Showing 1301 items
matching german australians
-
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, glass, c 1929-1950's ref: AGM mark on bottle base
TROVE : The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1957) Thursday 14 February 1867 p 1 Article 'THE EXHIBITION. OFFICIAL DISTRIBUTION OF PRIZES. The culminating point in the history of the Intercolonial Exhibition of 1866-7, was reached yesterday, when His Excellency Sir Henry Manners Sutton, Governor of Victoria, publicly received the reports of the jurors, and formally declared their awards. .........................CHEMICAL AND METALLURGICAL PRODUCTS AND PROCESSES....................... MEDALS - VIctoria .............John Kruse, chemist, Melbourne - For his fluid magnesia...........................'. Haines, Gregory, 1994, Á History of Pharmacy in Victoria, The Australian Pharmaceutical Publishing Company in association with the Pharmaceutical Society of Australai (Victoria) Ltd, Melbourne, Australia.opp. page 54, photo of 'John Kruse' and of 'John Kruse's pharmacy, Russell Street, Melbourne, 1866'. TROVE : Melbourne Punch (Vic. : 1855 - 1900) Thursday 21 January 1897 p 3 Article A Musical Genius. BY X. THERE is a chemist's shop in Hawthorn in the drawingroom over which some of the best, music that has ever been heard under the Southern Cross has been discoursed. Here John Kruse, the famous violinist , has delighted his late father with his violin. Here Nellie Mitchell's (Madame Melba's) voice found appreciative admiration long before she became famous. It is the shop of John Kruse, chemist and druggist, the inventor of fluid magnesia, insecticide and a world of well-known articles of daily consumption. The old mail died some time back, but lived long enough to gratify his chief wish, viz,, to see his famous son, Herr Johann Kruse. John journeyed from Germany to see his dying father. His brief but brilliant sojourn amongst us will be remembered by all lovers of music. TROVE: Colac Herald Friday 1 September 1876, page 4, Article. TROVE: The Argus Tuesday 2 July 1867, page 3, Advertisement. 'Felton Grimwade, 125 Russell Street, Melbourne'Clear glass bottle, oval shaped in section with text embossed on both sides and on base. Embossed on base 'M65' over '1923 6' over 'AGM'. Side 1 : 'KRUSES PRIZE MEDAL MAGNESIA' Side 2 : 'THIS BOTTLE IS THE PROPERTY OF FELTON GRIMWADE & CO PTY. LTD. MELBOURNE'. Over the numeral '1'.chemist, magnesia -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, glass, Between 1859-1941
TROVE : Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1957), Monday 17 January 1859, page 7 TO the PHYSICIANS of AUSTRALIA -WOLFE'S SCHIEDAM AROMATIC SCHNAPPS, A superlative Tonic, Diuretic, Anti-Dyspepsic and invigorating Cordial. This medical diet-drink is manufactured soley by the proprietor at his distillery, in Schiedam, in Holland, expressly for medicinal purposes. It is the pure tincture of juniper, distilled from the best barley that can be selected in Europe at any cost. It is flavored and medicated, not by the common harsh berry, but by the choice botanical variety of the aromatic Italian juniper berry, whose more vinous extract is distilled and rectified with its sphirituous solvent, and thus it becomes a concentrated tincture of exquisite flavor and aroma, altogether transcendent in Its cordial and medicinal properties to any alcoholic stimulant now in use In the world. It has been submitted to all the first chemists and physicians in the United Slates, who endorse it over their own signatures as one of tho great essentials of the materia medica. It is now proscribed with great success In gravel, grout, rheumatism, obstruction of the bladder and kidneys, dyspepsia, whether acute or chronic, in general debility, sluggish circulation of the blood, inadequate assimilation of food, and exhausted energy, are acknowledged by the whole medical faculty and attested in their highest written authorities. Put up in quart and pint bottles, enveloped In yellow paper, with the proprietor's name on the bottle-, cork, and label. For sale by all the respectable druggists and merchants. UDOLPHO WOLFE WILKINSON BROTHERS and Co., sole agents for Australia. Depots at Melbourne and Sydney. TROVE : Farmer and Settler (Sydney, NSW : 1906 - 1955), Tuesday 30 March 1915, page 2 TRADING WITH UDOLPHO WOLFE. At the Sydney summons court on Wednesday morning, Laurence Edward Moss and Lawrence David Phillips were charged with having attempted to trade with the enemy by means of a letter addressed and posted to Udolpho Wolfe Company, Hamburg, Germany. There was a second information alleging that on or about December 7 last they attempted to trade with the enemy by means of a cable addressed and trans-mitted to Wolsey, New York. At the request of Mr. Campbell, K.C., who appeared for the defence, an adjournment to April 7 -was granted. Bail was allowed, each in £200, with a surety in £200. TROVE : Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 - 1954), Wednesday 19 November 1941, page 4 WOLFE'S Aromatic SCHNAPPS Wolfe's Schnapps is now distilled in Australia from the original formula of Udolpho Wolfe. It remains, as before, a beverage of unique medicinal properties — Appetising, Refreshing, , Stimulating — as good for women as for men. -Wolfe's 'Schnapps for your health's sake FOR VICTORY-buy War Bonds Now . W.B.157.13 Olive green glass bottle for stopper seal, square in section, slightly tapering toward base, text embossed on three sides, circular ring embossed inside impressed circle on base.Side 1. : 'UDOLOPHO WOLF'S'. Side 2 : 'SCHIEDAM'. Side 3 : 'AROMATIC SCHNAPPS'. Base : an embossed ring inside a round impressed into the square base.schnapps, schiedam, gin, udolpho wolfe -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, glass, C. 1866 - 1895
