Showing 272 items matching "midwifery"
-
![Australian Nursing Federation aged care campaign badge, [1990s-2000s?]](/media/collectors/5bb42dc221eaf31100db1d3b/items/5c64e94c21ea6a1300c11c26/item-media/5c64e95821ea6a1300c12f52/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationAustralian Nursing Federation aged care campaign badge, [1990s-2000s?]
Button distributed to and worn by Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) members. The ANF has been campaigning for more funding and qualified nurses to improve the quality of aged care for the past several decades, and continues to do so. Aged care campaigning became particularly prominent in the late 1990s and 2000s, with large campaigns by both the national and state/territory branches of the ANF. The Royal Australian Nursing Federation became the Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) in 1989, and then became the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation in 2013, suggesting this badge is from the 1990s or early 2000s.Circular blue, green and white plastic badge. Silver metal, plastic-coated, with safety pin fastener adhered to back. Badge printed with 'Quality Aged Care needs Qualified Nurses' and the ANF [Australian Nursing Federation] logo. 'needs' is italicised and 'Qualified Nurses' is underlined.nursing, nurses, unionism, aged care, lobbying, funding, badges, buttons, pins, staffing, trade unions, labour history, workforce, patient care, australian nursing federation, victoria -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Stopcock, Hewitt, George Barth & Co. Ltd, c. 1895
When Hewitt introduced his regulating stopcock in 1887, attempts were made to dilute the nitrous oxide with air and so obviate the element of asphyxiation. The method was to be seen in London, mainly in dentistry and minor surgery, so late as 1930. It was not very successful. To give even 10% of oxygen (which is not enough) the gas-mixture must contain 55% of air and 45% of nitrous oxide. The latter is thus so diluted by atmospheric nitrogen as to be incapable of producing anaesthesia except by asphyxiation. "Gas-air" was confined to analgesia, for example in midwifery. (Source: Penn catalogue)Brown leather facemask attached to metal inhaler and stopcock device that has been sectioned to reveal its inner workings. The various exposed channels have been painted either green, red, blue or purple.Engraved into side of stopcock: HEWITT'S / N20-02 / 1895 / G. Kaye sect. 1952. •Stamped into other side of stopcock: [indecipherable] BARTH & CO. / SOLE MAKERS / 54. POLAND STREET LONDON.W.frederic hewitt, stopcock, nitrous oxide, oxygen, gas-air -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History Collection
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History CollectionFunctional object - Two metal silver plated double toast holders
Item engraved with MCH (Margaret Coles maternity wing at the Alfred Hospital). MCH opened in 1943. "This maternity wing, which has been named after Mrs Coles, wife of Mr G. J. Coles, who gave more than £35,000 toward it." "The hospital's Margaret Coles House delivered maternity services from 1943-1984."An item that was used in MCH which is no longer in existence. Triangular with three bars of equal size with diamond shaped engraved crest 1st/ Floor/ M.C.H. / Hexagram star shaped emblem/ scroll inscribedmch, ahnl, alfred hospital, alfred hospital nurses league, melbourne hospitals, margaret coles, maternity care, obstetrics, midwifery -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph, Black & White, 'Oak Bank' later 'Whitehouse' Ann St. McKinnon c1920, c1960
'Oak Bank ' , in Ann Street McKinnon, was originally owned by Mr Robert Smith. The house was later renamed 'The Whitehouse' and was still in use as a General Hospital in the 1950's, known as the Ann Street Hospital.. This small hospital handled some Surgery, Midwifery and general Medical cases from the fast growing Bentleigh / McKinnon area. As time progressed the Hospital became too small, and was unable to meet new medical standards When Moorabbin Community Hospital opened c1974 in Centre Road East Bentleigh, the Ann St Hospital closed. The Moorabbin Hospital is now a campus of Monash Medical Centre Clayton. 'The Whitehouse' was used as a general Hospital for the residents of McKinnon, Bentleigh, and Ormond for many years during the 20thC.Colour photograph showing Mrs John Marriott ( nee Ann Smith) , her son Fred Marriott standing outside 'The Whitehouse' undated ? c1960Back ; Handwritten informationoakbank house mckinnon, whitehouse mckinnon, ann street general hospital, moorabbin community hospital, monash hospital clayton, smith robert, lees seedling growers ltd. thomas street mckinnon,mith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen, smith vic, chaff cutter, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, mckinnon, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationAustralian Nursing Federation aged care campaign badge, 2006
