Showing 736 items matching " 1800s"
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, Saunders, Unknown
The photograph depicts the two-storey building of the Bank of Victoria which was built in 1858 and was replaced in 1867 after a fire destroyed the original building. The branch had originally opened under John Farran in 1856 before the office building was erected in Beechworth. The building was located on the corner of Ford and Camp streets and embodied the dignified appearance of Beechworth during the mid-1800s due to the building's features. The Bank of Victoria was designed by "Smith and Watts" and built from white brick and render, which cost three thousand and seven hundred pounds to construct. The building was inspired by a formal Italian villa, including square-headed windows, cornices, and a parapet. The ground floor consisted of banking chambers, a strong room, and servants' quarters. The residential quarters were located on the second floor.The photograph is significant as it depicts not only depicts a building of importance to the town of Beechworth but it also shows aesthetic significance due to the style it was built in. As the Bank of Victoria was constructed in the classic Italian style, it exemplifies the classic quality and refined manner of this architectural style. This building style represents the image Beechworth held for itself at that time, which was a sophisticated and distinguished town.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on paper.Reverse: 23/80 / Beechworth / (Indecipherable) / Banking to (Indecipherable) / Sydney / “Bank of Victoria” / BMM 8692.1 / [Stamped: ILFORD]bank of victoria, beechworth, banks, beechworth bank, 1858, 1867, ford street, camp street, victoria, john farran, smith and watts, italian architecture, italian style building, brick building, brick, banking, money, fire, building destroyed -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTin Coffee and Chicory, circa mid to late 1900's
Chicory was mixed with coffee to reduce the amount of coffee bean required to be used. This coffee "substitute" was due to the repeated fluctuations in availability of coffee beans (and price fluctuations) in the USA in the late 1800s and early 1900s resulting in the search for substitutes and additives to bulk out the available supplies. This was especially so during times of the major World Wars. Chicory was an excellent choice of fillers as it did not greatly influence the strong coffee bean taste. The first choice in USA households was coffee not tea and the influence of the American servicemen's thirst for coffee was a major thrust into the Australian "colonial" preference for a "cuppa" tea. Rural areas took longer to acquire a coffee "break" but with more and more subliminal advertising through "American" films the rural regions developed a growing preference for coffee, however the tea break alias "smoko" has lingered on.This coffee and chicory blend tin container is very significant to the Kiewa Valley in that it demonstrates that even in rural regions of Australia tastes and drinking preferences have changed by subliminal advertising as time goes by. The American "influence" whether by the "invasion" of friendly troops during the major wars or the avalanche of "American films" has altered some of the "dinky-di" Australian "true blue" tastes and mores. The availability of "straight " coffee supplies to rural areas was also in proportion to the level of all weather transport routes. In the late 1800's and early 1900's road freight had to contend with dirt roads, flooded roads, bush fires and grazing cattle/sheep in rural areas. The easier access that city households had with regard to replenishment of food and drink products, up until the mid 1900's, was severely retarded in rural areas. This extensively rusted tin of "Bushells Blue Label" Coffee and Chicory has an octagonal shaped body with a "push/pull" lid(tin).Three sides has reproduced painted ladies in "Roman dress" ladies picking the coffee beans. There is no reproduction of any chicory roots. There are two "Indian dressed" field workers(pickers) with turban head dress. On one side of the tin is "directions of use, net weight and manufacturer details."Bushells Coffee & Chicory", "NET 1-Ib. weight", " No. 144" "Under the Pure Food Act N.S.W. 1938" "by Bushells Ltd. No 144"chicory / coffee drinks, tin hydrated drink, rural food and drink consumption patterns, tinned food and drink -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Pot
Modern iron cooking ‘ranges’ were being introduced from the late 18th century, however a vast number of people cooked in open fireplaces, well into the 1800s. Generally they were fitted with iron rods suspended above the fire or ‘cranes’ that could be swung in and out for easier and safer access to the pots that hung from them. These cooking systems may seem rudimentary, but a skilled cook knew how to manage pots, pans, cauldrons and pokers and expose them to the right type of heat by positioning them in various parts of the fireplace. They were also very versatile, enabling multiple cooking techniques – boiling, stewing, frying, roasting, toasting – all at the same time, using different types of vessels and utensils. https://blogs.sydneylivingmuseums.com.au/cook/hearth-fire-cookery/This type of item was used extensively over the centuries over open fires. It is still used in camping.Metal cooking pot with handle designed to hang the pot over an open fire.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, kitchenware, cooking, open hearth cookery -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Former Barkly Street Uniting Church, Ballarat, 2015, 07/04/2015
