Showing 288 items matching "coils"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Wire, ca. 1878
the coil of copper wire was recovered from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. [References: Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village information sheets and documents] Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Coil of copper wire from the wreck of the ship Loch Ard. Wire is fused together and has heavy encrustation. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, copper wire, wire coil -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumUniform - LEGGINGS, LEATHER, 1943
Pair of leather leggings with leather straps and brass buckle rectangular shape coiled cylinder shape.Stamped in leather .1) "D.C.D. / 1943 / 15 / DEPART OF DEFENCE / 5" .2) "D.C.D. / 1943 / 15 / s depart of defence"passchendaele barracks trust, uniform, leggings -
 Wangaratta High School
Wangaratta High SchoolTelephone
ALCATEL Tochfone Telephone Cream corded telephone body and handset with grey buttons and coiled cordTouchfone -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyGlasses and Box
Handmade sewing basket from Estate of Nancy Scheney's aunt.Reading glasses with gold coloured metal frames. Coiled woven basked with blue felt lining.spectacles, sewing baskets -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Tool - Engineer's hammer
Large "Engineer's hammer with metal & copper coiled wire around wooden handle. "Cross Pein"tools, hammer, "cross pein" -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyFunctional object - Pen, Stick on ball pen, 1970c
Ball pen for household or office use, with stick on mount to avoid the pen being removed from the desired location. This item is unused and in original packaging.Cream plastic ball point pen attached by coil to stick-on holder, in bubble pack mounted on card"Stick-on ball pen" "Made in Hong Kong"ball point pens, pens -
 Morongo Old Collegians
Morongo Old CollegiansBadge
A round silver badge with four leaf-type attachments, with a cross in centre, sitting on a bar with coiled ends.education, school, morongo, geelong, girls, boarding, presbyterian, uniting, history, badges, private-girls-school, 1920-1994, kindergarten-year-12, sint-lucernae-ardentes, lucy shaw, gertrude pratt, dulcie brookshaw -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Coil - Inductance
Inductance coil for a crystal set. Cross wound to minimize capacitance between normally wound adjacent turns.communication, radio -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionElectrical Instrument, Wire caged heat source
... coils ...Two wire covered elements in steel mesh, oblong case with handle. Screws at each end undo to allow access to inside of cageMaker's plate: "Made by A.H.GRACE, Sydney Prim volts - 240 Sec volts - 116 Watts 600heat source, wire cage, electrical, coils -
 Nhill Aviation Heritage Centre
Nhill Aviation Heritage CentreMemorabilia - Morse Key
Possibly a training keyMorse Key with sounding coil and wire connectors. Mounted on a wooden box with removable bottom panel retain by screws.nonemorse key, -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Police Report - Casterton Police Station, 1912, 16/11/1912
Barry was a police officer stationed at Portland 1969 - 71. Stables were to be demolished. he was instructed to clean them out, and take the contents to the tip. He retained these documents and donated them to the Cultural Collection.Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - larceny, six coils of wire, Casterton police stationBack: Continuation of 'Steps taken, where information sent etc from front pagepolice report, theft, casterton -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Handwritten supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - Larceny 1914, 03/06/1914
Dartmoor Police Station records.Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - larceny, coil of fencing wire, Dartmoor police station. -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, 35 MeV betatron donut
Black and white photograph of 35 MeV betatron donut. Showing electron exit beam “pancake” deflector coils -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Toggle rope
In the Vietnam conflict, Australian troops used these ropes at night and crossing rivers to assist in keeping soldiers together. They were also used with wooden poles when making stretchers in the field and to secure prisoners.Green fibre rope assembly, single leg, polyester toggle rope. Rope is coiled with a loop at both ends.toggle rope, vietnam war, military equipment, rope, vietnam -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncFunctional object, Wood & Metal Shoe Expandable Stretcher by Flarta, Unknown
