Showing 706 items matching "general design"
-
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Badge - Australasian Medical Congress attendee badge associated with Professor F J Browne, 1951, 1955
Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. A collection of objects found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers were transferred from the Archives to the Museum collection in 1994.Round copper coloured badge attached by two metal links to a rectangular bar. The bar is designed to hold a small name plate. The badge features a map of Australia as the central design overlaid with a representation of the Staff of Asclepius (a serpent entwined around a staff). Front of badge carries the words, "AUSTRALASIAN MEDICAL CONGRESS/ (B.M.A.) 9TH SESSION/ SYDNEY 1955".browne fj, australian medical congress, numismatics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Badge - Royal Army Medical Corps cap badge worn by F J Browne, World War I, 1915 (approximate)
Issued to Royal Army Medical Corps soldiers, this cap badge would have been worn by Francis Browne during World War I. Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. Collection of objects transferred from the Archives to the Museum collection found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers.Dark brown metal cap badge. Design features a crown sitting atop a laurel wreath, which surrounds a representation of the Rod of Asclepius (serpent wrapped around a rod). A scroll is affixed below the wreath which is inscribed 'ROYAL ARMY MEDICAL CORPS'.world war i, numismatics, browne fj -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumProwse Collection Box WP11 See details in Description section
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (item) - Wamira documents and drawings
XYZ456 -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumArchive (Item) - Box Baa 98 Boeing (Gaf / Asta) Collection
Description: Flight Manual - Jindivik Mk 3A Target Aircraft (2 copies) MinTech Publication 74 Volumes 3 to 5 - Jindivik Mk 103B Aircraft MinTech Publication 74 Volumes 1 and 6 - Jindivik Mk 103B General & Technical Information & Repair Schemes Covers 1 t Level of Importance: National. Historical Details: DAP/GAF/ASTA constructed many overseas designs under licence in Australia (Beaufort, Beaufighter, Lincoln, Canberra and F18) however they also designed and constructed a number of significant local designs that were successful in oversea's markets includi -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumArchive (Item) - Box Baa 106 Boeing (Gaf / Asta) Collection
Description: WRE Manual WRE 245 - J Band Repeater Unit GAF B3B/1 Book 1 - Jindivik Mk3B and Mk 203B - General & Technical Information GAF B3B/1 Book 2 - Jindivik Mk3B and Mk 203B - General & Technical Information (2 copies) WRE JB/OP No 1 - Jindivik Targ Level of Importance: National. Historical Details: DAP/GAF/ASTA constructed many overseas designs under licence in Australia (Beaufort, Beaufighter, Lincoln, Canberra and F18) however they also designed and constructed a number of significant local designs that were successful in oversea's markets includi -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumArchive (Item) - Box Baa 108 Boeing (Gaf / Asta) Collection
Description: GAF/B3B/1 Book 1 - JINDIVIK Mk 203B - GENERAL AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION GAF/B3B/1 Book 2 - JINDIVIK Mk 203B - GENERAL AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION GAF B4A-C00-050 Vol 1 - JINDIVIK Mk 4A DEVELOPMENT TRIALS REPORT GAF B4A-C00-050 Vol 2 - JINDIVI Level of Importance: National. Historical Details: DAP/GAF/ASTA constructed many overseas designs under licence in Australia (Beaufort, Beaufighter, Lincoln, Canberra and F18) however they also designed and constructed a number of significant local designs that were successful in oversea's markets includi -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumArchive (Item) - Box Baa 111 Boeing (Gaf / Asta) Collection
Description: (Containing 4 large binders) Willis Electric Co, Warwickshire - Electro-pneumatic Relay - Equipment drawing file General Assy No WL100, WL200, Spec WL99 03/1961 - 1963 WRE - Transponder Set, X-Band Drawings74776 - 150-71 1966/67 GAF - Ji Level of Importance: National. Historical Details: DAP/GAF/ASTA constructed many overseas designs under licence in Australia (Beaufort, Beaufighter, Lincoln, Canberra and F18) however they also designed and constructed a number of significant local designs that were successful in oversea's markets includi -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumArchive (Item) - Box Baa 114 Boeing (Gaf / Asta) Collection
