Showing 63 items
matching wolfe
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, c. 1890's
The photograph taken on Sunday September 6, 1891, shows the Port Campbell Rocket Rescue Crew and Equipment at Wreck Beach, Moonlight Head, preparing to save the stranded men on the wreck of the barque Fiji. The man standing in the middle, front of the photograph, facing the ocean, is Herbert Maxwell Morris, a farmer at Barruppa near Princetown, also a member of the Rocket Rescue Crew. The Rocket Rescue lifesaving method used an explosive rocket to shoot a light line from shore across to the distressed vessel. The line was then secured to the ship’s mast and a heavy, continuous line was then sent out with a ‘breaches buoy’ attached (a buoy similar to the seat of a pair of trousers). The stranded seafarers would sit in the seat and be pulled along the line to safety. A lot of skill was needed to set up the line to reach its target and the Crew trained regularly to keep up their skills. The three-masted iron barque Fiji was built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on May 22, 1891, bound for Melbourne under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The Cape Otway light was sighted on September 5, 1891. However, the bearing was different from Captain Vickers’ calculations. At about 2:30am the next morning land was reported only 4-5 miles away. The captain tried to redirect the ship in the rough weather without success and the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The crew burned blue lights fired rockets to signal distress. The lifeboats either capsized or were swamped and smashed to pieces. Two younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore with a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, Julius Gebauhr, a 17 year old German able seaman, reached shore safely on his second attempt but had cut the line lose with his sheath-knife when it tangled in kelp. He climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. Later that morning a young man, William (Willie) Ward, saw the wreck of the ship close to shore near Moonlight Head from the cliffs and the alarm sent for help from Princetown, six miles away. At around the same time a Mott’s party of land selectors, including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson, was travelling on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head. They were near Ryans Den when they found Gebauhr in the scrub, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife. They thought the man may be an escaped lunatic, due to his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech. After Gebauhr threw his knife away they realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German as he talked about the wreck. They gave him food, brandy and clothing, and he was taken to a nearby guest house Rivernook, owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Most of the party went off to the wreck site. Stanmore and Dickson rode for help from both Port Campbell for the two Rocket Rescue Crew buggies, and Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The vessel S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. Half of the Port Campbell Rocket Crew and equipment arrived after a 25 mile journey and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the weary crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. The Office in Charge of the Rocket Crew, W. Tregear, ordered the rocket to be fired but the light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line, successfully set up by Herbert Morris, crossed the ship and was secured. The anxious sailors tried to come ashore along the line but some were washed off as the line sagged with too many on it at one time. Other nearly exhausted crewmen made their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Rocket Crew members and onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag the half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Herbert Morris, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody, who was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield. Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to help one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken who was trying to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck where they were both hauled back on board. Wilkinson was unconscious, possibly from hitting his head on the anchor before they were brought up. Plunken survived but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. The 26 year old Bill Robe hauled out the last man; it was the captain and he’d been tangled in the kelp. Only 20 minutes later the wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach. Their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji and they were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by locals soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. There was public criticism of the rescue. The important canvas ‘breeches buoy’ and heavy line for the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue as they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. The communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time. The boat that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much cargo looting occurred. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. Years later Bill used the pocket watch to pay a debt, and it was handed down through that family. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach pays tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife are amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji that are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The man identified in the photograph, Herbert Maxwell Morris, was the nephew of the Victorian era artist, William Morris. Herbert had sailed from England to Australia and was about 25 years old when he joined the Rocket Rescue Crew at Port Campbell. His successful rocket line firing at the Fiji wreck site was noted by author Jack Loney in one of his historic shipwreck books. Later Morris moved from his property at Baruppa to Laver’s Hill to run a more profitable enterprise. This photograph is significant as an image of a historical event, being the willingness of local volunteers to aid in the saving of lives of stranded seafarers. It gives a clear picture of the use of Rocket Rescue Equipment in shore-to-ship rescues. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes. The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment; Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history, possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history, and potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Black and white photograph. Subject is the Rocket Rescue Crew from Pt Campbell on Wreck Beach, Moonlight Head, at the wreck site of the barque 'Fiji'. September 6, 1891.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, pocket watch, fob watch fiji, william vickers, william robe, bill robe, gebauhr, stansmore, carmody, wreck bay, moonlight head, fiji shipwreck 1891, rocket crew, port campbell rocket crew, lifesaving crew, photograph of rocket crew, herbert morris, warrnambool, shipwreck artefact, mott, william ward, rocket rescue, breeches buoy, rivernook guest house -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, C. 1891
Photograph shows the ship FIJI where she met her demise, in Wreck Bay, on the shipwreck coast of South West Victoria. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Black and White Photograph of the ship "Fiji" taken from Wreck Creek. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, pocket watch, fob watch fiji, william vickers, william robe, bill robe, gebauhr, stansmore, carmody, wreck bay, moonlight head, fiji shipwreck 1891, port campbell rocket crew, wreck bay victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDog, 19th century
This toy dog was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.China toy dog salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and is tan in colour. The dog is solid with a pitted surface1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Rope Sample, After September 1891
The light line or rope used to construct this Turk’s Head knot was part of the line line-throwing apparatus used by the Rocket Rescue Crew. In normal operation a rocket carrying the line was fired over a ship, fastened to the ship, then hauled by the crew to pull a heavier rope from shore, which would have a canvas ‘breaches buoy’ attached to it. A tripod or triangle would be used to keep it free from breakers and rocks. One by one the crew on the wreck would sit in the buoy and be hauled safely back to shore. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967.This rope is part of the collection of artefacts from the wreck of the Fiji. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Rope salvaged from the distress rocket rope line used in the rescue of the crew of the sailing ship “Fiji”. The light-weight brown rope has been crafted into a decorative 'Monkey fist' or 'Turk’s head' knot using three interwoven strands. 1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, rope, moonlight head, wreck bay, distress rocket, line, light line, rocket rescue apparatus, rocket equipment, rocket line -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCandlestick holder, Made on or before 1891
