Showing 702 items
matching iron roof
-
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Myoora, 405 Alma Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H0490 From the Victorian Heritage Register Database - Citation for Myoora https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/275 (as at 6/10/2020) Myoora, 405 Alma Road, North Caulfield, was designed by Reed, Henderson & Smart and can be attributed to Anketell Henderson. It was built in 1886 and 1887 for Thomas Christian, who had founded the fabled gold mine, the Day Dawn at Charters Towers. He never occupied the house although his widow lived there for some time. The house was subdivided into three and later six flats. Myoora was one of many large mansions on broad acres with gardens in Caulfield. Perhaps the grandest was Labassa. The mansions date from the 1850s through to the late 1890s. The siting of Myoora on a ridge influenced its planning and composition. A central hall and corridor along the ridge is entered from the centre of the more formal north facade. The entrance is marked by an elaborately detailed tower. A stair turret provides a second accent. The western end of the building is completed by a massively detailed chimney as the service wing. The south facade enjoyed an outlook to port phillip from a two-storey cast iron verandah. Bay windows, chimneys, the tower and the turret and minor details are brought together in a sophisticated asymmetrical composition. This is reflected in the planning. The asymmetry of Myoora pivoting on the tower is the most notable feature of the building. The walls are built of cement rendered brick. The cement render has not been painted. The roof is slate. The balconies and verandah are cast iron. The footings and cellar are bluestone. The architectural firm Reed, Henderson & Smart was very prominent in Victoria in the nineteenth century. Anketell Henderson was an eminent and well respected member of the profession. He worked successfully in London and interstate as well as in Victoria. They were better known for commercial and public buildings. Myoora is an important private commission. The style of Myoora is a combination of details from the Continental and English Renaissance through the boom style and the Queen Anne style. There is also an early influence from the American Romanesque style especially in the stair turret. The latter style was important at the turn of the century and Myoora is a significant precursor. Other buildings of a similar scale survive in Caulfield and elsewhere. Labassa, the most fabulous, is quite different stylistically as are most of the other comparable mansions. Stonnington is perhaps closer but relies on different details from the Queen Anne style and lacks any American influence. For its historical associations through its owners and architects, for its style and composition and for its intactness, Myoora is significant at a State level. The craftmanship of Myoora is what could be expected of a building of the time and type. It is relatively intact and in fair condition. The main staircase has been removed, minor alterations to decorative features have occurred and additions have been made to the exterior.Page 13 of Photograph Album including three black and white photographs. Two of the photos are in a portrait orientation and arranged in the top half of the page. The other photo in landscape orientation is towards the left on the bottom section of the page.Handwritten: 13 [bottom left]caulfield north, trevor hart, alma road, mansion, myoora, tower, thomas christian, 1880's, queen anne, cement rendered brick, unpainted, balconies, verandahs, anketell henderson, continental and english renaissance, american romanesque, cast iron balconies, views, cast iron work, reed henderson & smart, flats, gardens, asymmetrical style, slate roofs -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Myoora, 405 Alma Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H0490 From the Victorian Heritage Register Database - Citation for Myoora https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/275 (as at 6/10/2020) Myoora, 405 Alma Road, North Caulfield, was designed by Reed, Henderson & Smart and can be attributed to Anketell Henderson. It was built in 1886 and 1887 for Thomas Christian, who had founded the fabled gold mine, the Day Dawn at Charters Towers. He never occupied the house although his widow lived there for some time. The house was subdivided into three and later six flats. Myoora was one of many large mansions on broad acres with gardens in Caulfield. Perhaps the grandest was Labassa. The mansions date from the 1850s through to the late 1890s. The siting of Myoora on a ridge influenced its planning and composition. A central hall and corridor along the ridge is entered from the centre of the more formal north facade. The entrance is marked by an elaborately detailed tower. A stair turret provides a second accent. The western end of the building is completed by a massively detailed chimney as the service wing. The south facade enjoyed an outlook to port phillip from a two-storey cast iron verandah. Bay windows, chimneys, the tower and the turret and minor details are brought together in a sophisticated asymmetrical composition. This is reflected in the planning. The asymmetry of Myoora pivoting on the tower is the most notable feature of the building. The walls are built of cement rendered brick. The cement render has not been painted. The roof is slate. The balconies and verandah are cast iron. The footings and cellar are bluestone. The architectural firm Reed, Henderson & Smart was very prominent in Victoria in the nineteenth century. Anketell Henderson was an eminent and well respected member of the profession. He worked successfully in London and interstate as well as in Victoria. They were better known for commercial and public buildings. Myoora is an important private commission. The style of Myoora is a combination of details from the Continental and English Renaissance through the boom style and the Queen Anne style. There is also an early influence from the American Romanesque style especially in the stair turret. The latter style was important at the turn of the century and Myoora is a significant precursor. Other buildings of a similar scale survive in Caulfield and elsewhere. Labassa, the most fabulous, is quite different stylistically as are most of the other comparable mansions. Stonnington is perhaps closer but relies on different details from the Queen Anne style and lacks any American influence. For its historical associations through its owners and architects, for its style and composition and for its intactness, Myoora is significant at a State level. The craftmanship of Myoora is what could be expected of a building of the time and type. It is relatively intact and in fair condition. The main staircase has been removed, minor alterations to decorative features have occurred and additions have been made to the exterior.Page 14 of Photograph Album including two black and white photographs that are arranged in landscape orientation in the centre of the page with one beneath