Showing 45 items with the theme 'Built Environment'
-

A Station with a Town Attached
"Don't you overlook that Maryborough station, if you take an interest in governmental curiosities. Why, you can put the whole population of Maryborough into it, and give them a sofa apiece, and have room for more." Mark Twain, during his 1895 tour of Australia.
Twain’s remark stuck, and Maryborough became known as the railway station with a town attached.
Why was Maryborough chosen for one of the nation's grandest stations? Was it meant for Maryborough, Queensland? Was it indeed a ‘governmental curiosity’, a monumental bureaucratic mistake?
In fact, neither is the case. The Maryborough Station tells a much larger story: the vision for a rail-connected Victoria in the age that preceded the motor engine. Maryborough would be a crucial junction between the Wimmera, Geelong, Ararat, Warrnambool, Ballarat, Bendigo and Melbourne, especially for freight such as wheat.
The original station was built in 1874 but, as part of the 'Octopus Act' of 1884, Parliamentarians began arguing the case for a grander station.
The new Queen Anne style red brick building with stucco trimmings and Dutch-Anglo influences was erected in 1890-1, with 25 rooms, an ornate clock tower, Flemish gables, oak wall panels, a large portico, and a spectacular platform veranda - the longest in country Victoria.
Here, oral histories, expert opinions and archival photographs from local collections are presented, giving us a sense of the station's importance, its role in an earlier era and, as a magnificent late 19th century Australian building, the place it continues to hold in the district.
-

Sound in Space
Music always interacts with the architecture in which it is heard.
Melbourne has some wonderful acoustic environments. Often, these spaces were built for other purposes – for example the splendid public and ecclesiastical buildings from the first 100 years of the city’s history, and more recent industrial constructions.
Exploiting ‘non-customized’ spaces for musical performance celebrates and explores our architectural heritage.
For 30 years, the concerts of Astra Chamber Music Society have ranged around Melbourne’s architectural environment. Each concert has had a site-specific design that takes advantage of the marvellous visual qualities, spatial possibilities, and acoustic personality of each building.
The music, in turn, contributes a new quality to the perception of the buildings, now experienced by audiences as a sounding space - an area where cultural issues from music’s history are traversed, and new ideas in Australian composition are explored.
In this story take a tour of some of Melbourne’s intimate, hidden spaces and listen to the music that has filled their walls.
For further information about Astra Chamber Music Society click here.
-
Tales from the deep
As the rest of the world became enthralled in the exciting and mysterious world of scuba diving - devouring the anecdotes of early adventurers such as Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Lloyd Bridges - Victoria’s own pioneers were hard at work.
John Black is one of Australia’s early underwater explorers. He began his career in abalone diving in 1951 and became involved in the new and developing sport of scuba diving in the 1960s.
At the time, specialty equipment was hard to get so John and his colleagues used the DIY attitude to create boats out of wooden planks and Victa lawnmower engines and breathing equipment using hoses and hotel CO2 gas tanks. With these extraordinary apparatus they were among the first to enter the pristine underwater wilderness of the Gippsland coast.
John’s stories describe the evolution of diving gear, the triumphs and near-misses of working in a burgeoning field and the excitement of being the first to dive on the remains of Victoria’s spectacular shipwrecks.
John was interviewed as part of the Heritage Victoria East Gippsland Oral Histories project in 2003. This story includes audio extracts from his interview and a transcript of his full interview.
-

