Showing 7667 items
matching canning
-
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPostcard, Rose Stereograph Co, "Elizabeth Street from Lonsdale Street Melbourne", c1934
Rose Series postcard No. P 1701 titled "Elizabeth Street from Lonsdale Street Melbourne". Has a number of cable trams in the view, the closest one being a Brunswick tram. There is a policeman on point duty. In the view are signs for G A Grano Mantle manufacturers, Smiths Pawnbroker, State Savings Bank, MIchaels Camera store, one horse-drawn cart, and motor vehicles. On the west side footpath under an awning is a "Keep to the left" for pedestrians. Flinders St Railway Station can be seen in the far distance. The Brunswick cable tram line was closed Sept. 1935.Yields information about Elizabeth St, c1930Postcard - printed real photograph with Rose Stereograph Co. name on the rear.On rear in pencil "KM-M-076" and a Ken Magor stamp.trams, tramways, flinders st station, cable trams, elizabeth st -
 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Buildings, Sussex Street, Linton, 1988
Photograph taken in 1988 of buildings in Sussex Street, Linton: house was previously Bill and Georgie Hall residence and before that a cake shop run by Stella Ralf (Stella Ralf also taught piano). Next to it can be seen the former Bennett garage building. Bennett shop and garage (petrol station) 1920s-1940s. Later (1970s-1981) run as op-shop by Mrs. Surman to raise money for Maxwell Park C.E.B.S. camp. House had a later incarnation as a laundromat in 1980s - at this time many women were still without electricity on outlying farms and house blocks.Colour photograph showing green painted timber house with pitched roof and small verandah, white trim, next to brick building with pitched roof and verandah over footpath, brick pillars. "Stella Ralph's old shop (cake) later Bennett garage"stella ralf, bennett's garage, stella surman, bill hall, georgina hall -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Dollarbird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Dollarbird is so-named because of the coin-shaped patches on the tips of their wings, which is clear when in flight. They have distinctive blue-green colouring on their backs and wings, and a bright blue throat. This species migrates to northern and eastern Australia for breeding, between the months of September and April. These birds migrate to New Guinea and nearby islands in the Winter, but can be found in Japan and India also. This species resides in open wooded areas, preferring hollow-bearing trees for nesting. They can be found spending most of their time perched on high branches in search of insects, and will often 'hawk' at dusk above the tree-tops, hovering on the wing for lengthy periods. This specimen is a good example of this species, however the distinctive coin-patches on the tips of the wings are partially hidden by the tuck of the wing. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This adult Dollarbird has a brown body and head, blue-green back and wings. It has a distinctive bright blue or purple plumage around its throat. The tips of the wings are brown. The pale-blue coin shaped patches on the tips of the wings are just visible. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing-tag: 96a / Australian Roller / Catalogue, page, 25. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, dollarbird, australian birds, broad-billed roller -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Blue-faced Honeyeater, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Blue-faced Honeyeater is commonly located in northern and eastern mainland Australia. It is also found in Papua New Guinea. This species prefer to reside in tropical locations or those which are sub-tropical and wetter temperate or semi-arid zones. It can be located in open forests and woodlands close to water. Due to these locations along with it's propensity for feeding on the fruit and flowers of the banana in northern Queensland, this species is colloquially known as the "Bananabird". These birds commonly reside in pairs, family groups or small flocks. They can often be found socialising with other species including the yellow-throated miner and the Little Friarbird. The Blue-faced Honeyeater feed on insects and invertebrates, but also may eat nectar and fruit from native and exotic plants. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The blue-faced Honeyeater is large in size with bright white and black colouring. The bird also has golden olive-green colouring on it's rear, tail and wings. Around the eyes is strikingly blue coloured skin which has faded significantly on this particular specimen. It also has a pair of glass eyes to replace the original which do not survive the taxidermy process. There is a patch of dark colouring on the plumage of the stomach and neck of the bird. This dark batch is surrounded by white plumage which also forms a white band across the back of the neck. This specimen is stylized placed on a wooden mount. The bird's feet are attached to a thin stick and the stick attached to the mount.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, honeyeater, blue-faced honeyeater -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Nankeen Kestrel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Nankeen Kestrel, a small type of falcon, can be found all over Australia, usually in grassland or farmland areas. This falcon is carnivorous and hunts all manner of small prey including mice, lizards, insects, and other birds. When hunting, Nankeen Kestrels can be seen hovering in the air searching for prey. Nankeen Kestrels are generally monogamous, staying with the same breeding partner for multiple seasons. The Nankeen Kestrel is known for its reddish-brown feathers, spotted with a distinctive black pattern on its back, and have black-tipped wings and tail band, a stark contrast to its white chest. Females tend to be larger, and males will have a grey head and neck area. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Nankeen Kestrel is relatively small and slender. It is mostly reddish-brown, streaked with darker coloured areas. The tips of the wings and tail feathers are tipped in black. The chest is white with streaks of reddish-brown. The areas around its eyes, beak, and feet are a bright yellow. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing-tag: 19. / Unnamed / Catalogue page, 5 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, nankeen kestrel, falcon -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Gang Gang Cockatoo (male), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Gang-gang Cockatoo can be found throughout much of south-eastern Australia. They reside in mountainous forests and open woodlands, often in small groups or larger flocks at sources of food and water. They eat mainly seeds from native trees and shrubs along with wattles, eucalypts and hawthorns. The Gang-gang Cockatoo is also known to incorporate berries, nuts, fruits and insects to their diet. The sound made by this type of Cockatoo is often described as a rasping screech which resembles the sound of a rusty hinge being moved.This type of call is made when the bird is in flight. These birds also fond of attention and can pick their own feathers if they are bored. The name "gang gang" derives from a New South Wales Aboriginal language, either the Ngunnawal or Wiradjuri. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The male Gang Gang Cockatoo is standing stylised on a wooden perch. The Cockatoo has a dark slate-grey coloured body with a scarlet red/orange coloured head with a wispy crest. This specimen stands with its wings positioned to its sides and has round glass bead eyes. The bill has a hooked shape and is horn-coloured. The legs and feet of this specimen are dark grey.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, cockatoo, gang-gang cockatoo, cockie -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Gang Gang Cockatoo (female), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Gang-gang Cockatoo can be found throughout much of south-eastern Australia. They reside in mountainous forests and open woodlands, often in small groups or larger flocks at sources of food and water. They eat mainly seeds from native trees and shrubs along with wattles, eucalypts and hawthorns. The Gang-gang Cockatoo is also known to incorporate berries, nuts, fruits and insects to their diet. The sound made by this type of Cockatoo is often described as a rasping screech which resembles the sound of a rusty hinge being moved.This type of call is made when the bird is in flight. These birds also fond of attention and can pick their own feathers if they are bored. The name "gang gang" derives from a New South Wales Aboriginal language, either the Ngunnawal or Wiradjuri. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Gang-gang Cockatoo has a grey head and crest with brown glass eyes. The beak is hooked and a pale bone colour. The neck and torso of the cockatoo is patterned with orange and black stripes. The feathers of the underparts and back are slate-grey with an edging of pink and yellow. The female cockatoo has more yellow in their feathers than the males which gives them a further barred appearance. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, australaisian shovelor, shovelor, cockatoo, gang-gang cockatoo, cockie -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncBook, Hyland House, Alan Marshall's Australia, 1981
One of a collection of books by local writer Alan Marshall held at EDHS. This one is of "anecdotes and yarns" as described by Marshall before its publication in July 1981 in the Canberra Times. Alan Marshall's Australia, the Australia of "I Can Jump Puddles" has vanished. No longer do we have time to sit on the sliprail and exchange yarns, to drive buggies down long, quiet dusty roads, or to watch the king-hit merchant operating in some small hotel. Even the Cu-nims hold no terrors for a Boeing 427! And yet - Alan Marshall's Australia lives for all those who read this book. Meet Lance Skuthorpe who tethered an old bull in Bourke Street and offered £5 to anyone who could ride it for half a minute and Binjarrpooma, the Arnhem Land terror. Accompany Alan in his horse-drawn caravan or buggy to country sales, pubs and stations and listen with him to great bush eccentrics, lairs and yarn spinners. Go further back and remember Conversation Lollies, the cigarette cards you collected and the school yard games. Can you recall how to test an axe blade, choose a pocket knife, or the penetrating power of Goanna Oil? But this book is more than a nostalgic journey into the past ; it is history for the young and a timely reminder for us all - it is our roots. - Front end papers viii, 165 p. : ill. ; Two copiesISBN 0908090390alan marshall, prose, short stories, ancedotes, australia, tales, yarms -
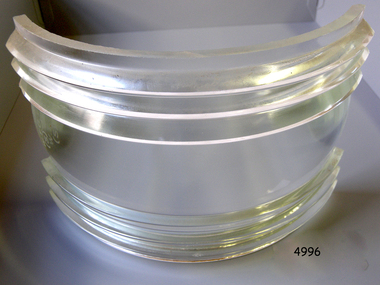 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Fresnel Glass Lens, Early 20th century
A Fresnel lens is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use primarily in lighthouses. Made from high-quality glass Fresnel lenses were used originally in lighthouses and later for many other applications They were later being used for automobile headlamps, brake, parking, and turn signal lenses, and many other applications. Fresnel lenses used in lighthouses were considered state of the art from the late 19th through to the middle of the 20th century. The subject item is a Fresnel replacement lens used in a ships navigation light. For lighthouses, these lenses have now been replaced with much less expensive and more durable aerobeacons, which themselves often contain plastic Fresnel lenses. The lens design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The catadioptric form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source making the light visible from greater distances.The subject item at this time cannot be associated with a historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, the item is a replacement for a ships navigation light and it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Fresnel glass replacement lens for a navigation side lamp of a ship. W.T.G (S) and 10x7 S.STR.ENGL.125warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fresnel lens, maritime light, ships navigation light, augustin-jean fresnel, lighthouse lenses, lighthouse, navigation, warning light -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, steel hacksaw 'Marples', 20thC