The World War One windows in the Barkly Street Uniting Church resulted from a request made in 1919 from the Barkly Street Young Men's Club who raised money to pay for the project. The window was designed by the Fisher Company, and was unveiled on 14 March 1920 at a total cost of 171 pounds 10 shillings. The windows are considered to be one of the most remarkable war memorial windows in Victoria, and the 1800s English Gothic-style front facade is believed to be protected by a City of Ballarat heritage overlay. Historical experts believe the windows were designed by renowned stained-glass window-maker William Montgomery. The centre window depicts a young soldier bearing an Anzac badge underneath the British and Australian flags. The image of the solider is surrounded by 24 crosses, a single dove and a bugle. A number of colour photographs of the interior of the Barkly Street Uniting Church taken while the church was offered for sale.barkly street uniting church, barkly street methodist church, world war one, world war one memorial, stained glass, soldier, religion, church -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Two silver jam spoons, c1900
Electroplated silver spoons were commonly used in the late 1800s to early 1900. These spoons were owned by Mrs Alice Dinsmore, grandmother of Mrs. Jean Raper of Wodonga. Spoon 1 (at the top of the image) bears the hallmark of George Waterhouse & Co of Sheffield, England. II is labelled EPNS which stands for Electroplated nickel silver. Spoon 2 bears the makers mark WM & S, the mark of William Mammatt & Sons of Sheffield which operated under that name from 1886 until 1906. In 1901 Maxfield & Sons and the associated businesses of J.& J. Maxfield and W. Mammatt & Sons were converted into a single liability company under the style of J. & J. Maxfield Ltd and in 1908 was reformed as Maxfield & Sons (Silversmiths) LtdThis item is from the Raper Collection donated to the Wodonga Historical Society by Mrs. Jean Raper.2 silver plate jam spoons. The spoons are both electroplated and have clearly discernible hallmarks imprinted on them.On spoon 1: W & Co EP in separate shields. On spoon 2: "WM & Ssilver spoons, domestic items, silver cutlery -
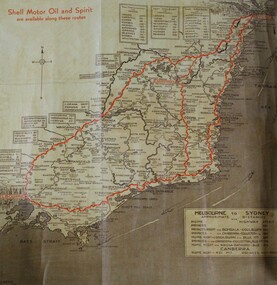 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncMap - Hamilton-Smith Collection Highway Map c. mid 1900s
The Hamilton-Smith collection was donated by the children of Grace Mary Hamilton-Smith nee Ellwood (1911-2004) and William John (Jack) Hamilton-Smith (1909-1984) who settled in Wodonga in the 1940s. The Ellwood family had lived in north-east Victoria since the late 1800s. Grace’s mother, Rosina Ellwood nee Smale, was the first teacher at Baranduda in 1888, and a foundation member of the C.W.A. Rosina and her husband Mark retired to Wodonga in 1934. Grace and John married at St. David’s Church, Albury in 1941. John was a grazier, and actively involved in Agricultural Societies. The collection contains significant items which reflect the local history of Wodonga, including handmade needlework, books, photographs, a wedding dress, maps, and material relating to the world wars.This item has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of social life in mid-twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history and social history.A brown and tan highway map with red road markings showing the south east of Australia from Melbourne to Sydney map, highway, wodonga, melbourne, sydney, travel, hamilton-smith, hamilton-smith collection, driving, drive, car, road -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - LYDIA CHANCELLOR COLLECTION: A WHEEL TURNS FULL CIRCLE
A newspaper article titled 'A wheel turns full circle. Amy Huxtable looks at the recent rebirth of Bendigo's wine industry.' Wine making was one of the main industries in Bendigo in the 1800s. Mr. Jean T. Deravin of Chateau Dore Vineyard was a skilled vigneron. In 1893 phylloxera was found in some vineyards and all vineyards were needlessly pulled out. A new era in wine making was begun in the 1970s. Mr. Deravin's great grandson Ivan Grose now has grapes back at Chateau Dore. In February 1971 a new era in Bendigo wine making began with grapes grown in Bendigo by Mr. Ron Andrew of Maiden Gully were first released as wine by Chateau Tahbilk and Matchett's. There are two photos in this article - a selection of the Shiraz and Cabernet Sauvignon released on the 13/02/76 and a photo of Mr. Ron Andrews holding his first vintage. Note in the background behind Mr. Andrews are his historic stables which he restored. 13/02/1976.bendigo, industry, vineyards and wine making., lydia chancellor collection, collection, wine growing, vineyards, bendigo wine making, wine history, history, vintage wines, mr. jean deravin, mr. ron andrews, chateau dore, chateau tahbilk, industry, amy huxtable, grapes, buildings -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, 1960s
Taken around 1960s, this photograph shows the banks of Lake Sambell. Lake Sambell is named after Mr. L. H. Sambell who was instrumental in the lake's formation. Lake Sambell is the original site of the open sluice operation of Rocky Mountain Mining Company in the 1800s and the early 1900s. In the early 1920s, it was reconstructed as a recreational lake and was formally opened to public on 6 October 1928. The opening event was attended by townspeople and Beechworth's Minister of Lands Mr. Bailey. In the late 1930s to early 1940s, Lake Sambell redeveloped. The first development aimed to raise the banks by six feet to double its present area and to make the water cleaner. Another redevelopment in the 1940s was made possible by the Beechworth and District Progress Association. It involved raising the banks to five feet to provide swimming facilities, paddling pool and caravan park. This photograph holds Historic significance because of its connection to the development of Beechworth district.Sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paperObverse: Reverse: 3533 /beechworth, water scheme, water reserve, catchments, beechworth water reserve, beechworth catchments, municipal council, lakes, reserve, water supply, political projects, environmental changes, mr. l. h. sambell, sambell, rocky mountain mining company, recreational lake, minister of lands, mr. bailey, swimming pool, paddling pool, caravan park, swimming facilities, lake redevelopment, funding -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1950s
