Showing 13992 items matching "tasmanian-built"
-
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. Digital imageThe Grange, Irelandknowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
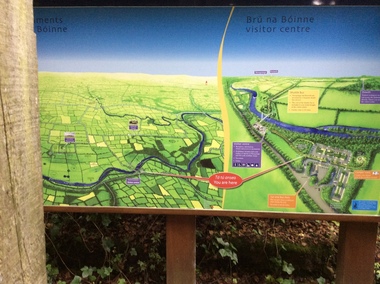 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Sign, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Mt Dandenong & District Historical Society Inc.
Mt Dandenong & District Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Post Office and 'Mountjoy', Mt. Dandenong North, 1913
Rose Series post card #182Copy of Rose Series postcard #182 showing Kalorama Gap in 1913. Haystacks in foreground with Mountjoy Guest House and Beulah Tea Rooms/Mt Dandenong North Post Office in centre. This photograph has a detailed inscription on the back handwritten by John Lundy-Clarke in 1974.Kalorama Gap in 1913 The elm trees are in the centre of the picture. One of these is really two as two suckers of the further tree were twisted together by Fred Jeeves in 1898 and grew as one tree. The other was planted in 1880. The shop is the shop of Mrs Eliza Hand and daughter Florence. The closed in far end of the verandah was the Mount Dandenong North Post Office. The large house is “Mountjoy” owned and run by the Jeeves Family from 1908 till 1943. It was built in 1905 by the Paynters who sold to Ellis Jeeves in 1908.He moved his line of coaches from “Kalorama” his old homestead and housed the horses in a line of stables behind “Mountjoy”. Price’s house, which contained their shop, the first one on the mountain, opened 1906, can be seen faintly behind the pine tree opposite the bend in the road, which was the main road then and now is Ridge Road. The Price’s house just shows in two tiny pieces, one on each side of the pine tree half way up. The house to the right of and high up the pine tree is Walker’s cottage which exists today opposite Jack Kidd’s home at the far edge of Lt 2 Village Settlement and was between Main Road and Barbers Road which runs down the left behind the elms. Walker’s homestead can be seen near left edge of picture 2/3 way up. The roof of the Methodist Church shows among trees left of picture. This, like Mrs Hand’s shop was built on portions separated from Isaac Jeeves’ Selection “C” known as Jeeves Saddle. kalorama gap, five ways, mountjoy, john lundy-clarke, beulah tea rooms, post office, fred jeeves, paynter, jeeves, frederick jeeves, price, walker, jack kidd -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societycertificates, 1909, 1911, 1912
These four certificates belonged to William Hunter. William Hunter (1893-1971) was a resident of Tatura and Mallacoota. He was a soldier, surveyor and amateur naturalist. The certificates include two first prizes for surveying, a technical scholarship for full day courses and a certificate for Applied Mechanics. William received his Surveying Certificate in April 1916. In June 1887, the Working Men's College opened after Francis Ormond, a noted Victorian philanthropist and member of parliament, suggested that a technical institute be built in Melbourne, offering further education for working men and women. He had offered to match the sum raised through public subscription if the government could provide a site for the College. William Hunter made valuable contributions to our knowledge of far East Gippsland plants. His records were meticulous. These certificates are part of his history.Four card certificates of merit for "Annual Examinations" from the Working Men's College, The Technical College and School of Mines for the Metropolitan District.All four certificates awarded to "William Hunter" and signed by Mordaunt Arundel Hall (accountant & chief clerk WMC) as the Acting Director.hunter-william-surveyor -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This photograph was taken of an avenuw of acacias on Sydney Rd, Beechworth. Picture on the left hand-side is a row of Liquidamber trees also known as American storax, hazel pine, bilsted, redgum, satin-walnut, star-leaved gum, alligatorwood, or simply sweetgum. On the right is a row of English Oak trees commonly known as common oak, pedunculate oak, or European oak. Behind the English oaks is Old Beechworth Goal. Many of the trees in the Beechworth township were planted in the 1860's and today have exceptional historical, botanical or cultural value. Their place within the built environment reflects the importance in the Victorian era of town planning for a community, wealthy in gold and civic pride.Black and white rectangular photograph. The image is printed on gloss photographic paper and mounted on cardboard. Obverse: NO INSCRIPTION Reverse: 7760 The old Acacia Avenue alongside the jail. Sydney Road Beechworth Gardens & Parks beechworth, acacia avenue, gaol, sydney road, burke museum, photograph, post card, english oak, liquidambar -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, Helen Penrose, Seeds of Hope St John of God Hospital Warrnambool 1939-2014, 2014