Button distributed to and worn by Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) members. The ANF has been campaigning for more funding and qualified nurses to improve the quality of aged care for the past several decades, and continues to do so. The 'Aged care nurses worth more not less' campaign was run throughout 2005-2006 during private aged care enterprise bargaining negotiations. Claims focused on unsafe staffing levels and an inadequate skill mix of registered and unregistered staff. The Royal Australian Nursing Federation became the Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) in 1989, and then became the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation in 2013, suggesting this badge is from the 1990s or early 2000s.Circular pink and black plastic badge. Silver metal, plastic-coated, with safety pin fastener adhered to back. Badge printed with 'Aged care WORTH MORE NOT LESS' and the ANF [Australian Nursing Federation] logo. 'NOT LESS' is underlined.nursing, nurses, unionism, aged care, lobbying, funding, badges, buttons, pins, trade unions, labour history, staffing, workforce, patient care -
 Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses League
Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses LeagueGillian Bartlett (nee Johnston), 1958, Student Midwife, Paediatric & Midwifery Notes - Royal Women's Hospital, Melbourne
bartlett, nurse, ballarat base hospital, ballarat, paediatrics, notebook, midwifery, royal women's hospital, 1958, student midwife -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Hospital window, Ernie Harris, Warrnambool builder, 1938
This window was removed from the Marcus Saltau House building in the Warrnambool and District Base Hospital when the building was demolished in 2009. Marcus Saltau House was erected in 1938 to provide for intermediate, private and midwifery patients. The builder was Ernie Harris of Warrnambool. The building commemorated the work of Marcus Saltau who was on the Warrnambool Hospital committee for over forty years and the President of that committee for thirty years. Marcus Saltau (1869-1945) was a Warrnambool produce merchant and politician involved in many Warrnambool ventures, including the establishment and development of the Warrnambool Woollen Mill and the Nestles Milk Factory at Dennington. The Jean Buick Saltau Maternity Ward at the Warrnambool Hospital was established by Marcus Saltau in 1928 in memory of his first wife. This window is retained as a memento of a significant building in Warrnambool that no longer exists.This is a circular window with four triangular panels of glass contained within a white painted ridged wood frame.marcus saltau house warrnambool, marcus saltau, ernie harris warrnambool, jean buick saltau maternity ward, warrnambool woollen mill -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Elliot-type obstetrical forceps used by Colin Noel de Garis
These forceps belonged to the late Colin Noel de Garis. Also donated was a foetal scalpel electrode applicator- see donation form. There is a note that former honorary curator Peter Renou collected the donation. Peter Renou does not recall being involved in the donation.( Source: Grainne Murphy 15 November 2010.) This design of obstetrical forceps, with a screw in the handle, was introduced by George Thomson Elliot (1827-1871), a New York obstetrician. (Source: National Museum of American History, 'Obstetrical forceps') The 'sliding pivot' on the forceps was designed to prevent the compression of the baby's head. (Source: Elliot, GT, 'Description of a new midwifery forceps : having a sliding pivot to prevent compression of the foetal head, with cases', c.1860)"The Elliot forceps and its modifications (Elliot, Tucker-McLane, Tucker-Luikart) have shorter blades and an accentuated cephalic curve that is more suitable for a rounded fetal head that has not undergone extensive molding. In addition, Elliot instruments, because of their overlapping shanks, do not distend the perineum in the same way as the separated shanks of the Simpson-type forceps." (Source: Sakornbut, EL, 'Chapter 18 - Intrapartum Procedures', in Ratcliffe SD et al (eds.), 'Family Medicine Obstetrics', 3rd ed., 2008) Obstetric forceps, Elliot's. Consists of long shanks, made of forged chrome plated metal with metal handle, four finger grips, and distinctive screw and pin at the end of the handles. This screw functioned as a means of regulating the lateral pressure of the handles when in use. obstetric delivery -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Digital image, c.1922
The photograph appeared in the MDNS Annual Report of 1922 and is taken on the veranda of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) Nurses Home at 39 Victoria Parade, Collingwood. The Sisters lived and worked out of the Nurses Home from June 1914 to 1953. They attended the disadvantaged in the inner suburbs of Melbourne. The Sisters and Matron are wearing the grey uniform and hat with a red Maltese cross is in the centre of the hatband which was introduced in 1921. These Sisters, plus two others visited 29.079 visits in the metropolitan area and in suburbs as far distant as Elwood, Glen Huntly, Deepdene, Essendon and Fairfield. Of the 1666 patients on the books 394 were midwifery patients nursed in their own homes. It is believed the Matron in the photograph is Matron Reynolds. In February 1885 it was recognized that nursing care was needed for the sick poor in inner Melbourne. The Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) was founded on the 17th of February with one Trained nurse (Nurse) who qualified under the Hospital training system, commencing on the 1st of May, and a second employed six months later, both working in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. From its inception the Society was at the forefront of health care. They provided high quality nursing care; educated their patients in the curing and prevention of disease; teaching the importance of cleanliness and good nutrition, both by verbal instruction and demonstration, even supplying soup and milk when needed. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bag containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron. The also supplied equipment, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing clean bed linen and nightdresses and clothes as necessary. In 1891 the first Nurses Home was rented for 1 year at £65 per annum at 66 Cardigan Street, Carlton; Nurses wages were now £60 per annum. A Doctor gave lectures from the Home to the public on the understanding and prevention of diseases. The Society decided to commence a Midwifery Service and Nurse Fowler, who had previously worked for the Society, was re-employed as their first trained Midwife. She began home births in August 1893 giving them Ante Natal care, taking midwifery bundles and providing clothes for the babe as needed. Following birth, she gave Post-natal care to the mother and babe twice a day for three days and then daily for a week, and longer if required. She resigned after twelve months and Nurse Wilkie was appointed to the position. As well as walking, the Nurses used Public transport in the limited areas it ran, though a taxi was used by the Nurses and Midwife in emergencies and at night. Late in 1891 the Society moved to larger rented premises at 49 Drummond Street and in 1902 moved to 188 Leicester Street, Carlton. The Nurses were becoming exhausted, particularly in the heat of summer. Permission to use bicycles was given to them in 1898 and the Society decided to purchase their own in 1903. A business man offered ‘new free wheel’ bicycles at £13 each, which included maintenance for one year. Bells and wooden frames were added at a cost of £5 per frame so the Nurses could carry extra equipment. Nurses bags were strapped to the handlebars. Soup was made for those in need 2-3 times a week, and if patients could not arrange to have it collected, the soup was delivered by the Nurses on their bicycles. Their use caused a change in uniform, with white pith helmets, and veils covering them and tied under their chins, now being used. In 1904 the Society relocated to rented premises at 5 Royal Terrace, Nicholson Street in Fitzroy. In 1913 a Nurse had her ‘board and residence, uniforms, bicycles and laundry expenses’ provided and was paid £50 a year for her first six months. At the end of a year her salary was increased by £5, and later she earned £60 a year. Over the years the Nurses complained their veils became wet in the rain and asked for a change of uniform, but this did not occur until 1921. In 1914 the Society was at last able to purchase their own premises, 'Floraston' 39 Victoria Parade in Collingwood. During the Spanish Influenza epidemic, in 1919, MDNS appealed for assistance to procure Motor vehicles so the Nurses could visit an influx of cases. Through trusts, grants and donations four 'Ford 'T Model' cars were procured which enabled the Nurses to triple their visits. It was recorded on the 21st of May, that the seven Nurses had visited 1,212 persons with influenza in the last three months, how many visits to each is not known. In the whole of 1918 the Nurses, including midwifery cases, visited 1,100 persons. It was also recorded on May 7th the Nurses were delivering 100 quarts of soup to the needy each morning. In winter they also carried wood in the cars to distribute to their destitute patients as needed. In 1921-22 many of the people nursed by the Trained nurses (Sisters) suffered from malignant and tubercular disease, often the Sister would visit to find the patient was desperately ill living in a room alone and no one there to even give them a drink. In these cases the Sister would send them to hospital, but if possible most cases were nursed in their home. During July 1921- 30 June 1922 the four Midwifery trained Sisters averaged 8 confinement cases a week and sometimes gave Post Natal care to 15 to 18 patients a day. At the time of confinement a Student from the Women's Hospital accompanied the MDNS Sister and if complications occurred the patient was transferred to the Women's Hospital. The Society often had to provide blankets, sheets, set of baby clothes and night gowns for the mother. In many instances the Society provided milk for many months. The midwifery Sisters often travelled long distances in the cars Through constant use the cars were in such a poor state they were sold in 1927 and the Sisters went back to using public transport, as well as their bicycles which continued to be used in inner areas until 1945.. The Midwives used taxis when a birth was imminent. Black and white photograph showing 9 Sisters, 5 standing at rear and Matron, in the centre, of 4 seated Sisters on a balcony wearing their Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) uniforms of grey coats, with revered collars and belt, over their partly seen grey uniforms with white collars. Five of the Sisters are wearing glasses. All are wearing grey brimmed hats with a Maltese cross in the centre of the lighter colour hatband. Part of deep metal scroll work of the veranda rail can be seen. A concrete wall is behind the Sisters.mdns, mdns matron, miss reynolds, royal district nursing service, rdns, melbourne district nursing society, mdns uniforms -
![Australian Nursing Federation aged care campaign badge, [2006-2011?]](/media/collectors/5bb42dc221eaf31100db1d3b/items/5c490ca421ea731428fc731d/item-media/5c490cb121ea731428fc84a5/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationAustralian Nursing Federation aged care campaign badge, [2006-2011?]