A hacksaw is a fine-toothed saw, originally and principally for cutting metal. They can also cut various other materials, such as plastic and wood; for example, plumbers and electricians often cut plastic pipe and plastic conduit with them. On hacksaws, as with most frame saws, the blade can be mounted with the teeth facing toward or away from the handle, resulting in cutting action on either the push or pull stroke. In normal use, cutting vertically downwards with work held in a bench vice, hacksaw blades should be set to be facing forwards. Joseph Marples & Son Pty Ltd Traditional Craftsmans Hand Tools made in Sheffield. The finest quality hand made tools, backed by over 170 years of manufacturing heritage. .In the 1840’s Joseph Marples was one of several ‘Marples’ (most of which were related) in Sheffield manufacturing joiners tools, such as brass inlaid rosewood & ebony braces, boxwood spokeshaves, beech planes, gauges and squares. The business has remained within the family to this date, and has been based in Sheffield since those early days. Although modern technology has been used in some instances, many of the traditions of manufacturing fine hand tools has remained the same using selected materials and hand finishing, indeed the same threads are used in the gauges as were used over 100 years ago. A steel hacksaw. 'Marples' with bladeMARPLEStools, woodwork, metalwork, carpentry, pioneers, market gardeners, early settlers, moorabbin, cheltenham, bentleigh, ormond, joseph marples & son pty ltd, sheffield , england, -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Fruit Preserving Jar, John Landis Mason, 1858-1910
The Masons patent of Nov 30th, 1858 phrase was originally embossed on countless glass fruit jars and canning jars, most ranging in age from circa 1858 to the mid-1910s. John Landis Mason was awarded patent No 22186, issued on November 30, 1858, by the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office it was termed an "Improvement in screw-neck bottles", for his invention concerning the process of creating a threaded screw-type closure on bottles and jars. Similar screw-threading had been done before on some bottles, but the process of forming the upper lip area of the container so that it was smooth, even, and sturdy enough for a lid of standard size to be screwed thereon was difficult and expensive to do properly, often with unsatisfactory results. His improvement revolutionized home canning in the United States and many other countries. In any case, throughout the next 60-odd years, production of jars with the Nov. 30, 1858 embossing continued at a high rate, with untold tens of millions being produced. The phrase was soon considered an important marketing device, adding to the perception of quality and reliability of the container to the average consumer. This perception continued to at least 1879 21 years after the patent was issued, nearly every glass bottle factory was likely producing their version. The 1880s and 1890s likely saw the peak of popularity of these jars. A considerable percentage have a mold number or letter on the base, a means of identifying the particular mold in use at the factory.An early item used in most kitchens by women who preserved fruit and vegetables before the arrival of refrigeration giving a snapshot into the domestic lives of families during the late 19th to early 20th century's and how they preserved food for later use without refrigeration. Preserving jar, glass, with metal screw top lid. Glass has side seams, impurities and slightly concave base. It has been hand blown into a mould. Inscription is moulded into glass. Moulded into glass: MASON'S / PATENT / NOV 30TH / 1838"warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, food preserving, mason jar, john landis mason, domestic container, glass jar, fruit & vegetable jar, domestic jar, food preparation, handmade glass, blown glass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Fruit Preserving Jar, John Landis Mason, 1858-1910
The Masons patent of Nov 30th, 1858 phrase was originally embossed on countless glass fruit jars and canning jars, most ranging in age from circa 1858 to the mid-1910s. John Landis Mason was awarded patent No 22186, issued on November 30, 1858, by the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office it was termed an "Improvement in screw-neck bottles", for his invention concerning the process of creating a threaded screw-type closure on bottles and jars. Similar screw-threading had been done before on some bottles, but the process of forming the upper lip area of the container so that it was smooth, even, and sturdy enough for a lid of standard size to be screwed thereon was difficult and expensive to do properly, often with unsatisfactory results. His improvement revolutionized home canning in the United States and many other countries. In any case, throughout the next 60-odd years, production of jars with the Nov. 30, 1858 embossing continued at a high rate, with untold tens of millions being produced. The phrase was soon considered an important marketing device, adding to the perception of quality and reliability of the container to the average consumer. This perception continued to at least 1879 21 years after the patent was issued, nearly every glass bottle factory was likely producing their version. The 1880s and 1890s likely saw the peak of popularity of these jars. A considerable percentage have a mold number or letter on the base, a means of identifying the particular mold in use at the factory.An early item used in most kitchens by women who preserved fruit and vegetables before the arrival of refrigeration giving a snapshot into the domestic lives of families during the late 19th to early 20th century's and how they preserved food for later use without refrigeration. Preserving glass jar. Glass lip with metal screw top lid. Inscription pressed into glass."Mason's Patent Nov 30th 1858"warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, food preserving, mason jar, john landis mason, domestic container, glass jar, fruit & vegetable jar, food storage, preserving jar -
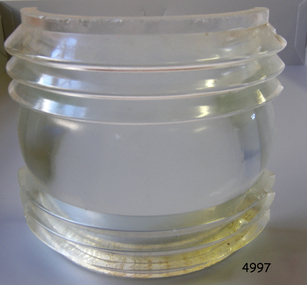 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Fresnel Glass Lens, Early 20th century