The extensive fashion and design collection of the Kew Historical Society has been assembled over a number of decades. One subsection of this collection is shoes, designed and manufactured for Australian women by Australian and European designers. Many of the shoes, while often mass-produced, were generally constructed by skilled artisans using traditional shoe-making techniques. The shoes date from the 1890s to the 1980s. Expandable wood and metal shoe stretcher. The expansion is controlled by a coiled spring. The name of the manufacturer is stamped on the toe section.FLARTA shoe expanders, flarta -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumVertical Electromagnetic Tuning Fork, between 1928 and 1954
Triangular, footed base with coiled, coated wire on adjustable stand between side of tuning fork. NOTE: HEAVY OBJECTFront of tuning fork base: '100 / V. D' Sticker on base: '1D4' Stamped on base of fork: 'GRIFFIN & TATLOCK / LONDON' Plaque on base: 'GRIFFIN & TATLOCK LTD / LONDON / GLASGOW / EDINBURGH / [griffin logo] / MANCHESTER / LIVERPOOL' Sticker on side of base: 'NAT. PHIL. LAB / NO / UNIV. OF MELB.'tuning fork, griffin & tatlock, laboratory apparatus, electromagnetic -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Accessory - Evening Bag
Belonged to Annie Hall, mother of donor who lived in Blackburn Small, gold mesh evening bag, ball-clip clasp: gold coil-metal handle (genuine Regal mesh)park lane handbags -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncMemorabilia - Lock of hair of Thomas Henty (1775-1839) in a hollowed Cartwheel Penny
This King George III 1797 penny, colloquially described as a ‘Cartwheel’ because of its large size and thick rim, was manufactured in Great Britain from 1797-99. The penny and the twopence were the first coins shipped to New South Wales by the British Government. In 1800, Governor King issued a proclamation that forbade their export. This coin is one of the 132,000 coins sent to Australia in 1800. It is not uncommon to find cartwheel pennies used as containers. They were reputedly used to conceal a more valuable coin or for smuggling. The penny was purchased by the Society as part of a small collection of Henty memorabilia and portraits from the owner of Moorabool Antiques, Geelong in 2021, which had in turn acquired the item from the estate of Dennis Alston of Alston's Antiques in Hamilton, Victoria.This cartwheel penny, used to contain a lock of hair of Thomas Henty (1775-1838), is of statewide significance to Tasmania, where he settled and died, and to Victoria, where his children and their descendants were notable pioneers, squatters and subsequently landowners in the Western District. The item is also of national significance for its strong connection to the Henty family, notable British settlers of southeastern and southwestern Australia in the 1830s. The connection to Kew (Vic.) is that members of the Henty family owned important mansions in Kew in the 19th century. Thomas Henty was the father of Stephen George Henty of 'Findon', and Francis Henty of 'Merino Downs' in the Western District and 'Field Place', Kew. Numerous members of the Henty family are buried in the Boroondara General Cemetery.Object of personal memorabilia. Coiled and bound lock of hair of Thomas Henty contained in a hollowed-out copper 'cartwheel' penny.OBVERSE: Georgius III . D : G . REX / REVERSE: Britannia 1797 / SELLER'S LABEL: Lock of hair from the late Thomas Henty, born 1775thomas henty, henty family, launceston, west tarring -- sussex (uk), tasmanian pioneers, australia - early settlers, cartwheel pennies -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Myoma Screw, Late 19th century
A myoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumour in the muscle of the uterus. This myoma screw is used in surgery to remove such fibroids. It can be done abdominally or via the vagina. The fibroid is ‘screwed’ and clamped before removal. The myoma screw is almost crude in its simplicity. It has a straight shaft with an oval handle and a corkscrew head. This myoma screwwas donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The Myoma Screw is still in use today for the removal of fibroids. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Myoma screw, from W.R. Angus Collection. Doyen's, abdominal and gynaecological use. Coiled end, loop handle. Inscribed "LONDON" Inscribed 'HAVRICK(?) LONDON'flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, myoma screw, tumor, surgery, gynaecology, myoma, fibroids -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Supplementary Report of Criminal Offence Report - 1914, 08/06/1914
Dartmoor Police Station Records.Hand written , supplementary report of Criminal Offence report - larceny of a coil of wire. Dartmoor Police Station 8th June 1914 -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, DC Voltmeter/Ammeter: Model D.14, 1950s
Used for teaching chemistry principles of measuring electrical power.A teaching / demonstration model with large scale and transparent panels. Polished wooden frame. Direct current - moving coil Volt-AmmeterBlack tape on front panel "PHYSICS"chemistry, electrical power, physics, voltmeter, ammeter, direct current, scientific instrument -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - tug, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority ArchivesBack: Howard Simmonds, Ken Johnston - blue biro - Black stamp (Feb '82 ' 62 (?92)port of portland archives, tug, tug crew, marine, maritime, harbour -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societypaper weight
