Showing 96 items
matching themes: 'built environment','kelly country','aboriginal culture','gold rush','family histories'
-
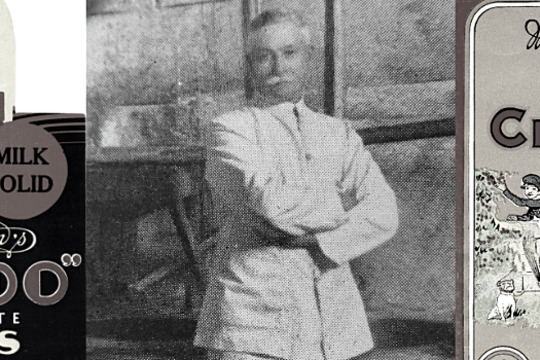 History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of Victoria
History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of VictoriaMacRobertson's Confectionery Factory
MacRobertson Steam Confectionery Works was a confectionery company founded in 1880 by Macpherson Robertson and operated by his family in Fitzroy, Melbourne until 1967 when it was sold to Cadbury.
This story accompanies the 'Nail Can to Knighthood: the life of Sir Macpherson Robertson KBE' exhibition which took place at the Royal Historical Society of Victoria in 2015.
-

Restoring St Nicholas
St Nicholas church in Humffray St, Ballarat East, was built in 1867. Originally named the Bible Christian Church, it was built by Cornish miners in the evenings and weekends after they had returned from their work at the diggings.
Like most buildings of its time it was built to last, constructed of solid brick with lime mortar. By the 1970s, the mortar was crumbling and the church community of the time re-mortared it with cement, a process we now know was incorrect for buildings of its age. The cement mortar, combined with rising damp, caused salt attack in many of the original bricks and the building literally began to crumble.
In 2009 the Greek Orthodox community of St Nicholas approached the City of Ballarat, Heritage Victoria and the trade school at the University of Ballarat to form a unique partnership to restore the church. This project allowed young apprentices to learn traditional trade skills and practice the technique of mixing and using lime mortar. In the process, the humble church has had its life extended, and the Greek community have a religious and cultural centre they can use for generations to come.
-
 Kitty Owens
Kitty OwensSummon the Living
Prior to the advent of electronic sound systems, bells were heard ringing throughout the day.
Large bells were attached to buildings. Handheld bells sat on tables and mantel pieces. Bells rang for morning prayer, school time, half time, and dinner time. Bells announced a fire in town or the death of a local. Some bells were passed around within their local community, or re-purposed as presentation gifts, being easily engraved and potentially useful.
This story was originally inspired by Graeme Davison’s book The Unforgiving Minute: How Australia Learned to Tell the Time.
-

William Barak
Diplomat, artist, story-teller and leader, Wurundjeri (Woiwurung) man William Barak worked all his life to protect the rights and culture of his people, and to bridge the gap between settlers and the land’s original custodians.
Barak was educated at the Yarra Mission School in Narrm (Melbourne), and was a tracker in the Native Police as his father had been, before becoming ngurungaeta (clan leader). Energetic, charismatic and mild mannered, he spent much of his life at Coranderrk Reserve - a self-sufficient Aboriginal farming community in Healesville.
Barak campaigned to protect Coranderrk, worked to improve cross-cultural understanding and created many unique artworks and artifacts, leaving a rich cultural legacy for future generations.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
Further information on William Barak can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site.
-

Pangerang Country with Freddie Dowling
Indigenous Warning: Please be aware that this story contains imagery and representation of people that may be deceased, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
In this story Freddie Dowling, Pangerang Elder, introduces us to several Pangerang stories and sites.
The Pangerang people were a nation of sub-clans who occupied much of what is now North Eastern Victoria stretching along the Tongala (Murray) River to Echuca and into the areas of the southern Riverina in New South Wales. Their land includes the Wangaratta, Yarrawonga and Shepparton areas through which the Kialla (Goulburn) and Torryong (Ovens) Rivers flow. The approximate boundaries are south to Mansfield, west to Echuca, east to Chiltern and north to near Narrandera in New South Wales.
Freddie Dowling learnt the stories of the indigenous people of this area from his grandmother, Annie Lewis, and his father, Frank ‘Munja’ Dowling.
The Pangerang words used in this story were written down by Annie Lewis in 1900. She learned them from her mother, Luana ‘Lily’ Milawa. Freddie remembers that both his grandmother and father spoke these words. His father also taught him to speak while hunting and travelling in the bush of their country.
The word Pangerang is often written and known as Bangerang, and Banerang, 'because, in our language, "puh" and "buh" sound similar' (Freddie Dowling).
-
 Abbey Martin
Abbey MartinThe McIntyre Family
The First World War was an event that involved the whole world.
Thousands of Australian troops were sent into battle in support of Britain and France. Among them were two brothers, John and Jim McIntyre. John McIntyre's experiences are particularly well documented because he brought back many objects from all the places he visited. He also sent many postcards home to his family during the war.
John Lachlan McIntyre was born at Beeac, Victoria in December 1890. He enlisted in the 1st AIF in July 1915. John fought on the Western Front, taking part in the battles of Fromelles and the 2nd Battle of the Somme. He was severely wounded at Fromelles and spent 12 months in hospital in England before returning to the front.
-
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustIndigenous Stories about Sport
Less well known is the fact that the first Australian cricket team to tour Britain was an all-Aboriginal team in 1868.
Against the express wishes of the Board of Protection of Aborigines, the Aboriginal 11 was smuggled aboard a ship bound for Sydney and then Britain. Between May and October 1868 they played 47 matches in Britain - they won 14, lost 14 and drew 19, a creditable outcome. A non-Aboriginal Australian team did not tour Britain until ten years later.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

