Showing 6434 items
matching sold
-
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - First Methodist Church, Wodonga
Land for the Methodist Church in Wodonga was reserved in 1864. By 1865 the Reverend Francis Neale, a Wesleyan minister was appointed to Albury from where he supervised the congregation at Wodonga Creek until a church was built in 1873. By 1885 Wodonga and the other preaching places on the Victorian side of the Murray had become a separate circuit under the Reverend L. J Rowlands. This circuit included Bethanga. Kiewa. Leneva, Kergunyah and Bonegilla. In the 1960s the Methodist congregation built a new chapel in Hovell Street, Wodonga. The creation of the Uniting Church during the 1970s meant that the services were held in the former Presbyterian Church and joint Sunday School classes were conducted in the Methodist Hall. In 1961 the Church building and land was purchased by the Ukrainian Community for £2,000. Ukrainian Catholic families in Wodonga donated £100 each towards the purchase. Additional fund raising such as carol singing in nearby towns (Benalla, Wangaratta, Albury and Wodonga) assisted with the purchase of the Church. The former Methodist Church was in poor condition and the members of its new congregation undertook the replacement of the floor, the footings, replastering of the walls and the construction of an altar. The renovations cost a further £400. Once a month a priest came up from Melbourne to conduct services in the Church. On completion it was blessed by Bishop Ivan Prasko to become St Olga's Catholic Church (Ukrainian). In 1965 the Church was dedicated to its patron St Volodymir, with Bishop Varlamm (Sydney) and Bishop Donat (Melbourne) taking part in the ceremony. The members of the Ukrainian Catholic community also built a hall and smaller chapel in Hunt Street, Wodonga. With a declining congregation, this property became more manageable to maintain than the original brick building and the decision was made to close the building in 2010. In 2022 the building and extensive block of land in Church Street was sold commercially for potential redevelopment.These images are significant because they depict an early Wodonga Church building.A collection of coloured photographs depicting the first Methodist Church in Wodonga, Victoria It was a red brick church with a steeply pitched gable roof and parapeted gable walls. There was a small front porch with matching roof and gable treatment to the front. Simple timber Gothic windows were along the sides, with a tri-partite window above the porch. Two sections of this window featured stained glass, the other was opaque glass. Red brick buttresses were topped with white-painted render, as were the parapets, and the windows were also outlined with white painted render. Timber joinery was painted white. A front path led directly to the porch and the Church was flanked by mature oak trees. A small, relatively modern red brick skillion extension was added to the rear of the building.wodonga churches, methodist church wodonga, ukrainian catholic church wodonga -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Paper Fastener, 1919-1923
The Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener is what is known as a stapleless stapler. It uses the Bump fastening method which was patented in the U.S. in 1911. The Ideal measures 4.75″ H x 3.125″ W x 1.875″ L and weighs 6.5 ounces. It was manufactured and sold in Japan but also exported to England. The case is made of stained wood with the fastening mechanism made of polished steel. From unsubstantiated sources I understand the wood is Japanese Boxwood, but I cannot verify that at this time. The markings on the front and reverse are done in black paint. The two patents listed on the reverse side of the fastener are Japanese patents. They were granted in March and September 1918 respectively. The patents were granted to two different men. The letters CK on the reverse of the fastener seem to be the initials of the two patent holders. If the design of a C superimposed over the K is a trademark as indicated, it would imply that the two patent holders went into business together to manufacture the Ideal Fastener. I’ve been unable to determine fully the names of the patent holders, but the K seems to refer to a Mr. Kuroda who was the author of the later patent. The Ideal fastener was sold alongside the Clipless Stand Machine (available 1911-1923) and Bump Fasteners in Japan. The latest patent number on the Ideal is from September 1918. Furthermore, there was also an all-steel model of the Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener being sold in 1922. While the available evidence is both sparse and largely circumstantial, I believe the Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener would have been sold from 1919 until about 1923. Furthermore, with the availability of an all-steel model in 1922, it is likely that this newer model would have been introduced as the replacement for the wooden-cased version giving me further reason to believe that this would not have been sold after 1923. The fastener was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. Dr. Angus was in England in the 1920’s and could very well have purchased the Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener during his study time there. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” and includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. [References; Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener, Antique Outings http://antiqueoutings.com/ideal-clipless-paper-fastener/ ; Australian College of Ophthalmologists, Vol 11, 1970.; Medical Directory of Australia listing, alphabetical says 1929, Royal College of Surgeons Edinburgh says 1928; Documents re Dr Angus from daughter Berry McDade, received at Flagstaff Hill Maritime; Portland Examiner, June 13, 1969; The Advertiser (Adelaide) 14th Nov, 1910 - Blind restored to sight – Dr Edward Ryan, Melbourne; The Hamilton Spectator, Wed 15th April 1914 – Ararat man with eye affliction attended to by Drs E & T Ryan; The Nhill Hospital, first 100 years, 1885-1985, by Jan Doust; The Horsham Times, Tuesday 6th January 1885 – Dr Edward Ryan appointed to Nhill Hospital; People who passed this way – Warrnambool and District Historical Society; Warrnambool Base Hospital Report 1969-1970 The Standard, 22/6/1990; The Argus, 1970; Letter to Mrs G Angus from John Lindsay, Flagstaff Hill, 8/5/1973; ] This Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener is significant as a rare example of a clipless paper fastener used as office stationery of the 1920’s. This Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener is significant for its association with the W.R. Angus Collection, which is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Paper fastener, clipless or stapleless. Part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Branded Ideal Clipless Paper Fastener, made in Japan. Push down action on wooden handle, metal cutting mechanism cuts and folds the cut flap to join two pieces of paper. Stained wood base, sides and handle, floral fabric under base. Inscriptions on sides and base are in black paint print. Early to mid 1900’sPrinted on sides “IDEAL CLIPLESS PAPER FASTENER” and “TRADE MARK (K with a C through it) PATENT NO. 45105 46743” and stamped into base "MADE IN JAPAN"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, ideal stapleless stapler, ideal clipless paper fastener, ideal paper fastener made in japan, paper fastener, office stationery, patent 45105 46743, ideal clipless paper fastener ck, logo ck c over k -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessels - Sail and Steam, c. 1972-1975