Description: GAF - GAF/B3B/1 Book 1 - Jindivik Mk 203B General and Technical Info 1970 BAE - BT14134 Issue 1 - Flight Limitations and Recommendation for Jindivik Mk 103B Target Aircraft - 700 Series July 1984 GEC Avionics (UK) - ASTA System Manual 256TP Level of Importance: National. Historical Details: DAP/GAF/ASTA constructed many overseas designs under licence in Australia (Beaufort, Beaufighter, Lincoln, Canberra and F18) however they also designed and constructed a number of significant local designs that were successful in oversea's markets includi -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumArchive (Item) - Box Baa 115 Boeing (Gaf / Asta) Collection
Description: RAAF Flight Manual JIN1119 - Jindivik Mk 3A Target Aircraft GAF/ASTA Publication B4-P01 Book [?] - Jindivik Mk 4A General & Technical Information 1983 to 1987 GAF/ASTA Publication B4A-P05 - Jindivik Mk 4A Flight Manual 1987 to 1982 Level of Importance: National. Historical Details: DAP/GAF/ASTA constructed many overseas designs under licence in Australia (Beaufort, Beaufighter, Lincoln, Canberra and F18) however they also designed and constructed a number of significant local designs that were successful in oversea's markets includi -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumPlan (item) - CAC Wirraway Agricultural Conversion XP.77 Drawing, C.A.C Wirraway Agricultural Conversion XP.77, 02/1957
This schematic was drawn by W. J. Watkins for the Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation during February 1957. It shows the XP-77 experimental conversion of the Wirraway general-purpose military aircraft. This drawing appears to depict the early stages of the CAC's Ceres design, which later had limited success as an agricultural aircraft carrying out tasks such as crop spraying. As the prototype first flew in February 1958, this diagram represents part of the development process for that aircraft. It also demonstrates an important phase in the history of the CAC, where, after the Second World War, the company was innovating in an attempt to stay relevant after the rapid shrinking of the RAAF. -
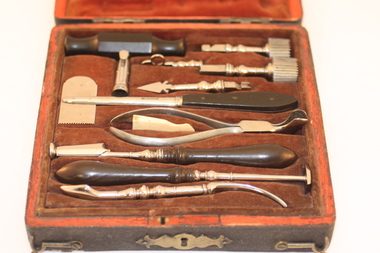 Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and Archives
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and ArchivesTrephine case
From Neurological Society of Australia. Wooden case with key. Contents (12 parts) include trephines, various sizes; perforator; key; ebony trephine handle; Hey skull saw; elevator; steel forceps; brush; lenticular; five pointed rugine. 18th or early 19th century.TREPHINE & SKULL SAW IN CASE OF SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS: EIGHTEENTH OR EARLY NINETEENTH CENTURY. This set of surgical instruments contains, in a wooden case covered with shagreen: two trephines and a perforator , with a key to remove the trephine centring pins a detachable ebony handle a Hey skull saw with the name BLACKWELL an elevator a pair of steel forceps a bone or ivory brush to clean the trephines a lenticular a 5-pointed rugine. The trephines are conical, with slight tapering to prevent over- penetration; they are approximately 17 and 20 mm in diameter. Each has a sharp centring point, which 5 can be removed. Hand trephines are operated with one hand, being rotated like a gimlet, by alternating pronation and supination of the forearm, which also exe1ts downward pressure. The skull saw was used where trephining was difficult, as in some depressed fractures; it was popularised by William Hey (1736-1819) of Leeds, though described by earlier writers. Hey, a Yorkshireman, studied in St George's Hospital, London, but worked with great distinction in the Leeds General Infirmary. The lenticular, a curious instrument seen in many eighteenth century illustrations, was used to smooth the margins of bone defects. The rugine could be used to scrape granulations. The design of the trephines and of most of the other instruments strongly suggests an English origin, probably in the eighteenth century. A very similar trephine is figured by the London surgeon Percivall Pott2 in 1779. Bennion l [ists three instrument makers named Blackwell, none earlier than 1817. Most of the instruments have been plated, presumably with nickel, at a date that must be much later. The nickel plating shows little sign of wear. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - CAC Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation Engineering Design Manuals, CAC-EDM Engineering Design Manual Part 1 : General Requirements
... CAC-EDM Engineering Design Manual Part 1 : General... Engineering Design Manual Part 1 : General Requirements Manual CAC ...Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation -
 Jewish Museum of Australia
Jewish Museum of AustraliaKathryn Tilley, Afikoman pouches, by Kathryn Tilley, 2007