Photograph of 2 teams with hoses and reels in a race as part of a CFA competition. Fire brigade competitions have been running for almost 150 years with the first State Championship held in Melbourne in 1874. State Championships have continued every year since 1873. The event goes on regardless of weather conditions or natural disasters. The only cancellations being due to WWI and WWII. In the 1950s, the Rural State Championships were developed to reflect the unique skills of rural brigades. The competitions started out as 'Demonstrations' with the introduction of hose reels into the fire service in the mid 1800s. This was to assist in getting hose and other necessary equipment to the scene of a fire faster. Brigades soon find that competing with other brigades improved their training and efficiency. The State Championship became the peak of the season's competitions conducted by districts and associations across the state. Black and white rectangular photo reproduction printed on matte photographic paperemergency services, beechworth, fire brigade, firemen, photograph, competition, black and white, fire -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncBook, Georgina Allen, Escape to Eltham: A report on the Lanes who left Limerick for Australia, 2013
ESCAPE TO ELTHAM traces the family of John and Anna Lane who lived in Shanagolden in County Limerick during the early and middle parts of the 1800s. They lived during a time of conflict and famine. This story follows the movements of their son, Richard, and daughter, Anne, who migrated to Australia. The marriage of Anne to Tobias Butler and Richard's life establishing his farm on the Yarra River in the 1850s are explored. Marriage, children, deaths and a murder in 1861 are changes forced on the family. Richard's son, Patrick, marries a young Bridget Carrucan but when the global recession of the 1890s decimates Patrick's businesses he heads to the arid Western Australian goldfields to 'make his fortune'. The large family follows and settles in Boulder where the behaviour of a couple of the boys gets them into scapes with the law. This story celebrates the tenacity of a family whose members left adversity in Ireland hoping for a kinder life in Australia.john lane, anna lane, richard lane, patrick lane, bridget carrucan -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyCan Mortein Powder, late 1870s to early 1920s
The can(product) of powdered Mortein was used throughout Australia and especially in rural regions where environmental conditions of crops, cattle and other livestock resulted in greater amount of "invasions" from insects. The eradication of unwanted invaders into the homestead required either manual extermination or a relevant poison which in low doses would not affect humans. Fly squats were still a good measure of eradication of flying pests however those lurking in cupboards or "hard to get at" locations needed a method, such as the Mortein powder to do the deed. This product and especially this can was used at the fore front of pest eradication. Powders and pellets are still in use 100 years later and the core ingredient is still environmental friendly and meets health conscious modern Australians. The basic product has survived the passage of time and was invented by a German immigrant to Australia in the late 1800s.This can and what it represents to rural households and outhouses, is in some ways immeasurable to the peace, health and tranquility within the household of all the families within the Kiewa Valley. Although small in size the relief of those within the sanctity of the home from annoying pests is enormous. The relief not only physical but also mentally to those residents, from the sometimes grueling and painful rural existence in a "sunburnt" countryside cannot be truly expressed in words. Kiewa Valley residents are part of the sometimes harsh rural environment where the introduction of helpful products such as this powder are noticed and used more prolifically. Any product, especially invented within Australia, which allows for a easier existence is of a great significance.This small cylindrical can contains powder of crushed the chrysanthemum flowers(pyrethrum extract) and has two circles of small circular perforations in the lid (to allow contents to be sprinkled onto other surfaces). It is constructed of mild steel with both ends crimped onto the main cylinder. A paper information label has been adhered to the outside of the cylinder.Printed on the outside label is: 1st line "MORTEIN!" 2nd line "THE GREAT INSECT DESTROYER" underneath "(Registered)" and underneath "It is without doubt the best and most reliable Insect powder in the World" underneath this line "In order to use Mortein with profit it is best to get a Mortein spreader through", next line "which by pressure of the hand the powder is ejected and well diffused." An inflection mark appears over the e in "Mortein" as to signify that the word "mort" is french for (dead) and the "ein" is german for "one". The word "mortein" therefore is diffused and translated into "dead one". A thin line separates the above from the list of insects which the powdered contents will kill together with the suggested application targets. T the bottom of the instructions is printed the manufacturer "J. HAGEMANN PTY. LTD., MELBOURNE," Below is "Sole Proprietors"natural insecticide products, environmentally friendly products, household pest dispensers, australian inventions -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Reference Botany, Botany - A Junior Book For Schools, 1927
