Showing 1567 items
matching colonial
-
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Black & White Photograph/s set of 19, Mar. 1972
Set of 19 black and white prints, all 89mm square of Bendigo trams, date machine printed on print is "Mar 1972". 981.1 - Tram 21 at North Bendigo terminus, with level crossing in background. Has destination "Golden Square" and two SEC roof ads. 981.2 - tram 2? at Eaglehawk, with destination "Depot", two SEC roof ads and "Leo A. Hughes Photographer" on side of building in background. 981.3 - tram 2? at Eaglehawk, side on view. 981.4 - tram 26 at Quarry Hill terminus looking back into city. 981.5 - tram 7 en route to North Bendigo at the site of the Bridge St. loop. Has a Peters Ice Cream truck and Sandhurst Fruit Juices truck on right side of photograph. 981.6 - tram 2 at Quarry Hill terminus. 981.7 - tram 2? at one of the loops on the Eaglehawk line, inbound? 981.8 - bogie tram at Charing Cross with fountain in background. Side on view looking south. 981.9 -trams 7 and 21 on Golden Square/North Bendigo line with bogie tram in background, at Charing Cross. Same as item 972. 981.10 - bogie tram at Charing Cross - has buildings in south west corner in background, including Colonial Mutual Life and an advertisement for the Herald newspaper. 981.11 - trams 25, 7 and two other trams at Charing Cross. 981.12 - trams 2 and 26 and three others at Charing Cross. 981.13 - tram 25 at Golden Square terminus, with Rodda's Golden Square Hotel in the background. Tram showing destination of "Nth Bendigo" 981.14 - tram 24, showing "Special" on depot access track. Has two Johnnie Walker roof ads on side. 981.15 - as above, but tram on bridge outside depot. 981.16 - trams 25 and 28 at depot 981.17 - tram 24 showing "Special" on depot access track with a single truck car in background. 981.18 - trams 2 and 26 at Charing Cross. Has advertisements for "Armstrong Tyre Service" and "Cohn's drinks" on buildings in background. 981.19 - Bendigo 2 at location?, about to enter a loop or double track section. Has hotel in background. On rear of each photo in the top left hand corner is a print number 1 to 19 in ink and location notes, generally "Bendigo"trams, tramways, charing cross, bendigo, golden square, quarry hill, tram 2, tram 21, tram 7, tram 24, tram 26 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGramophone, 1911
Until late 1925, all record players reproduced sound by purely mechanical means and relied on a so-called "amplifying" horn to efficiently couple the vibrations of the stylus and diaphragm to the space occupied by the listeners. In 1906, the Victor Talking Machine Company, Columbia's arch competitor, introduced a line of models in which the horn and other hardware were concealed within a cabinet, made to look like fine furniture rather than a mechanical device. They named the new style a "Victrola". It quickly proved to be very popular and successful. Other makers, adopting the distinctive suffix, introduced their own "-ola" internal horn machines, such as Edison's Amberolas and Columbia's Grafonolas. They were soon outselling the external horn models. At first, like nearly all other early record players, all Grafonolas were driven by a spring motor that the user had to wind up with a crank before playing a record. In 1915, Columbia began to introduce electric-motor-driven models, as a majority of urban areas had been wired to electrical grids. The electrified Grafonolas supported both alternating and direct currents from 110 to 220 volts. Electrified Grafonolas never gained the popularity enjoyed by the spring motor-driven versions due to substantially higher prices and a lack of electrical service in rural areas. Grafonolas were manufactured under the 1886 United States Letters Patent No. 341,214 which Columbia Graphophone company acquired through its predecessor American Graphophone Company. Two models were available; a portable table model and bigger stationary floor model, offering limited mobility through the application of casters. The most notable table models included Grafonola Favorite introduced in 1911 and Grafonola Savoy introduced in 1915. The most notable floor models included Grafonola Symphony Grand introduced in 1907, Grafonola Regent introduced in 1909, Columbia Mignon introduced in 1910, Grafonola Princess introduced in 1911, Columbia Colonial introduced in 1913. Various period Grafonolas were introduced in 1917 to cater to an increasingly prosperous clientele. Columbia Phonograph Company began to manufacture a series of ornate, limited edition period machines. These were highly priced (some as high as US$2,100 ) special orders that provided consumers with options to choose styles which matched their interior décor. Although the Gramophone does not have a large monetary value, it is of social significance as it demonstrates the progress made in audio reproduction from the first Edison cylinder machines to improvements that allowed ordinary people to be able to buy music discs and enjoy music in their own homes. Gramophone with internal horn, floor model, mechanically operated by a crank handle. Colombian Grafonola Princess (Type F2) brand. Gramophone is in a wooden display cabinet with room for record storage underneath and is complete with handle. Manufactured in 1911 by Columbia, USA."Columbia Grafonola Type 2 Made in USA"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, record player, gramophone, mechanical gramophone, floor model gramophone, gramophone record, columbia graphophone company, american graphophone company, columbia, grafonola, grafonola princess, music, playing music, audio reproduction, sound equipment, domestic entertainment, 1911 gramophone -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncBook, Giordano Nanni et al, Coranderrk; We will show the country, 2013
Comprises twenty-three extracts from the Minutes of Evidence of the Coranderrk Inquiry, accompanied by an analysis of the historical text and context. The book relies strongly on primary-source materials and accurately references historical analysis from scholarly and Aboriginal perspectives. This book is derived from a verbatim-theatre performance in which professional actors portrayed the witnesses who gave evidence before the 1881 Coranderrk Inquiry.; Inscriptions and Markings: illustrations, photographs, facsimiles, maps, portraits About the book One of the first sustained campaigns for justice, land rights and self-determination in colonial Australia was undertaken by the Aboriginal people of Coranderrk reserve in central Victoria. Despite having created an award-winning farm they were targeted for removal to make way for white settlement. As skilled communicators and negotiators, they lobbied the government, in alliance with their white supporters, and succeeded in triggering a Parliamentary Inquiry in 1881. Coranderrk – We Will Show The Country derives from a unique verbatim-theatre performance where professional actors brought to life the witnesses who gave evidence before the 1881 Parliamentary Coranderrk Inquiry. Rescued from dusty archives, and including renowned Wurundjeri leader, William Barak, those witnesses continue to speak to contemporary audiences. Here, their powerful petitioning can be read alongside that of their non-Aboriginal allies, and those who would move them off their land. The book features a concise and accessible history of the Coranderrk Aboriginal Station and of the events that led to the appointment of the 1881 Parliamentary Coranderrk Inquiry. The book also contains a special edition of the verbatim script which has been annotated and referenced so as to provide a blueprint of how the original minutes of evidence from the 1881 Parliamentary Coranderrk Inquiry were adapted into a theatre script. Each scene of the play has also been introduced with a short biography of each character and a discussion of the key themes raised in their testimony. Supplementing the verbatim script of the performance, the book includes a range of historical images and stills from the ILBIJERRI Theatre Company’s production. Coranderrk – We Will Show The Country celebrates the spirit of collaboration between black and white in pursuit of justice, and offers an engaging way to learn about our past – and to think about our future. Coranderrk - We Will Show The Country. (2023, October 19). Retrieved from http://www.minutesofevidence.com.au/education/coranderrk-we-will-show-the-country-book/Ex Yarra Plenty Regional Library copyaboriginal australians, coranderrk, first nations people, healesville, indigenous history, performance, play -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Sgt Tyrrell George Evans with fiancee, Mary Pitt Withers outside the Withers family home, Southernwood, Bolton Street, Eltham, c.1917
Present day Google Street View https://goo.gl/maps/PZZMoEdJYUXbgf4a8 Tyrrell George Granville Evans was born on 17th August 1892 Enlisted (No. 789) 7 July 1915 as a Private and was assigned to the 31st Battalion. Promoted to Sergeant 1 Nov 1915. Disembarked Suez 7 Feb 1916 Admitted to 32nd Stat. Hospital in France 21 July 1916 with a gunshot wound to the left arm. According to daughter-in-law, Janet Evans, on 19 July 1916, in the battle near Pozieres on the Somme, he was hit by a German high explosive shell and was unconscious and badly wounded. His left arm was shattered, and he had a bullet wound on his leg. Embarked at Boulogne on H.S. Cambria for Middlesex War Hospital, England 24 July 1916. Evans returned to Australia and was discharged medically unfit, 7 April 1917. After months in the Caulfield Hospital his arm could not be saved, and it was amputated 18 July 1917. On July 6, 1918, Tyrrell George Granville Evans married Mary Pitt Withers at Eltham, daughter of artist Walter Herbert Withers (deceased) and wife Fanny (nee Flinn). They had three children, Mary Roberta Evans born February 8, 1921, at Balwyn and twins Shirley and Joyce born June 10, 1922. Mary died 17 days later, June 27, 1922, at Balwyn. Tyrrell had to cope with three children under three years old and a missing left arm. He had been lefthanded before his war injuries. He had help from the family, especially his sister. On August 1, 1924, Tyrrell George Granville Evans married Marian Frances Wilcox and they had two children: Barbara Marian, born 27 July 1925 and Tyrrell Granville, born 3 July 1928. The children were all brought up together in Glen Iris. Tyrrell became renowned as a one-armed golfer and tennis player. He was Senior Vice-President of the Lawn Tennis Association of Victoria and was on the committee of the Metropolitan Golf Club. At the time of his retirement, he was General Manager of the Colonial Meat Company. Tyrrell died September 3, 1962 and was succeeded by sixteen grandchildren. Contributed to by Janet Evans (daughter-in-law), 27 May 2024Many items in this collection have suffered from significant water damage and black mouldjohn withers collection, eltham, tyrrell george granville evans, mary pitt withers, 1917, bolton steet, scan - 620 format 6x9 negative, southernwood -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageUniform - Tunic, 1899-1903