History of St John of God Hospital, Warrnambool 1939-2014This is a book of 78 pages with a stiffened cardboard cover. The cover is greyish-white with a colour photograph of the hospital and background blurred images of St John of God nuns on the front cover. The book contains printed material, maps, tables, black and white and colour photographs and illustrations.non-fictionHistory of St John of God Hospital, Warrnambool 1939-2014st john of god warrnambool hospital, glenrye, healthcare, warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Plate, Rolfe dinner plates x 4, 1864
These dishes were part of a crockery set used in the George Rolfe household at Lyndoch, Warrnambool. George Rolfe (1836-1919) was a Melbourne tea merchant who acquired land at the mouth of the Hopkins River in Warrnambool from the 1880s on as a holiday home. He developed the property over the years, adding a windmill and reservoir, bone and chaff sheds, a stable, jetty and boathouse and an extensive garden. In 1891 he married Mrs Annie Lake and it was his stepdaughter, Florence Lake who built the house, Lyndoch in the 1920s. This building today forms part of an Aged Care Facility. This item is part of the larger Rolfe dinner set as described on Victorian Collections at VC001421 and VC001422These dishes are of importance as they belonged to the George Rolfe family of Lyndoch, Warrnambool. They demonstrate the quality of the household goods used by more affluent families in the second half of the 19th century. These are four china serving dishes or plates which are part of a set of crockery used in the Rolfe Lyndoch household in Warrnambool. The dishes have a circular base with a circular dish resting on the base. The dishes have or had two handles with these handles and the edges of the dishes being gold trimmed. Around the rim of the dishes is a pattern of loops and dots etc of teal and gold. One dish (.1) has no handles, one dish (.4) has one handle only and two dishes are cracked (.3 & .4) . Two dishes are stained, one severely (.2 & .4) ‘Minton’ george rolfe, florence lake -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Plates, Rolfe Saucers x 6, 1864
These saucers are part of a crockery set that belonged to George Rolfe and his family. George Rolfe (1836-1919) was a tea merchant in Melbourne who bought land at the mouth of the Hopkins River in Warrnambool in the 1880s. He had adjoining land and the properties of ‘Shipley’ and ‘Fairy Hill’ and developed ‘Lyndoch’, adding stables, jetty, boat house, windmill and reservoir, chaff and bone sheds and an extensive garden. In 1891 he married Annie Lake and it was his stepdaughter, Florence Lake who built the ‘Lyndoch’ house still standing today. ‘Lyndoch’ today is now the site of an Aged Care Facility. This item is part of the Rolfe Dinnerset as described on Victorian Collections at VC001420 and VC001422.These saucers, part of a crockery set, are kept because they belonged to George Rolfe, a prominent property owner and farmer in Warrnambool in the late 19th century and early 20th century. The items, dating from 1864, have social significance showing the type of crockery used by a more affluent family in the 19th century. These are six circular china saucers with a gold rim and ornamentation in a scallop design in gold and teal around the rim and the outer edges. The base of the saucers has a gold rim. One of the saucers has a chip on the edge and four show significant wearing of the inner gold circle. Some of the outside gold edging also shows wear. The maker’s marks and name are indented on the bottom of the saucers ‘Minton’ lyndoch, warrnambool, rolfe and co., george rolfe, history of warrnambool, florence lake -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.China, Cups x 4, 1864
These dishes were part of a crockery set used in the George Rolfe household at Lyndoch, Warrnambool. George Rolfe (1836-1919) was a Melbourne tea merchant who acquired land at the mouth of the Hopkins River in Warrnambool from the 1880s on as a holiday home. He developed the property over the years, adding a windmill and reservoir, bone and chaff sheds, a stable, jetty and boathouse and an extensive garden. In 1891 he married Mrs Annie Lake and it was his stepdaughter, Florence Lake who built the house, Lyndoch in the 1920s. This building today forms part of an Aged Care Facility. This item is part of the larger Rolfe dinner set as described on Victorian Collections at VC001421 and VC001422These cups are part of a crockery set, and are kept because they belonged to George Rolfe, a prominent property owner and farmer in Warrnambool in the late 19th century and early 20th century. The items, dating from 1864, have social significance showing the type of crockery used by a more affluent family in the 19th century.Four small white cups decorated with aqua band around the top of each cup . A scalloped pattern of dots are suspended from the solid band which is decorated with a row of gold dots. There is a gold rim at the base of the cup.Mintonrolfe, lyndoch, warrnambool, minton cups, mrs annie lake -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Artefact, Old gaol lock, c.1880