This book was a highly regarded reference book for students in primary and lower secondary schools within Victoria from the late 1800s to the mid 1900s. The book provided students with the fundamental knowledge of botany for the era in which it was produced. As this book was targeting a junior schooling level (basic), it could cover a greater and extended reader population. Teaching institutions could, because of its straight forward, basic written information, retain this book's circulation for a greater length of time, thereby optimising the return against the greater initial costs of importing it from England.This book was produced in a time where learning was at a relatively slower pace (due to a smaller source and supply of material). The availability of a large range of cheap reference books such as that offered from 1971 on wards via the internet "Project Guttenberg" in the form of electronic books, has dramatically provided a larger source of reference material. The significance of this book on botany, is that it was highly effective for the era in which it was produced and in particular the students at a rural based school. Being in a rural area students were able to identify local vegetation to the various life cycles of plants presented in this mainly United Kingdom/European referenced book. The students in the Kiewa Valley and attending a rural school, where in a position to study all the fundamental teaching that this book encompassed. This in one way provided students in the valley a slightly better appreciation between book and real life (on the land, in the field and by the river). Later publications of this book had additional Australian references in them.This hard covered book(cloth strengthened) is faded(aged) beige in colour and consists of 204 pages. It is printed in English (black print) on both sides and contains illustrations of both free hand sketches and photographs of plants, both foliage and roots systems. The book is arranged in three sections: three pages of preface, two of contents (28 chapters). The last four pages contain the appendix and index.On spine "BOTANY" underneath "R.H. YAPP" and at bottom the Cambridge coat of Arms and below this "CAMBRIDGE" The front cover "BOTANY" underneath this "A JUNIOR BOOK FOR SCHOOLS" and below this a an illustration of a four leaf petal(flower of Germander Speedwell) the same as appears on the cover of edition 2, however this book is edition 3. At the bottom is "R.H. YAPPschool, botany, text books, science experiments, nature -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - A collection of assorted stoneware and ceramic canisters
Stoneware or pottery canisters were widely used throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries for storing and preserving a wide range of kitchen food ingredients. Bendigo Pottery was established in 1858 and is Victoria's oldest working pottery. It was founded by George Duncan Guthrie (1828–1910) who abandoned his potter’s wheel in Scotland to join the Australian gold rush. He found a clay deposit perfectly suited for the production of ceramics, so returned to his former profession as a master potter. The population explosion created by the Australian gold rush resulted in an increased demand for all kinds of locally manufactured goods. The Bendigo Pottery became one of regional Victoria’s most important industrial enterprises. By the late 1800s the Pottery was making all kinds of household wares. One of its most popular lines was the mass produced, affordable and functional earthenware such as these canisters.These items are significant on a state and national level due to the importance of Bendigo pottery as a major Victorian manufacturer whose products were widely used in Australian homes.A group of 3 stoneware and ceramic canisters of assorted sizes. The tallest canister bears the Bendigo Pottery makers mark. The flour canister with the lid and the third canister are unmarked. Similar canister were produced by several companies in the early to mid 20th century. They were commonly used for storing flour, salt and other commodities.At bottom of largest canister "BENDIGO POTTERY" above straight linebendigo pottery, earthernware, kitchen utensils -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBadge - Hamilton-Smith Collection Wodonga Golf Club c1965
The Hamilton-Smith collection was donated by the children of Grace Mary Hamilton-Smith nee Ellwood (1911-2004) and John Hamilton-Smith (1909-1984) who settled in Wodonga in the 1940s. The Ellwood family had lived in north-east Victoria since the late 1800s. Grace’s mother, Rosina Ellwood nee Smale, was the first teacher at Baranduda in 1888, and a foundation member of the C.W.A. Rosina and her husband Mark retired to Wodonga in 1934. Grace and John married at St. David’s Church, Albury in 1941. John was a grazier, and actively involved in Agricultural Societies. The collection contains significant items which reflect the local history of Wodonga, including handmade needlework, books, photographs, a wedding dress, maps, and material relating to the world wars. This badge was awarded to Grace Hamilton-Smith for being the best left handed player of the Wodonga Golf Club in 1965.This item has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of social and sporting life in mid-twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history and social history.A metal, gold plated badge with green detailing and a depiction of two crossed golf clubs. On face of badge: "WODONGA/G.C/ASSOCIATES'.sport, sporting, golf, golf club, hamilton-smith, ellwood, wodonga, wodonga golf club -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, Border Morning Mail newspaper, 14/5/2979