This candlestick holder is one of the artefacts salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a glass bottle and a sample of rope from the distress rocket. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.This candlestick holder is Artefact Reg No Fiji/2, part of the Fiji collection. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Candlestick holder or Chamber Candle. Made of china, off white in colour with crazed glazing. The round concave dish has the base of a round candle holder in centre (remainder of holder has been broken off). The base of a circular china finger ring is attached to both the rim and the dish, about ¾ of the way towards the centre - the top 2/3rds of the finger ring is broken off. A conical thimble-like spike, placed about a quarter of the way around from the finger ring, is intact. This spike was probably used to hold a candle snuffer of similar but larger size and shape. The candlestick holder was recovered from the wreck of the Fiji.1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, fiji, pocket watch, moonlight head, candlestick holder, candle holder, chamber candle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's leg, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
This doll’s leg was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s leg salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded leg, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) is for a small doll. The leg is solid rather than jointed, and goes from the lower thigh down to the foot, which has a shoe-shaped heel. The white coloured leg is finished with glazed paint and the shoe of the foot is painted black. The leg is discoloured in places with a tan colour. There is a groove around the top of the leg, which would enable the leg to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, dolls limb, dolls leg, toys, doll's leg, doll's limb -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's arm, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
This doll’s arm was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s arm salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded arm, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) is for a small doll. Its hand has the fingers touching each other with the thumb tucked into the palm. The white coloured arm is finished with glazed paint. The arm is discoloured in places with a tan colour. The arm is solid rather than jointed and goes from hand to upper arm. There is a groove around the top of the arm, which would enable the arm to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, doll's arm, doll's limb -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's leg, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
This doll’s leg was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s leg salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded, shapely leg, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) and tan in colour, is for a small doll. It has a shoe shaped foot complete with heel. The leg would have probably been finished with paint and the shoe would also be painted on. However this leg has no paint remaining. The leg is solid rather than jointed and goes from foot to lower thigh. Around the top edge of the thigh is a groove, which would enable the leg to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, dolls limb, dolls leg, toys, doll's limb, doll's leg -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSlate pencil, Made on or before May 1891
Slate pencils were made from a rod of soft slate material and used for writing on thin slate boards. The slate boards were approximately 9cm x 12cm used in schools for writing practice in place of pencil and paper, which were more expensive and less durable. They could be used then easily erased for re-use. In work places, slate boards were sometimes bound into slate books The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Remnants of a black slate pencil salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. Pencil has no casing and is in three pieces. One piece is broken laterally and has a rounded end. The other two pieces have a longitudinal break and fit together. (The nature of the break indicates a material of natural formation, for example sedimentary rock such as slate.) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, slate pencil, pencil, slate board, writing, stationery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Monkey, ca. 1891
This toy monkey was part of the cargo from Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool-based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation of Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous southwest winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30 am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17-year-old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut loose with his sheath knife when it became tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach and then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10 am on Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in a singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath knife, ready for all emergencies. At first, they were concerned about his wild and shaggy-looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 remaining on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29-year-old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26-year-old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of Fiji smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Master's Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism of the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue were in half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. The essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers' homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the lootings, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand-crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, and limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, a sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Toy white China monkey in a seated pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and is creamy sand colour with a rust-coloured mark on its face. The surface is slightly pitted. It was salvaged from the wreck of the ship FIJI. 1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMonkey, 19th Century
This toy monkey was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy monkey is classified as Fiji 5 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Ceramic toy monkey salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The monkey is in a seated pose with its arms around its knees. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an orange colour. The surface is slightly pitted.ceramic, china, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey, ornament -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMonkey, 19th century
This toy monkey was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy monkey is classified as Fiji 5 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy monkey salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The monkey is in a seated pose with its arms around its knees. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an pinkish brown colour with darker orange in its lap. The surface is worn and slightly pitted.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRabbit, 19th century
This toy rabbit was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife This toy rabbit is classified as Fiji 4 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy rabbit salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The rabbit is in a lying pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an orange-sandy colour with darker orange markings. The surface is slightly pitted.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, rabbit -
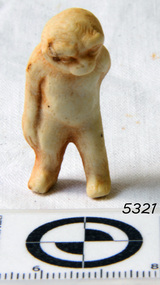 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGorilla, 19th century
This toy gorilla was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife This toy gorilla is classified as Fiji 7 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy gorilla salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The gorilla is in a standing pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is pale creamy colour with a slightly pitted surface.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, gorilla -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCat, 19th century
