Showing 827 items
matching lessing
-
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBox Sample Dandy Starch, circa mid to late 1900's
This brand of starch was first manufactured in 1914, during the First World War, and continued to cover the other wars and military conflicts that followed. It was a time when Australian made was important due to the limited supplies coming from England and Europe. This was a period when the demand for "home grown" produce was at its peak. This was in a time when by necessity not by the "Buy Australian" campaign (of later years) which was the major factor for the demand of goods. It was in a time when starch was used in formal clothing to put a "crisp" or fresh new appearance for clothes. The important social more of "clothes make the person" was in vogue. This is a sample box provided by the manufacturer as an advertising and promotional method of prospective customers becoming aware of the product. This type of promotional avenue brought results and ensured that this type of advertising and inducement by manufacturers would be ingrained as a lasting avenue through to the 2nd Millennium This box which once contained starch powder is very significant to a rural semi isolated region because it clearly demonstrates that the social mores of the city were also entrenched into the rural population. The fashion of the day, even in remote areas, especially rural, were still a requirement to be maintained on certain special occasions. Cleanliness and stiff "upper lip" persona were just as important in the rural sector as in city and Government circles. Institutions such as hospitals, Government Offices and the legal personnel were bound by the fashion of the starch appearance (no dirt sticks to a personage with the "starch" look). Appearances, especially the first ones, were the judgmental image that remained in the uppermost regions of the viewer.This box with white writing and a "formally clad" man on a navy blue background held Australian grown maize based starch powder(1 LB gross). The package is made from 200 gsm thick cardboard. As production was made during the two World Wars 1914 to 1945 the promotion was heavily focused on Australian made and Australian grown maize.The front(has "Sample" on top) the rest inscriptions are the same on each cover both and back, "DANDY" below this a figure outlined in white on a navy blue background "hat and tails" outfit. Next to the sketch in smaller lettering" STRONGER THAN OTHER STARCHES. LESS REQUIRED". Below the figure "GLOSS" and below this in larger print "STARCH". Below this and in smaller print "CONTENTS. NETT WEIGHT 14 1/2 ozs" Below this and in smaller print "MANUFACTURED BY MAIZE PRODUCTS PTY LTD FOOTSCRAY VICTORIA" On one side of the box and in large white print on royal blue background"PURITY, STRENGTH AND UNIFORMITY." On the other side are the manufacturers directions. On the left side "FOR RAW STARCH" Underneath and in smaller print,"Dissolve in warm water a quantity to give the required thickness. Add bluing if required Stir before each using. On the right side "FOR BOILING STARCH" underneath this in small print"Mix well in small quantity of cold water to creamy consistency. Add boiling water, and stir constantly while cooking. Allow to cool, and add blueing if required. Underneath these two sets of instructions is "Make your consistency thinner than if using another kind of Starch"household starch, household cleaning, domestic laundering. -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Peter Pidgeon, Grave of Patrick Carrucan, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 5 April 2021
Whilst the three original Carrucan pioneers and their spouses are all buried at Eltham, only one gravestone (that of Patrick Carrucan) exists. Like many of the poor farmers of these early times, their graves were not marked with any permanent stone monuments and have deteriorated to become unmarked graves over the years. Patrick Carrucan, born in 1831 in Ireland, was the second oldest son of Patrick and Bridget Carrucan. He married Mary O'Brien in Ireland in 1856 before migrating to Australia, accompanied by Mary’s father, to join his sister Bridget Coleman in Eltham who had migrated in 1853. Patrick and Mary purchased a farm at the corner of Dalton and Bible Streets, initially living in a hut. After a few years, a more substantial house was built with assistance from Mary's father, who then returned to Ireland. The farm gradually prospered, with cattle, poultry and an orchard. Patrick and Mary had ten children (Bridget, Michael, Susan, Patrick, Thomas, Mary Anne, Catherine, Margaret, Frances and Annie) and lived in Eltham for the rest of their lives. In later years, the Sweeney and the Carrucan families intermarried, as did most of the old Catholic farming families of the Eltham District. Patrick died 6 October 1894 aged 63, reputedly from a broken back after being run over by his own bullock cart. Mary died in 2 Nov 1927 aged 90. They, together with other family members, are buried in a family plot in Eltham Cemetery, though only Patrick is recorded on the gravestone. Patrick's gravestone was in such disrepair that Betty Erickson (nee Carrucan) paid to have a new one erected in the late 1970s. Unfortunately, this gravestone, like the original, only honours Patrick Carrucan and does not record the other family members buried in this family plot. Betty wrote in 1989 "our people were farmers; the Sweeneys well-educated and prosperous, the Carrucans on a somewhat less favoured scale, but solid workers and providers." Patrick Carrucan Who departed this life 6 Oct. 1894 Aged 63 yearsBorn Digitaleltham cemetery, gravestones, patrick carrucan -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Literary Work, John F. Moodie Heddle, Seven In the Half-Deck, 1949
This book is a true account of the experiences of seven Australian boys beginning their career as seamen on the last voyage of the ‘John Murray’ when they became stranded on a South Pacific Island. The author John F. Moodie Heddle was an apprentice on board at that time. The publisher firm of Longmans, Green & Co. was founded in 1724 in London by Thomas Longman under the name Longman. In August of that year, he bought the two shops and goods of William Taylor and set up his publishing house there at 39 Paternoster Row. The shops were called Black Swan and Ship, and it is said that the 'ship' sign was the inspiration for Longman's Logo. After many changes of name and management, including the name Longman, Green, Longman and Roberts from 1859 to 1862, the firm was incorporated in 1926 as Longmans, Green & Co. Pty Ltd. The firm was acquired by Pearson in 1968 and was known as Pearson Longman or Pearson PLC. The three-masted iron baque 'John Murray' was built and registered in Glasgow, UK, in 1877 as a general cargo vessel maned the 'Loch Ryan'. It traded between the UK and Australia from 1877 to 1909. In 1909 the Loch Ryan was purchased by the Defence Department of Victoria, refitted at Williamstown as a training vessel and renamed ‘John Murray’. It was commissioned from 1910 to 1917 for reforming juvenile offenders as seamen for the Navy and Merchant Navy. The training project ceased after reports of the treatment of the boys. Although 411 did their training under this scheme, the success rate of them qualifying to serve on other vessels was less than twenty per cent. The ship was named after John (Jack) Murray (1851-1916), who was born near Koroit. He was the 23rd Premier of Victoria (1909-1912), and a Warrnambool Member of Parliament for twenty years. In 1917 the John Murray was sold to the Government of Australia to serve during the Great War, World War I. The ship was loaded with a cargo of dynamite and petroleum at San Francisco then departed for Melbourne when, during its passage, it was wrecked at Malden Island reef in the mid-Pacific Ocean on May 29th, 1918.The book gives us a first-hand account of the wrecking of the sailing ship John Murray, named after a past Warrnambool Member of Parliament for twenty years and the 23rd Premier of Victoria, born locally, near Koroit. The book is significant for its association with the vessel John Murray, which was formerly the 'Loch Ryan' of the Loch Line General Shipping Company of Glasgow. The same company owned the Loch Ard, which was wrecked and tragically lost 52 lives. The book is significant as a record of one of the many clipper ships that traded between the United Kingdom and Australia, with goods collected from other countries along the way. The book has an important connection to Victoria's training ship John Murray, which aimed at reforming delinquent juveniles to be suitable as seamen for Australia's Navy or Merchant Navy.Seven In The Half-Deck: An account of the wreck of the Barque John Murray Author: John F. Moodie Heddle Publisher: Longmans Green & Co Date: 1949 Beige cloth hardcover book with colour sleeve pasted to front cover, depicting a lifebuoy with a sailing ship in the centre. Some words of the title are in rope-inspired writing. There are inscriptions on a label on the spine, a sticker on the front loose endpaper, and the image on the cover.. Label; typed text "RA 910.453 HED" Inside front loose endpaper has sticker "Warrnambool Children's Library" On lifebuoy: "JOHN MURRAY" "MELBOURNE"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, seven in the half-dec, true story, wreck of the barque john murray, shipwreck, john murray, barque, wreck, john f. moodie heddle, j f moodie heddle, longmans green & co, j moodie heddle, warrnambool children’s library, 1949, melbourne, the john murray, loch ryan, loch line, general shipping company, government of victoria, training ship, juvenile reformation, delinquent boys, james & george thomson, iron barque, three-masted ship, clipper ship, uk to australia trade, dynamite cargo, petroleum cargo, maldon island reef, 1909-1917, 1910, 1918, 23rd premier of victoria, warrnambool member of parliament, koroit, juvenile delinquent training, navy training, royal australian navy, merchant navy, first-hand account of a shipwreck -
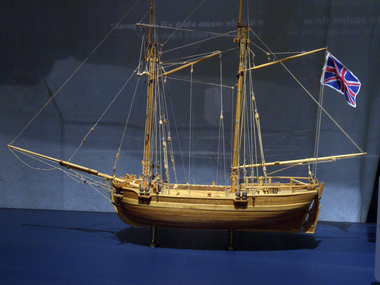 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCraft - Ship Model, H.M.S. Lady Nelson, 1988
This model of the ship H.M.S. Lady Nelson was researched and built as the vessel Lady Nelson by David Lumsden, a professional ship model builder. His Majesty's Armed Survey Vessel Lady Nelson was commissioned in 1799 to survey the coast of Australia. This vessel was purpose-built before the British Admiralty requested plans for a Schooner for Port Jackson. At the time large parts of the Australian coast were unmapped and Britain had claimed only part of the continent. The British Government were concerned that, in the event of settlers of another European power becoming established in Australia, any future conflict in Europe would lead to a widening of the conflict into the southern hemisphere to the detriment of the trade that Britain sought to develop. Against this background, Lady Nelson was chosen to survey and establish sovereignty over strategic parts of the continent. Lady Nelson left Portsmouth on 18 March 1800 and arrived at Sydney on 16th December 1800 after having been the first vessel to reach the east coast of Australia via the Bass Strait. Before that date, all vessels had sailed around the southern tip of Tasmania to reach their destination. Lady Nelson's survey work commenced shortly after she arrived in Sydney, initially in the Bass Strait area. She was involved in the discovery of Port Phillip, on the coast of Victoria, in establishing settlements on the River Derwent and at Port Dalrymple in Tasmania. She also successfully chartered much of the Victorian coastline and was heavily involved with the exploration of the Queensland coast with Matthew Flinders; investigated the Hunter River; made numerous visits to New Zealand and Norfolk Island and was involved in the founding of numerous settlements. In comparison to most colonial vessels, the Lady Nelson was technically unique she was fitted with sliding keels, or centreboards, and water-tight trunks reaching to the deck. Captain Schank invented these sliding keels that, when raised, reduced her draught to less than six feet. Her life as an exploration vessel ended while accompanying HMS 'Tamar' to Melville Island in 1825, the 'Lady Nelson' was captured and later abandoned by pirates off the island of Babar (Indonesia). This brought the vessel's 25 years of coastal exploration and navigation to a close.The Lady Nelson made was the first British ship to survey of the southern or south-western coast of Australia and traverse the Bass Strait. The vessel holds a special place in Australia's history of exploration as the first to explore and establish settlements in the then-new British colony of Van Diemans Land. The model gives an insight into what life must have been like onboard sailing vessels of the time and Australia's early history of establishment and exploration. This model acts as an important legacy of the full-scale ship which no longer survives. Ship model of the 60 ton British brig HMS Lady Nelson. Timber model of a two-masted brig with rigging but no sails, displaying the British Union Jack flag. The ship is in a glass exhibition display case on metal stand. HMS Lady Nelsonflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, by captain john schanck, sliding keels or centreboards, lady nelson, british brig hms lady nelson, david lumsden ship model builder, lieutennant james grant, bass strait discovery, surveying king island and port phillip bay, philip gidley king -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePrint - Landscape, Jean Baptiste Camille Corot, Souvenir of a Journey to Coubron, 1908-mid-20th century
