Showing 132 items
matching themes: 'built environment','gold rush','immigrants and emigrants','local stories','service and sacrifice'
-

Marianne Gibson's Crazy Patchwork Quilt
In 1876, the Japanese Pavilion at the Philadelphia Centennial Exposition caused quite a stir. It featured ceramics and other art objects that were asymmetrical, or “crazed”. Whilst the interest created in America was telling of the whole mood of modernism (which questioned and reformed traditional aesthetic ideas), its effect on the everyday lives of women was seen in the groundswell of support for crazy patchworking (also known as crazy quilting).
Crazy patchwork became a hugely popular ‘craze’ that lasted until the 1920s, with women’s publications full of the opinions of both followers and protestors. Crazy patchwork is differs considerably from traditional patchwork quilting: where traditional patchwork is batted, or filled, and composed of precise patches arranged into neat and sometimes complex geometric patterns, crazy patchwork consists of uneven patches that are composed of any variety of fabrics (especially exotic fabrics at the start of the craze) and are embellished with all sorts of trimmings: lace, embroidery, buttons, ribbons. In addition to this crazy patchwork quilts are very personalised.
Crazy quilts broke all the rules of traditional quilts and were highly experimental and creative: makers were not afraid to use clashing colours or to cover every surface with designs. Cushions and pillows were also made to the style. It was through this craze and Victorian women’s domestic creative work that modernism was ushered into the home.
Marianne Gibson was born in Armagh, Ireland in 1837. As a young woman she and her sister accompanied their uncle to Australia and settled in Wangaratta. In 1864 Marianne married Alexander McCullen Gibson, who operated a successful general store.
Marianne’s skill with needlepoint, her access to fine fabrics of the day, including silks and European lace, and her creative instinct can all be seen in the remarkable Crazy Patchwork Quilt known as the Marianne Gibson Quilt. Replete with Australian motifs, including flora and birdlife, and personal symbols, such as tributes to a child she lost, the quilt is dated and signed by Marianne, indicating both her creative ownership and her intention for the quilt to be kept as an heirloom.
It is precisely because it was honoured as an heirloom that it survives in such condition to this day. Donated to the collection of the Wangaratta Historical Society by Alma Gard, it is one the finest and best-preserved crazy patchwork quilts from the Victorian era in the world.
-

Geelong Voices
Stories of World War 1, World War 2 and the Vietnam War as told by Geelong residents.
During World War 1 and World War 2 Geelong residents - whether joining the Armed Forces as soldiers, nurses, pilots, or helping out at home on projects such as the Australian Women’s Land Army - were swept up in the action. Motivated by youthful enthusiasm, the desire for adventure, and intense feelings of patriotism, they joined in hordes. For many, however, the war was not what they expected.
The Geelong Voices Oral History Project was established in 2001. The project collected recordings of diverse programs broadcast by a range of groups - including multicultural groups, women’s groups, trade unions, Aboriginal groups, youth groups and Senior Citizen’s groups - on 3YYR, Geelong Community Radio from 1988 to 2000.
Keeping in Touch and Koori Hour were two such programs. Keeping In Touch was a nostalgic program hosted by Gwlad McLachlan. Gwlad conducted interviews delving into historical aspects of Geelong and Geelong West, including world scale events such as WW1 and WW2, that shaped both the city and its people.
Koori Hour was a Wathaurong Aboriginal Co-operative Radio Program hosted by a range of people including Richard Fry and Gwenda Black, and consisted of talk about community activities, messages to friends and family, music and discussions about current events. One such event was the launch of “Forgotten Heroes” a book about the overlooked contribution of Aboriginal people to the Australian Armed Forces.
Over 200 of these interviews were recorded off the radio by Gwlad’s neighbour and her husband, Colin. Many of these recordings have been preserved and are available to listen to in digital format at the State Library of Victoria and the Geelong Heritage Centre.
-

Savoy Ladies Group
The Italian community of Myrtleford, in the picturesque Ovens Valley in alpine North Eastern Victoria, arrived mainly to work in the tobacco industry which once thrived in the area. The region now has a distinctive Italian-Australian culture with settled second, third and fourth generation Italian families.
Tobacco farming was a lonely experience for many of the Italian women who migrated to Myrtleford. Unlike their husbands, the women stayed largely on the farms and lacked social contact outside of their immediate circle. Once their children grew up and mechanisation changed the labour requirements on the farms, women were frequently on their own.
The Myrtleford Savoy Ladies Group was founded in 1983 by nuns concerned about the social isolation of women in the area. It has been a great success, forming a network of companionship amongst women of Italian heritage to this day.
Cultural Warning: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users of this website are warned that this story contains images of deceased persons and places that could cause sorrow.
-