This toy cat was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.This toy cat is classified as Fiji 10 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy cat salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The cat is in a resting pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is tan in colour with a slightly pitted surface.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, cat -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRubber ball, 19th century
This rubber ball was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. A press report notes that the balls collected from the Fiji’s cargo were originally red and white. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy rubber ball is classified as Fiji 3 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Rubber ball salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The rubber is perishing and the surface is pitted and bumpy. The material is tan in colour with a slightly pitted surface. 1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, rubber ball -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRubber ball, 19th Century
This rubber ball was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. A press report notes that the balls collected from the Fiji’s cargo were originally red and white. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy rubber ball is classified as Fiji 3 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Rubber ball salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The rubber is perishing and the surface is pitted and bumpy. The material is tan in colour with a slightly pitted surface. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, wreck bay, moonlight head, 1891, cargo, rubber ball, toy, fiji, captain vickers, william vickers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBottle, circa 1885 - 1891
This bottle was one of the items salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji in 1891. Joseph Bosisto began manufacturing Eucalyptus Oil in Australia from 1854. This bottle is marked ‘J. BOSISTO”, which probably dates it from 1885 when the company J. Bosisto & Co. was formed. The marking on the bottom of the bottle “GERMAN/B_ _ E” could mean that the bottle was imported by J. Bosisto from Germany. In the early years bottles were imported from overseas countries including England and Germany. In 1872 the Melbourne Bottle Works was established to supply the bottles locally and more cheaply but had difficulty keeping up with the supply. From 1865 Australian-made Bosisto’s Eucalyptus Oil began to be exported to England then later to Germany and other countries. Bosisto’s Eucalyptus Oil won many prizes at exhibitions between 1854 – 1891. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, this glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. The glass bottle is registered as “Artefact Reg No Fiji/1”. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Clear glass oval medical bottle with rounded corners and flattened sides on front and back surfaces. Opening of bottle has a lip around it and could have been sealed with a stopper. There is a chip in the lip. One face of the bottle has a rectangular border with a name embossed vertically on it, “J. BOSISTO / RICHMOND”. The oval base of the bottle also has letters embossed on it “GE_ _AN” “B _ _ _ _ _”. There is also a large chip out of the base. The sides of the bottle have a vertical joining line. The bottle was recovered from the wreck of the Fiji.Flat side of bottle has rectangular border with “J BOSISTO / RICHMOND” embossed in the centre. The base of the bottle has “G E . . A N/B . . . . . .” embossed on it. Other letters have been removed with the chip. (probable wording was ‘GERMAN/BOTTLE)warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, fiji, 1891, glass bottle, medicine bottle, bosistos, j bosistos, german bottle -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncBinder, Eltham District History, Eltham Road Board, 1856-1871; Research by Keith Chappel, 1971-1974
Eltham District History, Eltham Road Board, 1856-1871Two binders containing 486 A4 pages (photocopied) of mostly handwritten notes from research undertaken of Public Office Records of Victoria various holdings. Some photocopies from source reference books. Includes 20 page subject index (handwritten) at front and 5 pages of notes and sources at rear and a photocopy of short biography of Keith Chappel.a. foley, a. harkness, a. mackie, a. mcintyre, a. von ziegler, a.a. vivian, a.d. kinninmont, a.d. quadri, a.h. grimshaw, a.w. page, aboriginal reserve, aborigines, abraham quarman, abraham rooks, abraham taylor, adam goudie, aenaes harrison, agnes black, agnes charlton, agnes dalrymple, ah chong, ah cock, ah hein, ah lie, ah sing, albert lunson, albert ness, albert parker, albert ramseyor, alert hunt, alex cameron, alex eason, alex mcandrew, alexander crichton, alexander donaldson, alexander falconer, alexander innes, alexander james, alexander mcdonald, alexander miller, alexander thompson, alexander walker, alexander white, alfred armstrong, alfred burgess, alfred davey, alfred deschamp, alfred eddy, alfred hinley, alfred hooper, alfred hubbard, alfred lowman, alfred smith, alfred whelpton, alice power, allen heeps, allwood, amelia neuman, amos taylor, anderson, andersons creek, andrew brown, andrew byrne, andrew harkness, andrew herbert, andrew ross, andrew smith, angus mcdonald, ann emmott, ann mcphee, ann odea, ann plunkett, ann snell, ann tatty, annie ashmore, annie herbert, annie stuart, anthony beale, anthony currie, ants nest, archibald mcphee, arthur connor, arthur lyttle, arthur rooke, arthur young, arthurs creek, arthurs creek school, august ostling, b.o. wallis, barkers creek, barr, belton, benjamin bain, benjamin jenken, benjamin lawford, benjamin rice, benjamin shaw, benjamin smith, benjamin wallis, benjamin walton, berry, bismark hotel, black calf gully, black thursday, boomers gully, bridget bunker, bridget hailes, bridget kearse, bruno hirt, burns, bushranger, c. twiss, c.h. bade, caleb sherar, caledonia, caledonia diggings, campbell hunter, carl euman, caroline davey, catherine kennedy, cathren brock, cecilia farman, chamberlain, chapman, charles caldwell, charles campbell, charles dale, charles draper, charles fowler, charles green, charles hawkins, charles hempel, charles hirt, charles hirtson, charles jefer, charles jesse, charles kerchevell, charles lidgerwood, charles morris, charles peake, charles prince, charles rielly, charles roberts, charles rowand, charles simms, charles souter, charles swan, charles verso, charles wells, charles whelpton, charles williams, charles wingrove, charles woodley, charleys gully, charlotte beltison, charlotte goodwin, ching ah hock, christine brennan, christine mckenzie, christmas hills hotel, christmas hills school, christopher battaila, christopher twiss, chune grove, church of england, church of england school, clarissa milton, cleir hills, colin amos, constable quirke, constable talty, cornelius haley, cornelius stewart, cottles bridge, councillors hotel, cricket, cucksons brewery, d. nicholson, d.w. morrissey, dalry, daniel charleston, daniel harding, daniel jepps, daniel mccarthy, daniel mckenzie, daniel mcloughlin, daniel oloughlin, david boyd, david christian, david clark, david creighton, david rogers, david rolfe, david sharp, david shawcross, david smith, david stevenson, diamond accommodation store, diamond reef mine, dickson, dixon bertram, donald cameron, donald mcmillan, donaldson, dougald mcphee, dr barclay, dugald mcphee, dugald taylor, duncan fraser, duncan smith, dungey, e. hildebrand, e. stichlins, e.f. falkiner, e.j. hughes, e.m. garsed, e.w. morrissey, edith staff, edmund clarke, edmund cuckson, edmund hall, edmund picket, edward bage, edward beltison, edward bunker, edward ford, edward hindley, edward jackson, edward jones, edward kelly, edward qualtrough, edward staff, edward tresain, edward weller, edward whelpton, edward whilpson, edwin biley, edwin cartwright, edwin cohen, edwin deschamp, edwin mcleish, edwin rodda, edwin smith, effie rodda, eliza bellamy, eliza dawson, eliza howell, eliza nield, eliza smith, elizabeth cockshutt, elizabeth eiles, elizabeth fitch, elizabeth gillespie, elizabeth harris, elizabeth herbert, elizabeth hollow, elizabeth le juge, elizabeth plunkett, elizabeth whelpton, ellen hurst, ellen kearse, ellen quarman, ellen sweeney, ellen white, ellis, eltham cemetery, eltham hotel, eltham lower park, eltham market, eltham police station, eltham pound, eltham quarry, eltham racecourse, eltham roads board, eltham school, emile hude, emily anderson, emily blamire, emily coutie, emma smith, emma taylor, ephraim wyett, ernest baillie, ernest henrick, ernest steer, esther porter, ethel baillie, evan jones, evelyn hotel, evelyn observer, ewen cameron, ewen jones, f. chrimes, f. grundel, f.e. falkiner, f.r. howard, fanny benson, fanny white, felix hude, felix noisette, ferdinand ramseyer, flora vale, florence hurst, fogarty, forbes mackenzie, fords creek, frances kearse, francis baker, francis hales, francis raselli, francis steer, frank eiles, frank rogerson, frank tanner, fraser, fred