatre’s "just for fun" neighbour, Luna Park.
It’s surprising to discover, then, that the Palais wasn’t always regarded with such affection. When the original building – a dance hall called the Palais de Danse – was being constructed in 1913, over 800 locals attended a public meeting to protest it being given a license. They voiced fears that it would lower the tone of St Kilda, “have a demoralising effect on young people", and be "common with a big C”. The battle was won by the building owners, the three Phillips brothers (American immigrants who also built Luna Park), and an entertainment venue has stood on the site ever since.
The Palais Theatre is a magical place for Melburnians. It’s where generations of us have danced cheek to cheek, watched movies in the darkness, screamed lustily at the Rolling Stones, thrown roses at the feet of Margot Fonteyn and Rudolph Nureyev, and given standing ovations to Dame Joan Hammond’s awe-inspiring soprano. Your grandparents probably had their first date there. Ask them about the Palais and watch them smile.
The theatre is underwent restoration in 2016-17, which preserved the heritage value of the site and ensured the Palais remains a live performance venue and cultural icon in St Kilda for many generations to come. The restoration was funded by the State Government of Victoria and the City of Port Phillip.
-
 Lynda Tieman
Lynda TiemanS.S. Casino
The steamship SS Casino served the Western District of Victoria for almost fifty years during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
A popular cargo ship, the Casino was a regular sight on the Moyne river and along the coast. The ship was an integral part of coastal life until she was shipwrecked in the 1930's, and objects from the Casino can now be found in collections from across the region and gathered here on Victorian Collections for the first time.
Transporting large quantities of wool, potatoes, onions, grain, sheep, cattle and other produce provided a great economic opportunity to business men in Port Fairy and in March, 1882, the Belfast & Koroit Steamship Company was formed with a capital of £20,000 in 10,000 shares. The SS Casino on her delivery voyage from England was due in Warrnambool to load potatoes for Sydney and the Directors inspected and purchased her there.
She arrived in Port Fairy on 29th July, 1882, steaming triumphantly up the Moyne River, and was greeted with cheers by a large crowd, many of whom had come from the surrounding countryside. She operated alone for almost all of the next 49 years. She was much loved by the whole Port Fairy community and the coastal ports that she serviced, bringing news and goods from far away and transporting passengers.
A celebration for the Casino's fiftieth anniversary was planned for the 29th July, 1932. Unfortunately soon after 9 o'clock on the morning of Sunday 10th July, 1932, disaster struck when the Casino was lost at Apollo Bay together with the lives of the Captain and 9 crew members.
-
 Open House Melbourne
Open House MelbourneModern Melbourne
Modern Melbourne is a series of filmed interviews and rich archival material that documents the extraordinary lives and careers of some of our most important architects and designers including Peter McIntyre, Mary Featherston, Daryl Jackson, Graeme Gunn, Phyllis Murphy, Allan Powell and Peter Elliott.
Melbourne’s modernist architects and designers are moving into the later stages of their careers. Their influence on the city is strong and the public appreciation of their early work is growing – they have made an indelible mark on Melbourne. Much of their mid-century modernist work and latter projects are now represented on the Victorian Heritage Register.
Many of the Modern Melbourne subjects enjoyed a working relationship and a friendship with Robin Boyd, the influential architect who championed the international modernist movement in Melbourne.
-
 Kitty Owens
Kitty OwensSummon the Living
Prior to the advent of electronic sound systems, bells were heard ringing throughout the day.
Large bells were attached to buildings. Handheld bells sat on tables and mantel pieces. Bells rang for morning prayer, school time, half time, and dinner time. Bells announced a fire in town or the death of a local. Some bells were passed around within their local community, or re-purposed as presentation gifts, being easily engraved and potentially useful.
This story was originally inspired by Graeme Davison’s book The Unforgiving Minute: How Australia Learned to Tell the Time.
-

Federation Square
It’s increasingly hard to imagine Melbourne without Federation Square. Home to major cultural attractions, world-class events, tourism experiences and an exceptional array of restaurants, bars and specialty stores, this modern piazza has become the city’s focal point; its heartbeat.
Since opening in 2002, Federation Square has received more than 90 million visits. It is currently number two for national and international visitation to Melbourne and is regularly among Victoria’s top two attractions in the state for local visitors.