History in Place
The History in Place project connects teachers and students with their local history via a community collecting society or museum.
History in Place provides an innovative and practical implementation of the new Australian Curriculum in History and Victoria's Framework of Historical Themes. It provides a framework for students to engage with their local history and heritage in a fun and challenging way using digital technologies. The program has been designed for grades 5 and 6, but has also been used for year 9s.
History in Place can be initiated either by schools or by community museums and heritage organisations. Students use collection items and interviews with local experts to create short films using tablet devices.
This story includes examples of what happens during a day of History in Place, examples of student films from the program pilot and an education toolkit (available from the Education Resources tab below) which includes course materials, instructional materials and everything that a museum and school need to implement the program.
The pilot program partnered 6 primary schools from across Victoria with local museums.
Museums participating in the pilot were: Barwon Park, Burke Museum, CO.AS.IT Museum, Golden Dragon Museum, the Mildura Arts Centre and Yarra Ranges Museum.
The project is a partnership between the Heritage Council of Victoria, the History Teachers' Association of Victoria and Culture Victoria. The pilot was funded by the Telematics Trust.
During the History in Place pilot, students used the Linking History site to research their films. Linking History is an experimental pilot in the practical application of linked open data, and is part of Portrait of a Nation: History In Place Access Project which is a Centenary of Canberra project, proudly supported by the ACT Government and the Australian Government.
-

From Here and There
From Here & There is a cultural exchange and story telling project through making.
The project connects contemporary art and design practice with traditional Indigenous cultures and artefacts to tell a story that explores the past and the present; dislocation and home; community and identity.
Designer & artist, Philippa Abbott engaged with two Victorian indigenous weavers – Master weaver Aunty Marilyne Nicholls & Journey woman Donna Blackall - to learn their process of weaving. The process entailed going out on to Country to collect materials, visiting their homes and families and tracing current cultural identity through understandings of place, of recent family movement, clan lineage and through the weaving technique itself.
By learning the weaving technique the collaboration then looks to develop a new artefact together that explores current and future story creation.
The process was a collaboration with, and documented by, Greta Costello – a Melbourne based photographic artist working in cross-cultural dialogues.
-

Felon Families
Stories of Women Prisoners and their Families
"Life in the colony of Victoria during the 19th century could be fraught with difficulties for families and, particularly, for women. The problems they encountered in hard times were exacerbated by distance from the support and friendship of their extended families. If women found themselves unable to cope, the repercussions for the whole family could be tragic.
The stories and images of women who passed through Victoria’s penal system in the 19th century include: Elizabeth Scott, a young girl forced into marriage, living in an isolated part of the country, and the first woman hanged in Victoria; the baby farmer Frances Knorr; Martha Needle who's story is unusual because her crimes arose not out of the severe circumstances of colonial Victoria but from universal, age-old family and personal dysfunction; Emma Williams a single mother who drowned her baby son and brought the Champion newspaper to claim in October 1895 that her case would "exhibit Victoria to the world as the very lowest and most degraded of all civilised communities"; and Janet Dibden who wrote poetry while imprisoned at the Old Melbourne Gaol. It also includes Ellen Kelly the mother of bushranger Ned Kelly, who told her son "Die brave, die like a Kelly" before he was hanged."
The text above has been abstracted from an essay Felon families: Stories of women prisoners and their families written by Diane Gardiner for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The full text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Language, A Key to Survival: Cantonese-English Phrasebooks in Australia
Most international travellers today are familiar with phrasebooks. These books provide a guide to pronunciation, useful vocabulary, but most importantly lists of useful phrases to help travellers negotiate their way around a country where they don't speak the language.
Anyone who has tried to communicate across the language divide without such a tool knows how valuable they are.
This web story explores how Chinese from the gold rush period onwards have used phrasebooks to help them find their way in Australia. You can compare examples of Cantonese-English phrasebooks from different eras; watch Museum volunteers Nick and David speak English using a gold-rush era phrasebook; learn a little about the lives of some of the people who owned these phrasebooks; and hear Mr Ng and Mr Leong discuss their experiences learning English in Australia and China in the early to mid-twentieth century.
This project is supported through funding from the Australian Government's Your Community Heritage Program.
-
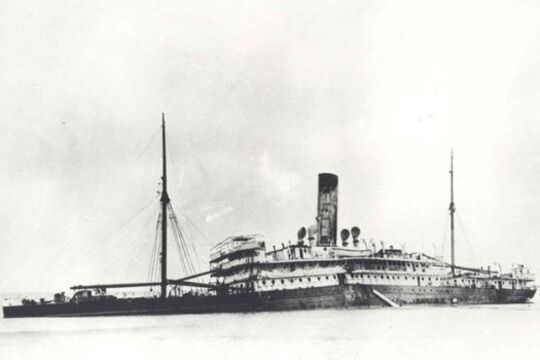
Tales from the deep
As the rest of the world became enthralled in the exciting and mysterious world of scuba diving - devouring the anecdotes of early adventurers such as Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Lloyd Bridges - Victoria’s own pioneers were hard at work.
John Black is one of Australia’s early underwater explorers. He began his career in abalone diving in 1951 and became involved in the new and developing sport of scuba diving in the 1960s.
At the time, specialty equipment was hard to get so John and his colleagues used the DIY attitude to create boats out of wooden planks and Victa lawnmower engines and breathing equipment using hoses and hotel CO2 gas tanks. With these extraordinary apparatus they were among the first to enter the pristine underwater wilderness of the Gippsland coast.
John’s stories describe the evolution of diving gear, the triumphs and near-misses of working in a burgeoning field and the excitement of being the first to dive on the remains of Victoria’s spectacular shipwrecks.
John was interviewed as part of the Heritage Victoria East Gippsland Oral Histories project in 2003. This story includes audio extracts from his interview and a transcript of his full interview.
-