Famous French artist Jean Baptiste Camille Corot, 1796-1875, was trained in the classical landscape style. His inspiration came from his travels around France and Italy. He developed a soft poetic or romantic style of work which became very popular. He had the skills to bring'light' into his paintings. The original oil on canvas painting by Corot is held at The National Gallery in the United Kingdom. It is titled 'Souvenir of a Journey to Coubron' and is one of twenty-seven of his works at the Gallery. Corot visited Coubon, east of Paris, many times. In 1873 during his stay there he sketched the scene that became the basis of this painting. This reproduction print was made by The Medici Society Ltd., founded in England 1908. The Society's aim was to make artwork affordable and available to the general public. The name Medici was chosen to honour the support and encouragement given to artists in the 15th century by Lorenzo de' Medici (1449 - 1492), known as Lorenzo the Magnificent, and his family. His profile is on the company's trademark. The Medici Society still produces Fine Art reproduction prints as well as selling original works. The print was framed by Westminster Art Gallery in Camperdown, London. The handwritten text on the back of the artwork adds some background to the artist: Corot was apprenticed to a Draper but changed to his profession at the age of 22 years. When he went from a poor artist to achieving wealth and fame he generously supported his less fortunate fellow artists. Corot found that the light and shade in a natural scene meant more to a landscape painter that what could be learned by following the principles of the academies. Corot was 51 years old before he sold his first picture. He though that he was the only artist that could really paint 'light'. The National Gallery, Victoria, has an original oil on canvas by Corot "the bent tree", created 1856-1860. It is in a similar style to this print "Souvenir of a Journey to Coubron", which was likely to have been painted around the same time.This high quality reproduction print was produced in the early-to-mid 1900;'s. This advancement in technology allowed everyday people to own and enjoy the fine art that was previously only accessible to the wealthy. The print is significant for its association with the famous 19th century artist Jean Baptiste Camille Corot.Print of a painting by Jean Baptiste Camille Corot, depicting a landscape with two buildings amongst trees and a boatman in the marshy foreground. The print is famed in carved timber with a cream matt, behind glass. there is an inscription on bottom right of print and further stamped and handwritten inscriptions of the reverse paper. The is a genuine Medici Society Fine Art reproduction print and was framed by Westminster Art Gallery.Original artwork painted and signed by artist "COROT" White sticker with"32" Reproduction print by the Medici Society, London Stamp "Westminster Art Gallery / 91 CAMBERWELL RD. / CAMBERWELL E.6." Text on Corot's history Underlined statement "GENUINE MEDICI PRINT "flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, jean-baptiste-camille corot, french artist, jean corot, camille corot, print, souvenir of a journey to coubron, coubron, 19th century artist, medici society, reproduction print, westminster art gallery, fine art -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Dentist Drill, Late 19th century
The design of this and other similar treadle powered dental engine (or dentist drill) was in common use by dentists from the 1870’s into the 1920's. When electricity became accessible to most communities the electrically powered dental engines began to take over from the treadle power. Over the ages teeth were extracted using picks and scissors and other gouging instruments. Bow drills, hand drills and even a "bur thimble" drill were later used to prepare cavities for filling. Some drills were made bendable by attaching flexible shanks between the metal bur and the handle, giving access to the teeth at the back of the mouth. Other mechanical devices were introduced along the way, such as clockwork drills, but they were hard to handle and inefficient. Over the centuries “dentistry has been performed by priests, monks and other healers. This was followed by barbers; the barber’s chair may well have been the precursor to the dental chair. “(SA Medical Heritage Society Inc.) In 1871 James Morrison patented the first commercially manufactured 'foot treadle dental engine', the first practica dental engine although others had been introduced as early as 1790 (by John Greenwood). Handmade steel burs or drills were introduced for dental handpieces, taking advantage of the significant increase in the speed of the drill. In 1891 the first machine-made steel burs were in use. The treadle drill reduced the time to prepare a cavity from hours to less than ten minutes. In 1876 the Samuel S. White Catalogue of Dentist Instruments listed a 12 ½ inch wheel diameter dental engine, with 14 bright steel parts, for sale at US $55 In today’s market, this is the equivalent to US $1200 approx. The specifications of that dental engine are very similar to the this one in our Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s collection. It is interesting to note that workings of a similar treadle dentist drill were used and modified to power a treadle spinning wheel of one of the volunteer spinners at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The foot treadle dental engine was a milestone in dental history. “Historic importance of treadle powered machines; they made use of human power in an optimal way” (Lowtech Magazine “Short history of early pedal powered machines”) The invention of a machine to speed up the process of excavation of a tooth lead to the invention of new burs and drills for the handpieces, improving speed and the surgical process of dentistry. They were the fore-runner of today’s electrically powered dental engines. This treadle-powered dentist drill, or dentist engine, is made of iron and steel and provides power for a mechanical dental hand-piece that would be fitted with a dental tool. The drill has a three footed cast iron base, one foot being longer than the other two. A vertical C shaped frame is joined into the centre of the base, holding an axle that has a driving-wheel (or flywheel) and connecting to a crank. A slender, shoulder height post, made from telescoping pipes, joins into the top of this frame and is height adjusted by a hand tightened screw with a round knob. On the post just above the frame is a short metal, horizontal bar (to hold the hand-piece when it is not in use). A narrow tubular arm is attached to the top of the stand at a right angle and can move up and down. At the end of the arm is a firmly fixed, flexible rubber hose protected for a short distance by a sheath of thin metal. At the end of the hose there is a fitting where the drill’s hand-piece would be attached; a small, silver coloured alligator clip is also at the end. A treadle, or foot pedal, is hinged to the heel to the long foot of the base, and joined at the toe to the crank that turns the driving-wheel. There is a spring under the toe of the treadle. The metal driving-wheel has a wide rim. Touching the inside of the rim are four tubular rings that bulge towards the outside of the driving-wheel, away from the pole, and all meet at the hub of the axle. The axle is bulbous between the inside of the driving-wheel and the frame then passes through the frame and is attached on the other side. The driving-wheel has a groove around which a belt would sit. The belt would also fit around a pulley on the arm, at the top of the post. The pulley is joined to a rod inside the arm and this spins the drill's hand-piece and dental tool holder. The two shorter feet of the base are made from a long metal bar that has been curved outwards, and its centre is bolted to the base of the pole. Under the ends of the curved legs of the base are wedge shaped feet. The driving-wheel is decorated in light coloured paint on both sides, each side having three sets of floral decals evenly spaced around them, and each about a sixth of the wheel's circumference. Similar decoration is along the sides of the frame. The foot pedal has decorative cutout patterns in the centre of the foot and at the toe. On the long foot of the stand is some lettering with a fine, light coloured border around it. The lettering is hard to read, being a dark colour and flaking off. There are also remnants of fine, light coloured flourishes. The foot pedal has lettering of the maker’s trade mark cast into the metal at the ball of the foot. Lettering on the base is peeling and difficult to read. The foot pedal has a trade mark cast into it that looks like a combination of ‘C’ , ‘S’ , ‘A’, ‘R’. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dentist, teeth, dental drill, dental engine, treadle drill, foot powered drill, treadle engine, orthodontics, dental surgery, james morrison -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Dentist Drill, Late 19th century
The design of this and other similar treadle powered dental engine (or dentist drill) was in common use by dentists from the 1870’s into the 1920's. When electricity became accessible to most communities the electrically powered dental engines began to take over from the treadle power. Over the ages teeth were extracted using picks and scissors and other gouging instruments. Bow drills, hand drills and even a "bur thimble" drill were later used to prepare cavities for filling. Some drills were made bendable by attaching flexible shanks between the metal bur and the handle, giving access to the teeth at the back of the mouth. Other mechanical devices were introduced along the way, such as clockwork drills, but they were hard to handle and inefficient. Over the centuries “dentistry has been performed by priests, monks and other healers. This was followed by barbers; the barber’s chair may well have been the precursor to the dental chair. “(SA Medical Heritage Society Inc.) In 1871 James Morrison patented the first commercially manufactured 'foot treadle dental engine', the first practica dental engine although others had been introduced as early as 1790 (by John Greenwood). Handmade steel burs or drills were introduced for dental handpieces, taking advantage of the significant increase in the speed of the drill. In 1891 the first machine-made steel burs were in use. The treadle drill reduced the time to prepare a cavity from hours to less than ten minutes. In 1876 the Samuel S. White Catalogue of Dentist Instruments listed a 12 ½ inch wheel diameter dental engine, with 14 bright steel parts, for sale at US $55 In today’s market, this is the equivalent to US $1200 approx. The specifications of that dental engine are very similar to the this one in our Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s collection. It is interesting to note that workings of a similar treadle dentist drill were used and modified to power a treadle spinning wheel of one of the volunteer spinners at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The foot treadle dental engine was a milestone in dental history. “Historic importance of treadle powered machines; they made use of human power in an optimal way” (Lowtech Magazine “Short history of early pedal powered machines”) The invention of a machine to speed up the process of excavation of a tooth lead to the invention of new burs and drills for the handpieces, improving speed and the surgical process of dentistry. They were the fore-runner of today’s electrically powered dental engines. This treadle-powered dentist drill, or dentist engine, is made of iron and steel and provides power for a mechanical dental handpiece that would be fitted with a dental tool. On the foot is painted lettering naming it "The Brentfield" and there is a fine line of light coloured paint creating a border around the name. The paint under the lettering is peeling off. The drill has a Y-shaped, three footed cast iron base, one foot being longer than the other two. A vertical frame is joined into the centre of the base, holding an axle that has a driving-wheel (or flywheel) and connecting to a crank. A slender, shoulder height post, made from adjustable telescoping pipes, joins into the top of this frame. On the post just above the frame is a short metal, horizontal bar (to hold the hand-piece when it is not in use). A narrow tubular arm is attached to the top of the stand at a right angle and can move up, down and around. There is a pulley each side of the joint of the arm and a short way along the arm is fitted a short metal pipe. A little further along the arm a frayed-ended cord hangs down from a hole. At the end of the arm is another pulley and a joint from which hangs a long, thin metal pipe with two pulleys and a fitting on the end. A treadle, or foot pedal, is joined to the long foot of the base, and joined at the toe to the crank that turns the driving-wheel. The metal driving-wheel has a wide rim. Touching the inside of the rim are four tubular rings that bulge towards the outside of the driving-wheel, away from the pole, and all meet at the hub of the axle. The axle fits between the inside of the driving-wheel and the frame then passes through the frame and is attached on the other side. The driving-wheel has a groove around which a belt would sit. The belt would also fit around a pulley on the arm, at the top of the post. The pulley is joined to a rod inside the arm and this spins the drill's hand-piece and dental tool holder. The foot pedal has a cross-hatch pattern on the heel and the ball of the foot has tread lines across it. The end of the toe and the instep areas have cut-out pattern in them. "The ____/ Brentfield / __ DE IN L___" (Made in London) painted on the long foot of the base. Marked on the drill connection is “Richter De Trey, Germany”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dentist, teeth, dental drill, dental engine, treadle drill, foot powered drill, treadle engine, orthodontics, dental surgery, james morrison, the brentfield, richter de trey, german dental fitting, london dental drill -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Forest Metriverter, Side Rule