Button distributed to and worn by Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) members. The ANF has been campaigning for more funding and qualified nurses to improve the quality of aged care for the past several decades, and continues to do so. Aged care funding and commitment to workforce improvements were a particular focus of enterprise bargaining for the Victorian Branch around 2006-2011, and similar issues formed the basis of a large federal ANF campaign conducted around the same time entitled 'Because we care'. The Royal Australian Nursing Federation became the Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) in 1989, and then became the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation in 2013. This historical background suggests the badge is from around 2006 to 2011.Circular red, white and blue plastic badge. Silver metal, plastic-coated, with safety pin fastener adhered to back. Badge printed with 'VALUE AGED CARE NURSING PROPERLY FOR BETTER RESIDENT CARE' and the ANF [Australian Nursing Federation] website address of the time (www.anfvic.asn.au).nursing, nurses, unionism, trade unions, aged care, funding, badges, buttons, pins, labour history, staffing, wages, workforce, patient care, australian nursing federation, campaigning -
![Australian Nursing Federation campaign badge, [1990s-2000s?]](/media/collectors/5bb42dc221eaf31100db1d3b/items/5c52885721ea6c10d8c5b82e/item-media/5c52886521ea6c10d8c5d066/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationAustralian Nursing Federation campaign badge, [1990s-2000s?]
Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) badge promoting Enrolled Nurses (also known as Division 2 Nurses, ENs). ENs are registered health practitioners who have completed, at a minimum, a diploma qualification in order to practice. ENs typically work under the direction and supervision of a registered nurse to provide support and care for patients in a range of healthcare settings. This badge was possibly distributed to ANF EN members attending the 1999 Annual ANF Division 2 Conference that focused on pathways to the future for this group of nurses. The Royal Australian Nursing Federation became the Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) in 1989, and then became the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation in 2013, further suggesting this badge is from the 1990s or early 2000s.Circular green and purple badge. Silver metal, plastic-coated, with safety pin fastener adhered to back. Button printed with 'A.N.F. [Australian Nursing Federation] securing a future for Enrolled Nurses'.nursing, enrolled nurses, division 2 nurses, nurses, badges, buttons, pins, trade unions, labour history, patient care, australian nursing federation, victoria -
 Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses League
Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses LeagueGillian Bartlett (nee Johnston), Nursing Badges - Ballarat Base Hospital, Royal Women's Hospital Melbourne, Midwifery Victoria & General Nursing England & Wales
bartlett, nurse, 1954, ballarat base hospital, ballarat, badge, royal women's hospital, midwifery, england & wales, gillian johnston, victoria -
 Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - The Kerrigan Family from Mildura trained in the 1960s
The Northern District School of Nursing opened in 1950 in to address the issues around nurse recruitment, training and education that had previously been hospital based. The residential school was to provide theoretical and in-house education and practical training over three years. The students would also receive practical hands-on training in the wards of associated hospitals. The Northern District School of Nursing operated from Lister House, Rowan Street, Bendigo. It was the first independent school of nursing in Victoria and continued until it closed in 1989. The book "The First of its Kind" was published in 2015. Printed in Bendigo by "Bendigo Modern Press". Memories compiled by Peter Rosewall; who attended the last NDSN school PTS 108 between 1986 - 89.Six typed pages about the Kerrigan family from Mildura. Four of the siblings trained from 1970. Kathleen Kerrigan School 76 trained at St John of God hospital. Francis went to School 90, Michelle to school 106. James began his training in school 97. All completed general nursing. The story begins with Kathleens training, but most information is about Francis and James. James was a male nurse who completed his training at Lister House, but the males were accommodated away from the female trainees. Francis went on to do midwifery and later psychiatric nursing and Janes worked in Private Investigation. Also included are two photographs of firstly school 95, Group 2 1980 and School 96, Group 1 1980. There is information about being a male trainee nurse in a mostly female occupation.Six pages of photographs and questions and answers about nursing. nursing, student nurses, ndsn, male nurses in training, lister house -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Book, Raynalde, Thomas et al, The byrth of mankynde otherwyse named the womans booke, 1560