TROVE : The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1957) Thursday 14 February 1867 p 1 Article 'THE EXHIBITION. OFFICIAL DISTRIBUTION OF PRIZES. The culminating point in the history of the Intercolonial Exhibition of 1866-7, was reached yesterday, when His Excellency Sir Henry Manners Sutton, Governor of Victoria, publicly received the reports of the jurors, and formally declared their awards. .........................CHEMICAL AND METALLURGICAL PRODUCTS AND PROCESSES....................... MEDALS - VIctoria .............John Kruse, chemist, Melbourne - For his fluid magnesia...........................'. Haines, Gregory, 1994, Á History of Pharmacy in Victoria, The Australian Pharmaceutical Publishing Company in association with the Pharmaceutical Society of Australai (Victoria) Ltd, Melbourne, Australia.opp. page 54, photo of 'John Kruse' and of 'John Kruse's pharmacy, Russell Street, Melbourne, 1866'. TROVE : Melbourne Punch (Vic. : 1855 - 1900) Thursday 21 January 1897 p 3 Article A Musical Genius. BY X. THERE is a chemist's shop in Hawthorn in the drawingroom over which some of the best, music that has ever been heard under the Southern Cross has been discoursed. Here John Kruse, the famous violinist , has delighted his late father with his violin. Here Nellie Mitchell's (Madame Melba's) voice found appreciative admiration long before she became famous. It is the shop of John Kruse, chemist and druggist, the inventor of fluid magnesia, insecticide and a world of well-known articles of daily consumption. The old mail died some time back, but lived long enough to gratify his chief wish, viz,, to see his famous son, Herr Johann Kruse. John journeyed from Germany to see his dying father. His brief but brilliant sojourn amongst us will be remembered by all lovers of music. TROVE: Colac Herald Friday 1 September 1876, page 4, Article. TROVE: The Argus Tuesday 2 July 1867, page 3, Advertisement. 'Felton Grimwade, 125 Russell Street, Melbourne' Clear glass ellipse in section bottle, with embossed text on both sides and initials and numerals on base.'KRUSES PRIZE MEDAL MAGNESIA', 'This bottle is the property of FELTON GRIMWADE & CO Pty Ltd Melbourne on sides. 'S1935' 'AGM' on base.magnesia, kruse, felton, grimwade, chemist -
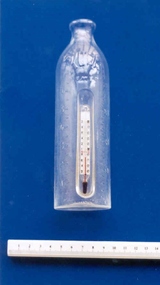 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Infant feeding bottle with thermometer, 'Kuwa', Germany, c. 1925
The neck of this bottle is quite wide and would have been fitted with quite a large teat. The use of an inbuilt thermometer on this bottle by the manufacturers, Kuwa, was quite innovative.Cylindrical glass feeding bottle, with calibrations for 1 to 8 (ounces) and 50 to 200 (mls). There is a vertical recess in centre front of the bottle, which contains a thermometer. There are two vertical seams in the glass, and a longitudinal bubble in the glass near the neck. Embossed on the neck of the bottle: "Kuwa" and "Made in Germany" on the lower front of bottle near the base."KUWA"; "MADE IN GERMANY"infant feeding -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Chadborn modification Schimmelbusch ether inhaler used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Dr. Curt Schimmelbusch (1860-1895), a German physician, designed his original mask around 1889 while an assistant surgeon. Surgical assistants were often assigned the task of delivering the anesthetic. During anesthesia it was not uncommon for ether and chloroform to get onto the patient’s skin, causing irritation. Chloroform can even cause burn-like reactions. Schimmelbusch designed the rim of his mask so that both sides curve away from the patient’s face to form a kind of trough. He intended the trough-like rim to collect excess anesthetic that would otherwise have trickled onto the patient’s face. To anesthetize a patient, gauze was stretched over the metal bars and fastened in place by the hinge. The mask was placed over the patient’s nose and mouth, and the anesthetic was applied in drops or lightly poured onto the gauze so that the patient breathed in evaporated anesthetic as well as air. This type of mask is sometimes still used today for ether anesthesia in developing countries when other means are not available. (Wood Library Museum of Anesthesiology) This particular object is a modified version of Schimmelbusch's design, known as Chadborn's modification.Oval shaped chromium plated mask with two metal strips linked front to back and side to side to create a dome. An oval shaped mobile wire frame is attached to the lower part of the mask by a hinge at the back, approximately two inches from the lip of the metal handle. A "U" shaped bit of metal is attached to the front of the mask which acts as a clip to fasten the wire frame to the lower section of the mask.anaesthesia -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Plaster figurine of Virgin Mary collected by Dr Frank Forster, c1974?