Artist's statement: I chose to make these afikoman pouches even though they may not be familiar to or used by all Jewish families. In these little pouches, a small piece of matzah would be placed in the pouch and then hidden in the house for the children to find during the Passover meal. On finding it, a gift is given. The story of Passover and Judaism in general have been kept alive over the centuries. I wanted to honour the passing down of the Torah through the generations, and, in particular, the role of children in its transmission. I have used the Australian desert as a metaphor for the great wilderness crossed by the People of Israel. A recent trip to Broken Hill and beyond inspired me to work with the subtle colours and textures of that landscape and I have incorporated into the work found objects, stones and beads collected there. (2007, New Under the Sun: Australian Contemporary Design in Jewish Ceremony III)machine embroidered -
 St Kilda Historical Society
St Kilda Historical SocietyPhotograph, Donald McDonald, Herford, 1872
Large residence on large elevated block for Frederick Christian Lange (1832-1888) and family in 1870. The architect Lloyd Tayler (1830-1900) designed it in an Italianate style. Over time adjoining allotments were purchased until the gardens covered nearly 15 acres. Lange was in partnership with Emil Thoneman trading under the name of Lange & Thoneman, merchants and general importers. Lange was also one of the local directors of the local Australasian directors for the Swiss Lloyd Marine Insurance Company. William Officer (1835-1913), pastoralist, bought the property from Lange in 1888 for 23,500 pounds. Following Officer's death the grounds were subdivided in 1914 and the house finally demolished in 1940. Noting the spelling difference, there is now a street named 'Hertford Street' very close to this location. black and white photograph copyAlma Road south west corner Lansdowne Road built for Federick C Lange (Merchant) Photo 1872 -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayDouble Headed Rail, circa 1872 - 1883
Double Headed Rail from Ravenswood Station Siding which was dismantled circa 1987 the two rails were stored for a time at Maldon before being donated to Puffing Billy Museum Bearing makers marks of Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield, North East Derbyshire, England from 1872 - 1883 Double-headed rail In late 1830s Britain, railway lines had a vast range of different patterns. One of the earliest lines to use double-headed rail was the London and Birmingham Railway, which had offered a prize for the best design. This rail was supported by chairs and the head and foot of the rail had the same profile. The supposed advantage was that, when the head became worn, the rail could be turned over and re-used. In practice, this form of recycling was not very successful as the chair caused dents in the lower surface, and double-headed rail evolved into bullhead rail in which the head was more substantial than the foot. Info from Wikipedia - Rail Profile https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rail_profile The first records of double headed rail being used In Victoria by Victorian Railways was in 1859, the rails, chairs, oak and trenails were imported from UK. After the 1870’s the Victorian Railways went over to using flat bottom rails, but they still needed replacement double headed rail for lines already laid and this continued up to at least 1883 Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield England from 1872 - 1883 Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway The Melbourne, Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway Company received parliamentary assent in February 1853 to build Victoria's first inland railway from Melbourne to Williamstown, and Melbourne to Bendigo and Echuca. Construction commenced in January 1854 with work on a pier at Williamstown but lack of funds slowed progress, eventually prompting the company to sell out to the government. The 100-mile (162 km) section to Bendigo opened in October 1862. Its cost of £35,000 per mile made it the most expensive railway ever built in Australia. In 1864, the line was extended to Echuca, tapping into the booming Murray-Darling paddlesteamer trade. info from Museums Victoria - Victorian Railways https://museumsvictoria.com.au/railways/theme.aspx?lvl=3&IRN=450&gall=456 1863 Ravenswood Station open on the 1st Feb 1863 Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Ravenswood Siding When the Victorian Railways were established in 1856 they adopted one of the popular British permanent way standards - heavy 80lb (36.3kg) double-headed rail held up right in cast iron chairs attached to transverse timber sleepers by wooden pegs called trenails. The Ravenswood Railway siding was constructed in 1862 with 12 feet wrought iron double-head