Showing 2374 items
matching irish
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - GATHERING OF THE CLAN: THE MCKAYS OF DRUMMARTIN AND SUNSHINE, 1864
Newspaper copy,Gathering of the Clan, The McKays of Drummartin and Sunshine. Like many other early immigrants to Australia, this family came from Ireland, and like so many arrivals they made for the diggings.This family's name became famous for its contribution to agriculture through the Sunshine Harvester, the invention of Hugh Victor McKay, which revolutionised farming in Australia.Weekly Timesnewspaper, weekly times, h.v.mckay the sunshine harvester -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationPhotograph - digital, Clare Gervasoni, Ballaarat Old Cemetery Headstone for Catherine Hanley, 01/12/2013
Photograph of a broken Ballaarat Old Cemetery marble Headstone for Catherine Hanley, native of Tipperary, Ireland. She died on 16 July 1870. Also her sister, Margaret Robertson who died on 04 April 1886 aged 45, and their mother Margaret Hanley who died on 06 May 1889 aged 70 years. ballarat irish, ballaarat old cemetery, headstone, hanley, catherine hanley, margaret hanley, margaret robertson, robertson -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - M.A. Mackay music book
Brown cover book with the name M.A. Mackay in gold letter on the front. Index of songs handwritten on second page. The songs included are: Der kobold; Gavotte chevaleresque; Waldesrauchen; Com'e gentil; Rhapsodie hongroise No.5; La truite; Polish dances; La gazelle; Irish diamonds; Schumann schlummerlied. Aileen and John Ellison Collection."No. 2" on first page. music, mackay -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchCertificate - Wooden framed document, Thank You Australia, Republic Of Korea, ca.2010
Certificate in Gold Frame (rectangular). Certificate shows the Republic of Korea & Australian Flags highlighted. On the bottom of certificate shows the flags of (in miniature) -Australia Belgium Canada Columbia Denmark Ethiopia France Greece India Ireland Luxembourg Netherlands New Zealand Norway Philippines Sweden Thailand Turkey United Kingdom United States of America. ( In Writing) THANK YOU Australia. 60 Years of Commitment. 60Years of Friendship. The year 2010 marks the 60th anniversary of the outbreak of the Korean War. The peace, prosperity and liberties that we cherish today are built on your selfless sacrifices and contributions. Korea is forever indebted and we will continue to build the trust and friendship between our nations. Our profound respect and gratitude is directed to the brave service men and women of the 21 United Nations Allies korean war, 60th anniversary, republic of korea, un, united nations -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaBook, Gollock, G. A. (Georgina Anne), 1861-1940, At the sign of the flying angel : a book of the sailor at the coastline, 1930
This book documents help and guidance provided by the Christian church to merchant seafarers as they traverse the world, particularly at their points of departure and arrival, and the interactions and activities that they are involved in at these ports.Medium--sized hardcover book of 244 pages. Cover of mid-blue colour, blank front and back covers, book title and author at top of spine in gold print. Book contains a number of illustrations and maps. London : Longmans, Green and Co., 1930 xi., 244 p., [16] leaves of plates : ill., maps, 2 ports. ; 20 cm. non-fictionThis book documents help and guidance provided by the Christian church to merchant seafarers as they traverse the world, particularly at their points of departure and arrival, and the interactions and activities that they are involved in at these ports.flying angel, reverend alfred gurney goldsmith, georgina anne gollock, ethel augusta godfrey 1861-1935, alice sibthorpe tracy -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. William Corly Butler, 1929
Methodist minister. Born Ireland 1869; died Cheltenham 1955, aged 86.Sepia portrait of Butler as a man of approximately 60 years of age, wearing clerical collar and rimless glasses."Rev. W. Corly Butler 1929"butler, william corly -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Clare Gervasoni, John and Anne Farrelly's Headstone, Tower Hill Cemetery, 26/07/2009