This lock was once used in the old 19th century gaol in Gilles Street, Warrnambool. The gaol is part of a group of four heritage buildings which comprise a police station, a police residence, police stables as well as the gaol. These were built between 1883 and 1888 from the designs of the Victorian Public Works Department architect, E.R. Laver. He was responsible for the designs of many 19th century country police stations, post offices and courthouses in Victoria. The four heritage buildings, of which the gaol is one, are important because they are some of the few surviving Warrnambool 19th century bluestone buildings. Today they form part of the South West Tafe Complex. This lock is of considerable interest as one used in the Warrnambool 19th century gaol building. The door on which it was used appears to be walled up now. This is a large iron lock with a base plate with three rivets and a projection piece. There are three curved iron pieces on the plate and these are fixed to the plate with 12 rivets. The bolt is rounded and moves under the three curved pieces across the plate. There are two other curved pieces, part of the bolt locking system. The lock has surface rust. warrnambool police and gaol heritage buildings, history of warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Bottle, R F Kennedy & Co Chemist, Early 20th century
This bottle came from the pharmacy business of R.F.Kennedy and Co of Warrnambool. Richard Frank Kennedy (1826-1903) was born in England and came to Warrnambool in 1883 where he quickly established a large pharmacy business in Timor Street. In 1891 he built a mew shop which was described as one of the most elegant and best-stocked chemist’s shops in Victoria. He was a retail, wholesale and manufacturing chemist with large workshops at the back of his building. Kennedy was active in community affairs in Warrnambool and a foundation member of the Warrnambool Bowls Club as the first Vice-President and an early President. The business continued after Kennedy’s death, trading as ‘R.F. Kennedy and Co.’ Richard Frank Kennedy was one of the most significant businessmen in Warrnambool in the late 19th century. The products of his chemist shop and factory were distributed all over Victoria and beyond. The bottle, although damaged, is an example of the smaller-size bottle in use at the shop he founded. This is a small, clear glass bottle used at the pharmacy of R.F. Kennedy and Co, of Warrnambool. It has a rectangular body with curved edges, a circular-shaped neck and a moulded circular opening. There is no stopper. The top rim is chipped and the bottom of the bottle near the base is cracked with parts missing. The name of the pharmacy is embossed on the side of the bottle. ‘R.F. Kennedy & Co. Chemists Warrnambool’ r.f. kennedy, chemist, chemists in warrnambool, history of warrnambool -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Mt Beauty Community Centre original colour plan and photos of upgrade in 2000, 1. Dated March 22nd, 1962 2. Photographs taken during renovations in 2000
The Community Centre was built in the early 1950’s as an all-purpose hall for the social and recreational use of the workers and families employed on the Victorian state government Kiewa Hydro-electric scheme. The hall was originally called Mt Beauty Recreation Centre and later changed to Mt Beauty Community Centre. It has been the heart of the community for over 65 years and had a heritage listing put on it around the year 2000. The Alpine Shire secured a heritage grant and the hall was restored to its former glory in 2000. In heritage circles it is claimed that the hall is the best example of a 1950’s construction town community hall, which is still functioning anywhere in AustraliaThe Community Centre was and is a very important part of life in the small remote community of Mount Beauty and a range of activities have taken place in the Community Centre over the past 65 years- Picture theatre; Dances and balls; A physical education and boxing club run by Alex McCollough for 30 years; School and social club concerts; Girls gymnastics; Drama group productions, revues and pantomimes; Callisthetics and ballet; Badminton; Wedding receptions and birthday parties; Music festival events; Staging area in times of natural disaster; The library for many years; Shire and community meetings; Secondary College gymnasium for many years and shelter for the Community Market in inclement weather 1 – 1972 specifications for colour scheme of original Mt Beauty Recreation centre, Typed on buff foolscap paper with small colour swatches and letter of explanation to Mr A.J. McCullough. 2 – Set of 10 colour photographs of the upgrade and extension to Mt Beauty Community Centre undertaken in 2000. Photos mounted 2 to a page on blue copy paper. 3. Second copy of No.1 above. Also - typed A4 sheet re history of "The Mount Beauty Community Centre"1 – Header on pages-Mate’s Colour Bar Personal Colour Scheme for Recreation Centre Mt Beauty Vic. 21/3/62. Accompanying letter to A.J McCullough signed by Colour Consultant Ena Chatuein 2. First page of photos, written in black felt marker – Mt Beauty Community Centre 30/11/00 mt beauty, community centre -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Kiewa River, Stocking and Crossing the Kiewa River by Jan Hunter (nee Chick), 2020
The Chick brothers, Alf, Les and Allan, plus friends, began trout fishing and camping in the Kiewa Valley before the early 1930s. Les continued his connection with the Kiewa River until his death in 1972. Fingerlings were placed in the Kiewa River from the early 1880s. Keegan's Bridge is a crossing near Upper Gundowring and about 4 km south east of Dederang. References to the crossing were made in the early 1900s and a petition presented to Council in 1904 calling for a bridge.The bridge was built and opened in 1907. The photos are of the release of fingerling trout in the Kiewa River, thought to be at Keegan's Bridge. The fingerlings were transported in drums on the back of trucks. The photos are c1940s.The Kiewa Valley has been a popular spot for fishermen, tourists and campers from the 1880s. One of the many attractions has been the excellent fishing along the Kiewa River due to the regular release of fish especially brown trout. This continues to the present day (2020) when a few fish were marked with $$ signs for the lucky fisherman who caught them. This attracts visitors, their families and boosts the economy and dates back to visits at the Tawonga Pub prior to the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme.19 page book with black plastic spine and clear plastic cover over the beige paper cover with title , author and black & white photo. Note: In KVHS photo collection there are 4 good quality reproduction photos on photographic paper. These have been produced professionally. These photos of Jan Hunter's are featured on the second page of her book. These also have a letter attached. The book is a pre-research paper & is No 33 of the Albury and District Historical Society Papers. The sub-title is "Trout releases and Keegan's Bridge / from the newpapers, 1882-1935"None on the book but a letter is attached from Jan Hunter, the author as a follow up to the photos she donated. On the photos - On the back: Fujifilm / Fujicolor Crystal Archive / Paper / Production - run codekiewa river; trout; fish; keegan's crossing; keegan's bridge; fingerlings; chick family; camping; tourism -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Certificate, Loyal Victoria Lodge, mid 1940s
The Loyal Victoria Lodge was established in Warrnambool in1862. It was a Lodge connected with the Friendly Society Manchester Unity Independent Order of Oddfellows. Friendly Societies were established to give members assistance in times of illness and hardship and to offer insurance against such events. The MUIOOF had its origins in Manchester, England. The Warrnambool Lodge built the Oddfellows Hall in Koroit Street in 1869 and in 1872 it joined with other friendly societies and established the Friendly Societies Park in Koroit Street. The MUIOOF joined with the Australian Natives Association and today the new name in Australian Unity. No details are available on W. A. McLean but the certificate indicates that he served his country during World War Two.This certificate is of considerable interest as the Loyal Victoria Lodge was a pioneer friendly society in Warrnambool with its history going back to 1862. It is also a good example of the certificates given to Warrnambool residents who had rendered significant war time service in World War Two.Framed Certificate featuring text and a coloured picture. The picture includes: a dove, five scrolls, a laurel wreath surrounding a globe, three women in long dresses, three young children, two stylised flower beds, rays of light, a hill and four coats of arms. It is covered with clear plastic with a metal back and metal prop. WARRNAMBOOL DISTRICT INDEPENDENT ORDER OF ODDFELLOWS IN VICTORIA MANCHESTER UNITY FRIENDLY SOCIETY. The Officers and Members of the Loyal Victoria Lodge No. 4835 express grateful recognition and sincere appreciation to Bro. W. A. McLean for services rendered to God, King and Empire in Great War, 1939- 1945. N.G.Chas Gerock V.G. F.J. Toogood Rob Fairbridge Secretary. a circular red seal.