rail held in cast iron chairs with Ransom and May patent compressed keys. Trenails held the chairs to the sleepers and the joints were secured in joint chairs. Joints were subsequently joined using fish plates. It formed part of the Melbourne to Echuca rail line, initially known as the Melbourne, Mt Alexander and Murray River Railway. George Christian Derbyshire, the first Engineer-in-Chair of the Victorian Railways was responsible for the design and construction of the works. No new lines were built in Victoria using double-headed rail after 1870. The siding was disconnected from the main line in 1988. The Ravenswood Railway Siding demonstrates the original 1856 philosophy of the Victorian Railways to adopt British permanent way technology. The siding demonstrates significant aspects in the development of permanent way technology in England and Victoria over the period from the 1830's to the 1880's. The chairs in the Ravenswood siding are physical evidence of early railway technology rendered obsolete 120 years ago, namely joint chairs at rail joints and trenails to secure the chairs to the sleepers. The double-headed rail demonstrates an important stage in the evolution of British rail technology in the 1830s. The old fish plates, square headed bolts and square nuts demonstrate the success of fishing the rail joins. The Ravenswood siding demonstrates the earliest form of rail joint technology developed in England, and existing in Australia, the joint chair. In part of the siding the sequence of joint and intermediate chairs is consistent with the 1856 specifications, that sequence is rare with the joints secured in joint chairs. The survival of chairs in this sequence is rare and almost certainly demonstrates that they remained in continuous use at the same location from 1862 to 1988. This remnant of the Ravenswood siding has survived 126 years. The siding has proved to be the most significant of extant remnant double-headed sidings in Victoria, containing a rare combination of early permanent way technologies. Construction dates 1862, Info from Ravenswood Railway Siding Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/4693/download-report The remaining section of this siding is significant at the State and National levels in that it demonstrates the use of chaired rail by the Victorian Railways Department for the Trunk Lines and, more particularly, the following stages in the evolution of this long obsolete method of permanent way construction: a) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs at regular intervals inferring that the original wrought iron rail lengths were 12 feet, as is known through documentary sources to have been the case. The survival of chairs in this sequence is unique and almost certainly demonstrates that they have remained in continuous use at the same location and in the same sequence from 1862 to 1988 . b) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs designed for use with trenails. c) The use of later intermediate chairs designed for use with steel pins and the use of fished joints with steel double head chaired rail, representing a second method of constructing the permanent way using chaired rail technology. info from Ravenswood Siding - Melbourne/Echuca Railway Line - Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/70103/download-report Addition to Citation for Melbourne to EchucaRailway Line 1/10/1990 Double Head Rail The surviving lengths of double head rail with chairs on this railway compare with one surviving similar remnant on the Geelong to Ballarat railway and are representative of permanent way construction techniques applied exclusively to the two trunk railways of the 1860's. In this respect they are rare survivors and may be unique at the national level and of technical importance at the international level to the extent that they enhance contemporary understanding of early railway building technology. Surviving lengths of chaired double head rail survive at Kyneton, Ravenswood and Bendigo on this railway and include a number of different types of cast iron intermediate and joint chairs with hardwood keys and metal pins. The Ravenswood siding is of special significance for the diversity of chair types and for the sequence of chairs recalling rail lengths known to be associated with construction of the line in 1862. Construction of the Railway Tenders closed on 24 March 1858 with no less than 133 tenders being received. A contract was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937 to commence work on 1 June 1858 and complete the line by 31 July 1861. Cornish and Bruce made quick early progress with the Melbourne to Sunbury section being officially opened on 13 January 1859. The line was officially opened to Bendigo (Sandhurst) on 20 October 1862 