Showing 200 items with themes 'Creative Life' or 'A Diverse State'
-
 Jane Routley and Elizabeth Downes
Jane Routley and Elizabeth DownesDegraves Street Subway & Campbell Arcade: The underground artspace
When you first come down the stairs, the Degraves Street Subway seems a bit daunting.
The long, pale pink tiled corridor with its blocked-off doorways and blotched asphalt, seems the perfect place for a mugging. A mysterious blind alley, which used to be an opening into the Mutual Store (and the earliest bowling alley in the CBD), leads off to your right. But stick with this corridor. It’s safe and is actually the route into the Campbell Arcade - a little slice of indie fringe artist-land which I think is a fine place to be.
-

1956 Flood
In 1956, a monster flood overwhelmed the banks of the Murray and Darling Rivers, producing floodwaters in surrounding towns and rural areas that reached over 30 feet above normal levels.
The Murray Darling Environmental Foundation's 1956 Flood video features historical footage - including photographs and wonderful super8 film from personal collections - that document the rise and flow of the waters, and the monumental effort mobilised to tackle them.
It is presented here in 3 extracts.
The full video is over 25 minutes long, and copies can be obtained from:
Emma Bradbury, Murray Darling Association, Post Office Box 1268, Echuca 3564
Email: [email protected]
-
 Hamilton Gallery / Public Galleries Association of Victoria
Hamilton Gallery / Public Galleries Association of VictoriaFrom Watercolours to Decorative Arts
Bequests have been critical to Victoria’s regional galleries, with the wealth generated from farming and the discovery of gold in leading to the establishment and the continuous expansion from colonial times through to today.
Hamilton Art Gallery was established through a bequest from a local grazier, Herbert Buchanan Shaw. The Shaw Bequest consisted of paintings and prints, European silver and glass as well as English, Chinese and Japanese ceramics dating from the 18th century.
Ten years after it was established, Hamilton Art Gallery acquired a group of watercolours by 18th century painter Paul Sandby through a grant from the state government. An upper floor was added to the gallery to accommodate these works.
The collection has continued to grow through gifts, grants and bequests. The original bequest of 870 items has expanded to 8,500 items, making Hamilton Art Gallery one of the largest and most diverse regional gallery collections in Australia, spanning watercolours to decorative arts.
Today, the gallery is divided into six spaces – upstairs you will find the Sandby collection, Asian art, the Print room and Australian art, while on the ground floor you will discover the Shaw Gallery of decorative arts and the Ashworth Gallery for travelling exhibitions.
Featured here is a selection of works from the gallery’s collection – from watercolours by Paul Sandy to world class examples of decorative arts together with work by Australian artists dating from the 19th century to contemporary times. Watch a video to learn about the initial Shaw Bequest and experience the richness and diversity of Hamilton Art Gallery’s collection acquired through the generosity of benefactors and governments over the past fifty years.
-

Unearthing a 19th Century Chinese Kiln
When gold was discovered in Victoria in 1851, stories of treasures of mythical proportions quickly flowed across the world. Desperate to support their families, Chinese men turned to the new opportunities available at ‘Tsin Chin Shan’ - the land of the New Gold Mountain. The majority of Chinese migration to the Bendigo goldfields occurred during the mid-1850s when 16,260 males and one female arrived at Guichen Bay in South Australia and walked overland to Victoria.
By the end of the Bendigo gold rush, many miners were drawn away from Bendigo by news of gold elsewhere in Victoria, Australia and New Zealand. As mining became less profitable, market gardening became a common Chinese occupation, with miners adapting their agricultural skills learnt in China to Australian conditions.
From the 1850s, up to 1,000 Chinese populated an area called Ironbark Chinese Camp. It was reported in 1859 that the large camp had greengrocers, butchers, barbers, doctors, gambling houses, a wine shop, and a joss house. That same year the A’Fok, Fok Sing and Company constructed their brick kiln near the southern end of the camp. The kiln was in operation until it was abandoned in 1886, when the site was transformed into a market garden. The camp area was occupied by Chinese people from the 1850s for at least a hundred years.