Decimal currency was spectacularly introduced in an overnight overthrow on 14 February 1966, but it took another 8 years before metrication finally arrived in the forest and timber industry. Eventually, the measurement of logs and sawn timber changed from imperial, and excruciating, measures such as super feet of sawn timber, billets and cunits (100 cubic feet) of stacked pulpwood and hoppus log volumes to simpler cubic metres. Measuring firewood was a particular nightmare. For example, there were standard chords, stove cords, kitchen cords, running cords, face cords, thrown chords, fencing cords, country cords, long cords, raummeter or steres (1m x 1m x 1m). A standard cord of firewood had a volume of 128 cubic feet, measured as a pile 8 feet long, 4 feet high and 4 feet wide (3.624 m3). And how about this for confusing…. in Victoria, an imperial or long ton (by measure) of green firewood was a stack 5 feet long billets (2 axelengths at 2′ 6″ each), one axelength high (2′ 6″) and two axelengths long (5 feet) equalling 62.5 cubic feet. For added befuddlement, there were three different sorts of tons: Imperial tons or long tons, American short tons and metric tonnes (spelled with two n’s). Not forgetting that a cubic imperial ton of firewood (40 cubic feet) which equalled 1.133 cubic metre. The metrication process began in 1974 and was completed by 1976 but the transition was not without its challenges along the supply chain for foresters, overseers, logging contractors, sawmillers, hardware stores and builders alike. Timber lengths changed from feet to metres but were still sold in multiples of one foot or 0.3 m (1.8, 2.1, 2.4, 2.7 etc) whereas a menacing lump of 4-Bee-2 transformed into a rather less colourful 100mm by 50mm. Measurement and calculations of area also became so much easier in hectares rather than complicated acres, roods and perches. The Forest Metriverter slide-rule was issued by the Forestry and Timber Bureau to make metric conversions easier.Forest MetriverterRoss Pennyforest measurement -
 Chiltern Athenaeum Trust
Chiltern Athenaeum TrustDomestic object - Butter knife belonging to W.C.Busse
Wilfred Clarence Busse, born in Chiltern in 1898, His family moved to the region during the gold rush and continued to reside in the area, purchasing land adjacent the Murray River. Busse completed his secondary education at Wesley College in Melbourne then studied law at the University of Melbourne. Busse went on to become a barrister, often in the chambers of Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933) a judge of the Supreme Court of Victoria. He worked most of his life in Chiltern as a Barrister and Solicitor and gained the unofficial title of historian of Chiltern, leaving behind several manuscript histories and a scrap book. Busse was an avid fictional writer and in 1930 he published two novels. Time spent on a Victorian station in his early twenties, as well as careful documentary research, informed the writing of his historical novels of bush life. "The Blue Beyond; A Romance of the Early Days in South Eastern Australia” and "The Golden Plague: A Romance of the Early Fifties." "The Golden Plague” won the T. E. Role gold medal for the best historical novel which went on to become a best seller. Busse often drew inspiration for his novels from his younger years living Chiltern. His passion for the region lead him to write “The History of Chiltern” which was published in a serial form in the Chiltern Federal Standard from 1922-1923. Wilfred Clarence Busse was a member of Chiltern Athenaeum (where this object is now held) up until his death in 1960, he is buried in the Barnawartha Cemetery. Likely Silverplate due to the intensity of the tarnishing of the metal, with indecipherable hallmarks on the handle, the method of production and the maker mark are unclear. The delicate swirling fernlike motif on this particular butter knife appears to be stylised in either Art deco the decorative arts and craft style favoured in Europe between 1880-1930's and less representational than examples of Australiana flora captured in silversmithing from the 1850's onwards produced in Australia. It is likely that those producing silverware at the time would be drawing on the decorative arts movement while incorporating elements of the natural beauty in the flora of their newfound environment into the silverware they produced.Wilfred Clarence Busse was of social significance to Chiltern, he helped to document the cultural story of the area in his published works "The Golden Plague" and "The Beyond Blue" by recounting his own upbringing in a bush lifestyle. He was a respected Barrister and was the unofficial historian of the Chiltern Athenaeum for many years. This butter knife represents a window into the domestic life of this person who was well loved in the area, and it continues its relationship to Busse as well as Chiltern by being held within the very collection he helped to maintain in his life. Domestic objects tell us the story about how people lived, objects of daily use hold particular meaning in that they can tell us the story of an individual, we feel closer to their life and habits, it humanises and connects us across time. Wilfred Busse ate food, he buttered his bread and he did it with a wonderfully decorated silver butter knife.A tarnished metal butter knife with engraved and embossed spiral fern details on the knife and handlesilverware, wilfred clarence busse, busse, chiltern, chiltern athenaeum, federal standard, t. e. role, "the blue beyond, a romance of the early days in south eastern australia”, "the golden plague: a romance of the early fifties.", "the golden plague”, wesley college, university of melbourne, sir leo finn bernard cussen, supreme court of victoria, gold rush, murray river, “the history of chiltern”, silversmithing, decorative arts, floral, flora, australiana, australian flora, arts and craft movement, australian silver, cussen, cutlery, butter knife, knife, silverplate -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Dorothy Wickham, Winter's Swamp, Ballarat, January to April 2014
Study of Winter's Swamp commissioned by BEN and completed by BHS. The swamp was named after one of the first European settlers in the district. Winter Swamp LAT -37 32 LONG 143 47, Parish of Dowling Forest, County of Grenville Winter Swamp, on the southwest corner of Ballarat West Town Common, was not included in the original proclamation of the Common in 1861. However, being marshland, it was not considered suitable for grazing, so was added to the Common soon after 1861. Winter Swamp is a large wetland with native and exotic pasture significant for wildlife. John Winter (Jock) was born in Berwickshire, Scotland. He married Janet Margaret Irving the daughter of Robert Irving, advocate, Bonshaw, Dumfries, Scotland. Winter died in Ballarat in 1875 and was buried at the Ballaarat Old Cemetery. He took up the run Bonshaw from 1841; Leigh River Buninyong 1842-46; Junction, Delatite, March 1851 to September 1862; with sons: Carag Carag and Corop, April 1857 to September 1872; Colbinabbin and Stewart’s Plains, April 1857 to December 1872; St Germains February 1867 to March 1871. (The name became Winter-Irving in 1890). Mr John Winter, who died on August 22 at the age of 72, was a man of some note it the mining community of Ballarat. He was a self-made man, and one of our oldest colonists, it being over a quarter of a century age since he took up county about Ballarat and settled at Bonshaw. He died very rich. It is calculated that if he had retained an interest in all his runs, his income must have been not less than £10,000 or £50,000 a year. Some eight or ten years ago he sold his Bonshaw pre-emption to the Bonshaw Gold mining Company for £20,000, and a few years later the ground belonging now to Winter's Freehold Company brought him £50,000 more, the payment being made at the requisition of the deceased in sovereigns. In these relations Mr. Winter has been closely identified with the mining industry at Ballarat. The deceased was a native of Lauder, in Berwickshire, and landed in Victoria several years before the gold discovery.The principle task of this project was the delivery of a report outlining the history of European settlement in the Skipton and Cardigan/Ballarat districts as pertinent to the use of and impact on the natural environment of the two reserves Skipton Common and Winter Swamp. The report was delivered in digital form only. The report, upon completion, was presented to the Network’s Committee in order to discuss the project. The report identified and described the uses of Skipton Common and Winter Swamp, and their impacts. In particular, this report examined farming/grazing (official and informal), mining, vegetation removal (including the removal of woodlands for timber, grasslands for pasture improvement) & use of riparian areas for access to water and timber removal. Recording the more benign and environmentally friendly uses such as picnicking, community activities, nature walks and the roles of organisations such as Field Naturalists’ and Bird Observers’ clubs, school and scout/guide groups will be relevant in helping to depict overall community attitudes towards the reserves; e.g.: has the Common generally been viewed as little more than a grazing paddock and fire hazard; has Winter Swamp always been the unknown natural asset that seems to have been its lot for at least the past 40 years? In this regard, the more contemporary history of actions surrounding the use and management of the reserves is of particular interest, in view of the extant evidence at both reserves; e.g. the actions of the Shire of Ballarat in the 1980s in establishing Winter Swamp as something of a competitor to Lake Wendouree but with a more environmental bent (although almost none of the plants used are indigenous species, but that is part of the story); the trotting track constructed on Skipton Common in the 1960s following representations to Premier Henry Bolte and the cropping of the western section of the Common to raise funds for the town’s new swimming pool, the fertilizing of the land putting an end to the native grassland vegetation. There are obviously multiple sources of information to source in preparing the report, however sources that the contractor is specifically requested to consult are the Skipton Historical Society, the former Skipton Common managers (specifically Graeme Pett), the Cardigan Windermere Landcare Group and the Learmonth Historical Society (believed to hold many of the former Shire of Ballarat’s records pertaining to the Council’s role as the Committee of Management for both Winter Swamp and the Ballarat West Town Common – Winter Swamp was split between 2 separate Crown Land tenures). The contractor is also encouraged but not required to utilise community newsletters, such as the Skipton Community Newsletter, to publicise and seek information about the project. Skipton Historical Society (Mary Bradshaw) contacted on Thursday 12 June 2.30pm. Mary lived on a farm out of Skipton but is currently living in the township. She remembers walking along the creek of the Common especially in spring and autumn in bare feet and that it was a very pretty place. There were a few snakes around the waterway in summer. People put cows and a couple of horses on the commonage to graze. Graeme Pett has always lived close to the Common and would know a lot about it. Other possible contacts would be Nicole Petress, Secretary of the Progress Association, and the Corangamite Council, Camperdown. Digital images of Winter's Swampwinter's swamp, ballarat, john winter, ballarat environmental network, mullawullah -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Aboriginal Community Elders Service et al, Aboriginal elders' voices : stories of the "tide of history" : Victorian Indigenous elders' life stories &? oral histories, 2003