This photograph is recorded as depicting the presentation by Mr Alan Dunlop to Cr Val Mason, Shire President, of a 2.86-gram solid gold nugget found in the area more than 100 years ago, at the Burke Museum. The gold is reported as attached to a small amount of milk quartz mounted onto a tie pin. The photo and an article about the donation appeared in the Border Morning Mail on Friday 14th May, 1979. Alan Dunlop, pictured, was Sir Edward 'Weary' Dunlop's older brother. The tie pin artefact being donated in this photo is entered into the Victorian Collections database as follows: 'This nugget was found on the Beechworth Goldfield in the late 1800s by Mr Fred McIntosh (Alan & Edward Dunlop's Uncle by marriage, husband of Elizabeth (Bessie) Dunlop), who had made it into a tie pin and presented it to the Dunlop family'. Furthermore, Val Mason was the first female president of the former Beechworth Shire for two terms and a councillor for nine years. This photograph is of historic significance as it depicts known individuals who have connections to key Australian figures. Alan Dunlop is the brother of famous war doctor Edward 'Weary' Dunlop, and both men are Beechworth locals. The object Alan holds is a tie pin made from gold found by the Dunlops' uncle. It's also significant as it documents visually the origin of the tie pin artefact in the Burke Museum collection, via donation by Alan Dunlop. In addition, it depicts Val Mason, the first female president of the former Beechworth Shire for two terms and a councillor for nine years. It is of social significance as it depicts two well-known and respected Beechworth locals handling a key artefact of significance to the Beechworth Goldfields, and therefore Beechworth local history. It also shows the Burke Museum in 1979, providing research potential for those interested in the history of the development of the museum's collection.Black and white, rectangular photograph printed on paper.Obverse: (lllegible) Reverse: A02653weary dunlop, gold, beechworth, val mason, tie pin, jewellery, goldfield, beechworth goldfield, fred mcintosh, bessie dunlop, elizabeth dunlop, dunlop, border morning mail, victorian collections, donation, burke museum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, 14/05/1979
Taken on 14 May 1979, this photo depicts Mr Alan J. Dunlop and his wife presenting a 2.86-gram solid gold nugget found in the Beechworth area more than 100 years ago, to the Shire President, Councillor Mrs Valerie Mason. The gold is reported as attached to a small amount of milk quartz mounted onto a tie pin, and was donated to the Burke Museum by the Dunlop family. Alan Dunlop, pictured, was Sir Edward 'Weary' Dunlop's older brother. The tie pin artefact being donated in this photograph is entered into the Victorian Collections, and records that the nugget was found in the Beechworth Goldfields by Mr Fred McIntosh, in the last 1800s. Fred McIntosh, the husband of Elizabeth (Bessie) Dunlop (the sister of Alan & Edward's father, John) had the nugget made into tie pin and presented it to the Dunlop Family. Furthermore, Valerie 'Val' Mason was the first female president of the former Beechworth Shire for two terms and a councillor for nine years. This photograph is of historic significance as it depicts known individuals who have connections to key Australian figures. Alan Dunlop is the brother of famous war doctor Edward 'Weary' Dunlop, and both men are Beechworth locals. The object Alan holds is a tie pin made from gold found by the Dunlops' uncle, and the provenance of the item – from goldfield to family collection to museum collection – provides a recent context with which to interpret the significance of gold-mining on present and future generations, as well as strong research potential on minerals known to be sourced in the area. In conjunction with other photographs in the collection, this photograph visually documents the donation and acquisition of the tie pin artefact into the Burke Museum Collection. In addition, it depicts Valerie ‘Val’ Mason, in her role as the president of the former Beechworth Shire. Val was the first female in this role, which she held for two terms, and was a councillor in the Shire for nine years. This photograph is of social significance as it depicts two well-known and respected Beechworth locals handling a key artefact of significance to the Beechworth Goldfields. It also shows the Burke Museum in 1979, providing research potential for those interested in the history of the development of the museum's collection. Colour rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: Polacolor (Registered Trademark symbol) Type 108 / LR / Mrs Valerie Mason / Mr Dunlop (Weary's brother) / Mrs Vivian Payne (erased) / 14-5-1979 A.J. Dunlop & wife with Cr. Mason /L85052P gold, nugget, tie pin, pin, beechworth, burke museum, goldrush, goldfield, dunlop, edward dunlop, weary dunlop, alan dunlop, valerie mason, fred mcintosh, gold mining, donation, museum, collection, president, councillor, shire, female -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyFolder - Kiewa Methodist Church, 1917 to 1962
The copy of a letter written by Harry H. Simmonds of Huon notes that "the church existed in 1905. It was built by Hill and McCormack with timber donated by Mr Ned Dunstan on ground donated by Mr James Thomas probably in the late 1800s. It was possibly called a Methodist Church because the donor of the land was a Methodist. It was used by the three Protestant Groups and maintenance was paid for by an annual area collection.The house on the west side was a Presbyterian Manse for many years and the block of ground on the north side was known as the Manse paddock in which the minister grazed his cow and horse." In 1936 there was a fence between the Kiewa Methodist Church was the Presbyterian Church in Kiewa. Its Certificate of Title is Volume 5134 Folio 1026783 (Sept. 1942.) In 1952, the church was made of wood with an iron roof. In 1954. Request to Yackandandah Shire re a fence from Kiewa Consolidated School entrance to the unused hedge adjacent to the Church. In 1958 there was correspondence re 'the strip of land on each side of the Church.' Churches were an important part of life during the late 19th century and early to mid 20th century and were built in the centre of town as was this one. These papers give an understanding of the work involved in maintaining a church. The letters and 'book' give a lot of names of local families involved with the Methodist Church at Kiewa. Yellow plastic spiral folder with 18 pages enclosed in clear plastic sleeves.Papers enclosed include accounts, payments, tenders and other correspondence relating to the Methodist Church at Kiewa dating from 1932 to 1962. Of particular interest is a black cardboard cover book dated 1917 re collection of donations from listed people. The latest date in the book is 1942.Enclosed in first plastic sleeve is a letter from the donor, Kathie Vines dated 15th July 2013methodist church; kiewa; harry h. simmonds; yackandandah council; -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Folder, Jarrold Cottage (White Cloud), 701 Main Road, Eltham, c.2002-c.2014