Collingwood Technical School
For over 140 years, the site of the former Collingwood Technical School on Johnston Street, Melbourne, has played an integral role in the well being of the local community.
It has been a civic hub, including courthouse (1853), Council Chambers (1860) and the Collingwood Artisans’ School of Design (1871). The school opened in 1912 when its first principal, Matthew Richmond, rang a bell on the street to attract new students. Collingwood was a poor and industrial suburb, and as a trade school, young boys were offered the opportunity to gain industrial employment skills.
Throughout the twentieth century, Collingwood Technical School supported the local and broader community. From training schemes for ex-servicemen who were suffering from post traumatic stress following World War I (1914-1918), to extra classes during the Great Depression, and the development of chrome and electroplating for machine parts for the Australian Army and Air Force during World War II (1939-1945).
The precinct between Johnston, Perry and Wellington Streets has transformed over time, including expansion with new buildings and school departments, and the change in the demographic of students as Collingwood evolved from an industrial centre to eventual gentrification. And in 1984, New York street artist, Keith Haring (1958-1990), painted a large mural onsite.
Collingwood Technical College closed in 1987 when it amalgamated with the Preston TAFE (Technical and Further Education) campus. Education classes continued until 2005 and the site sat empty for more than a decade, before a section was redeveloped for Circus Oz in 2013.
The former school now has a new identity as Collingwood Arts Precinct, and is being developed into an independent space for small and medium creative organisations. The heritage buildings will house the next generation of thinkers and makers, and will become a permanent home to the arts in Collingwood. -

St Paul's Cathedral
Refusing to set foot in the colony, the eminent Gothic Revivalist architect William Butterfield resorted to sending extremely detailed architectural drawings and plans of St Paul's Cathedral to Australia.
He even produced life-size drawings of columns, window tracery and other features, to ensure the antipodeans could get nothing wrong.
In the end however, he was defeated by distance, and St Paul's was completed by the Australian firm Reed, Henderson and Smart, and later, in the 1930s, the towers he designed (but were not built at the time) were shafted for a new design by Australian architect John Barr.
-
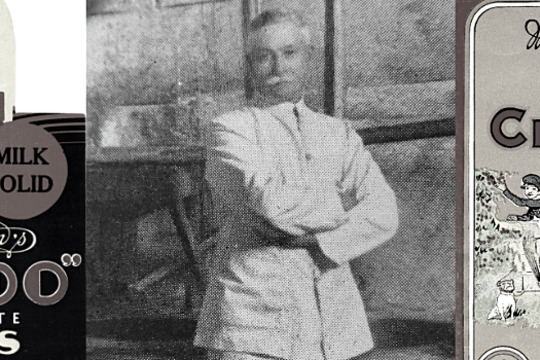 History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of Victoria
History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of VictoriaMacRobertson's Confectionery Factory
MacRobertson Steam Confectionery Works was a confectionery company founded in 1880 by Macpherson Robertson and operated by his family in Fitzroy, Melbourne until 1967 when it was sold to Cadbury.
This story accompanies the 'Nail Can to Knighthood: the life of Sir Macpherson Robertson KBE' exhibition which took place at the Royal Historical Society of Victoria in 2015.
-

World War One: Coming Home
From 1920 until 1993, Bundoora Homestead Art Centre operated first as Bundoora Convalescence Farm and then as Bundoora Repatriation Hospital.
For more than seventy years, it was home to hundreds of returned servicemen. These men were not only physically damaged by their wartime experiences, their mental health was also dramatically affected. Despite the severe trauma, sometimes it took years or decades for the conditions to emerge.
For some servicemen, this meant being unable to sleep, hold down a job, maintain successful relationships or stay in one place, whilst others experienced a range of debilitating symptoms including delusions and psychosis. While these men tried to cope as best they could, they were rarely encouraged to talk openly about what they had seen or done. The experience of war haunted their lives and the lives of their families as they attempted to resume civilian life.
At this time, there was little understanding around trauma and mental health. For some returned servicemen and their families, it was important that their mental illness was acknowledged as being a consequence of their war service. This was not only due to social stigma associated with mental illness generally, but also because war pensions provided families with greater financial security.
This is as much the story of the Bundoora Repatriation Hospital as it is the story of a mother and daughter uncovering the history of the man who was their father and grandfather respectively. That man was Wilfred Collinson, who was just 19 when he enlisted in the AIF. He fought in Gallipoli and on the Western Front, saw out the duration of the war and returned home in 1919. He gained employment with the Victorian Railways and met and married Carline Aminde. The couple went on to have four children. By 1937, Wilfred Collinson’s mental state had deteriorated and he would go on to spend the remainder of his life – more than 35 years – as a patient at Bundoora.
We know so little about the lives and stories of men like Wilfred, the people who cared for them, the people who loved them and the people they left behind. For the most part the voices of the men themselves are missing from their own narrative and we can only interpret their experiences through the words of authorities and their loved ones.
-