In 2005, a section of the mid 19th century Chinese brickmaking kiln was unexpectedly discovered. To determine the condition and extent of the kiln, Heritage Victoria archaeologists conducted a preliminary excavation, with support from an expert in South-east Asian kilns, Dr Don Hein, and support from numerous students and volunteers.
The excavation provided an insight into the size of the kiln, how it operated and a vivid illustration of the transfer of Old World technology to a new country. The A’Fok, Fok Sing and Company kiln is the only known example of a Chinese brick making kiln outside of China. In addition to the kiln, numerous artefacts related to the camp and its activities were discovered, including a variety of food jars, handmade gardening tools, buttons, combs, bowls, gambling tokens, and Clydesdale horseshoes (the horses were used to plough the fields).
The archaeologists covered the excavated section of brick kiln with sand and plastic to protect its fragile fabric. Another excavation is required to uncover the kiln’s working floor and investigate its flue and firing chamber. Only then will we be able to tackle the multitude of questions that still remain to be answered.
The kiln is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. For more information on the kiln or other heritage sites visit The Victorian Heritage Database
-

Wangaratta, Textile Town
It is 1919, the end of First World War, and a group of Wangaratta businessmen come together with a big idea: to build a woollen mill to create jobs, keep people in the town, draw workers and families from afar, and make the town prosper.
They start a share float and one of the men, William Callander, comes up with a bold plan to promote the project. His two daughters Alma and Lena take to the skies in an open biplane, seated on kerosene tins, to scatter leaflets across the region. The Wangaratta Woollen Mills is born, and soon becomes the largest mainland woollen mill in the nation.
It was the success of its textile industry that took Wangaratta from small country town to major rural city. But Wangaratta’s story as a textile town also reflects the making of modern Australia. It traces the path of post-war migration and the accompanying growth of Australia’s economy.
Following the Second World War Australia's prosperity began to boom and thousands of Europeans settled here. It was in this atmosphere, in 1946, that a Canadian company, Bruck Textiles, comes to Wangaratta and creates a population explosion, employing thousands of workers from places as diverse as Poland, Italy, Holland and Wangaratta itself.
Some of these workers' stories are presented here, as well as interviews with employees of Australian Country Spinners (formerly Wangaratta Woollen Mills). Photographs of the factories are also presented, along with moving image postcards of the industrial processes.
-
 Amanda Ahmed and Mali Moir
Amanda Ahmed and Mali MoirAn Eye for Eucalypts
In his hometown of Ararat, Stan Kelly (1911 – 2001) was known as an engine driver and as a talented painter of plants and flowers. A determined amateur, Stan painted at home on a small table and shared his talent by teaching botanical art in Ararat. Today, many Australians travelling overseas carry his artwork in their pocket.
Kelly is now recognised as one of Australia’s premier botanical illustrators, especially respected for his works on eucalypts. His first book, Australian Eucalypts in Colour, was published in 1949. His most celebrated work, Eucalypts Volumes I & II, was first published in 1969 and became a core reference for students of Australian botany.
Kelly received an Order of Australia Medal in 1980. In 2009, he was posthumously honoured when a selection of his botanical illustrations was adapted for the ‘N’ series Australian passport.
The Langi Morgala Museum in Ararat houses a permanent exhibit on Stan Kelly and his work, including a fine collection of his paintings.
A collection of over 500 of Kelly’s watercolour paintings is held by the National Herbarium of Victoria, Royal Botanic Gardens Melbourne.
-

Melbourne Trams: Step aboard!
'Introduction to Melbourne Trams: Step aboard!'
Written by Carla Pascoe, May 2012
Trams are what make Melbourne distinctive as a city. For interstate and overseas visitors, one of the experiences considered compulsory is to ride a tram. When Melbourne is presented to the rest of the world, the tram is often the icon used. The flying tram was one of the most unforgettable moments of the Opening Ceremony of the 2006 Commonwealth Games. When Queen Elizabeth II visited Australia in 2011, she was trundled with regal dignity along St Kilda Road in her very own ‘royal tram’.