the other. Handwritten: "Myoora" 405 Alma Road [top right] /Neg 87 c1890 [under top photo]/ Neg 89 c1890/ [under bottom photo]/ 14 [bottom right]caulfield north, trevor hart, alma road, mansion, myoora, tower, thomas christian, 1880's, queen anne, cement rendered brick, unpainted, balconies, verandahs, anketell henderson, continental and english renaissance, american romanesque, cast iron balconies, gardens, views, cast iron work, reed henderson & smart, flats, asymmetrical style, slate roofs -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Myoora, 405 Alma Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H0490 From the Victorian Heritage Register Database - Citation for Myoora https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/275 (as at 6/10/2020) Myoora, 405 Alma Road, North Caulfield, was designed by Reed, Henderson & Smart and can be attributed to Anketell Henderson. It was built in 1886 and 1887 for Thomas Christian, who had founded the fabled gold mine, the Day Dawn at Charters Towers. He never occupied the house although his widow lived there for some time. The house was subdivided into three and later six flats. Myoora was one of many large mansions on broad acres with gardens in Caulfield. Perhaps the grandest was Labassa. The mansions date from the 1850s through to the late 1890s. The siting of Myoora on a ridge influenced its planning and composition. A central hall and corridor along the ridge is entered from the centre of the more formal north facade. The entrance is marked by an elaborately detailed tower. A stair turret provides a second accent. The western end of the building is completed by a massively detailed chimney as the service wing. The south facade enjoyed an outlook to Port Phillip from a two-storey cast iron verandah. Bay windows, chimneys, the tower and the turret and minor details are brought together in a sophisticated asymmetrical composition. This is reflected in the planning. The asymmetry of Myoora pivoting on the tower is the most notable feature of the building. The walls are built of cement rendered brick. The cement render has not been painted. The roof is slate. The balconies and verandah are cast iron. The footings and cellar are bluestone. The architectural firm Reed, Henderson & Smart was very prominent in Victoria in the nineteenth century. Anketell Henderson was an eminent and well respected member of the profession. He worked successfully in London and interstate as well as in Victoria. They were better known for commercial and public buildings. Myoora is an important private commission. The style of Myoora is a combination of details from the Continental and English Renaissance through the boom style and the Queen Anne style. There is also an early influence from the American Romanesque style especially in the stair turret. The latter style was important at the turn of the century and Myoora is a significant precursor. Other buildings of a similar scale survive in Caulfield and elsewhere. Labassa, the most fabulous, is quite different stylistically as are most of the other comparable mansions. Stonnington is perhaps closer but relies on different details from the Queen Anne style and lacks any American influence. For its historical associations through its owners and architects, for its style and composition and for its intactness, Myoora is significant at a State level. The craftmanship of Myoora is what could be expected of a building of the time and type. It is relatively intact and in fair condition. The main staircase has been removed, minor alterations to decorative features have occurred and additions have been made to the exterior.Page 16 of Photograph Album including three black and white photographs. Two are arranged in landscape orientation on the right hand side of the page with the other photo in portrait mode on the left hand side. Handwritten: views from "Myoora" 405 Alma Road [top right] / Neg 181 Dec 1972 [under left side photo] / Neg 189 Dec 1972 [under bottom right photo] / 16 [bottom right]caulfield north, trevor hart, alma road, mansion, myoora, tower, thomas christian, 1880's, queen anne, cement rendered brick, unpainted, balconies, verandahs, anketell henderson, continental and english renaissance, american romanesque, cast iron balconies, panoramic views, streetscapes, cast iron work, reed henderson & smart, gardens, asymmetrical style, slate roofs, chimneys -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Myoora, 405 Alma Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H0490 From the Victorian Heritage Register Database - Citation for Myoora https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/275 (as at 6/10/2020) Myoora, 405 Alma Road, North Caulfield, was designed by Reed, Henderson & Smart and can be attributed to Anketell Henderson. It was built in 1886 and 1887 for Thomas Christian, who had founded the fabled gold mine, the Day Dawn at Charters Towers. He never occupied the house although his widow lived there for some time. The house was subdivided into three and later six flats. Myoora was one of many large mansions on broad acres with gardens in Caulfield. Perhaps the grandest was Labassa. The mansions date from the 1850s through to the late 1890s. The siting of Myoora on a ridge influenced its planning and composition. A central hall and corridor along the ridge is entered from the centre of the more formal north facade. The entrance is marked by an elaborately detailed tower. A stair turret provides a second accent. The western end of the building is completed by a massively detailed chimney as the service wing. The south facade enjoyed an outlook to port phillip from a two-storey cast iron verandah. Bay windows, chimneys, the tower and the turret and minor details are brought together in a sophisticated asymmetrical composition. This is reflected in the planning. The asymmetry of Myoora pivoting on the tower is the most notable feature of the building. The walls are built of cement rendered brick. The cement render has not been painted. The roof is slate. The balconies and verandah are cast iron. The footings and cellar are bluestone. The architectural firm Reed, Henderson & Smart was very prominent in Victoria in the nineteenth century. Anketell Henderson was an eminent and well respected member of the profession. He worked successfully in London and interstate as well as in Victoria. They were better known for commercial and public buildings. Myoora is an important private commission. The style of Myoora is a combination of details from the Continental and English Renaissance through the boom style and the Queen Anne style. There is also an early influence from the American Romanesque style especially in the stair turret. The latter style was important at the turn of the century and Myoora is a significant precursor. Other buildings of a similar scale survive in Caulfield and elsewhere. Labassa, the most fabulous, is quite different stylistically as are most of the other comparable mansions. Stonnington is perhaps closer but relies on different details from the Queen Anne style and lacks any American influence. For its