A Fresnel lens is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use primarily in lighthouses. Made from high-quality glass Fresnel lenses were used originally in lighthouses and later for many other applications They were later being used for automobile headlamps, brake, parking, and turn signal lenses, and many other applications. Fresnel lenses used in lighthouses were considered state of the art from the late 19th through to the middle of the 20th century. The subject item is a Fresnel replacement lens used in a ships navigation light. For lighthouses, these lenses have now been replaced with much less expensive and more durable aerobeacons, which themselves often contain plastic Fresnel lenses. The lens design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The catadioptric form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source making the light visible from greater distances.The subject item at this time cannot be associated with a historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, the item is a replacement for a ships navigation light and it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Fresnel glass replacement lens for a navigation lamp of a ship. None warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fresnel lens, maritime light, ships navigation light, augustin-jean fresnel, lighthouse lenses, lighthouse, navigation, warning light -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Fresnel Glass Lens, Early 20th century
A Fresnel lens is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use primarily in lighthouses. Made from high-quality glass Fresnel lenses were used originally in lighthouses and later for many other applications They were later being used for automobile headlamps, brake, parking, and turn signal lenses, and many other applications. Fresnel lenses used in lighthouses were considered state of the art from the late 19th through to the middle of the 20th century. The subject item is a Fresnel replacement lens used in a ships navigation light. For lighthouses, these lenses have now been replaced with much less expensive and more durable aerobeacons, which themselves often contain plastic Fresnel lenses. The lens design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The catadioptric form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source making the light visible from greater distances.The subject item at this time cannot be associated with a historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, the item is a replacement for a ships navigation light and it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Fresnel glass replacement lens for a navigation mast headlamp of a ship. Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fresnel lens, maritime light, ships navigation light, augustin-jean fresnel, lighthouse lenses, lighthouse, navigation, warning light -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Fresnel Glass Lens, Early 20th century
A Fresnel lens is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use primarily in lighthouses. Made from high-quality glass Fresnel lenses were used originally in lighthouses and later for many other applications They were later being used for automobile headlamps, brake, parking, and turn signal lenses, and many other applications. Fresnel lenses used in lighthouses were considered state of the art from the late 19th through to the middle of the 20th century. The subject item is a Fresnel replacement lens used in a ships navigation light. For lighthouses, these lenses have now been replaced with much less expensive and more durable aerobeacons, which themselves often contain plastic Fresnel lenses. The lens design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The catadioptric form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source making the light visible from greater distances.The subject item at this time cannot be associated with a historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, the item is a replacement for a ships navigation light and it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Fresnel round glass masthead replacement lens for a navigation lamp of a ship. Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fresnel lens, maritime light, ships navigation light, augustin-jean fresnel, lighthouse lenses, lighthouse, navigation, warning light -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Fresnel Glass Lens, Early 20th century
A Fresnel lens is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use primarily in lighthouses. Made from high-quality glass Fresnel lenses were used originally in lighthouses and later for many other applications They were later being used for automobile headlamps, brake, parking, and turn signal lenses, and many other applications. Fresnel lenses used in lighthouses were considered state of the art from the late 19th through to the middle of the 20th century. The subject item is a Fresnel replacement lens used in a ships navigation light. For lighthouses, these lenses have now been replaced with much less expensive and more durable aerobeacons, which themselves often contain plastic Fresnel lenses. The lens design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The catadioptric form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source making the light visible from greater distances.The subject item at this time cannot be associated with a historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, the item is a replacement for a ships navigation light and it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Fresnel glass lens for a ships masthead navigation lamp. Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fresnel lens, maritime light, ships navigation light, augustin-jean fresnel, lighthouse lenses, lighthouse, navigation, warning light -
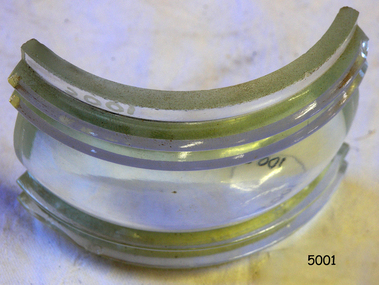 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Fresnel Glass Lens, Early 20th century