This book is a collection of Victorian Indigenous Elders' life stories and oral histories. The Elders share their stories in an attempt to ensure that both sides of Australia's history are finally heard. These stories tell of cultural resistance on missions, of defying assimilation laws, of forever moving around to save children from the welfare. They document the development of both fringe and urban communities and work in the Aboriginal rights movement. They clarify the ways in which these experiences have affected the individual authors along with the indigenous population in general. Also included in the book is a brief history and analysis of the legislation, policies, attitudes and strategies that have affected the lives of the authors and their families since colonisation. This aspect provides an historical perspective, encouraging a deeper understanding of the Elders' stories. Reconciliation can only eventuate with an understanding gained from hearing and including the voices of Indigenous Australians. Contents: The writing team Indigenous elders: keepers of knowledge; custodians of land and culture Aboriginal lands Missions and reserves Growing up running from the welfare /? Aunty Olive Jackson Respecting our Elders /? Aunty Lola James If your mother didn't tell you, then your grandmother did! /? Uncles Les Stewart Don't dwell on trouble /? Aunty Audrey Critch There are my people /? Aunty Gwen Nelson We were all cousins, more or less /? Aunty Iris Lovett-Gardiner Aboriginality is about culture, not colour /? Aunty Dianne Phillips Take up the opportunities we struggled to make /? Aunty Frances Gallagher Home /? Aunty Eileen Alberts We were supposed to forget our Aboriginality /? Aunty Gwen Garoni Not enough heart to say sorry? /? Uncle Brian Kennewell-Taylor Learning from indigenous elders: Keeping the traditions, keeping the culture strong; Since time immemorial; Invasion: the tide ran red; The flood of legislation; Stolen children; Cultural resistance: holding on to children traditions and land; Organised resistance: a movement is born; The 1950s: community resistance to race laws; The price of assimilation; The Aboriginal rights movement; After the flood: self-determination; Turning the tide Bibliography Appendix. Cultural custodianship: developing an indigenous methodology.maps, colour illustrations, b&w photographswiradjuri, victorian indigenous elders, oral histories, yorta yorta, dja dja wurrung, language maps, victorian missions and reserves, lake condah, framlingham, coranderrk, ramahyuck, lake tyers, wahgunyah, cummeragunja, moonahcullah, balranald, ebenezer, maloga, acheron -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomPhotograph, Col Frank Pearson
Francis Charles Pearson was born on 23rd August 1913 in Ballarat. During the course of his long life -he died just before his 96th birthday - he was a successful businessman, notably in the field of air conditioning, as well as a world renown farmer noted for his cattle breeding methods. This was in addition to a meritorious military career. Frank Pearson enlisted as a 16 year old cadet in 6 Field Company, Australian Engineers on 29 Jan 1930., CSM in 1935, he transferred to 2 Field Coy RAE on 1 July 1936. Next, he joined the cadre of 2 AA Searchlight Coy, RAE and was commissioned on 14 Oct 1939. That unit became 53rd AA Coy, providing personnel for 1/54 AA Coy late in 1939. Lt Pearson was was 2IC at this time. When the unit was mobilised on 14 Sep 1940, T/Capt Pearson was appointed OC. Seconded to the AIF on 14 May 1941 he was appointed to raise A Squadron, 2/6 Armoured Regiment, and once that was done, he raised B Squadron. Promoted temporary Major in June 1942 he served with the regiment in Stuart tanks during the difficult operations around Cape Endaiadere and Buna from October 1942 until April 1943. After return to Australia the regiment waited in vain for further operational employment. Frank Pearson was demobilised on 23 October 1945. With the raising of the Citizen Military Forces in 1948, Major Pearson was appointed 2IC 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles. On 1 January 1953 he assumed command of 4th/19th Prince of Walers's Light Horse Regiment, a post he held until the end of 1956. After service in more senior postings he retired with the rank of Colonel on 24 August 1964. From then until just a few years before his passing, Colonel Pearson remained actively involved in the life of his regiment. Following a couple of less successful attempts to do so, he was instrumental in establishing the regimental museum, these days the Unit History Room. Undaunted by a continuing sequence of changing venues it is to his credit that the history of the regiment is not only preserved but readily available to today's members of the unit and the general public. Coloured photo of Colonel Francis (Frank) Pearson OAM ED. Mounted in wooden frame.frank pearson, photographs -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Glass manufacturing has evolved over thousands of years. Glass making has been traced back to 3500 BC in Mesopotamia. The earliest known glass objects were beads, perhaps made by accident while working with metal. In the late Bronze Age, several civilizations discovered how to make vessels and glass bottles by wrapping threads of melted glass around cores of sand or clay. Later, moulds were used to form dishes and table wares. Around the 1st century BC, glassblowing was discovered. This made glass containers less expensive than pottery. Mould-blown glass, the process of blowing a piece of molten glass into a wooden or metal mould, was invented during the 1st century AD. This technique was faster with more consistent results. It paved the way for mass production. It wasn’t until the late 1800s that the production process to become more efficient. In 1887, a company in England created a semi-automatic process that could produce up to 200 bottles an hour. This process has been refined to the point where modern machines can yield more than 600 containers per minute. Blown vs. Manufactured Glass Bottles Nowadays, glass bottles, jars, and cups are usually manufactured on a bigger scale than is found in individual glassblowing studios. If we still depended on hand-blown glass for all of our glass containers, we would see some major differences in the process of creating bottles and jars. First, there's the time. Hand blowing glass takes a significant amount of time, even for one simple container. In contrast, hundreds of jars per minute can be made using modern technology. This leads to the second advantage: price. Because of the automated and streamlined process, the price for manufactured containers is much lower than that of hand-blown glass. Third, manufactured bottles will be much more consistently uniform than bottles blown by hand. Automated glass manufacturing produces nearly identical batches of jars. Glass blowing is awesome for unique, beautiful pieces of art. But for lots of lower priced and uniformly shaped containers, automatic manufacturing is the preferred method to create glass bottles and jars. https://www.containerandpackaging.com/resources/glass-bottles-brief-history The invention and development of glass for domestic items including bottles, has been nothing short of revolutionary. The use of glass bottles, that could be easily washed, led to improved hygiene, and mass manufacturing of drinks of all types, including milk, cordial and alcoholic beverages.Green Glass Bottle Possibly a ginger beer bottle.Concave indentation at the base. Also on base are two raised lumps. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, glass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Smoothing Plane, Heinrich Boker, Mid 19th to late 19th Century
A smoothing plane is typically used after the work piece has been flattened and trued by the other bench planes, such as the jack, fore, and joiner planes. Smoothing planes can also be used to remove marks left by woodworking machinery. When used effectively alongside other bench planes, the smoothing plane should only need a handful of passes removing shavings as fine as 0.002 inches (0.051 mm) or less. The work piece is then ready to be finished, or can be further refined with a card scraper or sandpaper. The smoothing plane is usually held with both hands, and used in a similar manner to the other bench planes. Though designed for smoothing, a smoothing plane can be used as an 'all-round' bench tool and for rougher work depending on how it is set up. Being smaller than other bench planes, the smoothing plane is better able to work on smaller work pieces and around obstructions. Since the 1700s wooden smoothing planes have predominantly been 'coffin shaped' wider in the middle and slightly rounded making them more manoeuvrable. It has also been claimed that the coffin design exposes more end grain, enabling the plane to better adjust to changes in humidity. Henry Boker Maker: Heinrich "Henry" Böker of Reimschied-Solingen, Germany and his family was making tools in the 17th century. In 1829 Hermann and Robert Böker added sabres to the company's offerings, in 1837 they emigrated to New York City and established a firm to import German cutlery. H. Boker sabres would be eventually supplied to some American soldiers during the Civil War. Heinrich Boker in 1869 , a relative of Hermann and Robert, established a cutlery firm in Solingen, a centre of industry and cutting tool manufacturing in Germany. The company became a leader in the manufacture of razors, scissors and eating utensils. As early as 1900 the majority of tools produced by Boker were distributed in the U.S. market by the New York branch of the family, and pocket knives became the company's most important product line. During WWII the Solingen factory was destroyed and all the equipment and inventory was lost. After the war the factory was rebuilt and the company resumed operations, but in the early '60s the company was sold to the scissors manufacturer Wiss & Sons, and in the early 70s Wiss sold out to Cooper Industries. At some point Heinrich Boker adopted the Americanised version of his name, Henry Boker and was used as a brand name for the company's products. A vintage smoothing plane of the coffin pattern made by Henry Boker the item is a rare and significant example of vintage woodworking tools used in the manufacture of wooden items.Smoothing Plane Coffin design. Blade marked Henry Bokerflagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, smoothing plane, heinrich boker, carpenters tool, cabinet makers tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Smoothing Plane, Heinrich Boker, late 19th to early 20th Century
A smoothing plane is typically used after the work piece has been flattened and trued by the other bench planes, such as the jack, fore, and joiner planes. Smoothing planes can also be used to remove marks left by woodworking machinery. When used effectively alongside other bench planes, the smoothing plane should only need a handful of passes removing shavings as fine as 0.002 inches (0.051 mm) or less. The work piece is then ready to be finished, or can be further refined with a card scraper or sandpaper. The smoothing plane is usually held with both hands, and used in a similar manner to the other bench planes. Though designed for smoothing, a smoothing plane can be used as an 'all-round' bench tool and for rougher work depending on how it is set up. Being smaller than other bench planes, the smoothing plane is better able to work on smaller work pieces and around obstructions. Since the 1700s wooden smoothing planes have predominantly been 'coffin shaped' wider in the middle and slightly rounded making them more manoeuvrable. It has also been claimed that the coffin design exposes more end grain, enabling the plane to better adjust to changes in humidity. Henry Boker Maker: Heinrich "Henry" Böker of Reimschied-Solingen, Germany and his family was making tools in the 17th century. In 1829 Hermann and Robert Böker added sabres to the company's offerings, in 1837 they emigrated to New York City and established a firm to import German cutlery. H. Boker sabres would be eventually supplied to some American soldiers during the Civil War. Heinrich Boker in 1869 , a relative of Hermann and Robert, established a cutlery firm in Solingen, a centre of industry and cutting tool manufacturing in Germany. The company became a leader in the manufacture of razors, scissors and eating utensils. As early as 1900 the majority of tools produced by Boker were distributed in the U.S. market by the New York branch of the family, and pocket knives became the company's most important product line. During WWII the Solingen factory was destroyed and all the equipment and inventory was lost. After the war the factory was rebuilt and the company resumed operations, but in the early '60s the company was sold to the scissors manufacturer Wiss & Sons, and in the early 70s Wiss sold out to Cooper Industries. At some point Heinrich Boker adopted the Americanised version of his name, Henry Boker and was used as a brand name for the company's products. A vintage smoothing plane of the Bismark pattern made by Henry Boker the this plane is now regarded as a collectors item and is an example of vintage woodworking tools used in the manufacture of wooden products.Smoothing Plane Bismark design. Blade marked Henry Bokerflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, smoothing plane, heinrich boker, carpenters tool, cabinet makers tool -
 Chiltern Athenaeum Trust
Chiltern Athenaeum TrustDomestic object - Spoon belonging to W.C.Busse