[26] p., cxxxi leaves, [2] l. of plates : ill ; 20 cm.non-fictionobstetrics, early works to 1800 -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationVideo recording and proceedings of 'Ethics and Legal Problems in Resuscitation' seminar, 20 March 1991, Geelong Hospital
Written proceedings and video recording of a seminar held at the Geelong Hospital on 20 March 1991. The topic of the seminar, ethics and legal problems in resuscitation, resulted in a heated debate among attendees. Several doctors took issue with a presentation by Megan-Jane Johnstone, a nurse, ethicist and academic, in regards to documenting decision-making, patients' rights and guidelines around resuscitation. Other speakers included Paul Mestitz (Physician at Geelong Hospital) and Brian Bourke (Barrister). The seminar took place from 7.45-9:45pm in the John Lindell Lecture Theatre at the Geelong Hospital. The content was donated to the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation (Victorian Branch) on a USB by Megan-Jane Johnstone, with the aim of raising awareness of how members of the medical profession debate and respond to ethical and legal concerns in healthcare. The original was given to the donor on VHS in 1991.115 minute video file (.mp4 multimedia format), transferred from VHS tape. In colour, with sound. Video shows proceedings of 'Ethics and Legal Problems in Resuscitation' seminar at The Geelong Hospital on Wednesday 20 March 1991. An image file shows a scan of the proceedings of the seminar, with handwritten notes indicating the name of those asking questions during discussion.ethics, nursing, legal, law, bioethics, medical ethics, patients rights, decision making -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Portable dental and midwifery anaesthetic machine, Commonwealth Industrial Gases Ltd, circa 1950
This gas anaesthesia machine comprises a four yolk manifold, two circular metal components for nitrous oxide and two for oxygen. It is mounted atop a four pointed stand on casters for portability. In addition to reducing valves and regulators, the main stand also supports a cream-coloured, cylindrical Austox fractional rebreather and an ether vaporiser with variable bypass control within a circular glass container. portable, anaesthesia, midwifery, dentistry, obstetrics, oxygen, nitrous oxide, commonwealth industrial gases ltd, cig, austox fractional rebreather, ether vaporiser, variable bypass control, 1950 -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationPhotograph of industrial action taken by nurses at Sunshine Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, 1993
Photograph provided by Catherine Hutchings, long-time Professional Officer at the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation (Victorian Branch). The photographer is unknown. This is one of three photographs depicting Australian Nursing Federation (Victorian Branch) members engaged in industrial action at the Sunshine Hospital in St Albans, Victoria, Australia in 1993. The dispute related to attempts by hospital management to reduce the nurses' access to ADOs (Allocated Days Off). The nurses engaged in rolling walk-outs to express their resistance, setting up out the front of the hospital with picnic rugs and chairs, food and drinks, umbrellas, and placards, to gain the awareness and support of the Victorian community. This industrial action occurred at a time when the Victorian Liberal government, led by Jeff Kennett (1992-1999), engaged in the widespread privatisation and rationalisation of many public services, including the health service. The Australian Nursing Federation, the union representing nurses in Victoria, was a strong opponent of the resulting job cuts and site closures, and engaged in various political and industrial campaigns during this time to protect and advance staffing levels, wages and working conditions.Colour photograph depicting Australian Nursing Federation (Victorian Branch) members engaged in industrial action outside the Sunshine Hospital, St Albans in the early 1990s (estimated 1993).nursing, nurses, victoria, st albans, sunshine hospital, western health, melbourne, industrial action, labour history, australian nursing federation, jeff kennett, 1990s history -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationPhotograph of industrial action taken by nurses at Sunshine Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, 1993
Photograph provided by Catherine Hutchings, long-time Professional Officer at the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation (Victorian Branch). The photographer is unknown. This is one of three photographs depicting Australian Nursing Federation (Victorian Branch) members engaged in industrial action at the Sunshine Hospital in St Albans, Victoria, Australia in 1993. The dispute related to attempts by hospital management to reduce the nurses' access to ADOs (Allocated Days Off). The nurses engaged in rolling walk-outs to express their resistance, setting up out the front of the hospital with picnic rugs and chairs, food and drinks, umbrellas, and placards, to gain the awareness and support of the Victorian community. This industrial action occurred at a time when the Victorian Liberal government, led by Jeff Kennett (1992-1999), engaged in the widespread privatisation and rationalisation