This original tunic or jacket is part of the full dress uniform of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery regiment. Its owner had the rank of Sergeant, as indicated by the three inverted chevrons. The Artillery design of the badges and buttons indicate the date of the tunic to be from 1893 to 1903. However the maker of the tunic, W. Moncton, began manufacture in Melbourne in 1899, so this the tunic can be dated between 1899 and 1903. The donor's grandfather was given this tunic but not the name of the original owner. It has since been suggested to the family that the tunic was worn by a local Western District Light Horse member. This could very well have been the case because mounted troops were officially referred to as the Light Horse in the late 19th to early 20th century. Several local men were involved in the Light Horse during the First World War. The donor's grandfather wore this tunic in the local district when riding a penny farthing bicycle. The donor's father also wore the tunic when dressed as a 'Captain' hosting a local disco dance. BRIEF MILITARY HISTORY- The Crimean War began In 1854 and many people in colonial Australia were afraid of a Russian attack. Volunteer forces were established to strengthen the British Imperial troops posted here. A battery of artillery was raised in Victoria as well as in other Australian states. In 1870 Australia became responsible for its own naval and military defence. The Volunteer Corps and Victorian Navy shared the responsibility of defending the existing forts, assisted by volunteer coastal and mobile field batteries. The Permanent Victorian Artillery force was established. It was disbanded in 1880 then re-formed in 1882 as the Victorian Garrison Artillery Corps. In 1895 the Geelong, Warrnambool, Port Fairy and Portland Batteries became part of the Western District Garrison Artillery. Many of the volunteers who served in the Artillery were from rural areas. They belonged to rifle clubs and were experience horsemen as well. Australia's defence at this time relied on these mounted troops, or Light Horse men. In 1899 the Victorian Garrison Artillery Corps amalgamated with the New South Wales and Queensland Permanent Artillery to become the Victorian Regiment of the Royal Australian Artillery (RAA). Then prior to Federation, the RAA and the Permanent Artillery of South Australia, Western Australia and Tasmania all combined, becoming the Royal Australian Artillery Regiment with two Batteries of Field Artillery; Battery A from Sydney and Battery B from Melbourne.This original uniform tunic of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery is significant for its association with Australia's military defence and the fortifications of our district, state and country. The tunic is also significant, representing part of the history and evolution of uniforms in the Australian military forces. The tunic is also significant in its representation of Australia's independence in forming its own defences. The tunic has local significance in its connection with local social events.Tunic or jacket, part of the full dress uniform of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery operating from 1893 to 1903. Original, single-breasted tunic of dark blue wool, red piping trim, black cotton lining in body. Sleeves lined with blue striped, white cotton. Front closure has eight brass buttons. Red band-style collar with hook-and-eye closure has gold bullion braid trim and a brass badge pinned each side at the front. Upper right sleeve has three inverted chevrons on red fabric with gold bullion braid trim (rank of Sergeant). Both sleeves have gold bullion braid 'Austrian knot' emblems stitched onto lower arm, with ends finishing on the inner sleeve. Shoulder epaulettes have red piping and smaller brass buttons. Closed back vent has vertical scalloped design with six brass buttons, in two columns of three, and red piping trim. Brass belt hook is attached to the left back waist, close to the seam (right side has a mark indicating a previous similar clip). Inside left breast is a concealed pocket. Tunic has both machine and hand stitching. All brass shank-style buttons have matching Artillery emblems with inscriptions on the back. The two brass collar badges have additional artillery emblems of exploding grenade and star as well as an inscription. Buttons were made for W. Moncton, of Melbourne and marked with his name. He traded from 1899, dating the tunic to between 1899 and 1903.Button front: Artillery emblem on front (field cannon facing left, in front of a muzzle-loading ram rod). Button back: engraved "W. MONCTON . MELBOURNE ." Collar badges: Artillery emblem (field cannon facing right | stars | exploding grenade | "AUSTRALIA")flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, uniform jacket, uniform tunic, garrison volunteer uniform, fortifications in victoria, victorian permanent artillery, pre-federation military uniform, sergeant's uniform, jacket, militia, victoria, victorian volunteer forces, victorian regiment, royal australian artillery, raa, field gun, sergeant, w. moncton, garrison, dress uniform, tunic, scarlet collar, red collar, scarlet piping, red piping, gold bullion, artillery emblem, light horse, artillery, mounted troops, victorian garrison artillery corps -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Printing Press, Harrild and Sons, 1866
This Albion printing press was manufactured by Harrild & Sons of London and exported in 1868 from London to the colonial Western Victoria town of Coleraine, population of 700 at that time. It was installed in the Colerain Albion printing office. It was used to print the first edition of the Coleraine Albion newspaper in 1868 and continued until publication ceased in 1974. The Albion Press is still being used today by a volunteer printer in the “Examiners Office” in the village at Flagstaff Hill. Amongst the items produced are printed paper bags for the Tea Rooms and posters for visitors. ALBION PRINTING PRESS The Albion press was invented and manufactured in London by Richard Whittaker Cope around 1820 and was still being produced in the 1930s. The Albion was manufactured under licence by several companies from the 1850s onwards, one of which was Harrild & Sons of Fleet Works, London. Harrild & Sons describes its business as “printing materials manufacturer”. The business was established in 1807 by Robert Harrild and named R. Harrild & Co. In 1813 he showed that rollers could be used to ink a printing plate instead of inking balls, the method in use at the time. He then established a company to make the rollers. Eventually his company would make other printing materials and equipment. Robert’s sons joined him in the 1830s, when the company was renamed Harrild & Sons, and they continued to run the company after his death in 1853 and up until the mid-1900s. COLERAINE ALBION PRINTING OFFICE The Coleraine Albion Printing Office was established by W.L. Ambler. The first issue of the Coleraine Albion was dated 4th January 1868. Arrangements had been made to receive news from Melbourne, nearby provinces, other colonies and England. The second issue on 18 January 1868 printed articles from many agencies, including the Melbourne Age and the Warrnambool Examiner. The Albion office was sold to William Hatherleigh, formerly of Portland, in October 1868. Thereafter the Albion office had many owners. The last was L. A. & E. Oliver, who took over in January 1972 and was the last to be stated as printers and publishers of the Coleraine Albion. The office was wound up in 1974. The Albion Press and other equipment was distributed to Star printing in Terang. Star Printing donated the Albion press to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village around 1980 and Stan Philp, owner of Philprint in Warrnambool, transported it to Warrnambool, brought it up to good working order and organised the supply of appropriate printer’s type. The Albion hand operated printing press is significant for producing the first newspaper in Coleraine, Western Victoria and continuing production for over 100 years. The Albion is technologically significant as a working example of a hand operated printer from the mid-19th century. The use of the printer is demonstrated by volunteers at Flagstaff Hill, printing items such as lolly and treat bays for use in the Village. The Albion is socially significant for its role in the isolated provincial colony, providing communication with the outside world, both in Australia and overseas. Newspaper printers were often amongst the first businesses of a small town. Printing press; hand operated Albion Press, Patent 2105. The machine has an upright iron frame at the back that supports the upper press that has a wooden handled metal bar is attached. The frame and legs support a thick metal flatbed. A metal leg supports the front of the press bed. The iron work is painted black with gold highlights. The decorative legs are finished with the golden feet of an animal. The frame above the metal bed includes a crown shaped finial symbol above the maker’s emblem. The maker’s details and the name of the printer are embossed on the upright frame. A plaque with the patent number is below a Lion and Unicorn emblem.Embossed maker’s emblem [A red cross - above a double ring – square inside ring – three banners below ring]. - Inside the double rings “PRINTING MATERIALS MANUFACTURE” - Inside the square, intertwined text “H & S” [representing Harrild & Sons] - Inside the three banners ““FLEET” “WORKS.” “LONDON.E.C.” Embossed across the shoulders “ALBION PRESS / HARRILD & SONS, / MAKERS LONDON.” Emblem above plaque [Lion and Unicorn] Embossed on the plaque “PATENT / 2105” Stamped into upright machine part above the printing bed “2105 / 1866” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, albion press, printing press, 1866 printing press, printing equipment, communications, coleraine albion printing office, coleraine newspaper, albion newspaper, south west victoria newspapers, harrild and sons london, richard whittaker cope, star printing terang, philprint, coleraine albion, hand operated press -