John and Ann Farrelly was born at County Cavan, Ireland. They arrived in Australia with their family.John and Anne Farrelly Headstone, Tower Hill Cemetery."In Memory of John Farrelly who died June 5th 1890 aged ?6 Years. Also his wife Anne who died April 5th 1890 aged 90 years. Also their son Edward who died March 1st 1926 aged 76 years.tower hill cemetery, john farrelly, anne farrelly, edward farrelly -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, John Edward Redmond, c1864, 1864
John Edward Redmond, was a prominent banker and businessman before entering Parliament as a member for Wexford constituency in 1859; his statue stands in Redmond Square, Wexford town.(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Redmond, accessed 21/01/2014) His great nephew, John Edward Redmond (1 September 1856 – 6 March 1918) was an Irish nationalist politician, barrister, MP in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and leader of the Irish Parliamentary Party from 1900 to 1918. He was a moderate, constitutional and conciliatory politician who attained the twin dominant objectives of his political life, party unity and finally in September 1914 achieving the promise of Irish Home Rule under an Act which granted an interim form of self-government to Ireland. However, implementation of the Act was suspended by the intervention of World War I, and ultimately made untenable after the Conscription Crisis of 1918. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Redmond, accessed 21/01/2014)Image of moustached politician John E. Redmond.ballarat irish, redmond, john redmond, irish nationalist party, irish home rule -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratPeter Lalor Lithograph, n/d
Peter Lalor rose to fame for his leading role in the Eureka Rebellion at Ballarat in 1854. He is the only outlaw to make it into parliament. The siege of Eureka culminated in November and December 1854 arising as the result of disagreement between disaffected gold miners (led by Peter Lalor) and colonial forces about compulsory mining licences. This lithograph is rare - the only one we are aware of.Eureka Stockade (Ballarat), politics and government (Victoria, Australia).Lithograph - sepia. Picture of Peter Lalor in Legislative Assembly speaker's regalia."The late Hon Peter Lalor, Ex-Speaker of the Legislative Assembly and leader of the Memorable Eureka Insurrection of 1854. Born - Tennikill, Queen's County, Ireland, 1827. Died - Melbourne, Victoria, 1889. Aged 62 years."btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, eureka stockade, lalor, peter, history - ballarat, politics and government -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumFinancial record - PAY BOOK ARMY & DEMOBILIZATION, 1939 - 45
Items issued to Lawrence Vernon Andrews VX 114736 2nd AIF. Refer Catalogue No4228 for his service history..1) Demoiblization Procedure booklet AAB. 87 No 266377, brown coloured covers, paper pages, black printing with entries in black pen. .2) Soldiers Pay Book No 242572, brownish coloured covers, paper pages, Black printing entries in black pen..1) Front cover, “VX114736 Pte Andrews, Lawrence Vernon, C/- Ireland Bros , Poowong South Gipps Victoria”, “1485”. .2) Front cover, “VX114736 ANDREWS LAWRENCE VERNON”, Stamped, “CANCELLED” twicedemobilization, pay books, 2nd aif -
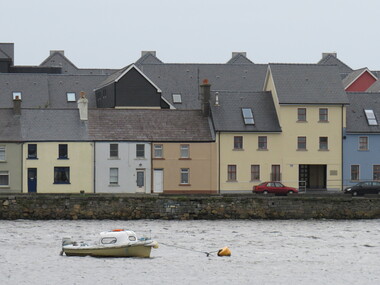 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Houses, Galway Bay, Ireland, 2016, 09/2016
Some Irish immigrants came from Galway, Ireland. Among them were Patrick Kennedy and Dennis Kinnane who emigrated as Bounty passengers on the Himalaya, arriving in the Port Phillip District in February 1842. Patrick Kennedy was the first person officially to be hanged in 1851 in the newly formed Colony of Victoria.houses, galway bay, ireland, dennis kinnane, patrick kennedy, hanging, colony of victoria, himalaya, port phillip district, kennedy, kinnane, 1842, galway -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Bradwell, C. 1870
Mr. James Orr (1844-1885) was born in Ireland and was a minister at Brighton Congregational ChurchHead and shoulders, sepia toned head and shoulders studio cabinet card portrait of Mr. James Orr. He is at an angle to the camera and is not looking at the camera.On the front: "BRADWELL LATE Grenville ... ROYAL ARCADE MELBOURNE"james orr congregational minister, brighton congregational church -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - INSTRUMENT OF SURRENDER OF JAPANESE FORCES, 1945