The history of trams is closely bound up with the history of this southerly metropolis. Melbourne’s tram system originated during the 1880s economic boom when the Melbourne Tramway and Omnibus Company opened the first cable line. Cable tram routes soon criss-crossed much of the growing city and cable engine houses can still be seen in some inner suburbs, such as the grand building on the south-east corner of Gertrude and Nicholson streets, Fitzroy. Some older passengers like Daphne Rooms still remember riding cable cars.
In the late 19th century, cable and electric tram technologies were vying for supremacy. Australia’s first electric tram line opened in 1889, running through what was then farmland from Box Hill station to Doncaster. The only surviving clue that a tram line once traversed this eastern suburb is the eponymous Tram Road, which follows the former tram route in Doncaster.
Gradually, various local councils joined together to create municipal Tramways Trusts, constructing electric lines that extended the reach of the cable system. In 1920 the tram system came under centralised control when the Melbourne and Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB) consolidated the routes and began electrifying all cable lines.
Manpower shortages during World War II meant that Australian women stepped into many roles previously reserved for men. The tramways were no exception, with women being recruited as tram conductors for the first time. After the war, tram systems were slowly shut down in cities around both Australia and the world, as transport policies favoured the motor vehicle. But thanks to the stubborn resistance of MMTB Chairman, Sir Robert Risson, as well as the wide, flat streets that characterise the city’s geography, Melbourne retained its trams.
Melbourne’s tram industry has always possessed a unique workplace culture, characterised by fierce camaraderie and pride in the role of the ‘trammie’ (the nickname for a tram worker). Many Trammies, like Bruce MacKenzie, recall that they joined the tramways because a government job was seen as a job for life. But the reason they often remain for decades in the job is because of the strong bonds within the trammie ‘family’. This is partly due to the many social events and sporting clubs that have been attended by Trammies, as Bruce MacKenzie remembers. It is also because the demands of shift work bond people together, explains Roberto D’Andrea.
The tram industry once employed mainly working-class, Anglo-Australian men. After World War II, many returned servicemen joined the ranks, bringing a military-style discipline with them. With waves of post-war migration the industry became more ethnically diverse, as Lou Di Gregorio recalls. Initially receiving Italian and Greek workers from the 1950s and 1960s, from the 1970s the tramways welcomed an even broader range of Trammies, from Vietnamese, South American, Turkish and other backgrounds.
Trammies perform a wide range of tasks critical to keeping the system running, including driving, track maintenance, tram maintenance, time tabling, customer service and more. But just as designs of ‘rolling stock’ have changed - from the beloved veteran W class trams to the modern trams with their low floors, climate control and greater capacity - so too have the jobs of Trammies changed over time. Bruce MacKenzie remembers joining the Preston Workshops in the 1950s when all of Melbourne’s fleet was constructed by hand in this giant tram factory. Roberto D’Andrea fondly recalls the way that flamboyant conductors of the 1980s and 1990s would perform to a tram-load of passengers and get them talking together. As a passenger, Daphne Rooms remembers gratefully the helping role that the connies would play by offering a steadying arm or a piece of travel advice.
Trams have moved Melburnians around their metropolis for decades. As Daphne maintains, ‘If you can’t get there by tram, it’s not worth going’. Everyone has memories of their experiences travelling on trams: some funny, some heart-warming and some frustrating. Tram driver, Lenny Bates, tells the poignant story of the blind boy who would sometimes board his tram on Collins Street and unhesitatingly call out the names of the streets they passed. As the films in this collection demonstrate, every passenger has their routes that they customarily ride and these routes take on a personal meaning to their regulars. You could say that every tram line has its own distinct personality. Whilst the way the tram system is run inevitably changes across time, one thing has been constant: trams have always played a central role in the theatre of everyday life in Melbourne.
-

The Koorie Heritage Trust Collections and History
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
The Koorie Heritage Trust was established in 1985 with a commitment to protect, preserve and promote the living culture of the Indigenous people of south-east Australia.
Today the Trust boasts extensive collections of artefacts, paintings, photographs, oral history recordings and library materials.