Wilfred Clarence Busse, born in Chiltern in 1898, His family moved to the region during the gold rush and continued to reside in the area, purchasing land adjacent the Murray River. Busse completed his secondary education at Wesley College in Melbourne then studied law at the University of Melbourne. Busse went on to become a barrister, often in the chambers of Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933) a judge of the Supreme Court of Victoria. He worked most of his life in Chiltern as a Barrister and Solicitor and gained the unofficial title of historian of Chiltern, leaving behind several manuscript histories and a scrap book. Busse was an avid fictional writer and in 1930 he published two novels. Time spent on a Victorian station in his early twenties, as well as careful documentary research, informed the writing of his historical novels of bush life. "The Blue Beyond; A Romance of the Early Days in South Eastern Australia” and "The Golden Plague: A Romance of the Early Fifties." "The Golden Plague” won the T. E. Role gold medal for the best historical novel which went on to become a best seller. Busse often drew inspiration for his novels from his younger years living Chiltern. His passion for the region lead him to write “The History of Chiltern” which was published in a serial form in the Chiltern Federal Standard from 1922-1923. Wilfred Clarence Busse was a member of Chiltern Athenaeum (where this object is now held) up until his death in 1960, he is buried in the Barnawartha Cemetery. The floral motif on this particular spoon appears to be stylised in the decorative arts and craft style favoured in Europe between 1880-1920 and less representational than examples of Australiana flora captured in silversmithing from the 1850's onwards produced in Australia. It is likely that those producing silverware at the time would be drawing on the decorative arts movement while incorporating elements of the natural beauty in the flora of their newfound environment into the silverware they produced. This spoon seems more likely to have been produced in Europe and imported to the colony. The hallmarks on the handle DON and BP indicate it may have been produced from English electroplating silver which is a more cost effective product than solid silver, most likely produced by Cooper Brothers, Don Plate Works, established in Sheffield in 1866 who distributed silverware in Europe, America and the colonies well into the 1950's.Wilfred Clarence Busse was of social significance to Chiltern, he helped to document the cultural story of the area in his published works "The Golden Plague" and "The Beyond Blue" by recounting his own upbringing in a bush lifestyle. He was a respected Barrister and was the unofficial historian of the Chiltern Athenaeum for many years. This spoon represents a window into the domestic life of this person who was well loved in the area, and it continues its relationship to Busse as well as Chiltern by being held within the very collection he helped to maintain in his life. Domestic objects tell us the story about how people lived, objects of daily use hold particular meaning in that they can tell us the story of an individual, we feel closer to their life and habits, it humanises and connects us across time. Wilfred Busse ate food and he did it from a beautiful silver floral detailed spoon.A silver tablespoon with floral embossed head and hallmarks embossed on reverse handleDON/ BP/silverware, wilfred clarence busse, busse, chiltern, chiltern athenaeum, federal standard, t. e. role, "the blue beyond, a romance of the early days in south eastern australia”, "the golden plague: a romance of the early fifties.", "the golden plague”, wesley college, university of melbourne, sir leo finn bernard cussen, supreme court of victoria, gold rush, murray river, “the history of chiltern”, silversmithing, spoon, decorative arts, floral, flora, australiana, australian flora, arts and craft movement, australian silver, cussen -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncHeadwear - Wool Felt & Jersey Hat, Ann Austin of Melbourne, 1960s
Ann Austin of Melbourne was the name of a Melbourne millinery house. Thelma Prentice was one of the partners in the house, and the chief designer/milliner. Very little information about the millinery house and the milliner are available online but there is an interesting article, published in the Brisbane Courier Mail on 8 October 1949 which describes the influence of French style on fashion and design in Australia. The article by Lucy Gough recounts the views of Thelma Prentice who had just returned from the Paris fashion shows. "Australian millinery toes line with Paris From LUCY GOUGH LONDON, October 7 (Special) Australian hats can compare very favourably with those designed in Paris, and are considerably cheaper, says Miss Thelma Prentice, partner in a well-known Melbourne millinery firm, who has just completed six months' visit to England and the Continent. An ordinary hat, Miss Prentice said, would cost at least £15 from any of the top Paris houses. Australia could achieve the same effect for a lot less money. Miss Prentice went to all the Important dress shows as well as the millinery houses in Paris, because she believes that millinery is an accessory to fashion and to obtain the best idea of new trends hats must be shown with frocks to get a complete follow-through and tie-up between the two. At their packed shows, with standing room only, Path and Dior were selling hats they designed, faster than many well known Paris millinery houses, Fath's favourite line was the becoming 'wing treatment,' which he achieved by a profile flattering side swing of material jutting out almost 10 inches from the face. This was completely different to the side drape already seen in Australia. Dior, as a direct contrast, was specialising in skull hats, which almost followed the hair line, to show very little hair at the back of the head. His cocktail hats were heavily sequinned and beaded. Every model was designed exclusively for short hair, and Miss Prentice, whose own hair is beautifully short cut by a Paris hairdresser, said that French mannequins' hair was so abbreviated at the back it was almost a semi-shingle. Hats generally she found were plain, with sharply angled self trimming, and black one of the most popular colours." The hat was donated by Kathleen Gervasoni, a resident of Kew, and during the 1970s a Mayoress of the former City of Kew. The Kew Historical Society’s fashion and design collection is comprised of costumes, hats, shoes and personal accessories. Many of these items were purchased or handmade in Victoria; some locally in Kew. The extensive hat collection comprises items dating from the 1860s to the 1970s. While most of the hats in the collection were created by milliners for women, there are a number of early and important men’s hats in the collection. The headwear collection is particularly significant in that it includes the work of notable Australian and international milliners.High crowned hat made of burgundy felt with decorative pink jersey turban folds attached to the side by clusters of pink beads. The hat was designed by Thelma Prentice of the ' Austin of Melbourne' millinery house. Label, inside centre crown, woven in black on white polyester: *ann austin / OF MELBOURNEmilliners, hats, ann austin of melbourne, thelma prentice, australian fashion - 1960s, kathleen gervasoni -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationCard from Queensland Nurses Union (Bundaberg Branch) to Catherine Hutchings, visiting Victorian nurses union staff member, 1993
Thank-you card given to Australian Nursing Federation (Victorian Branch) staff member Catherine Hutchings by staff at the Bundaberg Branch of the Queensland Nurses Union. In 1993, Victorian Branch staff travelled throughout Queensland, Western Australia and the Northern Territory for a series of meetings on recent events impacting nurses' conditions in Victoria. The meetings were strategically held ahead of the 1993 Federal election to discourage the election of a Coalition government. The election of the Coalition government in Victoria in 1992 had seen the introduction of the Employee Relations Act, which saw the end of the state award system in Victoria. This gave employers greater powers to establish wages and conditions and less power to the Industrial Relations Commission, foreshadowing what would later occur at a Federal level. An article in the Victorian Branch newsletter 'On the Record' from April 1993 describes the 'tour'. Entitled 'Vic. Nurses Spreading the Word in Queensland, Western Australia and the Northern Territory', it explains: "Catherine Huntchin[g]s and Elizabeth Hulme recently spent a week in Queensland informing nurses about the effect of a Liberal Government on nurses. As well, Tracy Austin visited WA to talk to nurses there about life under Kenneyt [sic]. Catherine and Liz held a total of 23 meetings from Cairns to Brisbane, as well as giving media interviews. It was well worth the effort and certainly there was much support given to nurses in Victoria. Perhaps the most interesting issue was that many nurses did not realise that they may find themselves in the same situation if we have a change in Federal Government. In February, Catherine went to the NT to talk to nurses in Darwin, Alice Springs and Katherine and despite some minor hiccoughs (the Health Department banned all the meetings so alternative venues had to be found) the turnout was gratifying - you have to be dedicated to attend a meeting held in a carpark in 32 C heat! Catherine says that the reception she received in both QLD and the NT was superb. "Everyone went out of their way to make us feel very welcome, and to shower us with sympathy over the situation. More important, is the fact that the information was distributed so no matter how the votes go on March 13 [1993, federal election] - they will be informed votes." she said. Catherine, Liz and Tracy extend sincere thanks to all interstate nurses who made their visits a success."Typed card given with flower bouquet. Printed on one side with personalised, typed message 'DEAR CATHERINE, UNITED WE STAND DEVIDED [sic] WE BEG THANKS FOR SPEAKING UP FOR US. FROM B'BERG [Bundaberg] BRANCH Q.N.U. [Queensland Nurses Union]'.nursing, nurses, unionism, solidarity, victoria, queensland, bundaberg, campaigning, 1993 federal election, 1992 victorian election, australian nursing federation, trade unions, politics, queensland nurses union, qnu, anf -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - EMLYN WILLIAMS AS CHARLES DICKENS, 1958
Emlyn Williams as Charles Dickens. Giving a Solo Performance of Scenes from the Famous Novels and Stories. Tour of New Zealand and Australia, 1958. D D O'Conner Productions Ltd.., in association with the Australian Elizabethan Theatre Trust. 1 Moving in Society. 2 Paul. 3 Mr Bob Sawyer Gives a Bachelor Party. 4 The Signalman. 5 Mr Chops. 6 The Fancy Ball. The Adoptions . . . The Desk . . . The Nature of the Performance. During the fifties of the last century, Charles Dickens, at the Height of his fame as a novelist, ventured on something quite new; he gave, in Birmingham, a public 'reading' of one of his stories. This turned out to be an historic occasion, opening up an extraordinary career for the great writer. Each 'Reading' was more sensationally successful than the last. The word was put into inverted commas because nothing could have been less like reading than Dickens's dramatic performance. Something like a hundred years later at the Criterion Theatre, EMILYN WILLIAMS appeared before the London public 'as Charles Dicken's, giving a solo performance of scenes from the novels.' At this point the actor had been a star of . . . Personal Manager for Emlyn Williams: Alan Cambell. Stage Director: Tony Ward. Secretary and Accountant: Aubrey Thomas. Manager for the Australian Elizabethan Theatre Trust: Mary Rawdon. EMILYN WILLIAMS. Emlyn Williams, as actor, playwright of director (often in all three capacities simultaneously) has been in the theatre since he acquired the degree of M.A. and shook from his feet the dust of Oxford. Born in Flintshire, North Wales, in 1905, the son of a village inn-keeper, he spoke only Welsh as a child and learned English at school - a boyhood freely depicted in his comedy, 'The Druid's Rest.' At the age of ten he won a scholarship to the local Holywell County School, and at the age of seventeen another scholarship (in French) to Christ Church, Oxford. Once at the University hw discovered the theatre, by means of the Dramatic Society, and realized at once it was to dominate his life. While he . . . Includes photo of E Williams. Advertisement for DECCA Records, Emlyn Williams as Charles Dickens, Volume 1.Back cover photograph of Emlyn Williams. Second Programme in Australia: Emlyn Williams as 'A Boy Growing Up' An entertainment from the stories of Dylan Thomas. 'Gorgeously Funny' - The observer, London. Cover well decorated with sketches and photo of Emlyn WilliamsPeerless Press Pty. Ltd.cottage, miners, emlyn williams as charles dickens. giving a solo performance of scenes from the famous novels and stories. tour of new zealand and australia, 1958. d d o'conner productions ltd.., in association with the australian elizabethan theatre trust. 1 moving in society. 2 paul. 3 mr bob sawyer gives a bachelor party. 4 the signalman. 5 mr chops. 6 the fancy ball. the adoptions . . . the desk . . . the nature of the performance. during the fifties of the last century, novelist, ventured on something quite new, in birmingham, a public 'reading'. an historic occasion, opening up a career 'reading' criterion theatre solo performance novels.' actor had been a star of . . . personal manager for emlyn williams: alan cambell. stage director: tony ward. secretary and accountant: aubrey thomas. manager for the australian elizabethan theatre trust: mary rawdon. actor, playwright of director (often in all three capacities simultaneously) degree of m.a. oxford. born in flintshire, north wales, in 1905, village inn-keeper, spoke welsh learned english at school. comedy, 'the druid's rest.' won a scholarship to the local holywell county school, and at the age of seventeen another scholarship (in french) to christ church, oxford. university he discovered the theatre, dramatic society. photo of e williams. advertisement for decca records, as charles dickens, volume 1.back cover photograph of emlyn williams. second programme in australia: emlyn williams as 'a boy growing up' stories of dylan thomas. 'gorgeously funny' - the observer, london. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Coorongite