by the Governor of Victoria, Sir Henry Barkly. A great banquet was held for 800 guests and this was followed by a grand ball. The extension of the line to Echuca was a relatively simple matter as that part of the line was across plain country without any significant engineering challenges. Tenders were called for the work in 1863 and the work was completed in 1864 by contractors Collier and Barry Apart from the line contractors, other firms directly involved were J Shire law and Co (sleepers), R Fulton, Langlands Brothers and Co, William Crossley (water supply), B Moreland, Langlands Brothers and Co (platelayers lorries), E Chambers (iron pins, traversers), Miller and McQuinstan (luggage vans and steam engines) and various contractors for building works. Info from Engineers Australia Engineering Heritage Victoria Nomination for Recognition under the Engineering Heritage Australia Heritage Recognition Program for the Goldfields Railways - Melbourne , Bendigo & Echuca Railway Page 25 - .2.9.2 Statement from National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Listing number B5323 for Mt Alexander/Murray Valley Rail Line: Page 69 - Theme 3 https://www.engineersaustralia.org.au/portal/system/files/engineering-heritage-australia/nomination-title/Melbourne_%20Bendigo_Echuca%20Railway%20Nomination.pdf The Melbourne, Mount Alexander and Murray River Railway Company was a railway company in Victoria, Australia. It was established on 8 February 1853 to build a railway from Melbourne to Echuca on the Victorian-NSW border and a branch railway to Williamstown. The company struggled to make any progress and on 23 May 1856, the colonial Government took over the Company and it became part of the newly established Department of Railways, part of the Board of Land and Works. The Department of Railways became Victorian Railways in 1859. Construction of the Bendigo line commenced in 1858, but this private consortium also met with financial difficulties when it was unable to raise sufficient funds, and was bought out by the Victorian colonial government. The design work was then taken over by Captain Andrew Clarke, R. E., Surveyor-General of Victoria, with bridge designs completed by Bryson and O'Hara The contract for the first stage of the line from Footscray to Sandhurst (now Bendigo), was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937.2s.2d ($6.714 million) with work commencing on 1 June 1858. Completion of the permanent way was to be by 31 July 1861 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melbourne,_Mount_Alexander_and_Murray_River_Railway_Company Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Victorian Railways : report of the Board of Land and Works November 1862 GP V 1862/63 no. 21 (2.8 MB) https://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1862-63No21.pdfHistoric - Victorian Railways - Double Headed rail Ravenswood Railway Station and Siding Victorian Heritage Database Reports Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1100 Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1786 National Trust VHR H1100 Mount Alexander and Murray River Rail way Line National Trust2 rail lengths of Double Headed Rail made of Iron makers marks : Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel and 20 joint chairs with metal rail pins Makers mark Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel (possible date 187? very hard to read ) puffing billy, double headed rail, wilson & cammell - dronfield - steel works, ravenswood station siding, melbourne to echuca rail line, initially known as the melbourne, mt alexander and murray river railway. -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway1920's Station Cash Box Tin - Hobbs & Co London, 1920's
1920's Station Cash Box Tin Made by Hobbs & Co London Lever Machine Made Alfred Charles Hobbs (October 7, 1812 – November 6, 1891) was an American locksmith and inventor. Hobbs went to London as a representative of the New York company of Day & Newell, which was exhibiting at the Great Exhibition of 1851. Hobbs had brought with him his boss's (Robert Newell) Parautoptic lock, designed to compete with, and surpass, the locks available at the time in Britain. He was the first one to pick Bramah's lock and the Chubb detector lock at the Great Exhibition of 1851 and forced the lock manufacturers to improve their designs. The lock controversy continues a subject of great interest at the Crystal Palace, and, indeed, is now become of general importance. We believed before the Exhibition opened that we had the best locks in the world, and among us Bramah and Chubb were reckoned quite as impregnable as Gibraltar— more so, indeed, for the key to the Mediterranean was taken by us, but none among us could penetrate into the locks and shoot the bolts of