Showing 896 items
matching tube
-
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumCoolidge X-ray Tube
The investigation of the x-ray appears early on to have been a priority research topic at the University of Melbourne’s School of Physics. This interest was sparked by the appointment in 1889 of Professor T.R. Lyle. Lyle, who was head of the school until 1915, is thought to have been the first person in Australia to have taken an x-ray photograph. A copy of this photograph can be found in the School of Physics Archive. For this particular experiment Lyle actually made his own x-ray tube. His successor, Professor Laby, continued to work with x-rays. During the 1920s Laby worked on the x-ray spectra of atoms and in 1930 he co-published with Dr. C.E. Eddy, Quantitative Analysis by X-Ray Spectroscopy. Also with Eddy, Laby produced the landmark paper Sensitivity of Atomic Analysis by X-rays. Laby went on to have an x-ray spectrograph of his own design manufactured by Adam Hilger Ltd. (see cat. No. 38). School of Physics, the University of Melbourne Cat. No. 22. Jacqueline Eager Student Projects Placement, Cultural Collections 2005 In 1913 Coolidge overcame the limitation of the narrow operating range of the gas X-ray tubes with the invention of the vacuum X-ray tube. A filament heated by an electric current directly releases electrons by thermionic emission. In thermionic emission, electrons are emitted from a metal surface directly by the application of an electric current to heat a wire filament. The electrons accelerate to the anode and produce X-rays. The anode has associated cooling fins due to the high temperatures attained by the release of kinetic energy by the electrons on colliding with the anode. Internal Glass sleeve: “A941/L2593/2821” -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionArtwork, other - Artwork - Decals, ZILLES COLLECTION: Car Dash Decals for Darryl James Rowe; Qualified Instrument Repairs, 1984-1986
Zilles Printers was begun by Lewis Zilles in the early 1930s. It was in McKenzie Street Ballarat. His son Jeffrey also became a printer - letterpress, offset and screen printer. The business became Zilles Printers/Graphics and was in Armstrong Street and later Bell Street Ballarat. Darryl James Rowe was a qualified instrument repairer. He specialized in Vintage car instruments on dash boards. These would include speedometers, car clocks, ammeters, oil gauges, ignition switches, temperature gauges, glass tube fuel gauges and dials repaired. He was located in Vickers Street Sebastopol. Documents relate to the years 1984 to 1986.Decal designs various sizes for car dash boards. Ledger showing orders from 1984Car makers, guages zilles printers, darryl james rowe, instrument repairer, ballarat, vintage cars, dash boards, decals, speedometers, car clocks, ammeters, oil gauges, ignition switches, temperature gauges, fuel gauges -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumMachine - Knitting Machine, Sock
Knitted fabric is made with a single yarn or sets of yarns moving in only one direction. Whether done by hand or by machine, the process is the same. The knitting needle loops the yarn through itself to make a chain of stitches. These chains, or rows, are connected to produce the knitted cloth. There are two types of commercial knitting machine. A flat-bed has its needles, one for each loop, arranged in a straight line to produce a flat fabric. A circular machine has its needles arranged on a rotating circle. The cloth forms as a tube which can be made into seamless clothing. Personal history of Edna Harris who used the machine.knitting machine, industry, design, socks, clothing, wool -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Probang
Until suction became available in the 1930s, maintenance of a clear airway during oral and nasal surgery relied on posturing of the patient, mopping with sponges or the temporary placement of swabs or throat guards. Removal of surgical debris such as polyps, blood clots or foreign bodies could only be effected by the finger or devices such as probangs. The Probang is inserted blind (perhaps guided by a finger), the main shaft can then be held in the left hand whilst the right hand withdraws the inner tube. This results in a fanning out of the linear strands which are visible proximal to the tip. Held in this position the instrument is withdrawn and is supposed to scoop out the offending mass. Long flexible metal rod covered in gum resin sheath with a ring grip at the proximal end and a smooth metal rounded edge tip for insertion into the airway for clearing of obstructive matter.Stamped onto gum resin sheath: MADE FOR / CARL ZOELLER BRISBANE / GERMANY Stamped onto gum resin sheath in gold leaf: [indecipherable - presumably manufacturer's label]probang, flexible, oral, airway, horsehair, anaesthesia, obstruction, dr sharkey, lidcombe state hospital -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rocket set, John Dennett, ca. 1860s
This rescue line-throwing rocket set was made for the Dennett rocket system, which was used by the Rocket Rescue crews in South West Victoria from around the 1860s to the 1890s. John Dennett - John Dennett was from Carisbrooke, in the Ilse of Wight, UK. In 1826 he invented, patented and demonstrated an improved method of rocket powered, line firing rescue equipment for saving lives. The rockets had a longer range than the mortars being used, they were lighter, needed less preparation time, only needed one line for repeated shots, and fewer people were needed to move the equipment. Very favourable reports of Dennett’s rockets were received by those in charge of His Majesty’s Naval and Military services. In 1832, Dennett’s rocket-thrown line was sent out to the wreck of the ‘Bainbridge’, and was responsible for nineteen survivors coming ashore in two boatloads, along the fired line. Dennett’s rocket received national fame, and a one-year contract to supply rockets to the Coastguards. He became known as ‘Rocket Man’ and his rockets were used in rescues at least until 1890, when his son Horatio was running the business. A rocket weighing 23 lb would have a range of about 250 yards (228 metres), on average. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria has had over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it, followed in 1864 by a rocket house to safely store the Rocket Rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost one hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain and improve their skills, summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The first use of a lifesaving rocket rescue system is often credited to Captain Manby and his invention of a life mortar, first used in 1808 to fire a line onto a ship to rescue lives. Henry Trengrouse’s invention of 1820 was the first to use a sky rocket’s power to throw a line, and his invention included a chair for carrying the shipwrecked victims to shore. In 1832 John Dennett invented a rocket specifically for shore to ship rescue. It had an iron case and an 8 foot pole attached and could shoot the line as far as 250 yards (about 230 metres). From the 1860s the rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It comprised a breeches buoy and traveller block that was suspended on a line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. Colonel Boxer, who had invented an early line-thrower, designed a rocket in 1865 with a range from 300 to 470 yards. It was the first two-stage rocket, with two rockets placed one in front of the other in a tube that carried the rescue line. The hemp line was faked, or coiled, in a particular way in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired, and the angle of firing the rocket was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol around 1920, which used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. Victoria’s Government adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain, which used Colonel Boxer’s rocket apparatus rescue method. The British Board of Trade published instructions in 1850 for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line attached, then firing it across the stranded vessel. A tally board was then sent out with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the continuous whip line and attach the whip block to a mast or sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a heavier hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser is then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rocket system could also be used from one ship to another.The Dennett rocket set is quite rare - there are not many examples in existence and little information is available. This Dennett's rocket set is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.A Dennett rocket set in six parts; the rocket head, three shafts (poles) and two rocket-head toting boxes. The rocket head, mounted on one of the shafts, is a long, red painted, iron tube with rounded ends and a protruding fitting around each end. The wooden rocket shafts are octagonal, with a metal sheath at the ends, carved elongated slots towards each end, and a scribed channel above the black foot. The rocket head toting boxes are thick timber, covered in fabric and painted black. They have a hinged wooden lid that slants downwards from back to front, and a metal closure. Small deliberate holes, in groups of four, on the box’s sides, indicate missing attachments, likely to have been handles. Impressed one a shaft "8"flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, william schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, rescue boat, lifeboat, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, captain manby, mortar, henry trengrouse, sky rocket, john dennett, shore to ship, colonel boxer, two-stage rocket, italian hemp, quadrant, schermuly, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, irish hand barrow, rocket head toting box, explosives, rocket shaft, rocket pole -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAccessory - Vintage Manicure Set