Further information on Tommy McRae can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site
-

The Ross Sea Party
As Shackleton’s ambitious 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition' of 1914 foundered, the Ross Sea party, responsible for laying down crucial supplies, continued unaware, making epic sledging journeys across Antarctica, to lay stores for an expedition that would never arrive.
In 1914 Ernest Shackleton advertised for men to join the Ross Sea Party which would lay supply deposits for his 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition'. Three Victorians were selected for the ten-man shore party: Andrew Keith Jack (a physicist), Richard Walter Richards (a physics teacher from Bendigo), and Irvine Owen Gaze (a friend of Jack’s).
The Ross Sea party commenced laying supplies in 1915 unaware that Shackleton’s boat Endurance had been frozen in ice and subsequently torn apart on the opposite side of the continent (leading to Shackleton’s remarkable crossing of South Georgia in order to save his men). Thinking that Shackleton’s life depended on them, the Ross Sea Party continued their treacherous work, with three of the men perishing in the process. The seven survivors (including Jack, Richards and Gaze) were eventually rescued in 1917 by Shackleton and John King Davis.
In total, the party’s sledging journeys encompassed 169 days, greater than any journey by Shackleton, Robert Scott, or Roald Amundsen – an extraordinary achievement.
Jack, Gaze and others in the party took striking photographs during their stay. Jack later compiled the hand coloured glass lantern slides, which along with his diaries, are housed at the State Library of Victoria.
-

History in Place
The History in Place project connects teachers and students with their local history via a community collecting society or museum.
History in Place provides an innovative and practical implementation of the new Australian Curriculum in History and Victoria's Framework of Historical Themes. It provides a framework for students to engage with their local history and heritage in a fun and challenging way using digital technologies. The program has been designed for grades 5 and 6, but has also been used for year 9s.
History in Place can be initiated either by schools or by community museums and heritage organisations. Students use collection items and interviews with local experts to create short films using tablet devices.
This story includes examples of what happens during a day of History in Place, examples of student films from the program pilot and an education toolkit (available from the Education Resources tab below) which includes course materials, instructional materials and everything that a museum and school need to implement the program.
The pilot program partnered 6 primary schools from across Victoria with local museums.
Museums participating in the pilot were: Barwon Park, Burke Museum, CO.AS.IT Museum, Golden Dragon Museum, the Mildura Arts Centre and Yarra Ranges Museum.
The project is a partnership between the Heritage Council of Victoria, the History Teachers' Association of Victoria and Culture Victoria. The pilot was funded by the Telematics Trust.
During the History in Place pilot, students used the Linking History site to research their films. Linking History is an experimental pilot in the practical application of linked open data, and is part of Portrait of a Nation: History In Place Access Project which is a Centenary of Canberra project, proudly supported by the ACT Government and the Australian Government.
-
 Rachael Cottle
Rachael CottleStories of Support
The 2016 Museums Australia (Victoria) Conference held at Phillip Island in October, was the inspiration for this story. A drive around the Island on arrival unearthed a surprise in Newhaven - the former Boys Home standing silent and abandoned, looming over the ocean.
Care homes were once an essential part of Victorian life. The gold rush and population increase in Victoria created a need for charitable organisations to provide care to those who could not care for themselves, most notably children. Providers of care have also included societies for people with special needs including the 'Deaf and Dumb', and the asylums and hospitals of Victoria. This continued until the late 20th century when reform was prompted by revelations of abuse in the institutional system. The care model has since shifted towards kinship and foster services.
Victoria’s former institutions of care are an important part of our history. Whilst many of the buildings—often architecturally brilliant— no longer exist, they are remembered through the photographs and artefacts held by collecting organisations across the state and catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-

Panorama: A question of perspective
TarraWarra Museum of Art is located in the picturesque Yarra Valley in Victoria, Australia.Visitors to the Museum are afforded a spectacular, resonant and panoramic experience of ‘nature’ through the north facing windows. The view stretches towards the distant Toolangi rainforest across planted vines, native bushland and farmland.