of many public services, including the health service. The Australian Nursing Federation, the union representing nurses in Victoria, was a strong opponent of the resulting job cuts and site closures, and engaged in various political and industrial campaigns during this time to protect and advance staffing levels, wages and working conditions.Colour photograph depicting Australian Nursing Federation (Victorian Branch) members engaged in industrial action outside the Sunshine Hospital, St Albans in the early 1990s (estimated 1993).nursing, nurses, victoria, st albans, sunshine hospital, western health, melbourne, industrial action, labour history, australian nursing federation, jeff kennett, 1990s history -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationPhotograph of industrial action taken by nurses at Sunshine Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, 1993
Photograph provided by Catherine Hutchings, long-time Professional Officer at the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation (Victorian Branch). The photographer is unknown. This is one of three photographs depicting Australian Nursing Federation (Victorian Branch) members engaged in industrial action at the Sunshine Hospital in St Albans, Victoria, Australia in 1993. The dispute related to attempts by hospital management to reduce the nurses' access to ADOs (Allocated Days Off). The nurses engaged in rolling walk-outs to express their resistance, setting up out the front of the hospital with picnic rugs and chairs, food and drinks, umbrellas, and placards, to gain the awareness and support of the Victorian community. This industrial action occurred at a time when the Victorian Liberal government, led by Jeff Kennett (1992-1999), engaged in the widespread privatisation and rationalisation of many public services, including the health service. The Australian Nursing Federation, the union representing nurses in Victoria, was a strong opponent of the resulting job cuts and site closures, and engaged in various political and industrial campaigns during this time to protect and advance staffing levels, wages and working conditions.Colour photograph depicting Australian Nursing Federation (Victorian Branch) members engaged in industrial action outside the Sunshine Hospital, St Albans in the early 1990s (estimated 1993).nursing, nurses, victoria, st albans, sunshine hospital, western health, melbourne, industrial action, labour history, australian nursing federation, jeff kennett, 1990s history -
 The Royal Women's Hospital
The Royal Women's HospitalTool - Packaging, Faliere's Phosphatine container
Phosphatine Falieres was invented by pharmacist Émile Falières in the 1880s and marketed as a fortifying cereal or "farine" [flour] for infants, enriched with calcium. Said to be easily mixed and easily digestible, the cereal was added to an infant’s milk. It was made in Australia and distributed by a number of pharmaceutical companies, in the 1950s by Joubert & Joubert. The Phosphatine Falieres company advertised extensively, marketing to doctors, nurses, and mothers always using pictures of rosy-cheeked children. Falières created charming three-dimensional chromolithography pop-up/pop-out/moveable images many of which had a little tab. When the tab was pulled, these colourful sales props showed happy and healthy children opening a tureen of food that was fortified with Falieres cereal. The collection of Nurse Florence Green RWHA_2018_069 contains one such item of ephemera. Green was a graduate of the Women’s Hospital’s midwifery nurse training scheme in 1914. She lived at Hawthorn. The container is a cardboard cylinder with a printed label (stained) covering the entire surface. It has a metal (rusted) lid. The word "BORAX" has been written on the side. -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History Collection
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History CollectionBook - Illustrated book, Thor Heyerdahl 1914-2002 et al, The Kon-Tiki expedition: by raft across the South Seas
The story of a daring voyage by the author and five companions on board a primitive raft from the coast of Peru to the Pacific Islands. Mr. Heyerdahl was convinced that the original Polynesians had come by sea from South America, and to prove that such a voyage was possible at that remote period, he and his party built the 'Kon-Tiki', similar to the rafts then used and embarked on it. After a voyage full of danger, but packed with interest they reached the islands where the Kon-Tiki was wrecked on a coral reef.Illustrated book with dustjacket. Book is bound in front cover, with image of a Polynesian mask embossed on the front. Title, author's and publisher's names are stamped in gilt on spine. Front cover of dustjacket has a black and light brown illustration of a raft at sea, along with title and author's name printed in white. The spine has similar information plus publisher's name in light brown print along with another illustration of a raft and a Polynesian mask. The back of the dust jacket (again in black and light brown) is a route map and labeled diagram of a raft (the Kon-Tiki). non-fictionThe story of a daring voyage by the author and five companions on board a primitive raft from the coast of Peru to the Pacific Islands. Mr. Heyerdahl was convinced that the original Polynesians had come by sea from South America, and to prove that such a voyage was possible at that remote period, he and his party built the 'Kon-Tiki', similar to the rafts then used and embarked on it. After a voyage full of danger, but packed with interest they reached the islands where the Kon-Tiki was wrecked on a coral reef.thor heyerdahl, kon-tiki expedition, ethnology-polynesia, ahnl -
