Showing 10061 items
matching son
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncBooklet, Duncan & Weller Pty Ltd, Old Kew Golf Links Estate, 1927, 1927
The booklet advertises the third sale within the Old Golf Links Estate which was a major subdivision of farmland in North Kew in the 1920sThe subdivision of the Kew Golf Links Estate was a major subdivision of farmland in Kew. The site was at one stage designated for industrial development and the building of a new Kodak factory. The decision by Council to oppose the redevelopment makes the beginning of the period when all industrial development was banned in Kew.6 page illustrated brochure advertising the third section of a major subdivision in Kew in 1927 including 75 charming home allotments and 7 valuable building sites. The brochure includes the subdivision plan. The front cover includes a colour illustration of the almost completed houses in Woolcock Avenue. Streets named include: Kilby Road, Kodak Avenue, Baker Avenue, Mathers Avenue, Coleman Avenue, White Avenue and Belford Road. Lots for sale are numbered. Existing buildings are designated with a square.subdivisions - kew (vic), kew golf links estate -
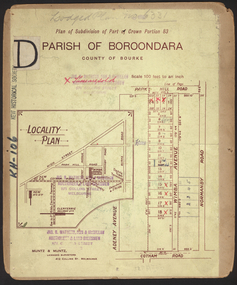 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Wimba Estate, Kew, c.1925-c.1929, ca. 1925-ca. 1929
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.In 1925, the City of Kew called for tenders for the construction of Wimba Avenue, Cadow Street and Lalla Street. Subsequent advertisements for the sale of land in Wimba Avenue continued from 1926 to 1929. The 18 lots (and a further five allotments on the eastern side of the street) offered for sale were unofficially described in the subdivision plan as the ‘Wimba Estate’. These lots began in Park Hill Road and extended almost to Cotham Road. The subdivision took its name from the house ‘Wimba’ in Cotham Road, which may have formed the southern boundary of the subdivision. (Wimba, at 235 Cotham Road was constructed between 1862-70). The Plan highlights the proximity and advantage of ‘electric’ trams in Cotham and Glenferrie Roads, and the Kew and Glenferrie Railway Stations. An oddity in the Plan is the reference to the electric tram terminus at Burke Road, given that the tramline had already been extended to Mont Albert in 1916.wimba estate, subdivision plans - kew, parkhill road – kew (vic.), normanby road – kew (vic.), wimba avenue – kew (vic.) -
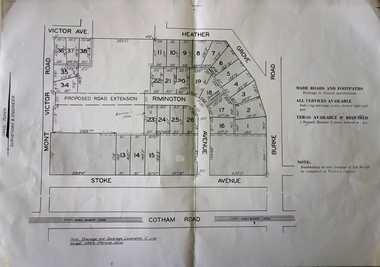 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan, F R Simms & Son, Land for Private Sale: Cnr Victor Avenue and Mont Victor Road, Kew, 1950-1960
George Rimington established The Parkhill Nursery in 1877. By 1910, it was more commonly known as Rimington’s Nurseries and well known for its sale of violets. After World War II, Rimington’s Nurseries were gradually subdivided and sold. The 38 allotments were released in sections, including lots 34 to 36 on the corner of Mont Victor Road and Victor Avenue. Previous lots in the subdivision had bordered Burke Road, Rimington Avenue, Heather Grove, and Stoke Avenue. The selling point as it had been in comparable estates for a century were the proximity to transport, schools and churches, as well as the high location and excellent views. The subdivision plan shows most of the lots in the entire subdivision: 1-11, 13-26, and 34-38. Presumably, lot 12 and lots 27-33 were still to be released.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.Subdivision plan advertising five superb home sites among lots in Burke Road, Stoke Avenue, Victor Avenue, Mont Victor Road and Heather Grove.subdivision plans - kew, rimington avenue -- kew (vic.), heather grove -- kew (vic), stoke avenue -- kew (vic.), burke road -- kew (vic.), mont victor road -- kew (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Bonnie Doon Estate, c.1908