A Fresnel lens is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use primarily in lighthouses. Made from high-quality glass Fresnel lenses were used originally in lighthouses and later for many other applications They were later being used for automobile headlamps, brake, parking, and turn signal lenses, and many other applications. Fresnel lenses used in lighthouses were considered state of the art from the late 19th through to the middle of the 20th century. The subject item is a Fresnel replacement lens used in a ships navigation light. For lighthouses, these lenses have now been replaced with much less expensive and more durable aerobeacons, which themselves often contain plastic Fresnel lenses. The lens design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The catadioptric form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source making the light visible from greater distances.The subject item at this time cannot be associated with a historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, the item is a replacement for a ships navigation light and it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Fresnel glass replacement lens for a navigation side lamp of a ship. Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fresnel lens, maritime light, ships navigation light, augustin-jean fresnel, lighthouse lenses, lighthouse, navigation, warning light -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayLarge Electric Staff Instrument, Webb-Thompson
Electric staff - Electric staff instruments The staff and ticket system was still too inflexible for busy lines, as it did not allow for the situation where the train intended to carry the actual token was cancelled or running very late. To provide for this, the electric train token system was developed. Each single-line section is provided with a pair of token instruments, one at the signal box at each end. A supply of identical tokens is stored in the instruments, which are connected by telegraph lines. A Staff can be removed from one instrument only if both signalmen co-operate in agreeing to the release. Once a Staff has been removed, another cannot be removed until the token which is "out" is replaced in either instrument. (There are variations on this sequence of events.) By this means, it can be ensured that at any one time, only one token is available to be issued to a driver. Staff belonging to adjacent sections have different configurations to prevent them being inserted into the wrong instrument. Nevertheless, in the Abermule train collision in 1921 and lax working procedures allowed the safeguards provided by the electric Staff system to be circumvented; a driver was handed a Staff for the wrong section, and without reading the information listed on the staff, proceeded on the mistaken belief that the Staff was correct. To prevent this, it became a requirement in the UK for the signals controlling entry to the single line section (starting or section signals) to be locked at danger unless a token has been released from the relevant Staff instrument. Historic - Victorian Railways Electric Staff Instrument Electric Staff Instrument made of Iron , Brass and Glasspuffing billy, electric staff instrument, victorian railways -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyPhotograph - Image, 2017
These quilts were made from 10 inch squares and sewn together. Each square had the name of the donor embroidered on it, the quilts were made by Red Cross members. The Shire Emblem was also added. One of these quilts was found after the 1939/45 war in Egypt and sent to the Museum in Rutherglen Scotland. The Council of Rutherglen Scotland was later amalgamated into South Lanarkshire, and the holdings of the Rutherglen Museum sent to the South Lanarkshire Museum. Martha Valentine communicated with the South Lanarkshire Museum, to enquire if they still held this item. Sharon Paton, of the South Lanarkshire museum replied with the comments: "Yes I can confirm the quilt (RG.1992.7) is part of the Rutherglen collections transferred to us by Glasgow City Council in 1995/6 during council re-organisation. We are very pleased you have given some more information on the history of the quilt since many of the items transferred to us at that time, did not arrive with a lot of historical information. I attach photographs of the quilt taken yesterday. Due to space restrictions in that store, I couldn’t unroll it fully, but hopefully before the end of this year we can do that when we are working in our storage sites. It was very easy to locate. It was last displayed around 2003/4 for our Treasures of South Lanarkshire exhibition at Low Parks Museum." We were pleased to see that it had a good home. Colour photograph of a handmade quilt. Photograph was printed from a digital image sent from the South Lanarkshire Museum in Scotlandquilts, handcrafts, red cross, world war ii, quilt -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyPhotograph - Image, 2017
These quilts were made from 10 inch squares and sewn together. Each square had the name of the donor embroidered on it, the quilts were made by Red Cross members. The Shire Emblem was also added. One of these quilts was found after the 1939/45 war in Egypt and sent to the Museum in Rutherglen Scotland. The Council of Rutherglen Scotland was later amalgamated into South Lanarkshire, and the holdings of the Rutherglen Museum sent to the South Lanarkshire Museum. Martha Valentine communicated with the South Lanarkshire Museum, to enquire if they still held this item. Sharon Paton, of the South Lanarkshire museum replied with the comments: "Yes I can confirm the quilt (RG.1992.7) is part of the Rutherglen collections transferred to us by Glasgow City Council in 1995/6 during council re-organisation. We are very pleased you have given some more information on the history of the quilt since many of the items transferred to us at that time, did not arrive with a lot of historical information. I attach photographs of the quilt taken yesterday. Due to space restrictions in that store, I couldn’t unroll it fully, but hopefully before the end of this year we can do that when we are working in our storage sites. It was very easy to locate. It was last displayed around 2003/4 for our Treasures of South Lanarkshire exhibition at Low Parks Museum." We were pleased to see that it had a good home. Colour photograph of a handmade quilt. Photograph was printed from a digital image sent from the South Lanarkshire Museum in Scotlandquilts, handcrafts, red cross, world war ii, quilt -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyPhotograph - Image, 2017