Restoring St Nicholas
St Nicholas church in Humffray St, Ballarat East, was built in 1867. Originally named the Bible Christian Church, it was built by Cornish miners in the evenings and weekends after they had returned from their work at the diggings.
Like most buildings of its time it was built to last, constructed of solid brick with lime mortar. By the 1970s, the mortar was crumbling and the church community of the time re-mortared it with cement, a process we now know was incorrect for buildings of its age. The cement mortar, combined with rising damp, caused salt attack in many of the original bricks and the building literally began to crumble.
In 2009 the Greek Orthodox community of St Nicholas approached the City of Ballarat, Heritage Victoria and the trade school at the University of Ballarat to form a unique partnership to restore the church. This project allowed young apprentices to learn traditional trade skills and practice the technique of mixing and using lime mortar. In the process, the humble church has had its life extended, and the Greek community have a religious and cultural centre they can use for generations to come.
-
 Jane Routley and Elizabeth Downes
Jane Routley and Elizabeth DownesDegraves Street Subway & Campbell Arcade: The underground artspace
When you first come down the stairs, the Degraves Street Subway seems a bit daunting.
The long, pale pink tiled corridor with its blocked-off doorways and blotched asphalt, seems the perfect place for a mugging. A mysterious blind alley, which used to be an opening into the Mutual Store (and the earliest bowling alley in the CBD), leads off to your right. But stick with this corridor. It’s safe and is actually the route into the Campbell Arcade - a little slice of indie fringe artist-land which I think is a fine place to be.
-

Young and Jackson Hotel
The Young and Jackson Hotel, built in the 1850s, is one of Australia's most well known hotels. It was built, as the Princes Bridge Hotel, on part of an allotment originally purchased by John Batman in 1837.
Young and Jackson were both born in Dublin, and "chummed together" to New Zealand chasing the Otago gold deposits in 1861. It is not known when they came to Victoria, but they purchased the lease on the Princes Bridge Hotel in 1875.
-
 Jane Routley and Elizabeth Downes
Jane Routley and Elizabeth DownesThe Concourse
Reading about Flinders Street Station can give you the impression this grand old building is past its useful life. Not so. This is a hardworking station – Melbourne’s public transport hub.
Over 100,000 commuters pass through the station every day, well up from the daily total of around 30,000 in the 1930s. In my childhood the concourse was smaller with iron pillars and a galvanized iron roof. I remember it being full of wooden shops, brown panelling and a floor that used to contain bottle top lids, pen caps, paper clips, broken chains and other intriguing items fossilized into the black asphalt.
-

Rippon Lea Estate
"Do you remember the garden in which you grew up, or the part the backyard played in your family life? Imagine if you had actually grown up in one of Australia's finest gardens.
Created in the English-landscape tradition which traces its roots back to Capability Brown and Humphry Repton, Rippon Lea is one of Australia's most important historic homes, exemplifying the lifestyle of wealthy families living in 19th and 20th century Australian cities. Although its architecture and that of its outbuildings is impressive, it is the mansion’s gardens, which are truly remarkable, both for their landscape qualities and because they have survived many threats and changes in the past 130 years.
Today, the amenities offered by a typical garden are still greatly valued: a safe place for children to play, somewhere to dry the washing, a plot for vegetables and a flower garden that adds colour and produces blooms for the home. Today as then, the scale differs but the experience of owning a garden - with its balance of utility and ornament - is essentially the same.
The National Trust of Australia (Victoria) now runs Rippon Lea as a museum, conserving the architecture and the landscape, and presenting the social history of the owners and their servants. Visitors to Rippon Lea enter a mansion preserved as the Jones family lived in it after their 1938 modernisation. In the pleasure garden the Sargood era is evoked by the staging of a range of performing arts events including opera, theatre, chamber music and outdoor activities."
The text above has been abstracted from an essay Solid Joys and Lasting Treasure: families and gardens written by Richard Heathcote for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-
 Brian Allison
Brian AllisonJohn Harry Grainger
Architect and Civil Engineer
John Harry Grainger was a creative figure, largely overlooked by history. He receives a brief mention in the much-examined life story of his famous son, the composer and pianist Percy Grainger, where he is depicted as a proud but ineffectual father.
Grainger's prolific output as an architect and his extraordinary talents for bridge building have not yet received due recognition.
The material presented here is sourced from the Grainger Museum Collection at the University of Melbourne. Additional material is held in the Public Record Office of Victoria and in the State Library of Victoria collections.
-