 J. Ward Museum Complex
J. Ward Museum ComplexBook - Medical Book, Tokology: A Book for Every Woman
Originally written in 1885 by Alice Bunker Stockham, an obstetrician and gynaecologist who practiced in the late nineteenth century. “Tokology” refers to the study of childbirth, midwifery, and obstetrics. Stockham wrote Tokology for women to give them knowledge about issues related to childbirth and maintaining their own health. Empowering women by informing them about their own bodies, the book gives women details that they may not have talked to their doctors about considering the lack of female doctors at the time of publication. Wide distribution allowed for women of a variety of socioeconomic backgrounds to have access to information that was often only accessible to those who had access to physicians and the knowledge they possessed. Tokology made progress in helping demonstrate the confidence that comes from being aware of how to maintain one’s own health instead of being subject to the fear that comes from the lack of knowledge. Tokology is more than just a book for every woman; it is an example of the power of education and distributing knowledge to a population to promote the health of a community. In some cultures, though, this book was also seen as taboo – hence the reason the illustrated plates were “hidden” within the inner back cover as is seen with this book.The book is significant is representing the thoughts and concepts surrounding female reproductive and child health in the late 19th century. Leather bound hardcover. Dark brown cover with black embossed print and borders. 386 pages. Pages show wear and ttear through use. Some pages are torn but the majority are good. Foxing on pages. Base of spine is torn away. Illustration plates in excellent condition. Publisher: Pater & Co. Melbourne 1898Inside front cover - T1 (scribbled out) T8 in blue ballpoint ink gynecology, obstetrics, mentalhealth, childbirth, reproductivehealth, womenshealth -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet - Annual Report, Ballarat and District Base Hospital, Ballarat and District Base Hospital Annual Reports (1977, 1978, 1981), 1977 - 1981
Before the training of nurses at the Ballarat College of Advanced Education (now University of Ballarat) Ballarat nurses trained at the Ballarat Base Hospital. The 1978 Annual report gives the following hospital background: 'The foundation stone for the original 42 bed hospital was laid on the existing site on 25th December, 1855. Ballarat at that time had a population of between 40,000 and 50,000 people, with the demands on the hospital services being mainly for medical care resulting from mining accidents. Medical, Nursing and General care were provided by the resident Surgeon, matron and wardsmen. Financial support depended on donations from churches masonic lodges, the public and bequests. The hospital today provides centralized health services and specialist medical, surgical and ancillart assistance to the communities in the Central Highlands Region. The trend in hospital financing today has changed and is based to a large extent on State and Commonwealth Grants. Contribution from the public remain important particulalry in the purchase of equipement and ultimately the services provided by the hospital. Since 1887 the Ballarat Base Hospital has been an important training centre for nurses. In 1978 the hospital not only caters for general nursing and midwifery training, but also provides under graduate training for medical students."3 booklets, each of about 20 pages. 1977 is light green covered, 1978 white with brown text, and 1981 mid green covered.edgar bartrop, ballarat college of advanced education, nursing, nurse, bcae, ballarat base hospital, shirley falkinder, shirley ogden, school of nursing, nurse educaiton, pathology, radiology, m stevens, winsome menedue, trained nurses league, contributers -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Federation University Courses 2022
A4 multicoloured Booklet listng the Federaton University Courses for 2022federation university, courses, business, engineering, education, pathway courses, humanities, social sciences, criminology, information technology, nursing, midwifery, paramedicine, health, performing arts, visual arts, psychology, science, sport health physical and outdoor education, higher degrees -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, glass, Post 1809