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The subdivision advertised as the Bonnie Doon Estate in Greensborough was first advertised in 1908. At that stage, the new subdivision included 15 allotments of between one and four acres. By the time the subdivision plan in the Kew Collection was created, only 12 lots of between ¾ and 2½ acres remained. Both the State Library and Kew plans emphasise the distance to the city being 13½ miles, which could be reached by train on weekdays and weekends. Unusually, the plan describes the suitability of lots as locations for ‘Week-end Homes’. Correspondingly, the train line is described as ‘The Holiday Resort for the Northern Suburbs’.bonnie doona estate, subdivision plans - greensborough -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Cotham Vale Estate, 1919
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The Cotham Vale Estate was a subdivision of land between Alfred, Thomas, Rowland and John Streets. It was promoted in the same time as the nearby Normanby Heights Estate. Cotham Vale included 28 allotments. Contemporary newspaper advertisements noted that the Estate ‘is most conveniently situated in a well elevated position, only 2 minutes from Cotham rd. Electric Cars, penny section to Kew station’.subdivision plans - kew, cotham vale estate, rowland street -- kew (vic.), thomas street -- kew (vic.), john street -- kew (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Golf View Estate, c.1922
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The subdivision advertised as the Golf View Estate in Camberwell included 32 allotments bordering on Glen Iris Road, Smith Street (now Smith Road), St Andries Street and Camberwell Road. In the post-war period in which the subdivision took place, the significance of Camberwell as the ‘Heathiest of Suburbs’ because of the undulating nature of its terrain and its high altitude was promoted. The sales pitch aimed at attracting and selling to ‘Gentlemen’ who could take advantage of the nearby trams, which would take them to the ‘heart of the city’.subdivision plans - camberwell, golf view estate -
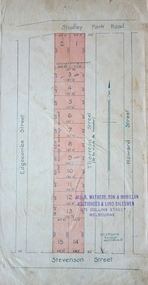 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Thornton Estate, 1918
The ‘Thornton Estate’ was the final subdivision of ‘Thornton’ in Studley Park Road. Thomas Cubitt Balmain originally owned Thornton, next to John Carson’s ‘Clutha’. Before its final subdivision, the Thomson family owned it. The Estate was a subdivision of 15 residential allotments running between Studley Park Road and Stevenson Street. The allotments faced these streets as well as Thornton Street, which the vendor undertook to make. Contemporary newspaper advertisements advised that ‘The estate possesses many advantages, notably its private and secluded, though convenient, position, splendid frontages and depths, and being close to the electric tram and Kew train, also within easy walking distance of the Victoria-street cable tram’. The terms offered purchasers were ten per cent deposit, with the balance to be paid in ten equal half-yearly payments at a rate of 5 per cent.The ‘Thornton Estate’ was the final subdivision of ‘Thornton’ in Studley Park Road. Thomas Cubitt Balmain originally owned Thornton, next to John Carson’s ‘Clutha’. Before its final subdivision, the Thomson family owned it. The Estate was a subdivision of 15 residential allotments running between Studley Park Road and Stevenson Street. The allotments faced these streets as well as Thornton Street, which the vendor undertook to make. Contemporary newspaper advertisements advised that ‘The estate possesses many advantages, notably its private and secluded, though convenient, position, splendid frontages and depths, and being close to the electric tram and Kew train, also within easy walking distance of the Victoria-street cable tram’. The terms offered purchasers were ten per cent deposit, with the balance to be paid in ten equal half-yearly payments at a rate of 5 per cent.subdivision plans - kew, thornton estate, studley park road -- kew (vic.), thornton avenue -- kew (vic.), stevenson street -- kew (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Glenferrie Road & Wellington St, Kew, c.1920s
Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.An unnamed subdivision in Kew including eleven lots for sale bordering Glenferrie Road, Wellington Street and Franks Grove.subdivision plans - kew, franks grove, wellington street, glenferrie road -
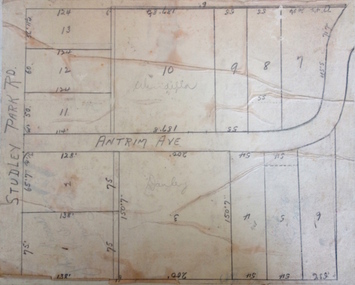 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Windella-Darnley Subdivision, Studley Park, 1920s
Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.Version 2 of two subdivision plans (the earlier is 2016.0305.1) for the section of Studley Park Road near the Junction on the south side. Named in the subdivision are the mansions of Darley and Windella (now demolished). Before the subdivision of Darley and Windella, both houses fronted Studley Park Road. Both houses appear to be advertised as lots in the subdivision. Bisecting the subdivision is a street, Antrim Avenue that was never constructed. A street, which was subsequently constructed in this vicinity, was Merrion Place, which now runs between Studley Park Road and Highfield Grove. There are 13 proposed lots in this subdivision in contrast to the earlier plan. This resulted from larger lots being proposed for Studley Park Road.subdivision plans - kew, studley park, windella, darnley, antrim avenue -- kew (vic.), studley park road -- kew (vic.), merrion place -- kew (vic.), merrion grove -- kew (vic.), highbury grove -- kew (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Eastlawn Estate, 1914
Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.The ‘Eastlawn Estate’ was surveyed and ready for auction in March 1914, three months before the outbreak of World War I. Sixty-six allotments, created on the ‘order of Mr & Miss Preston’ surrounded the mansion of Woodlands in Harp Road. Woodlands formed part of the Estate, being advertised as lot 1. The allotments faced High, Station and Wright Streets, Harp and Normanby Roads, and Woodlands Avenue. Pru Sanderson in the Kew Conservation Study (Vol.2, 1988) wrote that the Eastlawn Estate ‘covered the western half of the failed Harp of Erin Estate’. Contemporary advertisements promoted the Eastlawn Estate as: ‘There will be no more convenient district nor pleasant Suburb than East Kew for the busy business man. When the Electric Tram is laid, he will be able to journey quickly and pleasantly direct from Collins Street to his home in the Eastlawn Estate in about 20 minutes’. The actual plans of subdivision were included in advertisements in The Argus and in the local newspapers.subdivision plans - east kew, eastlawn estate -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
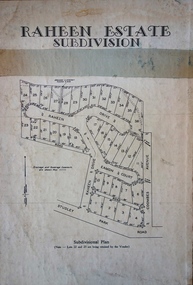
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Raheen Estate Subdivision, 1960
Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.The Raheen Estate Subdivision of 1960 involved the creation of 36 residential allotments and the sale of 34 of these. The land on which the subdivision was created had until 1960 formed part of the grounds of the mansion Raheen in Studley Park Road. In 1917, the Catholic Church had purchased Raheen and its lands. It was to become the home of Archbishop of Melbourne, Daniel Mannix, for 46 years. The sale of the subdivision took place three years before the Archbishop’s death. Subsequent archbishops were to reside at Raheen until its sale to the Pratt family in 1981. When the sale of the Estate was reported in the newspapers in 1960, it was described as the last big subdivision near Melbourne. At the auction, 33 of the 36 allotments were sold. The auction realised £315,750. Purchasers were advised that the vendor intended to keep lots 22 and 23. The alllotments in the subdivision required the construction of new roads. These included Eamon Court and Raheen Drive. The justification provided by the Church for the sale was that the estate was being sold to finance school building projects.subdivision plans - kew, studley park, raheen estate, eamon court, studley park road, coombes avenue, raheen drive -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
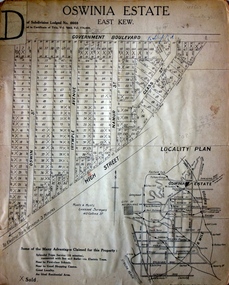
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Oswinia Estate, East Kew, c.1925