these masters. The mechanical spirit, however, is never at rest, and if it is lulled into a false state of listlessness in one branch of industry, and in one part of the world, elsewhere it springs up suddenly to admonish and reproach us with our supineness. Our descendents on the other side of the water are every now and then administering to the mother country a wholesome filial lesson upon this very text, and recently they have been "rubbing us up" with a severity which perhaps we merited for sneering at their shortcomings in the Exhibition. In 1854 he was awarded a Telford Medal by the Institution of Civil Engineers for his paper 'On the Principles and Construction of Locks'. Sign on a strong room door. Hobbs became one of the founders of the lock making firm of Hobbs Hart & Co. Ltd. The company started in 1851 and was formally registered as Hobbs and Co. in 1852. But by 1855 it had become Hobbs, Ashley and Company. The name then changed to Hobbs, Ashley and Fortescue, with an address at 97 Cheapside in London. Then for the next ninety years the address was 76 Cheapside in London. In 1860 Hobbs returned to America and lived in Bridgeport, Connecticut, and went on to hold a dozen patents for firearm ammunition manufacturing. In 1880 he listed himself as a "Superintendent Of Cartridge Factory" Info from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alfred_Charles_HobbsHistoric - Railways - Station Cash Box Tin 1920's Station Cash Box Tin - Hobbs & Co London Metal Tin - painted Black, Gold and Red with Brass Lock and HandleHobbs & Co London Lever Machine Made1920's station cash box tin, puffing billy -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumPhotograph, State Rivers and Water Supply Commission, 1957
This photograph was taken for the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission - for display purposes.Large sepia photograph dry mounted to cream board. Sign board with Engineer Ron Dickson looking at sign on left of photographState Rivers and Water Supply Commission / Goulburn Irrigation System / Enlargement and Remodelling Project / Design and Construction Depot / Enquiries at General Office.irrigation, victoria state rivers and water supply commission, ron dickson -
 City of Ballarat
City of BallaratSculpture - Public Artwork, George Allen, Mother Earth by George Allen, 1952
Mother Earth was created by modernist era sculptor George Allen. It is located in the western median strip at the intersection of Sturt and Raglan Streets. Made from Hawksbury stone on a granite base, the sculptor has created a female figure as the centrepiece, with two reliefs figures at the front and rear depicting a miner and a farmer. The work was created in commemoration of Mr Frank Pinkerton, an esteemed local lawyer in Ballarat. George Allen won the commission to design and execute the Pinkerton Statue in open competition in 1949. The statue is a significant work of one of Victoria's leading sculptors of the mid twentieth century, and controversy at the time surrounding its installation reflects the general attitude of the period to progressive public sculpture.Mother Earth was classified as regionally significant by the National Trust in 2003. The statement of significance below ha been provided by the National Trust, Victoria: The Pinkerton Statue by George Allen is of a simplified female figure which symbolises 'Earth', with smaller figures representing Mining and Agriculture carved in bas-relief at its base. The statue is carved in Hawkesbury Freestone and mounted on a granite plinth. It is located in a prominent position in central Ballarat. The statue in commemoration of Mr. Frank Pinkerton, an esteemed local lawyer, erected in Ballarat in 1952 is significant for aesthetic and social reasons at a Regional level. The statue is a significant example of the work of one of Victoria's leading sculptors of the mid twentieth century, and the controversy at the time surrounding its installation reflects the general attitude of the period to progressive public sculptures. George Allen won the commission to design and execute the Pinkerton Statue in open competition in 1949 against a large group of his peers. Following this. Allen was again successful in another major competition to design the National War Memorial for the Forecourt of the Shrine of Remembrance in Melbourne in 1951. Allen chose to work in a 'symbolic' manner using simplified forms with little detail, and relying on the strength of composition, 'boldness of statement' and the consideration of material for impact. Because of its lack of realism the Pinkerton Statue engendered much controversy, particularly within the popular press at the time, although it was generally appreciated in artistic circles. Allen had travelled extensively in Europe in the late 