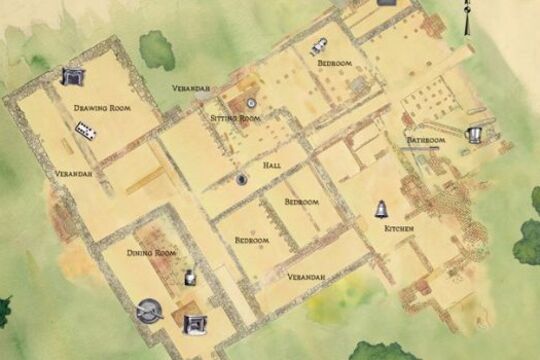
Melbourne's Homes
These house plans from the late 19th and early 20th Centuries, give us an indication of how those with the means to build larger houses lived.
Servant's quarters, groom's rooms, sculleries, stables, parlours and children's areas give us clues to social attitudes, relationships to children and employees, social mores and living conditions.
-

Wimmera Stories: The Dimboola Banner, communicating history
The first issue of the Dimboola Banner rolled off the press on 10 May 1879, printed by a Mr Henry Barnes and edited by his brother, William.
Many proprietors and editors have come and gone since then but today, more than 130 years later, the Banner is still published weekly, even though it’s now printed in Warracknabeal rather than in Dimboola itself.
Meanwhile, the former Dimboola offices of the Banner have been acquired by the Dimboola & District Historical Society and transformed into a Newspaper and Letterpress printing museum. The museum owns and operates a diverse collection of vintage presses, all in working condition.
Newspapers and printers have traditionally played a vital role in the life of country communities, and a long-time newspaper man comes to know most things there are to know about the life of their town and district. Joe Barry spent 54 years in the newspaper and printing business in Dimboola, which means he’s well qualified to impart a wealth of tales to visitors at the Dimboola Printing Museum.
The printing trade has seen many vast and radical technological transformations, particularly with the dawn and evolution of the current digital era. The Dimboola Printing Museum preserves a vast wealth of functioning relics from earlier eras of print technology, including letterpresses well over a century old in perfect working order.
The museum collection also includes a vast amount of loose type from the long-gone era of hand-set typography.
-

From Riches to Rags and Back Again
This story tells of St Kilda’s changing fortunes through its diverse housing styles.
St Kilda’s changing social status over time is visible in the different block sizes and the variety of homes, often sitting cheek-by-jowl.
St Kilda is a great place to live – its density makes it vibrant, exciting, close to the beach and the bay and it has plenty of parks – and it's within easy reach of the city. Waves of residents have washed through St Kilda, attracted in the boom times by its exclusivity and status, and in periods when the suburb was more down at heel, by cheap rents and low priced land.
The story is also an audio tour. Download the audio files and the map from the Heritage Victoria website, and head to St Kilda to see the houses for yourself.
The tour begins at Cleve Gardens, on the corner of Fitzroy Street and Beaconsfield Parade.
From the audio tour From Riches to Rags and Back Again, created by Heritage Victoria.
-