These quilts were made from 10 inch squares and sewn together. Each square had the name of the donor embroidered on it, the quilts were made by Red Cross members. The Shire Emblem was also added. One of these quilts was found after the 1939/45 war in Egypt and sent to the Museum in Rutherglen Scotland. The Council of Rutherglen Scotland was later amalgamated into South Lanarkshire, and the holdings of the Rutherglen Museum sent to the South Lanarkshire Museum. Martha Valentine communicated with the South Lanarkshire Museum, to enquire if they still held this item. Sharon Paton, of the South Lanarkshire museum replied with the comments: "Yes I can confirm the quilt (RG.1992.7) is part of the Rutherglen collections transferred to us by Glasgow City Council in 1995/6 during council re-organisation. We are very pleased you have given some more information on the history of the quilt since many of the items transferred to us at that time, did not arrive with a lot of historical information. I attach photographs of the quilt taken yesterday. Due to space restrictions in that store, I couldn’t unroll it fully, but hopefully before the end of this year we can do that when we are working in our storage sites. It was very easy to locate. It was last displayed around 2003/4 for our Treasures of South Lanarkshire exhibition at Low Parks Museum." We were pleased to see that it had a good home. Colour photograph of a handmade quilt. Photograph was printed from a digital image sent from the South Lanarkshire Museum in Scotlandquilts, handcrafts, red cross, world war ii, quilt -
 City of Warrnambool Rowing Club
City of Warrnambool Rowing ClubDevelopment Plaque, 16 july 2017
The people are L to R: Kathy McMeel (secretary), Annie Blanch (Boat Captain), Joanne Bone (president), James Tait (director of Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundations, Susan Finnigan (Grants Officer) and Clive Wooster (treasurer). • In February 2017 the club filled the base of the boathouse and poured a new concrete floor. • They had an opening to thank the donors, especially the Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundations and to celebrate with the community and rowers, past and present • Since 1996 rowers had to wade in foul, ankle to thigh high water to access the boat shed- this was for 3-5 months of every year- our facilities are now accessible and Warrnambool has a sporting venue for rowers that is safe and one the public can be proud of. • The Club thanked Barry Wilson for generously donating the plans and acknowledged the ‘term deposit’ raised over the last 10 years, by past and present members, which allowed the Club to contribute the additional funding required. • In particular The Foundations assistance made the project possible. The two philanthropic Foundations are a treasure for the community as they can step in and fill the gap where other funding sources cannot. In our case they were the major donors and we could not have contemplated this project without their assistance. We are truly grateful for the assistance of The Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundation. • Mr James Tait, a director of both Foundations to unveiled the commemorative plaque. Color photograph taken at the opening of the Redeveloped City of Warrnambool Rowing Club. Includes a brass plaque. The people are L to R: Kathy McMeel (secretary), Annie Blanch (Boat Captain), Joanne Bone (president), James Tait (director of Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundations, Susan Finnigan (Grants Officer) and Clive Wooster (treasurer).james tait, warrnambool, city of warrnambool rowing club, warrnambool rowing club, boathouse, boathouse redevelopment, gwen and edna jones foundation, ray and joyce uebergang foundation -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionPainting - Portrait of William Abendigo Thompson, c 1890
William Abendigo Thompson was English bare-knuckle boxer born in Nottingham, 1811- 1880 and whose name is (allegedly) borne by the City of Greater Bendigo. One of 21 children he started fighting aged 18 and began prizefighting aged 21. His career spanned from 1832–50, and is said to have lost only one fight. Later in life, after spending time in prison he became a Methodist evangelist preacher. While the artist and date of production of this work are unknown the initials JJLh (or n?) are just legible lower right on canvas. Other clues for an approximate date of creation include the similarity in composition of this painting to a popular aquatint of Bendigo by Charles Hunt Senior (1803 - 77). Based on the markings on the back of the canvas for Rowney and Co and the address given, we can ascertain that the canvas itself was manufactured between 1884 - 1896. The painting also includes an extract of the Conan Doyle poem 'Bendigo's Sermon' which was written in 1911. Given these three factors, a date for the painting can be surmised as post 1911. Stretched made by George Rowney’s is one of very few artists’ supply businesses with origins in the 18th century still trading today, as Daler-Rowney, albeit no longer in family hands. The business has been a significant supplier of canvases and panels from the 1810s. Naive, Primitive, British0348.1 Framed oil painting of the bare fisted knuckle fighter William Abendigo Thompson painted in a naïve style. Depicts Thompson, bare chested in an outdoor fighting ring with his fists raised with a water bucket at this feet. 0348.2 Typed note re the history of the naming of the City of Bendigo.Top centre front of painting; You didn’t know of Bendigo? That knocks me out! Who’s your board school teacher? What’s he about? Chock a block with fairy tales – full of useless cram And haven’t heard o' Bendigo the pride of Nothin’ All sing along together lower centre painting; William Abendigo Thompson centre Inner wooden frame; bendigo back of canvas; Geo. Rowney & Co 64 Oxford Street and Princes Ball Piccadilly London W sticker lower centre back of frame; donors name and address. Initials illegible lower right.city of greater bendigo sport -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Sphalerite, Unknown
