Showing 1738 items
matching region
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mr and Mrs Don Hayes, 20th May 2000
In this interview we hear from Don and Bobbie Hayes who met and were married in Beechworth. Mrs Hayes was born in Beechworth to a blacksmith and a teacher who had moved to the area not long before she was born in 1925. She discusses her family and the struggle her mother had being a city woman relocated to the bush and into a family who didn't accept her for her Methodist religious beliefs as they were a staunch Catholic family. After working in the Tannery when they first moved to Beechworth from Melbourne, Don got a job in the 1950's at the Beechworth Mental hospital known as Mayday Hills (est. 1862) and continued working there for the next thirty six years. Starting as a nurse Don would be one of three or four staff known then as attendants, who would oversee up to forty patients in a ward taking them out to work the land and gardens or chop wood on the grounds. Mrs Hayes also worked in the Hospital and discusses the need at the time to be earning to pay for large medical bills that came from two of their children, one having a congenital heart problem which was not covered by hospital benefits and the other displaced hips that required surgery. By the end of his time working at the hospital, Don was in charge of the patient training centre where those destined for discharge would be trained on how to cope in the world outside of the hospital grounds they were so used to. Both talk openly and with heartfelt candour, recalling their years spent among the patients of the hospital community, their sense of humour and compassion are evident and although the times and the jobs were definitely hard and the wages low, this couple cared deeply about the people they worked with and sit among those people from the local area who established Beechworth as a significant social welfare region. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.The significance of this oral history lies in the firsthand accounts from two people who were directly involved in the significant nursing work undertaken at Mayday Hills Mental hospital from the 1950's. Hearing the stories from those who were there and had lived experience, adds depth and we gain valuable insight into how and what the asylum was like for those who worked there and colourful details about the kinds of patients they encountered too, it adds human and personal context to what could otherwise become statistic and abstract information about a historic site. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, mayday hills hospital, may day hills, beechworth mental asylum, mental hospital, asylum, nursing, hospital, patient training centre, patients, social welfare -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
Taken some time between 1914-18, the photograph depicts an aerial view of Villers-Bretonneux in France, a region which was part of the Western Front during World War I. The image mostly shows rural landscape. The Western Front was the main theatre of war during World War I. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The German advance was halted with the Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both the French-British and German armies dug in along a meandering line of fortified trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France. The First Battle of Villers-Bretonneux occurred between 30 March - 5 April 1918. It took place during Operation Michael, part of the German Spring Offensive on the Western Front. The offensive began against the British Fifth Army and the Third Army on the Somme, and pushed back the British and French reinforcements on the north side of the Somme. The capture of Villers-Bretonneux, close to Amiens, a strategically important road and rail-junction, would have brought the Germans within artillery-range. In late March, troops from the Australian Imperial Force were brought south from Belgium as reinforcements to help shore up the line. In early April, the Germans launched an attack to capture Villers-Bretonneux. After a determined defence by British and Australian troops, the attackers were close to success until a counter-attack by the 9th Australian Infantry Brigade and British troops late in the afternoon of 4 April restored the situation and halted the German advance on Amiens. The Second Battle of Villers-Bretonneux occurred between 24 - 27 April 1918, during the German Spring Offensive to the east of Amiens. It is notable for being the first occasion on which tanks fought against each other. A counter-attack by two Australian brigades and a British brigade during the night of 24 April partly surrounded Villers-Bretonneux, and on 25 April, the town was recaptured. On 26 April, the role of the Moroccan division of the French army was crucial in pushing back German units. Australian, British and French troops nearly restored the original front line by 27 April.The record is historically significant due to its connection to World War I. This conflict is integral to Australian culture as it was the single greatest loss of life and the greatest repatriation