Showing 36 items with the theme 'Immigrants And Emigrants'
-

Savoy Ladies Group
The Italian community of Myrtleford, in the picturesque Ovens Valley in alpine North Eastern Victoria, arrived mainly to work in the tobacco industry which once thrived in the area. The region now has a distinctive Italian-Australian culture with settled second, third and fourth generation Italian families.
Tobacco farming was a lonely experience for many of the Italian women who migrated to Myrtleford. Unlike their husbands, the women stayed largely on the farms and lacked social contact outside of their immediate circle. Once their children grew up and mechanisation changed the labour requirements on the farms, women were frequently on their own.
The Myrtleford Savoy Ladies Group was founded in 1983 by nuns concerned about the social isolation of women in the area. It has been a great success, forming a network of companionship amongst women of Italian heritage to this day.
Cultural Warning: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users of this website are warned that this story contains images of deceased persons and places that could cause sorrow.
-

Chinese Australian Families
Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history
From the 1840s onwards, Chinese people have come to Australia inspired by dreams of happiness, longevity and prosperity - of 'jade and gold' in a new and strange land. For most of that time, Chinese people in Australia have been predominantly male. Most of them were temporary sojourners who came to earn money for their families back in the village - most did not intend to settle in Australia.
Despite the predominance of male sojourning, a small proportion of Chinese men in nineteenth-century Australia brought their wives and children to live with them, or married here. As Australian-born children of these families grew to adulthood, their parents would seek brides and grooms on their behalf amongst other Chinese families in Australia.
The majority of post-1905 Chinese brides of Chinese-Australian sons were never able to settle here. Some children were born in China or Hong Kong. Some were born in Australia. Families like this were split for decades, until immigration laws were relaxed.
In the nineteenth century, many of the Chinese men who wanted wives in Australia married or lived de facto with non-Chinese women. At least 500 European-Chinese partnerships are estimated to have occurred before 1900.
Despite repeated waves of racism and official discrimination from the 1840s to the 1970s, a sizeable number of families of Chinese background have put down roots in this country.
In 1973 the Whitlam government abolished racist provisions in immigration laws. Since then, the number of ethnic Chinese migrants has increased dramatically. They have come primarily as family groups - not as sojourners, but as permanent immigrants. They come not only from China and Hong Kong, but also from Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Cambodia and Indonesia, as well as from further afield. The Chinese are now a highly visible and generally accepted part of the Australian community of cultures.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay 'Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history' written by Paul Macgregor for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The full text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Post-War Europe
In 1945, Australian Prime Minister Chifley lead the Labor Party to power in Canberra and sought to change the national focus from agriculture to industry.
His government established the Department of Immigration, which soon introduced a policy of financially supporting migration to Australia. Due to the 2nd World War, large numbers of displaced people and refugees that took up this opportunity. Most came from Great Britain and Europe and on arrival were provided accommodation in hostels or transition camps in return for a commitment to provide labour on government funded projects for a period of two years.
These personal stories produced as part of the ACMI Digital Storytelling program recount the journeys of people in the Post War Immigration Scheme.
Discover the story of Australia’s involvement in the Second World War, from primary sources at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site : - Australia & WWII
-

Recent Arrivals
The Australian Government’s policy of mandatory detention of unauthorised arrivals by boat has been the subject of intense political and national debate in recent years around the ethics of detaining people who in many cases have fled their homeland to escape conflict or oppression.
These stories produced as part of the ACMI Digital Storytelling program document the experiences of people who have recently arrived in Australia.
-

Caroline Chisholm's Scrapbook
Caroline Chisholm, 19th century social reformer and philanthropist, left few personal effects to shed light on her remarkable life.
This scrapbook, handed down through the Chisholm family, and presented to the Museum by the family of a Chisholm historian, consists of material relating to Chisholm's work assisting immigrants, both to emigrate and once they had arrived.
In the scrapbook we find newspaper clippings, public notices, posters, correspondence and minutes; dating from 1843. Posters advertise the immigration lectures she gave across Great Britain; railway tickets stamped for free indicate the distances she travelled and the official support for her project; invitation cards reveal a woman circulating in high society, where fundraising efforts would have been concentrated; lists of names record the people she assisted financially to migrate to Australia.
The ephemera of life, so easily dispersed and discarded have been preserved in perpetuity in a humble ledger.
-
 Kate Luciano
Kate LucianoSchool Days: Education in Victoria
The exhibition, School Days, developed by Public Record Office Victoria and launched at Old Treasury Building in March 2015, is a history of more than 150 years of schooling in Victoria.
It is a history of the 1872 Education Act - the most significant education reform in Victoria, and a world first! It is a history of early schooling, migrant schooling, Aboriginal schools, women in education, rural education and, of course, education during war time (1914-1918).
This online exhibition is based on the physical exhibition School Days originally displayed at Old Treasury Building, 20 Spring Street, Melbourne, www.oldtreasurybuilding.org.au and curated by Kate Luciano in collaboration with Public Record Office Victoria.
-