Prue Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.The ‘Oswinia Estate’ subdivision in East Kew was planned and auctioned in the first half of the 1920s. 169 allotments were created in the triangular section of land bordered by High Street, Burke Road and the Government Boulevard (later Kilby Road). The only piece of land excluded was that where the previous Kew Pound had been located at the east tip of the triangle. Allotments were created fronting Glass, High, Namur, Oswin Streets, Irymple Avenue, and the Government Boulevard. The name for the Estate was derived from Oswin’s farm, which had been one of the largest landholdings in East Kew. The selling agents annotated the plan in our collection with crosses indicating those lots that had been sold. The inset locality plan is particularly interesting as it shows the route and stations of the Outer Circle Railway. When the subdivision plan was created, it included the proposed bridge over the Yarra at Burke Road. The bridge was to be officially opened in 1926.subdivision plans - east kew, oswinia estate, high street, glass street, namur street, government boulevard - kilby road, irymple street, oswin street -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
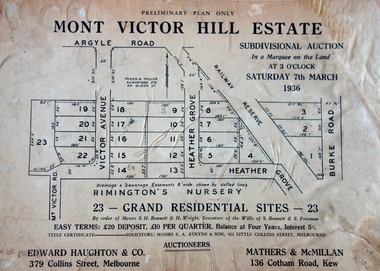
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Mont Victor Hill Estate, 1936
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.A preliminary plan for the Mont Victor Hill subdivision of 1936 which included 23 allotments bordering the Rimington Nursery in Mont Victor Road. The subdivision created allotments in Victor Avenue, Heather Grove and Burke Road. Bisecting the Estate and clearly marked on the plan is the Railway Reserve which at this stage was all that remained of the Outer Circle Railway. The auctioneers note on the plan that the subdivision was made possible by the order of Messrs S. H. Bennet & H. Wright, the executors of the Wills of S. Bennett & E. Foreman.mont victor hill estate, subdivision plans - kew -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
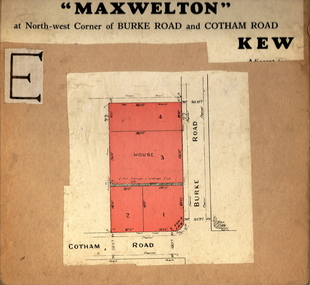
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Maxwelton, Kew, 1920-1940
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The subdivision, ‘Maxwelton’, included four lots in East Kew, at the northwest corner of Burke Road and Cotham Road. Lot 3 is identified as the location of an existing house. The site of the subdivision equates to that parcel of land where a contemporary block of three storey apartments at 1245 Burke Road is now located.subdivision plans - kew, mazwelton subdivision, burke road -- kew (vic.), cotham road -- kew (vic.) -
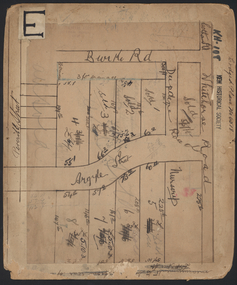 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Lodged Plan No.6518, 1920-1940
The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. Reconciling this hand-drawn subdivision plan with a modern map of the area is initially a challenge due to a change of street names. Argyle Road in the centre of the subdivision was to be renamed Deepdene Road, and the street named Deepdene Road on the plan was to become Deepdene Place. Of interest is the nursery on the corner of Argyle and Whitehorse Roads. During this period there were a number of nurseries servicing the Kew and Balwyn areas. The subdivision was essentially of the land formerly occupied by the house 'Deepdene'.subdivision plans - balwyn, deepdene, whitehorse road -- deepdene (vic.), deepdene road -- deepdene (vic.), burke road -- deepdene (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Normanby Estate, East Kew, 1913
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. The Normanby Estate, which was adjacent to Normanby Road, Kew East, included thirty-one lots for sale. Streets on the subdivision plan include Adeney Avenue, Park Hill Road, Normanby Road, Weir Street and Wharton Street. Cotham Road and its tramway are shown nearby. The plan is interesting as it shows Wharton Street, named after the architect and town planner George Wharton, who was the first chairman of the Municipality of Kew. The street was to later be renamed Cecil Street. Also shown are proposed ‘Municipal Gardens’ where Parkhill Drive is now located.subdivision plans - kew, normanby estate -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Violet Farm Estate, 1927