hurst, frederick falkiner, frederick hurst, frederick muller, frederick nink, frederick walker, frederick wharington, friedrich muller, fryers gully, furphy, g. donaldson, g. houghton, g. turnbull, geanetta hude, george assender, george bear, george beare, george benson, george bird, george boston, george brain, george brandt, george burley, george buswell, george coutie, george eiles, george ewings, george ford, george godber, george goodman, george gray, george griffiths, george hall, george herbert, george horn, george kirk, george langhorne, george mann, george mclelland, george mosely, george neumayer, george orchard, george parish, george porter, george purcell, george ralph, george reid, george rocke, george rogers, george rolfe, george stebbing, george stebbings, george stebbins, george switzer, george symons, george thompson, georgina hilton, glenda moriss, glengloy, gold, goulstone, greensborough police station, gulf station, h. jennings, h. mann, h.h. farquason, hannah sunderland, happy valley, harkness, harold scarce, harriet hunt, harriet smith, harry hollow, hazel glen, healesville, heinrich hirt, helena peters, henrietta hill, henry arthur, henry ashmore, henry austin, henry brown, henry dendy, henry dineen, henry fowler, henry gardner, henry green, henry griffin, henry hart, henry hirst, henry hirt, henry hopkinson, henry hude, henry hurst, henry inch, henry jones, henry mills, henry scarce, henry st paul, henry stevens, henry stooke, henry thomson, henry vogt, henry wallace, henry wilson, herbert rodda, herman henrick, hermann lampe, hermann steinmann, hester staff, hitchill, holbert, honoree hude, hotel de france, hugh mccann, humphrey peers, humphrey spicer, hurstbridge, hurstbridge general store, i.h. clarke, ida adelskold, ignatz kinzel, ira pimm, irene donaldson, isaac briggs, isaac hickson, isaac hill, isaac kerr, isaac varby, isaac williams, isabella donaldson, isabelle herbert, j. dungate, j. eccleston, j. harkness, j. hartley, j. hude, j. irvine, j. jones, j. manduell, j. mason, j. mcdonald, j. mcnamara, j. nichenson, j. renahen, j. scott, j. seymour, j.a. goold, j.a. panton, j.c. hughes, j.d. thompson, j.f. hughes, j.f. johnstone, j.g. walter, j.h. taylor, j.p. morris, jack ewart, jacob belsham, jacob goldstein, jacob morast, jam loon, james alexander, james anderson, james andrew, james andrews, james baines, james batchelor, james bond, james bradford, james brennan, james brock, james brown, james brunning, james buchanan, james cockburn, james cowan, james dalrymple, james donaldson, james duckworth, james goodwin, james harding, james harrison, james hartley, james hawkins, james hewish, james holinger, james hughes, james inglis, james jamieson, james johnson, james johnston, james kaye, james kew, james lindsay, james lindsey, james lynan, james macpherson, james mann, james martley, james mayger, james mccutcheon, james mcmahon, james mcpherson, james mess, james miller, james mitton, james morton, james murdoch, james murdock, james nickinson, james orford, james purcell, james qualtrough, james rudall, james simpson, james smith, james spence, james stonachan, james stuart, james suman, james surman, james sutherland, james thompson, james thomson, james walker, james walters, james watts, jane cleave, jane donaldson, jane mess, jane sadler, jane shaw, jane thomson, janefield, jean borelli, jeanette hudi, jeanne hude, johann muller, john ainsworth, john andrew, john baillie, john barr, john beale, john bell, john bellin, john blake, john blyth, john brock, john brown, john byers, john cameron, john candler, john carter, john cobbock, john cockshank, john cockshutt, john coleman, john connell, john crozier, john darroch, john dennis, john donaldson, john elsworthy, john fenton, john fitch, john gardner, john gast, john graham, john grimshaw, john haines, john haley, john harper, john harris, john hassall, john hayes, john heales, john herbert, john holland, john holman, john hood, john horner, john horton, john hughes, john jardine, john johns, john johnston, john jones, john kearse, john kilpatrick, john knell, john lawrey, john macadam, john mandell, john manduell, john marker, john mccoll, john mccolly, john mcdonald, john mcintyre, john mckimmie, john mcnamara, john mitchell, john moore, john morgan, john muller, john murray, john pearson, john peterson, john petty, john pullen, john quinn, john rawlings, john ryder, john sabelberg, john scott, john semar, john serman, john seymour, john shawcross, john smith, john staff, john steer, john stephens, john sweeney, john thompson, john thomson, john trahy, john walker, john weller, john wells, john williams, john williamson, john yates, john yeoman, john young, johnn mcdonnell, joseph bull, joseph burns, joseph caldwell, joseph caudwell, joseph coutie, joseph elliott, joseph emmott, joseph fayver, joseph furphy, joseph hall, joseph hibbert, joseph hilton, joseph johns, joseph lithgow, joseph panton, joseph rodda, joseph sands, joseph sanson, joseph schubert, joseph scott, joseph shaw, joseph smith, joseph spedder, joseph stevenson, joseph verco, joseph wilson, josiah hollis, josiah hullis, josiah thomas, judith furphy, julie williams, junction hotel, kangaroo forest, kangaroo ground, kangaroo ground cemetery, kangaroo ground general store, kangaroo ground hotel, kangaroo ground police station, kangaroo ground post office, kangaroo ground school, kate bolger, kath scarce, katherine kearse, kidd, kinglake, kinglake hotel, kingstown, l. storey, lan quan, lang, latimour, laura henrick, laurence paterson, leon berlioz, levinia henrick, lillian gillan, linton, little eltham, long gully, louis henrick, louis le juge, louis smith, louisa steinmann, louise miller, lower plenty bridge hotel, lucy tidell, lydia qualtrough, m.j. careton, m.s. adams, macrudden, maggs, mail coach, maplestone, margaret graham, margaret hollins, margaret kearse, margaret kennedy, margaret kinrade, margaret lynch, margaret mcbirney, margaret steinmann, marguerite borelli, maria reilly, maria st paul, maria trew, marian trew, marianne miller, marie wright, marion hillier, mark bunker, martha herbert, martin brennan, mary alexander, mary beltison, mary bradford, mary bridgman, mary brock, mary bull, mary eiles, mary hopkinson, mary kearse, mary lean, mary mcinerney, mary miller, mary parmington, mary pearson, mary pickles, mary robertson, mary rodda, mary ross, mary smith, mary surman, mary weller, matilda jordan, matilda mcmillan, matthias watson, mawson, mechanics institute, michael callanan, michael fenton, michael kearse, michael mctyne, michael merritt, michael oday, michael odea, midgley hall, mills, minnie watts, miss bellon, morgans gully, mount joy, mr donnan, mr omeare, mr page, mrs greenaway, mrs havard, mrs hude, mrs morris, muller, murrays bridge, n.d. whyte, ned kelly, new caledonia creek, nicholas rodda, nillumbik, norman mcphee, old caledonia gully, oliver gourlay, one tree hill, owen finnegan, panton hill, panton hill hotel, panton hill post office, panton hill school, parambool, patrick armstrong, patrick bourke, patrick burke, patrick callaghan, patrick green, patrick harrington, patrick kearse, patrick lynch, patrick mcintyre, patrick o'callaghan, patrick rodgers, patrick sheahan, peach grove, perinella bull, perry, peter carrucan, peter flyn, peter ford, peter lawlor, peter patterson, peter snodgrass, peter watson, philip korfman, phillip gakden, phillip kaufman, phillip korfman, pierce brennan, pierce power, poo long, pound bend, pretty hill, queenstown, queenstown cemetery, queenstown police station, queenstown school, r. mackie, r.a. davidson, rebecca noisette, rebecca weller, reefers hotel, research, research gully, research gully hotel, research hotel, research school, rev dobinson, rhoda coutie, richard brook, richard capper, richard dunstan, richard goulding, richard heales, richard lane, richard matthews, richard rodda, richard searle, richard smith, richard wallis, richard warren, richard woolcott, robert alice, robert bourke, robert burke, robert charlton, robert clarke, robert cunningham, robert dugdale, robert grant, robert hall, robert harris, robert hempel, robert hill, robert hurst, robert lowman, robert mcadam, robert mckee, robert nink, robert norman, robert pontessey, robert sharp, robert smith, robert steel, robert stevenson, robert strong, robert surnam, robert wood, robina joyce, rogerson, roman catholic church, rossiter, rudolph muller, ruth mess, ruth sadler, ruth stevenson, s. smith, s. stewart, salters rush, sam deacon, samuel bird, samuel brace, samuel cameron, samuel candler, samuel cole, samuel cracknell, samuel dagley, samuel flier, samuel furphy, samuel merriman, samuel moseley, samuel mosley, samuel smith, sarah howard, sarah moseley, sarah raston, sarah walters, second watery gully school, self, shin hun, simon armstrong, smiths gully, smiths gully mechanics institute, smiths gully school, sophia greenaway, spanish gully, st andrews, st andrews hotel, st helena, stack, stanley smith, stephen gonnet, stephenson