James Harrison: Journalist, Inventor and Visionary
Although largely unacknowledged today, James Harrison was a major figure in the history of the city of Geelong. A politician, engineer, inventor, publisher and journalist, he was a man of huge energy and diverse talents.
In the 1850s he invented the worlds first ice-making machine from experimentations begun along the Barwon River in Geelong. He was also the founding editor of the Geelong Advertiser, after purchasing an old press from John Pascoe Fawkner and he was an important public commentator in the colony. He was a member of Geelong's first town council and represented Geelong in the colony of Victoria's Legislative Assembly.
Although travelling to Britain, and producing the first large commercial ice making machines, his business enterprises were not a success. He pioneered the development of a precursor to the modern refrigerated transport container but it failed during an experimental shipment of refrigerated beef to England and he was financially ruined.
After his death at Point Henry, Geelong in 1893 the people of Geelong paid for his tombstone and it was inscribed with the biblical quotation "one soweth, one reapeth".
-
 Rural City of Wangaratta / State Library Victoria
Rural City of Wangaratta / State Library VictoriaThe Last Stand of the Kelly Gang: Sites in Glenrowan
Ned Kelly, born in June 1855 at Beveridge, north-east of Melbourne, Northern Victoria, came to public attention as a bushranger in the late 1870s.
He was hanged at the Melbourne Gaol, November 11th, 1880. Kelly is perhaps Australia’s best known folk hero, not least of all because of the iconic armour donned by his gang in what became known as the Siege at Glenrowan (or The Last Stand), the event that led to Ned Kelly’s capture and subsequent execution.
The siege at Glenrowan on Monday, June 28th, 1880, was the result of a plan by the Kelly Gang to derail a Police Special Train carrying Indigenous trackers (the Gang's primary targets), into a deep gully adjacent to the railway line. The plan was put into effect on Saturday, June 26 with the murder [near Beechworth] of Aaron Sherritt, a police informant, the idea being to draw the Police Special Train through the township of Glenrowan, an area the local Kellys knew intimately. After the Glenrowan Affair, the Kelly Gang planned to ride on to Benalla, blow up the undermanned police station and rob some banks.
However, Ned miscalculated, thinking the train would come from Benalla not Melbourne. Instead of the 12 hours he thought it would take for a police contingent to be organized and sent on its way from Benalla, the train took 31 hours to reach Glenrowan. This resulted in a protracted and uncertain wait, leading to the long period of containment of more than 60 hostages in the Ann Jones Inn. It also resulted in a seriously sleep deprived Kelly Gang and allowed for the intervention of Thomas Curnow, a hostage who convinced Ned that he needed to take his sick wife home, enabling him to get away and warn the Police Special train of the danger.
Eventually, in the early morning darkness of Monday, June 28th, the Police Special train slowly pulled into Glenrowan Railway Station, and the police contingent on board disembarked. The siege of the Glenrowan Inn began, terminating with its destruction by fire in the mid afternoon, and the deaths of Joe Byrne, Dan Kelly and Steve Hart. Earlier, shortly after daylight on the 29th, Ned was captured about 100 metres north east of the Inn.
Glenrowan is situated on the Hume Freeway, 16 kms south of Wangaratta. The siege precinct and Siege Street have State and National Heritage listing. The town centre, bounded by Church, Gladstone, Byrne and Beaconsfield parade, including the Railway Reserve and Ann Jones’ Inn siege site, have State and National listing.
-