The region is surrounded by a spectacular mountain range that includes Mt Baw Baw, Mt Donna Buang, Mt Juliet, Mt Riddell and Mt Toolebewong. As these names attest, we are situated in an area of significant Indigenous history and colonisation. Tarrawarra is a Wurundjeri word that translates approximately as ‘slow moving water’ and is the name given to the area in which the Museum is located.
The Yarra Valley sunsets, soundscapes, seasonal changes, Indigenous histories, ecological vulnerabilities and environmental challenges are in a complex and ever changing entanglement. Since 2012, the Museum has explored this context through special exhibitions and commissions, forums and performances, screenings and lectures. As such, the Museum has sought to understand the complexity of our site, and with that, the broader intersections between art and landscape. Artists provide us the opportunity to ‘see’ the landscape in a different way. They imagine it, call it into being, reflect upon it, animate it, unravel its hidden histories, and expose its ecological sensitivities.
Panorama, the exhibition, was an integral part of this ongoing conversation and imaginative exploration. Our intention was not so much to write a narrative history of Australian landscape painting. Rather, it was to be attuned to the intermingling of voices, points of view, perspectives - colonial and modern, contemporary and Indigenous – that comprise the uniquely Australian persistence to unravel the ‘patter’ of nature.
As a phenomenon to which we are all very accustomed, it is easy to overlook the simple fact that for a landscape to come into being it requires a ‘point of view’, a subjective consciousness to frame a particular expanse of the natural world. As the art historian Simon Schama remarks in his landmark survey on the genre, Landscape and Memory, ‘it is our shaping perception that makes the difference between raw matter and landscape’. [i] The centrality of the viewer’s position in constructing a vista is clearly evident in terms such as ‘perspective’, ‘prospect’, and ‘view point’ which are synonymous with ‘position’, ‘expectation’, and ‘stance’. This highlights that there is always an ineluctable ideological dimension to the landscape, one that is intimately entwined with a wide range of social, economic, cultural and spiritual outlooks. Turning to the notion of the panorama, a brief survey of its conception and infiltration into everyday speech, reveals how our way of seeing the landscape is often tantamount to the formation and delineation of our personal, communal, and national identities.
The term panorama was first coined to describe the eponymous device invented by the British painter Robert Barker which became a popular diversion for scores of Londoners in the late 18th century. Consisting of a purpose built rotunda-like structure on whose cylindrical surface landscape paintings or historical scenes were displayed, ‘The Panorama’ contained a central platform upon which viewers observed the illusionistic spectacle of a sweeping 360 degree vista. With its ambitious, encyclopaedic impulse to capture and concentrate an entire panoply of elements into a singular view, it is telling that this construction would soon give rise to an adjective to describe, not only an expansive view extending in all directions, but also a complete and comprehensive survey of a subject. As the curators Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline argue, these different meanings convey ‘the very essence of the panoramic phenomenon: the central role of perspective, a certain appropriation of the world that follows, the feeling of dominating a situation simply due to having a wide and complete view’.[ii] Indeed, as art historian Michael Newman reveals, the whole notion of the panorama originated in military conceptions of the landscape as a battlefield, whereby strategic vantage points are key to tactical planning.[iii] Underlying its transformation into a form of popular entertainment, the panorama is rooted in a particular form of political authority based on surveying, mapping and commanding the subject of the view.
In this exhibition, the term panorama was invoked to acknowledge that ways of perceiving the landscape have their own histories which have arisen out of particular social, political and cultural contexts. As the landscape architect Anne Whiston Spirn contends: ‘In every landscape are ongoing dialogues; there is “no blank slate”; the task is to join the conversation’.[iv]However, far from claiming to present an unbroken view or a complete survey, Panorama challenged the very notion of a single, comprehensive monologue by presenting a series of works which engaged with the discourse of landscape in a diverse range of voices. Taking advantage of the tremendous depth and strength of the TarraWarra Museum of Art collection gifted by its founders Eva Besen AO and Marc Besen AC, the exhibition was staged in two parts, with a different selection of paintings exhibited in each half. Displayed in distinct groupings which explored alternative themes and concerns, Panorama highlighted the works of key artists who have redefined, expanded and interrogated the idea of the landscape in ways which suggest that it is far from settled.