1930's, but his work mainly reflected influences from early modem sculptors in the United Kingdom such as Frank Dobson and Eric Gill. The Pinkerton Statue was the first example of modem sculpture to be erected in Ballarat and is an excellent example Allen's own work and the changing artistic culture of the period. Allen himself said that it reflected the "spirit of the time". A large Hawkesbury Freestone statue of a female figure and smaller figures representing Mining and Agriculture carved in bas-relief at its base. The statue is mounted on a granite plinth.CENTRAL FIGURE EARTH EMERGING FROM RELIEF FIGURES REPRESENTING THE INDUSTRIES OF MINING AND AGRICULTURE.pinkerton, mother earth -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchCommemorative Plate, Crown Lynn Potteries Limited, 1978
Round white ceramic plate with various royal, imperial and military gold emblems bordering an image of a brown building. Original cardboard box has also been retained.Front: "Commemorative Plate for the official opening of the Queen Elizabeth II Army Memorial Museum 15th October 1978" Back: "Queen Elizabeth II / Army Memorial Museum Plate / This plate has been created as one of 2,000 only, to commemorate the official opening of the Queen Elizabeth II Army Memorial Museum in Waiouru, by the Governor-General, Hist Excellency the Rt Hon Sir Keith Holyoake, GCMG, CH, on the 15th October 1978. / This plate design was authorised by the Chief of General Staff, Major General R.D.P. Hassett, CB, CBE, and approved by the New Zealand Herald of Arms. / 319"ceramic, commemorative plate, army memorial museum plate, army memorial museum -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaEquipment - Printing block, 1935 - 1966
The Rays' badge was was adopted by the General Grand Council in Melbourne in 1935 from a design submitted by South Australia.The shape of the badge represented the love with which every child of God is encircled. The ivy leaf was for friendship and the lines represented the good deeds which go out from each young life as rays of light to bring sunshine in others. This meaning was adopted in 1948. In 1966, General Grand Council in Sydney, decided to discontinue the use of the Rays' badge in favour of the one badge for the whole organisation. Wooden cube shaped block with a metal printer's die attached. The die is a replica of the Methodist Girls' Comradeship Rays' Section round badge emblem of an ivy leaf from which emanates the sun's rays. "R"methodist girls' comradeship rays' section, methodist church of australasia, printing -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Script, Robin Boyd, University of the Air. Design in Australia 1. The International Blender, 1964
Robin Boyd was involved in creating several television programmes, as author and presenter. 'Design in Australia' was an eight part series for the ABC television series 'University of the Air'. (Items D184-D193 contain all the manuscripts except part six titled 'Communications'.) In Part 1, Boyd discusses the general framework of the series in which the relationship between an Australian identity and a homogenising cultural force reinforced by technology and mass production is explored. Boyd questions the wholesale acceptance of imported ideas and goods, and instead advocates a critical examination of the Australian design culture, a search of an originality that does not fall into the myths of bush values.This is a draft script for the ABC television program 'University of the Air', subtitled 'Design in Australia', broadcast in 1965. Item D191 is the revised version.Typewritten (c copy), foolscap, 12 pagesuniversity of the air, design in australia, robin boyd, australian design, nationality, national style, manuscript -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Script, Robin Boyd, University of the Air. Design in Australia 1. The International blender. Working Script, 06.11.1964
Robin Boyd was involved in creating several TV series for the ABC University of the Air. 'Design in Australia' was an eight part series. (Items D184-D193 contain all the manuscripts except part six titled 'Communications'.) In part 1, Boyd discusses the general framework of the series in which the relationship between an Australian identity and a homogenising cultural force, reinforced by technology and mass production, is explored. Boyd questions the wholesale acceptance of imported ideas and goods, and instead advocates a critical examination of the Australian design culture, a search of an originality that does not fall into the myths of bush values. (Same content as item D184, differing Video cues of LHS of page.)This is a script for the ABC television program 'University of the Air', subtitled 'Design in Australia', broadcast in 1965. Item D184 is the draft version.Typewritten (c copy), foolscap, 9 pagesuniversity of the air, design in australia, robin boyd, australian design, nationality, national style, manuscript, ohm2022, ohm2022_30 -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationFunctional object - Telephone, Ericofon Telephone Handset