History in Place
The History in Place project connects teachers and students with their local history via a community collecting society or museum.
History in Place provides an innovative and practical implementation of the new Australian Curriculum in History and Victoria's Framework of Historical Themes. It provides a framework for students to engage with their local history and heritage in a fun and challenging way using digital technologies. The program has been designed for grades 5 and 6, but has also been used for year 9s.
History in Place can be initiated either by schools or by community museums and heritage organisations. Students use collection items and interviews with local experts to create short films using tablet devices.
This story includes examples of what happens during a day of History in Place, examples of student films from the program pilot and an education toolkit (available from the Education Resources tab below) which includes course materials, instructional materials and everything that a museum and school need to implement the program.
The pilot program partnered 6 primary schools from across Victoria with local museums.
Museums participating in the pilot were: Barwon Park, Burke Museum, CO.AS.IT Museum, Golden Dragon Museum, the Mildura Arts Centre and Yarra Ranges Museum.
The project is a partnership between the Heritage Council of Victoria, the History Teachers' Association of Victoria and Culture Victoria. The pilot was funded by the Telematics Trust.
During the History in Place pilot, students used the Linking History site to research their films. Linking History is an experimental pilot in the practical application of linked open data, and is part of Portrait of a Nation: History In Place Access Project which is a Centenary of Canberra project, proudly supported by the ACT Government and the Australian Government.
-

Digital Stories of the Land
Stories of the Land is a collection produced as part of the Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) digital storytelling program.
These stories explore the land as a thread that connects people to their surroundings. The personal narratives provide a way for understanding place on its own terms and often those terms can be challenging; drought bushfires and isolation for those who live on the land.
People across Victoria have shared stories as part of this ACMI collection capturing the essence of the land as a setting to their lives inextricably linked to the experiences and events that have shaped them.
-

Eureka Stories
What is Eureka and what happened there?
In the early hours of 3 December 1854 a force of police and other troops charged a reinforced camp constructed by miners on the Eureka gold diggings. About 150 diggers were inside the stockade at the time of the attack. In the fighting, 4 soldiers and about 30 other people were killed, and another 120 people taken prisoner. Thirteen people from the stockade were charged with treason – these men were either tried and found not guilty, or charges against them were dropped.
Many people think of the Eureka Stockade as a battle between the diggers (rebellious Irish fighting for democracy) and the police and colonial militia (the forces of the British Crown in the Colony). It’s nice to have a single story to make sense of everything. Eureka, however, is not a single simple narrative. Several stories intertwine and involve many of the same people and places. Let’s look at some of them.
The Hated Gold Licences
In 1854, people mining for gold around Victoria had to pay a monthly fee of 30 shillings for the right to mine, regardless of how much gold they found. Someone who had been looking for gold unsuccessfully for months still had to pay the same fee as someone who was pulling out gold by the pound. Diggers argued that it was an unfair tax, imposed on them without their consent, as they did not have the right to vote. (After the Goldfields Royal Commission the licensing fee was changed to a tax on gold when it was being exported.)
Not only did the diggers resent the licence fee, they were angry at the way the goldfields police went about checking that miners had licences. Diggers claimed that police were beating people up or chaining them to trees if they could not produce a licence, and undertaking unnecessary inspections on people they didn’t like. Resentment of the licence fee and the conduct of police in their “licence hunts” was expressed across the Victorian goldfields.
The Unfair Treatment of Diggers by the Police and Justice System
People around the Victorian goldfields were also unhappy with the lack of thoroughness with which police had investigated a number of goldfields crimes. They were concerned about what they thought was the unfair and secretive way people were charged and convicted of crimes. There were claims by people living on the goldfields that it was necessary to bribe police and government officials in order to do business and stay safe. As the goldfields populations increased, tensions between the goldfields communities and police and other government officials rose.
In Ballarat a series of events (a murder, an arrest and a hotel burning) in late 1854 involving police and Ballarat locals led to the arrests of three men for burning down the Eureka Hotel. These arrests caused enormous disquiet in the area, adding weight to calls by the Ballarat Reform League and other organisations around the goldfields for a fundamental change to the system of government in the Colony – the next element in our Eureka story.
Demands for a Democratic Political System
Since the early 1850s people had been calling for the government to abandon the gold licensing system, remove the gold commissioners, and provide the Colony with a better policing and justice system. Despite an investigation by the Victorian parliament into the goldfields in 1853 (a Legislative Council Select Committee) the government did not make significant changes. By November 1854 an organisation called the Ballarat Reform League had formed in response to official inaction and had written a Charter of democratic rights. They organised a "monster meeting" in Ballarat on 11 November 1854, to have it accepted, and met with Governor Hotham on 27 November 1854, to demand his acceptance of the Charter, and the release of the three prisoners charged with burning down the Eureka Hotel.
Population Explosion
The people calling for these changes to taxes, justice and political participation came from many different parts of the world, such as the United States, Canada, England, Ireland, Scotland, Italy, Germany. This corner of South-Eastern Australia was rapidly changing as thousands and thousands of people arrived to search for gold. Many of these people were educated and from middle-class or merchant backgrounds. The domination of squatters running sheep on large land holdings was being challenged by dense populations of people in goldrush regions generating enormous wealth in the colony, and a desire from these recent arrivals to take up land, and have a say in the making of laws.
We have looked at some parts of the Eureka story; at what unfolded around the colony as a result of this mix of people, events and system of government. There are many other stories about Eureka. To find out more, you can explore the stories through original documents at Eureka on Trial.
-
 Clare Gervasoni, Margaret Evans, and Amy Tsilemanis
Clare Gervasoni, Margaret Evans, and Amy TsilemanisTrailblazing Women of Ballarat
From the first woman to graduate from any Australian university to leading artists, those who gazed towards the heavens, and others who broke through male dominated barriers, women are not only present but deserve to be celebrated.
This exhibition, originally held at the School of Mines Ballarat (SMB) E. J. T Tippett library, showcases these significant contributions and untold stories through items from the Federation University Historical Collection.
Do you know of other Trailblazing women associated with the university through time who deserve recognition? Let us know so that we can help to capture and share their stories!
-