This response is in part a result of the extraordinary range of event activities held each year. Federation Square is host to more than 2,000 events a year including New Year’s Eve celebrations, Melbourne Festival, Melbourne International Comedy Festival, Melbourne Food and Wine Festival, large public rallies, live sites for major sporting events as well as school holiday and Christmas programs.
Federation Square also hosts major attractions and world-class galleries including The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) and the Melbourne Visitor Centre.
Federation Square is managed by Fed Square Pty Ltd, which was established by the Victorian Government in 1999. Find more information about Fed Square’s history, architecture, the company’s commitment to social responsibility and more at Federation Square website.
-

100 Years of Flinders Street Station
Flinders Street Station: icon, meeting place, central to millions of city commuters. The building itself was the result an architectural competition held in 1902, and Mary Lewis, librarian, introduces us to the original winning entry, held at State Library of Victoria.
Explore the changing, and unchanging, face of Melbourne's streetscape with images of Flinders St, from photographs of the late eighteenth century to the works of art that Melbourne's famous railway station has inspired.
In 2010, Flinders Street Station celebrated its 100th birthday.
-
 Natalie Mastoris
Natalie MastorisTides of Change: Women of the Melbourne Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW)
In the lead up to International Women’s Day held on the 8th of March 2018, Melbourne Water celebrates and shines a spotlight on the past and continuing achievements of women within the organisation. Please join us in exploring the major milestones and social change within the MMBW, Melbourne Water and the Victorian Public Service.
Melbourne Water’s predecessor, The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW), was formed in 1891 to take responsibility for the city’s water supply and treatment. Initially, female employees were appointed to administrative and clerical positions. It wasn’t until 1939 that women stepped into more official, technical and specialist roles. These included positions such as chemistry assistants, machine operators and assistant drafts women.
Not only were women’s roles at MMBW based on their contribution to the operations of the organisation, many women were involved in social, recreational and cultural activities. Perhaps the greatest legacy of women at the MMBW was their efforts in building communities, enriching and empowering the lives of those around them.
-
 Erin Wilson
Erin WilsonUrban Fringe
Melbourne is an expanding city, with a growing population and sprawling urban development. It is predicted that by 2056 an additional 4 million people will settle in Greater Melbourne, increasing the population from 5 million to 9 million people over the next 30 years (1). While some expansion is vertical, in the form of high-rise developments, much of this growth is across the peri-urban fringe, described simply as ‘areas on the urban periphery into which cities expand’ (2) or ‘which cities influence’ (3).
In Melbourne, these peri-urban areas of most rapid growth are currently the local government areas of Cardinia, Casey, Hume, Melton, Mitchell, Whittlesea and Wyndham. With population growth comes the inevitable expansion of infrastructure, services and transportation. As the fringes of the city continue to sprawl, what was once the urban fringe and green edge of the city has to be negotiated, as it is increasingly encroached upon.
The artists and photographers in Urban Fringe examine these spaces on the fringe of the expanding city of Melbourne, where urban and natural environments meet, clash and coexist. Beginning with white colonisation and the myth of ‘terra nullius’, these artists discuss the treatment of the Greater Melbourne environment over time, consider the cost of progress, and explore protest and the reclamation of space.
-
 Elizabeth Downes
Elizabeth DownesThe Unsuspected Slums
Campaigner Frederick Oswald Barnett recorded the poverty facing many in the Melbourne slums of the 1930s.
“All the houses face back-yards…The woman living in the first house…was so desperately poor that she resolved to save the maternity bonus, and so, with her last baby had neither anaesthetic nor doctor.”
So observed campaigner Frederick Oswald Barnett of the poverty facing many in the Melbourne slums of the 1930s. After touring these slums with Barnett, it’s said the Victorian Premier, Albert Dunstan, couldn’t sleep for days.
In 1936 Dunstan established the Slum Abolition Board, and Barnett became vice-chairman of the newly established Housing Commission of Victoria in 1938.
A Methodist and accountant, Barnett became determined to improve the situation for the poor, sick, elderly and unemployed after encountering a slum in the 1920s. He was an astute crusader who coordinated letter writing campaigns and lectured throughout Victoria using many of his own poignant and arresting photographs of the cramped and unsanitary housing conditions.
-

Sound in Space
Music always interacts with the architecture in which it is heard.