historical associations through its owners and architects, for its style and composition and for its intactness, Myoora is significant at a State level. The craftmanship of Myoora is what could be expected of a building of the time and type. It is relatively intact and in fair condition. The main staircase has been removed, minor alterations to decorative features have occurred and additions have been made to the exterior.Page 17 of Photograph Album including four black and white photographs. All are arranged in landscape orientation with two on the top half of the page and the other two below.Handwritten: Neg 185 Dec 1972 [under top left photo] / Dec 1972 [under top right photo] / Dec 1972 [under bottom left photo] / Neg 153 Dec 1972 [under bottom right photo] / 17 [bottom left]caulfield north, trevor hart, alma road, mansion, myoora, tower, thomas christian, 1880's, queen anne, cement rendered brick, unpainted, balconies, verandahs, anketell henderson, continental and english renaissance, american romanesque, cast iron balconies, panoramic views, streetscapes, cast iron work, reed henderson & smart, gardens, asymmetrical style, slate roofs -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Myoora, 405 Alma Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H0490 From the Victorian Heritage Register Database - Citation for Myoora https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/275 (as at 6/10/2020) Myoora, 405 Alma Road, North Caulfield, was designed by Reed, Henderson & Smart and can be attributed to Anketell Henderson. It was built in 1886 and 1887 for Thomas Christian, who had founded the fabled gold mine, the Day Dawn at Charters Towers. He never occupied the house although his widow lived there for some time. The house was subdivided into three and later six flats. Myoora was one of many large mansions on broad acres with gardens in Caulfield. Perhaps the grandest was Labassa. The mansions date from the 1850s through to the late 1890s. The siting of Myoora on a ridge influenced its planning and composition. A central hall and corridor along the ridge is entered from the centre of the more formal north facade. The entrance is marked by an elaborately detailed tower. A stair turret provides a second accent. The western end of the building is completed by a massively detailed chimney as the service wing. The south facade enjoyed an outlook to port phillip from a two-storey cast iron verandah. Bay windows, chimneys, the tower and the turret and minor details are brought together in a sophisticated asymmetrical composition. This is reflected in the planning. The asymmetry of Myoora pivoting on the tower is the most notable feature of the building. The walls are built of cement rendered brick. The cement render has not been painted. The roof is slate. The balconies and verandah are cast iron. The footings and cellar are bluestone. The architectural firm Reed, Henderson & Smart was very prominent in Victoria in the nineteenth century. Anketell Henderson was an eminent and well respected member of the profession. He worked successfully in London and interstate as well as in Victoria. They were better known for commercial and public buildings. Myoora is an important private commission. The style of Myoora is a combination of details from the Continental and English Renaissance through the boom style and the Queen Anne style. There is also an early influence from the American Romanesque style especially in the stair turret. The latter style was important at the turn of the century and Myoora is a significant precursor. Other buildings of a similar scale survive in Caulfield and elsewhere. Labassa, the most fabulous, is quite different stylistically as are most of the other comparable mansions. Stonnington is perhaps closer but relies on different details from the Queen Anne style and lacks any American influence. For its historical associations through its owners and architects, for its style and composition and for its intactness, Myoora is significant at a State level. The craftmanship of Myoora is what could be expected of a building of the time and type. It is relatively intact and in fair condition. The main staircase has been removed, minor alterations to decorative features have occurred and additions have been made to the exterior.Page 18 of Photograph Album including four black and white photographs. All are arranged in landscape orientation with two on the top half of the page and the other two below.Handwritten: views from "Myoora" 405 Alma Road / [top right hand] / Neg 188 Dec 1972 [under top left photo] / Dec 1972 [under top right photo] / Neg 184 Dec 1972 [under bottom left photo] / Neg 168 Dec 1972 [under bottom right photo] / 18 [bottom right]caulfield north, trevor hart, alma road, mansion, myoora, tower, thomas christian, 1880's, queen anne, turret, cement rendered brick, unpainted, balconies, verandahs, anketell henderson, continental and english renaissance, american romanesque, cast iron balconies, panoramic views, streetscapes, cast iron work, reed henderson & smart, asymmetrical style, gardens, slate roofs -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Halstead, Bambra Road, Circa 1972
... is the substantial three storey tower with its Mansard roof and cast-iron ...This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.From the Victorian Heritage Register Database - Citation for Halstead, 23 Bambra Road as at (as at 12/10/2020) https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/276: Halstead is believed to be the oldest standing residence in Caulfield constructed in 1857 with subsequent additions during the 19th Century. The house was built for and owned by James Dickson, a stock agent, until his death in 1880. Although on a much reduced parcel of land, Halstead is one of the few remaining remnants of Caulfield when it was an area of mansion houses occupied by town residing squatters, professional and business men. It is important for its place in the socio-economic history of south eastern suburban Melbourne, the inland pattern of development stretching from Malvern through Murrumbeena. Architecturally the single storey building displays a history of alteration and addition. Its main front presents with a single storey cast iron verandah across the full width, including the two pavilion wings at each end. Located towards the rear on the Halstead Street side is the substantial three storey tower with its Mansard roof and cast-iron balustrade which makes the house clearly visible from Halstead Street and Bambra Road. Because of internal alteration the importance of the building relates to the exterior only of the main house. Halstead is believed to be the oldest standing residence in the city of Caulfield. https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/43645: "Halstead" is regionally important as a surviving large villa from the early Victorian (1850's) period, offering insights into the lifestyles of the privileged in Caulfield at that time. The later tower is of architectural interest for its use of Medieval Romanesque enrichment.Page 33 of Photograph Album with one landscape