Replica figurine. Muttergottheit, loosely translated, means 'Mother Goddess'. Inscribed underneath in Frank Forster's hand.Early Christian style figurine depicting Muttergottes (Virgin Mary - German) figure wearing toga and veil, holding a swaddled infant. Plaster with ochre over-painting, most likely modern replica. Sticker attached to base is printed with German text that reads 'Muttergottheit/Trier, Altbachtal/2. Jh. n. Chr.' The numbers '1974' and '0216' have been handwritten on the base of the figurine. -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Examination chair associated with the Faculty of Anaesthetists, Royal Australian College of Surgeons, c1900
Likely to be a German designed operating chair. Very similar to operating chair shown in [Aesculap] Aktiengesellschaft fur Feinmechanik vormals Jetter & Sheerer, "Illustriertes Musterbuch", 1904, Tuttlingen, South Germany, p. 720, no. 34, 412 Fig 1 & 2. Early twentieth century examination chair constructed of metal and leather. The structure is metal and painted with cream enamel. The seat and seat extension are covered in brown leather. It has two folding sections with metal leg rests, and a base on castors. There are three holes in each arm rest, possibly indicating missing attachments. The chair is adjustable to horizontal.examination, furniture, royal australian college of surgeons -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Uterine flushing tube associated with Professor Bruce Mayes, c1932
Item originally belonged to Professor Bruce Mayes, University of Sydney c1950-65. According to Professor Warren Jones the item had been in a back room of the medical facility and Professor Mayes gave it to Warren Jones, otherwise it may have been thrown out. Warren Jones took it with him to Adelaide where he practiced from 1975. This item may have originally been imported from Germany.Uterine flushing tube, possibly Bozeman-type. Curved metal device in a loose 's' shape, with a bulbous point at one end, just above two circular metal loops which sit either side of main metal stem. Manufacturer is unknown.obstetric delivery -
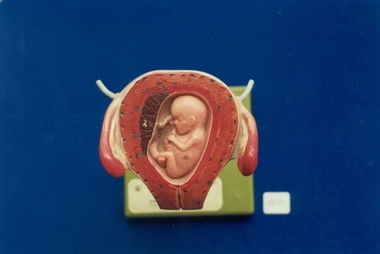 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Monat Obstetric teaching model associated with St George's Hospital Antenatal Clinic, SOMSO
This model came from the Antenatal Clinic at St George's Hospital, Kew. The hospital in Kew was closed in 1998 and the services transferred to Box Hill Hospital. Julie Collette, former General Manager, donated this and other items to the Museum collection in 1998.Teaching model, uterus in cross-section revealing12 week embryo. Plastic, painted with numbered sections, model on a green plastic stand with "SOMSO" stamped on base, "MADE IN W- GERMANY' stamped underneath base. One of four models in the series, this is the third of the four.education -
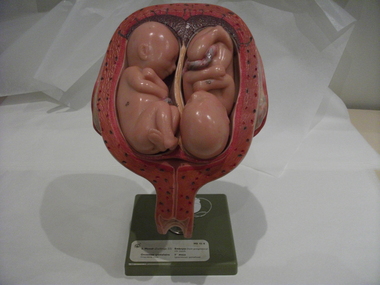 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Monat Obstetric teaching model MS 12/8 associated with St George's Hospital Antenatal Clinic, SOMSO
This model came from the Antenatal Clinic at St George's Hospital, Kew. The hospital in Kew was closed in 1998 and the services transferred to Box Hill Hospital. Julie Collette, former General Manager, donated this and other items to the Museum collection in 1998.Teaching model, uterus in cross-section revealing 20-week embryo. Plastic, painted with numbered sections, model on a green plastic stand with "SOMSO" stamped on base, "MADE IN W- GERMANY" stamped underneath base. One of four models in the series, this is the fourth of the four.education -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane
Prior to World War II an international competition was held for design of a standard sailplane for use in Olympic competition in 1940 in Finland. The design chosen was the “Meise” from DFS in Germany and its designer Hans Jacob. The 1940 Olympics were cancelled due to the outbreak of war and post war international gliding competition has been organized as World Championships, not as an Olympic event. After the war the Meise was manufactured by firms in Europe and a few were built by amateurs from plans. In 1945, a United Kingdom firm, Chilton Aircraft Limited, revised the plans for the DFS Meise Olympia keeping its aerodynamic shape and prepared new technical drawings for the production of the Chilton Olympia. It engaged Elliotts of Newbury (a firm with aircraft production experience during the war) to built a set of wings for its prototype. The wings were made by Elliotts but it apparently refused to let Chiltons have the jigs required to build more wings. The matter was resolved by Chiltons transferring its production rights and equipment to Elliotts. Elliotts produced several batches of Olympias (the “EON Olympia”) – probably about 150 in total from 1947 including Marks 1, 2 and 3 versions (featuring some structural changes and design improvements). The Australian Gliding Museum’s Olympia is a Mark 2 (actually 2B according to the logbook) which can be distinguished by the built in main wheel and blown Perspex canopy. It was designated as serial number EON/O/34 by Elliotts. It was damaged badly at Bristol, UK, in 1949. The wreckage was acquired by a Melbourne based syndicate including Dave Darbyshire, and imported into Australia. Additional damage occurred in shipping due to the need to shorten the wings to fit them into a crate. The syndicate rebuilt the glider and re-launched it in 1956 (registration number VH-GHR). It was flown by the syndicate and several gliding clubs in Victoria and South Australia until about 1972. A potentially airworthy example of a now rare sailplane of historical importanceSingle seat wooden sailplane, partly restored.australian gliding, glider, sailplane, dfs, hans jacob, meise, olympics, eon olympia, chilton aircraft, elliotts of newbury, dave darbyshire, great eastern gliding club, barossa valley gliding club, murray bridge gliding club -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumFunctional object - Rudder from Geelong Gliding Club Primary Glider, 1929
The Geelong Glider Club was formed in June 1929 at a meeting held at the Belmont Common hangar of Percy Pratt. The club built a Zogling (Primary Glider) based on plans obtained from Germany and flew it off nearby hills at Lovely Banks and other places in the Geelong region. The checked rudder design (without logo and markings) is evident in a picture of a Geelong Glider Club Zogling flying at Tower Hill near Warrambool, Victoria, at Easter 1931 and this lends support to the conclusion that the rudder was part of the Club’s first glider. The logo and markings appear to be a more recent elaboration to the design. Exhibit is a historical link to the earliest gliding activities of the Geelong Glider Club.Fabric covered wooden framed primary glider rudder with metal levers decorated with silver and dark red checkered design. The item has a cat logo on one side and markings on the other of places where the Geelong Gliding Club flew in its early years.On port side – Cat logo. On starboard side – Geelong Glider Club; and place names including Geelong Aerodrome, Batesford, Ceres, Lovely Banks, Tower Hill, Koroit, Mount Moriac; and years, 1929-1933 australian gliding, glider, zogling, primary glider, rudder, geelong gliding club, lovely banks, tower hill. koroit -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1952-1953