A small glass paper weight consisting of a round glass dome with a scooped out centre which has a long coiled wire prong.paperweight commerce-equipment stationery -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societychild's rocking chair, c. late 19th, early 20th Century
This chair is presumed to be Ruth Richardson's chair from when she was a child. A child's rocking chair, frame of round wood and highly finished, seat and backrest of coffee coloured canvas, coiled springs are made of metal.child's-rocker spring-rocker richardson-family -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBrace
Brace metal, coiled wire around top handle & middle handle. Auger bolted to brace. 112cm x 31cm. Brace 53cmflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchEquipment - German Parachute Cord WWII
This rope was part of a German Parachute cord from the Second World War. German paratroopers, or Fallschirmjager, were often at the forefront of German military actions. Australian soldiers faced a Fallschirmjager assault during the invasion of Crete in 1941.German paratrooopers, or Fallschirmjager, were an elite unit within the German military. Australian forces faced the Fallschirmjager during the airborne invasion of Crete in 1941. This object has the capacity to tell the story of that engagement.A length of frayed rope taken from a Second World War German Parachute. Coiled, with black and red threads running through the structure.german, paratrooper, parachute, fallschirmjager, crete, 1941 -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Radio Handset
A typical handset for a heavy duty radio communications set used in the field in Vietnam.Curved black plastic phone handset with coiled lead. There is a five pin plug/screw on plug at the end of the cord. Heavy duty unit.Handset H-250/U. Sonetronics Contract DAAB07-93-D-G010 US on handset. MFG 79 566 May 94 on the lead.handset, field radio, vietnam war, communications, signals, radio -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncDecorative object - Vintage Battery Clock, Smiths Industries Ltd, c1962
Smiths patented moving coil clocks incorporating transistors, but did not put any models on the market until 1962 when they announced the Sectronic, which had a moving coil movement. This movement had three hairsprings which served to carry current to the coils. These were one of the first battery operated clocks created. This clock is representative of 1960s timepieces. These were the first battery clocks.A small round clock with Roman numerals and gold circular design around the centre. The clock was produced by Smiths Industries Ltd. in England. It is battery powered and features the Smith Sectronic battery which was first introduced in 1962. In centre of clock face "SMITHS/SECTRONIC BATTERY/MADE IN GREAT BRITAIN" clocks, smith sectronic -
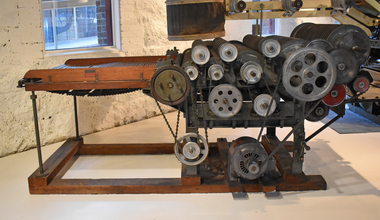 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumMachine - Carding Machine, CSIRO, 1960s
After scouring, the wool fibres are still tangled together. Carding untangles the fibres by brushing and straightening. The wool moves through a series of wire brush rollers that revolve at different speeds and in different directions to tease apart the wool. The fibres emerge from the machine as a continuous filmy web - called a sliver. The sliver must be thinned and divided into strands before the next process. Carding machines constantly require tuning. A highly skilled technician maintained and adjusted the speed of the rollers on the machine. This machine was developed by the CSIRO in the 1960s as a small-scale experimental machine. Industrial carding machines were four times the size of this one. Gold plaque on display with machine until 2018 read: G.H. Mitchell & Son, Adelaide have celebrated 125 Years of involvement with the Australian Wool Processing Industry by contributing the funds necessary to restore The Carding Machine, Noble Comb & The Gill Box. Also another gold plaque read: Experimental Carding Machine donated to The National Wool Museum by C.S.I.R.O Ryde has been rebuilt by Nick Sokolov of Comb Research & Development with the help of Bernard Tolan.Carder with small roller missing at coiling end. Driven by three horse power motor. Wooden slated feed table synchronised to overall gearing.carding machine, machines, wool industry, manufacturing, wool processing -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societywooden club
A carved black wooden club with a thick scaled snake coiled around it. At the clubbing end is a solid round ball. It is handmade and believed to have originated in the New Hebrides.weapon wood-carving new hebrides hunting