Chinese Australian Families
Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history
From the 1840s onwards, Chinese people have come to Australia inspired by dreams of happiness, longevity and prosperity - of 'jade and gold' in a new and strange land. For most of that time, Chinese people in Australia have been predominantly male. Most of them were temporary sojourners who came to earn money for their families back in the village - most did not intend to settle in Australia.
Despite the predominance of male sojourning, a small proportion of Chinese men in nineteenth-century Australia brought their wives and children to live with them, or married here. As Australian-born children of these families grew to adulthood, their parents would seek brides and grooms on their behalf amongst other Chinese families in Australia.
The majority of post-1905 Chinese brides of Chinese-Australian sons were never able to settle here. Some children were born in China or Hong Kong. Some were born in Australia. Families like this were split for decades, until immigration laws were relaxed.
In the nineteenth century, many of the Chinese men who wanted wives in Australia married or lived de facto with non-Chinese women. At least 500 European-Chinese partnerships are estimated to have occurred before 1900.
Despite repeated waves of racism and official discrimination from the 1840s to the 1970s, a sizeable number of families of Chinese background have put down roots in this country.
In 1973 the Whitlam government abolished racist provisions in immigration laws. Since then, the number of ethnic Chinese migrants has increased dramatically. They have come primarily as family groups - not as sojourners, but as permanent immigrants. They come not only from China and Hong Kong, but also from Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Cambodia and Indonesia, as well as from further afield. The Chinese are now a highly visible and generally accepted part of the Australian community of cultures.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay 'Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history' written by Paul Macgregor for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The full text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Federation Square
It’s increasingly hard to imagine Melbourne without Federation Square. Home to major cultural attractions, world-class events, tourism experiences and an exceptional array of restaurants, bars and specialty stores, this modern piazza has become the city’s focal point; its heartbeat.
Since opening in 2002, Federation Square has received more than 90 million visits. It is currently number two for national and international visitation to Melbourne and is regularly among Victoria’s top two attractions in the state for local visitors.
This response is in part a result of the extraordinary range of event activities held each year. Federation Square is host to more than 2,000 events a year including New Year’s Eve celebrations, Melbourne Festival, Melbourne International Comedy Festival, Melbourne Food and Wine Festival, large public rallies, live sites for major sporting events as well as school holiday and Christmas programs.
Federation Square also hosts major attractions and world-class galleries including The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) and the Melbourne Visitor Centre.
Federation Square is managed by Fed Square Pty Ltd, which was established by the Victorian Government in 1999. Find more information about Fed Square’s history, architecture, the company’s commitment to social responsibility and more at Federation Square website.
-

Young and Jackson Hotel
The Young and Jackson Hotel, built in the 1850s, is one of Australia's most well known hotels. It was built, as the Princes Bridge Hotel, on part of an allotment originally purchased by John Batman in 1837.
Young and Jackson were both born in Dublin, and "chummed together" to New Zealand chasing the Otago gold deposits in 1861. It is not known when they came to Victoria, but they purchased the lease on the Princes Bridge Hotel in 1875.
-
 Jane Routley and Elizabeth Downes
Jane Routley and Elizabeth DownesDegraves Street Subway & Campbell Arcade: The underground artspace
When you first come down the stairs, the Degraves Street Subway seems a bit daunting.
The long, pale pink tiled corridor with its blocked-off doorways and blotched asphalt, seems the perfect place for a mugging. A mysterious blind alley, which used to be an opening into the Mutual Store (and the earliest bowling alley in the CBD), leads off to your right. But stick with this corridor. It’s safe and is actually the route into the Campbell Arcade - a little slice of indie fringe artist-land which I think is a fine place to be.