This aircraft, the first glider built by Schneiders after they immigrated to Australia, was test flown on 3 January 1953 by Dave Darbyshire and Owen Lewis. It is the only machine of its type. It is essentially a Grunau Baby 2B with a Perspex enclosed cockpit, wing airbrakes and a landing wheel. However, the wing design came from an existing Grunau 3 type that was being built in Germany. The glider has given extensive service for a number of owners – including the Gliding Club of Victoria, Sunraysia Gliding Club, Millicent Gliding Club, Max Bugler of Morwell and Garth Hudson of Brighton in Victoria. Prior to being donated to the Australian Gliding Museum in January 2001 the glider had logged over 2200 hours flying time from over 9000 flights. The glider is an improved Grunau Baby design that Edmund Schneider built after coming to Australia.Single seat glider of wood and fabric construction, with steel wing struts. Currently painted crème with yellow details. Underside of fuselage is painted orange.australian gliding, grunau, grunau baby, schneider, gliding club of victoria, sunraysia gliding club, millicent gliding club, darbyshire, lewis, bugler, hudson -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, Circa 1971
The Vogt LO150 is a sailplane first produced in 1954. Designed in Germany by Alfred Vogt, the LO150 is of wood construction. It has a two piece wing of 15 metre (49 feet) span and a fuselage of monocoque design. The first of the type to be imported into Australia arrived in late 1955. In January 1956 this aircraft type was used to create a world speed record of just under 75 km/h for speed around a 300 km triangle and went on to win the Australian National Gliding Championships. The Museum’s LO150 (VH-GUC) – serial number EB71 was imported from Germany in 1971 by the late Frank Erdmann and an ownership syndicate formed. Following Erdmann it has had a number of owners. Much of its usage was at Bacchus Marsh and Horsham with excusions elsewhere for competition. This Vogt LO150 was last flown on 3 January 1988. Overall, since arriving in Australia, it has flown 315 hours from 273 launches, which is a commendable average performance of over an hour per flight. VH-GUC was donated to the Museum by Warren Mayfield in 2002. Substantial glue deterioration was discovered in one wing and, as a result, a decision has been made not to restore the glider to an airworthy condition. In due course the glider will be repainted and further prepared for display. This exhibit is an example of the Vogt LO150 semi-aerobatic competition sailplane.Single seat competition sailplane of wood construction.Builder's serial number EB71australian gliding, glider, sailplane, vogt, lo-150, erdmann, mayfield, geelong gliding club -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider, 1974
The “Northrop” is an American copy of the “Zogling” which was designed in Germany in the 1920s as a training glider. Apparently, the Northrop primary glider takes its name from a Marvin Northrop of Minneapolis who imported a Zogling from Germany and from that glider had plans drawn and published in a magazine called Modern Mechanics in 1930. The Australia Gliding Museum’s Northrop was built over the period of 1970 to 1974. The project was conceived by a pioneer of Australian gliding, Ken Davies, about 1969, as a hobby project and to experience afresh gliding flight of the early years. By that time, few primary gliders, which performed a fundamental role for gliding clubs in the 1930s and 1940s, remained in Australia. Ken began construction and was helped to finish the project by two old time Gliding Club of Victoria members, Dave Darbyshire and Rudi Feil. The glider was test flown on 8 March 1975 at Benalla. The glider was stored at the Gliding Club of Victoria and flown on special occasions in the 1980s. Later it was damaged at the 1996 vintage glider rally at Ararat as a result of a heavy landing. Storage was then provided for the glider by the Victorian Motorless Flight Group at Bacchus Marsh until it was returned to Dave Darbyshire for restoration in 1998. Fully restored, the glider was donated by Iris Davies and Dave Darbyshire to the Australian Gliding Museum in April 2001. This exhibit is the type of machine that formed the basis of the sport of gliding from 1929 to about 1945. The glider consists of an open (uncovered) wooden framed fuselage (painted blue) with a brown vinyl covered seat, fabric covered wooden framed wings of constant chord (painted silver) with provision for attachment of semi-circular cane wing skids, and fabric covered wooden framed tailplane, elevators and rudder (painted silver). When assembled the airframe is wire braced.australian gliding, glider, northrop, zogling, davies, darbyshire, feil, gliding club of victoria, victorian motorless flight group -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1962
This ES Ka6 sailplane (VH-GRW, serial number 55) was built under licence from Alexander Schleicher in 1962 by Edmund Schneider Limited. It was one of 12 Ka6s, with minor variations from the Schleicher product, built by Schneiders in Australia. It was test flown at Parafield Aerodrome, Adelaide, on 8th September 1962. By way of background, the Schleicher KA 6 series of sailplanes were designed by Rudolf Kaiser in Germany. They were quite successful in the Standard Class in the late 1950s and 1960s. Over 1400 were produced. The first owner of VH-GRW was the Victorian Motorless Flight Group which, at the time, was based at Berwick Airfield on the outskirts of Melbourne. On 22 April 1972, the ownership passed to a syndicate of members from the VMFG. It again changed ownership in July 1974. The new owners were another syndicate based at Campbelltown in New South Wales. The glider went to a Tasmania syndicate in June 1976 and finally to the Soaring Club of Tasmania. In total VH-GRW recorded 3369 hours air time from 4952 launches. It was used very little after 1996. This exhibit is an example of the Scheicher Ka6 sailplane type that were built by Edmund Schneider in Australia.Plywood, spruce and fabric covered high wing single seat sailplane. The airframe has been restored to the point of repainting. Currently the fuselage, rudder and the wings aft of the main spar are coated with pink dope. The tailplane retains the white gloss finish of the glider prior to the restoration work. The cockpit to be refitted (with instruments etc). Serial number 55. The manufacture details are displayed on a metal plate fixed to the main bulkhead. australian gliding, glider, sailplane, schneider, schleicher, ka6, rhonsegler, victorian motorless flight group, soaring club of tasmania -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1969