Information pertaining to the former Jarrold Cottage built in the early 1850s which has been in the Skipper family since 1944 Contents: 1 Journal Article: Jarrold Cottage; This quaint house survived fire and flood, Eltham Shire, newsletter c.2002, p10-11 2. Newspaper article: Cottage of 1800s, 100 Years of News Special Edition, (Leader Newspapers), August 27, 1997, p36 3. Jarrold Cottage (7), extract from tourist drive map publication (unknown) 4. Journal Article: Eltham . . . then and now, written by Judy Lewis, Eltham Town Community News, pp10-11, date unknown with hand written comments/corrections by Diana Bassett-Smith. Features Jarrold Cottage, Southernwood and Walter Withers and the former CBA Bank building. 5. Artice: Jarrold Cottage or White Cloud Cottage, compiled by Harry Gilham (2 pages)Folder of information on Jarrold Cottage consisting of 5 A4 photocopies and one A3 (colour) two page journalbootmakers cottage, cba bank, eltham, jarrold cottage, main road, southernwood, walter withers, white cloud cottage -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Certificate - Independent Order of Rechabites Certificate for Helen Blackman, 1949
Certificate issued by the Independent Order of Rechabites Temperance Friendly Society to Victorian state school children who had passed the temperance physiology examination. The Independent Order of Rechabites began in Salford, England in 1835. It was named after Rechab, a leader in the Old Testament, who instructed his tribe to refrain from drinking alcohol. During the Industrial Revolution the idea of temperance became popular as damage was caused to families by alcohol. In Australia it was first established in Tasmania in the mid 1800s. In 1847 a branch was created in Victoria, and it then spread to other States. Members were provided with assistance during times of sickness, death and hardship. The Victoria District of Rechabites (District No. 82) was established in the 28th January 1861 In its heyday the Victoria Rechabites’ membership numbers grew and grew to the extent that there were at one stage in excess of 36,000 members associated with the Victorian Rechabites in the late 1800’s to early 1900’s covering approximately 250 operating Tents. The certificate was issued to Helen Marion Blackman in 1949. Helen was a resident in the City of Moorabbin.Certificate issued by the Independent Order of Rechabites Temperance Friendly Society to Victorian state school children who had passed the temperance physiology examination. Independent Order of Rechabites - Salford Unityindependent order of rechabites, blackman, city of moorabbin, school children -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Brown paper shopping bag from Adda & Co. Paris, c. early 20th century
Adda & Co operated a business at 52 Boulevard Haussmann, Paris.The store sold crocheted silks, furs and hides. History of shopping bags: Before the late 1800s, shopping bags didn’t exist. Shoppers would either carry their goods home in baskets, or have the merchant deliver them to people's homes, until 1852 when Francis Wolle, a schoolteacher in Pennsylvania, invented a machine to produce paper shopping bags. This invention would allow customers to carry items home in disposable paper bags. Soon after, owners of department stores and retailers began to realise that paper shopping bags could be used to help market their brands, and as such custom shopping bags with printed logos became common place. Carrying a shopping bag from certain shops became a type of status symbol for consumers, providing evidence that one was well-off, had good taste, or both.The paper shopping bag is a rare survival of ephemera related to a retail store called Adda &Co that operated at 52 Boulevard Haussmann, Paris. The arrival of waves of more than ten million migrants by boat is one of the major themes in Australia’s history. The paper shopping bag is representative of personal items purchased for migrant journeys as markers of domesticity, warmth and making oneself at home in a new land that speaks of the transnational lives embedded in threads of migration.A brown paper shopping bag with a printed logo and store information in black inkparis, department store, shopping, adda & co, flagstaff hill, maritime museum -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Hamilton-Smith Collection Photograph of Gertrude Foord c. early 1900s, The Crown Studios: Vice-Regal Photographers
The Hamilton-Smith collection was donated by the children of Grace Mary Hamilton-Smith nee Ellwood (1911-2004) and John Hamilton-Smith (1909-1984) who settled in Wodonga in the 1940s. The Ellwood family had lived in north-east Victoria since the late 1800s. Grace’s mother, Rosina Ellwood nee Smale, was the first teacher at Baranduda in 1888, and a foundation member of the C.W.A. Rosina and her husband Mark retired to Wodonga in 1934. Grace and John married at St. David’s Church, Albury in 1941. John was a grazier, and actively involved in Agricultural Societies. The collection contains significant items which reflect the local history of Wodonga, including handmade needlework, books, photographs, a wedding dress, maps, and material relating to the world wars. This photograph is of Gertrude Foord (1885-1968), an aunt on the Hamilton-Smith family tree. Much of the needlework and textiles in the Hamilton-Smith collection belonged to Gertrude. This item has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of social and family life in early twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history and social history.Black and white studio portrait photograph of a woman dressed in early 1900s dress, mounted on card.Handwritten inscription in bottom centre: "Love from/Gertrude". photograph, family photographs, photo, 1900s, edwardian, studio portrait, portrait -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncTextile - Hamilton-Smith Collection Beaded Textile c. late 1800s - early 1900s