The Ericofon, sometimes known as the 'Cobra' for its distinctive single-piece design, was distributed by the Postmaster General from around 1963. Components were imported from Sweden, with the outer casing produced at the Ericsson factory in Broadmeadows. LM Ericsson Rotary Cobra Handset - grey upright handsetwalsh st furnishings, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationLetter, NSW Attorney General, Letter regarding Utzon and Opera House completion to Solicitors (Mr Barkell and Mr Peacock) for Peter Kollar and others, 23.03.1966
The advice given to the Attorney General regarding completion of Opera House in accordance with Utzon's design is at variance with the suit of Mr Barkell and Mr Peacock that works cannot be completed without Utzon's employment. The Attorney General will consider other expert evidence submitted by Mr Barkell and Mr Peacock. Utzon had resigned on 28 February, 1966. Robin Boyd’s desk cupboard contained two exercise books (item D482.1-D482.2) and assorted articles, essays and other material regarding the building of the Sydney Opera House, inserted inside the front cover of Walkabout magazine, July 1966 (item P1377). This publication is one of those inserts. Many of these were collected by Boyd’s eldest daughter, Mandie, who recalls that her father was writing a book, but was very disillusioned with the way the entire Opera House saga unfolded.Photocopy, 2 pages, part of plastic folder stuck on first pagesydney opera house, utzon, sydney opera house project, walsh st library -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Museum of Victoria Education Service, Aboriginal perspectives, 1996
... The kit is designed for the general public, teachers... photographs, colour photographs The kit is designed for the general ...The kit is designed for the general public, teachers and students, to give an understanding of Australian Indigenous people and culture and to break down stereotypes that are common in the school system and the wider community. The information presented is about the cultural, spiritual, economic and religious aspects of pre-contact societies. The impact of invasion on traditional societies and the post-colonial history of Australian Indigenous people is explored.Maps, b&w illustrations, b&w photographs, colour photographsculture, history, john batman, batman treaty, coranderrk mission, koorie culture, lake condah mission, kinship systems, aboriginal art, dreaming stories, kulin, gunai/kurnai, mara, wotjobaluk, wudjubaluk, koori -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. General Motors Building (1968), New York, New York, USA. (Architects: Edward Durell Stone and Emery Roth.)Made in Australia / 27 / JUL 69M2slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. General Motors Building (1968), New York, New York, USA. (Architects: Edward Durell Stone and Emery Roth.)Made in Australia / 26 / JUL 69M2slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1970
Robin Boyd was appointed Exhibits Architect for the Australian Pavilion at Expo ‘70 in Osaka and travelled to Osaka several times in 1969-1970. Boyd designed the innovative Space Tube, which had over 25 exhibition boxes, projecting from it. Amongst the topics covered were Australian scientific innovation (including brain research, immunology, Antarctic research, Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Power Scheme, rainmaking, and the night sky), Australian sport, house interiors, car manufacturing, Australian music and art, and Japanese-Australian relations.Colour slide in a mount. General view Osaka Expo '70, Japan, with Australian Pavilion in the backgroundMade in Australia / 13 / MAY 70M3expo 70, osaka, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1970
Robin Boyd was appointed Exhibits Architect for the Australian Pavilion at Expo ‘70 in Osaka and travelled to Osaka several times in 1969-1970. Boyd designed the innovative Space Tube, which had over 25 exhibition boxes, projecting from it. Amongst the topics covered were Australian scientific innovation (including brain research, immunology, Antarctic research, Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Power Scheme, rainmaking, and the night sky), Australian sport, house interiors, car manufacturing, Australian music and art, and Japanese-Australian relations.Colour slide in a mount. General view Osaka Expo '70, Japan, with Australian Pavilion in the backgroundMade in Australia / 5 / MAY 70M3expo 70, osaka, robin boyd, slide