Melbourne has some wonderful acoustic environments. Often, these spaces were built for other purposes – for example the splendid public and ecclesiastical buildings from the first 100 years of the city’s history, and more recent industrial constructions.
Exploiting ‘non-customized’ spaces for musical performance celebrates and explores our architectural heritage.
For 30 years, the concerts of Astra Chamber Music Society have ranged around Melbourne’s architectural environment. Each concert has had a site-specific design that takes advantage of the marvellous visual qualities, spatial possibilities, and acoustic personality of each building.
The music, in turn, contributes a new quality to the perception of the buildings, now experienced by audiences as a sounding space - an area where cultural issues from music’s history are traversed, and new ideas in Australian composition are explored.
In this story take a tour of some of Melbourne’s intimate, hidden spaces and listen to the music that has filled their walls.
For further information about Astra Chamber Music Society click here.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
-
 Kitty Owens
Kitty OwensAnother Night
Lighting fades away when a lamp is blown out, or when a switch is clicked off, but the history of lighting has left traces in Victorian cultural collections.
This story looks at items and images relating to the history of lighting in Victoria and considers the various lightscapes created by different types of lighting. This story is inspired by the book Black Kettle and Full Moon by Geoffrey Blainey.
After thousands of years of Aboriginal firelight, European households spent their evenings in dim smoky rooms huddled around a spluttering pool of light. Bright lighting was a luxury. As new energy sources and lighting technology became available nights became brighter, extending the day and changing the night time.
-
 Elizabeth Downes
Elizabeth DownesTallangatta: The town that moved
Every now and then, when the Hume Dam is at a low ebb, the ghostly remains of old Tallangatta, in northern Victoria, can be seen above the water. Now located 39 kilometres east of Wodonga, Tallangatta is known as 'the town that moved'.
In 1956, 2 hotels, 4 petrol stations, numerous shops and businesses, 4 churches, more than 900 residents and all the usual public amenities of a country town were relocated 8 kilometres west of the old site. The original location was then flooded under 6 feet of water after the Hume Dam was expanded.
During 1954 the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission took more than 180 photos in and around the town, documenting houses, businesses and facilities before they were moved. Other images capture the remarkable feat of transporting the buildings to the new site, such as a weatherboard house being carefully towed toward a narrow bridge. Many photos give a vivid picture of the commercial centre of a small country town in the mid-1950s. Advertising signs promote Sennitts Icecream and The Argus newspaper, cluttered shops are packed to the gunnels with equipment and staples for small town life before large chain stores, supermarkets and cars changed country towns forever.
The shops and houses are distributed along straight Towong Street. Cars were scarce and bicycles were an important form of transport in the wide and mostly empty streets. Men and women in the 2 hotels were still segregated in the ladies lounge and main bar; and the hotel’s kitchen equipment was basic. The town offered butchers, barbers, and hairdressers, while the garages, plumbers, and hardware stores served both town and farming needs.
The Tallangatta photographs are part of The Rural Water Corporation Collection of more than 50,000 photographs held at The State Library of Victoria. This collection covers a range of water management projects and activities during the first half of the 20th century.
-
 Rachael Cottle
Rachael CottleStories of Support
The 2016 Museums Australia (Victoria) Conference held at Phillip Island in October, was the inspiration for this story. A drive around the Island on arrival unearthed a surprise in Newhaven - the former Boys Home standing silent and abandoned, looming over the ocean.
Care homes were once an essential part of Victorian life. The gold rush and population increase in Victoria created a need for charitable organisations to provide care to those who could not care for themselves, most notably children. Providers of care have also included societies for people with special needs including the 'Deaf and Dumb', and the asylums and hospitals of Victoria. This continued until the late 20th century when reform was prompted by revelations of abuse in the institutional system. The care model has since shifted towards kinship and foster services.
Victoria’s former institutions of care are an important part of our history. Whilst many of the buildings—often architecturally brilliant— no longer exist, they are remembered through the photographs and artefacts held by collecting organisations across the state and catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-

Melbourne and Smellbourne
Over the last 150 years Victoria has experienced a number of landmark capital works and landscaping projects in response to its changing economic, environmental and cultural relationship to water. The sewerage system that we take for granted today had to be built from scratch.
For all the grandeur that was 'Marvellous Melbourne' in the 1880s, the city was nicknamed 'Smellbourne', and for good reason. The building of Yan Yean Reservoir in the 1850s had ensured the availability of fresh water, but there was still no sewerage system.