Sphalerite or sphaelerite is named from the Greek word for 'treacherous' or 'deceiver' as specimens can vary widely in appearance, making them hard to visually identify. It is a zinc sulfide with the chemical composition (Zn,Fe)S, the most important ore of zinc. Specimens of sphalerite can contain iron as a substitute for up to 25% of the usual zinc present, as well as trace elements of gallium, cadmium, geranium and indium. Small amounts of arsenic and manganese may also be detected. Sphalerite is found in igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. It forms when carbonate rock encounters acidic, zinc-bearing fluid. It often forms in veins or in fissures of the existing rock, with colours and crystal shapes dependent on the composition of the the combining elements. It forms isometric crystal shapes including cubes, tetrahedrons, octahedrons, dodecahedrons. This specimen was collected in approximately 1852, in Broken Hill, NSW, as an adjunct to the Geological Survey of Victoria. It was donated to the Museum in 1868. Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole.The specimen is significant as an examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century.A pipe-shaped specimen of sulfide-mineral zinc ore displaying patches of black, brown, beige and gold colouring. The main item has associated broken pieces. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, mineralogy, indigo shire, geological survey, sphalerite, sphaelerite, zinc ore, broken hill, nsw, victoria, galena, fluorite, chalcopyrite, lead, cadmium, gallium, germanium, indium, iron -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Sand Goanna, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Sand goannas are the second largest species of carnivorous lizards found across mainland Australia. They can grow up to 160cm in length and can weigh as much as 6kg. Their common name is derived from "iguana", since early European bush settlers in Australia likened goannas to the South American lizards. Goannas retain special cultural and historic significance within Australian folklore and Indigenous culture. They were an important traditional native food source and are commonly represented in Aboriginal Dreamtime stories. In some Aboriginal languages, the sand goanna is called "bungarra"; a term also commonly used by non-Aboriginal people in Western Australia. In Pitjantjatjara and other central Australian languages, goannas are called "tingka". This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.Small goanna with a streamlined body and textured scaly skin in different shades of olive and brown. It has a long neck and a long tail which narrows towards the tip. The goanna has four short, stocky legs which meet with large, curled claws. Its mouth is slightly slightly open, and it has two black glass eyes.On tag: BMM / 5892 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, lizard, goanna, sand goanna, monitor lizard, various gouldii -
 Bacchus Marsh & District Historical Society
Bacchus Marsh & District Historical SocietyPainting, View of Bacchus Marsh from Stamford Hill circa 1880s
The date of the scene depicted in this painting has not been identified. The painting has no artist signature or date. The view depicted is from an area close to the present day Madden Drive in Bacchus Marsh. The angle of the view suggests the artists viewpoint may have been from a spot close to the intersection of Madden Drive and Muir Street looking east over the town. Several buildings constructed in the 1860s and 1870s can be seen in the painting. These include Saint Andrews Presbyterian Church (now Uniting Church), built 1865, Stone Villa in Bennett Street, the Bacchus Marsh Court House, the former National Bank and the Border Inn, all on Main Street, and in the distance Saint Bernard’s Catholic Church. Buildings such as Simon’s Garage erected in 1913, on the corner of Main Street and Grant Street are not shown. In the foreground running horizontally Grant Street can be seen. The view of Grant Street shows very few buildings. One house in the centre of the picture is Murdoch's Cottage. A brick house constructed in 1868 on the corner of Grant Street and Waddell Street. To the right of the picture along Grant Street no buildings are shown. The store built by John Jory in 1890 at 60-62 Grant Street which survives as a building in 2025 is not shown. Some allowance for artistic interpretation must be allowed but based on what the scene depicts it suggests a scene of Bacchus Marsh in the late 1870s or 1880s. Print reproduction of an oil painting. Framed. Undated. Unsigned. BMDHS Location: AR/B12/Beside (on floor)views bacchus marsh vic., paintings bacchus marsh vic., landscapes bacchus marsh vic. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Northern Hawk Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Northern Hawk-owl is a nomadic and generally solitary bird, although they can occasionally be seen in pairs. While these birds resemble owls, their behaviour is more similar to that of a hawk, hence their name. Normally active during the day (similar to the hunting habits of a hawk), they prefer to reside in boreal forest, grasslands, shrublands and temperate, cold and polar zones. Located in North America, Europe and Asia, these owls can also occasionally be found during migration, in the northern United States. There are three subspecies in North America, Central Asia and Siberia. At the present time (2021), its numbers are stable and so it is therefore considered of ‘least concern’ on the IUCN Red List, indicating it is not yet endangered. This particular specimen has been correctly mounted and presented as a relatively accurate representation of the actual bird. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Northern hawk-owl's face features white and brown soft feathery plumage and a dark brown border around its face/chin area, with a dark cream curving beak soft yellowy brown coloured eyes. Its front breast feathers are generally off white in colour with some flecks of brown. It has a long brown tail with off white banding, with creamy white claws. The owl has speckled brown and white plumage over the back of its body and wings and some areas of more solid brown are present around the back of its neck and top of wings. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and two identifying tags hang from its right leg, while a metal numbered tag hangs from its left.Swing-tag: 38 / Rayed Swin Owl –/ See Catalogue, Page 53. Tag with faded script: No 33 Strix[?] / misarea[?] / Sweden[?] Metal tag - digits on metal tag appear to read, either ‘5028’ or ‘6028’taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, surnia ulula, strigidae, northern hawk-owl, hawk-owl, canadian owl, hudsonian hawk-owl, owl, canada, asia, europe, north america -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Wedgetail Eagle