Wikpedia : James Murray (physician) Sir James Murray (1788–1871) was an Irish physician, whose research into digestion led to his discovery of the stomach aid Milk of Magnesia in 1809. He later studied in electrotherapy and led the research into the causes of cholera and other epidemics as a result of exposure to natural electricity. He was the first physician to recommend the breathing in of iodine in water vapour for respiratory diseases. Born in County Londonderry, Murray became a licentiate in midwifery having studied at the Edinburgh College of Surgeons in 1807. He undertook studies in pharmaceuticals, an area in which he became competent. In 1809 he developed the foundations of a fluid magnesia, which contained a base ingredient of magnesium sulfate. He modified it in order for it to act as an aid for "weak nerves", low fever, spasms, cholera, and diarrhoea. He named his recipe Fluid Magnesia, and set up the company Sir James Murray & Son in order to successfully market it. Murray graduated from the University of Edinburgh as a Doctor of Medicine in 1829, and became the resident physician to Henry Paget, 1st Marques of Anglesey, in 1831, a post Murray held until the 1840s. Murray was knighted in 1833 and received an honorary degree in Medicine from Dublin University the following year. He was appointed as an inspector of anatomical schools in Ireland, and was a member of the central board of health, as well as the resident physician to the Netterville Dispensary and the Anglesey Lying-In Hospital, Dublin. Murray died at his home in Dublin on 8 December 1871. Large clear green tinted glass bottle with small neck, for stopped seal, oval in section. Embossed text on two sides, concave impression in base. Seed bubbles in the glassSide 1 : 'SIR J MURRAY'S PATENT RECARBONATED FLUID MAGNESIA'. Side 2 : 'LONDON & DUBLIN'. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Document, Nurse A Watt , Cheltenham Nursing Home c1900, c1900
Nurse A. Watt was a registered Nurse who owned the Cheltenham Nursing Home, located up on the hill, at 200 Charman Road Cheltenham c1900. With Dr. Fleming Joyce, she brought many local identities into the world. Len Allnutt recalls that his brother, Ray, was born there in 1924. Nurse Watt had an excellent reputation for her care and ability in the local area. One recorded event was when in November 1910 Constable Edwards was shot by his son David, at his police house, after an episode of domestic violence involving Constable Edwards long suffering wife - the mother of David. Const. Edwards was first taken to the Police Station, but later taken by Shire ambulance to Nurse Watt's Cheltenham Nursing Home. At 8pm, Edwards was operated on by Dr. Joyce and Dr. Weigall. Despite the surgery, Edwards died the next day of haemorrhage and shock. David was convicted of manslaughter. Dr A Fleming Joyce was the Shire Medical Officer c1914 - 1930. Nurse Watt bequeathed her Estate to the Methodist Church. ( H. Stanley CMHS)c1900 Nurse A Watt had an excellent reputation for her care and ability in the Cheltenham area where Medical, Surgical and Midwifery Cases were received at her Nursing Home in Charman Road. She also accommodated convalescent cases. She worked with Dr A.Fleming Joyce and Dr Weigall.a) Advertisement / Leaflet for Nurse A.Watt c1900 b) Black & White photograph of the Cheltenham Nursing Home, 200 Charman Road Cheltenham c1900watts nurse a, joyce dr. a f., cheltenham nursing home c1910, charman road cheltenham, nursing, medicine, midwifery, victoria police force, smith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen,, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, mckinnon, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards -
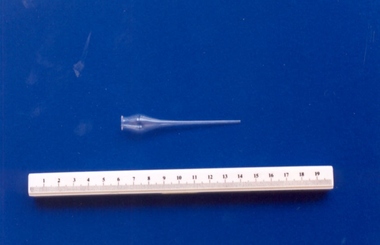 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Glass cannula associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
Used to either irrigate the eye, instill medicated drops or tasks such as wound irrigation or the evacuation of fluid under the skin. Cannulas (or eye droppers as they are commonly called) were used both in homes and hospitals during the late 1880s and the early 1900s and were commonly available at chemists. The long tapered end gave the operator control over the rate of flow of the fluid in the bulb.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920.She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Canula (or eye dropper) made of glass. Finely tapered at one end, with an open ended bulb at the other end. -
 Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses League
Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses LeaguePupil Midwife Case Book, 1972 & Midwifery Examinations, 1973_Margaret Leviston
Hard Copiespupil, midwife, case book, 1972, midwifery, examinations, 1973, leviston -
 Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses League
Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses LeagueMidwifery Students, 1943-1944
Mary Cunningham, Joyce Hovey, Margaret Neagle, Kathleen Bryant Elsie Caldecoat, Gwen Wood, Elsie Lonergon, Elizabeth Johnson Elizabeth Johnson became charge ward sister, Ward 3, Children's Ward, Eildon House, Ballarat Base Hospital.Hard Copymidwifery, students, 1943, 1944, cunningham, hovey, neagle, bryant, caldecoat, wood, lonerdon, johnson -
 Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses League
Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses LeagueMidwifery Staff, Eildon House - c. late 1930's
Hard Copymidwifery, eildon, rollo, gale, eckersley, curley, 1930's