Early Photographs - Gold
These images are part of the first photographic series of Australian scenes presented for sale to the public. Produced by the studio of Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree in 1858, these photograph are from a series of 53 collectively known as the Fauchery-Daintree Album.
Using the latest collodion wet-plate process, Fauchery and Daintree produced their collection of albumen silver prints at a time when the sales of photographs were flourishing.
Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree produced iconic images of both early gold diggers and the landscapes scarred by the exploding search for gold, which attracted miners from all over the world and created the boom that made Melbourne the fastest growing metropolis of the time.
Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree were both migrants who tried their luck on the goldfields – Daintree coming out from England in 1853, Fauchery from France in 1852.
Unsuccessful on the goldfields, in 1857 they combined forces to produce a series of photographs titled Sun Pictures of Victoria, capturing important early images of the goldfields, Melbourne Streets, landscapes and portraits of Indigenous Victorians. Using the new collodion wet-plate process, they created albumen silver prints of a rare quality for the time.
Further information on Antoine Fauchery's time in Melbourne can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site.
-
 Carissa Goudey
Carissa GoudeyMaking & Using Transport on the Goldfields
During the nineteenth century, horse-drawn vehicles were an essential part of life in rural Victoria.
In Ballarat, local coachbuilding firms assisted with the town’s growth in more ways than providing passage to the diggings. Horse-drawn vehicles were vital for the delivery of goods, responding to emergencies and often symbolised one’s social standing.
The Gold Rush ushered in a period of incredible growth for colonial Victoria. Ballarat’s escalating population and burgeoning industries highlighted the need for horse-drawn transport – not only for getting to the diggings, but also for delivering goods and building material, responding to emergencies and performing significant social rituals.
In the early nineteenth century, the goldfields were dominated by vehicles either imported from England or English-style vehicles built locally. Coaches, carriages and carts were typically constructed part-by-part, one at a time. As a result, each vehicle was highly unique.
By the mid-1850s, the American coachbuilding tradition had arrived on the goldfields. The American method, which had been developing since the 1840s, relied on mass-produced, ready-made components. In comparison to English designs, American coaches were known to be more reliable for goldfields travel; they were primed for long-distance journeys on rough terrain and were less likely to tip over.
As the nineteenth century progressed, a plethora of English, American and European vehicles populated Ballarat – both locally made and imported. The abundance of coaches, carriages and carts – and their value to the Ballarat community – can be seen in photographs and objects catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-

William Buckley
After convict William Buckley’s escape from a Victorian settlement he was discovered by the Wathaurang people who thought this pale, 198cm giant carrying a spear was the ghost of one of their leaders.
Buckley had arrived at Port Phillip from England in 1803 with about 300 soldiers, settlers and convicts after being sentenced to transportation for life. Before the Port Phillip and Sullivan Bay (Victoria’s first official European settlement) settlement was abandoned, Buckley escaped. He wandered alone for weeks before he was befriended by the Wathaurang people.
Over the next 32 years Buckley lived with the Wathaurang, learnt their language and customs, married and had a daughter. In 1835 he finally emerged to meet Batman’s colonising party and tried to work as an intermediary between settlers and aborigines, but felt he wasn’t trusted by either.
His name lives on in Australian slang with the ironic saying “you’ve got Buckley’s chance” or “Buckley’s hope”.
Further material can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site:-
William Buckley's Escape
Buckley and the Aborigines
Buckley's return to European life