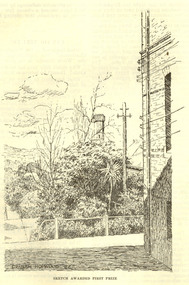 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet - Magazine, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1927
Every year the Ballarat School of Mines (S.M.B) produced a magazine, between 1898-1967. The 1927 magazine Editorial Staff- A.T Morrison, E. Van Beek, G. Dimsey, G. Inglis, L. Hillman, J. Muir, J. Johnson, N. Nicholls, B. Saunders, Dr. J. R. Pound, Mr. H. Jolly, A. Proctor, and J. Walters. Contains list of course students for 1927. Listing of School Council and staff for 1927 (inside front cover). Listing of departments, courses and fees (approximate) available at S.M.B . (inside back cover) *Articles -Mr. John Rowell regarding his receiving the Crouch Memorial Prize -S.M.B. Procession, 1927 -S.M.B. Ball July 20th at the City Hall -Letter to Editor 'The Chemists' Trip to Melbourne mentioning a tour of the Footscray Technical School; an exploration of the Mount Lyell Chemical Works; visits to the Colonial Sugar Refining Company, The Melbourne Mint, the Deer Park Explosive Works (met with former S.M.B. students, A. Perry and H. R. Kofoed), Nobel (Australasia) Ltd. -Mentions of Literary Society activities -Geelong trip by school football team July 18th to play Gordon Tech. -Extract from the 'People's Paper', July 14 regarding the S.M.B Gala Night and the election of Miss S.M.B. -Mentions of the Mica Smith Scholarship -4th Annual reunion for Past Students Association, 23rd October -Descriptive article on Port Arthur -Tour of the Mount Lyell District, with mentions of the North Lyell Mine, Port Kembla, Lake Margaret Hydro Electric Works -Paper making -A brief description of the rubber industry -Decorating for the Gala Ball -Sporting activities, 1926 and 1927 -The Junior Techs class and sporting activities. Mentions of their participation in the Procession *Prints -S.M.B. Botanical Gardens by Graham Hopwood, awarded first prize -Caricatures unknown subjects, though to be staff and students at the school *Photographs -Editorial Staff -S.M.B. Athletic Team, 1926- Winners of the Herald Shield -S.M.B. Football Team, 1927 -School of Mines Girls' Basket Ball team, 1927 -Girls' Hockey Team, Ballarat School of Mines, 1927 -Winners of the Thompson Shield, 1926. Premiers N.C.D.- J.T.S.A. (Junior Technical School Association) *Advertisements -A.N.A. Hall, Camp St. 'The Rollicking English Company- "The Rivals", presented by the School of Mines Dramatic Company. Wednesday, 14th September, 1927.Green soft covered book relating to the Ballarat School of Mines student activities for the year 1927. smb, ballarat school of mines, hockey, ballarat school of mines botanical gardens, graham hopwood, basketball, netball, a.t morrison, e. van beek, g. dimsey, g. inglis, l. hillman, j. muir, j. johnson, n. nicholls, b. saunders, dr. j. r. pound, mr. h. jolly, a. proctor, j. walters -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Cow Bell, James Barwell, 1860s-1878
This brass cow bell was recovered from the wreck of the sailing ship ‘Loch Ard’ at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria, from late 1960s to early 1970s. Cow bells were listed as part of the cargo on board the Loch Ard. This bell is now part of the John Chance collection. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s divers also recovered similar bells from the Loch Ard wreck in 1973. One of them was found in a sandy hole in the centre of the wreck site. All of the recovered cow bells are without their hangers. A bell of this size could have been used by horse or cattle teams. Cow bells were a common Colonial item. They were hung around the necks of grazing domestic cows and goats, bullock and horse teams, even camel teams so that they could be found again. Sheep and cattle drovers used them as a warning for night time disturbances such as wild animals. The maker of the cow bell, James Barwell, was a bell founder established in Birmingham, England, from 1784. In 1842 he acquired Fiddian’s firm of ‘Steam and Water’, keeping its name and stamping it on some of his products. According to his advertisement in the Exhibitors guide for the Church Congress of 1887, he made bells and fittings for churches and schools. He also made bells for cloches and chimes, and made tuned musical handbells. He repaired and reproduced bells, and he had a team of experienced ringers to “inspect towers and report upon the tone and condition of bells and fittings.” In 1903 he became incorporated as a Limited Company, ‘engineers’ and plumbers’ brasswork, and bell founders.’ In 1914 he advertised as ‘Cock and Bell Founders’, specialising in plumbing and engineering fittings, church bells, and “every description of hanging and hand bells.” Some of Barwell’s products were stamped with his maker’s mark (his initials J. B. either side of a cross entwined with a ‘B’ in an oval of oak leaves (for Birmingham)). James Barwell bells were no longer made after 1920. James Barwell was among makers who exported bells to the Australian colony from the 1860s. Early Australian iron animal bells were also made from the 1860s by blacksmiths such as Anthony Morgan from 1861, August Menneke from 1867, and Samuel Jones from 1868. Few brass bells were produced here in those times. This bell is historically significant as typical of a cow bell used by farmers and herdsmen in Colonial Victoria. Its significance is increased by being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The cow bell is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Cow bell; heavy brass, flat top, pyramid shape, rectangular head, shoulders flare out to rectangular mouth. The head has two same-sized tooled holes for adding the hanging yoke. Inscription on top and one side. Encrustations are on the metal in places. The hanger and clapper are missing. Made by James Barwell of Birmingham.Stamped on the head "BARWELL / - - - / - - -- ING" [Perhaps BARWELL - - - BIRMING. Could size be in centre? 3 3/4 IN?] Stamped on side [motif] (undecipherable) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, loch ard, mutton bird island, glenample, eva carmichael, tom pearce, james barwell, cow bell, horse bell, bell founder, bell smith, vintage bell, birmingham bell foundry, farmer, shepherd, drover, stock bell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has some diagonal creases and a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Base is uneven. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth has cork seal. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Pushed up base has pontil mark. White discolouration in a narrow line down the body. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth has cork seal. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has a line with a long bump where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth has cork seal, partly removed, with content remnants inside. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Base is uneven. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth is sealed, and has remnants of tape on outside. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below. Slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has some diagonal creases and a distinct line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. It has a bubble and diagonal crease lines. Base is uneven. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections, bubble in glass. Bottle has foul smelling contents inside. Mouth has hard capped cork seal with black, hard rubber capped stopper. Side of mouth has ship or mark. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has some diagonal creases and a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Base is uneven. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Bellows, 1862-1875
This bellows was used at the Warrnambool Racecourse by Master Farrier, Brian Chapman (1931-2017), during the 1970s but its history before then is still being investigated. The bellows have continued to be used from 1978 at Flagstaff Hill's blacksmith's workshop. Even today, in 2021, this same bellows are used by a volunteer blacksmith as he demonstrate the skills and tells of the importance of the blacksmith trade to colonial Australia. This 1860s double-action bellows is a typical form of blacksmith's or shipsmith's bellows. The end is forge-fitted with an iron nozzle or tube, called a tuyere or Tue iron, which concentrates the air to fan the fire or furnace. Tuyeres were traditionally made of cow horn. The double-action design of this bellows efficiently moves air both in and out of the chambers in the one movement of the long handle. The bellows was manufactured by John C. Onions of Birmingham, England, between 1862 and 1875. The stamp with the text, Gold Medal 1862, was also used on the business’ advertising. In 1875 the company was registered and began using the name John C. Onions Limited. JOHN C. ONIONS - John C. (Collingwood) Onions (1841-1904) was the son of a bellows maker of the same name. Onions (born 1841) and his wife Helen married in 1867 and they named one of their children John Collingwood Onions (1868-1913), as was the family tradition. He was well known as a Birmingham manufacturer of patented bellows and other forge-related equipment. He sold to the wholesale and retail markets for both local and overseas customers, including the British colonies. An 1862 advertisement points out that John C. Onions was a “Bellows manufacturer and contractor to Her Majesty’s Honourable Board of Ordinance” and His Imperial Majesty the Emperor of the French [Napoleon Bonaparte]”. The advertisement includes a sketched portrait of the Emperor Napoleon III, and an Imperial Autograph Letter dated May 23, 1854, from Napoleon, Palace of the Tulleries to Mr J C Onions of Bradford Street, Birmingham. In 1863 the company registered a patent on portable forges. In 1871 there were eight employees. John C. Onions Limited became a registered company in 1875. In 1876 an advertisements included that the company were smiths for hearths and tools in general and showed a row of six medallions including one with “Napoleon III, Emperor” and his portrait, and another “ _ _ _ 1862 MEDAL”. Their advertising