Showing 123 items with themes 'Creative Life' or 'Local Stories'
-
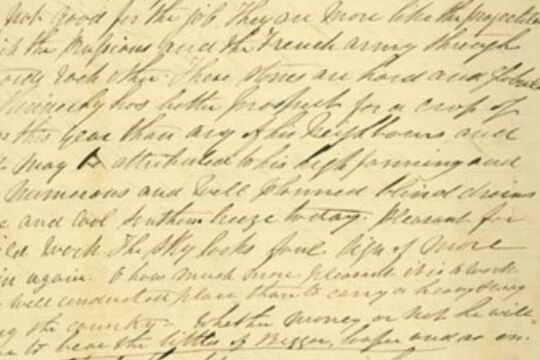
The Welsh Swagman
Joseph Jenkins was a Welsh itinerant labourer in late 1800s Victoria.
Exceptional for a labourer at the time, Jenkins had a high level of literacy and kept detailed daily diaries for over 25 years, resulting in one of the most comprehensive accounts of early Victorian working life.
Itinerant labourers of the 1800s, or 'swagmen', have become mythologised in Australian cultural memory, and so these diaries provide a wonderful source of information about the life of a 'swagman'. They also provide a record of the properties and districts Jenkins travelled to, particularly around the Castlemaine and Maldon area.
The diaries were only discovered 70 years after Jenkins' death, in an attic, and were in the possession of Jenkins’s descendants in Wales until recently, when they were acquired by the State Library of Victoria in 1997.
-

Among Mates: Caulfield RSL
In the wake of the First World War, a generation of men returned to Australia.
Irrevocably altered by their war experiences, many also found they had to contend with unemployment, debilitating injuries and trauma. It was this atmosphere that gave rise to the formation of small service clubs, with the protection of returned servicemen’s rights high on the agenda.
The 11th Australian General Hospital, set up to deal with the extraordinary number and severity of soldiers’ enduring injuries and illnesses, was situated in Caulfield. The hospital convalescents formed the basis of The Caulfield and District Returned Sailors and Soldiers Social Club, established in August, 1918. A year later, the club was chartered, and Caulfield went on to become one of the most prominent and influential RSL clubs in the country, with such members as Stan Savige, the founder of Legacy, and Harold Cobby, the WW1 Air Ace, and patrons such as Sir John Monash. Over half a dozen Victoria Cross winners were early members of the club.
The collection at Caulfield RSL is mainly a result of donations from members and their families. Many items are souvenirs of war, collected by the soldiers on their journeys, and include arms, uniforms, trench art, photographs, and documents.
-
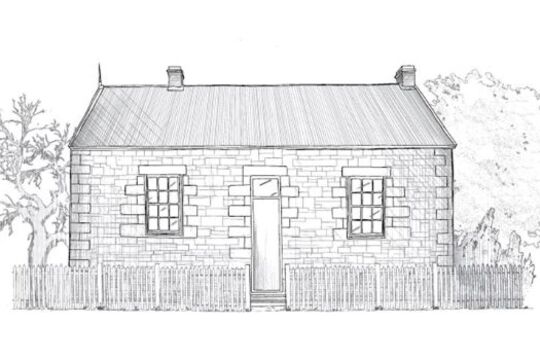
What House Is That?
More than just bricks and mortar, our homes are prisms, reflecting the society of the time they were built. Through them, we can understand the changing context of social, economic and architectural history, and the values and assumptions of the people who built and lived in them.
What house is that? is an exploration of the social and architectural history of Victoria’s housing styles. From our earliest Victorian cottages through to the light filled, open plan houses of the Modern era, we look at the houses Victorians call home.
The nine images and text give an overview of each of the main housing styles of Victoria’s history from the 1840s onwards. The 15 videos feature interviews with architects, historians and residents and explore the styles in more detail. This collection of images, text and videos comes from an interactive website created by Heritage Victoria.
-