Andy Clapham owned and operated a boat yard on the Maribyrnong River in Footscray, Victoria. The river runs into Port Phillip Bay (sometimes known as Hobson’s bay) at Williamstown, an area with a history of trades associated with the shipping and construction industry. Andy Clapham’s photographs include those of the Reginald M and one of Polly Woodside, another vessel restored and used as a maritime exhibition. Andy Clapham’s letter of 1972 was posted in a and envelope with an early Australian decimal currency stamp showing the profile portrait of Queen Elizabeth II, and valued at 7 cent. Andy offered invaluable advice to the Flagstaff Hill Historic Park Planning Board regarding the purchase a vessel suitable for use as an exhibit once Flagstaff Hill was opened. The Planning Board was set up by the Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce and approved by the City Council and State Government. Flagstaff Hill was investigating vessels in Adelaide and Tasmania as well as Melbourne. Andy looked at several vessels in 1972-1973. He also serviced the Reginald M among other vessels belonging to Captain Julian Dyson of Yarra Ferries, who had casually offered the vessel to Flagstaff Hill as a price that was unattainable at the time. Flagstaff Hill later requested photographs of the hull to discern the dimensions and also the condition of the timbers as well as wanting advice on its seafaring capability. In 1972 the Flagstaff Hill Historic Park Planning Board – Chairman J. (John) S. Lindsay (1972-1980), Secretary J. (James) Mark – wrote a letter of appreciation to Mr A. (Andy) Clapham of 3 Charles Street Footscray ... “Dear Mr. Clapham, The Board has asked me to write to you to express our appreciation for the assistance you have offered us through our Chairman John Lindsay. The information you have already given us has been invaluable, in that is shows us that we have not been setting out to do something that is impossible. We look forward to receiving further information from you as it becomes available and we appreciate that you must be busy enough without our problems. Members of our Board hope to call and see you on a trip to Melbourne in the near future. The Board is optimistic about the future of Flagstaff Hill as a Maritime Museum and look forward to you visiting Warrnambool to examine what we believe will be an ideal site. Yours faithfully, James Mark.” ABOUT the vessel “Reginald M” The vessel “Reginald M” was a two-masted, timber coastal vessel built by John Henry Murch in Birkenhead, Port of Adelaide, South Australia. It was named after Reginald Murch. (It was occasionally referred to as the Reginald “Emm”). Its construction took approximately 6 months using many materials and fittings from salvage yards. It is believed that the keep was hewn from two telegraph poles! Reginald M was launched at Largs Bay in 1922. Reginald M was approximately 30 metres long and was fore-to-aft ketch rigged with an ‘auxiliary’ motor to support any loss of sail power. The Reginald M was built to service the coastal ports of South Australia to Port Victoria on the York Peninsular, Spencer Gulf. It freighted cargo from port to port cheaply and efficiently. It had a very shallow draft and a flat bottom, enabling it to come close to shore and sit high and dry at low tide, or to be beached on the sand. It could easily skim over reefs due to its flat bottom. Wagons could be loaded and unloaded directly from the side of the vessel. Over the years her cargo included guano, barley, wool, horses, cattle, timber, explosives, potatoes, shell grit and gypsum. The Murch brothers from Port Adelaide were owners of the Reginald M and Richard Murch as the Captain. On April 9, 1931, Reginald M weathered a large storm in St. Vincents Gulf, SA, suffering much damage; the mast snapped and the crew laboured for four hours to free it up by severing the mast and rigging. The crew patched it up and slowly returned to Port Adelaide with only a portion of the insured cargo being damaged. The crew members at that time were owner Mr John Henry Murch of Wells Street Largs Bay, Skipper Mr R Murch – John’s brother, Murray – son of Captain Murch and Seaman John Smith. At some stage it seems that the Reginald M was used as a Customs vessel “H.M.C. No. 3, Pt Adelaide” as shown in a photograph in Flagstaff Hill’s collection. In 1969 Reginald M’s last freight trip left Marion Bay, carrying grain, wool and explosives. In late 1970 it was sold to the Mount Lyall Mining and Railway Clompany and used as a barge to carry explosives. In 1972 The Navy League of Strahan, Tasmania, purchased the vessel for use by the Strahan Sea Cadet Unit at Macquarie Harbour; it was renamed “T.S. Macquarie”. (This plan did not come to pass.) In 1974 Mr Andrew Rennie of East Brighton, Melbourne, brought Reginald M for shipping purposes, He sailed it from Strahan to Melbourne, planning to use it for pleasure sailing. The Reginald M was later sold at auction to Captain Julian Dyson, owner of Yarra Passenger Ferries in Melbourne. Later in 1975 funds became available to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village to purchase the Reginald M. It was then restored and used as an exhibit here for many hears. Flagstaff Hill’s collection also includes various objects related to the Reginald M: - Photographs of Reginald M over the years in various aspects of its use - a life buoy with the inscription of “Pt. Adelaide” - helm section that was removed and replaced during restoration - a bullet found in pieces of timber during the 1979 restoration ABOUT THE POLLY WOODSIDE On the bow in the Polly Woodside's photograph is the word "RONA". the Polly Woodside was built at Belfast in 1885. In 1904 the vessel was sold to A.H. Turnbull of New Zealand and renamed "RONA". The letter and photographs are significant for their association with the Reginald M, an Australian built coastal trader now on the Australian Register of Historic Vessels (number HV000562). The letter and photographs are also significant as part of both the history of Flagstaff Hill and the history of the vessel “Reginald M” that has been on display in the lake for many years. Objects retained from this boat are included in Flagstaff Hill’s collection of maritime history.Packet with photographs and negatives in a KODAK envelope. The photographs are of two sail and steam vessels; twelve (12) black and white photographs of the 'Reginald M', and one (1) colour photograph of the Polly Woodside, plus six (6) negative strips. Included int he packet is a letter in stamped and postmarked envelope addressed to Mr A Clapham of Footscray. The envelope postmarked 9 Dec 1972, with the Warrnambool postcode 3280, A 7c Australian postage stamp in attached to the envelope. They are associated with Flagstaff Hill’s acquisition of the vessel “Reginald M”. Envelope "9 DEC 1972 / 3280" Postage stamp "7c" "Australia" Inscriptions on one Reginald M;; "REGINALD M" and "Pt ADELAIDE H.M.C. No. 3" Inscriptions of the Polly Woodside; "RONA / MSC" "MHI / NO. 1" Ball point ink, reverse of photograph "POLLY WOODSIDE"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, vessel reginald m, reginald emm, t. s. macquarie, h.m.c. no. 3, pt adelaide, australian register of historic vessels (number hv000562), boat building trade, jack murch, john henry murch, birkenhead, port adelaide sa, largs bay sa, coastal trader south australia, 1920 ketch reginald m, marion bay produce, mount lyall mining and railway company, navy league of strahan, tasmania, melbourne ferry company, flagstaff hill historic park planning board, john lindsay, james mark, andy clapham of footscray, andy clapham boat builder, kodak photograph packet envelope, kodak super-size prints, kodak australia pty ltd, australian postage stamp 1972 - 7c -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Edendale Farm Homestead, 29 January 2008