The Hamilton-Smith collection was donated by the children of Grace Mary Hamilton-Smith nee Ellwood (1911-2004) and John Hamilton-Smith (1909-1984) who settled in Wodonga in the 1940s. The Ellwood family had lived in north-east Victoria since the late 1800s. Grace’s mother, Rosina Ellwood nee Smale, was the first teacher at Baranduda in 1888, and a foundation member of the C.W.A. Rosina and her husband Mark retired to Wodonga in 1934. Grace and John married at St. David’s Church, Albury in 1941. John was a grazier, and actively involved in Agricultural Societies. The collection contains significant items which reflect the local history of Wodonga, including handmade needlework, books, photographs, a wedding dress, maps, and material relating to the world wars. In the nineteenth and early twentieth century prior to the mass production of clothing and textiles, needlework, alongside motherhood, was the defining work of women. Hand sewing and embroidery was central in the everyday lives and domestic roles of women.This item is unique, handmade and has a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of social and family life in early twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history, social history and women’s history.Bronze and gold embroidery and bead work on black mesh.needlework, beading, sewing, sew, hamilton-smith collection, hamilton-smith, ellwood, handmade, domestic, women, women's history -
 Merri-bek City Council
Merri-bek City CouncilLithograph, Megan Cope, Black Napoleon (Eulope), 2019
Working across installation, video and painting, Quandamooka artist Megan Cope investigates issues relating to colonial histories, the environment and mapping practices. Black Napoleon (Eulope) is part of a series of lithographs that highlights what Cope sees as ‘just one of the many stories of powerful and clever people defying Empire’ at the turn of the 19th century in Australia. The Black Napoleon series was produced as part of the Australian Print Workshop’s French Connections project. The project aimed to produce new work responding to the National Archive in Paris, with a focus on cultural materials relating to early exploration of Australia and the Pacific. It was important to Cope that she did not simply repeat the material of the archive, which was collected and conserved within a colonial framework. Instead, Cope’s work addresses Eulope’s sovereignty and role in resisting invasion. Eulope was a Quandamooka man named after Napoleon Buonaparte because of his leadership in battles against British forces, which invaded Stradbroke Island in the early 1800s. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyscales, Circa 1850's
Scales were used in the Tarnagulla area of Central Victoria by Albert Charles Nicholls, who was a licensed assayer. This information comes from David Gordon of the Tarnagulla.com web-site. “The Nicholls family were very well known and highly respected at Tarnagulla in the 1800s. Albert's father, William Nicholls, was a leading figure in the gold mining community, and he both managed and owned quartz processing facilities for decades. He was probably the leading mining expert at Tarnagulla in a town full of mining experts, and it was said that no man at Tarnagulla had handled more gold over the years that him. (think in terms of tons of gold!) I would imagine the assaying equipment was probably passed in due course by William to Albert Charles. There are records of Albert Charles mining at Tarnagulla with his father as a young man, but AC apparently came down to the city when the gold began to fade. There are records of him living in Kew up until his death in 1932. He was employed as a draper for a long period.” This item is a significant item which is part of the history of gold mining in Victory.Gold assayer's scales, a very sensitive balance used in the assaying of gold, silver, etc.The scales are comprised of two circular brass pans suspended via brass chains to a metal balance.scales gold technology assayers tarnagulla -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Bottle, Chemist - Dr Laws Kennedy, Early 20th century?
This is a bottle that contained Dr Law’s medicine for diseases of the liver and kidney. In the late 1800s Richard Kennedy, the Warrnambool chemist, had the sole rights to produce Dr. Law’s medicines in his manufacturing business. Dr Law, from Boston, U.S.A., was a prolific and popular producer of patent medicines. This bottle may have been produced during the time of Richard Kennedy or later on the 20th century when the business of R.F.Kennedy and Co., was still operating or it may have come from any local chemist selling Dr Law’s products in the 20th century. The fact that the label on the bottle has an image of a lighthouse on it is a further link with Richard Kennedy who used a lighthouse image as his trademark (albeit a different image).Richard Kennedy came to Warrnambool in the late 19th century and established a retail, wholesale and manufacturing pharmaceutical business in Timor Street. This business was regarded as one of the largest and finest in Victoria. Richard Kennedy was prominent in community and civic affairs in Warrnambool. This bottle is of interest as a good example of the many patent medicines available in the 19th century. Dr Law’s remedies were sold world-wide. It is also of interest because of its possible link s with the prominent Warrnambool chemist, Richard kennedy. This is a glass bottle with a cork stopper that has been pushed into the neck. The glass was originally clear but it is now very black and stained from the dried liquid that was in the bottle. The label on the front of the bottle, pasted on, has black and white printing with an image of a lighthouse in the middle. The label on the back is pasted on and contains directions for use of the medicine. Both labels are very stained. ‘Dr Law’s Great Cure for Diseases of the Liver and Kidneys’dr law of boston, history of warrnambool, richard kennedy, chemists of warrnambool -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Hamilton-Smith Collection Bible c. 1800s - 1900s, Eyre and Spottiswoode, LTD
The Hamilton-Smith collection was donated by the children of Grace Mary Hamilton-Smith nee Ellwood (1911-2004) and John Hamilton-Smith (1909-1984) who settled in Wodonga in the 1940s. The Ellwood family had lived in north-east Victoria since the late 1800s. Grace’s mother, Rosina Ellwood nee Smale, was the first teacher at Baranduda in 1888, and a foundation member of the C.W.A. Rosina and her husband Mark retired to Wodonga in 1934. Grace and John married at St. David’s Church, Albury in 1941. John was a grazier, and actively involved in Agricultural Societies. The collection contains significant items which reflect the local history of Wodonga, including handmade needlework, books, photographs, a wedding dress, maps, and material relating to the world wars. This Christian bible belonged to Grace Hamilton-Smith (nee Ellwood). The inscriptions indicate it was owned and used while she was at boarding school in Melbourne in the 1930s. It was published by the London printer Eyre and Spottiswood, established in 1739.This item has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of social and family life in early twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history and social history.A black cloth bound Christian bible containing old and new testaments. On inner front page proper left upper corner in pencil: "Grace W Ellwood/"Braeside"/Bethonga./Victoria/Grace Ellwood/Morris Hall/Sth Yarra". On inner front paper proper left lower corner in pencil: "Grace Ellwood/Morris Hall/M.L.L. GLS/1925-6-7".bible, religion, christianity, hamilton-smith, ellwood, wodonga, school, jesus -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBooklet - Hamilton-Smith Collection Suitcase with Booklets and other Publications c. early to mid 1900s
The Hamilton-Smith collection was donated by the children of Grace Mary Hamilton-Smith nee Ellwood (1911-2004) and John Hamilton-Smith (1909-1984) who settled in Wodonga in the 1940s. The Ellwood family had lived in north-east Victoria since the late 1800s. Grace’s mother, Rosina Ellwood nee Smale, was the first teacher at Baranduda in 1888, and a foundation member of the C.W.A. Rosina and her husband Mark retired to Wodonga in 1934. Grace and John married at St. David’s Church, Albury in 1941. John was a grazier, and actively involved in Agricultural Societies. The collection contains significant items which reflect the local history of Wodonga, including handmade needlework, books, photographs, a wedding dress, maps, and material relating to the world wars. The ephemeral edition of 'Australian Bush Songs' visible inside the case was published in 1937 in Melbourne by Allan & Co. It contains children's songs drawing on Australian themes which were popular and well-known in the 1930s. This item has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of social and family life in early twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history and social history.A brown vinyl suitcase containing song books, periodicals and magazines c. 1920s - 1930s.hamilton-smith, ellwood, hamilton-smith collection, wodgona, books, reading, songs, song, singing, children, child -
 Wooragee Landcare Group
Wooragee Landcare GroupPhotograph, circa April 2003
This photograph was taken in the Mount Pilot Chiltern National Park. It was taken during a search for the tiger quoll conducted by a team of volunteers from the Wooragee Landcare Group. The tiger quoll is also known as the spotted-tail quoll and is found in the national park. The 2003 bushfires caused worry for the safety of the tiger quoll, hence the need for a search for it. Mount Pilot Chiltern National Park is located near Chiltern in Victoria. It's most notable landmarks include Mt Pilot and Woolshed Falls. It also has many mines from the Gold Rush in the late 1800s. It is home to much flora and fauna, including the tiger quoll. The park is also home to the box-ironbark forest that once was present in most of north-eastern Victoria. The park is a large tourist destination as in there are many bushwalks and other attractions for visitors. In 2003, bushfires raged through Mount Pilot National Park and destroyed much of the environment. Some of this damage can be seen in the burnt trees in the picture. This photograph represents the work that goes into protecting a important species like the tiger quoll and there has been much work done to preserve it. This photograph was taken when the Wooragee Landcare group went to ensure the survival of this species, highlighting how the tiger quoll is being protected. This photograph also demonstrates the significance of Mount Pilot Chiltern National Park. The park has many special flora and fauna that can only be found in this area. For example, the box-ironbark forest and the tiger quoll. The forest used to stretch over much of north-eastern Victoria and is therefore reminiscent of what that area of Victoria was once like. This park is historical for this reason but it is also historical through it being once goldfields from the Gold Rush in the 1800s.Landscape coloured photograph printed on gloss paperReverse: WAN NA 0ANA2N0 NNN- 1 1636 / [PRINTED] (No.8) / 922mount pilot, mount pilot chiltern national park, chiltern, victoria, landmark, woolshed falls, gold rush, tiger quoll, flora, fauna, spotted tail quoll, marsupial, andy murray, andy murray quolls, carnivorous marsupial, forests, rainforests, coastal heathlands, woodlands, photograph, species, wooragee, wooragee landcare group, wooragee landcare, bushfires, identification, search, dna, droppings, box ironbark forest, ironbark, box iron bark -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone in two pieces. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whale bones, whale skeleton, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone piece. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips