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these.The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A subdivision plan for nineteen ‘bonny, airy building blocks’ on either side of Violet Grove, Kew East. Violet Grove runs between High Street and Harp Road. Like many other subdivisions in Kew and East Kew, older houses (Lots 1 and 13) were often included in the subdivision. Such houses were in some instances the original properties that were subdivided, or in the case of the Violet Grove subdivision, new houses such as the weatherboard villa on lot 13. This villa is advertised as having a tiled roof, 5 rooms, panelled hall, double doors (Rooms 14 x 12 ft. 6 in. (2) 14 x 12, 12 x 11, 13 x 11). A bricked front verandah, a tiled stove recess and existing sewerage connection added to its saleable potential. Water, electric light and power, and gas were all offered as part of the deal. Violet Grove now has about 35 houses, which indicates that the 19 lots of the subdivision were to be further subdivided by purchasers. [A similar plan is in the Batten & Percy Collection of the State Library of Victoria.]subdivision plans - east kew, violet farm estate, violet grove -- kew (vic.), boorool road -- kew (vic.), harp road -- kew east (vic.) -
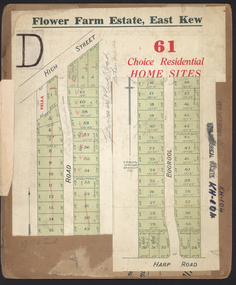 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Flower Farm Estate, East Kew, 1922
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. The subdivision called the ‘Flower Farm Estate’ in Kew East occurred in 1922. It included 61 lots on either side of Boorool Road between High Street and Harp Road. In an advertisement in The Argus in the same year, the proximity of the estate to the newly erected shops at the corner of Harp Road and High Street is noted. The Flower Farm Estate and similar subdivisions in Kew East were assisted by the extension of the High Street tramline in 1924.subdivision plans - east kew, flower farm estate, high street - kew east (vic.), boorool road -- kew east (vic.), harp road -- kew east (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Palmyra Estate, 1918
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers & McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. In 1918, Punch reported the sale of the Palmyra Estate. ‘Adjoining the Findon Estate at Kew is Palmyra, one of the most charming localities in this most desirable of all suburbs. Palmyra has frontages to Findon, Bakewell, Carson and Stevenson streets. Facing Carson street are eight blocks of 60 by 140; on Stevenson-street four of 60 by 232; and there are four of 60 by 233 on Bakewell-street.’ [Bakewell Street and Findon Street were later to be amalgamated into Findon Crescent.]subdivision plans - kew, studley park, palymyra estate, stevenson street -- kew (vic.), carson street -- kew (vic.), bakewell street (findon crescent) -- kew (vic.) -
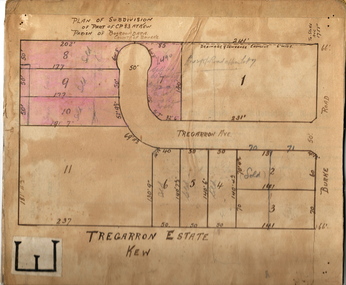 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Tregarron Estate, Kew, c.1929
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.In January 1929, the Kew City Council called for tenders to construct Tregarron Avenue. The subdivision of the Tregarron Estate in Kew was for 11 lots bordering Tregarron Avenue and its entrance from Burke Road. The plan includes annotations that indicate the measurement of each block and the placement of the drainage and sewerage easements. This plan is interesting for a number of factors. The house blocks today have different street numbers, some blocks were to be further subdivided, and at the time of the subdivision, alterations were still being made to the extent of lots offered; lots 2 and 3 on the plan were subdivided and reoriented.subdivision plans - kew, tregarron estate, tregarron avenue -- kew (vic.), burke road -- kew (vic.) -
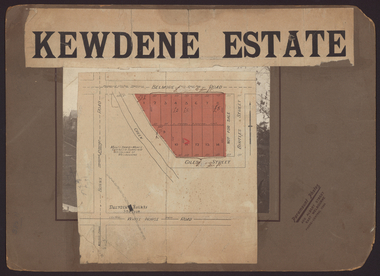 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Kewdene Estate, 1937-1939
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers & McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. The advertisement for the ‘Kewdene Estate’ subdivision is pasted over a photograph of a property for sale. This is typical of the reuse of promotional materials in the period during, and subsequent to World War I. The subdivision included 14 lots bordered by Belmore Road, Birtles Street and Giles Street. On the other side of the subdivision [Glass] Creek is noted. The subdivision plan also shows part of the Outer Circle Railway and Deepdene Railway Station.subdivision plans - east kew, kewdene estate, belmore road -- kew east (vic.), giles street -- kew east (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