motto was “For Excellence of Quality”. In 1885 the company merged with William Allday and Sons to become Allday and Onions. This mid-19th century bellows has local historical significance as it were once used by blacksmiths at the Warrnambool Racecourse in the annual racing event that continues today. This bellows is significant as a working example of equipment used in the 1800 and 1900s in the trace of blacksmiths and other metal working smiths. The bellows is technologically significant as it shows the progress from simple bellows to the double-action bellows, a time saving and efficient improvement. The manufacturer John C. Onions is historically significant as a family business that began in the 1600s and continued up until the 1980s.Bellows; large, oval, mechanical double-action smith’s bellows, manually operated, in working condition. The paddles of wood that form the top, middle sections and base of the bellows have flexible leather pieces attached firmly between them, forming airtight double lungs. Cut-outs in the panels allow the bellows to fill with air then force it out. A long handle is connected to pump the bellows and control the quantity and force of the air. The blasts of air are forced through the metal nozzle or tuyere at the end of the bellows and into the forge’s fire. Inscriptions are impressed into the wood on the upper paddle or board of the bellows. There are three circular stamps containing text. Text impressed in the wooden upper paddle of the bellows has been assumed to read “JOHN C. ONIONS, PATENTEES & MANUFACTURERS, BIRMINGHAM””?” “EXTRA” “AWARDED FOR EXCELLENCE OF QUALITY”, made from the following readable text :- “JOHN C ONIONS“ “PATENT - - - & MAN - - - - - - - - -“, “BIR - - - - HAM“, “ _ ERA - - - - “- XTRA-“, “- - - - - - - FOR EXCELL-“ “OF - - - - ITY” Text in the stamp “ - - ECE - - “, “ - - - - - / 1862 / MEDAL”, “- ITY” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, john collingwood onions, john c onions, allday and onions, bellows, smith’s bellows, 19th century bellows, double-action bellows, double-acting bellows, double lung bellows, double chamber bellows, blacksmith tools, blacksmith trade, blacksmith craft, blacksmith equipment, forging equipment, john c onions patented double-action bellows, brian chapman, warrnambool racecourse, blacksmith, shipsmith, iron smith, mechanical bellows -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Charles Withers (aka Bill) and Sgt Tyrrell George Evans at work on the Withers property, Southernwood, Bolton Street, Eltham, c.1917
Charles Meynell Pitt Withers (aka Bill) was the youngest son of artist Walter Withers and Fanny (nee Flinn). He was born at Eltham 5 February 1902. Tyrrell George Granville Evans was born on 17th August 1892 Enlisted (No. 789) 7 July 1915 as a Private and was assigned to the 31st Battalion. Promoted to Sergeant 1 Nov 1915. Disembarked Suez 7 Feb 1916 Admitted to 32nd Stat. Hospital in France 21 July 1916 with a gunshot wound to the left arm. According to daughter-in-law, Janet Evans, on 19 July 1916, in the battle near Pozieres on the Somme, he was hit by a German high explosive shell and was unconscious and badly wounded. His left arm was shattered, and he had a bullet wound on his leg. Embarked at Boulogne on H.S. Cambria for Middlesex War Hospital, England 24 July 1916. Evans returned to Australia and was discharged medically unfit, 7 April 1917. After months in the Caulfield Hospital his arm could not be saved, and it was amputated 18 July 1917. On July 6, 1918, Tyrrell George Granville Evans married Mary Pitt Withers at Eltham, daughter of artist Walter Herbert Withers (deceased) and wife Fanny (nee Flinn). They had three children, Mary Roberta Evans born February 8, 1921, at Balwyn and twins Shirley and Joyce born June 10, 1922. Mary died 17 days later, June 27, 1922, at Balwyn. Tyrrell had to cope with three children under three years old and a missing left arm. He had been lefthanded before his war injuries. He had help from the family, especially his sister. On August 1, 1924, Tyrrell George Granville Evans married Marian Frances Wilcox and they had two children: Barbara Marian, born 27 July 1925 and Tyrrell Granville, born 3 July 1928. The children were all brought up together in Glen Iris. Tyrrell became renowned as a one-armed golfer and tennis player. He was Senior Vice-President of the Lawn Tennis Association of Victoria and was on the committee of the Metropolitan Golf Club. At the time of his retirement, he was General Manager of the Colonial Meat Company. Tyrrell died September 3, 1962 and was succeeded by sixteen grandchildren. Contributed to by Janet Evans (daughter-in-law), 27 May 2024Many items in this collection have suffered from significant water damage and black mouldjohn withers collection, eltham, tyrrell george granville evans, 1917, bolton steet, scan - 620 format 6x9 negative, southernwood, charles meynell pitt withers -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Coorongite
Coorongite is a dark, rubber-like, highly resilient structureless algal deposit. In the Coorong district of South Australia it occurs in moderate quantities associated with the coastal swamps and sand dunes which extend for a considerable distance east of the mouth of the Murray. This particular specimen was recovered from the south of the Coorong River, South Australia. A type of sediment rich in organic matter, Coorongite is the unlithified end-member of the sapropelic coal series. The members of the sapropelic coal series can be ranked in order as sapropel (the unlithified form), sapropelic-lignite, and sapropelic-coal (the lithified forms) based on increasing carbon content and decreasing volatile content. Sapropel (Coorongite) is an unlithified dark, pulpy, fine organic mud containing concentrations of algae and miospores that are more or less identifiable. Coorongite is typically found as an algae like substance, that can be found in irregular size pieces. Coorongite was believed to be dried up oil due to its rubber-like texture. The Coorongite is also soft to the point where it can be cut into with a knife or it can be broken and torn by hand. Otherwise known as 'Kurangk', the Coorong River is home to the Ngarrindjeri people, which acts as both a place for gathering food and a spiritual place. In 1852 the first sight of Coorongite was found along the Coorong River. The finders mistook the Coorongite for dried up oil, which lead to the belief that there were oil reserves under the Coorong River. Between the 1860s and the 1930s the Coorong River became a place where mining oil and Coorongite became precedent. Nowadays, the local council and the South Australian Government are working together with the Ngarrindjeri people to sustain and preserve the Coorong River and the culture that is with it. Soon after gold was discovered in 1851, Victoria’s Governor La Trobe wrote to the Colonial Office in London, urging ‘the propriety of selecting and appointing as Mineral Surveyor for this Colony a gentleman possessed of the requisite qualifications and acquaintance with geological science and phenomena’. Alfred Selwyn was appointed geological surveyor in Australia in 1852 which began the Geological Survey of Victoria. Selwyn went on to collect geological samples and catalogue thousands of specimens around Australia. In 1853-69 the Geological Survey issued under Selwyn's direction sixty-one geological maps and numerous reports; they were of such high standard that a writer in the Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London bracketed the survey with that of the United States of America as the best in the world. During his years spent in Australia, Selwyn collected numerous significant geological specimens, examples of which are held in collections such as the Burke Museum.Coorongite is considered to be a mineral with a unique texture, where it can be both hard and soft. Coorongite can also be considered to be a rare mineral, as it is only located along the Coorong River and due to the mining of it, has left very few sources. It was believed at one point that Coorongite could be used to replace oil. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Three solid varyingly hand-sized pieces of wooden appearing organic matter derived from the river in the Coorong District in South Australia. A rubber-like, highly resilient structureless algal deposit.Specimen 245 page 69 / in Descriptive Register / "Elcestic Bitumen, / Coorangite" South of / Coorung River, South Australia . / C. WIllman / 15/4/21burke museum, beechwoth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineraology, coorong, coorong river, kurangk, ngarrindjeri, south australia, coorongite, coorongite specimen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Ammunition, Before 1878
The objects are a small sample of small gauge lead shot raised by Flagstaff Hill divers from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site in 1976. Companion pieces are in the Maritime Village collection. The three masted, iron hulled, LOCH ARD was wrecked against the tall limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island in the early hours of the first of June 1878. Included in her diverse and valuable cargo were 22 tons of lead shot, packed in cloth bags and wooden casks. Bulk quantities of lead shot, uniformly round balls of dull grey metal ranging from 2mm “birdshot” to 8mm “buckshot”, were routinely exported to the Australian colonies. Shot was used mostly as projectiles fired from smooth bored guns to bring down moving targets such as wild ducks and small game. It was also useful as ballast, when a dense, “pourable” weight was required to fill cavities or establish volume within a measuring container. The production of consistently round spheres of lead shot required the pouring of molten metal through a sieve and then a long drop through the atmosphere to a water filled basin for final cooling and collection. This “shot tower” process was first patented by William Watts of Bristol in 1782. His calculation of a 150 feet fall was not only to form evenly spherical droplets through surface tension, but also to provide partial cooling and solidification to each shot before they hit the water below. The value of his innovation was the minimising of indentation and shape distortion, avoiding the expense of re-smelting and re-moulding the lead. Lead shot was already being produced in Australia at the time the LOCH ARD loaded her cargo and left Gravesend on the second of March 1878. James Moir constructed a 157 feet circular stone shot tower near Hobart in 1870, with a peak annual production of 100 tons of lead shot sold in 28 pound linen bags. However colonial demand exceeded this source of local supply. The continued strength of the market for lead shot in the Colony of Victoria prompted substantial investment in additional productive capacity in Melbourne in the next decade. In 1882 Richard Hodgson erected the 160 feet round chimney-shaped Clifton Hill shot tower on Alexandra Parade (VHR H0709) and in 1889 Walter Coop built the 160 feet square tower-shaped Melbourne Central shot tower on La Trobe Street (VHR H0067). At its peak, the Coop Tower produced 6 tons of lead shot per week, or 312 tons per annum. The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. A quantity of 2mm and 4mm lead shot ammunition retrieved from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site. They are concreted together by sediment. There are (6) small pieces with some single shot and a larger conglomerate of cemented shot. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, lead shot, colonial industry, melbourne shot towers, victorian metallurgy, colonial imports -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, X-ray, left arm of C.S.M. Tyrrell George Evans, Sern. 789, 31st Battalion, AIF, 1916
No. 11 AGH X-Ray Department photo of a gun shot wound to left arm suffered July 1916 in France by C.S.M. Tyrrell George Evans, Sern. 789, 31st Battalion, AIF Tyrrell George Granville Evans was born on 17th August 1892 Enlisted (No. 789) 7 July 1915 as a Private and was assigned to the 31st Battalion. Promoted to Sergeant 1 Nov 1915. Disembarked Suez 7 Feb 1916 Admitted to 32nd Stat. Hospital in France 21 July 1916 with a gunshot wound to the left arm. According to daughter-in-law, Janet Evans, on 19 July 1916, in the battle near Pozieres on the Somme, he was hit by a German high explosive shell and was unconscious and badly wounded. His left arm was shattered, and he had a bullet wound on his leg. Embarked at Boulogne on H.S. Cambria for Middlesex War Hospital, England 24 July 1916. Evans returned to Australia and was discharged medically unfit, 7 April 1917. After months in the Caulfield Hospital his arm could not be saved, and it was amputated 18 July 1917. On July 6, 1918, Tyrrell George Granville Evans married Mary Pitt Withers at Eltham, daughter of artist Walter Herbert Withers (deceased) and wife Fanny (nee Flinn). They had three children, Mary Roberta Evans born February 8, 1921, at Balwyn and twins Shirley and Joyce born June 10, 1922. Mary died 17 days later, June 27, 1922, at Balwyn. Tyrrell had to cope with three children under three years old and a missing left arm. He had been lefthanded before his war injuries. He had help from the family, especially his sister. On August 1, 1924, Tyrrell George Granville Evans married Marian Frances Wilcox and they had two children: Barbara Marian, born 27 July 1925 and Tyrrell Granville, born 3 July 1928. The children were all brought up together in Glen Iris. Tyrrell became renowned as a one-armed golfer and tennis player. He was Senior Vice-President of the Lawn Tennis Association of Victoria and was on the committee of the Metropolitan Golf Club. At the time of his retirement, he was General Manager of the Colonial Meat Company. Tyrrell died September 3, 1962 and was succeeded by sixteen grandchildren. Contributed to by Janet Evans (daughter-in-law), 27 May 2024Many items in this collection have suffered from significant water damage and black mouldjohn withers collection, eltham, 1916, gun shot wound, tyrrell george granville evans, x-ray, mary pitt withers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Compass, c. 1839
This magnetic compass is a good size to fit easily into a person's pocket or personal luggage and is protected from knocks by its wooden case. It could have been used for reference when travelling on land or sea. There is no visible manufacturer's mark, which may mean that it was not of high monetary value. Leith is a district of Edinburgh in the country of Scotland, the U.K. It was once the Port of Edinburgh and many migrant ships departed from here bound for the Australian colony. It had a busy shipbuilding industry, with wet and dry docks. It appears from the inscription on the case "Chas Gray, LEITH, 1839" that this pocket compass once belonged to Charles M. Gray (Chas is a common abbreviation for the name Charles). The inscription coincides with the name, place and date that the Western Victorian pioneer Charles M. Gray left Scotland and arrived in Australia. Charles Gray was born in Anstruther, Scotland, in 1818. His family was connected with the Royal Marines, which may have created his nautical instruments such as this pocket compass. Charles Gray arrived in Hobson's Bay on 15 June 1839 on the ship “Midlothian”. That same ship had departed from Leith, Scotland on February 15th 1839. Did Charles Gray acquire the pocket compass in Leith, perhaps as a gift or a souvenir of his motherland? Charles Gray was an early squatter and went on to become a very successful settler as a sheep pastoralist in the Western District of what is now Victoria (originally the colony of New South Wales). He and his wife had a large property called “Nareeb Nareeb”, Green Hill Creek District (now Glenthompson), Victoria, from 1840-1886. He was also a local Councillor and Justice of the Peace, and had an interest in the local indigenous people; he named his property after their tribe. Charles returned to England in 1890 and died there in 1905. Charles Gray had written an account in 1890 of his life at Nareeb Nareeb, called Western Victoria in the Forties: "REMINISCENCES OF A PIONEER The Western District in the 1840's By Charles Gray" , a valuable historical reference to colonial Victoria. His book was published by the Hamilton Spectator in 1932. Charles Gray's photograph is one of 713 historical photographs of early Victorian settlers, created as a montage by Thomas Foster Chuck in 1872. The State Library of Victoria holds the framed montage titled “The Explorers and Early Colonists of Victoria”. To qualify for inclusion on this montage the Settlers must have arrived in Victoria before 1843. Charles Gray's photograph is number 349! The pocket compass is associated with Charles Gray, one of the early squatters and settlers in Western Victoria, possibly given to him as a parting gift on his emigration to Van Diemans land in 1839. The item is very significant as it's connection with one of Victoria's early pioneers is well provenanced by the inscriptions on the wooden case. Pocket compass, brass, set into a square wooden case with hinged lid and small hook catch. Compass is marked with 360 degrees and compass points and has two pointers; one to show magnetic north and one to set the direction of travel. Hinges are triangular and inset into the wood. The lid has an attached brass plaque with the inscription "Chas Gray, Leith, 1839" (It likely belonged to Charles Gray, Leith, UK, who migrated to Port Philip Australia in 1839 and became a successful pastoralist.) “Chas Gray / LEITH / 1839” engraved on brass plaque on lid.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, magnetic compass, pocket compass, charles m. gray, chas gray, migrrant from leith 1839, charles gray anstruther, scottland, ship midlothian 1839, squatter western victoria, settler western victoria, hobson's bay port phillip australia, charles gray nareeb nareeb - green hill creek district, western victoria in the forties: reminiscences of a pioneer by charles m. gray 1890, leith edinburgh u.k., western victoria in the forties: reminiscences of a pioneer - montage by thomas foster chuck 1872, charles gray, reminiscences of a pioneer, the western district in the 1840's, compass, scientific instrument, nautical instrument, direction, directional compass, navigation -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Ice Chest, 1927
This particular small ice chest was once part of the domestic furniture of Dr W.R. Angus and his young family in 1927 when they lived in the Nhill and Ballarat districts. The family relocated to Warrnambool in 1939 and brought the ice chest with them. An ice chest, also called an icebox or refrigerator, was invented by Thomas Moore in 1802 and had become a common home appliance from the mid-1800s until around the 1930s, when electric refrigerators became affordable and safe. The non-mechanical ice chest allowed perishable food to be kept fresh for longer than the food-safe or ‘Coolgardie’ used in colonial days in Australia. It required the use of ice blocks, which were delivered to households by the ‘iceman' and his horse and cart. The ice man would use an ice pick to cut the blocks into the right size for the buyer’s ice chest. The ice came from an ‘ice house’, a factory where the ice was made. The ice chest required a block of ice to be placed into the insulated top section on top of the corrugated iron stand. The ice would cool the air and the cool air would flow downwards through the oval hole under the stand and into the refrigerator compartment below. The water from the melted ice would drain from the sloping floor of the top compartment and into the hooded pipe. The pipe went through the refrigerator and ended below its floor, where the drained water would be collected in the metal bowl placed there for that purpose. The lip on the bowl allowed it to be easily removed and emptied at regular intervals before it overflowed. W.R. Angus Collection- The W R Angus Collection spans from 1885 to the mid-1900s and includes historical medical and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward and Thomas Ryan of Nhill, Victoria. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. He and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the part-time Port Medical Officer responsibility and was the last person appointed to that position. Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the early planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill, where they contributed to the layout of the gardens. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This ice chest is significant for representing a method of refrigeration and food preservation used in the 19th to mid-20th centuries when people were beginning to afford powered domestic refrigerators. After the second world war, most households replaced their food storage cupboards and ice chests with refrigerator appliances. The ice chest is also significant for its connection with the domestic furniture of Dr W.R. Angus and his family, and its inclusion in the W.R. Angus Collection.Ice chest; single front wooden cabinet with two doors and a flap, and three accessories. The top door is a lid with a metal handle at the front and two metal hinges along the back. The front door has two metal hinges on the right-hand side and has a metal lever catch. A hinged flap fits between the front legs at bottom of the ice chest and swings upwards. The front legs have wheels. The insulated top compartment has a metal lining and its floor slopes towards the centre of the back wall. In the floor are a formed oval air-flow hole and the open end of a pipe that has a hood partly covering it. The front compartment is an insulated metal-lined cupboard with a vertical pipe down the centre of the back wall and horizontal rails in the centre of each side wall. The accessories are a rectangular corrugated iron stand, a rectangular wire grid shelf and a round aluminium bowl with a lip and two sides pushed in. The ice chest was made circa 1927 and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr roy angus, dr ryan, doctor angus, dr angus, ice chest, ice box, antique, food preservation, refrigeration, domestic equipment, kitchen appliance, refrigerator, non-electric refrigerator, non-mechanical refrigerator, w.r. angus collection -
 Chiltern Athenaeum Trust
Chiltern Athenaeum TrustDomestic object - Spoon belonging to W.C.Busse
Wilfred Clarence Busse, born in Chiltern in 1898, His family moved to the region during the gold rush and continued to reside in the area, purchasing land adjacent the Murray River. Busse completed his secondary education at Wesley College in Melbourne then studied law at the University of Melbourne. Busse went on to become a barrister, often in the chambers of Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933) a judge of the Supreme Court of Victoria. He worked most of his life in Chiltern as a Barrister and Solicitor and gained the unofficial title of historian of Chiltern, leaving behind several manuscript histories and a scrap book. Busse was an avid fictional writer and in 1930 he published two novels. Time spent on a Victorian station in his early twenties, as well as careful documentary research, informed the writing of his historical novels of bush life. "The Blue Beyond; A Romance of the Early Days in South Eastern Australia” and "The Golden Plague: A Romance of the Early Fifties." "The Golden Plague” won the T. E. Role gold medal for the best historical novel which went on to become a best seller. Busse often drew inspiration for his novels from his younger years living Chiltern. His passion for the region lead him to write “The History of Chiltern” which was published in a serial form in the Chiltern Federal Standard from 1922-1923. Wilfred Clarence Busse was a member of Chiltern Athenaeum (where this object is now held) up until his death in 1960, he is buried in the Barnawartha Cemetery. The leaf shaped motif of this particular spoon appears to be stylised in a simple form of decorative arts and craft or even Art Nouveau style favoured in Europe between 1880-1920 and less representational than examples of Australiana flora captured in silversmithing from the 1850's onwards. According to Christine Erratt, due to the goldrush in the 1850's, there was increased wealth in the colony and an influx of immigrants from Europe to Australia who brought with them silversmithing skills which began ‘the golden age’ of Australian silver', Erratt says that 'Australia's unique flora has been portrayed in the decorative arts since the early colonial times of the last decade of the 18th century. The use of Australian flora to decorate silverware is of particular interest and diversity'. It is likely that those producing silverware at the time would be drawing on the decorative arts movement while incorporating elements of the natural beauty in the flora of their newfound environment into the silverware they produced. There are no discerning maker hallmarks to place where it was produced or ascertain the material accurately.Wilfred Clarence Busse was of social significance to Chiltern, he helped to document the cultural story of the area in his published works "The Golden Plague" and "The Beyond Blue" by recounting his own upbringing in a bush lifestyle. He was a respected Barrister and was the unofficial historian of the Chiltern Athenaeum for many years. This spoon represents a window into the domestic life of this person who was well loved in the area, and it continues its relationship to Busse as well as Chiltern by being held within the very collection he helped to maintain in his life. Domestic objects tell us the story about how people lived, objects of daily use hold particular meaning in that they can tell us the story of an individual, we feel closer to their life and habits, it humanises and connects us across time. A tarnished small silver teaspoon with leaf-shaped head and slim handlesilverware, wilfred clarence busse, busse, chiltern, chiltern athenaeum, federal standard, t. e. role, "the blue beyond, a romance of the early days in south eastern australia”, "the golden plague: a romance of the early fifties.", "the golden plague”, wesley college, university of melbourne, sir leo finn bernard cussen, supreme court of victoria, gold rush, murray river, “the history of chiltern”, silversmithing, spoon, decorative arts, floral, flora, australiana, australian flora, arts and craft movement, australian silver, cussen -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Printmaking - Silkscreen, Lin Onus, 'Walawala Garrkman' by Lin Onus, 2001
Lin ONUS (1948-1996) Language: Wiradjuri / Yorta Yorta Lin Onus played a pivotal role in the recognition of Aboriginal art as an expression of a contemporary and dynamic living culture. Prior to his premature death at just 47 years of age he was a prominent, strident, yet non-confrontational agent in renegotiating the history of colonial and Aboriginal Australia. His father, Bill Onus, was the founder of the Aboriginal Advancement League in Victoria and a prominent maker of artefacts in Melbourne. As a young Koori growing up, Lin lived in a cultural environment that included exposure to visiting Aboriginal artists, including Albert Namatjira. He began his artistic life assisting his father in decorating artifacts, went on to develop skills working with metal and painting with air brush as a panel beater; and by 1974 he was painting watercolors and photo-realist landscapes. In the 1970's he completed a set of paintings on the first Aboriginal guerrilla fighter Mosquito, which holds pride of place on the walls of the Advancement League in Melbourne, to this day. Lin Onus was a largely self-taught artist. Particularly important in his development was his visits to Garmedi (Arnhem Land) starting in 1986. Jack Wunuwun, the Yolngu artist, introduced him into the Murrungun-Djinang clan and gave him permission to use some of traditional images in his paintings. His cultural education on the Aboriginal side was also provided by visits to Cummeragunja with his father, and stories told by his uncle Aaron Briggs, known as 'the old man of the forest' who gave him his Koori name - Burrinja, meaning 'star'. They would sit on the banks of the Murray River within view of the Barmah Forest, Lin's spiritual home, the subject of many of his later paintings and his final resting place. Lin's father had been of the Yorta Yorta people from the Barmah Forest country, and Lin also used images from this area in his paintings. The images in his works include haunting photorealist portrayals of the Barmah red gum forests of his father's ancestral country, and the use of rarrk cross-hatching-based based painting style that he learned (and was given permission to use when in Arnhemland). His painting Barmah Forest won Canberra's national Aboriginal Heritage Award in 1994. (http://www.cooeeart.com.au/aboriginal_artist/lin_onus/A, accessed 18 May 2015) This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Framed limited edition silkscreen.Signed 'Onus' lower right (posthumously by Tiriki Onus) Edition 68/80art, artwork, lin onus, onus, printmaking, screenprint, aboriginal, dreaming, frogs, available -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Lindsey Arkley, The hated protector : the story of Charles Wightman Sievwright, protector of Aborigines 1839-42, 2000
"The hated Protector" tells for the first time the real story behind the extraordinary experiences of Charles Sievwright, Assistant Aboriginal Protector from 1839-42 in what was then part of the British colony of New South Wales, but is now the Western District of the Australian state of Victoria. Sievwright, an Edinburgh-born former British army officer, lived in the bush with his young family as he tried to save the Aborigines of the District from extinction. In doing so, he would isolate himself from the rest of his fellow whites. The hated Protector tells of this process. The book should appeal to anyone interested in British colonial and Australian history, particularly in the years of first contact between British settlers and the Aborigines. More broadly, it should also appeal to anyone interested a story of one man's battle against overwhelming odds, where the price of failure was numerous deaths. It is a story of hatred, prejudice, courage, determination, and hope. In telling Sievwright's story, Lindsey Arkley draws largely on original archival material, including official reports, journals and letters, found in Melbourne, Sydney, Hobart, Edinburgh and London. Most has never before been published. The archival material is supplemented by contemporary newspaper accounts, and some oral history. Full notes are given to all sources, and the book is indexed and lavishly illustrated with drawings by Joan Bognuda, as well as about 80 paintings and samples of documents. Contents: 1. In the bush 2. "Equal and indiscriminate justice" 3. "A few doses of lead" 4. "A curse to the land" 5. "The most unpopular man" 6. Retaliation 7. A hostage debate 8. Hallucinations 9. A mass escape 10. Possessors of the soil 11. Move to Keilambete 12. Bureaucratic 13. "A hideous pandemonium" 14. Divine visitations 15. Pay backs 16. Explanations 17. A squatter on trial 18. Claptrap and deceit 19. The black cap - 20. To Mt Rouse 21. "The impending evil" 22. In the balance 23. An arrest at Mt Rouse 24. A fair moral name 25. Roger's trial 16. Intensified evidence 27. A declaration of war 28. Mr Cold Morning 29. Holding ranks 30. To rags 31. Fightback 32. Return to London 33. The inquiry 34. Judgement 35. And what remains.maps, document reproductions, b&w photographs, colour photographs, b&w illustrationscharles wightman sievwright, racial policies, british colonial history, race relations, victorian history -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumEphemera - Timetable, Yarra Trams, Set of 15 Yarra Trams timetables, 7/1999 to 9/2001