Edendale Farm is Nillumbik Shire Council's environment centre situated in Gastons Road, Eltham between the railway and the Diamond Creek. The homestead on the property was built in 1896 and is of historical significance, being the subject of a Heritage Overlay under the Nillumbik Planning Scheme. The Edendale property was originally part of an extensive land purchase in 1852 from the Crown by pioneer Eltham farmer Henry Stooke. He initially purchased 51 acres and later expanded his holdings by purchasing another three adjacent Crown allotments extending northerly from Josiah Holloway's Little Eltham subdivision. Despite clearing the land, Stooke did not build on this property, choosing to live on his property "Rosehill" at Lower Plenty. In 1896 Thomas Cool, Club Manager of the Victoria Coffee Palace in Melbourne purchased 7 acres of the original Stooke land and built the house now known as Edendale. Cool did not farm the land, instead using it as a gentleman’s residence, retiring to Eltham at weekends. In 1918 he purchased an additional 7 acres but in 1919 he sold the property. Later owners included J.W. Cox, the Gaston family and D. Mummery. In the 1980s the Eltham Shire Council purchased the site for use as a Council depot, but this use did not proceed. Subsequently, it was used as the Council pound. The Edendale Farm Pet Education and Retention Centre was established in the summer of 1988/1989 and was set up to replace the existing dog kennels with a high standard pet retention centre. The design style of the building was established to compliment the features of the existing house. It was equipped with 10 retention pens, a veterinary room and a pet education area where school children and other interested parties learnt about pet care procedures. It was later developed into a community farm and was run by an advisory committee and in 2000 it became an Environment Centre. In early 2006 an advisory committee was established for the development of a master plan for future development at Edendale Farm. The committee included Russell Yeoman, a former long-time shire planner and founding member of the Eltham District Historical Society. At the time of filming the Master Plan and future for Edendale was about continuing to develop Edendale as a centre of environment learning and looking at expanding displays and school program, running a lot more of life-long learning and workshops around sustainable living. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p101 A sharp turn from busy Wattletree Road by the railway line, brings a surprise. Only 1.4 km from Eltham’s centre, sheep feed, blissfully unaware of the hectic suburban activity so close by. At the entrance to the 5.6ha Edendale Farm is another surprise. A work of art that looks like huge tree trunks transformed into bowler and top-hatted men. The Fences Act 1968 by Tony Trembath with Mark Cain and John Doyle, 1996, is classified by the National Trust of Australia as having Regional Significance. The title refers to a government act on disputes between neighbors over the placement of fences and boundaries. This takes a ‘wry swipe’ at a community divided by trivial squabbles. It also celebrates making do with limited resources.1 Further along on the left, the office wall is decorated with a massive Eltham Copper Butterfly, designed by Robert Tickner and made by school children with used plastic bottles and other waste material. Nillumbik Council runs Edendale as an Environmental Education Centre, to help preserve and enhance the local environment. As early as 1988 the former Eltham Shire Council realised Edendale’s importance in meeting people’s needs, particularly of children, to enjoy farmland. The centre, with the Eltham North Reserve to the north - including remnant bushland and open parkland - makes up the major part of the public open space for this area. The council considers this area will become increasingly important to the local community for recreational use.2 Educational programs aim to encourage community involvement to ensure the long-term rehabilitation and protection of natural bushland areas. Edendale is used by people of all ages - from school children to adults - for environmental programs and workshops, as well as for recreation, to enjoy the domestic animals and to picnic. Edendale is also home to the Environmental Works staff who manage reserves and roadsides and support Nillumbik Friends environmental groups. The Friends propagate plants at the nursery, which grows indigenous plants and sells these to the public.3 The centre demonstrates the sustainable living the farm teaches, with features like solar hot water and drive lighting and for the fireplace, logs of recycled cardboard. Edendale has had a varied history as a dog pound and even as a retreat for Thomas Cool, Club Manager of the Victoria Coffee Palace in Melbourne. His single-storey weatherboard house built in 1896, which still stands, was grander than most homes in Eltham. Although such buildings were common in many other parts of Melbourne, Eltham’s poverty and remoteness did not encourage such construction. The Victorian rectangular-shaped house, with a corrugated iron roof and veranda, has elegant large rooms, leadlight windows, ceiling roses, two bay windows and ornately carved wooden fireplace surrounds. Cool bought seven acres (2.8ha) from pioneer Eltham farmer Henry Stooke’s 200 acre (81ha) farm, which he had bought from the Crown in 1852. In 1918 Cool bought an extra seven acres (2.8ha) but in 1919 sold the estate to farmer John Cox. In 1933 Cox sold Edendale to Mrs Elizabeth Gaston, after whom the road leading to the centre was named. The property was owned by several Gaston family members, who called it Edendale, then by a police constable, Douglas Mummery, until the Shire of Eltham bought it in 1970. Oddly Edendale was known as Mummery’s for almost 20 years, although Mummery owned it only for a short time.4 The shire used Edendale as a dog pound until amalgamation with other municipalities in 1996. The pound then moved to the Yan Yean Road, Plenty site, which had been used by the former Diamond Valley Shire Council. To the west and north the centre is bounded by Diamond Creek and on the east by the Melbourne-Hurstbridge railway line. Part of the Research creek forms the centre’s southern boundary.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, edendale farm -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - PETER ELLIS COLLECTION: NEWSPAPER ARTICLE, 23rd May, 2015
Colour photocopy of article from Bendigo Advertiser. Dated Saturday, May 23, 2015. FAREWELL, MA.. When Peter received his Order of Australia Medal it was one of his proudest moments. He couldn’t resist wearing it on every occasion. FROM - PREVIOUS PAGE The Emu Creek Bush Band has performed at National Folk Festivals in four states and numerous times at the National Folk Festival in Canberra. They have also been mainstays of the Maldon Folk Festival for most of its history as well as doing dance programs for the Port Fairy Folk Festival on two occasions. Peter wrote and published many books related to traditional music and dance. These include: Three volumes of 'Collector's Choice' which is musical notations for bush dances coupled with much dance history which would have been lost without Peter's efforts, are 'Two Hundred Dancing Years- How to run a Colonial Ball' (Co-authored with Shirley Andrews (AM), 'Music Makes Me Smile- The Music of the Nariel Valley' (Co-authored with Harry Gardner), and his last completed book is titled 'The Merry Country Dance' with over 300 pages.. .. .. Grant. The first edition sold out in only a few weeks. Peter taught old time musicianship, accomplished as he was on the concertina and button accordion, tin whistle, and harmonica, as well as the Swanee whistle, piano and ukulele. In demand for workshops in music and dance at National Folk Festivals in Perth, Alice Springs, Maleny, Melbourne, Adelaide, Kuranda and more recently at several Canberra National Folk Festivals, he was a hit at festivals across the country. As a trained ballroom dancer, with many gold medals to his name, Peter passed on his knowledge every time he trained debutante sets in the Bendigo region. As an early environmentalist, he was a life member of the Bendigo Field Naturalists Club, secretary in the 1970's and actively involved in campaigns to save Lake Pedder and establish the Whipstick and Kamarooka State Parks (now part of the Bendigo National Park). He has discovered and named new plant species in the Whipstick Forest and propagated many Australian plants. Peter took regular guided tours through the Whipstick each spring, on wildflower educational tours. He was a keen and gifted photographer of local plant species. When Peter received his Order of Australia Medal it was one of his proudest moments. He couldn’t resist wearing it on every occasion. Funeral details. Family, friends and his supporters will farewell Peter.. .. .. ..person, individual, peter ellis oam -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - HOSKING AND HUNKIN COLLECTION: BIBLE, 1800s