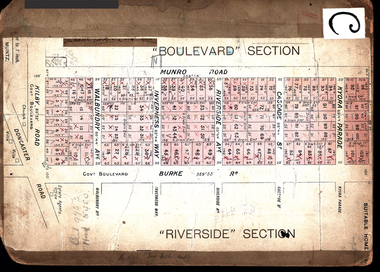
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Boulevard Estate - Boulevard Section, 1930-1936
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. This plan shows a subdivision with two sections: the ‘Boulevard Section’ and the ‘Riverside Section’. The first of these sections bordered Burke Road between Kilby Road and the farm beside the Yarra. Kilby Road, Munro Road, Burke Road and Old Burke Road bordered the 102 lots in the Boulevard Section of the plan. The streets within the Section included Walbundry Avenue, Inverness Way, Riverside Avenue, Cascade Street and Kyora Parade. These street names, at least in this subdivision plan linked the two Sections of the subdivision. At a later date, the City of Kew decided to alter the street names. Walbundry, Inverness, Riverside, Cascade and Kyora were all renamed as ‘Drives’ (e.g. Kyora Drive). The subdivision plan is of interest in that it names High Street in Kew as Doncaster Road. It also shows the location of the wooden church that was later removed to Yarraville on the corner of Kilby Road and High Street. The plan predates later developments such as the S. E. Dickens Supermarket.subdivision plans - east kew, boulevard estate, munro road -- kew east (vic.), kilby road -- kew east (vic.), burke road -- kew east (vic.), walbundry avenue -- kew east (vic.), inverness way -- kew east (vic.), riverside avenue -- kew east (vic.), cascade drive -- kew east (vic.), nyora parade -- kew east (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
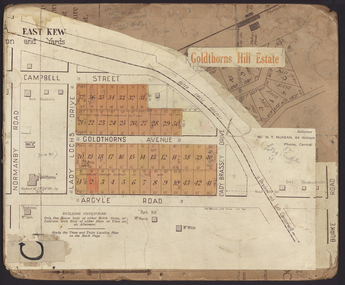
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Goldthorns Hill Estate, 1925
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. The Goldthorns Hill Estate subdivision was first put up for auction in 1925. The subdivision took its name from the mansion ‘Goldthorns’, shown on the plan between Normanby Road and Lady Loch’s Drive. Contemporary advertisements describe forty-three home sites being fro sale, yet only forty-one appear on this plan. Buyers were lured by the prospect of the proposed extension of the Burke Road tram to High Street. Discerning buyers were advised that only one house could be built per allotment, and that houses needed to be constructed of brick, stone or concrete and have a slate or tiled roof.goldthorns avenue -- kew east (vic.), lady loch drive -- kew east (vic.), argyle road -- kew east (vic.), lady brassey drive -- kew east (vic.), campbell street -- kew east (vic.), goldthorns -- kew (vic.), subdivisions -- kew east (viv.), goldthorns hill estate -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncMap - Subdivision Plan, Grenville Estate, 1922
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.In advertising the twenty-two sites of the Grenville Estate in Cotham Road and Alfred Street, Kew, the auctioneers emphasised the proximity of the development to shops, schools, and churches. That mansions surrounded the Estate was publicised as an added attraction. The plan shows how at this stage A regrettable aspect of this plan is that it is pasted over, and obscures a real estate photograph by the Kew photographer Josiah Earl Barnes.subdivision plans - kew, grenville estate, glenferrie road, alfred street, thomas street, cotham road -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Forres Estate, East Kew, 1919, 1919
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.An annotated subdivision plan for the Forres Estate, Kew East. The estate was advertised in 1919, the Melbourne Auctioneers being represented locally by Henry Kellett, Estate Agent of High Street, Kew. The name of the estate was derived from the mansion (demolished 2016) of the same name in Normanby Road, which was at one stage owned by the Mayor of Kew, Cr. J. S. Were.subdivision plans - kew, forres estate, argyle road, simpson street, hubert street, normanby road -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
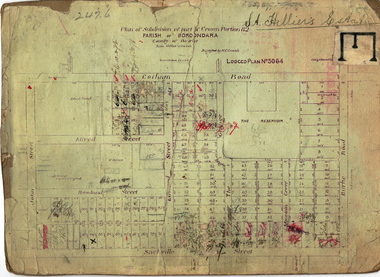
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, St Helliers Estate, Kew, circa 1910, c.1910