Further Information
[i] Simon Schama, Landscape and Memory, New York: Vintage Books, 1996, p. 10.
[ii] Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline, Introductory text for the exhibition I Love Panoramas, MuCEM and the Musées d’Art et d’Histoire, Geneva, 4 November 2015 - 29 February 2016, URL: http://www.mucem.org/en/node/4022
[iii] See ‘The Art Seminar’ in Landscape Theory, (eds. Rachael Ziady DeLue and James Elkins), New York and London: Routledge, 2008, p. 130.
[iv] Anne Whiston Spirn, ‘“One with Nature”: Landscape, Language, Empathy and Imagination’ in Landscape Theory, 2008, p. 45.
-

Working and Learning
Stories about our working lives, education, and looking to the future.
The videos include excerpts from "Lady of the Lake"- Gunditjmara Elder Aunty Iris Lovett-Gardiner's accounts of Lake Condah Mission and Indigenous experiences there and excerpts from the film "Baranjuk" about Uncle Wally Cooper a Yorta Yorta Elder.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

Dame Nellie Melba
“...the voice, pure and limpid, with an adorable timbre and perfect accuracy, emerges with the greatest ease.” Arthur Pougin, in Le Ménestral (Paris), May 12, 1889.
Dame Nellie Melba (1861 – 1931), was Australia’s opera superstar, performing in the great opera houses of the world - the Paris Opera, La Scala, the Metropolitan Opera House, and the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden, where she became prima donna, returning season after season.
The extensive Melba Collection at the Victorian Arts Centre includes costumes, records, accessories, letters, programs, photographs, opera scores and other personal effects. Other holdings of interest include 78rpm disks at the State Library of Victoria.
-
 Amy Tsilemanis
Amy TsilemanisTalking Shop: Ballarat in Business & City Life at Ballaarat Mechanics' Institute
Between January and April 2019, the Ballaarat Mechanics' Institute hosted the exhibition Talking Shop, exploring a world of Peters ice cream cones, milk bars, vintage advertising, historic photographs and ephemera.
This nostalgia was complemented by contemporary photographs and creative responses exploring Ballarat’s shops and businesses. Community events throughout the exhibition invited the people of Ballarat to contribute their images and memories to the BMI collection, and are shared here in this story.
This exhibition was curated by Amy Tsilemanis at the BMI who worked with artists Pauline O'Shannessy-Dowling and Margie Balazic, collector John Kerr and Ballarat businesses, council, and schools to create a 'generative' exhibition where material and collaborations could grow.
Wanting to know more about Ballarat’s booming business history? Take a digital tour of the exhibition here: https://invictoria.com.au/talking-shop-exhibition
-
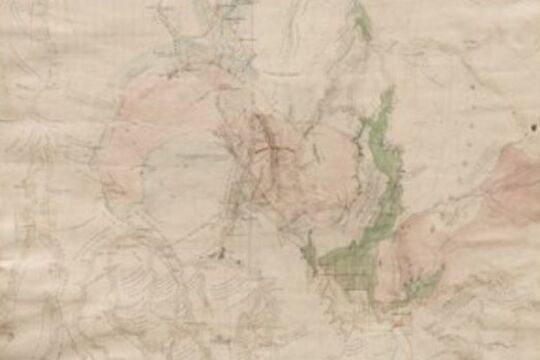
Mapping Great Change
This series of films and stories is centred on a beautiful and complex map with the ungainly name: Plan of the General Survey from the Town of Malmsbury to the Porcupine Inn, from the sources of Forest Creek to Golden Point, shewing the Alexandrian Range, also Sawpit Gully, Bendigo and Bullock Creeks.
In many ways, the map is a mirror of our times: the map is a record of the 'critical years' between 1835 and 1852 in which the dispossession of Aboriginal people of Victoria was allowed to occur; we contemporary people are in the "critical decade" for making the changes necessary to avoid catastrophic climate change.
If we fail to act effectively in this decade, it will be as loaded with moral and practical consequences for coming generations as the moral and policy failures of our colonial ancestors was for the Traditional Owners of the land.