photograph of the exterior of Halstead, taken from the street.Hand written: 33 [bottom left] trevor hart, caulfield north, bambra road, 1850's, halstead, james dickson, mansion, villa residence, cast iron verandah, pavillion wings, halstead street, victorian, tower, balustrading, decorative brackets, mansard roof, brick, slate roof, curved windows, single storey mansions, cast iron work, medieval romanesque style, slate roofs, gardens -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Kynaston now Kahlyn, Bambra Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/35575 From: Glen Eira Heritage Management Plan (1996) by Andrew Ward and Associates Significance: "Kynaston" is locally important as a large late Victorian villa residence, demonstrating something of the lifestyle to which a senior government bureaucrat could aspire during the late nineteenth century boom period. The design of the verandah, though defaced, is unusual in Caulfield and, therefore, important. A substantial late Victorian stuccoed Bool11 style villa residence with tower surmounting the entrance porch, fluted columns to the ground level verandah and parapeted balcony over, now built in with a sympathetic addition at the north-west corner. The principal rooms and staircase are intact and representative of the period.Page 34 of Photograph Album with two portrait photographs of exterior of Kynaston - 2 views highlighting the front of the mansionHand written: "Kynaston" now "Kahlyn" Bambra Road [top right] / 34 [bottom right] trevor hart, caulfield north, bambra road, 1850's, mansion, villa residence, cast iron verandah, victorian, decorative brackets, slate roof, curved windows, 1880's, kynaston, kynaston l murray, kahlyn private hospital, kahlyn, return verandah, enclosed verandah, cast iron work, double storey mansions, towers, balconies -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Glenferrie Street, 4, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages. From Glen Eira Heritage Management Plan 1996 by Andrew Ward: In 1905, most of portion 27 was vacant land, however Glenferrie Street had been formed and the land subsequently subdivided. In 1906, Robert Joseph Haddon, architect and painter, designed and built for his private residence, a brick house on the west side. Haddon named the house "Anselm". Also built on the property were a garage and fibro cement studio. "Anselm" is architecturally important at the State level as a substantially intact, highly personalised and boldly expressed house expressive the Arts and Crafts movement and incorporating Art Nouveaux enrichment in a variety of forms, the use of ornamental terra cotta tiles to the comer tower being of special note. Its importance at the State level is strengthened by its place as the home of the noted architect and Melbourne's most influential exponent (Freeland, J.M., Architecture in Australia, p. 213) of the Art Nouveaux movement.https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/4442 Victorian Heritage Register: What is significant? Anselm was designed by noted English born architect Robert Joseph Haddon(1866-1929) as his own house and constructed in 1906. A single storey Arts and Crafts influenced red brick house with attic, Anselm has a pyramidal slate roof with prominent chimney stacks. There is a octagonal corner tower with saucer shaped domed roof surmounted by a weather vane, and the tower has decorative terracotta panels immediately below the eaves line. The front door opens immediately into a large living or common room, screened from view by a timber and bottle glass screen. The large room was designed to function as a drawing and dining room. The house is rich with hand crafted details including door and window furniture, wrought iron gutter brackets, fireplaces (one with built in wood box), and fire tools. The interior decoration includes hand painted frieze of Port Phillip in the study, and a hand painted frieze of turbulent sea with sailing boats in the tiled bathroom. There is a small hand painted tile at the base of the tower which states ?This building was erected AD1906 from designs by Robt J Haddon FRIBA,Lond FRIVA Melb Architect?. He also designed an attic addition which was constructed in 1927. Anselm is substantially intact although the double casement window immediately to the south of the front door was originally circular....Page 60 of Photograph Album with three exterior photographs (one portrait and two landscape) of Anselm.Hand written: 4 Glenferrie Street [top right] / ANSELM 4 Glenferrie St [under top photo] / 60 [bottom right] trevor hart, anselm, art nouveaux, arts and crafts, tower, bay window, glenferrie street, robert joseph haddon, 1900's, terra cotta tiles, double storey, caulfield north, corner tower, gates, cast iron work -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Glenferrie Street, 4, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages. From Glen Eira Heritage Management Plan 1996 by Andrew Ward: In 1905, most of portion 27 was vacant land, however Glenferrie Street had been formed and the land subsequently subdivided. In 1906, Robert Joseph Haddon, architect and painter, designed and built for his private residence, a brick house on the west side. Haddon named the house "Anselm". Also built on the property were a garage and fibro cement studio. "Anselm" is architecturally important at the State level as a substantially intact, highly personalised and boldly expressed house expressive the Arts and Crafts movement and incorporating Art Nouveaux enrichment in a variety of forms, the use of ornamental terra cotta tiles to the comer tower being of special note. Its importance at the State level is strengthened by its place as the home of the noted architect and Melboume's most influential exponent (Freeland, J.M., Architecture in Australia, p. 213) of the Art Nouveaux movement. Victorian Heritage Register https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/4442 What is significant? Anselm was designed by noted English born architect Robert Joseph Haddon(1866-1929) as his own house and constructed in 1906. A single storey Arts and Crafts influenced red brick house with attic, Anselm has a pyramidal slate roof with prominent chimney stacks. There is a octagonal corner tower with saucer shaped domed roof surmounted by a weather vane, and the tower has decorative terracotta panels immediately below the eaves line. The front door opens immediately into a large living or common room, screened from view by a timber and bottle glass screen. The large room was designed to function as a drawing and dining room. The house is rich with hand crafted details including door and window furniture, wrought iron gutter brackets, fireplaces (one with built in wood box), and fire tools. The interior decoration includes hand painted frieze of Port Phillip in the study, and a hand painted frieze of turbulent sea with sailing boats in the tiled bathroom. There is a small hand painted tile at the base of the tower which states ?This building was erected AD1906 from designs by Robt J Haddon FRIBA,Lond FRIVA Melb Architect?. He also designed an attic addition which was constructed in 1927. Anselm is substantially intact although the double casement window immediately to the south of the front door was originally circular....Page 61 of Photograph Album with one exterior photograph (portrait) of Anselm.Hand written: 61 [bottom left] trevor hart, anselm, art nouveaux, arts and crafts, tower, bay window, glenferrie street, robert joseph haddon, 1900's, terra cotta tiles, double storey, caulfield north, corner tower, brick house, attics -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Clarinda Street, Circa 1972