turner, stephensons bridge, steven anderson, stevensons corner, sumner, susan dickson, susan street, susan walke, sutherland, t. davidson, t. mclaughlin, t. symons, t.a. aldwell, t.b. drummond, t.b. henderson, t.e. johnston, t.h. subelly, tarrawarra, theis, theodore sabelberg, theresa lynch, thomas anderson, thomas armstrong, thomas baillie, thomas batt, thomas bell, thomas benson, thomas bibbs, thomas boardman, thomas bradford, thomas bull, thomas cattery, thomas cochrane, thomas cook, thomas cottle, thomas cousins, thomas downward, thomas edwards, thomas evans, thomas grierson, thomas haines, thomas harmer, thomas hunniford, thomas huntford, thomas hurry, thomas jardine, thomas jones, thomas kearse, thomas kennedy, thomas marland, thomas martin, thomas mcinerney, thomas morrison, thomas mundy, thomas murphy, thomas murray, thomas peacock, thomas plunkett, thomas postlethwaite, thomas prior, thomas qualtrough, thomas smith, thomas stone, thomas sunderland, thomas swatling, thomas sweeney, thomas symons, thomas walke, thomas wall, thomas wright, thomas young, tim shaw, toll gate, tom collins, tommys hut, true, upper diamond creek, upper diamond creek school, view hill, virtue hall, w. cockayne, w. craig, w. foster, w. marriott, w. ridley, w. trenoweth, w.a. page, w.b. andrew, w.b. burnley, w.b. phillips, w.c. shortt, w.w. herbert, walter barlow, walter hillier, walter joyce, walter knell, walter mckimmie, walter mcnicoll, walter thomson, walter wippell, warburton carr, warrandyte, warrens hotel, watery gully, watsons creek, watsons creek hotel, wattle glen school, wellers hotel, weymss donaldson, whipstick gully, white cloud, wild dog creek, wild dog gully, wiliam albert, william aitken, william albert, william anderson, william andrews, william barr, william barrow, william bell, william bond, william bowden, william bremmer, william brewer, william bridgman, william burnley, william buswell, william cant, william clarke, william cleave, william crozier, william dawson, william dodging, william ellis, william finn, william fitzgibbon, william ford, william foster, william garland, william ghosley, william golding, william goodwin, william graham, william gray, william grimshaw, william hall, william harding, william herbert, william hoilett, william hopkinson, william howitt, william howlett, william hubbard, william hunt, william inglis, william jarrold, william joyce, william kidd, william kilpatrick, william kommer, william lodge, william mclaughlin, william mcmurray, william mitton, william moore, william mosley, william murphy, william nicholson, william normage, william norman, william nuttall, william phillips, william quarman, william ronald, william sadler, william scott, william seaville, william sharp, william smith, william spicer, william taylor, william thomson, william tobin, william underwood, william walsh, william walshe, william walters, william watkins, william west, william wilmot, william wilson, william wolverston, william woods, wolfe, woodley, yarra bank, yow yow creek, a. brewer, a. easson, a. edwards, a. melville, a.m. ross, a.r. larrimour, aborigine reserve, advertisements, agricultural district, alan bernhard horsley, albert frederick charles glover, albert h price, albert h.c. price, albert henry charles price, alex easson, alexander campbell, alexander melville, alexander thomas haley, alexander thomson, alfred j. lowman, alice may peake, alie haley, alistair knox, alistair samuel knox, allandale road, allendale road, allwood run, andrew, andrew mckay, anton william brinkkotter, archibald brown, argus, arthur chichester allen, arthur edwin cracknell, arthur john braid, arthur robert traynor, atlas of australia 1886, b. lawford, b. mess, barry thale houston, basil y hall, basil yaldwyn hall, bell street, benjamin baxter, benjamin bowater, benjamin thomas taylor, benjaomin o. wallis, bible street, billis, bolton street, brewery, brisbane street, buckingham, bushrangers, c. brown, c. carroll, c. hirt, c.s. haley, c.s. wingrove, c.t. harris, caledonia run, cam, cattle, charis meta alexander pelling, charles brown, charles ellis, charles hicks bath, charles newman, clara gonnet, claude bryan gibbs, clifford henry goulding seear, coleraine, colin t. bell, collectors, collingwood, commissioner airey, coplin thomas bell, cornelius john stewart, cornelius sharp haley, cornelius sharpe haley, county of evelyn, culla hill, cutto hill, d. ryan, daily news newspaper, dalton street, daniel jepp, derek cecil o'beirne, diamond creek, diamond creek post office, diamond creek railway station, diamond creek run, diamond creek station, diamond creek township, divisions, doctor, donald alfred neil, donald charles maling, donald ingersole, donald kennedy, douglas anderson, e. cameron, e. falkiner, e. stooke, e.t. peers, edward dumaresq, edward heller, edward james, edward wilson, edwin stooke, elections, electoral districts, electoral roll, electrified railway, eltham, eltham district description, eltham district history, eltham district road board, eltham post office, eltham railway station, eltham road district, eltham road district board, eltham shire council, eltham shire councillors, eltham shire history, eltham town common, eltham village, eltham-hurstbridge railway, ely street, eric dudley butler, eric nichol staff, eric percival harmer, ernest james andrews, eve may edwards, evelyn and mornington division, evelyn division, everard albert hale, ewn hugh cameron, f. stone, f.d. wickham, flour mill, fountain of friendship hotel, francis bradley, francis joseph favier, francis regiereals(?), francis watson rosier, frank haley, frank wayne maas, franklin william nankervis, frederick charles barrett, frederick edward falkiner, frederick eldred griffith, frederick filed durham, frederick gration, frederick kirk gration, frederick vincent squire, fredrick ninck, g. drabble, g. haley, g. hodgkins, g. lee, g. thomas, g. thomson, g.d. boursiquot, g.f. belcher, garden hill, geoffrey charles dreverman, geology, george d'arley boursiquot, george ellis parker, george fletcher, george frederick belcher, george haley, george hirt, george louie cresp, george love, george robertson, george turnbull, george wise, godalmin street, gold mining, goodman, gordon melville, government gazette, graham lindsay bride, grazing, greenhill, greensborough, grierson, gun maker, h. g. james, h. stooke, h. taylor, h.g. jhones, h.t. beams, harold edward bartlett, heatherleigh, heidelberg, helen louise wells, henry creswell, henry gilbert jones, henry holloway, henry peers, herbert eric rundle, herbert hewitt, herbert rutter, hoddle, holiday resort, horace hilton, house of assembly, hugh larimour, hurst, i. barrow, i. rooks, ian g smedley, ian gordon smedley, industry, isaac rooks, isidore t. wilmor, j. alison, j. brown, j. cameron, j. carfrae & co., j. ferguson, j. frank, j. garthwaite, j. greaves, j. greitzner, j. irish, j. lindsay, j. murray, j. o'brien, j. stevenson, j. wilson, j.b. phipps, j.b. rodda, j.f. imley, j.g. foxton, j.g. fraser, j.h.f. hawke, j.k. zahn, j.m. holloway, j.p. imley, jack cato, jack clendinnen gill, jacob belcham, jacob greitzner, jakeb greitzner, james bailey, james cox, james d mealy, james darley mealy, james frank, james frederick mackay, james graham, james johnstone, james kay bryce, james mclaren, james murray, james oliver white, james pearson imley, james pearsons imley, james rosier, james ryan, jane thompson, jersey, johann karl zahn, john a porter, john alexander hampton lewis, john alison, john b. wilson, john barter bennett, john blackmore phipps, john blakemore phipps, john carfrae, john dane, john g. foxton, john gerald searle, john greaves, john green foxton, john greenlaw foxton, john henry sabelberg, john johnstone, john lee smith, john lindsay, john lindsay beale, john mann, john mason, john pape, john porter, john samuel lithgow, john stevenson, john verran mcconnell, john wilson, jonathan scott, joseph anderson panton, joseph bromley shallard, joseph garthwaite, joseph smedley, joseph walter henry bradbury, josiah morris holloway, k.e. dunstan, m kinglake, keelbundora, kenneth chareles crompton, kenneth donald macmillan, kenneth frederick hines, kenyon, kerby street, kinglake school, krelbundora, l. jenyns, l.m. bill, lancefield, land act 1862, land act 1865, land act 1869, land alienation, land settlement, legislative council, leopold kershaw lawry, leslie christopher docksey, leslie edward clarke, little eltham school, m. o'shea, m.h. fitzpatrick, mail run, mail service, main road, map, margaret moody, martin fogarty, mary leak, maxwell alexander spence, medical practitioner, michael o'shea, miss haley, moira, morang, mr. ford, mrs galbraith, n. gillies, n. rodda, name, names, neil stewart roberts, norman ernest charles williams, opening, orchard district, p. ryan, p.a.c o'farrell, p.p. cotter, parish of nillumbik, parish of nillumbik 1856, patrick costello, patrick turnbull, percy downer, peter andrew charles o'farrell, peter fair, peter graham, petr lawlor, phillip cumming, photographer, plenty river, polling place, polling places, porter street, portrait, post office, post office directory 1868, princes bridge, proclamation, r. boston, r. hepburn, r. lane, r. wadeson, r.d. mess, r.s.h. moody, radley (rodney) douglas quin, rag mill, railway lines, raymond clive duncan, registrar, research state school no. 2959, reserve for aborigines, reynolds road, richard jones and co, richard robert woolcott, river plenty, robert alan bell, robert benn (ship), robert cadden, robert cunningham white, robert david taylor, robert hepburn, robert kenneth marshall, robert miller, robert reid, robert stewart hull moody, robinia joyce, rodda family, rosemount, rupert norman maskell, ryans road, s. evans, s. wekey, samuel evans, samuel phillips, samuel ramsden, samuel w. scott, searle, shire of diamond valley, sigismund wekey, sly grog seller, sources, south province, south yarra, st kilda, stanley simpson addison, strathbogie, strippers of bark, stuart alexander donaldson, sweeneys lane, sweeny, sylvia ruth houston, t. archer, t. huntley, t. murray, t. stephens, t. watkins, t.a. stork, t.b. daling, t.b. darling, t.c. darling, t.milthorpe, t.p. cross, tannery, tenders, terence alphonsus collins, the explorers and early colonists of victoria, the story of the camera in australia, thomas bell darling, thomas clarke, thomas darling, thomas foster chuck, thomas grant, thomas henry bowman, thomas herbert power, thomas irvine, thomas maltby, thomas mccombie, thomas scarce, thomas sweeny, thornton street, town of eltham, vaccinations act, victorian government gazette, virtue hall station, virtue hill, w. archer, w. brown, w. gordon, w. inglis, w. jones, w. matthew, w. mcdonald, w. williams, w. wilson, w.r. belcher, w.t. fitzpatrick, walter craig, walter wipple, warringal, water wheel, wattle glen, whittlesea, william acland, william adams, william b. burnley, william buckingham, william c. farrell, william cleve, william craig, william frederick ford, william george gray, william henry hull, william john taylor, william john turner clarke, william johnson, william jones, william lorimer, william morris, william redmond belcher, william thomas cochrane, william vasey houghton, william walker, william wandliss herbert, william white, willie haley, willie stanley dawson, yan yean, yarra flats, yarra river, yielima, york street, yow yow gully, zig zag road, frederick george hurst, grimshaw, mrs s marshall, mrs mcclelland, bushfire -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Ballarat School of Mines Associates Board 1951-1957, c1984
In the early 1880s the Ballarat School of Mines Council introduced a three year course of training under the professors to qualify students in the following professions: 1. Mining Engineering 2. Metallurgy 3. Geology 4. Electricity [45] Each of these courses had an additional, but optional, fourth year of study. The prescribed subjects of study for an Associateship was set out in the Calendar of the Ballarat School of Mines in each year. Any student who passed the prescribed examinations in any of the above courses was issued with a Certificate of Competency, and conferred with the distinction of Associate. By the 1890s the professorial staff had drawn up a curriculum leading to an Associateship of the Ballarat School of Mines. The first two years work was to be common to all courses, but in the third and subsequent years the student wold be devoted to a specialised branch of study. The Associateship was to be conferred in one of another of the following Courses: Agriculture, Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, [Geology], Metallurgy and Mining Engineering. All were three year courses except for Agriculture which was two years. Each course was conducted in accordance with a prescribed curriculum and syllabus. During the 1910s there was an expectation that candidates for the Associate course should have attained the age of sixteen, and have received preparatory training equivalent to University Matriculation at least in the subjects of Elementary Mathematics, English Grammar and Composition, or have passed through Junior Technical School. In 1960 an new procedure for admission to graduate status as Associates was introduced to the Ballarat School of Mines where Associateship would be conferred at a public ceremony. After 01 July 1976 graduates of Ballarat College of Advanced Education and Ballarat College of Advanced Education were admitted in major studies relating to mining for Australian accreditation and overseas purposes. Ballarat School of Mines Associates could ascribe ASMB after their name.Black and white photograph of Associatedsof the Ballarat School of Mines from 1951-1957.Associates of the Ballarat School of Mines :Lists names 1989-1964ballarat school of mines, smb campus, electrical engineering 1958, brian w. schreenan civil engineering 1958, clifford j. restarick metallurgy 1958, john t h. clelland metallurgy 1958, donald c. stevens mining engineering 1958, john g. wolfe civil engineering 1959, james e. mcneil electrical engineering 1959, patrick h. nally civil engineering 1959, graham j. willey metallurgy 1959, stanley p. kisler civil engineering 1959, donald j. overall electrical engineering 1959, brian j. mclennan civil engineering 1959, philip j. davis art 1959, bruce v. mcdougall mining engineering 1959, lancelot j. matthews mechanical engineering 1959, alan w. wilson mechanical engineering 1959, alan w. wilson electrical engineering 1959, george a r. lewis art 1959, noel e. meagher electrical engineering 1960, john l. collier mining engineering 1960, john l. collier civil engineering 1960, frank andrewartha mechanical engineering 1960, norman leckie art 1960, lansell j. groat civil engineering 1960, boon thiam lu mining engineering 1960, oswyn n. hails civil engineering 1960, john a. watts applied chemistry 1960, thomas b. gallagher civil engineering 1960, brian a. bellingham civil engineering 1961, alan c leviston applied chemistry 1961, walter j wynd civil engineering 1961, francis d benjamin civil engineering 1961, leonard e fox mechanical engineering 1961, yan kai chung applied chemistry 1961, george d mcgrath mechanical engineering 1961, john r sawyer mechanical engineering 1961, ronald horgan applied chemistry 1961, douglas j vendy civil engineering 1961, john a barnes electrical engineering 1961, brian w smith metallurgy 1961, william r carlyon metallurgy 1961, chris p livitsanos metallurgy 1961, lawrence g trevan civil engineering 1961, richard g dunlop mechanical engineering 1961, ronald m ingleton mechanical engineering 1961, peter m robinson mechanical engineering 1961, david j jelbart mechanical engineering 1961, john g hollway mechanical engineering 1961, george m hetherington civil engineering 1961, david w brown mechanical engineering 1961, john r gowan civil engineering 1961, geoffrey a christian civil engineering 1961, arthur c burrow mechanical engineering 1961, john n mcarthur applied chemistry 1961, graeme r bromley mechanical engineering 1961, william davison civil engineering 1961, ben a johnson electrical engineering 1961, ben a johnson civil engineering 1961, allan j tinney civil engineering 1961, thomas h j coad applied chemistry 1961, brian h duthie civil engineering 1961, basil c bautovich mechanical engineering 1961, reece pullen electrical engineering 1961, john d carmichael electrical engineering 1961, william j spencer civil engineering 1961, neil a brogden civil engineering 1961, michael villani civil engineering 1961, ralph j hepburn mechanical engineering 1961, peter w linaker mechanical engineering 1961, peter j matthews mechanical engineering 1961, edgar mca bartrop mining engineering 1961, donald j stewart, brian schreenan -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, J.A. Hoskin & Son, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1954, 1954
Editorial, Principal's Page, Prominent Personalities, Eureka Stockade, Two ex-students tell of their work and conditions in East Africa and Canada, The Art School, Literary Society, Boys Sport, Football, Cricket, Baseball, Athletics, Tennis, Chris Sanos - another ex-student describes his recent trip to Greece, Junior School, Ballarat wins Final - Football Premiers 1954, Some Impressions of London, House Notes, School Council. Members of Staff, Roll Call Diploma Students, Junior Technical School Boys' and Girls' Students ListingGray soft covered magazine with red and brown titlesballarat school of mines, magazine, j. collier, john skuja, janice wilton, murray gillan, neil andrews, ellen freemantle, alan johnson, graeme willey, diana mainwaring, b. v. mcdougall, margaret little, lance matthews, philip davis, john barnes, cliff restarick, philip kempe, barry jones, harold everett, j. jenkin, r. howard, d. lavery, j. williams, j. barnes, j. murray, j. wolfe, j. clelland, t. gallagher, w. maxwell, n. andrews, b. bellingham, f. shearer, n. spears, i. schunke, d. schmidt, g. willey, r. furlong, g. rasdell, b. tozer, l. matthews, w. saggers, b. taylor, j. watts, a. johnson, b. matthews, r. dunlop, b. mclennan, g. ditchfield, m. gillin, j. cleelland, b. singleton, d. overall, g. crawford, chris sanos, nancy rimmington, janice tonkin, herbert "andy" andrews, leonard (a.p.c) doull, harold m. everett, murray "gilligan" gillin, alan "johno" johnson, khoo teng seong, douglas "myxo" lockhead, lancelot "willey" matthews, bruce "frugal" mcdougall, "aal" pitzen, john "cheesy" skuja, brian francis "tailspin" taylor, john "tucks" watts, lola andrich, j. spencer, r. cutter, p. collier, g. paddle, n. richards, i. pike, b. cushion, b. knight, g. van berkel, d. stevens, n. stevens, b. stevens, l. major, l. copeman, k. norman, n. hodder, l. johns, l. curtis, h. hay, l. furlong, g. new, j. hamilton, r. day, a. clarke, b. parker, p. agrums, l. dean, w. swan, r. carlson, t. white, m. walsh, r. gilbert, w. edmends, b. vurlow, d. wakeling, a. haywood, d. sarah, k. rogers, l. cook, j. mcleod, p. hatton, p. fisher, r. lambert, j. vincent, t. lugg, g. matthews, w. etty, n. twaits, m. o'brien, w. davidson, i. lightfoot, p. cahill, n. slocum, d. martin, j. leckie, marjorie garner, r. hall, i. beaumont, barbara o'connell, b. duthie, l. boyd, i. kinnane, d. baldock, p. nunn, j. strickland, d. robertson, n. everett, b. whittle, w. widdop, j. richards, b. tresize, k. buchanan, m wunhym, j. caddy, g. kerr, j. collins, r. sansom, i. gitsham, k. weightman, g. gilmer, e. waller, r. mcbride, j. jardine, lynette reynolds, marion ritchie, p. mchenry, h. cromb, c. veal, j. van buerghel, g. templeton, k. page, e. tozer, b. wilson, g. minehan, g. smith, j. bennett, n. pike, l. reynolds, m. ritchie, m. wunhym, l. willis, m. nolan, j. rogers, e. kinnane, g. cody, j. mills, j. cunningham, m. eggleton, n. rimmington, m. marshall, n. gay, e. hosking, v. jolly, j. mchenry, rosalie hall, brian duthie, m. lesins, l. hotchin, g. hill, e. richards, l. jardine, m. roberts, i. siver, d. mclennon, k. warhurst, r. rowse, e. snowball, g. jill, n. bromley -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Booklet, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1955, 1955
School Council, Members of Staff, Editorial, Principal's Page, Prominent Personalities, Tales from Malaya, Literary Society, Boys' Sport, Football, Baseball, Cricket, Tennis, Swimming, Athletics, Amateur Cycling, The Dear Departing, Magazine Committee, Accident!, The Apprentices, Bee-Keeping, Roll Call, Junior School, Ballarat Junior Technical School Members of Staff, House Notes, A.T.C. The activities of the Air Cadets, Girls' House Notes, Junior Technical School, Ballarat North Junior Technical School - Headmaster's Page, Ballarat North Junior Technical - School Members' of Staff - Students' Gray soft covered magazine with red and blue titlesFront inside cover has signatures.ballarat school of mines, magazine, glen baxendale, john skuja, graham willey, stan kisler, r. w. richards, janet steele, john collier, jim murray, eillen grundell, john clelland, bill maxwell, ron furlong, judy johnson, russ whitcher, anita young, jimmy durant, alf hannah, gordon thurling, r. dunlop, j. wolfe, i. schunke, d. schmidt, j. murray, b. tozer, r. furlong, b. singleton, n. richards, f. andrewartha, j. barnes, p. collier, a. orgill, w. maxwell, n. brogden, b. bellingham, b. gallagher, g. rasdell, j. williams, j. clelland, n. spears, t. prior, b. matthews, b. dixon, j. barker, g. ditchfield, a. clarke, t. seabrook, w. saggers, b. mclennan, n. beanland, p. nally, i. fraser, j. gowan, g. hewitt, s. nandhabiwat, p. quinlan, g. crawford, jim mcneil, bill saggers, frank andrewartha, john barnes, peter ditchfield, richard dunlop, alan orgill, pat quinlan, david schmidt, terry seabrook, russell whitcher, john williams, barrie r. smith, saml. l. clemens, beth byrne, beverley briggs, john procter studios, "buck" rodger, jack aitkin, diana mainwaring, bob jones, brian blenkiron, geoff o'brian, peter nunn, douglas poole, denis bryans, brian duthie, g. bromley, b. thompson, graham paddle, j. spencer, j. leckie, w. widdop, m. eggleton, m. marshall, c. veal, m. judd, r. day, b. conry, h. smith, a. minotti, e. kinnane, r. white, j. mchenry, m. o'brien, w. edmends, n. slocum, a. bethune, g. mckenzie, l. jones, g. weightman, r. whitcher, r. janson, k. delaland, g. blomley, l. leckie, l. matthews, r. widgery, g. gilmer, t. lugg, l. tuddenham, g. wright, j. hamilton, b. parker, d. wakeling, r. cutter, g. cheeseman, b. patterson, n. hocking, g. pett, b. stevens, j. mckenzie, l. dean, w, tresize, m. lesins, marcia ellsworth, betty gist, b. o'connell, j. mortimer, janice rowe, k. mcbeath, b. augustine, c. ludbrook, v. gill, b. squire, m. walsh, j. pollock, i. sproule, j. cromb, r. duncan, g. sawyer, g. walker, n. porter, e. waller, r. carlson, k. johnston, l. willis, s. mcgregor, a. clark, i. boyd, norma davies, i. kinnane, p. agrums, r. latter, r. harwood, d. sarah, d. mclennan, n. delosa, g. stevens, j. furlong, g. hocking, j. davenport, v. scott, d. pollock, laraine edwards, helen smith, janet mchenry, merle gillingham, j. hunt, j. strange, e. r. willingham, r. handmer, j. rash, a. f. hetherington, d. dow, w. etty, a. haywood, j. vincent, p. athanitis, l. kinnane, d. hughes, l. fox, j. caldwell, r. champneys, d. ridgway, j. van berkel, m. ritchie, m. bolster, j. hankin, n. pike, j. bennett, g. tonkin, n. davies, h. wunhym, b. hay, j. carroll, r. gilchrist, glenys spielvogel, b. strange, g. lee, h. a. smith, w. leishman, j. flynn, a. wright, g. henderson, j. vagg, k. howell, g. collinson, s. stepnell, j. clarke, r. brown, g. spiers, k. jenkins, l. deppler, b. silvey, n. bromley, j. sarah, g. hinks, g. dunstone, b. mciver, r. hepburn, b. gavin, b. clack, k. fisher, l. mcdonald, r. mckenzie, p. hall, b. harrison, d. vincent, b. lugg, j. allen, w. sawall, a. brumby, j. richards, e. jamieson, m. litchfield, g. munning, g. martin, n. nugent, t. fletcher, j. mcnicol, d. mackay, kevin rogers, g. turnbull, b. gamble, g. russell, i. watkins, a. brogan, r. chibnall, j. gullock, r. kinnersley, g. brown, w. parkinson, r. priddle, r. burge, b. reid, l. reed, g. nicholls, w. wilkins, b. pittard, w. ellis, d. hodgers, j. witherden, b. antonio, n. malthouse, g. keddie, c. harris, n. currie, j. mcadam, b. flynn, j. whelan, b. tait, w. troughton, n. bedggood, i. franklin, n. yean, j. caroll, r. elshaug, r. whitten, f. loader, g. pike, n. dell, william saggers -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazines, Various
Pale green soft covered magazine with red and black ink. 56 pages including advertisements. 1. Fourth Term, 1907. Included an article on Cornish Mining. 2. 1946 3. 1945 4. 1949 5. 1950 6. 1951 7. 1944 8. 1942 9. 1941 10. 1960 - School Council, Members of staff, Editorial, Principal's Page, Literary Society, That First Day, Prominent Personalities, Conferring of Diplomas, The Begonia Parade, Efficient Reading?, The Sporting Pages, Enter the Modern, Tradition, The Ceremony, Roll Call - List of Students' 11. 1939 12. 1909 13. 1908 ballarat school of mines, robert norton, c. t. tay, n. delosa, bill boggs, alan bethune, janis erdmanis, alan rock, peter agrums, gail trewanack, tony white, norm nash, graeme "curly" williams, chong thung "jack" tay, noel whitcher, malcolm peel, k. blee, roberta pittard, margaret timmins, i. menner, r. nicholson, g. titheridge, g. johnson, p. agrums, d. pope, r. wollermann, g. hall, g. hart, n. nugent, a. bethune, k. penna, s. white, t. white, j. pollock, k. rogers, l. campbell, n. bromley, t. scanlon, j. davis, j. miller, k. kirton, b. hickey, w. moore, m. mckinnon, i. weir, r. coutts, g. thurling, anthony yeung, y. kwong, r. champneys, j. erdmanis, a. webb, d. taylor, j. rash, n. nash, c. tai, s. chand, t. gan, k. e. ooi, c. poh, m. mallett, l. rawlings, a. patterson, g. le couteur, m. hewitt, e. grummett, a. rock, r. miller, g. ikstrums, b. lonsdale, d. holmes, g. leishman, r. norton, t. brauer, n. whitcher, p. lockyer, lois morris, eric mcgrath, helen ross, g. cornell, i. menz, l. j. matthews, l. j. groat, o. n. hails, p. j. davis, n. l. nash, s. mason, mr and mrs barry singleton, john wolfe, brian duthie, cornish mining, j. skuja, s. rowe, a. kinnane, w. maddox, sturt street ballarat -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Booklet, J. A. Hoskin & Son, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1955, 1955
Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1955Pale blue front page soft cover with burgundy and navy blue inscriptions on front coverballarat school of mines students' magazine, staff, sports, bob jones, j. spencer, j. leckie,, graham willey, j. wolfe, i. schuke. d. schmidt, j. murray, b. tozer, staff, sports, glen baxendale, john skuja, bob ellsworth, arch collins, alec mcphee, murray lonie, alec ross, harvey maddern, m. shoppee, con martin, max wilson, harold steane, john collier, eileen grundell, janet steele, jim murray, jhon clelland, bill maxwell, judy johnson, anita young, ron furlong, russ whitcher, jimmy durant, alf hannah, gordon thurling, frank andrewartha, john barnes, peter ditchfield, richard dunlop, stan kisler, jim mcneil, alan orgill, pat quinlan, bill saggers, david schmidt, terry seabrook, russell whitcher, john williams, john proctor studios, ballarat junior technical school air training corps, cadets, bob jones, air training corps, william saggers -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Ballarat School of Mines Minute Book, 1956-1961, 1956-1961
Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat has a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. In 2016, Federation University Australia announced plans to take possession, over a two-year period, of Monash’s Berwick Campus in the south-east corridor of Melbourne. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is headquartered in Ballarat and offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. The name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses.Hard Cover book, partly bound in leather with Ballarat School of Mines Council Minutes, and Finance Committee minutes. ballarat school of mines, ballarat school of mines council, ballarat school of mines council minutes, ballarat school of mines finance committee, josephine brelaz schlarship, a.j. affleck, h.l. allnut, arblaster, h.e., aston, robert, barker, k.c., barrell, g.w., beaston, c.w, benney, v, blackwood, r.r., noel brelaz, brelaz guido, brinsden, neville bunning, james caldwell, callow, n.l, clelland, john, corbould, day, p.l., dewsnap, n.f., w.g. durant, elliott, m., faulkner, f, ferguson, f.e., finn, william, gallagher, b., garner, l, gordon, i.r., hancock, v, heseltine, mary, hooper, noel, hullick, k, m.b. john, johnson, alan ernest, johnson, b.a., bullarto, bullarto excursion, ballarat gaol, m.b. john brassworks, motor mechanics huts, 90th anniversary, josephine brelaz, v. hancock, alfred mica smith, john wolfe, s.d. wynes, r.w. richards award, spargo creek, spargo creek excursion -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumMagazine (item) - CAC The Aeroplane magazine planes and drawings Bristol Beaufighter Curtiss Hawker Hurricane Spitfire Messerschmitt Me 109 Me 110 Focke Wolfe 190 Halifax Junkers 88 Catalina Rolls Royce Merlin, CAC The Aeroplane magazine WW2 planes and engine drawings
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook - CAC The Aeroplane magazine planes and drawings Bristol Beaufighter Curtiss Hawker Hurricane Spitfire Messerschmitt Me 109 Me 110 Focke Wolfe 190 Halifax Junkers 88 Catalina Rolls Royce Merlin, jochen prien & peter rodeike, Messerschmitt bf 109 f, g,& k series, January 31st 2024
Excellentnon-fiction -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncNegative - Haeusler Glass Negatives Collection - Dolly Hughes (Mrs Jack Wolfe) with a sheep and lamb
The Wodonga Historical Society Haeusler Collection provides invaluable insight into life in late nineteenth and early twentieth century north east Victoria. The collection comprises manuscripts, personal artefacts used by the Haeusler family on their farm in Wodonga, and a set of glass negatives which offer a unique visual snapshot of the domestic and social lives of the Haeusler family and local Wodonga community. The Haeusler family migrated from Prussia (Germany) to South Australia in the 1840s and 1850s, before purchasing 100 acres of Crown Land made available under the Victorian Lands Act 1862 (also known as ‘Duffy’s Land Act’) in 1866 in what is now Wodonga West. The Haeusler family were one of several German families to migrate from South Australia to Wodonga in the 1860s. This digital image was produced from one of the glass negatives that form part of the collection, probably taken by Louis Haeusler (b.1887) with the photographic equipment in the Wodonga Historical Society Haeusler Collection. This item is unique and has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of domestic and family life in early twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history and social history.Digital image created from the Haeusler Glass negative collection. A child, Dolly Hughes, with a sheep and lamb. There are trees and a fence line in the background.wodonga pioneers, haeusler family, glass negatives, dry plate photography, dolly hughes -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Booklet, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1956, 1956
School Council, Members of Staff, Editorial, Principal's Page, Prominent Personalities, The Worshipful Company of Plumbers, Controlling the Menace of Radio-active Bombs, Sports Awards 1956, Football, Athletics, Cricket, Baseball, Tennis, Literary Society, The Dear Departing, The Struggle for Malayan Merdeka (Independence), Junior School, Boys' Form Notes, House Notes, Ballarat North Technical School, Roll Call, Ballarat Junior Technical School - Members of Staff and Students', Ballarat North Junior Technical School - Members of Staff and Students'Gray front page soft cover with red and black inscriptions on front cover, 84 pages.ballarat school of mines students' magazine, school council, members of staff, staff, sports, i. tregenza, mrs hanrahan, mr r. t. white, mrs r. t. white, mr and mrs l. f. wilson, mrs barnett, r. j. king, j. halliday, b. antonio, p. montgomery, w. wilkins, g. keddie, j. clarke, g. nicholls, k. burgej. gullock, w. doyle, m. moore, d. mcleod, b. gamble, j. allen, g. wilson, r. elshaug, r. chibnall, r. gamble, m. elsey, w. dowler, j. taylor, g. caddy, b. flood, g. rapkins, r. whitten, r. priddle, r. wilson, j. carroll, m. tucker, f. trigg, i. franklin, n. dell, n. yean, c. judd, j. richards, w. sawall, w. wilson, k. penna, k. rogers, b. harrison, g. martin, l. mcdonald, a. brumby, r. mckenzie, g. manning, j. sarah, t. fletcher, john clelland, john collier, john matthews, norman leckie, phil kempe, harold steane, russell ewins, jeff coward, cliff restarick, don stevens, frank whitworth, bill burrow, keith mccoll, marian ritchie, elizabeth kinnane, ballarat girls' junior technical school, dressmaking, commercial, mascot, m.b. john aggregate shield, hume and iser swimming shield, alf clark, warwick wtty, garner, n. haig, p. agrums, raaf cadets, sunshine biscuit factory, north tech, choir, hor khoo, norman dalton, bill sadler, neville spears, ian schunke, john wolfe, bernie gallagher, nelson hails, don overall, brian tozer, harry brue, beverly briggs, denis bryans, barry singleton, alan clarke, beth byrne, n. hails, j. matthews, b. gallagher, j. collier, d. overall, p. robinson, john benn, fred leigh, j. lacy, mr garner, warwick etty, worshipful company of plumbers, plumbing, air training corps, cadets, ballarat north junior technical school, ballarat north technical school, r.w. richards, richard w. richards, dick richards, l.f. wilson -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Booklet, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1952-1961, 1952-1961
1957 - Art Lending Library, Neville Bunning, Dana Street Primary School - The Original Ballarat Junior Technical School, ATC, Flight Cadets; Ballarat Junior Girls' Technical School, Ballarat North Junior Technical School, Roll Call 1960 - Ballarat School of MNes Literary Sociaty, begonia parade, Efficient reading, enter the modern, Lois Morris, sheetmetal, G. Cornell Obituary, I. Menz Obituary, metallurgists' Society, Olympic games 1961- Red, black and white soft covered magazine of the Ballarat School of Mines Information outlined in the magazine includes: The Richard W. Richards Medal, Philips Electrical Industries scholarship, A.F. Heseltine scholarship, Hong Kong To-Day (by Daniel Yung), A Treatise on Mount Morgan, Bath Push, The Stud Room, A Gentlemen's Excursion to Beaufort House, Electrical Laboratory, Metallurgical Laboratory, The Australian Aboriginal in Modern Civilization (J. Kavanagh) , The history of Electricity ballarat school of mines, ballarat junior technical school, cadets, flight cadets, airforce cadets, ballarat school of mines students' association, noel delosa, noel whiticher, bob coutts, noel kelly, les dobie, noel murphy, malcolm peel, peter agrums, ian weir, sue mole, val baker, neil bromley, kevin oscar rogers, h.e. arblaster, richard w. richards, dick richards medal, keith hindson, james tinney, walter tooth, john bethune, vilma sansom, betty clark, travers duncn, joyce wilson, lex lockhart, jim beattie, joyce stevens, slim ingleton, john skuja, murray gillan, graeme willey, diana mainwaring, eureka stockade, east africa, canada, sumatra, chris sanos, greece, malaya, bee-keeping, worshipful company of plumbers, hong kong, daniel yung, mount morgan, history of electricity, peter robinson, john clelland, davis schmist, harry brue, harry brew, rex hollioake, broken hill, excusions, john wolfe, beverly selkirk, barry singleton, mara jekabsons, bill widdop, frank pomeroy, art lending library, john mckenzie, ballarat girls' technical school, robert norton, graeme williams, alan bethuse, janis erdmanis, alan rock, gail trewanack, tony white, ching thung tay, jack tay, noel whitcher, norm nash, helen ross, eric mcgrath, g. cornell death, i menz death, john wolffe, brian duthie, bill durant, w.g. durant, heather walton, heather durant, beverly singleton, neville bunning