Coorongite is a dark, rubber-like, highly resilient structureless algal deposit. In the Coorong district of South Australia it occurs in moderate quantities associated with the coastal swamps and sand dunes which extend for a considerable distance east of the mouth of the Murray. This particular specimen was recovered from the south of the Coorong River, South Australia. A type of sediment rich in organic matter, Coorongite is the unlithified end-member of the sapropelic coal series. The members of the sapropelic coal series can be ranked in order as sapropel (the unlithified form), sapropelic-lignite, and sapropelic-coal (the lithified forms) based on increasing carbon content and decreasing volatile content. Sapropel (Coorongite) is an unlithified dark, pulpy, fine organic mud containing concentrations of algae and miospores that are more or less identifiable. Coorongite is typically found as an algae like substance, that can be found in irregular size pieces. Coorongite was believed to be dried up oil due to its rubber-like texture. The Coorongite is also soft to the point where it can be cut into with a knife or it can be broken and torn by hand. Otherwise known as 'Kurangk', the Coorong River is home to the Ngarrindjeri people, which acts as both a place for gathering food and a spiritual place. In 1852 the first sight of Coorongite was found along the Coorong River. The finders mistook the Coorongite for dried up oil, which lead to the belief that there were oil reserves under the Coorong River. Between the 1860s and the 1930s the Coorong River became a place where mining oil and Coorongite became precedent. Nowadays, the local council and the South Australian Government are working together with the Ngarrindjeri people to sustain and preserve the Coorong River and the culture that is with it. Soon after gold was discovered in 1851, Victoria’s Governor La Trobe wrote to the Colonial Office in London, urging ‘the propriety of selecting and appointing as Mineral Surveyor for this Colony a gentleman possessed of the requisite qualifications and acquaintance with geological science and phenomena’. Alfred Selwyn was appointed geological surveyor in Australia in 1852 which began the Geological Survey of Victoria. Selwyn went on to collect geological samples and catalogue thousands of specimens around Australia. In 1853-69 the Geological Survey issued under Selwyn's direction sixty-one geological maps and numerous reports; they were of such high standard that a writer in the Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London bracketed the survey with that of the United States of America as the best in the world. During his years spent in Australia, Selwyn collected numerous significant geological specimens, examples of which are held in collections such as the Burke Museum.Coorongite is considered to be a mineral with a unique texture, where it can be both hard and soft. Coorongite can also be considered to be a rare mineral, as it is only located along the Coorong River and due to the mining of it, has left very few sources. It was believed at one point that Coorongite could be used to replace oil. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Three solid varyingly hand-sized pieces of wooden appearing organic matter derived from the river in the Coorong District in South Australia. A rubber-like, highly resilient structureless algal deposit.Specimen 245 page 69 / in Descriptive Register / "Elcestic Bitumen, / Coorangite" South of / Coorung River, South Australia . / C. WIllman / 15/4/21burke museum, beechwoth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineraology, coorong, coorong river, kurangk, ngarrindjeri, south australia, coorongite, coorongite specimen -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Peter Pidgeon, Grave of Anne Hunniford (nee Hamilton Burgoyne) and Anne Jane Hunniford, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 5 April 2021
On February 1, 1854, the first Eltham Post Office was established. At that time, the number of permanent residents would have been fairly small, probably less than 200. In 1855 Thomas Hunniford was appointed as Eltham's postmaster (replacing Frederick Falkiner). He operated the post office from his general store in Maria Street (now Main Road) near Bridge Street (originally facing Bridge Street but later altered to face Main Road). His daughter, Miss Anne Hunniford, was a teacher at Eltham Primary School in her early adult years. Sometime between 1864 and 1868 the management of the post office passed from Thomas Hunniford to his daughter, Anne who managed the Eltham Post Office until illness forced her to retire in 1928. A big improvement in communication was provided for Eltham residents when a telegraph office was established at the post office in 1877. During 1923 a manual telephone exchange was provided at Eltham, the first two subscribers being J.J. O’Connor and Eltham Police Station. Anne was succeeded by her nephew Neville Burgoyne whose family were then running the store, which had been rebuilt and modernised in 1926 to accommodate an expanded post and telegraph office. Anne knew everyone and was respected for her kindly actions in her official and private capacities. In her time there was no official letter delivery to houses; residents were expected to collect their mail at the post office. But if an important letter or telegram arrived, Anne would try to find someone willing to deliver it. Jock Read recalled he started his own private "mail run"; he would charge people 1/- per week to take their letters to the post office for mailing and would return with their mail. Anne died in 1928, aged 73. She is buried in Eltham Cemetery with her mother and with a Burgoyne child born much later. Burgoyne's store was further extended in 1940 and still stands though has undergone several modifications and businesses. In 1954 the post office moved to a shop in the main Eltham shopping centre, then in 1958 a purpose-built post office was opened near the entrance to the railway station. In Loving Memory of Anne Hunniford Nee Hamilton Burgoyne Born Ireland 1813 Died Eltham 1899 Also her daughter Anne Jane Hunniford Born Eltham 1855 Died Eltham 1928 Brenda May Burgoyne Born 16. 8. 1956 Died 18. 6. 1958 Rest In PeaceBorn Digitaleltham cemetery, gravestones, anne hunniford (nee hamilton burgoyne), anne jane hunniford, brenda mary burgoyne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClothing - Petticoat, late 19th century to early 20th century
This petticoat was one of several items donated from the estate of Susan Henry OAM nee Vedmore (1944 - 2021). It is in very good condition and appears to be from the Edwardian era - early 20th century. A petticoat is a lady's undergarment - worn under a skirt or dress. They provided warmth, modesty and shape to the dress. In the middle of the 19th century, petticoats were worn over hoops, bustles or in layers. Petticoats varied according to the style of the outside skirt or dress. Plain petticoats tended to be worn with everyday wear whilst better dresses (party dresses or silk gowns) were worn with petticoats that often had more trim and embellishments. Edwardian petticoats had less volume than Victorian era petticoats and they had a "dust ruffle" or lining under a lace flounce. The "dust ruffle" protected the lace flounce and gave the petticoat more flare at the bottom, greater freedom when walking as well as saving the flounce (which was often made of finer material) from everyday wear and tear. Tucks are another feature of Edwardian petticoats - when the lace at the bottom became worn, it could be cut off and the tucks released. This extended the life of the petticoat. This petticoat features an intricate trim of broderie anglaise. Although broderie anglaise was a lace that could be made by hand, it was very time consuming to make. St Gallen was a city in Switzerland that had become known for producing quality textiles. At the beginning of the 19th century, the first embroidery machines were developed in St Gallen. Factories used embroidery machines but people also had them in their homes. They were able to produce broderie anglaise for export. By the early 20th century, machine made lace, fabric, ribbons etc. were being sold in drapers shops all over England and Wales to women who were making clothes and furnishings for their families. It is highly likely that the lady who made this petticoat brought the lengths of broderie anglaise already made to embellish and personalise her petticoat. Susan's family (Harold and Gladys Vedmore) immigrated to Australia from Wales in 1955 and settled in Warrnambool. Susan was well known in the Warrnambool community for her work supporting children and families across the district - particular those with disabilities, or those who were homeless, unemployed or isolated. Susan was the founding trustee of the "Vedmore Foundation" - a Warrnambool philanthropic trust set up in 2010 to support a range of charitable and not-for-profit causes by providing grant assistance. In 2021, she was awarded a Medal of the Order of Australia for services to the community.This item is an example of the needlework skills of women in the late 19th century - creating pintucks and adding lace to personalise and embellish a practical item of clothing. It is also significant as an example of a practical solution to the difficulties that women of this era faced with regard to the washing of clothes and household linens.A white lawn petticoat with a 22.5 cm opening that fastens with 2 small buttons and a drawstring tie. It is decorated with two wide pintucks followed by two gathered frills (or flounces) - one decorated with three rows of narrow pintucks and a single row of broderie anglaise and the bottom frilled hem finished with 3 rows of broderie anglaise in a flower design. The two bottom frills are lined with plain white cotton fabric.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, petticoat, lady's petticoat, undergarment, lady's undergarment, lingerie, edwardian petticoat, broderie anglaise, lace, machine made lace, hand sewn, machine sewn, draper's shop, susan henry oam, vedmore foundation -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Resuscitator Unit, c. 1960
Mechanical resuscitation devices, such as the Pulmotor and Lungmotor, were popular in the early part of the twentieth century. Their use waned in the 1920s as significant bodies like the British Medical Research Council and American Red Cross refused to endorse them. The most popular of the resuscitators to emerge in the 1930s was the E&J (Ericson and Johnson) resuscitator. The device was soon widely available, vigorously promoted with support from many medical practitioners. They were soon to be found in hospitals, emergency services like the ambulance and fire brigade, and voluntary life-saving organisations. In Australia, Norman James, director of anaesthesia at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, developed an interest in equipment for ambulances and the resuscitation of drowning victims. Little in the way of practical, portable equipment was available to either the ambulances or the voluntary life-saving organisations, such as Surf Life Saving Australia (SLSA); American resuscitators, like the E&J, were expensive and bulky to import. James designed a simple portable resuscitation device for local use after being approached by Jack Conabere, secretary of the Elwood Life Saving Club (ELSC). The resulting Royal Melbourne Hospital resuscitator, or the R.M. resuscitator as it was marketed, was a simpler, manual version of those available overseas. It was gas driven with a plunger, marked “Press”, and a safety valve. The small working unit attached directly to the facemask. Once the patient was positioned facedown and the airway cleared of debris, the mask was placed firmly over the face. The plunger allowed gas to flow and lung inflation; releasing the plunger allowed expiration. This simple resuscitator was marketed by Commonwealth Industrial Gases (CIG) and became very popular in Australia with volunteer and professional rescue organisations. It represents one of the many innovations in resuscitation equipment that resulted from cooperation between volunteer life savers and medical practitioners. Norman James worked closely with Jack Conabere and the Government Pathologist to develop the equipment. ELSC was the first life saving club to use the resuscitator on the beach. While conducting an early training exercise on 23 December 1951, they used it to successfully resuscitate a man who had drowned after capsizing his home made yacht. The R.M. resuscitator was also used in more inventive ways. At Fairfield Hospital in Melbourne, a group of physiotherapists and doctors did some innovative work with polio patients, teaching them glossopharyngeal (or “frog”) breathing, as a means of becoming less dependent on ventilators. In 1981, the Australian Standards Association stated that the RM head failed to meet its revised standards and it was withdrawn from the market. Red leather suitcase with black leather trim with metal studs. There are clip locks for locking the suitcase in the closed position. The suitcase contains equipment for oxygen resuscitation. There is a space allocated for two oxygen cylinders, however there are no cylinders present.Embossed into metal plaque: The C.I.G. / Oxy-viva / PORTABLE UNIVERSAL OXYGEN RESUSCITATORresuscitation, portable, surf life saving australia, royal melbourne hospital, rm resuscitator -