Three photocopies of the Instrument of Surrender of Japanese Forces in New Guinea, New Britain, New Ireland, Bougainville and adjacent islands. Signed by the Commander in Chief of the Japanese Imperial Southeastern Army and the Lieutenant General, General Officer Commanding First Australian army. Received on board H.M.S. Glory off Rabaul at 1130 hours, sixth day of September 1945.document, certificate, instrument of surrender -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Container - Tobacco tin
Donated by Box Hill Historical Society"Erinmore Flake" tobacco tin - empty. Lid is mustard in colour with red decoration and "Murrays" in red printed on the top. "Erinmore Flake" is in the mustard colour with red background in centre of lid. Below is an outline of a pineapple in red with 'Trade Mark' also in red. 'Made in Northern Ireland by Murray Sons & Co. Ltd Belfast' in small red printing below the pineapple.Vacuum packed to open lever here ---> Net weight when packed 2 Oz/56.7 grammes.tobacco, smoking -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationPhotograph - digital, Headstone of Mary Roberts and Her Brother John Commons
Photograph of the Ballarat Old Cemeteryheadstone of Mary Roberts and her brother John Commons. John Common was from Tipperary, Ireland. He died on 08 June 1858 aged 26 years. Also his sister Ann who died 21 November 1863 aged 35. Mary Roberts died 07 October 1866 aged 42 years.ballarat irish, ballaarat old cemetery, headstone, roberts, commons, mary roberts, john commons, ann commons -
 South Gippsland Shire Council
South Gippsland Shire CouncilPrint, Boats at Wicklow Harbour
Colour print of a watercolour painting titled "Boats in Wicklow Harbour". Set in cream card window mount. Features boats, water, buildings and low hills in the distance. Colours of red, greys, creams, blues and browns. Title printed lower left corner and artists signature lower right corner. Produced by Wicklow Scenic Prints. Made in Ireland. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - LA TROBE UNIVERSITY BENDIGO COLLECTION: BENDIGO TEACHERS' COLLEGE STUDENTS
A black and white photograph of Bendigo Teachers' College Group A2 students in 1956. They are Barry Edwards, R. Ireland, N. Kilby, J. Lovelace, R. McKendrick, E. Haw, M. Hogben, D. Ireson, J.Jeffrey, V. Jones, M. King, L.Lee, J. Madin, M. Mannes, J. Martin, D. Merlo and A. Moodie. See 3320.100bendigo, education, bendigo teachers' college students, la trobe university bendigo collection, collection, education, bendigo, bendigo teachers' college, students, photo, photos, photograph, photographs, tertiary education, teacher training, miss j.c. burnett, mr. geoff pryor, history -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyBook, Hugh Mahon, Patriot, Pressman, Politician - Jeff Kildea (Vol 2 1901 to 1931), 2020
Hugh Mahon (1857-1931) was a resident of Ringwood at the time of his death and was buried in Box Hill cemetery.Full title: Hugh Mahon, Patriot, Pressman, Politician by Jeff Kildea - Volume 2: Politician: the years from 1901 to 1931."This book, the second part of a to-volume biography of Mahon, covers the period from his election to parliament in 1901 until his death in 1931. It describes his almost 20 years as a backbencher and a ministe during which he gained a reputation as one of the brainiest men in parliament as well as one of the most controversial. It provides an insight into his reluctant decision to oppose conscription in 1916 and examines in depth his commitment to Irish self-government and the circumstances of his dramatic expulsion from parliament in 1920. The volume also looks at Mahon's career as managing director of the Catholic Church Property Insurance Co. and his intervention in Irish politics dujring the debatge over the Anglo-Irish treaty. It is the story of a flawed genius who simultaneously evoked high praise and damning criticism." -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Joseph Winter, c1864
