Showing 3731 items
matching 1840-1977. | nathalia district (vic.) -- history.
-
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Simpson's cranioclast used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Prior to the 1900s, complicated births, particularly where there was a disproportion between the size of the woman’s pelvis and the foetus’ head, often meant the death of the baby and the mother. Instruments for removing a dead or ailing foetus from within the mother were used to attempt to save the mother’s life. The cranioclast, first invented by Dr. James Simpson in the mid-19th century and later redesigned by others, was used for fetal destruction and removal. Fundamentally a strong pair of forceps, the cranioclast was used to crush the skull, decreasing its diameter. In some cases, this would allow normal uterine contractions to expel the foetus; in others, the physicians would use an obstetrical hook to pull the body out of the mother. Doctors disagreed as to the pelvic diameter that would necessitate this drastic intervention, but generally found that 3 to 3.5 inches was the smallest size through which a living infant could pass. Equally of debate was the pelvic size through which the dead fetus could be extracted. When vaginal extraction was deemed unadvisable, Caesarian section would be performed. As caesarean section became safer and more common with the advent of anaesthetics and antiseptic techniques, the use of cranioclasts and obstetrical hooks diminished. (Museum of Health Care, Kingston) Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Hinged metal tool with bakelite handles at one end and serrated teeth at other end. The instrument is in two sections. The right or upper blade has a black bakelite handle. There are two screws on the inside of the handle, 5.5cm apart. In the centre of the blade is a screw notch in the shape of a small horseshoe. On the inner side of the blade is a depression extending most of the length. The left, or lower, blade also has a black bakelite handle. There are two screws on the inside of the handle approximately 6cm apart. Mobile metal clasps in the shape of an 'S' , with three serrations, is attached to the distal end of the handle, which enables the blades to be opened or closed. destructive instruments -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
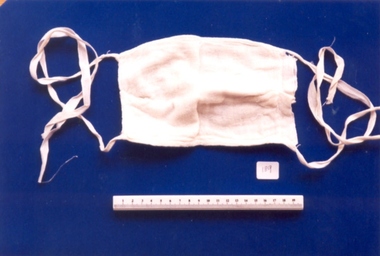
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Surgical gauze mask used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Mask is made up of several layers of muslin gauze sewn together with cotton tape. The ends of the tape were used to tie the mask to the doctor's face covering the nose and mouth.surgery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Iodine bottle used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Small amber coloured glass bottle used to store iodine. Bottle has a clear glass stopper.antiseptic -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Chloroform bottle used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, W.J. Bush & Co
The use of chloroform as an anaesthetic for humans was first demonstrated by Edinburgh surgeon James Young Simpson in 1847. It was used as an anaesthetic in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Amber glass bottle (empty) with clear glass stopper. Bottle carries its original label which "W.J. Bush & Co. Ltd. London ... Chloroform.."". On the base is the number "12" and "AS 9A"anaesthesia -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Silk umbilical tape in glass vial used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Allen & Hanburys, England
To use this tape, the tube would be broken in half using cat-gut breakers.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Glass vial, containing silk umbilical tape [193.2] in sterile solution. The tape is wound around a flat spool.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Two glass vials of 'Ethicon' catgut #3 used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Ethicon
Tanned or chronic catgut came from top quality catgut (fat free). A hardening process was then applied to the muscle durations. The process was introduced and perfected by the firm of Mersons of Edinburgh, makers of sterile surgical ligatures in the early 1930s. Once processed the catgut was preserved in an iod-asceptic preserving spirit and hermetically sealed in glass tubes. It was completely sterile and ready for immediate use. The length of the catgut in each tube was five feet, or 2.5m, and could be wound onto glass winders in assorted colours.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Two glass vials [195.1,.3] with catgut number three "Ethicon" [195.2,.4] in sterile solution. Vials are moulded and sealed at both ends.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Bottle of iodine solution used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, W.L. M.F.C. Co
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Round glass bottle [196.1] containing iodine solution with glass stopper [196.2] and metal screw cap [196.3]. Bottle has a ridged neck and is approximately half filled with iodine solution. obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Lamprecht's anaesthetic (chloroform) bottle used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Lamprecht
The use of chloroform as an anaesthetic for humans was first demonstrated by Edinburgh surgeon James Young Simpson in 1847. It was used as an anaesthetic in the 19th and early 20th centuries.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Amber glass bottle [197.1] with long neck and matching stopper [197.2]. The text "Lamprecht's" and "36587" stamped into the glass. Bottle is round with a fluted, vase like top and a small spout. Stopper is topped by a circular knob and tapers towards a point."Lamprecht's" "36587"anaesthesia -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Towel used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
These types of towels were introduced into hospitals in the 1900s, where they were used mostly in operating theatres and on dressing trays. The towels became too costly to launder and were replaced by more modern disposable materials.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Thick cotton/linen towel, with a 'bubble' or 'chain' design in the material. The word "Hospital" is woven into the central band. There is a 1.25cm machined hem on unsealable sides.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Towel used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
These types of towels were introduced into hospitals in the 1900s, where they were used mostly in operating theatres and on dressing trays. The towels became too costly to launder and were replaced by more modern disposable materials.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Thick cotton/linen towel, with a 'bubble' or 'chain' design in the material. The word "Hospital" is woven twice into the central band. There is a 1cm machined hem on unsealable sides.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Enamel jug used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
This is a one pint general purpose enamel jug. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Cream coloured jug, made of enamelled metal with a blue rim. Inside the jug are markings for imperial and metric capacity.infant care -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
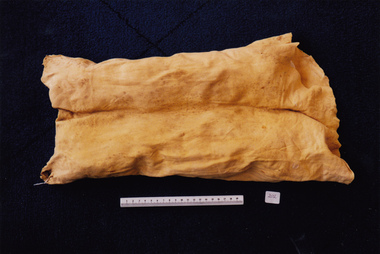
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Chamois bag used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Chamois bag originally used for obstetric forceps. The bag is sewn down the centre to form two compartments.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
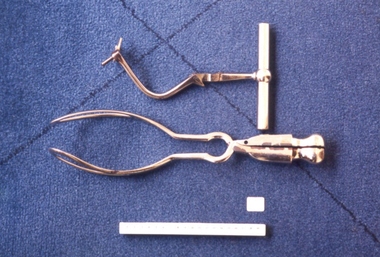
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Barnes-Neville axis traction obstetrical forceps used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Allen & Hanburys, England
Neville Barnes Obstetric Forceps have a cephalic and pelvic curve and are used for delivery of babies presenting as occipitoanterior. When used, the left blade is put on first followed by the right blade – the baby is then pulled down until the occiput is under the symphysis, then pulled around. (RACGP)Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Set of metal forceps. Consists of two blades [204.1,.2] and detachable traction axis [204.3]. Inner aspect of right hand blade is inscribed ' Allen and Hanbury's - London'. '3' inscribed on axis traction handle.'Allen & Hanburys - London', '3'obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
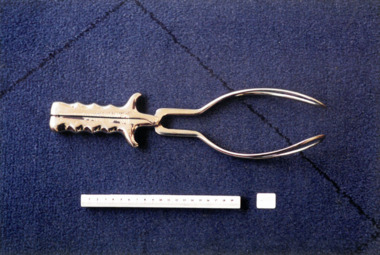
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Simpson-type obstetrical forceps used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Skidmore, 1851- 1898, approximate date of manufacture
These are long obstetrical forceps following the design of Sir James Young Simpson (1811-1870). They are longer and heavier than Simpson's type of short forceps and were used to deliver babies from higher up the birth canal. Simpson's long and short forceps were adapted in many later designs. (Science Museum Group)Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Metal forceps, consisting of two blades with detachable traction axis.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Doctor's medical bag used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
The Gladstone bag was first developed in the mid 19th century and was named after British politician William Gladstone, a four-time Prime Minister of the United Kingdon. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Leather gladstone bag with leather handle and leather strap. Lining of bag is torn. Base of bag carries the words 'SOLID LEATHER' and the number '20'. surgery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medicinal vials in box used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Pituitrin was used for the induction of labour prior to birth and for the treatment of post-partum haemorrhage (from vasopressin's vasoconstrictive properties). Morphine is used for the short term management of severe pain. Hyosine Hydrobromide, also known as scopolamine, is used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Selection of four medical vials in a small cardboard box. Vials contain Pituitrin [206.5, 206.6] , Morphine Suphate [206.2] and Hyosine Hydrobromide [206.3, 206.4]. Box is labelled ""HERMETTE"/PITUITARY EXTRACT" drugs -
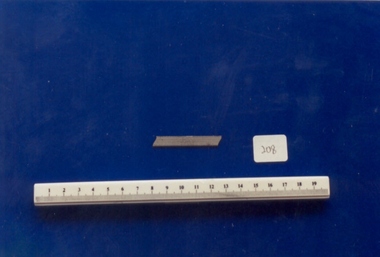 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Vial cutting blade used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