 Chiltern Athenaeum Trust
Chiltern Athenaeum TrustDomestic object - Spoon belonging to W.C.Busse
Wilfred Clarence Busse, born in Chiltern in 1898, His family moved to the region during the gold rush and continued to reside in the area, purchasing land adjacent the Murray River. Busse completed his secondary education at Wesley College in Melbourne then studied law at the University of Melbourne. Busse went on to become a barrister, often in the chambers of Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933) a judge of the Supreme Court of Victoria. He worked most of his life in Chiltern as a Barrister and Solicitor and gained the unofficial title of historian of Chiltern, leaving behind several manuscript histories and a scrap book. Busse was an avid fictional writer and in 1930 he published two novels. Time spent on a Victorian station in his early twenties, as well as careful documentary research, informed the writing of his historical novels of bush life. "The Blue Beyond; A Romance of the Early Days in South Eastern Australia” and "The Golden Plague: A Romance of the Early Fifties." "The Golden Plague” won the T. E. Role gold medal for the best historical novel which went on to become a best seller. Busse often drew inspiration for his novels from his younger years living Chiltern. His passion for the region lead him to write “The History of Chiltern” which was published in a serial form in the Chiltern Federal Standard from 1922-1923. Wilfred Clarence Busse was a member of Chiltern Athenaeum (where this object is now held) up until his death in 1960, he is buried in the Barnawartha Cemetery. The leaf shaped motif of this particular spoon appears to be stylised in a simple form of decorative arts and craft or even Art Nouveau style favoured in Europe between 1880-1920 and less representational than examples of Australiana flora captured in silversmithing from the 1850's onwards. According to Christine Erratt, due to the goldrush in the 1850's, there was increased wealth in the colony and an influx of immigrants from Europe to Australia who brought with them silversmithing skills which began ‘the golden age’ of Australian silver', Erratt says that 'Australia's unique flora has been portrayed in the decorative arts since the early colonial times of the last decade of the 18th century. The use of Australian flora to decorate silverware is of particular interest and diversity'. It is likely that those producing silverware at the time would be drawing on the decorative arts movement while incorporating elements of the natural beauty in the flora of their newfound environment into the silverware they produced. There are no discerning maker hallmarks to place where it was produced or ascertain the material accurately.Wilfred Clarence Busse was of social significance to Chiltern, he helped to document the cultural story of the area in his published works "The Golden Plague" and "The Beyond Blue" by recounting his own upbringing in a bush lifestyle. He was a respected Barrister and was the unofficial historian of the Chiltern Athenaeum for many years. This spoon represents a window into the domestic life of this person who was well loved in the area, and it continues its relationship to Busse as well as Chiltern by being held within the very collection he helped to maintain in his life. Domestic objects tell us the story about how people lived, objects of daily use hold particular meaning in that they can tell us the story of an individual, we feel closer to their life and habits, it humanises and connects us across time. A tarnished small silver teaspoon with leaf-shaped head and slim handlesilverware, wilfred clarence busse, busse, chiltern, chiltern athenaeum, federal standard, t. e. role, "the blue beyond, a romance of the early days in south eastern australia”, "the golden plague: a romance of the early fifties.", "the golden plague”, wesley college, university of melbourne, sir leo finn bernard cussen, supreme court of victoria, gold rush, murray river, “the history of chiltern”, silversmithing, spoon, decorative arts, floral, flora, australiana, australian flora, arts and craft movement, australian silver, cussen -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyNewspaper, Summer's Times. Lord Somer's Camp, 1977
A newsletter printed at Somer’s Camp in 1977. It reflects some of the activities the campers experienced. There was news of sporting events and winners of contests. Also a crossword and some cartoons. The authors are not identified but could be some of the junior Legatees. Legacy has provided camps for junior Legatees for many years. It started in the early years when Legacy organised outings to the property of Legacy founder, Legatee Stan Savige, who had a place in Balnarring close to the beach. In later years children went to camps around Victoria. Occasionally it was to Lord Somers Camp in Somers. Some of the name mentioned in the text: Chaplain Charles Sligo, Fire officer David McPherson, Games director Peter Johnstone, PR Officer Les Phillips, Bursar Robin Kelly. Also section leaders: Keith Williamson, Peter Chapman, Fraser Zielinski, Andrew Russell, John Jones, Campbell Mathieson, John Higgins, Mark Lane. The editorial explains the aims of the camp. "Lord Somer's Camp sets out not so much to teach a method of life as to instil one by example. This may sound rather ominous, as though you are being brain washed - and perhaps in a way you are. The high-powered pressure which is put on you by Slush and by Group Leaders tries to do in less than a week what would take years by any other means. . . In fact what the pressure does achieve may be quite different for different people. . . Cooperation was discussed yesterday. Many of you have possibly already been forced to see that a group of people can achieve nothing unless they work together. Even after one day on the sports field you would realise tag in an event such as the tug-of-war you will never succeed unless every one works together in perfect harmony. . . The second ideal mentioned above was unselfishness. Nearly every problem in the civilised world today, whether it be war, social unrest, inflation, industrial strife it can be traced back to a selfish attitude on someone's part. An unselfish attitude is a very difficult thing to develop but once obtain can not only do good for the individual but for the whole community. Big Camp tries to establish this attitude on in the new participants at camp by the example of others.It is only when one realises that all the organisation of and running of this camp, and indeed of the whole PowerHouse Organisation, is on a voluntary, unpaid level that it impossible to gain some inkling of the extent of this unselfish example, to understand the amount of effort people will make to continue something they believe in." A record of the camp activities at Somers in 1978.Newsletter published at Somers Camp to highlight activities and attendees.Dated 18 January 1977 on second page.camp, junior legatee outing, lord somers camp -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaFurniture - Volum Medicine chest
This chest is the typical mid-18th century model. Thought to have belonged to captain James Volum.A medicine chest was a necessity for all sea journeys. Sometimes surgeons were onboard ships if there were passengers but on merchant ships, the captain had to be able able to look after his crew. A medium size mahogany cabinet with four protruding feet, small free hinged handles on left and right sides which are positioned approximately 5/8ths up from the bottom of the item, these handles can hinge 100 degrees upwards. The front and back 6/8ths of the cabinet can hinge open, as can the top of. Both front and back doors can be locked closed with their own respective hook latch which is on both sides of the cabinet. The top lid can be locked by interacting with a metallic keyhole which is present on the front of the cabinet close to the top. Revealed by opening the top lit is storage location with two rows of three storage spaces and one row of four. Revealed by opening the front door, is a single shelf with six divided locations for an equal number of glass containers, though only five remain in complete form. Below this self are three rows of drawers of differing dimensions, each with a small white knob. There are two drawers of equal width in the first row. Each drawer has four equally divided sliding pieces on its top face. When removed, these lids reveal a respective small space. Present on small paper labels on each of these lids are identifiers of the material which was stored. There are three equally sized drawers in the second row, which are less wide than the previous row. Only two of the drawers in this row have lids, of which each only have a single lid which covers a single compartment, each of these have a single label on them. The middle drawer contains a small glass mortar and pestle which are restrained by small wooden fixtures within the drawer. There are two drawers of equal width and greater height than any of the previous drawers in the third row. The first drawer has a single compartment containing multiple vials of varying dimensions, some of which feature a paper label with a respective inscription. Some of these vials are broken. In the second drawer has no lid which covers its four equally sized glasses. These are restricted by a wooded piece with four circular cut-outs. Revealed by opening the back door are two equally sized and spaced shelves which both have four divided locations which are filled by eight respective glass containers. These glass containers are of similar design to those in the front compartment but are larger. Some of these glass jars have paper labels like those found on previous glass containers.Label on top lid:volum collection, medecine chest, portable furniture, geelong, peterhead, scotland, captain, seafaring, whaling, london, bishopsgate, old gravel lane, london docks, tobacco dock, james burrows -
 Conservation Volunteers
Conservation VolunteersKey Document: First Green Corps National Conference, Canberra, 21-24 February 1998, Conference Organisers David Clark and Mark Purcell, Proceedings of First Green Corps National Conference, Canberra, 21-24 February 1998