... verandahs cast iron work slate roofs Handwritten: Clarinda Street ...This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages. Page 44 of Photograph Album with one photograph of a house at 14 Clarinda Street.Handwritten: Clarinda Street [top right hand corner] / 14 Clarinda Street Elsternwick with Caulfield South written in different pen underneath / 44 [bottom right]trevor hart, caulfield south, clarinda street, verandahs, cast iron work, slate roofs -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Noel L. Harvey, Yendon Railway Station, 1968, 03/12/1968
... jambs and chimney. The roof is corrugated iron. The platform.... The roof is corrugated iron. The platform edge is also of bluestone ...Buninyong had no railway station so residents would travel to Yendon to catch the train. The Yendon Railway Station building was demolished soon after this photograph was taken. The bluestone was purchased by John Vernon, and was used to construct retaining walls in a garden enclosure between the first two buildings at the new Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education campus at Mt Helen. This is now known as the courtyard between building 'F' and building 'G' at the University of Ballarat mt Helen Campus. The following article was published in the Ballarat Courier on 06 December 1968. 'Yendon Station to be demolished - The old bluestone railway station at Yendon is to be demolished. C.A.D. Fisken told Buninyong Shire Council of the proposal at its meeting yesterday. Fortunately, he said, the beautiful stonework would not be lost. It would be used and incorporated in the new School of Mines building at Mt Helen. the retention of the century-old building was the subject of representations by Council to the Railways following the closure of the station for goods traffic 'some time ago'. The building had also been noted by the National Trust as one of special interest. The Railways Department advised the meeting that an inspection had been made at the Yendon level crossing, but no recommendation could be made at present for installation of flashing light signals.'Bluestone building with dressed bluestone door and window jambs and chimney. The roof is corrugated iron. The platform edge is also of bluestone construction. The building is the former Yendon Railway Station (now demolished) on the Ballarat -Geelong main line (the original Melbourne to Ballarat mainline). When the line was opened, this station may have been originally called Buninyong as it was built a number of years before the Ballarat to Buninyong branch line was built. This this has subsequently caused some confusion. The station was later renamed Yendon. Verso in blue ballpoint pen 'No 47 Yendon Railway Stn' Stamped in purple ink 'N.L. Harvey & Son, Photographers, 131 Sturt Streeet Ballarat, Phone 25766, After hours 23397, Will photograph anywhere anytime any place. (in pen 3/12/68),university of ballarat, ballarat institute of advanced education, yendon, railway, bluestone, john vernon -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Historical, Flagstaff Hill, Harbourmaster’s Quarters, 1970s
... . On the left of the red roofed residence are iron buildings used.... On the left of the red roofed residence are iron buildings used ...The photograph shows a cottage, Harbourmaster’s quarters that still stands on the east of the Lady Bay Lighthouse and Historic Precinct at Flagstaff Hill in Warrnambool. The name was changed to the Lighthouse Lodge, and today guests can stay at the property. This photograph, a print, is one of a set of five that show the site of Flagstaff Hill. It is presumed to have been taken by John Lindsay, Founding Director of Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village. One of the photographs in the set has the pencil inscription "Photo J Lindsay". It was taken in the early 1970s during the initial stages of the development of Flagstaff Hill as a Museum and Maritime Village. The photographs belonged to the donor's grandparents, who lived in the Warrnambool district of Allansford/Naringal. The photograph is a record of the site and surrounds of Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village before its development and opening in 1975. It shows the cottage on the east of the Lighthouse Complex,. The building is now known as Lighthouse Lodge. The photograph is significant for recording the location and condition of the residence on the Hill.Coloured photograph, glassy print, one of a set of five. Photograph shows the cream timber cottage, Harbourmaster’s quarters to the east of the lighthouse complex at Flagstaff Hill, Warrnambool. On the left of the red roofed residence are iron buildings used, at the time, by the Lands Department. The photograph's paper has the printer's watermark on the back. The early 1970s photograph is presumed to have been by John Lindsay, Warrnambool.Label on the back: "WOODEN RESIDENCE TO THE EAST OF THE PROPERTY / The gun emplacements are immediately behind, and the iron huts to the left rear of the residence are used by the Lands Department who plan to vacate, for other premises."flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, 1970s, photograph, flagstaff hill site, john lindsay, cannon emplacement, residence, wooden residence, timber residence, iron huts, lands department -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Metal ship's bolt, Russell & Co, Circa 1886
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution meant that shipbuilders could build ships using iron. These iron ships could be much larger, with more space for cargo and they didn't need as much work to keep them in good condition. Isambard Kingdom Brunel's "Great Britain" built in 1843, was the first ship to be built entirely of wrought iron. In the 1880's steel began to be used instead of iron. Ships also began to be fitted with steam engines although a great deal of coal was needed to travel even short distances. For this reason, ships continued to be fitted out with sails even though some came with engines. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. This particular artefact was one of many found by John Laidlaw (a local Warrnambool diver) when diving on the Falls of Halladale in the 1960's. In August 1973, John Laidlaw and Stan McPhee went on to discover the underwater location of the Schomberg - a passenger ship sailing from Liverpool that ran aground on December 26th 1855 near Peterborough which now lies in 825 metres of water. When John Laidlaw died, his family donated a number of artefacts to Flagstaff Hill.This item is significant as it was recovered from the Falls of Halladale by a local diver. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).A thick metal bolt with a flattened head at one end, a smooth shaft approximately 4 cm long followed by a 6 cm long screw section - some of which is damaged and flattened. The end appears to have had a part broken off and is showing rust damage. flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill divers, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, great ocean road, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, falls of halladale, falls of halladale wreck, shipwreck artefact, artefact, diver, john laidlaw, bolt, metal bolt, metal artefact, ship's bolt -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Brass rod, Russell & Co, Circa 1886