HOSKING AND HUNKIN COLLECTION: Small Bible inside envelope. On Binder: New Testament Inside front cover: This Book Belongs to Ellen Nancarrow November 8th 1857 Redruth Coomb Inside second page: This is a present given to Emily Hoskong by her Aunt Helen a a token of Love November 1860. Bible Details: The New Testament of our Lord and Saviour Jesus Christ translated out of the original Greek and with the former translations diligently compared and revised, by his Majestiy's special Command appointed to be read in Churches. Oxford prineted at the Univerity Press for the British and Froreign Bible Society, instituted in London in the year 1804; and sold to Subscribers at the Society house Earl Street, Blackfriers, London. Diamond's 48's 1856. Cum Privilegio Note inside BibleBible given to Emily Hosking (m. Emmanuel Hunkin) from her aunt Ellen (Nancarrow) Redruth Coomb. 8 Nov 1860 prior to sailing to Victoria. Nancarrow = Valley of the Stags. On front of envelope: Her New Testament a precious possesion. Bible given to Emily Hosking (b. 12-2-1854 d. 22-5-1905) by her mother's sister Ellen Nancarrow (b 17 Mar 1827 husband Wm Hosking m. 1853 Rev. John Cornwall Wm. D. 10 July 1914) in 1860 8th Nov before leaving for Australia. Liven and mined at Eaglehawk, Vic. Then Rushworth area (farming) Emblen Hosking nee Nanacarrow RedruthCoomb Cornwall b. 6/3/1831 d. 20/5/1895 Gobarup. Rear of envelope: Yellow and black stickers (Women with flowers and Man with Scythe, and St. Piran's) written on 'Cornish Patron Saint's day - 5th March. Address Label: Ms Betty Night, 29 Gilbertson Street Essendon Vic 3040 Separate page of Notes: A note in the front of Hymn Book Emily Hosking born 12/2/1854 married 1873 her book. A reward - The Bible Christian Sabbath School, Sailors Gully June 29th 1868. Hyms - Bible Christian 2nd edition 1890. Bible Christian Book Room 26 Paxxxx Road E.C. Mrs E. Hunkin Eaglehawk B.C. Church January 21st (18) 94 Husband Emmanuel Huskin born 21/1/1852 - collection of hymns Wesley hymns Emmanuel Hunkin. 2. A collection of hymns Emmanuel Hunkin, Eaglehawk Bendigo.book -
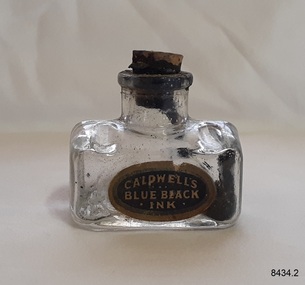 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Caldwell’s Ink Factory, Late 19th to early 20th centuries
This design of the bottle is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. The Caldwell’s handmade glass ink bottle was mouth-blown into a three-piece mould, a method often used in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with the maker's name engraved into the mould section for the base. The glass blower would cut the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool and join a mouth onto the top, rolling the lip. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. This method of manufacture was more time-consuming and costly to produce than those made in a simple two-piece mould and 'cracked' off the blowpipe. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. This particular bottle is unusual as it has four sloping indents at the corners of the shoulder, most likely for resting a pen with its nib upwards and the handle resting on a flat surface. Most of the bottles made during this era had horizontal pen rests that were indented into both of the long sides of the shoulder. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. This only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. Caldwell’s Ink Co. – F.R. Caldwell established Caldwell’s Ink Company in Australia around 1902. In Victoria, he operated from a factory at Victoria Avenue, Albert Park, until about 1911, then from Yarra Bank Road in South Melbourne. Newspaper offices were appointed as agencies to sell his inks, for example, in 1904 the New Zealand Evening Star sold Caldwell’s Flo-Eesi blue black ink in various bottle sizes, and Murchison Advocate (Victoria) stocked Caldwell’s ink in crimson, green, blue black, violet, and blue. Caldwell’s ink was stated to be “non-corrosive and unaffected by steel pens”. A motto used in advertising in 1904-1908 reads ‘Makes Writing a Pleasure’. Stationers stocked Caldwell’s products and hawkers sold Caldwell’s ink stands from door to door in Sydney in the 1910s and 1920s. In 1911 Caldwell promised cash for returned ink bottles and warned of prosecution for anyone found refilling his bottles. Caldwell’s Ink Stands were given as gifts. The company encouraged all forms of writing with their Australian-made Flo-Eesi writing inks and bottles at their impressive booth in the ‘All Australian Exhibition’ in 1913. It advertised its other products, which included Caldwell’s Gum, Caldwell’s Stencil Ink (copy ink) and Caldwell’s Quicksticker as well as Caldwell’s ‘Zac’ Cough Mixture. Caldwell stated in a 1920 article that his inks were made from a formula that was over a century old, and were scientifically tested and quality controlled. The formula included gallic and tannic acids and high-quality dyes to ensure that they did not fade. They were “free from all injurious chemicals”. The permanent quality of the ink was important for legal reasons, particularly to banks, accountants, commerce, municipal councils and lawyers. The Caldwell’s Ink Company also exported crates of its ink bottles and ink stands overseas. Newspaper advertisements can be found for Caldwell’s Ink Company up until 1934 when the company said they were the Best in the business for 40 years.This hand-blown bottle is significant for being the only bottle in our collection with the unusual sloping pen rests on its shoulder. It is also significant for being made in a less common three-piece mould. The method of manufacture is representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that is now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottle is of state significance for being produced by an early Melbourne industry and exported overseas. This ink bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Ink bottle; rectangular base, hand-blown clear glass bottle with its own cork. The bottle has side seams from the base to the mouth, an indented base and an applied lip. The corners of the shoulder sides have unusual diagonal grooves that slope down and outwards that may have been used as pen rests. Inside the bottle are remnants of dried blue-black ink. The glass has imperfections and some ripples on the surface. The bottle has an attached oval black label label with gold-brown printed text and border. The base has an embossed inscription. The bottles once contained Caldwell’s blend of blue black ink.Printed on label; “CALDWELL's BLUE BLACK INK” Embossed on the base "CALDWELLS"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, blue black ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, cork seal, f r caldwell, caldwell’s ink company, albert park, south melbourne, inkstands, stencil ink, copy ink, quicksticker, zac cough mixture, three part mould, cauldwells, cauldwell's -
 Brighton Historical Society
Brighton Historical SocietyFlag, W. Morgan & Co, School flag, circa 1910s - 1930s
This flag was used by Rosbercon Girls Grammar School, which operated in Brighton from 1906 until 1941. The school was established in 1906 by the Tisdall family. The Tisdalls were a family of educators: Irish-born Henry Thomas Normanton Tisdall and his wife Lucy taught for many years at the Walhalla State School in Gippsland, along with Lucy's sisters Alice and Clara Weekes. Three of the Tisdall daughters, Ethel, Constance and Theodosia (Theo) followed their mother and aunts into the teaching profession. Constance in particular considered education her true calling and harboured a dream of one day being principal of her own school. After Henry's death in 1905, faced with financial uncertainty and several unmarried daughters to support, Lucy Tisdall decided to take a risk. She sold the family's Toorak home and, together with her sister Alice, leased 'Ashburnham', a large Victorian villa at 106 North Road, Brighton. The plan was to open a private school, with Ethel and Constance as co-principals and Lucy, Alice and Theo teaching and managing the household affairs. This came as a "joyful surprise" to Constance, who was only informed of the plan after it had been finalised. The school was named Rosbercon after Henry's home village in County Wexford, Ireland. The crest, designed by son Bert Tisdall around 1910, featured a crowned letter 'A' above the motto "amor vincit omnia" ("love conquers all"), both inspired by a verse in Geoffrey Chaucer's "The Prioress's Tale": "about her arm she bore/A paire of bedes gauded all in grene,/And theron heng a broche of gold full shene,/On which there was first writ a crowned 'A',/And after, Amor Vincit Omnia." It was a motto Constance held close to her heart, embodying her values as a teacher. Reflecting in 1961, she