Set of 15 Yarra Trams timetables, blue green cover with route number on cover, giving details of popular destination, check points, use of Metcards and contact details, tram hire, frequency, Some include maps. .1 - Route 11 - West Preston - City - July 1999 - 24 Pages .2 - Route 12 - South Melbourne and St Kilda Beach - City - July 1999 - 24 pages .3 - Route 48 and Route 34 - North Balwyn - City or via Latrobe St - East Melbourne, includes references to Routes 23, 24, 27 and 30 - July 1999 - 28 pages, includes a small map. .4 - ditto - August 2000 .5 - ditto - September 2001 .6 - Route 70 - Wattle Park - City - October 1999 - 24 pages .7 - Route 70 - Wattle Park - City via MCG - December 2000 - 24 pages - includes a map .8 - Route 75 - East Burwood - City - July 1999 - - 24 pages .9 - ditto - August 2000 .10 - Route 86 - Bundoora RMIT - Colonial Stadium via Bourke St - March 2000 - 28 page. .11 - Route 96 - St Kilda Beach - East Brunswick -March 2000 - 24 pages .12 - Route 109 - Mont Albert - Port Melbourne - July 1999 - includes references to route 23, 24, 27. 30 and 34 - 36 pages .13 - Route 109 - ditto includes La Trobe St services - September 2001 - 36 pages .14 - Route 112 - South Melbourne - St Kilda Beach to West Preston via City, including temporary combination of routes 11 and 12, route 11 and Route 12 - August 2000 - 48 pages. .15 - Route 112 - notes that it the combination of Routes 11 and 12 - September 2001 - 48 pages. .16 - Route 11 - West Preston - City - Nov. 1998 - 24 pages .17 - Route 48 - North Balwyn - City - Dec. 1998 - 24 pages .18 - Route 34 and 48 - North Balwyn - City and City LaTrobe - East Melbourne - August 2000 - 32 pages .19 - Route 109 - Port Melbourne - Mont Albert - Nov. 1998 - 24 pages.Some have notes such as "OPR", and number notes and notes written inside about changes or errors in ink. See History.trams, tramways, yarra trams, tram services, timetables, route 11, route 48, route 34, route 23, route 24, route 27, route 30, route 70, route 75, route 86, route 96, route 109, route 112 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, circa 1825
HISTORICAL INFORMATION In an article dated 26 March 1963, the Warrnambool Standard reported: “A cannon which has lain on the ocean floor since the barque, Children, was wrecked at Childer’s Cove on January 15, 1839, was raised by three Warrnambool skindivers at the week-end…The cannon, weighing about 750 lb. and 4-ft. 6-in. in length…is in excellent order considering the length of time it has remained under-water”. No conservation measures were taken at that time, other than chipping off the marine growth with hammers and cold chisels. The minutes for the 4 February 1974 meeting of the Flagstaff Hill Planning Board recorded that “a cannon recovered some time ago was lying in the garden of [one of the three original divers] and that it could be picked up at any time”. Peter Ronald, past Manager and Diver for Flagstaff Hill, notes that the CHILDREN cannon would have been recovered by the other divers around 1964. When the cannon came into care of Flagstaff Hill it was given basic conservation relevant to the time. (At the same meeting the Board was advised of the recovery of an anchor from the wreck of the CHILDREN by Flagstaff Hill divers (Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden, and Hank Howey and Andrew Coffee), and its interim relocation in the sea at the end of the Warrnambool Breakwater while awaiting conservation). The CHILDREN was owned by the pioneering Henty family of Portland. She was en route from Launceston to Adelaide, when she foundered in rough conditions at Childers Cove on 14 January 1839. The CHILDREN was a small three-masted barque, only 29 metres long and 254 tons weight, with 14 crew members and 24 passengers (including 9 children) on board. The ship was also carrying an awkwardly ballasted cargo of 1500 sheep, 8 bullocks, 7 horses, 5000 London house bricks, 6 whaling boats, and general trade goods. When the CHILDREN was driven into the limestone stack at the entrance to the cove, the seas smashed her into pieces within half an hour, and 16 lives were lost. The CHILDREN was an all-wooden ship, built in 1825 at Liverpool, and her shipwreck in 1839 is one of colonial Victoria’s earliest and most significant maritime disasters. There is little left to mark the tragedy on the seabed now, apart from some of the house bricks intended for the Henty’s Portland Bay settlement. Despite its poor condition, the CHILDREN’s signal cannon remains an important and interpretable record of her demise, (along with her anchor, the bottom half of her ship’s bell, and portions of a brass porthole - artefacts that are also in the Flagstaff Hill collection). In 2015 the CHILDREN cannon will undergo further conservation. (Conservation Management Plan for Victorian Guns and Cannon, South Western Victoria, May 2008, ref W/F/06) The shipwreck of the CHILDREN is of state significance — Victorian Heritage Register No. S116.A 1.3 metre iron 6pdr cannon recovered from the wreck of the CHILDREN. The shape of the cannon tapers from a thick round breech to a flared muzzle, with an 8 centimetre bore, and two side trunnions for pivoting on a wooden gun carriage. It was recovered from the shipwreck site of the CHILDREN by local divers in 1963. This small muzzle-loading signal cannon is in poor and unrestored condition. The cannon’s upper profile of smooth grey metal casing has corroded off, leaving an extensively oxidised rough red surface of crumbling iron. The bottom half of the cannon remains intact although the outer smooth casing also appears to be separating from the iron core of the barrel. Original grey casting is also missing from the breech and muzzle ends of the cannon. Corrosion and spalling of the upper surface layer of the cannon has removed the maker’s marks and specificationsflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, the children, ship’s cannon, signal cannon, childers cove, 1839 shipwreck, conservation of marine artefactsm, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, cannon, 6pdr small bore cannon, children cannon, defence, children, shipwreck, 1839 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFinancial record - Medical Accounts, c. 1929
The accounts records in the Medical Accounts book start in February 1929 and refer to many of Warrnambool’s local names and addresses. The ledger book belonged to Dr John Hunter Henderson who conducted his medical practice from his home and surgery at Birchwood, 214 Koroit Street, Warrnambool, from 1904-1939. This particular accounts book spans from February 1929 to May 1931. Dr Henderson retired in 1939 and moved to Melbourne. His home, medical practice and many of his surgery’s items, including the Medical Accounts Book, were transferred to Dr William Roy Angus in that same year. The patients’ addresses on page 1 of the ledger include John Lee of St Marys Road, Wangoom. John Lee’s name has two entries on this page. He Grandfather, also John Lee, was a notable pioneer of the district. JOHN LEE John Lee was born in 1884 and died in 1948. His father (1845-1892) and grandfather (1814-1887) were also named John Lee. John Lee’s Grandfather, Grandmother, Father and Uncle arrived in Australia from Ireland in 1852. The colonial family settled in St Marys Road, Wangoom, Victoria and have a long association with the district. John Lee, born in 1814, is proudly listed amongst the names on the commemorative Warrnambool Pioneers Board, having arrived in Australia In 1852. In 1855 John’s Grandfather John Lee, aged 41, was head teacher of the Tower Hill School on the south bank of Tower Hill. Two years later, in 1857, the north bank of Tower Hill was surveyed and named the township of Koroit. In November of that year John Lee continued on as head master, now at the newly built Tower Hill Lake National School Number 618, on land that is now Victoria Park Recreation Reserve, on High Street, Koroit. John died in Warrnambool in 1887 but even 50 years later an ex-student wrote a letter to The Age newspaper, recalling memories of John Lee, his head master of the 1860s at the Tower Hill Lake Common School in Koroit. DR WILLIAM ROY ANGUS Doctor Angus had previously practiced in Nhill. The accounts book and many more items of Dr Angus were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Dr Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. The Medical Accounts Book is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr John Henderson from 1904+1939 and Dr Angus until he retired, from 1923 - 1969. The Medical Accounts Book is significant as a record of the names, addresses and health of the people in Warrnambool and District in the early 20th century. The Book is significant for its early 20th century association with two local doctors, Dr John Henderson and Doctor William Roy Angus, whose practices span from 1904-1969. The Book is also significant historically for its association with the ancestors of patient John Lee, whose Grandfather is recognised on the Warrnambool pioneer Board as one of the early pioneers in Victoria, arriving in 1852. Ledger, Medical Accounts Book. Title is Bruck’s Condensed Medical Account Book. Book has hardback, green cover, bound and reinforced with red leather and printed title in gold lettering. The pages of index tabs in the beginning of the book have no entries. The first page of the accounts section of the book have the hand written heading “February 1929”. The book continues until the end of May 1931. Inside both front and back cover are hand written notes in different scrips. Both black and blue ink has been used. The book belonged to Dr John Hunter Henderson. It is part of the W.R. Angus Collection."Bruck’s Condensed Medical Account Book"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, medical treatment, medical history, medical accounts, medical administration, medical record 1929, ledger, bruck’s condensed medical account book, john hunter henderson, william roy angus, edward ryan, thomas francis ryan, john lee, tower hill school, tower hill lake national school, koroit primary school, victoria school 628, st marys wangoom, warrnambool pioneer, birchwood, 214 koroit street warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Balance Scale, 1850s