In March 1995 ATCV had circulated a proposal for an ‘Australia Corps’. The proposal emerged over time from ATCV board and staff through debate and experience. ATCV Board member Alan Wright had written earlier: “There is in our society a terrible vacuum for adolescents to give expression to their independence and idealism in a constructive way, a chance to try themselves out independent of their parents/teachers in adult roles.” ATCV’s Brisbane office manager Phil Harrison had first been involved with ATCV as a volunteer from UK, drew together ideas about an ‘Australia Corps’, that had been discussed with Alan Wright, John Fenton and others at the ATCV staff/board planning workshop at Sorrento in December 1993 and “…based upon our experience and participation in the LEAP program and observations of Conservation Corps around the world”. The concept of a six-month program for young people with a training wage and accredited training which encouraged both competencies and personal development emerged, with a standard format of ten participants working fopr six months under the direction of a supervisor. The ‘Australia Corps’ proposal was widely distributed to Federal, State and Territory parliamentarians and received positive feedback. The Liberal Party, then in Opposition, included the idea of a “Green Army” in their environmental policy, placing more emphasis on environmental outcomes and less on job creation than the Keating ALP Government had. A young and up-and-coming parliamentarian, Tony Abbott MP, was enthusiastic and was to visit several ATCV projects (both before and after Green Corps started) to learn about their workings direct from volunteers and CVA staff. Several times he visited projects with Ian Smith project and Ian recalls being impressed by the efforts he made to talk at length with all participants. Tony Abbott took a personal interest in the progress of Green Corps. Colin Jackson and Phil Harrison were guests of Abbott in Parliament House, Canberra, on the evening of 20 August 1996. The Federal Treasurer, Peter Costello, announced in his first Budget Speech that: - “the Government will provide $42 million over the next 3 years to establish the Green Corps. The Green Corps will be open to young Australians aged 17 to 20 to demonstrate their commitment to the environment by working on projects to preserve and restore Australia's natural environment and cultural heritage. The projects will also contribute to their career and employment prospects through training, skills development, work experience and personal development.” ATCV’s chief executive officer Colin Jackson worked with senior staff Madeline Townsend, Garry Snowden, Phil Harrison, and John Fenton to fine-tune the ATCV proposal. On the strength of unique national coverage and credible record ATCV went on to win the tender to administer and manage the day-to-day operations of the Green Corps program for five years (1997-2002). Winning a $36 million contract was a big breakthrough for ATCV. Fourteen years before, a small non-profit group had started in Ballarat in country Australia with a vision – but little else. Its key people had shaped opinion and won political support for a concept. There was about to be transformation from hand-to-mouth existence into a nation-wide business with resources to build for the long term. This documents records many positive comments about Green Corps and ATCV's implementation of it.24pp illustrated booklet printed in green and some gold.atcv green corps australia-corps tony abbott mp phil-harrison -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Plant Stand, Late 19th Century (1898)
During the years 1869-1935 there were well over 250 registered bamboo furniture producers in Britain. The earliest recorded firm was Hubert Bill of 14 Little Camden St, London N.W., who claimed to have been established in (1869) while Daniel Jacobs & Sons of Hackney Road, London, were still in business in 1915, after 45 years of production. Design, quality, price and methods of construction were fairly consistent throughout the whole period, but it was the imaginative and often eccentric choice of subject matter that marked differentiation between the various firms. While most produced standard tables, stands and fire-screens, the more adventurous offered for sale items such as corner shelve units, charcoal barbecue grills and musical tea tables. Shelves were often covered with embossed leather paper designs, at first imported from Japan and then later produced in England. Some firms incorporated the knobbly roots of the bamboo stems into their designs, generally to form feet. Occasionally handles to drawers and cupboards were made with these roots although they were more commonly carved as imitations. Handles were mostly of cheap metal or brass. The ends of the bamboo canes were capped with stamped metal or turned bone, ivory or wooden discs. Methods of construction fell into three categories. First and most common is that of pegging. Bamboo stems being hollow, thick dowels can easily be glued into the joints. Some firms farmed out this work of `plugging' the ends of the canes to part-time workers at home. The second method, that of pinning, was far less satisfactory as bamboo tends to split lengthwise and therefore the jointed pieces eventually disintegrated. The most efficient method was that patented in 1888 (patent No 2383) by the firm of W. F. Needham in Birmingham. It consisted of metal shoes and covers for all joints which were made by wrapping a metal strip around the stems and soldering the overlapping ends. Some joints were further strengthened by a small pin or screw. Needham was by far the largest and most successful manufacturer and their individual and superior method of construction undoubtedly gained them their reputation. A. Englander & Searle of 34 Gt Eastern St and 31 Mare St, Hackney, London, were a firm particularly concerned with methods of construction. Although they seem to have entered the bamboo furniture market at a comparatively late date, about 1898, they produced inexpensive' bamboo, aimed particularly at the export trade. Stating in their catalogue that bamboo furniture “can be exported in one piece or it can be exported in pieces and put together again. The fixing up is much facilitated by a system of marking and numbering. Further, no glue is required for putting together as the screw system only is applied”. This method of construction best fits the Etagere and this item in the flagstaff collection and it is believed to have been made by A Englander & Searle, exported in a knock down form to Australia, purchased in kit form from a dealer here and put together by the purchaser. The bamboo plant stand is a significant item as it highlight furniture fashion of the late Victorian era. This item was highly sort after in its time and although mass produced, not many examples remain because the item is so fragile so this example is a valuable addition to the Flagstaff collection. It is believed,the construction method used is by a notable and respected maker in England of bamboo furniture that was aimed specifically at the export market and probably came to Australia in kit form to be assembled by the purchaser.Bamboo plant stand with octagonal top edged with tortoise shell bamboo the top is of wood and supported by four tortoise shell bamboo legs joined at the base by a square cane covered shelf. The tortoise shell appearance is brown lacquer. Item is part of the Giles Collection. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, furniture, plant stand, bamboo furniture, etagere, victorian furniture, simulated bamboo, tortise shell, a englander & searle, domestic furniture, giles collection, henry giles, cooramook, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century household goods -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Saucepan
It is no secret that copper is currently experiencing a huge upsurge in popularity. This is mainly thanks to its beautiful colour featuring heavily in the ranges of countless homeware retailers. There is, however, far more to this lustrous metal than just its appearance. For example, it has a greater level of thermal conductivity than any other metal (except silver); roughly 60% higher than aluminium and 3000% higher than stainless steel. This means copper is capable of heating up very quickly when compared to other metals. Perhaps a less commonly known property of copper is it being inherently antimicrobial. A wide range of harmful microbes are unable to survive for more than a couple of hours when in contact with a surface made of copper or one of its alloys (brass and bronze). This has led to it often being used for frequently touched surfaces such as door knobs, push plates and taps. A seemingly perfect material for cooking, it is therefore no surprise that it has been used in kitchens for millennia. But exactly when did we learn to utilise copper and its valuable assets? Origins It is hard to pin down an exact date when copper cookware was first introduced. Pieces discovered in regions of the middle east were dated as far back as 9000BC, suggesting cooking with copper began during the Neolithic period (≈10000-2000BC). As civilisations became increasingly capable in metallurgical techniques, metals such as copper became more widely used. It would have been around this time that copper replaced stone as the material used for making tools and cooking vessels. The use of copper is also well documented in Ancient Egypt. Not only was it used to produce water and oil containers, but it was also used to in medical practices. The antimicrobial nature of copper was exploited long before the concept of microorganisms was fully understood. The Smith Papyrus, a medical text written between 2600 and 2200BC records the use of copper in sterilising wounds and drinking water. Tin Lining Although copper is essential to many processes within the human body, it can become toxic if consumed in excess. It was this knowledge that gave rise to lining cookware with tin, a technique used for hundreds of years to prevent copper leaching in to food. These tin linings would eventually wear out and during the 18th and 19th century, it was common for people to send pans away to be re-tinned. This practice is becoming increasingly rare, as are the craftsmen who perform it. Despite this, there are still manufactures producing tin-lined copper cookware who also offer a re-lining service. Perhaps the best known of these is Mauviel, a French manufacturer who have been making this type of cookware since 1830. Tin has now largely been replaced by stainless steel as an interior cooking surface. Not only is it more cost effective, but the high grade of stainless steel used in premium cookware (typically 18/10) is highly resistant to corrosion and more durable than tin.Copper saucepans are still used in many kitchens.Small copper saucepan with long handle and three ridges around the circumference. Extensive corrosion.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, copper, saucepans, kitchen equipment -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Burke and Wills Memorial at Bendigo Cemetery, 2018, 02/09/2018
Robert O'Hara Burke and Thomas Pope Besnard were childhood friends. As sexton of the local Back Creek Cemetery Thomas Besnard organised a subscription to raise the money for a monument to Burke, Wills and Gray. A subscription of one shilling, no more and not less, was asked so all subscribers were equal. The Bendigo monument was designed by Adam Duncan and features a Corinthian column mounted on a foundation stone, topped with a Grecian urn draped with the Union Jack. The stone for the monument was quarried from New Chum Mine. The site in the Bendigo Cemetery was selected by Besnard so the monument was on a grass knoll well clear of any other graves. The design included landscaping with a path and garden beds that provided dignified access. The Burke and Wills Monument in Bendigo has been entered on the Register of the National Estate as being important for its association with historical events and developments associated with exploration in the early days of Colony of Victoria. Two conifers remain from the original group sent by Mueller of the Melbourne Botanical Gardens to develop the garden layout on the knoll. These two trees are listed as Significant Trees by City of Greater Bendigo. The foundation block was laid on 20 August 1862 by Chairman of the Bendigo Municipality, Charles Burrows – exactly two years after the Expedition left Melbourne. A half day holiday was declared by Bendigo Council, and a procession left the Bendigo Town Hall and marched to the cemetery where 8000 people were gathered and another 4000 lined the route. John King was unable to attend due to ill health. Chairman of the Municipality of Bendigo, Charles Burrows, gave a long address, and diaries of members of the expedition, the Sandhurst Almanac, the Bendigo Advertiser, the Bendigo Independent Evening News, photographs of the deceased, photographs of Public Buildings in Bendigo, a Sydney half sovereign and all the silver coins of the Realm were wrapped in a Union Jack and placed in a niche in the foundation stone. Fifteen months later a column was erected on the foundation stone after Besnard openly criticised the Memorial Committee for their lack of action. The Bendigo Advertiser was disappointed at the location of the monument preferring a more central location and in 1893 an attempt was made to move the monument to Rosalind Park. On 19 May 1893, Mr Minto, the City Surveyor of the Bendigo MunicIpality reported it would cost £25, and no other action occurred. In 1940 the land around the memorial was sold off as grave sites and the paths and garden beds disappeared with graves now surrounding the base of the monument. The Burke and Wills Monument in Bendigo Cemetery was entered on the Register of the National Estate for its association with historical events and developments associated with exploration in the early days of Colony of Victoria. Two conifers remain from the original group sent by Mueller of the Melbourne Botanical Gardens to develop the garden layout on the knoll. These two trees are listed as Significant Trees by City of Greater Bendigo.Burke and Wills Memorial at Bendigo Cemetery, 2018Erected by the people of Bendigo in honor of the Victorian Explorers, Burke, Wills, Gray and King who first crossed the continent of Australia. King alone surviving the privation and suffering under which his three brave ill-fated companions sank. A.D. 1862. Robert O'Hara Burke, leader of the Victorian Expedition, left Melbounre 24th August 1860. Reached Carpentaria 12th Feby 1861. Died on his return at Coopers Creek, 30th June 1861. Charles Gray, died also on his return at Polygorum Swamp. 17th April 1861. William John Wills, second in command, died also near Coopers Creek, 29th June 1861. bendigo cemetery, burke and wills, burke and wills memorial, william john wills, john o'hara burke, charles gray, polygonum swamp, coopers creek, victorian expedition, carpentaria, bendigo public cemetery, bendigo remembrance park, thomas pope besnard