wrote, "In a school without punishments, a school with love and understanding between teacher and pupil - with a love of teaching on one side, and a desire to learn on the other, love would indeed conquer all." The school's opening day in 1906 proved less than auspicious, with no pupils arriving at all. The women persisted and by the end of the first week, five students had been enrolled. From here, the school grew steadily in size. A new schoolroom designed by architect Harold Desbrowe-Annear was built in the house's orchard to accommodate the increasing numbers, but by 1911 the Tisdalls began looking for larger premises. They leased the nearby property 'Hazeldean' at 124 North Road and, during the 1912 school holidays, the Desbrowe-Annear schoolroom was raised onto a lorry drawn by sixteen horses and moved down the road to what would become Rosbercon's new home. In 1923, Constance instituted a modified version of the Dalton Plan, an education model based on individualised learning. Girls in senior years were encouraged to work more independently, making regular use of the reference library and working to a monthly assignment schedule. The school performed well academically and in competitive sport, but over time was eclipsed by the nearby Firbank Church of England Girls' Grammar School (established 1909), whose institutional backing provided it with access to wider resources and facilities than those of the small family-run Rosbercon. At the end of 1933, Ethel and Theo retired and Constance became principal of St Anne's Church of England Girls' Grammar School (now Gippsland Grammar) in Sale. Rosbercon was sold to Miss Iris Hay, who served as principal from 1934 until the school's closure in 1941. Following her own retirement in 1947, Constance Tisdall settled in Erica Avenue, East Malvern, in a house named 'Rosbercon' after her former school. She continued teaching English literature, mostly to migrants, and enjoyed regular visits from former students. Well into the late 1960s, old Rosbercon girls continued a tradition of coming together for an annual reunion on the first Saturday in November, on which day Constance would fly the school flag at her home.Large navy blue flag with horizontal maroon stripe at top and bottom, and school crest in centre. Stylised maroon "A" topped with yellow crown. Yellow scroll below with motto in navy blue letters: "AMOR.VINCIT.OMNIA".flag, school flag, rosbercon girls grammar school -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Eltham Lower Park, 20 April 2008
Originally a race course, the park has brought the community together with a variety of activities. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p45 Once used for horse racing, which attracted visitors from Melbourne, the Eltham Lower Park has brought the community together with a wide range of activities. Horse riding is now enjoyed as a recreation in the park as are other sports. The park also includes the Diamond Valley Railway miniature trains and a sanctuary for the rare and vulnerable Eltham Copper Butterfly. Eltham Lower Park, with other parks, forms an almost continuous green band from Eltham’s centre, along the Diamond Creek to the Yarra River.1 Before European settlement the Wurundjeri people met on this land, particularly at the junction of the Diamond Creek with the Yarra River, which they called Birr-arung. This is commemorated by the sculpture, Not just a Pretty Place by Aleks Danko, winner of the 2000 Nillumbik Art in Public Places Award. The first European to settle here was probably Henry Foley, who in 1841 used it as part of his pastoral run. Foley sold his leasehold to Joseph Wilson in 1845, who soon after sold it to Frederick Falkiner.2 During the 1840s the future park was part of a government square mile (2.6 sqkm) reserve, north of the Yarra, within the Parish of Nillumbik, later named Eltham. Soon the land was used for horse racing after nearby residents cleared ten acres (4ha) in the early 1850s. A three-quarter of a mile (1.2km) race secured the winner the £10 Publican’s Prize. In response to popular demand, the newly formed Eltham District Road Board petitioned the Surveyor General of the Colony of Victoria, in 1856, for 36 acres (14.6ha) of crown land for a racecourse and recreation. By 1858 the Eltham races had become an institution. ‘Many skirmishes occurred and the way home was paved with temptation, with sly-grog for sale.3 In the early 1870s, two jockeys were sons of the police officer in charge of the Eltham Police Station, Miles S Lyons.4 Another ten acres (4ha) was added to the area in 1866 and 12 acres (4.8ha) – Hohnes Hill – in 1870. In 1866, two acres (0.8ha) on the creek banks became an animal pound with William Walsh the pound keeper in 1870, but this was later incorporated into the park. By 1877 the area was called a public park but horse racing and training continued into the 1920s. In the mid-1900s trotters were trained on a circuit road. In 1953 the Eltham Pony Club was established and used a cross-country course on Hohnes Hill. From the mid 1950s the club held the Eltham Easter Fair at the park, later to include a procession along Main Road from the town centre to the park. The park also attracted picnic parties and campers from the inner suburbs as did Wingrove Park, and businesses catering for visitors, sprang up on the opposite side of Main Road. Bus-loads of school children visited the park for Gould League bird days in the 1960s. In 1979 the Eltham Shire Council bought Lenister Farm, linking the park with the Yarra River. The Lenister Farm wetland includes a bird hide, viewing platform and interpretive signs.5 Pioneer Henry Stooke, later Road Board chairman, bought the 11 acres (4.5ha) - later to become Lenister Farm - from the Crown in 1862. Stooke never lived on this site and the two houses at Lenister Farm were built in the 20th century. Since its formation in 1871, the Council has controlled this crown land, which it named Eltham Park. But in the 1920s Eltham Council bought land near the town centre for a park, which it named Eltham Central Park. To avoid confusion the Council renamed Eltham Park, Eltham Lower Park. Since 2004 the Yarra footbridge has linked the park with the Yarra Valley Metropolitan Park and the Main Yarra Trail.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham lower park, eltham park -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Plough, Syracuse Chilled Plow Co, 1876-1900
The Syracuse Chilled Plough Company was created in 1876 and specialised in the manufacture of agricultural ploughs. Harry Wiard invented the chilling process in plough manufacture. The company was originally founded as the Robinson Chilled Plough Company in 1876 and changed its name 3 years later. At its peak, in the early 20th century. The company made more than 100,000 horse-drawn ploughs and road scrapers of various designs that were sold from the Syracuse plant each year and exported around the world. The company slogan of the day was, “The sun never sets on a Syracuse plough." Eventually, other farming implements were added to the line. The company employed more than 300 people in its local plant, which covered a square block on the cities Near West Side. In 1910-11, Deere and Company began expanding its holdings, and with the success of the Syracuse Chilled Plough Company, Deere sought to acquire the company. The management of the Syracuse operation after John Deere took over remained in the hands of Wiard and Chase, and the manufacturing operations were left in Syracuse. The only change from previous Syracuse operations was the selling of the companies products through Deere retail outlets instead of directly to the trade. The factory in Syracuse continued to produce ploughs until 1955. The subject item in the Flagstaff collection is an early model Syracuse Chilled plough with a wooden beam frame it is very much lighter in weight and was adapted to work sandy or light loamy soil. This plough has a sloping landside, which tends to keep the clods and dirt from falling into the furrow, making the ploughman's work much more comfortable and easy. This design was made in eight sizes for both right and left-handed ploughing and became very popular in the far West and South of the USA. Note: The definition of a chill plough means : a plough having the share and mould-board of chilled semi steel or cast iron.The subject item is believed to be a very early plough given its wooden beam frame and was made before 1900 probably around 1880. This makes it a significant example of the types of plough that early settlers were using in Victoria. There would not be very many of this type of vintage plough left with a wooden beam and frame, making it today a desirable collector's item. Syracuse Wood Beam Chilled single furrow plough metal wheel in front. Syracuse Chiller Co Syracuse & 50 L stamped on ploughshare.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plough, syracuse chiller co, chiller plourh, farm equipment, furrow -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Scale, Early 20th century