This item was rubbed several times on each side of a glass ampoule or vial to make a cut in the glass, after which the head of the ampoule/vial was snapped off.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Small metal blade, approximately 4.5cm in length. The upper edge of the blade is smooth, and the lower edge has a line of fine serrations for cutting. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Tool - OERTLING SCALES IN GLASS CASE
Beam balance (gold scales) made by Oertling - London. The balance is in a case made of mahogany and fully glassed, it has two draws. The brass scales are built into the case. The maker's name is present on the base of the scale. There is a brass knob that fits in the front to make adjustment to the scales and also on either side of the exterior case to set the top of the scales. There are two front draw, the left one is missing the drawer knob.mining, equipment, scale, ludwig oertling (1818-1893) was born near hamburg and gained his apprenticeship in instrument-making with his brother johann. he immigrated to london in 1840, where he joined instrument-maker and assayer george makins (1815-1893). oertling collaborated with makins and built his first balance, which was "a twin-column assay type with a light lattice beam". by 1851, the year of the great international exhibition of the works of all nations, oertling had established his own instrument-making business, employed five instrument-makers, and by 1861, ten staff were engaged in designing and making instruments, principally analytical balances. oertling's first twin-column beam balance was the prototype for all oertling assay balances that were produced during the next century and exported to the british colonies: australia, new zealand, canada, south africa and india, to europe and america. -
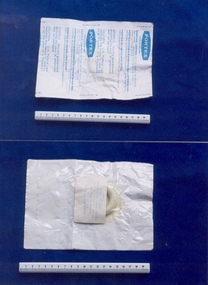 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Ring pessary associated with Dr Geoff Bishop, c. 1977, Portex Ltd, England, c1977
This pessary came from Professor Geoff Bishop's rooms, Mollison House, 386 Albert Street, East Melbourne. As well as the UK, Portex had divisions in the USA and Canada. The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids. Portex brand ring pessary in original packaging. Consists of circular ring of cream vinyl, in sterile sealed pouch with transparent plastic at back. Stamped on pouch "PORTEX ENGLAND", and the text "USE BY FEB 77" and "CONTROL No F/1 505". The ring is size 700/300/056 - 56mm. A sticker on the back of pouch gives instruction for cleaning the pessary.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Ceramic feeding cup associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c.1866-1920
This type of cup was designed for use by an adult and was in common usage from the early 1900s to the 1930s. Feeding cups were used both in the home and in hospitals, and were also often made of white enamel. Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them the museum collection in 1993. Feeding cup made out of white china, now discoloured. The cup has a curved spout (similar to a teapot spout) with a handle. There are four small holes inserted inside the cup diagonally at the proximate end of the spout. midwifery -
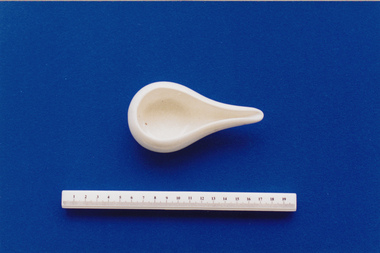 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pap boat associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866-1920, 1880 (approximate)
Pap boats date from approximately 1710 and were in extensive use until the end of the nineteenth century. They were used to feed pap to infants or invalids. Pap was a mixture of breadcrumbs, flour, rice or barley mixed with fluids such as broth, milk (if the infant was lucky), water, wine and even beer, to aid the digestion of pap it was often pre-chewed by the nurse or nanny. Pap was a popular form of infant nutrition for almost 300 years and used in many well to do homes. For unwanted or illegitimate infants in foundling homes it was often the only form of sustenance, however, and as a result the mortality rate was appallingly high. Despite a growing number of experts advising against the use of pap, it nevertheless persisted as a major source of infant nutrition in many nurseries until the late 1800’s, largely due to the ignorance of nannies and nurses who took great delight in disregarding the advice of physicians, who they believed were usurping their position in the household. ‘Nanny knows best’.(Amgueddfa Cymru - National Museum Wales, 'Pap Boat')Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993. Small round white china container with an extended slim lip. Fluid capacity approximately 30-90ml. The boat has been made from two moulded sections. infant care, infant feeding, midwifery -
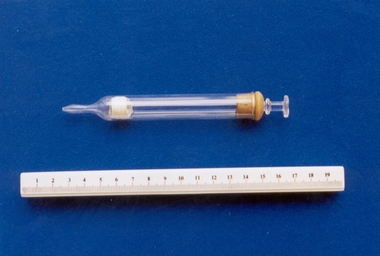 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Glass wound irrigator syringe associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
Glass wound irrigating syringes were in general use from approximately 1915 to the beginning of the 1940s.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993. Glass wound syringe, with wood cap at distal end and cork bung inside a glass barrel with tapered end. irrigation, midwifery -
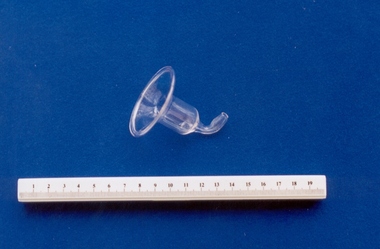 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Glass nipple shield associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