Home manicure sets became increasingly popular during the 1920s. The manicure tools are made of steel and the handles and case are fashioned from xylonite, a form of celluloid. Xylonite (derived from the Greek word ‘xylon’ meaning ‘wood’) is best known for use in products made by the British Xylonite Co. Ltd. Among the earliest items made from the material were knife handles, tubes and insulating materials for electric cables. Because of its light-weight and durability, xylonite became widely used in domestic items such as coral jewellery and manicure sets throughout the early twentieth century. This item does not bear a brand name but was manufactured in England c1932 This item is significant because it is representative of accessories used by women in the early part of the Twentieth century and was donated by a member of the Wodonga Community.A shell shaped manicure case made from xylonite or celluloid. The case is lined with blue velvet. The set includes nail scissors, a nail file and buffer as well as other implements. Also in the set are 2 small round containers.On back of case: Made in Englandvintage manicure set, women's accessories -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchPhotograph - Framed photograph of the submarine HMAS Onslow
The Onslow was decommissioned in 1999. She was one of 5 other Oberon's and gave the Royal Australian Navy a formidable submarine force. The motto of the submarine arm is " Strength, silence, surprise". She was laid down in 1967 , launched 1968 and commissioned 1969. She had a length of 89.9M a beam of 8.07M she had speed of 15 knots above water and 12 knots submerged. She had compliment of 60 sailors and 8 officers. Her armament consisted of six 21 inch bow torpedo tubes capable of launching anti-ship and anti-submarine Mk48 torpedoes and anti-ship UGM 84 Harpoon missiles. The Onslow was built in Scotland.Wooden framed photograph of the Oberon Class submarine.Below the photograph the wording "The Oberon class submarine HMAS ONSLOW one of the six boats of the Australian Submarine Squadron". -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBottle Corker, late 1800's to early 1900's
This hand held, wooden bottle corker would have been used by soft drink or wine producers to insert corks into their bottles to seal the drink inside. It seems it may have had a metal tip on the end of the plunger, as do other similar bottle corkers, because this plunger has a compressed end and a ring shape impressed into the wood a little way up from the tip. How to use the bottle corker … - soak a long, bullet shaped cork in water to soften it - place the bottle corker over the bottle’s neck - insert the cork through the side opening and place onto the metal funnel - push the plunger down onto the cork, forcing it into the tapered, which will squeeze the cork to size as it enters the bottle. Use a mallet or hammer if necessary The design of this bottle corker is very similar to “"Redlich's Apparatus for Corking Bottles", which was invented and patented by Henry Redlich of Chicago, USA, in 1862, US patent #35,325. H. Redlich’s gave the following instructions for the use of the bottle corker: “DIRECTIONS: SOAK THE CORK, DROP INTO THE OPENING AND TAP THE PLUNGER WITH A MALLET OR HAMMER.” This hand held, wooden bottle corker would have been used by soft drink or wine producers to insert corks into their bottles to seal the drink inside. It seems it may have had a metal tip on the end of the plunger, as do other similar bottle corkers, because this plunger has a compressed end and a ring shape impressed into the wood a little way up from the tip. How to use the bottle corker … - soak a long, bullet shaped cork in water to soften it - place the bottle corker over the bottle’s neck - insert the cork through the side opening and place onto the metal funnel - push the plunger down onto the cork, forcing it into the tapered, which will squeeze the cork to size as it enters the bottle. Use a mallet or hammer if necessary The design of this bottle corker is very similar to “"Redlich's Apparatus for Corking Bottles", which was invented and patented by Henry Redlich of Chicago, USA, in 1862, US patent #35,325. H. Redlich’s gave the following instructions for the use of the bottle corker: “DIRECTIONS: SOAK THE CORK, DROP INTO THE OPENING AND TAP THE PLUNGER WITH A MALLET OR HAMMER.” Bottle corker, a hand operated wooden corking device for sealing bottles. Bottle corker has two parts comprising a wooden plunger rod with knob handle, and wooden cylinder containing a metal tube that is flared to a funnel shape on the top. The cylinder has a hole the diameter of the rod at both ends and an oval insertion slot in one side. The tip of the plunger rod is slightly compressed and it has an indented line around the circumference as though it has had something attached to it. Manufactured in the late 1899s to early 1900s in Melbourne.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, cork -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - TRAINING STAND FOR .303 IN LEE ENFIELD RIFLE, 21 Bn. AIF, c1915-1918
This is a WW1 stand for mounting a .303 rifle, to train soldiers in shooting.This device consists of two parts; 1. Top part has an adjustable 'arm' . At the end of each arm is a leather covered 'U' section. Under the arm is a large threaded rod and knurled knob, this is to adjust elevation. At the center of the arm is a pivot that can lock into position. This top section is mounted on a tripod, it can be removed. 2. This is a steel tripod made out of 'T' section steel. There are fixed cross braces about 40 cm fom bottom. The top has a tube section within which the upper arm mounts.Marked on one leg is "XXI". Believed to be from 21st Bn. AIF. on the top of that leg is a very small arrow head.ww1, training, .303 rifles -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionEquipment - Object, Artist's Box, c 1940
Edith (Alice) Watson (1914–2010) studied at the Ballarat Technical Art School, at the School of Mines Ballarat, from 1930 until 1933. Watson was warmly regarded in her home town, Murtoa, easily winning local fundraiser, ‘Most Popular Girl’ in 1936. Upon graduating, Watson taught at the Murtoa High School, living with her parents until their deaths 1972 and 1988. Watson was 74 years old. Alice Watson died in Ballarat, aged 95, having conserved her beautiful student folio. Alice's comprehensive folio of Ballarat Technical Art School work is held by the University's Geoffrey Blainey Research Centre.A cardboard box containing items used by Alice Watson to produce paintings. The items included are: tubes of oil colour; two paint palettes; paint brushes; imperial measure tape measure; pencils; an erasure; two pencil sharpeners; a roll of brown, gummed tape; small, round container of various pins; a State Savings Bank Victoria ruler; and a collection of scraps of artists paper held together with a metal clip which includes a list of paint colour names and a design tracing of a fuschia. There is a small, plywood, stretching board. alice watson, edith alice watson, ballarat school of mines, artists workbook, ballarat technical art school, paint, oil paint -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
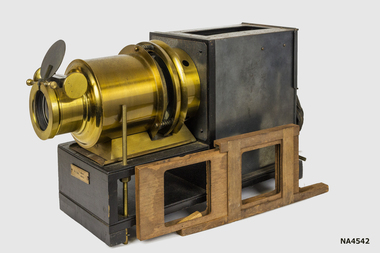
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Equipment - Projector, C1920
Owned by Newspaper photographer living in Wattle Park c 1960s.Possibly Nepera Brand, Name on Slide Boxes.1.A Wooden Case with a Sliding Rear Door for Projector. 2. Projector, Wood & Brass, Black Metal Box at rear for lamp & electric lead, spare lens inside. Brass lens holder & Focus adjuster at other end. 3. Wooden slide holder holds two slides, and fits between body and lens tube. 4. Spare lens marked 6 In EQUI with sliding collar. 5. 3 packs of glass slides. 4. Grey tin containing slides. Slides stored in .09.13.No 510324 on Lens Adjuster Ron.230577, 7in, Est 1816, Trade mark. London Made. Without name Australasia Pty Limited.photography, photographs / slides / film, projectors -
 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental Collection
8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental CollectionHeadwear - Busby, 1854 circa
8th Hussars formed part of the Light Brigade which took part in the famous charge.Busby which belonged to C R Burn Esq 8th Hussars with metal box for hat and metal tube for plume. Busby was worn at Balaclava during the Crimean War 1854. Leather inner with brown fur outer covering; red cloth flap on right side; gold braid, white horsehair plume and red feathers at base or plume, gilt link chinstrap. The busby was presented as a gift to 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles by its affiliated British regiment, 8th Queen's Royal Irish Hussars in 1954.On lid of hat box: " C R Burn Esq 8th Hussars" and "Hawkes and Co Piccadilly London"busby, hat, military, cavalry, hussars -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway Museumbanner - 1,000,000 miles, Jun. 1968
Used on tram 27 to celebrate is "1,000,000" miles, but later work determined that there had a been an error in addition of the miles operated statistics - see reference for the background story. Three copies held. See item 3315 for other copies.Demonstrates a banner to mark a tram that had been calculated to achieve 1,000,000 miles of running in Ballarat.Bammer - Painted on treated white linen, banner used to celebrate Tram No. 27, reaching 1,000,000 miles. Has wording in large red capital letters "This tram has just completed 1,000,000 miles in Ballarat". Fitted with metal eyelets in each corner and centre of top and bottom edges. See Reg. Item 3316 for photo taken by The Courier on 29/6/1968. Has been rolled around a tube for storage. Not known who made it - SEC or TMSV. See item 3315 for another two copies.tramways, trams, million miles, banner, signs -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
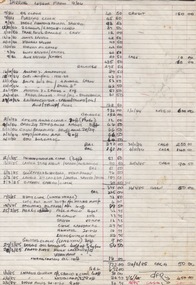
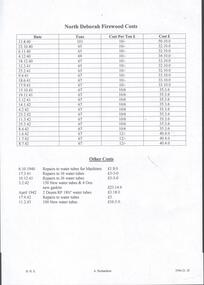
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - NORTH DEBORAH GOLD MINING CO N. L. - NORTH DEBORAH FIREWOOD COSTS
Handwritten list of tons of wood, with typed copy of same, of cost per ton, total cost and the date. (1940 - 1942). Other costs for the repair and purchase of new water tubes and the dates (1940 - 1943). On the reverse is a list of wages from North Deborah August 1953, Basic Wage increase of 3/- per Week. Lists all the different workers and the amount they receive per week and per shift for 40 hours. Basic Wage 11 pound 12 shillings per Week. Albert Richardson Collection. document, gold, north deborah gold mining co n. l., north deborah gold mining co n. l., north deborah firewood costs, wages at august 1953 -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Renton circle valve absorber, sectioned, Dr Douglas Renton, 1931
The Renton circle valve absorber has been sectioned to show the valve connection points. The inside is a creamy brown colour, encased in black on the outside. A larger silver metal valve runs through the centre, and to it attaches a flat, reflective silver metal disc as a dial indicating "EXH", "ABS", and "REB", with a black needle. The system includes tubes and valves for oxygen entry, gas expiration, connection to soda lime cannister, rotary valve, and rebreather bag, with a broken, deteriorated segment of the bag still attached.valve, anaesthesia, soda lime, rebreathing -
 Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory LightstationWeights
The seven weights (0008.4 and 0136.3) are circular in shape with a hole in the centre and a groove cut across the radius. They were specifically designed to fit into a weight tube, which allowed movement of the weights that were used for driving the clockwork mechanism for turning the lighthouse lens. They are most likely original to the Chance Brothers system installed in 1913, which was originally equipped with a set of ten, each weighing around thirty kilograms.The weights were moved vertically in similar fashion to the way weights move on a grandfather clock. As the weight fell, the optic clock was driven and the lens was turned. To keep the clock turning, the weight needed to be wound back up to the top of its travel. Lighthouse keepers had to constantly wind the clock to keep the light active, and at least two keepers needed to observe a strict roster of hours. When electric motors were invented, weights became obsolete and the motors were able to turn the optic for as long as there was power to drive them. Wilsons Promontory’s Chance Bros. kerosene operated light, which was turned by a clockwork mechanism, was replaced by small electric motor in 1975, reducing the number of keepers and eliminating the need for weights. Cape Schanck has a set of fourteen weights remaining in situ in the lighthouse weight tube as well as another four detached weights, two of which may be associated with the 1859 mechanism. A small number of detached cast iron weights and two associated rods remain at the Point Hicks Lightstation and one weight is displayed in the lantern room at Cape Otway.The Wilson Promontory weights have first level contributory significance for the insights they provide into the technology and operations of a late nineteenth/early twentieth century lighthouse which has since been superseded. They are well provenanced and are significant for their historical value as part of the lightstation’s Chance Brothers optical system installed in 1913.Four circular disc shaped lead weights, all with a narrow section cut out to the middle of shape. (as in slice of cake) -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - RIFLE CLEANING KIT, 1962 - 1973
1. String pull through - it is made of a 3 part cord. One cord has a metal tube, the other end has a loop. 35cm from the loop end is another loop (it still retains a bit of oily cleaning cloth when last used.) One of the three cords has snapped. 2. Same sort of pull through as above. - still rolled up tightly. 3. Wire bristle brush for barrel cleaning. It has a brass end for screwing to a rod. The bristles are two diameters. A lot of fluff is caught up in the small bristles.rifle cleaning equipment, vietnam war -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Winborn, Arthur T, The Use of Oxygen Breathing Or Rescue Apparatus for Work in Noxious Atmospheres, Etc, c1912, c1912
Green hard covered cloth book of 127 pages. Images include the Monmouthshire Colliery Owners' Rescue Association (T. Braithwaite, J.F. Tallis, A.S. Tallis, W. Stewart, W. Gregson. Robert Jordon, T.H. Deakin. W.H. Routledge, B. Nicholas); A.T. Winborn of the Miners' Rescue Station, Crumlin; Draeger apparatus in use; Dragerwerl Lubeck, Water Gauge for testing Injector, Injecting sample air into test tube containing lime water, Meco Apparatus, Pneumatogen Self Rescue Type, Animal Air-Testerbreathing, poison, mine rescue, rescue apparatus, oxygen breathing rescue apparatus, a.t. winborn, monmouthshire colliery pwners' rescue association -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Gas Fitting, Before 1878
The artefact is a short cross-section of part of a functional part of a brass fitting that suspended a gas lamp, providing structural support, and internally, supplying the gas for its ignition. It combines elegant design with the elements required for safe and efficient delivery of gas. It was recovered from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site. There are similar artefacts in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The LOCH ARD left Gravesend (London) on 2 March 1878, bound for Melbourne, with a crew of 37, 17 passengers, and a diverse and valuable cargo of manufactured goods, luxury items, and refined metal. Some of the cargo was intended for Melbourne’s first International Exhibition to be held in 1880. At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south west coast near Port Campbell. Only two people survived the disaster — Tom Pearce, a male crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a female passenger. The cargo proved too difficult to salvage in the vessel’s exposed condition and was largely written off. The manifest of goods in the LOCH ARD’s holds included “Fittings gas (4 cases)”. The gas lighting of streets, public buildings, and the dwellings of wealthier private citizens, was already well advanced in the cities and major towns of the Australian colonies. In 1841 Sydney was the first to be gas lit with 23 street lamps, 106 hotel lamps, and 200 private residences connected to the Darlinghurst “gasometer” by an underground network of metal pipes. “The dim days of oil and tallow are gone by!” pronounced one newspaper, flushed with civic pride. The 1850s Gold Rush promoted a similar attitude of confidence and affluence in the Colony of Victoria. In 1855 Melbourne was connected to its own system of subterranean gas pipes despite the same high rates of 25 shillings per 1000 cubic feet being charged, (reduced to 15 shillings in 1865 with cheaper sources of coal). By1858 Kyneton had its own gasworks to light the town (fuelled by eucalyptus leaves) and Geelong followed suit in 1860. Had the LOCH ARD reached its intended destination in 1878, it is probable that the 4 cases of brass gas light fittings on board would have found a ready market.The gas fitting is significant for its association with the LOCH ARD shipwreck, which is of State significance and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register S417. The fitting is an example of a late 19th-century plumbing and light fitting.A pressed brass gas light fitting, recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The elegant and functional fitting extends from an ornate 8cm diameter ceiling flange, and comprises two short lengths of fluted column pipe with a brass joiner that are severed (cut off) at the end. Within this decorative outer layer of 3cm diameter is a full length brass tube liner, which is in turn protecting a narrow 0.75cm copper gas pipe that also runs full length. The artefact is generally unrestored with reddish/cream sandstone concretion, but is in good condition.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, gas lamps, gas lighting, gas works, brass fittings, gas pipes, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, victorian affluence, colonial gas lighting -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumNewspaper, The Courier Ballarat, "Tram track rider woes", "GP seeks action", "I have the answer", Mar. 2011
Yields information about newspaper articles about the problem of cyclists and the tramway rails at depot junction.Two sheets from The Ballarat Courier, regarding issues with the tram tracks at Depot junction and cyclists. .1 - Front page with headline "Tram track rider woes" of The Courier, Ballarat, 19/3/2011 written by Kim Stephens, photo Dominic O'Brien, and on page 2, GP Phillip Dover who was injured after falling off his bicycle. Page 3 - The Courier, 22/3/2011 - "I have the answer", about Kelvin England with a suggestion of a rubber tube in the flangeway, including a photograph. Article by Pat Nolan, Photo Lachlan Bence. depot junction, cyclists -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway Museumbanner - 1,000,000 miles, Jun. 1968
Used on tram 27 to celebrate is "1,000,000" miles, but later work determined that there had a been an error in addition of the miles operated statistics - see reference for the background story. Two copies held. See item 9651 for a 3rd copy.Demonstrates a banner to mark a tram that had been calculated to achieve 1,000,000 miles of running in Ballarat.Bammer - Painted on treated white linen, banner used to celebrate Tram No. 27, reaching 1,000,000 miles. Has wording in large red capital letters "This tram has just completed 1,000,000 miles in Ballarat". Fitted with metal eyelets in each corner and centre of top and bottom edges. See Reg. Item 3316 for photo taken by The Courier on 29/6/1968. Has been rolled around a tube with tissue paper for storage. Not known who made it - SEC or TMSV. 3315.1 - As above, held by the BTPS since 1971.On rear in blue ink "Dash Banner, Car No. 27, 29th/6/68". Has pencil layout marks visible.tramways, trams, million miles, banner, signs -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumHeadwear - FLYING HELMET, C.1939 - 45
The helmet belonged to Henry Victor Evans No 418655 RAAF. Refer 1760.4. Type B flying helmet made of dark brown leather and lined with chamois. There is a leather chin strap fastened on the left with a white metal buckle. On the inside of the helmet on either side of the face are two snap fasteners with a strip of chamois backed webbing fastened between them for securing an oxygen mask or face protector. There is a buckled strap across the back of the neck with two thinner buckled straps running vertically above it. Another thin buckled strap is secured across the front of the helmet. A circular ear piece is sewn on either side of the helmet with a zippered opening. Inside each piece is a brass fitting for attaching gosport tubes. Brown leather Flying Helmet, yellow suede lined inside."N361". Hand written "V.H.Evans".flying helmet, raaf, headwear, leather -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaEquipment - Object, Soundscriber dictaphone, 1945-1960
The Sound Scriber Dictaphone allowed recordings to be imprinted into a soft disk that could then be replayed later. This was useful for blind stenographers who could transcribe the audio recording. The lid contains a speaker into which sounds are made, the front knob is allows for 'Talk' or 'Listen' and three other dials on the device allow for the tubes to be turned on/off, starting/stopping the turntable and the recording volume to be 'Dictation' or 'Conf". There are two measuring tapes placed near the recording head and the Listen head, which show the minutes in the recording. The large disk that is placed on this machine has been stopped at the 12 minute mark. At the rear of the device are two plugs, one of which is for electrical supply. This model of dicta phone remained popular until magnetic tapes.1 hinged leather case over a metal and wood machineSound Scriberaudio equipment, assistive devices -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Personal Effects, Cigarette holder bakelite, c1940
A cigarette holder is a fashion accessory, a slender tube in which a cigarette is held for smoking. Most frequently made of silver, jade or bakelite, which was popular in the past but now wholly replaced by modern plastics, cigarette holders were considered an essential part of ladies' fashion from the mid-1910s through the early-1970s. Traditionally, men's cigarette holders were no more than 4 inches ( 10cm ) long The holder was also used as a practical accessory, as before the advent of filtered cigarettes in the 1960s, the holder served several purposes. A holder kept tobacco flakes out of the smoker's mouth, kept the thin cigarette paper from sticking and tearing on the smoker's lips, prevented nicotine stains on fingers, cooled and mellowed the smoke and kept side-stream smoke from stinging the smoker's eyes A Bakelite gentleman's cigarette holder c1940cigarettes, cigars, tobacco, bakelite, plastic, market gardeners, pioneers, moorabbin, cheltenham, bentleigh -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumMachine - Sock Knitting Machine, G Stibbe and Co, c.1928
Knitted fabric is made with a single yarn or sets of yarns moving in only one direction. Whether done by hand or by machine, the process is the same. The knitting needle loops the yarn through itself to make a chain of stitches. These chains, or rows, are connected to produce the knitted cloth. There are two types of commercial knitting machine. A flat-bed has its needles, one for each loop, arranged in a straight line to produce a flat fabric. A circular machine has its needles arranged on a rotating circle. The cloth forms as a tube which can be made into seamless clothing. Dellruss Pty Ltd original owner Llyold Henry Coburg. Mock ribber fitted post World War 2. In use from c.1928 until 1978.Stibbe Maxim circular sock knitting machine.sock knitting machine, manufacturing, textiles, socks, machines, circular, clothing, industry, wool -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Photograph - Reproduction photograph of Dr Lawson Tait, c.1891
Robert Lawson Tait (1845-1899) was a Scottish doctor and surgeon instrumental in the development of gynaecology as a field during the 19th century. Tait has been credited "with introducing a number of gynecologic surgeries, or surgeries related to women’s reproductive health. Those included procedures for treating abscesses, removing ovaries, and fallopian tubes, and treatment of the gallbladder." He also "argued for strict cleanliness during surgery as well as a more specific focus on performing surgeries to treat diseases of the female reproductive system. Tait’s surgical techniques and advocacy not only aided in the development of hygiene in surgery, increasing patient survival, but also helped develop the field of gynecology, which contributed to a centralized focus on the health of the female reproductive system." (Arizona State University, Embryo Project Encyclopedia)Black and white reproduction of a portrait photograph. Photograph is of a man in a dark coloured three-piece suit, with a white shirt and striped tie. The man has mutton chop sideburns and long, dark hair, which is parted about his right eye. The man is looking to camera right. The image is in an oval cutout on a white background. Handwritten reproduction of signature beneath the photograph reads 'Lawson Tait/1891'. The photograph is mounted in white card and housed in a black wooden frame. There is an old object label attached to the back of the object. A sticker noting the framer of the image (Jarman the Picture Framer) is attached to the back of the work at upper centre. A wire and two hooks have been attached to the back of the frame for hanging. -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Yankauer, c. 1904
Sidney Yankauer, M.D. (1872-1932), an ear, nose and throat specialist and pioneer in bronchoscopy, practiced at the Mount Sinai Hospital in New York. Dr. Yankauer, a prolific inventor of medical equipment, might best be known for the tube he designed for suctioning the mouth and throat. Yankauer introduced the wire-mesh anaesthesia mask around 1904. The drop method involved placing the mask over the patient’s nose and mouth, and then placing gauze over the mesh of the mask. Next, liquid anaesthetic, such as ether or chloroform, was applied in drops or lightly poured onto the gauze so that the patient breathed in evaporated anesthetic as well as air. The gutter around the base of the mask was designed to catch any residue of the harmful anaesthetic. (The Wood Library Museum, 2016; Museum of Healthcare Kingston, 2016)A metal tear-shaped mask with gauze wire dome, gutter around the base and detachable spring piece with open circular handle to secure cloth over gauze. Found inside medical carry box #899Stamped underneath neck of circular handle: HATRICKdr [e.s.] holloway, hatrick, yankauer, drop method, mask, gauze -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Syringe, 1853
Charles Gabriel Pravaz (1791-1853) was a French orthopedic surgeon and inventor of the hypodermic syringe. In 1844, Irish physician Francis Rynd (1811-1861) invented the hollow needle. In 1853, French physician Charles Pravaz developed the first practical metal syringe. Pravaz added a fine, hollow needle to the end of his syringe instead of the tube. This was an important innovation. Yet in the pre-antiseptic era it was a mixed blessing. The use of injections rather than oral drug administration can more readily promote the spread of disease as well as facilitating its cure. An understanding of the germ theory of disease - and the cardinal importance of using sterile needles - awaited the discoveries of Lister, Pasteur and Koch. But intravenous injection allows extremely rapid pain-relief - and the induction of general anaesthesia when suitable agents were developed.Small ornate metal syringe with raised ridge at either end and in the middle. Tapers to a point at the distal end with pencil like extrusion. Finger ring at the proximal end.pravaz, intravenous, hyperdermic, subcutaneous, syringe, needle -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySewing Machine
Sewing machines were used by some ladies to mend and make clothes for the family as shops were some distance away and bought clothes were much more expensive. The sewing machines were also used to sew items for fund raising e.g.. Church and School fetes.Used in the Kiewa Valley.The machine has a brown wood veneer base and a lid with a metal handle in the centre of the top. There is a long screw that fits in a hole at the top of the lid. The screw can be lifted out and used to open and take off the lid. Inside there is a black metal machine which is fitted onto the wooden base. There is a compartment in the base, right of the wheel of the machine, which holds an instruction manual and a tube of ""Singer" lubricant for electric machines". The light, above the needle is covered by bakelite. A leather belt runs around the wheel on the right to enable the machine to run. There is a foot pedal and an electric cord attached."Singer Manufacturing Company" - gold embossed "No. EL 249 355" - oval disc "99K" - disc "Singer Manfg. Co. - discsewing machine; singer manufacturing company; kiewa valley -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - FIRST AID KIT, Possibly post WW2
.1) - 2.) Canvas bag with strap, khaki, brass press studs. .3) - .8) Group 3 bandages & 3 dressings in paper wrapping. .9) - .13) Cardboard box with lid containing 3 ampoules of tincture of iodine. .14) Sealed paper pocket containing safety pins. .15) - .17) x 3 bottles containing tablets. .18) Metal tin with attached lid. .19) Roll of adhesive tape. .20 - .21) Tube of Tannic of Acid Jelly in cardboard box. .22) Small brush. .23) Dressing fabric. .24) Gauze bandage. medicine-first aid, military history - equipment, passchendaele barracks trust