Winter was Treasurer of the Irish National League. "AUSTRALIAN AID TO IRELAND. - GRATEFUL ACKNOWLEDGMENTS. The following letters have been received:— "The Irish National League, "43 O'Connell-street Upper, "Dublin, 14th Oct., 1886. "My Dear Mr. 'Winter, — I beg to acknowledge receipt of your favour of the 16th August, enclosing; draft for £250 from the Irish National League of Australasia towards the Irish Parliamentary Fund. The treasurers of the fund, to whom I have handed the draft, are transmitting by this mail a formal receipt for the amount of your generous contribution. ' I am very happy to learn from reports which have appeared in our newspapers here within the past few days that the vacancy in Melbourne has been accepted by our worthy, able, and patriotic prelate, the Most. Rev. Dr. Carr, Bishop of Galway. While the Catholic people of the diocese of Melbourne will find in Dr. Carr an able, zealous, and dignified prelate; of whom they will haye every rea son to be proud, the Irish Catholics of the diocese will, in an especial sense, find in him one who knows the wants of their country, who is deeply in sympathy with .the just feelings and aspirations of her people, and who is second to none in his desire to see his native land happy and prosperous I thought our friends in the Federal Council of the League would be anxious to know what man ner of man the new prelate is, and, therefore, writing to you so soon after his appointment I think it my duty to say so much. "Assuring our friends of our warm gratitude for the generous assistance they are continually giving us in the struggle in which we are en gaged — I remain, my dear Mr. Winter, yours sincerely, T. Harrington. "Joseph Winter, Esq., Advocate office, Melbourne," ''The Irish National League, 43 O'Connell-street Upper, " Dublin; 12th October, 1886. 'My Dear Sir, — I beg to acknowledge with thanks receipt of your letter of 16th August, with 'draft for' £250 from the Federal Council of the Irish National League of Australasia to the Parli mentary Fund. Joseph G. Biggar. ' 'J. Winter, Esq.' ' ; IRISH PARLIAMENTARY ELECTION FUND. The following acknowledgment has been received by the Rev. J. H. O'Connell, Victoria : — " The Irish National League, 45 O'Connell-street Upper, Dublin, 12th October, 1886. '"Rev. Dear Sir, — I beg to acknowledge with best thanks receipt of your letter of 24th August, with draft for £1000 towards the Irish Parliamentary Fund from the Executive Committee of the Irish Parliamentary Fund of Melbourne.— Yours faithfully, "Joseph G. Biggar. "Rev. J. H. O'Connell, St. George's Presbytery, Carlton, Melbourne." (Sydney Freeman's Journey, 4 December 1886) MR JOSEPH WINTER AND THE IRISH NATIONAL LEAGUE - Mr Joseph Winter, of Melbourne, has received a courteous letter from Mr. Harrington, M.P., enclosing the following official document : — ' On the motion of the Right Hon. the Lord Mayor, T. Sexton, M.P., seconded by Dr. B. J. Kenny, M.P., the following resolution was unani mously adopted by the Organizing Committee of the Irish National League :— 'That we have heard with regret of the proposed retirement from the treasurership of the Irish National League of Australia of Mr. Joseph Winter, manager of the Melbourne Advocate, and we seize this opportunity of placing on record our appreciation of tbe signal services which he has rendered to the Irish people by his unselfish and devoted advocacy of their cause, especially during the past eight years, during which time the sum of £27,487 has reached the home move ment through his hands. We desire to assure Mr. Winter that his services will not be forgotten by his countrymen in Ireland, and we venture to express the hope that the Irishmen of Australasia may still be permitted to command them.'(Sydney Freeman's Journal, 6 April 1889) Image of a moustached man known as Joseph Winter.ballarat irish, winter, bishop carr, carr, joseph winter, irish national league -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyBook, Ballyshanassy - A History of the Burwood District, 1991
Ballyshnassy was the original name for part of Burwood; Bally in Ireland meaning town, so it was Shanassy's town.History of Burwood (Victoria), researched and compiled by Alyssa Clarkson as part of her VCE studies. Includes transcript of interviews with long-time residents of the district, Mrs. N. Ashworth (nee Donaghey), Mrs. V. Dalzell (nee Nelson), Miss Una Harrison, Mrs. V. Smith (nee Rankin), Mrs. Walsh (nee Rice), and Mr. Fred Payne. -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyBook, Barbara Ann Hall, A Desperate Set of Villains, 1796_
Details the 244 Irish convicts transported to New South Wales on the ship "Marquis Cornwallis" in 1796.This book is devoted to only Irish convicts as a separate group.A 288 page book with a multi coloured outer cover.Pencil notes on inside cover.irish convicts, marquis cornwallis, transportation -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Michael Cooney, c1864, 1864
Michael Cooney was born in 1839 in Ireland. He arrived in the United States sometime during childhood. He moved to California from Kalamazoo, Michigan in about 1864 with is Irish born wife, Catherine. Cooney is buried at Holy Cross cemetery in Colma, California. (http://boards.ancestry.ca/surnames.cooney/689/mb.ashx, accessed 21 January 2014)Image of Judge Michael Cooney.ballarat irish, cooney, michael cooney -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyArticle, Montmorency Who? by R. F. Riddiford 1985, 22/02/1985
Traces the name 'Montmorency' to France, then to Canada and Ireland. Makes some connection (unsubstantiated) to the naming of the suburb of Montmorency.3-page article, copied on pale blue paper.montmorency, r f riddiford -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, History of Durham Lead by J. Crombie, 1934, 1934
... irish ...John Charles Crombie was the son of James Andrew Crombie and Martha Houston and was born at Hardies Hill 1862. John Charles Crombie married in Victoria in Martha Crosier 1893. They were living at Durham Lead, Victoria for the birth of their children in the 1890s. John Charles Crombie died in 1937 at Oakleigh aged 74.A4 copy of an handwritten document by J. Crombie called 'History of Durham Lead, Hardies Hill, Garibaldi and Grenville'.j. crombie, durham lead, garibaldi, elaine, irish, scottish, cornish, john charles crombie, j.c. crombie -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1896
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1896, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 9 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887.Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1896. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1896, Inner band, some letters hidden - HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1896, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1896
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1896, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 9 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1896. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1896”, Inner band, [some letters hidden] “HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1896, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1897
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1897, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 6 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then counter-stamped and used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced, removing the power from the States. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1897. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1897, Inner band, some letters hidden - HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1897, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1898
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1898, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 9 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1898. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1898, Inner band, some letters hidden - HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1898, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - CONSTABLE JOHN BARRY COLLECTION: INVITATION TO MR AND MRS BARRY FROM LORD EGLINTON, 04/02/1857
Invitation from the Lord Lieutenant and the Countess of Eglinton to Mr J. F and Mrs Barry on the 4th of February 1857. On invitation: 'The Chamberlain is directed by Their Excellencies the Lord Lieutenant and the Countess of Eglinton to request the pleasure of Mr. J.F and wife Barry's company on Friday evening the 4 of Feby at 10 o'clock. Dancing Castle' Lord Eglinton was Lord Lieutenant of Ireland from 1858 - 1859.document, invitations, dance, invitation, dance, lord lieutenant and the countess of eglinton, mr i f and mrs barry -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Textile - Flags
The Red Ribbon Agitation took place in Sandhurst in 1853 when the miners protested against the Licence fee imposed by the Government.Replicas of various flags used during the Red Ribbon Agitation (1853) re-enactments. There are flags of Scotland, Ireland, France, Germany, Canada, Switzerland, USA, Union Jack and two St Piran's Flag of Cornwall. The Red Ribbon replica flag has four segments: Gold Scales, Emu/Kangaroo, Pick/Shovel and Gold Cradle and a Roman bundle of sticks.flags, red ribbon agitation