The Phoebus is a fibreglass composite sailplane that was designed by H. Nagele, R. Linder and R. Eppler in the early 1960s for competition flying. It is a derivative from the Akaflieg Stuttart Phonix which was the first sailplane to be built of fibreglass. The first Phoebus, a Standard Class design with a 15 metre wingspan, flew in 1964. The Phoebus C is the open class version of the type that was introduced in 1967. It has a 17 metre wing span, retractable wheel and tail brake parachute. Several hundred Phoebus sailplanes (all versions) were made by the manufacturer Bolkow at Ottobrun in Germany before production ended in 1970. The Museum’s Phoebus C, serial number 866, was built in 1969. It was donated to the Museum by Ian Cohn in 2008. Early fibreglass design that was manufactured in numbers. The Phoebus is a modern looking single seat glass fibre sailplane with a ‘T’ tailplane. It is finished in white with light red detailing including thin red stripe on wings and some red striping on fuselage sides from nose to underneath wings.Serial number 866 on plate affixed inside cockpit – registration VH-GSW which has been painted on the sides of the fuselage rear of the wings. A Freistaat Bayern crest has been applied to each side of the vertical stabilizer. australian gliding, glider, sailplane, bolkow, phoebus, cohn, nagele, linder, eppler -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumEquipment - Glider – Hang Glider Type, 2013 - 2014
Otto Lilienthal (1848-1896) from Berlin, Germany, is widely credited as being the first person to make repeated successful gliding flights. He was known for adopting a thorough scientific approach founded on observations of the flight of birds in relation to the problem of inventing a man carrying heavier than air machine that would fly. He developed and tested bird-like gliders controlled by weight shift by the pilot (a similar method to modern hang gliders). The pilot held on to the glider with his forearms resting in hoops mounted on the main structural beam connecting the wings. The weight shift was achieved by the pilot swinging his trunk and legs. In contrast, the pilot of a modern hang glider is suspended below the glider and, with the use of an A-frame, allows the whole body to be moved around to achieve control. The Lilienthal design apparently had a tendency to pitch down and a tailplane was added to mitigate this problem. Lilienthal flew from hills in the Rhinow region and from a conical hill he built near Berlin. He made over 2000 flights. Importantly, for others seeking to progress manned flight at the time and also for the historical record, reports of Lilienthal’s flights (some with photographs) were published and Lilienthal detailed his experiences and corresponded with other flight pioneers. Lilienthal’s work became well known and influenced Orville and Wilbur Wright in their initial experiments with gliders in 1899 (although in their quest to design and fly an aeroplane they relied on new data created by wind tunnel testing). The replica built by Bruce Hearn is of the 1893 Lilienthal glider. It is very similar to the “Normal-Segalapparat” (Normal Glider) for which patent protection was later granted a few years later. The Lilienthal replica glider is an important addition to the AGM collection as it represents the beginning of successful gliding flight. Hang glider made of wood with wire bracing – yet to be covered with authentic cotton fabric. The glider has a small plate with identification details including name of builder (Bruce Hearn) glider, hang glider, lilienthal, hearn, replica -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1960
The Ka 2, a tandem two seat training sailplane of 15 metre wing span, was designed by Rudolf Kaiser for Schleicher in 1953. It was a versatile craft due to its good cross country soaring capability. With the Ka 2B, the design was improved in 1955 by lengthening the wing span to 16 metres and increasing the dihedral and tip washout. The fuselage was lengthened slightly as well. Schleicher built 42 Ka2s from 1953 to 1955 and 75 Ka 2Bs from 1955 to 1957. In addition Schleicher supplied kits for construction of the sailplane by independent builders. The Australian Gliding Museum’s example is the single Ka 2b built in Australia from plans and is designated as GFA-HB-47. The club concerned was the Illawarra Soaring Club of Sydney. The glider registered as VH-GHO and first flew in October 1960. However, within a short time it was badly damaged and needed major repairs which took over a year to complete. After lengthy service at Illawarra Soaring Club it was transferred to the Stirling Gliding Club in Western Australia in August 1976. Again it suffered damage in a landing accident in 1978. The damaged glider was put into storage at Northam where it remained for approximately 11 years. It was acquired by Mike Valentine in 1989 and brought back to flying condition at Bacchus Marsh, Victoria. The last entry in the log book is dated January 1997 at which time it had accumulated 1170 hours from 2446 flights. The last owner prior to transfer to the Australian Gliding Museum was John Ashford of the Geelong Gliding Club. The Museum's Ka 2B sailplane is a potentially airworthy example of this German 1950s sailplane type. It is a rarity in Australia as the only Ka 2b appearing on the Australian register.Tandem two seat sailplane of wood and fabric construction finished in cream and red colour schemeRegistration VH-GHO (with "HO" letters painted on the fin / rudder) Serial number - GFA HB 47 australian gliding, glider, sailplane, schleicher, kaiser, ka 2, illawarra soaring club, stirling gliding club, valentine, ashford -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider –Sailplane, 1960