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution meant that shipbuilders could build ships using iron. These iron ships could be much larger, with more space for cargo and they didn't need as much work to keep them in good condition. Isambard Kingdom Brunel's "Great Britain" built in 1843, was the first ship to be built entirely of wrought iron. In the 1880's steel began to be used instead of iron. Ships also began to be fitted with steam engines although a great deal of coal was needed to travel even short distances. For this reason, ships continued to be fitted out with sails even though some came with engines. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. This particular artefact was one of many found by John Laidlaw (a local Warrnambool diver) when diving on the Falls of Halladale in the 1960's. In August 1973, John Laidlaw and Stan McPhee went on to discover the underwater location of the Schomberg - a passenger ship that ran aground on December 26th 1855 near Peterborough which now lies in 825 metres of water. When John Laidlaw died, his family donated a number of artefacts to Flagstaff Hill.This item is significant as it was recovered by a local diver from the Falls of Halladale. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Long, slender, smooth brass rod tapering from 1.5 cm diameter at one end to .8 cm and widening back out to 1.5 cm at opposite end. One end has a smooth, rounded edge and the other end curves in and out with the end showing evidence of a piece having been broken off.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill divers, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, falls of halladale, falls of halladale wreck, shipwreck artefact, artefact, brass artefact, brass rod, brass fitting, diver, john laidlaw -
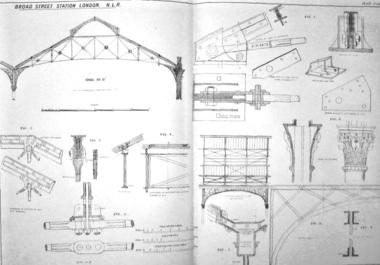 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Iron Roofs: examples of design, 1884 (exact)
... (black & white). 37 p. + plates. Iron Roofs: examples of design ...Book. Large brown hard cover. Title written in gold on front cover and on spine. Manufacturer name also written in gold on spine. Illustrations, plates (black & white). 37 p. + plates.civil engineering, design, roofing, iron and steel -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Frank Wright at the Ballarat City Baths, c1930, 1930
Frank Wright was a renown resident of Smeaton, where he was born. He lived at Laura Villa, and attended Smeaton State School. His father William was a gold miner and his mother's name was Sarah. Their family won many singing and instrumental awards. Frank was tutored by Percy Code and became the Australian Open Cornet Champion by the age of eighteen. A year later, Frank conducted the City of Ballarat Band, and later the Ballarat Soldiers’ Memorial Band. He formed the Frank Wright Frisco Band and Frank Wright and his Coliseum Orchestra. These bands won many South Street awards, and Frank as conductor won many awards in the Australian Band Championship contest. In 1933 Frank Wright sailed to England to conduct the famous St Hilda’s Band and was later appointed Musical Director of the London County Council, where he organized many amazing concerts in parks, in and around the London district. He was made Professor of Brass and Military Band Scoring and conducted at the Guildhall of Music and Drama. Frank was often invited to adjudicate Brass Band Championships around Europe, in Australia, including South Street and in New Zealand. The Frank Wright Medal at the Royal South Street competition is awarded to an individual recognized as making an outstanding contribution to brass music in Australia..1) black and white photograph of a man standing in front of a driving tower beside a swimming pool. Surrounding the pool is a corrugated iron structure containing walls, changing booths and a roof. This is supported by timber posts. The man is dressed in swimming costume (singlet and trunks) and is Frank Wright. The place is the Ballarat City Baths. .2) black and white photograph of a man standing on a spring board over a swimming pool. Surrounding the pool is a corrugated iron structure containing walls, changing booths and a roof. This is supported by timber posts. The man is dressed in swimming costume (singlet and trunks) and is Frank Wright. The place is the Ballarat City Baths..1) handwritten on back - Frank Wright 28, Taken Ballarat City Baths. Jan 1930 .2) handwritten on back - F.Wright, Ballarat City Baths, 4/2/30 3.) Frank Wright at the Ballarat City Baths, date unknownfrank wright, ballarat city baths, swimming costume, diving tower, spring board, changing booth -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFootwear - Rubber Boot, 1900-1908
The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roof tiles, barbed wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of the Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. This rubber boot is significant for being the only rubber boot in our collection. It is remarkable that it has survived almost seventy years underwater. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Rubber boot, left foot, Boot is ankle height and adult size. The heel appears to be solid rubber and the inner sole resembles leather. The rubber has come away from the outer boot in places, revealing a fabric base. Recovered from the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, russell & co., rubber boot, protective footwear, shipwreck artefact -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel - Sailing Ship, Foyle Photographic Studio, 1908
The photograph is of the sailing ship Falls of Halladale. The ship is in shallow water at Peterborough where it sank on November 14th 1908. The inscription on the photograph reads "Nov 4th 1908". The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The photograph shows the ship Falls of Halladale in full sail, demonstrating the sails used for power at sea.A sepia landscape photograph; image of a sailing ship in shallow water in full sail. The vessel is the"Falls of Halladale" aground off Peterborough 1908. A figure is in the foreground. Photographed in 1908 by Foyle of Warrnambool. A pencil inscription on the back is underlined. A white sticker is attached.In pencil on reverse "The Falls of Halladale / Wrecked at Peterborough / Nov 4th 1908" [Note: the ship was wrecked on Nov 14th 1908] On white sticker "131"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, photograph, falls of halladale, sailing ship, vessel, shipwreck, foyle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Photograph of the Falls of Halladale, at Peterborough 1908On back Foyle, Liebig St, Warrnambool flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, peterborough, photograph, foyle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGeological specimen - Slate, c. 1908