A Large Rare mid 19th Century Balance Scale (also called a Beam Scale) Made in England by W&T Avery a British manufacturer of weighing machines. The company was founded in the early 18th century and took the name W & T Avery in 1818. The undocumented origin of the company goes back to 1730 when James Ford established the business in the town of Digbeth. On Joseph Balden the then company’s owner’s death in 1813 William and Thomas Avery took over his scale making business and in 1818 renamed it W & T Avery. The business rapidly expanded and in 1885 they owned three factories: the Atlas Works in West Bromwich, the Mill Lane Works in Birmingham and the Moat Lane Works in Digbeth. In 1891 the business became a limited company with a board of directors and in 1894 the shares were quoted on the London Stock Exchange. In 1895 the company bought the legendary Soho Foundry in Smethwick, a former steam engine factory owned by James Watt & Co. In 1897 the move was complete and the steam engine business was gradually converted to pure manufacture of weighing machines. The turn of the century was marked by managing director William Hipkins who was determined to broadening the renown of the Avery brand and transforming the business into a specialist manufacture of weighing machines. By 1914 the company occupied an area of 32,000m² and had some 3000 employees. In the inter-war period the growth continued with the addition of specialized shops for cast parts, enamel paints and weighbridge assembly and the product range diversified into counting machines, testing machines, automatic packing machines and petrol pumps. During the second world war the company also produced various types of heavy guns. At that time the site underwent severe damage from parachute mines and incendiary bombs.Then from 1931 to 1973 the company occupied the 18th-century Middlesex Sessions House in Clerkenwell as its headquarters. Changes in weighing machine technology after World War II led to the closure of the foundry, the introduction of electronic weighing with the simultaneous gradual disappearance of purely mechanical devices. The continued expansion was partly achieved through a series of acquisitions of other companies. After almost a century of national and international expansion the company was taken over by GEC in 1979. Keith Hodgkinson, managing director at the time, completed the turn-around from mechanical to electronic weighing with a complete overhaul of the product range of retail scales and industrial platform scales. In 1993 GEC took over the Dutch-based company Berkel and the Avery-Berkel name was introduced. In 2000 the business was in turn acquired by the US-American company Weigh-Tronix, who already owned Salter, and is today operating as Avery Weigh-Tronix. Item made and used possibly around the 1850s by Victorian colonial government to check weights of goods being sold by early shop keepers on the gold fields item is very rare.James McEwan & Co were the retailers of W & T Avery scales in Victoria from 1852. A very rare item used probably to check weights used by merchants during colonial times by government inspectors in Victoria. A similar example exist in a NSW museum, the item is believed to have been made before W & T Avery expansion to the Soho foundry in Birmingham in 1885 and after 1818.Beam balance scale suspended from a wooden tripod, with metal trays suspended by three chain lengths. embossed on the balance beam W T Avery, Birmingham,flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, scale, avery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Stevenson Screen, Thomas Stevenson, ca. 1910
Stevenson screens were first introduced in Australia in the 1880s and were widely installed by 1910. The screens have been used to shelter and protect thermometers and other meteorological instruments from rain and direct heat while the holes and double-louvre walls allowed air to flow around them. Sometimes other meteorological instruments were included in the weather stations, so there were different Stevenson Screen sizes. This authentic, original Stevenson screen was previously owned by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology and was used for many years for weather readings at the Cape Otway Light Station in southwest Victoria. The Lighthouse Keepers recorded the readings for minimum and maximum temperatures at 9 a.m. every day from January 1865 until April 1994. The equipment was sheltered in a Stevenson Screen from 1902 until April 15 1994, when the mercury thermometer was replaced by a platinum resistance probe within an Automatic Weather Station (AWS). This Stevenson screen is one of the two screens that then became redundant. The other Stevenson screen was kept to display to visitors. Lightkeepers were no longer required at the Cape Otway Light station either, due to the automated system. The meteorological instruments donated with the screen were used for measuring temperature and humidity. They are mounted on a metal bracket that fits across the screw holes on the screen’s internal frame. The glass-covered Relative Humidity (RH) sensor was made by the renowned precision instrument maker, Rotronic AG of Switzerland, which was founded in 1965. The firm made its first electronic temperature and humidity instrument in 1967. Meteorological records have been collected in Australia from the 1800s. The records were collated, published and used as a basis for weather forecasts. Many sectors, such as maritime and agriculture industries, have relied on these figures for making important decisions. The quality and placement of the meteorological instruments used to measure temperature and humidity are of utmost importance for accuracy. In early colonial times, there were no national standards for meteorological instruments that would allow for accurate figures and comparisons. Once the Bureau of Meteorology was established (around 1908 to 1910) the department installed Stevenson screens throughout Australia, many at lighthouses and light stations, and the measuring instruments were standardised. The Stevenson Screen was named after its inventor, Scottish Civil Engineer Thomas Stevenson (1818-1887) who was also the father of Robert Louis Stevenson, author. Stevenson developed the small thermometer screen around 1867. It had double-louvred walls around the sides and a top of two asbestos sheets with an air space between them and was thickly painted with a white coating that reflected the sun’s rays. This design was modified in 1884 by Edward Mawley of the Royal Meteorological Society. Standards were set for the locations of the screens and instruments, including their distance above ground level and the direction the door faced.Stevenson screens played a significant part in providing a standardised shelter for all meteorological instruments used by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology from about 1910 until 1994. The readings from the instruments gave the meteorological statistics on which weather forecasts throughout Australia were based. This Stevenson screen was used locally at Cape Otway, along the Great Ocean Road in southwest Victoria, so contributed towards our local forecasts and weather warnings.Stevenson screen, original, from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology’s weather station at the Cape Otway Lighthouse. The screen is a white wooden cupboard with a slanted cover raised above the top. The top has ten drilled ventilation holes, and the sides and door are made of downward-slanting double louvres. Two brass hinges join the door to the lower edge of the screen and a metal fitting at the top edge allows for a padlock closure. The screen is supported on four short legs, each with a hole drilled from side to side for fitting to a frame. Inside the screen are two wooden frames fitted with hooks and screws. The floor has three boards; one across the back and one across the front at the same level, and a board wider than the space between these boards is fitted higher, overlapping them slightly. Inside the screen, a pair of electronic instruments with short electric cables is mounted on a metal bracket with drilled holes in it. One of the instruments is a Relative Humidity (RH) probe. It is 26 cm long and is a glass tube with a filter on one end and an electrical connection on the other. It has inscriptions on its label, showing that was made by Rotronic AG, Switzerland. The other instrument is a Resistance Temperature Device (RTD) thermometer. It is 22.5 cm long and has a narrow metal probe joined to a hexagonal metal fitting. A brass plate on the front of the screen has impressed inscriptions. The screen is Serial Number 01/C0032, Catalogue Number 235862.Stamped into brass plate "CAT. NO. / 253862 / SERIAL NO. 01/C0032" On instrument’s electrical fitting; “CD2” [within oval ‘+’ above S] “Serie693 op65 / 220/380V~16A” On instrument’s glass; “rotronic ag” “SWISS MADE” “CE / CH-8303 / Bassersdorf” Symbol for [BARCODE] “ART NO MP 101A_T4-W4W” “POWER 4.8.30VDC“ “OP. RANGE: 0-100%RH/-40+60° C” “OUT H 0-100% 0-1V” “OUT T -40+60°C -0.4..+0.6V” “SERIE NO 19522 009”flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, cotton region shelter, instrument shelter, thermometer shelter, thermoscreen, thermometer screen, measuring instruments, meteorological instrument, weather recording, weather station, lighthouse equipment, light station equipment, stevenson screen, marine instruments, mercury thermometer, platinum resistance probe, aws, automatic weather station, rotronic ag, swiss made, meteorological device, weather forecast, weather prediction, weather records, meteorological forecast, meteorological record, australian bureau of meteorology, bureau of meteorology, bureau, bom, relative humidity, rh, relative humidity probe, resistance temperature device, rtd, thermometer, temperature, humidity, cape otway, cape otway lighthouse, cape otway light station, rotronic, switzerland, swiss instrument, thomas stevenson, double-louvered walls, edward mawley, royal meteorological society, 01/c0032, serial number, cat. no. 235862, serial no. 01/c00323