The basic balance scale has been around for thousands of years and its accuracy has improved dramatically over the last several centuries, the principle behind this tool remains unchanged. Its parts include a fulcrum, a beam that balances on it, a pan at the end of the beam to hold the materials to be weighed, and a flat platform at the other for the counter-balancing weights. Balance scales that require equal weights on each side of the fulcrum have been used by everyone from apothecaries and assayers to jewellers and postal workers. Known as an unequal arm balance scale, this variety builds the counterweight into the device. Counter scales used in dry-goods stores and domestic kitchens often featured Japanned or (blackened) cast iron with bronze trims. Made by companies such as Howe and Fairbanks, the footed tin pans of these scales were often oblong, some encircled at one end so bulk items could be easily poured into a bag. Seamless pans were typically stamped from brass and given style names like Snuff (the smallest) and Birmingham (the largest). Some counter scales were designed for measuring spices, others for weighing slices of cake. In the 18th century, spring scales began to appear and would use the resistance of spring to calculate weights, which are read automatically on the scale’s face. The ease of use of spring scales over balance scales. One of the most common types of spring scales was the kitchen scale also known as a family or dial scale. Designed for horizontal surfaces, these vintage kitchen scales used the weight of goods in a pan at the top of the scale to force the spring down rather than the balance system. Such scales were common in early 20th century households and were sold by many companies. Many had flat weighing surfaces but some were topped by shallow pans. Companies such as Salters, Chatillon, and Fairbanks were the most popular brands used. These scales are significant as they identify one of the basic preparation items for the weighing of foodstuff in the family kitchen to prepare everyday meals. This item is significant as it gives a snapshot into domestic life within the average home in Australia around the turn of the twentieth century and is, therefore, an item with social relevance. Black cast iron, medium weighing scales, with a fulcrum which the beam that balances on, there is as scoop at one end for the material to be weighted and a flat circular disc at the other end that holds the weights. Around the cast iron base is an embossed leaf pattern. All the weights have their weight embossed within the casting.There are 5 weights, marked 2 oz, 4 oz,8 oz,1 lb,2 lb, This scale does not have any visual markings on the arms to identify a maker or true balance. It is therefore assumed that these scales were made for domestic use only.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, spring scale, scale -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Pill Maker Board
Before factory production became commonplace in medicine, dispensing was considered an art and pill machines such as these were a vital component of any chemist’s collection. This machine dates back to the days when your local chemist or apothecary bought, sold, and manufactured all his own drugs and medicines to everybody who lived within the local community. In Victorian times, there was no such thing as off-the-shelf medicine. Every tablet, pill, suppository, ointment, potion, lotion, tincture and syrup to treat anything from a sore throat to fever, headaches or constipation, was made laboriously by hand, by the chemist. Pill machines such as these first appeared in the mid-1700s and quickly became a staple of the Victorian chemist’s shop. A ‘pill mass’ of medicinal powders mixed with a binding agent would be hand-rolled into a pipe on the tile at the back of the machine. This would then be placed across the grooved brass plate and cut into equal-sized pills using the corresponding side of the roller. Once all the necessary ingredients for the pills had been measured and ground with a pestle and mortar a final ingredient was poured in, syrup – this acted as a binding-agent. You could then roll it into a sausage shape. The largest part of the machine is the board. This is set at an angle and is comprised of the rolling surface, the cutting grooves, and the collection-tray. The large flat surface is for rolling out the pill-paste into the sausage shape. This is then rolled towards the brass cutting-grooves. The paddle (the second piece) is flipped over so that the grooves there line up with the grooves on the board. Rollers on the ends of the paddle roll against the brass edges of the board, and they guide the paddle straight across the grooves, taking the pill-mass with it. The grooves on the paddle and the board slice up the pill-mass and, after rolling the thing back and forth a couple of times like a rolling-pin, the circular pills roll off the grooves and into the tray at the bottom. https://galwaycitymuseum.ie/blog/collections-spotlight-victorian-pill-making-machine/?locale=en The collection of medical instruments and other equipment in the Port Medical Office is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Pill making device including a grooved base board and grooved sliding board with two pill moulds.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, pills, pill maker, medicine, health -
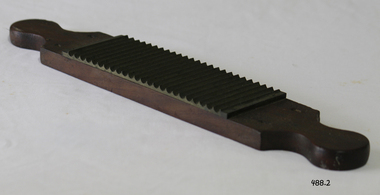 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Pill Rolling Pin
Used as tBefore factory production became commonplace in medicine, dispensing was considered an art and pill machines such as these were a vital component of any chemist’s collection. This machine dates back to the days when your local chemist or apothecary bought, sold, and manufactured all his own drugs and medicines to everybody who lived within the local community. In Victorian times, there was no such thing as off-the-shelf medicine. Every tablet, pill, suppository, ointment, potion, lotion, tincture and syrup to treat anything from a sore throat to fever, headaches or constipation, was made laboriously by hand, by the chemist. Pill machines such as these first appeared in the mid-1700s and quickly became a staple of the Victorian chemist’s shop. A ‘pill mass’ of medicinal powders mixed with a binding agent would be hand-rolled into a pipe on the tile at the back of the machine. This would then be placed across the grooved brass plate and cut into equal-sized pills using the corresponding side of the roller. Once all the necessary ingredients for the pills had been measured and ground with a pestle and mortar a final ingredient was poured in, syrup – this acted as a binding-agent. You could then roll it into a sausage shape. The largest part of the machine is the board. This is set at an angle and is comprised of the rolling surface, the cutting grooves, and the collection-tray. The large flat surface is for rolling out the pill-paste into the sausage shape. This is then rolled towards the brass cutting-grooves. The paddle (the second piece) is flipped over so that the grooves there line up with the grooves on the board. Rollers on the ends of the paddle roll against the brass edges of the board, and they guide the paddle straight across the grooves, taking the pill-mass with it. The grooves on the paddle and the board slice up the pill-mass and, after rolling the thing back and forth a couple of times like a rolling-pin, the circular pills roll off the grooves and into the tray at the bottom. https://galwaycitymuseum.ie/blog/collections-spotlight-victorian-pill-making-machine/?locale=enhe companion item to pill-maker base, item 488.2The collection of medical instruments and other equipment in the Port Medical Office is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century.Pill making device including a grooved base board and grooved sliding board with two pill mouldsNone.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, pill making, pill mould, medicine, health -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Picture, Lady Bay Ships at anchor, after November 1850