North Shore: Geelong's Boom Town 1920s-1950s
In its heyday of the 1920s - 1950s, North Shore (a small northern suburb of Geelong) was the hub of industrial development in Victoria’s second city.
Situated against the backdrop of Corio Bay, North Shore and its immediate surrounds was home to major industries including Ford, International Harvester, Shell, the Corio Distillery and the Phosphate Cooperative Company of Australia (the 'Phossie').
Residents grew up with these companies literally over the back fence and many of their stories depict childhood memories of mischievous exploration. Many residents were employed by the industries, some hopping from job to job, whilst others spent the majority of their working lives at the likes of Ford or the Phossie.
At the commencement of World War II in September 1939, much of the local industry was placed on war footing. Two thirds of the newly opened International Harvester was commandeered by the R.A.A.F. and an ad hoc airfield was established. The U.S. Air Force arrived shortly thereafter.
The presence of American servicemen has left an enduring impression on the North Shore community. Their arrival was the cause of much local excitement, particularly among the children who made a pretty penny running errands for them. They were also a hit with the ladies, who enjoyed a social dance at the local community hall. The story of the American presence in North Shore remains largely untold, and the reflections of local residents provide a fantastically rare insight into a unique period in Victorian history.
A special thanks to local historians Ferg Hamilton and Bryan Power for their assistance during the making of this story. Also thanks to Gwlad McLachlan for sharing her treasure trove of Geelong stories.
-
Viewbank: Unearthing a Colonial Homestead
Viewbank Homestead was one of the first grand homesteads built on the outskirts of Melbourne. Built around 1840, Viewbank was located near the junction of the Yarra and Plenty Rivers in Heidelberg.
The homestead was built in two phases. Originally a four room house, it was renovated and expanded in the 1850s and 1860s after it was acquired by wealthy squatter Dr Robert Martin.
Viewbank was destroyed by a professional demolition team in the early 1920s, long after the Martin family moved away from the area. By then, the house had fallen into disrepair and locals believed that it was haunted. For most of the 20th century, cattle grazed over the ruins and knowledge of the former grand homestead slipped from public knowledge until archaeologists returned to the site to unlock its secrets.
Between 1996 and 1999, Heritage Victoria conducted three excavations at the site with help from archaeologists from Melbourne, La Trobe and Flinders Universities, and more than 140 archaeology students and community members.
The archaeologists uncovered the stone foundations of the house and remnants of hand-made brick walls, fireplaces and other features. A range of artefacts were found during the excavation including children’s toys, coins, gaming tokens, thimbles and pins. A network of servant’s bells, fragments of marble fireplaces, and pieces of richly decorated plaster cornices reflect the affluence of the Martin family.
This story is made up of audio interviews with an archaeologist, an historian and a conservator. They discuss the Viewbank excavation, describe the artefacts found there and explain the process of their conservation at the Heritage Victoria conservation laboratory.
The Viewbank Homestead is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. For more information on the Viewbank or other heritage sites visit The Victorian Heritage Database.
-
 Open House Melbourne
Open House MelbourneModern Melbourne
Modern Melbourne is a series of filmed interviews and rich archival material that documents the extraordinary lives and careers of some of our most important architects and designers including Peter McIntyre, Mary Featherston, Daryl Jackson, Graeme Gunn, Phyllis Murphy, Allan Powell and Peter Elliott.
Melbourne’s modernist architects and designers are moving into the later stages of their careers. Their influence on the city is strong and the public appreciation of their early work is growing – they have made an indelible mark on Melbourne. Much of their mid-century modernist work and latter projects are now represented on the Victorian Heritage Register.
Many of the Modern Melbourne subjects enjoyed a working relationship and a friendship with Robin Boyd, the influential architect who championed the international modernist movement in Melbourne.
-
 Rachael Cottle
Rachael CottleStories of Support
The 2016 Museums Australia (Victoria) Conference held at Phillip Island in October, was the inspiration for this story. A drive around the Island on arrival unearthed a surprise in Newhaven - the former Boys Home standing silent and abandoned, looming over the ocean.
Care homes were once an essential part of Victorian life. The gold rush and population increase in Victoria created a need for charitable organisations to provide care to those who could not care for themselves, most notably children. Providers of care have also included societies for people with special needs including the 'Deaf and Dumb', and the asylums and hospitals of Victoria. This continued until the late 20th century when reform was prompted by revelations of abuse in the institutional system. The care model has since shifted towards kinship and foster services.
Victoria’s former institutions of care are an important part of our history. Whilst many of the buildings—often architecturally brilliant— no longer exist, they are remembered through the photographs and artefacts held by collecting organisations across the state and catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