The Wedgetail Eagle (aquila audax) is one of the largest birds of prey located in Australia, Indonesia and Papa New Guinea. It feasts mostly on rabbits but can target mammals as large as koalas, wombats, possums and small kangaroos. The darker the colouring, the older the bird is. A mostly dark brown feathering can suggest over 10 years old, though females are usually paler. This species mates monogamously for life. They circle high in the sky to avoid temperatures close to the ground and to assert their dominance over their territory. This specimen is lighter than many documented photographs of the species. They're usually less patchy / speckled with lighter colours on the chest and back. Documenting the wingspan of this specimen would be of interest because some have been measured up to 230cm. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This wedgetail eagle is posed with the head turned to the left. It has mostly dark brown feathers which is common for older birds in this species. Speckled light brown and white feathers cover it's neck, chest and a middle strip across the wings. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform. The bill is light grey and long legs dark brown. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, wedgetail eagle, aquila audax, birds of prey, australian bird, eagle -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPrototype fuel moisture meter
Bushfire behaviour is influenced by many things including temperature, relative humidity, forest type, fuel quantity and fuel dryness, topography and even slope. Wind has a dominant effect on the Rate of Spread (ROS), and also bushfire size, shape and direction. Fuel arrangement is as important as fuel quantity (tonnes/ha). Fibrous and ribbon bark, together with elevated and near-surface scrub fuels act as ladders which lead flames into the tree canopy. But the availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Since the 1930s foresters, firefighters and researchers have been working to develop quick and reliable techniques for measuring fuel moisture content. One of the most accurate methods is slowly drying a sample of fuel in a conventional oven for 24-48 hours to remove all the moisture and measuring the weight difference, but this takes time and is not practical in the field when rapid measurements are needed. But oven drying is often used as a benchmark to compare other methods. Microwave ovens are faster but can cause uneven drying and even char the fuel. They are also not very practical for use in the field. Some mathematical models rely on weather records such as rainfall, wind speed, evaporation, cloud cover, shading, relative humidity, slope, aspect and season of the year to predict soil and fuel moisture. The Keetch-Byram Drought Index of soil dryness is the most common. But complex fuels with leaves, twigs, grass etc make the predictive models often inadequate for fine fuels. The most common technique in Victorian forests until recently was the trusty Speedy Moisture Meter. Originally developed in England during the 1920s for measuring moisture in wheat and other grains it was adapted for Australian forest fuels in the 1950s (I think). Fuel was first ground using a Spong mincer, often attached to the bullbar of a vehicle, and a small sample placed into the Speedy together with a measure of calcium carbide and then sealed. A chemical reaction created gas pressure which was read on the external dial. There were important techniques with cleaning, mincing and using the chemicals with the Speedy to give reliable readings, but it was quick, inexpensive, robust, portable and practical in the field. It was used routinely before igniting a fuel reduction burn or measuring fuel moisture differentials on slash burns. But in about 1996, Karen Chatto and Kevin Tolhurst from the Department’s Creswick Research Station developed the Wiltronics Fuel Moisture meter which measured electrical resistance. Wiltronics is an Australian owned company operating from Ballarat. The final result was a kit that was portable, accurate and could reliably measure fuel moisture contents between 3% and 200%. Although expensive, it is now widely used by fire agencies around the world which has virtually relegated the Speedy to the back cupboard.Prototype Fuel moisture meterT-H Fine Fuel Meterforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Serving dish, Fish Dish, Early 20th century
This fish dish is an attractive household item which would have been used in the early to mid 20th century when the more affluent families in society were entertaining. It is not a common item and most likely would not be seen in households today. This dish has no known local provenance but is of considerable interest as a household item not seen today. It will be useful for display.This fish dish has an electro-plated nickel silver holder with two curved pieces of metal joined at the centre to form a base. There are four round metal balls at each end of the curved metal to stabilise the stand. Four curved metal pieces are attached to the base and hold a rectangular-shaped piece of metal and a handle. Fitting into this piece of metal is a cut glass container which is heavily patterned on the sides and base. The lid of this container is rectangular with rounded edges and silver-plated. The top of the lid has a silver-coloured free-standing fish model attached to the lid by a metal stud. The fish is a little loose on its stand. The handle can be folded down. ‘E P N S 62’ household items, history of warrnambool