These rectangular slates of 'beautiful, unusual, expensive, green' American roof tiles were recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. Salvaging began in 1974 by volunteer divers, using local cray-fishing boats. An efficient system was devised to recover up to 4,000 of the still neatly packed slates a day. Many of the 22,000 salvaged slates can be seen on the roofs of eight buildings in the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale (1886 - 1908), was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roof tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire.The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Rectangular slates of green American roof tiles, some with a red-brown stain. These are a sample of hundreds of slate roof tiles salvaged from the vessel FALLS of HALLADALENoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, cargo, slate, slate tile, green american slates, building material, wreck point, peterborough, bay of islands, russell & co., 1908 shipwreck, salvage, recover -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole Frame, Russell & Co, ca. 1886
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Porthole frame, from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale, porthole and glass missing, brass with screw dog (part broken) and one hinge, eight retaining bolt holes. flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, porthole frame, ship’s fitting, brass porthole, reconditioned porthole, falls of halladale, russell & co., porthole -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole Glass
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Porthole Glass, from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale, little encrustation. "Falls of H" written in black texta penporthole glass, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCap Liner, Between 1870 and 1908
This Zinc Cap Porcelain Liner was recovered from the (1908) shipwreck site of the FALLS OF HALLADALE. The purpose of cap liners was to assist with the safe preserving and storage of perishable foodstuffs in an age when refrigeration was generally unavailable. These round, coarse-glass inserts formed part of the screw lids used with the Ball Mason style of canning fruit jars. The liner was placed inside the zinc cap to stop the contents of the jar reacting with the zinc. It prevented the metallic tainting of food as well as the corrosion of the metallic lid. On March 30, 1869, Lewis R Boyd was issued with patent # 88439 for an “Improved Mode of Preventing Corrosion in Metallic Caps”. From the 1870s to the 1950s, large quantities of these liners were produced by a number of glass manufacturing companies. They are consequently difficult to date or identify. “It is assumed that most of the earlier versions of these liners have the name ‘BOYD’S’ or ‘BOYD’ embossed on them. Later versions may or may not have the name included in the lettering”. (http://www.glassbottlemarks.com). Only a few were made of porcelain, the great majority being made first of transparent and later of translucent or opaque glass. The different emblems of triangles, circles, and crosses embossed on the front face of the liners are assumed to signify mould or model types rather than the company that produced them. This particular artefact is one of 14 cap liners that were retrieved from the shipwreck site and are now part of the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village collection. The Maltese Cross and “BOYD’S GENUINE PORCELAIN LINED” lettering are unique to this piece. However, it is evident from the markings and materials of the other cap liners, that they originally formed sets or series. Six are larger (8 mm depth x 85mm diameter), of greenish hue with ground glass texture, and support the raised emblem of a compass needle. Two are medium-sized (75mm diameter) with two raised dots in a central circle and the lettering “Patd. APR 25.82”. This particular cap liner is likely to have also been one of a mass-produced line being imported from America. The iron-hulled sailing ship FALLS OF HALLADALE was a bulk carrier of general cargo en route from New York to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. The FALLS OF HALLADALE came aground on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in1908-09 and 1910. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). A circular translucent glass disc in good condition with raised upper case lettering around 8mm rim – “BOYD’S GENUINE PORCELAIN LINED” - and a raised central emblem of a Maltese Cross. On the reverse face in the centre of the disc, there is a raised numeral “3”. falls of halladale, wright, breakenridge & co of glasgow, unusual beautiful green american slates (roofing tiles), warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, zinc cap porcelain liner, boyd’s genuine porcelain lined, glass lid, opaque disc, food preserving, fruit bottling, cap liner, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, 1908 shipwreck -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSheave
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Wooden sheave from a block, from the wreck of The Falls of Halladale SW 13/1.74flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, block -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCap Liner
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Zinc Cap Porcelain liner, placed inside the zinc cap to stop the contents of the jar reacting with the zinc. Recovered from wreck of the "The Falls of Halladale". Artefact Rego No FoH 16.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, 1908 shipwreck -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageChair piece
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today in the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Chair piece, varnished wooden backstop from the chair with floral and leaf motif, from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, chair -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCribbage Board
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Cribbage board, with inscription "Falls of Halladale Wrecked Peterborough Nov. 1908" Falls of Halladale Wrecked Peterborough Nov. 1908flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, cribbage board, falls of halladale, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTile, c 1914
This clay roof tile was part of the ANTARES cargo, a large consignment of tiles on its way to Melbourne. THE ANTARES In mid-November 1914, after the beginning of the First World War, a young local man went one evening to fish near the Bay of Islands, west of Peterborough. He later arrived home hurriedly and in an agitated state declaring: "The Germans are coming!" His family laughed and disbelieved him, as this young fellow was prone to telling fictional tales. About a month later, on December 13th 1914, local farmers Phillip Le Couteur and Peter Mathieson were riding in the vicinity, checking on cattle. Phillip Le Couteur saw what he “thought was the hull of a ship below the cliffs.” He rode to Allansford and contacted police. The next day, two Constables and Phillip Le Couteur returned to the site, where they dug a trench near the top of the cliff and sank a log in it. To this they attached a rope, which they threw down the cliff face. Constable Stainsbury and Phillip Le Couteur then made the dangerous descent down the rope on the sheer cliff face. They found wreckage strewn around a small cove and a portion of a man's body under the cliffs. The hull of the ship could be seen about 300 metres out to sea. Some of the wreckage revealed the name Antares and the remains of the ship's dinghy bore the name Sutlej. During the next two weeks and with the help of the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew, two more bodies were found. Later investigations proved that the tragic wreck was indeed that of the Antares, reported overdue on the 207th day of her voyage from Marseilles, France, to Melbourne. She was a three masted, 1749 ton iron clipper, built in Glasgow in 1888 and originally named and launched as the Sutlej. Bought in 1907 by Semider Bros. from Genoa, Italy, she was refitted and renamed Antares. It was later realised that the local lad who a month earlier had declared he had seen German guns being fired, had probably seen distress flares fired from the deck of the Antares the night she was wrecked. She was last sailed under Captain Gazedo and wrecked at what is now known as Antares Rock, near the Bay of Islands. She had been carrying a large cargo of roof tiles from France to Melbourne, consigned to Mullaly & Byrne. Many of them are now to be seen amongst the battered and scattered remains of the wreck. Some of the timbers were found to be blackened by fire. An Information Board has been erected on the cliff top near to the site of the Antares wreck, at the end of Radfords Rd, west of Peterborough. (Ref: Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s “Antares” fact sheet, Victorian Heritage Database, Information Board at Peterborough, Flagstaff Hill Significance Assessment 2010) The Antares was one of the last of the 'tall ships' to be lost along the south west coast of Victoria, and is the only wreck that took the lives of all people on board. She is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHS S34. The Antares is significant as a sail trader carrying an international inbound cargo. It is part of the Great Ocean Road Historic Shipwreck Trail. Piece of a clay roof tile recovered from the wreck of the Antares. Has a relief of a horse on back. Artefact Reg No A/7.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, antares, tall ship, peterborough, 1914 shipwreck, phillip le couteur, peter mathieson, constable stainsbury, sutlej, antares rock., bay of islands, clay tile, roofing tile, roof tile -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Roof Tile, c 1914
This terracotta clay roof tile was part of a consignment of tiles in the cargo of ANTARES. THE ANTARES In mid-November 1914, after the beginning of the First World War, a young local man went one evening to fish near the Bay of Islands, west of Peterborough. He later arrived home hurriedly and in an agitated state declaring: "The Germans are coming!" His family laughed and disbelieved him, as this young fellow was prone to telling fictional tales. About a month later, on December 13th 1914, local farmers Phillip Le Couteur and Peter Mathieson were riding in the vicinity, checking on cattle. Phillip Le Couteur saw what he “thought was the hull of a ship below the cliffs.” He rode to Allansford and contacted police. The next day, two Constables and Phillip Le Couteur returned to the site, where they dug a trench near the top of the cliff and sank a log in it. To this they attached a rope, which they threw down the cliff face. Constable Stainsbury and Phillip Le Couteur then made the dangerous descent down the rope on the sheer cliff face. They found wreckage strewn around a small cove and a portion of a man's body under the cliffs. The hull of the ship could be seen about 300 metres out to sea. Some of the wreckage revealed the name Antares and the remains of the ship's dinghy bore the name Sutlej. During the next two weeks and with the help of the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew, two more bodies were found. Later investigations proved that the tragic wreck was indeed that of the Antares, reported overdue on the 207th day of her voyage from Marseilles, France, to Melbourne. She was a three masted, 1749 ton iron clipper, built in Glasgow in 1888 and originally named and launched as the Sutlej. Bought in 1907 by Semider Bros. from Genoa, Italy, she was refitted and renamed Antares. It was later realised that the local lad who a month earlier had declared he had seen German guns being fired, had probably seen distress flares fired from the deck of the Antares the night she was wrecked. She was last sailed under Captain Gazedo and wrecked at what is now known as Antares Rock, near the Bay of Islands. She had been carrying a large cargo of roof tiles from France to Melbourne, consigned to Mullaly & Byrne. Many of them are now to be seen amongst the battered and scattered remains of the wreck. Some of the timbers were found to be blackened by fire. An Information Board has been erected on the cliff top near to the site of the Antares wreck, at the end of Radfords Rd, west of Peterborough. (Ref: Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s “Antares” fact sheet, Victorian Heritage Database, Information Board at Peterborough, Flagstaff Hill Significance Assessment 2010) The Antares was one of the last of the 'tall ships' to be lost along the south west coast of Victoria, and is the only wreck that took the lives of all people on board. She is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHS S34. The Antares is significant as a sail trader carrying an international inbound cargo. It is part of the Great Ocean Road Historic Shipwreck Trail.Part of a terracotta roof tile from the wreck of the Antares Has sand encrusted to bottom of tile. Artefact Reg No A/6.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, antares, tall ship, peterborough, 1914 shipwreck, phillip le couteur, peter mathieson, constable stainsbury, sutlej, antares rock., bay of islands, terracotta tile, roof tile, clay tile, roofing material, building material -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLids
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Round glass lids (2) from Falls of Halladale wreck. Lids are semi-opaque due to sand abrasion. Artefact Reg No FoH/16.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lids, lid, falls of halladale, round glass lids, russell & co.