Restoring St Nicholas
St Nicholas church in Humffray St, Ballarat East, was built in 1867. Originally named the Bible Christian Church, it was built by Cornish miners in the evenings and weekends after they had returned from their work at the diggings.
Like most buildings of its time it was built to last, constructed of solid brick with lime mortar. By the 1970s, the mortar was crumbling and the church community of the time re-mortared it with cement, a process we now know was incorrect for buildings of its age. The cement mortar, combined with rising damp, caused salt attack in many of the original bricks and the building literally began to crumble.
In 2009 the Greek Orthodox community of St Nicholas approached the City of Ballarat, Heritage Victoria and the trade school at the University of Ballarat to form a unique partnership to restore the church. This project allowed young apprentices to learn traditional trade skills and practice the technique of mixing and using lime mortar. In the process, the humble church has had its life extended, and the Greek community have a religious and cultural centre they can use for generations to come.
-

The Apinis Loom
When Latvian refugees Anna and Ervins Apinis arrived in Australia in 1950 they brought with them a loom built of wood salvaged from bombed out German ruins, along with Anna's precious notebooks full of traditional fabric designs.
Anna Strauss was born in 1913 in Latvia. She attended weaving lessons in Leipaja from 1930 to 1933 and spent hours at the nearby Ethnographic Museum recording traditional fabric designs in her notebooks.
She married Ervins Apinis, an engineer, in 1938 and they had a son but soon World War II changed their lives. Ervins was conscripted into the German army while Anna fled Latvia, finally ending up in Memmingen Displaced Persons camp in Germany in 1945. There, they were finally reunited, remaining in the camp for five years until they migrated to Australia in 1950.
When they arrived at Parkes Holding Centre in New South Wales, they were so exhausted from their long journey, they slept on a huge wooden crate containing the traditional Latvian loom they had brought with them, built of wood scavenged from bombed German ruins. This loom is now at the Immigration Museum in Melbourne.
Anna continued her weaving traditions, passing her knowledge to her daughter Anita.
-

Made in Bendigo, Cold Beer!
In 1857 at the height of the gold rush, with people pouring into Central Victoria from all over the world, three brothers from Denmark – Moritz, Julius and Jacob Cohn – founded a small cordial factory in the booming town of Bendigo.
They went on to build an empire and, through introducing lager, which is served cold, to the country, changed the drinking preferences of Australians.
Cordial was a necessity at the time as water was considered unpalatable. The Cohn cordial products were successful and the brothers went on to produce other staples such as fruit preserves. The Cohn Brothers were canny businessmen and at the peak of their success Cohn products were sold across the country and exported to the United Kingdom and Asia. The brothers went on to hold prominent positions on the local Council, and were part of the group that founded the Bendigo Land and Building Society, which became the Bendigo Bank.
Traces of the impact that Cohn products had on the daily lives of Australians, particularly those in Central Victoria, can be found in vintage bottles, wooden crates and signs that have been collected and preserved.
The legacy of their business and civic activities are told through interviews with their descendent, Helen Bruinier, Bendigo Art Gallery Curator, Sandra Bruce, and Frank Barr, the sign painter of the Cohn’s Cordial sign in Bridge Street, Bendigo.
-

Second Generation
For many migrants, the real benefits of migration are seen in the second generation of the family, as migration has afforded life opportunities for their children that would have been unavailable to them in their homeland.
Through ACMI’s Digital Storytelling program, the children of migrants document their personal stories and share the richness and challenges of their bicultural lives in Australia.
-

Digital Stories of Young Adults
Being a teenage mother, expressing the power of music and defining identity and sexuality are just some of the stories shared by the young people who have taken part in the Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) Digital Storytelling program.
Inside each story is a profusion of ideas and emotions that are edited together as an illuminating way for the young storytellers to evoke memories, places and events that inspire them. Digital Storytelling provides a powerful multimodal learning tool that allows young people to tap into their creativity and critical awareness while allowing for a fluid manipulation and construction of technical and storytelling knowledge.
For more information visit the Australian Centre for the Moving Image website
-

William Buckley
After convict William Buckley’s escape from a Victorian settlement he was discovered by the Wathaurang people who thought this pale, 198cm giant carrying a spear was the ghost of one of their leaders.
Buckley had arrived at Port Phillip from England in 1803 with about 300 soldiers, settlers and convicts after being sentenced to transportation for life. Before the Port Phillip and Sullivan Bay (Victoria’s first official European settlement) settlement was abandoned, Buckley escaped. He wandered alone for weeks before he was befriended by the Wathaurang people.
Over the next 32 years Buckley lived with the Wathaurang, learnt their language and customs, married and had a daughter. In 1835 he finally emerged to meet Batman’s colonising party and tried to work as an intermediary between settlers and aborigines, but felt he wasn’t trusted by either.
His name lives on in Australian slang with the ironic saying “you’ve got Buckley’s chance” or “Buckley’s hope”.
Further material can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site:-
William Buckley's Escape
Buckley and the Aborigines
Buckley's return to European life
-

Paintings Porcelain and Photography
Geelong Gallery was established in 1896 by twelve passionate citizens who believed Victoria's second largest and fastest growing city deserved an art institution befitting an aspiring metropolis. Since then, Geelong Gallery has established a collection of some 6,000 items – significant amongst these items are their holdings of paintings, porcelain and photography.
The gallery’s collection of Australian painting tells the history of the region from colonial times to the early twentieth century. Eugene von Guerard’s View of Geelong provides a sweeping panorama of Geelong seen from a vantage point near the village of Ceres in the nearby Barrabool Hills in 1856. While Arthur Streeton’s painting Ocean blue, Lorne, one of the gallery’s most recent acquisitions, depicts a shimmering summery sky, a view through slender young gum trees and down to the pristine sand and aquamarine ocean below in the 1920’s.
Geelong Gallery has a large and specialised collection of British painted porcelain spanning 1750 – 1850. It is one of the most significant holdings in Australia and is part of a bequest by well-known local citizen Dorothy McAllister. A fine example is the 'Buckingham Palace' card tray by renowned manufacturer Worcester dating to the 1840’s.
The gallery’s photographic collection is very much of the twentieth century, but not without references to earlier times and other works in the collection. Polixeni Papapetrou’s photograph In the Wimmera 1864 #1 created in 2006 examines the narrative of the ‘lost child’ and refers to Frederick McCubbin’s late nineteenth century paintings of children ‘lost’ or at least wandering absent-mindedly through the Australian bush.
-

Family Stories
From the nuclear to the extended family, from groups of close friends, communities and neighbourhoods, to one on one relationships: family means many different things to different people.
Family describes our most cherished, and sometimes most difficult, relationships. In this collection of digital stories and videos, Victorians share their family stories.
Family stories include stories of immigration; disadvantage and survival, indigenous life, stories of sickness and health; life and death; childhood and old age.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that some of the videos in this story may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-
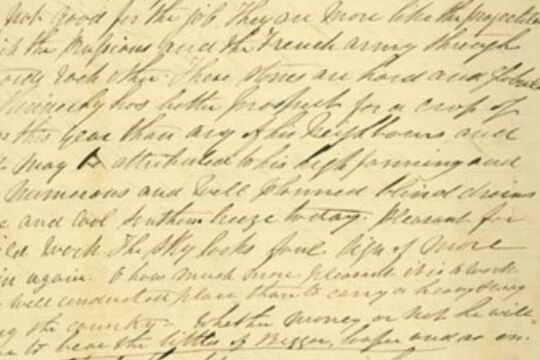
The Welsh Swagman
Joseph Jenkins was a Welsh itinerant labourer in late 1800s Victoria.
Exceptional for a labourer at the time, Jenkins had a high level of literacy and kept detailed daily diaries for over 25 years, resulting in one of the most comprehensive accounts of early Victorian working life.
Itinerant labourers of the 1800s, or 'swagmen', have become mythologised in Australian cultural memory, and so these diaries provide a wonderful source of information about the life of a 'swagman'. They also provide a record of the properties and districts Jenkins travelled to, particularly around the Castlemaine and Maldon area.
The diaries were only discovered 70 years after Jenkins' death, in an attic, and were in the possession of Jenkins’s descendants in Wales until recently, when they were acquired by the State Library of Victoria in 1997.
-

Nyabana Riek
Nyabana Riek left Nasir, southern Sudan, to escape civil war when she was only 9 years old.
With her older sister Mary, she travelled to a refugee camp in Itang, Ethiopia in 1986. But after years in various camps, the sisters made a dangerous trek at night across the mountains between Ethiopia and Kenya. The 12-hour journey was steep, sharp rocks tore their shoes and soldiers patrolled both sides of the border. They managed to cross the border into Kenya and then spent 3 years in a Kenyan refugee camp.
Finally, in 1995, Nyabana reached Australia. When she arrived, Melbourne's Sudanese community was small; she was the first teenager from the Nuer language group and spoke little English. But things are different now - more family members have come to Melbourne, Nyabana completed a Bachelor of Business Management, and the Sudanese community and support networks are growing.