60s & 70s waves
Since the 1960s Australia has welcomed migrants from Asia, Africa, Oceania, the Middel East and South America.
Many migrated to flee from the ravages of war, hunger, religious persecution or political repressions in their home country. Others were seeking a new beginning, a brighter future or reunification with loved ones.
These stories produced through ACMI’s Digital Storytelling program share the personal experiences of migration and settlement and are a testimony to the cultural diversity of modern Australia.
-
 Mark S. Holsworth
Mark S. HolsworthArt at Flinders Street Station
The average commuter passing through Flinders Street Station could remain blissfully unaware for their entire lives of anything more artistic in the station than the endless advertising images.
However, as befitting any major public building, there is some commissioned art at Flinders Street Station.
-
 Vicki Couzens
Vicki CouzensMeerreeng-an Here Is My Country
The following story presents a selection of works from the book Meerreeng-an Here is My Country: The Story of Aboriginal Victoria Told Through Art
Meerreeng-an Here is My Country: The Story of Aboriginal Victoria Told Through Art tells the story of the Aboriginal people of Victoria through our artworks and our voices.
Our story has no beginning and no end. Meerreeng-an Here is My Country follows a cultural, circular story cycle with themes flowing from one to the other, reflecting our belief in all things being connected and related.
Our voices tell our story. Artists describe their own artworks, and stories and quotes from Elders and other community members provide cultural and historical context. In these ways Meerreeng-an Here Is My Country is cultural both in its content and in the way our story is told.
The past policies and practices of European colonisers created an historic veil of invisibility for Aboriginal communities and culture in Victoria, yet our culture and our spirit live on. Meerreeng-an Here Is My Country lifts this veil, revealing our living cultural knowledge and practices and strengthening our identity.
The story cycle of Meerreeng-an Here Is My Country is presented in nine themes.
We enter the story cycle by focusing on the core cultural concepts of Creation, Country, culture, knowledge and family in the themes 'Here Is My Country' and 'Laws for Living'.
The cycle continues through ceremony, music, dance, cloaks, clothing and jewellery in 'Remember Those Ceremonies' and 'Wrap Culture Around You'. Land management, foods, fishing, hunting, weapons and tools follow in 'The Earth is Kind' and 'A Strong Arm and A Good Eye'.
Invasion, conflict and resilience are explored in 'Our Hearts Are Breaking'. The last two themes, 'Our Past Is Our Strength' and 'My Spirit Belongs Here', complete the cycle, reconnecting and returning the reader to the entry point by focusing on culture, identity, Country and kin.
Visit the Koorie Heritage Trust website for more information on Meerreeng-an Here Is My Country
-

Dimitri Katsoulis, Greek Puppet Master
Traditional Greek shadow puppet theatre evolved from the Turkish model, which dates back to at least the 16th century.
The central figure is the character Karaghiozis, who relies on his wit and cunning to extricate himself from precarious situations. He and other characters are involved in humorous and satirical moral tales that comment on social and political life.
Dimitri Katsoulis immigrated to Melbourne in 1974 to escape the Junta regime that repressed Greek artists. He had trained in Greece with theatre and film companies as an actor and technician, as well as in shadow puppetry with masters of the art form. While earning a living in a Melbourne metal factory, he co-founded the Children's Theatre of Melbourne. Dimitri performed Greek shadow puppetry until 1991, exploring contemporary and controversial issues such as women's equality, and the isolation of migrant women and children.
-

Wimmera Stories: The Dimboola Banner, communicating history
The first issue of the Dimboola Banner rolled off the press on 10 May 1879, printed by a Mr Henry Barnes and edited by his brother, William.
Many proprietors and editors have come and gone since then but today, more than 130 years later, the Banner is still published weekly, even though it’s now printed in Warracknabeal rather than in Dimboola itself.
Meanwhile, the former Dimboola offices of the Banner have been acquired by the Dimboola & District Historical Society and transformed into a Newspaper and Letterpress printing museum. The museum owns and operates a diverse collection of vintage presses, all in working condition.
Newspapers and printers have traditionally played a vital role in the life of country communities, and a long-time newspaper man comes to know most things there are to know about the life of their town and district. Joe Barry spent 54 years in the newspaper and printing business in Dimboola, which means he’s well qualified to impart a wealth of tales to visitors at the Dimboola Printing Museum.
The printing trade has seen many vast and radical technological transformations, particularly with the dawn and evolution of the current digital era. The Dimboola Printing Museum preserves a vast wealth of functioning relics from earlier eras of print technology, including letterpresses well over a century old in perfect working order.
The museum collection also includes a vast amount of loose type from the long-gone era of hand-set typography.
-
 Jary Nemo and Lucinda Horrocks
Jary Nemo and Lucinda HorrocksCollections & Climate Change
The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before.
Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans, is having an impact on a global scale. In particular, human activity has altered the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the world’s climate to change.
Already in the state of Victoria we are seeing evidence of this change around us. In the natural world, coastal waters are warming and bringing tropical marine species to our bays. Desert animals are migrating to Victoria. Alpine winters are changing, potentially putting plants and animals at risk of starvation and pushing species closer to the margins. In the world of humans, island and coastal dwellers deal with the tangible and intangible impacts of loss as sea levels rise, bush dwellers live with an increased risk of life-threatening fires, farmers cope with the new normal of longer droughts, and we all face extreme weather events and the impacts of social and economic change.
This Collections and Climate Change digital story explores how Victoria’s scientific and cultural collections help us understand climate change. It focuses on three Victorian institutions - Museums Victoria, the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria and Parks Victoria. It looks at how the information gathered and maintained by a dedicated community of researchers, curators, scientists, specialists and volunteers can help us understand and prepare for a hotter, drier, more inundated world.
The story is made up of a short documentary film and twenty-one examples highlighting how botanical records, geological and biological specimens and living flora and fauna provide a crucial resource for scientists striving to map continuity, variability and change in the natural world. And it helps us rethink the significance of some of Victoria’s cultural collections in the face of a changing climate.
-
 Eleanor Whitworth
Eleanor WhitworthMartin Hallett: In celebration of a career
Victoria is privileged to have a robust GLAM (Galleries, Libraries, Archives and Museums) sector. The capacity of our sector is the result of work undertaken by many dedicated people. We would like to take a moment to acknowledge and celebrate a colleague who has played a particularly significant role in ensuring the strength of the Victorian scene.
In April 2016, Martin Hallett retired from his role as Senior Manager of Victorian Cultural Network, part of the Agencies and Infrastructure unit of Creative Victoria. Martin was subsequently awarded with a Victorian Public Service Medal and a Lifetime Achievement Award at the Victorian Museum Awards for his four decades of work in the Victorian collections sector.
-

What’s Going On!
What’s Going On! was a groundbreaking exhibition presenting contemporary indigenous artists from the Murray Darling basin.
Taking Mildura as the centre, at the confluence of the Murray and Darling Rivers, the exhibition ranges from Menindee, Wilcannia and Broken Hill to the north and north east, Berri in the south west and Swan Hill to the east, dissolving State boundaries that fragment this distinct region. Uniting the artists in the exhibition are extended family networks and connections to country.
There is a much-loved story told by Aboriginal people on the Murray, that when you open out the swim bladder of a Murray cod, the tree-like forms of its skin reveal the place where the fish was born. Aboriginal children are sometimes told that this is the very same tree under which they were born. These various skin stories reveal the connection of people to the Murray Darling river system, where ‘everyone has a place under the tree’.
-

Images of Melbourne
Explore Melbourne through selected works from the National Gallery of Victoria.
These artworks capture phases of the city's development, and offer a portrait of the people, places and streetscapes that define it.
-

Dame Nellie Melba
“...the voice, pure and limpid, with an adorable timbre and perfect accuracy, emerges with the greatest ease.” Arthur Pougin, in Le Ménestral (Paris), May 12, 1889.
Dame Nellie Melba (1861 – 1931), was Australia’s opera superstar, performing in the great opera houses of the world - the Paris Opera, La Scala, the Metropolitan Opera House, and the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden, where she became prima donna, returning season after season.
The extensive Melba Collection at the Victorian Arts Centre includes costumes, records, accessories, letters, programs, photographs, opera scores and other personal effects. Other holdings of interest include 78rpm disks at the State Library of Victoria.
-

Digital Stories of Young Adults
Being a teenage mother, expressing the power of music and defining identity and sexuality are just some of the stories shared by the young people who have taken part in the Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) Digital Storytelling program.
Inside each story is a profusion of ideas and emotions that are edited together as an illuminating way for the young storytellers to evoke memories, places and events that inspire them. Digital Storytelling provides a powerful multimodal learning tool that allows young people to tap into their creativity and critical awareness while allowing for a fluid manipulation and construction of technical and storytelling knowledge.
For more information visit the Australian Centre for the Moving Image website
-

Illuminated by Fire
These short films, created for the Illuminated By Fire project by Malcolm McKinnon, tell a range of stories about living in some of the most fire-prone places on the planet.
They reveal a wealth of knowledge, experience and imagination in our response to fire.
The Illuminated By Fire project is about the places we care about and the story and role of fire within those places.
-

Kylie's Costumes
From Neighbours character, Charlene, to international pop sensation, Kylie Minogue’s costumes chart her rise, her style, and her creative energy.
The Kylie Costume Collection at the Arts Centre, Melbourne, shows the range and development of Kylie's persona through costume, and her collaborations with international and national designers.
As Kylie donates her costumes to the Arts Centre directly, curators are able to keep an extensive, chronological and very complete material record of Kylie's career, across her tours, album cover shoots, music videos, and red carpet and special events.