An appalling stench wafted from the many cesspits and open drains. 'Nightsoil' (as human waste was politely referred to) polluted the streets and ran into the Yarra. Nightsoil collectors frequently dumped their loads on public roads. Ignorance and neglect of the hygienic disposal of human waste had devastating results at this time when hundreds died in a savage outbreak of typhoid.
Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works
In 1891 the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was created. It immediately began plans to build an underground drainage system linked to a pumping station at Spotswood, located on the western banks of the mouth of the Yarra River. The sewage flowed by gravity to Spotswood, where it was then pumped to the Werribee Treatment Farm.
Spotswood Pumping Station
Spotswood Pumping Station built to pump Melbourne's sewage to Werribee, was finished in 1897. At the pumping station, steam engines (later replaced by electrical ones) worked to pump the sewage up a rising main to join the major sewer outfall at the head of the pumping mains near Millers Road at Brooklyn. The outfall sewer then carried the sewage to the Werribee Treatment Farm where it was purified and discharged into the sea.
Werribee Farm
Werribee was the perfect site for the MMBW's new sewage farm. The farm was the Board's most important project, and one of the largest public works undertaken in Australia in the nineteenth century.
Land at Werribee was cheaper than at Mordialloc - the other site considered. Rainfall was low compared with the rest of Melbourne, which meant the land would adapt well to irrigation. Werribee was also 9 miles (14.4 KM) away from the nearest boundary of the metropolitan district (Williamstown), and 24 miles (38.6 KM) away from the influential and well-to-do suburb of Brighton. The Chirnside family sold 8,857 acres (3.2 hectares) to the Board for 17 pounds per acre.
The Earl of Hopetoun, Governor of Victoria, turned the first sod of earth in a ceremony on May 1892, which marked the beginning of the building of the outfall sewer near Werribee.
Connection!
On 5 February 1898, a ceremony marked the official connection of Melbourne to the new sewerage system. Guests - politicians, board members, city councillors and federal delegates - boarded a steamer to watch the Governor, Lord Brassey, raise the penstock (the partition between the smaller and larger sewers) at the Australian Wharf. They then visited the pumping station at Spotswood and the sewage farm at Werribee. Horses and carts conveyed the 180 guests around the farm.
After lunch and toasts, many of which looked forward to the future of a federated Australia, MMBW Chairman Mr Fitzgibbon proudly declared it "was not a question of how much the scheme was going to cost, but how much it was going to save in the lives of the citizens." Before the work was completed he hoped to see those puny punsters and petty wits who spoke of Melbourne as Marvellous Smellbourne constrained to speak of her as one of the sweetest and healthiest cities of the world.
-
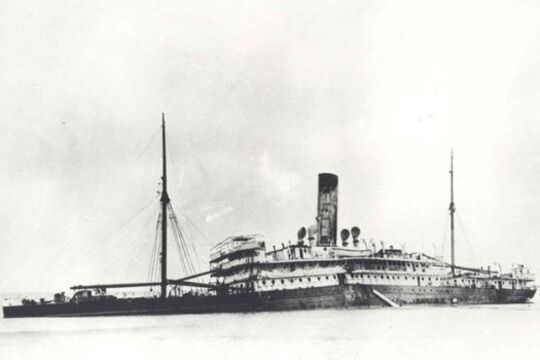
Tales from the deep
As the rest of the world became enthralled in the exciting and mysterious world of scuba diving - devouring the anecdotes of early adventurers such as Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Lloyd Bridges - Victoria’s own pioneers were hard at work.
John Black is one of Australia’s early underwater explorers. He began his career in abalone diving in 1951 and became involved in the new and developing sport of scuba diving in the 1960s.
At the time, specialty equipment was hard to get so John and his colleagues used the DIY attitude to create boats out of wooden planks and Victa lawnmower engines and breathing equipment using hoses and hotel CO2 gas tanks. With these extraordinary apparatus they were among the first to enter the pristine underwater wilderness of the Gippsland coast.
John’s stories describe the evolution of diving gear, the triumphs and near-misses of working in a burgeoning field and the excitement of being the first to dive on the remains of Victoria’s spectacular shipwrecks.
John was interviewed as part of the Heritage Victoria East Gippsland Oral Histories project in 2003. This story includes audio extracts from his interview and a transcript of his full interview.