The photograph shows sailing ships and a wreck in Lady Bay, Warrnambool. Lady Bay was once a very busy port of trade in Warrnambool and was also called the Port of Warrnambool or Warrnambool Harbour. THE “ENTERPRISE” 1847-1850 The wooden, two-masted schooner Enterprise was built in New Zealand in 1847 and registered in Melbourne, Australia. The Enterprise carried cargos of agricultural produce and other commodities for trade between the ports of the Colony. On September 14, 1850, the Enterprise was at anchor in Lady Bay under its Master, James Gardiner Caughtt, loaded with a cargo of wheat and potatoes. A strong south-easterly wind caused the vessel to drag on its only anchor and the rudder was lost. The gale-force wind blew it sideways and it became grounded. A local indigenous man, Buckawall, braved the rough sea to take a line from the shore to the Enterprise. All five members of the crew were able to make it safely to land. The Enterprise was wrecked. The Enterprise wreck was in an area called Tramway Jetty in Lady Bay. Since then the area became the location of the Lady Bay Hotel and now, in 2019, it is in the grounds of the Deep Blue Apartments. In fact, with the constantly changing coastline through built-up sand, the wreck site is now apparently under the No 2 Caravan Park on Pertobe Road, perhaps 150 metres from the high tide. Its location was found by Ian McKiggan (leader of the various searches in the 1980s for the legendary Mahogany Ship). DIFFERENTIATING the New Zealand Schooner “Enterprise” from John Fawkner’s “Enterprize“ Dr Murray Johns, Melbourne, says in his article The Mahogany Ship Story “… As I documented in 1985, the Warrnambool wreck was of an entirely different ship, also called Enterprize [with the spelling ‘Enterprise’], but built in New Zealand in 1847. Fawkner’s ship had already been sold to Captain Sullivan in 1845 and was wrecked on the Richmond Pier in northern New South Wales early in 1847. “ - (further details are in NOTES: and FHMV documents) This photograph is significant for its association with the screw steamer SS Edina, heritage listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S199. She had endeared herself to the people of Port Phillip Bay as a passenger ferry, part of their own history and culture. She played a significant role in the Crimean War, the American Civil War and the gold rush in New Zealand. She also served western Victoria for many years in her cargo and passenger runs. The SS Edina is famous for being the longest serving screw steamer in the world. After spending her first nine years overseas she arrived in Melbourne and her work included running the essential service of transporting cargo and passengers between Melbourne and the western Victoria ports of Warrnambool, Port Fairy and Portland. The photograph is also significant for its association wreck of the schooner Enterprise, also listed on the Victorian Heritage Listed VHR S238, being a New Zealand built but Australian owned coastal trader. The wreck was also significant for its association with indigenous hero Buckawall who saved the lives of the five crew on board. Photograph titled "Lady Bay" depicts Lady Bay, Warrnambool, with vessels including SS Edina, the Peveril and the Tommy, with remains of the 1850 wreck of the schooner Enterprise in foreground. Titled, in hand written script, “”Lady Bay”, “S.S. ‘Edina’, the ‘Perevil’ & the ‘Tommy’ & the wrecked "Enterprise” Written in pencil on back “Council”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, enterprize, enterprise, port of warrnambool, warrnambool harbour, peveril, tommy, ss edina, pleasure steamer edina, warrnambool steam packet company, david hay, james gardiner caught, tramway jetty, buckawall, lady bay, steam ship, travel, trade, coastal trader, edina, dinah, cargo run, shipping, victoria, port phillip bay, john watson, edward byam, indigenous hero, indigenous rescue -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Peter Pidgeon, Grave of John and Mary Murray, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 5 April 2021
Irish-born John Murray and his wife Mary (daughter of Thomas Sweeney) married in 1849 and settled in Eltham North. John and Mary were amongst the earliest inhabitants of Eltham. John was a farmer and their block of about 80 acres, called ‘Laurel Hill’, was on the eastern side of the Diamond Creek, extending east to beyond Zig Zag Road. It was later extended southward by the purchase of a further 60 acres. He is recorded as a supporter on the petition for a school in Eltham and he served on the National School Board of the Eltham school. John died in 1867 and is buried in Eltham Cemetery with Mary and with two of their grandchildren. Their eldest son Johnnie inherited the property. Then in about 1902 his younger brother James purchased about 50 acres on the western side of the Diamond Creek immediately opposite Laurel Hill, extending west to slightly past Wattletree Road. Eltham North Reserve now lies just beyond the southern boundary. James built a family home on top of the hill on the northern boundary, together with a dairy and milking shed and a food cellar. It is thought that the barn with stables was already there. When Johnnie died in 1912, the two properties (though severed by both the creek and the railway line) effectively merged. The land was worked as an orchard with apples, pears, quinces, and possibly apricots and peaches. Later it became a dairy farm. By 1986, almost all the land had been sold off for residential subdivision and the house had been condemned as unfit for habitation. John's grandson Jim retained a small portion of the land and built a new house. He kept the old one as a storage shed, but it was demolished after he died in 1993. The very old barn is still standing. Located in the Roman Catholic section In Memory of John Murray Who died Dec. 1867 aged 50 years Also his wife Mary Murray Who died 7th Sep. 1909 aged 76 years And of their grandchildren Thomas and Mary Ellen DrainBorn Digitaleltham cemetery, gravestones, john murray, mary ellen drain, mary murray, thomas drain -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Match Safe, after 1830's
This match safe was amongst various items collected from a sea dive in Port Phillip Bay. The diver was the caretaker of the Port Lonsdale Lighthouse, who dived on various wrecks in the bay during the 1960's. After the caretaker's death, his son sold off many of the shipwreck artefacts. The match safe was purchased from the caretaker's son in the 1990's by a previous owner of the Marine Shop, Queenscliff, Victoria. Pocket match safes or match safes were small portable boxes, or containers made in a great variety of forms and shapes, each with lids or covers to contain matches and retain their quality. Matches came into use around the 1830's and were produced extensively between the years 1890 and 1920. During this period everyone carried strike anywhere matches, so they could ignite stoves, lanterns and other devices. Early matches were unreliable and prone to ignite from rubbing on one another or spontaneously. Accordingly, most people carried a match safe to house their matches. Wealthy people had ‘match safes made of gold or silver, while common folk had ones made of tin or brass. They were made throughout the world including the United Kingdom, in the U.S.A., continental Europe and Australia. Significant English makers of cases were, Sampson Mordan and Asprey & Co. Significant American manufacturers of match safes include Wm. B. Kerr, Gorham, Unger Brothers, Battin, Blackington , Whiting, George Scheibler and Shreve & Co. Different patterns and types run into thousands as well as plain and decorative examples. They were also made in a wide range of materials, including pressed brass, pressed tin, gunmetal, nickel silver, gold, bone, ivory, the wood of varying types, early plastics like tortoiseshell and Bakelite, and ceramics. A distinguishing characteristic of match safes is that they have a ribbed surface, usually on the bottom, for lighting the matches. The item gives a snapshot into the social development through it's application in every day use match safes were used at a time when there were no safety matches and the early use of matches was a dangerous affair given they were easily combustive if rubbed together in a pocket for example. The item is also an example of the shipwreck artefacts gathered along the southwest coast of Victoria.Match Safe; hollow brass cylinder with ribbed match striker texture on base and screw thread around top. Fitted brass lid has an internal screw thread, and the top's flat surface has concentric circles design, with a twisted rope pattern grip around the edge. flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, shipwreck artefact, port phillip bay, port lonsdale lighthouse, wreck, 1960’s diver, queenscliff marine shop, match container, match safe, matches, fire lighter, fire safety, heat, fire, portable match safe, 19th century -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Mitre Saw Set, 1930-1955's
This Bodmann mitre saw set was used in the making of components for the ship model Sovereign of the Seas. It is part of a collection of objects used by Jim Williams, maker of fine ship models from about 1930-1955. Most of the components for the models, as well as many of the tools, were handmade by Jim Williams. Jim’s family has donated the ship model “Sovereign of the Seas” and many tools, accessories and documents used in the making of this and other ship models have been donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. ABOUT the BRAND NAME ON THE SAW - BODMANN and CO, Germany In 1927 the Brisbane Courier Mail described Bodmann and Co of Reinscheid, Germany as "manufacturers of guaranteed tools and hardware. It appears that at least the saw has been re-badges and sold by Bodmann because (1) there are remnants of a label on the saw blade similar in shape to the Bodmann label on the mitre set (2) the removed label reveals the name and logo of "ULMIA Schutz OTT Marke" (3) one of the "Bodmann" labels on the saw handle has been applied in a crooked manner, almost leaving off the last "N". ULMIA is a German manufacturer of high quality woodworking tools. A drawing of a very similar mitre bset with saw can be seen on the ULMIA website. In 2002 the long established company ANKE of Swabian Alb, Germany (makers of cut timber, workbenches and countertops) bought out the name and trademark rights of ULMIA. HISTORY OF SOVEREIGN OF THE SEA (brief) Ship model of HMS Sovereign of the Seas, scale model of 17th Century English war ship, was handmade and carved from plans, enclosed in airtight glass case. All components of that model, including even the smallest pulleys, were hand crafted using tools designed and made by Jim. Outstanding details include functional rigging and moving cannons. Please see our record 3732 of the mode Sovereign of the Seas for further details of the ship and the Jim Williams. This mitre saw set is connected with the hobby and skill of ship model making that has been crafted as a leisure activity for many generations. The hobby is often chosen by serving and retired mariners who appreciate the connection with maritime history. This mitre saw set was used by local Warrnambool man, Jim Williams, who was employed at Cramond and Dickson clothing store, and then at Fletcher Jones menswear for 27 years. It was used in making components for the model of the historic ship, the Sovereign of the Seas. The Sovereign of the Seas was a historic 17th century English war ship with important maritime heritage. Bodmann Mitre Saw set model 348, comprising metal, adjustable mitre saw on timber stand, and metal hand saw with Bakelite handle. The mitre saw is labelled with the trademark of Bodmann, Germany, and stamped with the model number 348. The saw has Bodmann trademark badges on each side of the handle; the text on one of these badges is not quite aligned. The saw blade has remnants of a label under which the stamped logo of ULMIA Schutz OTT Marke is clearly visible. Saw is fitted with two metal guides that slide onto vertical posts on the mitre saw. Metal measuring guide holds the wood job to the correct length. Saw has a protective brown paper wrapper. This mitre saw set is part of a collection of tools and accessories once used by Jim Williams, maker of a series of ship models 1930-1955 including “HMS Sovereign of the Seas”.On mitre saw- 2x logos "REGISTERED / BODMANN / TRADE MARK" and embedded stamp “348”. On saw - Remnant of logo on blade “ULMIA Schutz OTT Marke” with image of a church-like tall building, and 2x , "BEST QUALITY / BODMANN / MADE IN GERMANY” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, jim williams, james bernard williams, ship model hobby, ship model tools, ship model making equipment, ship model making accessories, wood working tool, model making tool, mitre box set, mitre saw, bodmann and co reinscheid, germany, ulna ott of of swabian alb, germany, anke of swabian alb, germany, sovereign of the sea, ship model, hobby, ship model tool, mitre saw set -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947.The photographer has captured the crew in a lifeboat surrounded by sea. The lifeboat is approaching the HMAS Swan II. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in May 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of rescue of crew from H.M.A.S. Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Men in life boat surrounded by water. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at that time. flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, lifeboat, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking of the ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. This black and white photograph showing the vessel at sea is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The photograph is taken from a nearby vessel, likely to be the HMAS Swan II, which took the survivors onboard. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking of the ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Figures onboard a vessel are looking towards figures on the sinking vessel. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the starboard side of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the sinking ship with the crew still onboard. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941 . The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Figures can be seen onboard the damaged vessel. The number of the ship-type is clearly visible on this starboard profile of the ship. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.Text on side of ship "J202"flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the rescue boat approaching the sinking ship with the crew onboard. There small boat has several figures onboard. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Figures onboard a larger vessel look across at rescue vessel heading towards the sinking ship. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the damaged ship tilting down on the starboard side. The ship-type number is still mostly visible. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea, with, it seems, crew still on board.. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the ship leaning at an angle towards the sea. There appears to be figures near the bow. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the ship tilting towards port side and the bow dipping. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued, transferring from one vessel to another, which is likely to be the HMAS Swan II. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Survivors are helped from one vessel to another by seamen. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney, 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows injured men being assisted onboard a vessel at sea. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Image shows men in a lifeboat beside men in a ship, at sea. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued, transferring from a lifeboat to the ship. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows men being taken onboard a ship from a small boat. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper