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.In the subdivision of part of Crown Portion 82, bordered by John and Sackville Streets and Cotham and Burke Roads, over 100 lots were offered for sale. In addition to the designated lots, a number of key locations are also identified. These include the Genazzano Convent to the north of Cotham Road, the Reservoir, St Hilary’s and the land holding of Colonel Parnell on the corner of John Street and Cotham Road. On the Plan, No. 5064, is the handwritten name ‘St. Hellier’s Estate’. St. Helliers, the home of the Dumaresq family is shown beside St. Hilary’s.subdivision plans - kew, st helliers estate -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Jas R Mathers Son & McMillan, East Kew Tramway Estate, 1915
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The East Kew Tramway Estate was a subdivision of two separate parcels of land between Adeney Avenue and Normanby Road. The larger section included 54 lots facing Adeney Avenue, Argyle Road, and Campbell, Hunter and Wishart Streets. [Hunter and Wishart Streets were created as part of the subdivision.] A further 17 allotments faced Normanby Road, Hubert and Campbell Streets. [The name of Hubert Street was later to be changed to Cecil Street.] The promotion of the sale referred to the advantages of living between two tram routes, in High Street and Cotham Road. On the plan, quaintly drawn trams mark these routes. Also on the plan is the route of part of the Outer Circle [Railway] Line.east kew tramway estate, subdivision plans - east kew -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Jas R Mathers Son & McMillan, Macartney Estate, East Kew, c. 1925
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.The Macartney Estate subdivision advertised 21 lots for sale on either side of Macartney Street (now Macartney Avenue) and Evans Road in what was then designated as East Kew. Most of the houses shown on the south side of Macartney Street then, as now, have rear entrances on Mount Street, however a number of these blocks have since been further subdivided to allow for the building of new houses on the rear of a block. Brougham Place is marked on the plan but is now called Daniell Place."C"subdivision plans - east kew, macartney estate, macartney street, mount street, evans road, brougham place -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Jas R Mathers Son & McMillan, The Dale Estate, Deepdene, 1918
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The Dale Estate in Deepdene was made possible by the death of Robert Sparrow Smythe, Australian journalist, newspaper editor/owner and theatrical manager. Smythe lived in his residence ‘Highate’, Deepdene until his death in 1917. In the subdivision proposed one year later, before the end of the First World War, 18 allotments were to be created. The very fragmentary plan in the Society’s collection notes that a large weatherboard [house] will need to be removed. This may be Smythe’s own home. The proposed subdivision included allotments facing Burke and Whitehorse Roads and Dale Street. Bordering the subdivision is the Deepdene Station and the Outer Circle Railway Line. The clear directions on the plan indicate that in 1918 it was possible to travel by train from Deepdene to East Camberwell and Ashburtonsubdivision plans - deepdene, the dale estate -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Jas R Mathers Son & McMillan, Clifton Estate, Kew, c. 1916
Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The Clifton Estate was an ambitious subdivision. It included 61 allotments bordering Cotham and Park Hill Roads, and Florence and Adeney Avenues. It is difficult to ascertain the exact year when the ‘Clifton Estate’ was surveyed, subdivided and first auctioned. The uncertainty may be due to allotments being released during the First World War. The subdivision took its name from the house ‘Clifton’ (lot 5) on the corner of Adeney Avenue and Cotham Road. The outline of Clifton (since demolished) and the extent of its land following the subdivision are represented on the plan. The auctioneers have also shown ‘Maryfield’ and ‘Wimba’, the neighbouring properties in Cotham Road, on the plan."B"subdivision plans - kew, clifton estate, cotham road, adeney avenue, florence avenue, park hill road