The FS-24 Phonix is the first sailplane design to be built using a moulded fiberglass sandwich technique. It was designed by Hermann Nagele and Richard Eppler leading a group setup for the purpose at Stuttgart Technical University in the early 1950s. Initial construction was undertaken at workshops of Wolf Hirth and the first prototype was completed at the Bolkow Aircraft Company where Nagele and another member of the group, Rudi Lindner, had gained employment. It flew on 27 November 1957. Two further prototypes were built incorporating a T-tail and other refinements. Eight in all were built before production was stopped in 1961. A number of gliding records were broken in Phonix sailplanes in Germany in 1962-1963. It was found to have a best glide ratio of 40:1. The Museum’s example, No. 403 was originally a prototype built on 25 May 1960 [Registration D-8354]. It was converted at Bolkow to a Phonix T in 1963 and sold to a private owner in Switzerland [Registration HB-746] and later then to gliding club Segelfluggruppe Solothurn in 1965. The glider returned to Germany in 1971 (Meersburg) and re-registered as D-0738. It moved to a new owner in Allershausen in 1976, and again to Lindhoft in 1982. In 1983 the glider was sold to owners at Hasselt, Belgium and given registration OO-ZQD. In 1989 a further change of ownership occurred and the glider went to Leusden in the Netherlands where it was registered as PH-949. In 2006 the Phonix No.403 was imported into Australia by John Ashford of the Geelong Gliding Club. On 30 January 2007, it was registered as VH-GRP. However, as at January 2016 it has not been flown in Australia. In the course of its flying history the glider was damaged several times and repaired. At one stage a larger rudder was fitted and later on this modification was reversed. With the original conversion to a Phonix T and subsequent repairs and changes to equipment the weight of the airframe increased from 182 kg to approximately 220 kg. Nevertheless, the wing loading is a modest 20kg/square metre. As at January 2016, minor repairs and airworthiness certification are required to return the glider to flying condition. This exhibit is highly significant as it is one of only eight of this pioneering sailplane design. It is the only one in Australia. Glassfibre single seat sailplane, finished white with blue stripes on fin and rudder.Australian registration GRP on rudder; Serial Number 403 and Vintage glider club of Netherlands plaque in cockpitaustralian gliding, sailplane, glider, fs-24, phonix, nagele, eppler, lindner, stuttgart technical university, bolkov aircraft company, segelfluggruppe solothurn, ashford, geelong gliding club. -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider - Sailplane, 1967
The Ka 8 was designed by Rudolf Kaiser in 1957 and built by Alexander Schleicher. It has been described as the single seat version of the Ka 7 Rhonadler. The Ka 8 proved popular with clubs in its role as a sailplane for early solo flying. Over 1100 were produced. The Museum’s example is a Ka 8B which is the second variant of the design, distinguishable by a larger blown Plexiglas canopy and improved ailerons. The particular glider was built by the RAAF Williamtown Gliding Club from kit supplied by Edmund Schneider Ltd of South Australia as agent for Alexander Schleicher. It was test flown on 8 July 1967. For a period from August 1994 it was owned by a syndicate at the Bendigo Gliding Club. The last entry in the log book is dated January 1995 at which time the glider had accumulated 1148 hours from 2303 flights. From 1967 to 1994, the glider was flown at numerous places including Williamtown, Bellata, Warkworth, Dubbo, Waikerie, Quirindi, Tamworth, Redding, Narromine, Leeton and Keepit. During 1994 and 1995 it was flown a small number of times at Bendigo. A notable flight recorded in the logbook is dated 31 October 1971 when W. Kenny reached 11,000 feet in height during a flight of 5 hours 10 minutes. The last owner prior to the transfer of the glider to the Australian Gliding Museum in 2015 was John Ashford of the Geelong Gliding Club. The glider carries Serial Number 8478-SH and appears to have been registered firstly as VH-GPA and secondly as VH-GMA. The last registration (VH-GMA) was cancelled in 2011.This Kaiser Ka8B sailplane, when fully restored, will be an airworthy example of a popular 1960s German club sailplane type. It is a rarity in Australia as only 4 of the type have been registered and flown here.Single seat sailplane made with a steel tube framed fuselage and wooden wings. A glass plastic moulding has been used to form the top of the fuselage forward of the cockpit. The structure is fabric covered.The glider serial number 8478-SH and the registration VH-GMA.australian gliding, glider, sailplane, schleicher, kaiser, ka 8, schneider, raaf williamtown gliding club, bendigo gliding club, geelong gliding club, ashford -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane
The ES49 glider / sailplane was designed by Edmund Schneider in Germany before he migrated to Australia in the early 1950s. In Germany the ES49 was put into limited production by the Schleicher factory from 1951 to 1953 (8 produced). In Australia the ES49 is commonly referred to as the “Wallaby”; two were built by the Adelaide Soaring Club with assistance from Edmund Schneider Ltd and one independently from plans by Eric Hader and members of the Cooma Gliding Club. The Museum’s ES49 – serial number GFA-HB-36 - was built at Gawler from 1955 to 1958 and registered as VH-GLL on 15 January 1959. It was the second of the ES49s built by the Adelaide Soaring Club. Originally it had a rather distinctive appearance due to the use of a sleek P51 Mustang canopy to enclose the forward seating position of the cockpit. The glider, together with its sister VH-GDK, was used at the Gliding Federation of Australia National Gliding Schools at Gawler. In 1964 the glider was transferred to the Newcastle Gliding Club, Newcastle, in New South Wales and then in 1966 it went to the Albury and District Gliding Club, Albury, New South Wales. The Snowy Mountains Gliding Club, Khancoban, New South Wales acquired the glider in 1968 where it remained until 1974. In 1974 the glider transferred into private hands at Wodonga, Victoria, for two years and then to interests at Albury until 1985. At that stage the glider was acquired by a private owner at Bathurst, New South Wales, who undertook a restoration that included, amongst other work, the fitting of a more conventional cockpit canopy. The glider was at Warkworth, New South Wales in 1992 and became to be owned by Eric Oates who preserved it until he donated it to the Australian Gliding Museum. According to the logbook for VH-GLL held by the Museum, the glider was last flown in November 1990 and at that time had logged 2758 hours and 57 minutes from 15775 launches. The fuselage is currently under restoration at the Museum’s Dave Darbyshire workshop. The ES49 – VH-GLL – is an example of the state of wood and fabric dual place sailplane design in the late 1940s. The glider served the Adelaide Soaring Club and subsequent owners well as a training and general purpose sailplane over many years. It is a rare example of the type (one of 4 existing in the world). Tandem two seat high wing strut braced glider-sailplane finished in silver grey colour scheme.australian fliding, glider, sailplane, schneider, es 49, wallaby, oats, adelaide soaring club, hader, cooma gliding club, newcastle gliding club, albury & district gliding club, snowy mountains gliding club -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider - Sailplane, 1937
The Golden Eagle is an original design by Geoff Richardson. Geoff commenced gliding in the early days of the sport circa 1933 in Melbourne, flying at Coode Island and Mt Frazer. In 1934, he began construction of a secondary type glider but scrapped it upon realizing that a better design was needed. He conducted further research and came up with a sailplane of similar size and general arrangement to the Grunau Baby but with a “Gull” wing using a Gottingen 535 wing section (the same as for the Grunau Baby). Geoff did all the technical calculations himself and even made up and tested a Casein glue for the construction. Geoff competed construction of his new sailplane (which he called the “Golden Eagle”) in 1937 and it was test flown at Laverton at the western edge of Melbourne in September 1937. On the same day, at Laverton, the Gliding Club of Victoria flew its new Grunau Baby 2 sailplane which it had imported as a finished machine from Edmund Schneider in Germany. The Golden Eagle was found to fly well, having a similar performance to the Grunau Baby. In the 1950s, the Golden Eagle was modified by rebuilding the front of the fuselage to enclose the cockpit with a Perspex canopy. A landing wheel was incorporated behind the skid. Spoilers were added to the wings and a trim tab to the elevators. The Golden Eagle has been flown with the VMFG (Victorian Motorless Flight Group) for most of its long life. When donated to the Australian Gliding Museum in 2016 by Alan Patching it was probably the oldest, continuously airworthy glider in the world. Having regard to the historical significance of the Golden Eagle, the Museum has decided to not to fly it anymore to avoid risk of loss or damage. The exhibit is of great significance for Australian gliding history – the Golden Eagle is a flyable 1930s aircraft in excellent condition that was designed and built by an Australian gliding pioneer. Single seat wood and fabric sailplane finished with white wings, tailplane and rudder and yellow fuselage Registration letters “FC” on fuselage nose port side, Australian flag, Vintage Gliders Australia and VMFG decals on rudder, “Golden Eagle” lettering in red on each side of the fuselage below the canopy, Aboriginal flag decal on port side of fuselage below the canopy. australian gliding, glider, sailplane, golden eagle, richardson, patching, vmfg, victorian motorless flight group -
 Polish Museum & Archives in Australia
Polish Museum & Archives in AustraliaPennant, La Casa de Banderin, 08/1955
In 1955 the Polish Community in Chile wanted to Commemorate the 10th Anniversary of the ending of the 2nd World War but, since it was not a happy occasion, as Poland had been betrayed and placed in the Soviet sphere of influence, they chose to create a Pennant with a plea for the Patron Icon of Eastern Poland - Our Lady of the Sharp/Morning Gate (Matka Boska Ostrobramska/Zaranna) in Vilnius (Wilno) - to give them a new Miracle on the Vistula, in reference to an epic battle which took place on 15th August 1922 on the banks of the Vistula (Wisla) River in which the Polish troops defeated the Soviet Army and turned back the march of Communism to the West. This particular Pennant was purchased by Stanislawa Zamecznik (nee Zakrzewska), while living in Chile after deportation from her birth place in Sianozatki near Bychov (Bychow) to Schweningen in Germany from which they emigrated to South America as Displaced Persons. It was brought to Australia when the Zakrzewski Family emigrated from Chile in 1956, first to Port Augusta and then subsequently to Sydney.It is significant in that it tells the story of the aspirations of the Polish Diaspora displaced from it's Homeland in the Kresy Region and scattered throughout the World, including the Americas and Australia.Pennant of red cloth with screen printing in white, mustard yellow and black hung on copper wire with gold cord Front: Polish inscription "KROLOWO POLSKI / BLAGAMY CIE O NOWY / CUD NAD WISLA / SANTIAGO DE CHILE / 15.VIII.1955" Back: Spanish inscription "LA CASA DE BANDERIN AHUMADA 61"polish pennant polski proporczyk orzel eagle matka boska ostrobramska zaranna our lady of vilnus santiago chile cud nad wisla miracle on the vistula -
 Polish Museum & Archives in Australia
Polish Museum & Archives in AustraliaYMCA membership Germany DP
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Postcard - ACC LOCK COLLECTION: GRAVE OF GERMAN AIRMAN BARON VON RICHTHOFEN AT BERTANGLES, POSTCARD, 1914-1918
Postcard, WW1, B&W image of the grave of German airman, Baron von Richthofen, shot down in the Somme area. He was buried at Bertangles by members of the Australian Flying Corps. The grave is mounded with earth with flowers on top. At the head of the grave is one propeller stuck in the ground. Richthofen's body was moved a couple of times before his final resting place in Germany.postcard, postcard, ww1, baron von richthofen, grave, somme, bertangles -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Postcard - ACC LOCK COLLECTION: STEENWERCK, AFTER GERMAN OFFENSIVE - INTERIOR OF THE CHURCH, POSTCARD, PATTERN, 1914-1918
Postcard, WW1, B&W image of the interior ruins of the church at Steenwerck after a German offensive. Collapsed roof timbers in front of a damged end of the church. Copy AZ 10 Published by J.M.Hamilton & Coy. Sydney Australiapostcard, postcard, ww1, france, steenwerck, ruins, church -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Will Davies, Last one hundred days : the Australian road to victory in the First World War, 2018
... , the Germans attacked. In response, Australian soldiers were involved ...In March 1918, with the fear of a one-million-man American army landing in France, the Germans attacked. In response, Australian soldiers were involved in a number of engagements, culminating in the Second Battle of Villers-Bretonneux and the saving of Amiens, and Paris, from German occupation. Then came General John Monash's first victory as the Commanding Officer of the newly formed Australian Corps at Hamel. This victory, and the tactics it tested, became crucial to the Allied victory after 8 August, the 'black day of the German Army'. On this day the major Allied counteroffensive began, with the AIF in the vanguard of the attack. The Australians, with the Canadians to the south and the British across the Somme to the north, drove the Germans back, first along the line of the Somme and then across the river to Mont St Quentin, Péronne and on to the formidable Hindenburg Line, before the last Australian infantry action at Montbrehain in early October. Fast-paced and tense, the story of The Last 100 Days is animated by the voices of Australian soldiers as they endured the war's closing stages with humour and stoicism; and as they fought a series of battles in which they played a pivotal role in securing Allied victory. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, notes, ill, p.340.non-fictionIn March 1918, with the fear of a one-million-man American army landing in France, the Germans attacked. In response, Australian soldiers were involved in a number of engagements, culminating in the Second Battle of Villers-Bretonneux and the saving of Amiens, and Paris, from German occupation. Then came General John Monash's first victory as the Commanding Officer of the newly formed Australian Corps at Hamel. This victory, and the tactics it tested, became crucial to the Allied victory after 8 August, the 'black day of the German Army'. On this day the major Allied counteroffensive began, with the AIF in the vanguard of the attack. The Australians, with the Canadians to the south and the British across the Somme to the north, drove the Germans back, first along the line of the Somme and then across the river to Mont St Quentin, Péronne and on to the formidable Hindenburg Line, before the last Australian infantry action at Montbrehain in early October. Fast-paced and tense, the story of The Last 100 Days is animated by the voices of Australian soldiers as they endured the war's closing stages with humour and stoicism; and as they fought a series of battles in which they played a pivotal role in securing Allied victory. Collapse summary world war 1914- 1918 - campaigns - western front, western front - australian participation - 1918 -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Craig Deayton, The battle of Messines : 1917, 2017
On 7 June 1917, the British Second Army launched its attack on Messines Ridge, detonating 19 giant mines beneath the German front-line positions. By the end of the day, one of the strongest positions on the Western Front had fallen, a place of such importance that the Germans had pledged to hold it at any cost. It was the greatest British victory in three years of war. The first two years of the First World War had represented an almost unending catalogue of disaster for the Australians. Messines was not only their first real victory, it was also the first test in senior command for Major General John Monash who commanded the newly formed 3rd Division and would later be hailed as Australia's greatest soldier. Messines was a baptism of fire for the 3rd Division which came into the line alongside the battle-scarred 4th Australian Division, badly mauled at Bullecourt just six weeks earlier in one of the worst defeats of the war. The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described by one Australian as '72 hours of Hell'. After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would be the ultimate test for the Australians. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, ill (col), p.172.non-fictionOn 7 June 1917, the British Second Army launched its attack on Messines Ridge, detonating 19 giant mines beneath the German front-line positions. By the end of the day, one of the strongest positions on the Western Front had fallen, a place of such importance that the Germans had pledged to hold it at any cost. It was the greatest British victory in three years of war. The first two years of the First World War had represented an almost unending catalogue of disaster for the Australians. Messines was not only their first real victory, it was also the first test in senior command for Major General John Monash who commanded the newly formed 3rd Division and would later be hailed as Australia's greatest soldier. Messines was a baptism of fire for the 3rd Division which came into the line alongside the battle-scarred 4th Australian Division, badly mauled at Bullecourt just six weeks earlier in one of the worst defeats of the war. The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described by one Australian as '72 hours of Hell'. After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would be the ultimate test for the Australians. Collapse summary world war 1914-1918- campaigns - western front, battles of messines - australian participation - 1917 -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Peter Fitzsimons, Fromelles and Pozières : in the trenches of hell, 2015
... world war 1914-1918 - australian participation - fromelles ...In the Trenches of Hell On 19 July 1916, 7000 Australian soldiers - in the first major action of the AIF on the Western Front - attacked entrenched German positions at Fromelles in northern France. By the next day, there were over 5500 casualties, including nearly 2000 dead - a bloodbath that the Australian War Memorial describes as 'the worst 24 hours in Australia's entire history. Just days later, three Australian Divisions attacked German positions at nearby Pozi�res, and over the next six weeks they suffered another 23,000 casualties. Of that bitter battle, the great Australian war correspondent Charles Bean would write, 'The field of Pozi�res is more consecrated by Australian fighting and more hallowed by Australian blood than any field which has ever existed . . .' Yet the sad truth is that, nearly a century on from those battles, Australians know only a fraction of what occurred. This book brings the battles back to life and puts the reader in the moment, illustrating both the heroism displayed and the insanity of the British plan. With his extraordinary vigour and commitment to research, Peter FitzSimons shows why this is a story about which all Australians can be proud. And angry.Index, bibliography, notes, ill (maps), p.816.In the Trenches of Hell On 19 July 1916, 7000 Australian soldiers - in the first major action of the AIF on the Western Front - attacked entrenched German positions at Fromelles in northern France. By the next day, there were over 5500 casualties, including nearly 2000 dead - a bloodbath that the Australian War Memorial describes as 'the worst 24 hours in Australia's entire history. Just days later, three Australian Divisions attacked German positions at nearby Pozi�res, and over the next six weeks they suffered another 23,000 casualties. Of that bitter battle, the great Australian war correspondent Charles Bean would write, 'The field of Pozi�res is more consecrated by Australian fighting and more hallowed by Australian blood than any field which has ever existed . . .' Yet the sad truth is that, nearly a century on from those battles, Australians know only a fraction of what occurred. This book brings the battles back to life and puts the reader in the moment, illustrating both the heroism displayed and the insanity of the British plan. With his extraordinary vigour and commitment to research, Peter FitzSimons shows why this is a story about which all Australians can be proud. And angry.world war 1914-1918 - campaigns - western front, world war 1914-1918 - australian participation - fromelles and pozieres