A rubber teat would be attached to the top of this nipple shield for breast feeding. From 1801 onwards, nipple shields were available in a variety of materials, such as pewter, horn, bone, ivory, wood, glass and silver. They varied in shape from a bell to a flatter, cap shaped appliance. With the application of the nipple shield, the baby was able to take milk from the breast without giving added trauma to the nipples. In the ante partum period the nipple shield could be worn to assist in drawing out flat nipples; or, as it was known during this period, for the formation of "new nipples". (Fildes, Valerie. 'Breasts, Bottles & Babies - A History of Infant Feeding', 1986) Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993. Glass nipple shield. Shape resembles that of a bell.infant feeding, midwifery -
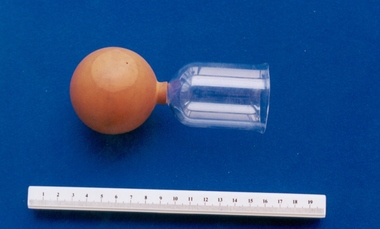 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Cupping glass associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
Cupping glasses were in use from the early 1700s onwards. Their purpose was to draw the nipple out from the areola in preparation for breast feeding. They were also used for expressing small quantities of breast milk. Other possible uses include drawing fluid from other parts of the body for conditions such as oedema of the limbs or abdomen.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993. Cupping glass, consisting of a glass tube connection and red rubber hand pump.midwifery, infant feeding -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Furgusson-style fetal stethoscope associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
The Furgusson stethoscope was in use from 1866. It is made all in one piece and has no attachments.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Fetal stethoscope consisting of an ebony tube with flanges at each end. The large flange would be placed onto the abdomen and the small flange would be placed to the ear to hear the fetal heart beat.diagnostic instruments, midwifery -
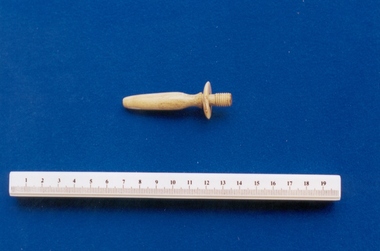 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Enema syringe connection associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
This is a connection for a bone rectum pipe for a manual Indian rubber enema syringe.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920.She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Small, elongated connection with openings at both ends. The connection narrows at the distal end (patient's end), and has a flange at proximal end, where the connection attaches to a rubber bulb.midwifery -
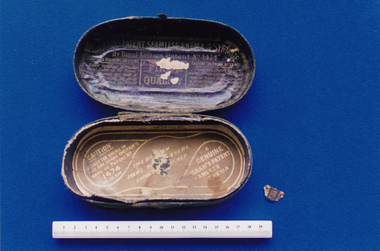 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Enema syringe case associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920, 1880 (approximate)
The enema box was used by midwife Mary Howlett in the 1880s on her district rounds. It was used to hold Ingram's Patent No. 1474 Seamless Enema Syringe, but the syringe is missing.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920.She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Oval shaped black leather case with gold clip. Base (.1) and lid (.2) have become separated. Instructions for use, and how to clean the instrument, are pasted inside the lid and base of the box.midwifery, irrigation -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Transcript of lecture given by Frank Forster, "Mrs Howlett and Dr Jenkins: Listerism, and early Midwifery practice in Australia", 14 June 1965
This paper was read on 14 June 1965 by Dr Frank Forster at a meeting of the section of Medical History, Victorian branch, Australian Medical Association, according to Ann Tovell, who worked at the AMA and in association with Frank. It was likely that Frank Forster acquired the midwifery box belonging to Mrs Mary Howlett at the former Eastern market that was located on the corner of Bourke and Russell Streets up to the early 1960s.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920.She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.A5 size paper transcript of lecture. Reprinted from The Medical Journal of Australia, 1965, 2. Pages are numbered 3 to 21.midwifery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Intravenous drip regulator associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
Similar in style to a 'Record' syringe adapter.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920.She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Glass regulator from a rectal saline apparatus. Regulator consists of a glass bulb with a glass flange at the base, which connects to a glass pipe. intravenous device, midwifery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Test tube and case associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
This type of test tube would have been used to collect blood or other bodily fluids. IT may also have been used to boil urine to identify the presence of urinary abnormalities such as sugar albumen acetone or bile.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920.She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Glass test tube with a thin glass lip in original cylinder cardboard case. Case is in two section, lid and body - lid is lined with white cardboard.diagnostic testing, midwifery