of casualties in the country's history. Australia’s involvement in the First World War began when the Australian government established the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) in August 1914. Immediately, men were recruited to serve the British Empire in the Middle East and on the Western Front. Additionally, the record's significance is enhanced by its depiction of Villers-Bretonneux. The battles that occurred in this town during World War I are especially historically significant to Australia as this is where the Australian Imperial Force had one their greatest World War I victories. An Australian flag still flies over Villers-Bretonneux in the present. Furthermore, a plaque outside the Villers-Bretonneux Town Hall recounts the battles fought to save the town in 1918. Kangaroos feature over the entrance to the Town Hall, and the main street is named Rue de Melbourne. More officially, recognition of the significance of the battle in Villers-Bretonneux is found at the Australian National Memorial, which was built just outside the town. It commemorates all Australians who fought in France and Belgium and includes the names of 10,772 who died in France and have no known grave. Each year, a small ceremony is held at the memorial to mark the sacrifice made by the soldiers. Lastly, the record has strong research potential. This is due to the ongoing public and scholarly interest in war, history, and especially the ANZAC legend, which is commemorated annually on 25 April, known as ANZAC Day.Sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper.Obverse: yAE.2.35. / 125 / 62d.2834.35.36.VA.5. / 12.G.18-11 / F.-(?)" /military album, wwi, world war i, villers-bretonneux, australian imperial force, aif, france, war, army, conflict, germany, 1918, battle -
 City of Greater Geelong
City of Greater GeelongAcrylic on Canvas, Big Day Out, 2010-2011
Rohan Robinson is an artist born in Geelong, and attended “the Mill” part of Deakin University in 1980-82, studying Fine Art. In 2010-11, he was the manager of Kayili Artists Aboriginal Corporation, at Patjarr in the Gibson Desert W.A., where he oversaw the development and marketing of artworks of the corporation’s members. The community is the remotest in Australia and averaged 25 people, mostly consisting of elderly people and part of the Ngaanyatjarra region, with some members not having any consistent contact with white fellas up to the mid 1960’s. During his time it was common for all the community members to go out hunting and having a visit to important areas, where members would get some tucker of rabbits and lizards and honey ants and perhaps some “meow meow” and have a nice sleep in the shade on the warm sand. Robinson would often take his painting gear along and do some work on unstretched linen on the desert ground, he would paint for a while and then perhaps lie around with the elders or follow one of the expert hunters and observe from a distance [several meters] the skills of elderly women casually walking through some recently burned spinifex knocking cowering bunnies on the head with a steel rod. It was on one of these occasions, when this particular painting was being conceived, that after returning from the hunting mission, he was informed by some of the mob, that an elder had been spending time looking at this work in it’s infantile stage...”You know the old fella over there, he been looking at that painting of yours” It was later in the day, when returning to Patjarr, that the elder Arthur Robertson approached Robinson, and demanded/asked that Robinson paint his stories for him. Mr Robertson was suffering from Parkinson’s disease, and was having trouble painting, but had been doing some brilliant work with Posca markers. It was with a certain reluctance that Robinson agreed, as he felt this to be a “political hot potato in some quarters” but also respected a relationship between artists beyond the cultural divide. Mr Robertson demanded that they start immediately and armed with pencil and paper they created the notes for several paintings under Mr Robertson’s direction. The painting that you are viewing is signifcant in that it was the catalyst for this relationship between the two artists. Mr Arthur Robertson died later that year 2011.Gold framed blue and earth tone painting. Painting depicting four circles with mountain and sky in the background. -
 Melton City Libraries
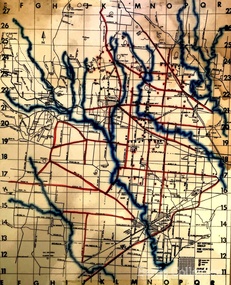
Melton City LibrariesMap, Mount Cottrell Fire group, Unknown
"In 1966, the Mount Cottrell Fire Brigades Group was formed as a way of consolidating the smaller groups around Melton, Rockbank, Toolern Vale, Sydenham, Truganina and Werribee. Its headquarters were established at the home of Ernest ‘Bon’ and Edna Barrie in Ferris Road, Melton. Captain Bon Barrie was a member of the Melton Fire Brigade and elected group and communications officer of the new Mount Cottrell Brigades Group". Fire Brigade Meeting 14th September held at Rockbank Formation a new Group in Region 14 Present: R/O H Rothsay, Assistant R/O R Orchard Tru? G Summerton Purpose of Group The pooling of the equipment in the area should be co-ordinated under one leader. The Brigade and private equipment should be co-ordinated under one leader. Formation was carried unanimously. To be called Mt Cotterill Group. Rockbank nominated Captain E W Barrie elected, Secretary K Watt Toolern Vale. Names listed C/O K L McNaughton Anakie Group COO/O R B Chirnside Lieut J Richmond Capt E Gillespie Toolern Vale Eddie L/ T S Atkin Stan L/T B Storey Bert Sec K Watt Keith Capt E W Barrie Melton Bon L/T K Gillespie Keith A Gillespie Arthur L/T G Lunson George L/T J Robinson Jeff Capt A Marquand Truganina Alan L/T I Cowie Ian Sec T Gard Tom Capt G Harrison Rockbank a/ps G Harrison N Harrison N Fisher a/ps S Hirt Melton Steve Pres M Chomley Sydenham Capt S Hughes Stan Capt L Waterson Werribee Lex Res/o J Hanson G/O S Cooper Bacchus Marsh Syd P/GO W Lidgett Wal Pro/O D Dunton G/O T Healy R C [Mt Macedon] Tom Reg Sec G Douglas Hand written notes of Edna Barrie Typed by Wendy Barrie Maps of the Mt Cottrell Fire groupemergency services, maps -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Peter K Austin, Endangered languages : beliefs and ideologies in language documentation and revitalisation, 2014
1.Introduction /? Julia Sallabank pt. 1 Case Studies: Beliefs and Ideologies in Endangered Language Communities 2.Paradoxes of Engagement with Irish Language Community Management, Practice, and Ideology /? Tadhg O. Hifearnain 3.Fluidity in Language Beliefs: The Beliefs of the Kormakiti Maronite Arabic Speakers of Cyprus towards their Language /? Chryso Hadjidemetriou 4.Reflections on the Promotion of an Endangered Language: The Case of Ladin Women in the Dolomites (Italy) /? Olimpia Rasom 5.Minority Language Use in Kven Communities: Language Shift or Revitalization? /? Anna-Kaisa Raisanen 6.Going, Going, Gone? The Ideologies and Politics of Gamilaraay-Yuwaalaraay Endangerment and Revitalization /? Peter K. Austin 7.Language Shift in an `Importing Culture': The Cultural Logic of the Arapesh Roads /? Lise M. Dobrin pt. 2 Language Documentation and Revitalization: What and Why? Contents note continued: 8.Ideologies, Beliefs, and Revitalization of Guernesiais (Guernsey) /? Julia Sallabank 9.Local Language Ideologies and Their Implications for Language Revitalization among the Sumu-Mayangna Indians of Nicaragua's Multilingual Caribbean Coast Region /? Eloy Frank Gomez 10.Must "We Save the Language? Children's Discourse on Language and Community in Provencal and Scottish Language Revitalization Movements /? James Costa 11.Revitalizing the Maori Language? /? Jeanette King 12.What Are We Trying to Preserve? Diversity, Change, and Ideology at the Edge of the Cameroonian Grassfields /? Jeff Good 13.The Cost of Language Mobilization: Wangkatha Language Ideologies and Native Title /? Jessica Boynton 14.Finding the Languages We Go Looking For /? Tonya N. Stebbins 15.Meeting Point: Parameters for the Study of Revival Languages /? Christina Eira pt. 3 From Local to International: Interdisciplinary and International Views Contents note continued: 16.Conflicting Goals, Ideologies, and Beliefs in the Field /? Simone S. Whitecloud 17.Whose Ideology, Where, and When? Rama (Nicaragua) and Francoprovencal (France) Experiences /? Michel Bert 18.UN Discourse on Linguistic Diversity and Multilingual ism in the 2000s: Actor Analysis, Ideological Foundations, and Instrumental Functions /? Anahit Minasyan 19.Language Beliefs and the Management of Endangered Languages /? Bernard Spolsky.maps, b&w photographs, tables, graphsendangered languages, language revival, education, language research -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Ian and Wendy with Grandma Barrie, c.1943
Jessie May born on 30th November 1883, Jessie, known as Ma Barrie to her grandchildren, was the daughter of schoolteacher, Thomas John Lang and Mary Elizabeth Coates. In 1896 Thomas and Mary Elizabeth moved to Melton. Mr Lang’s previous school was Coliban SS No 1920. Mr Lang was the Head Teacher at Melton until 1917. In 1910 he was a Committee Member Melton Mechanics Institute and Public Library at its establishment. He was a Life Member of the Melton Mechanics Institute Jessie lived in various locations around Central Victoria, particularly Pastoria and Melton. When her father was Head Teacher at Melton State School no 430, she met her future husband, Charles Ernest Barrie. The couple were married at the Methodist Church Melton on the 23rd August in 1906. They lived in the newly built house beside the Chaff Mill on the corner of Station and Brooklyn Road Melton South. Their eldest child was Mary Ena was born on the 7th of October 1907. IN 1909, Ernest Wesley (Bonnie) was born 29th April (Ascot Vale). In 1910 the family moved to a farm in Trundle NSW. The Chaff Mill was sold to Glover Onians – HSK Ward. Later the original mill was burnt and replaced, and in 1977 a fire destroyed it again and it was not rebuilt. In 1911, the family returned to Melton buying the “Darlingsford” farm in May. The weather was too at Trundle for Jessie. Their address was Elizabeth Street Moonee Ponds. William Cecil was born on the 23rd of February 1912 and Charles Edgar was born on 1st June 1913. In 1916 they lived in Moonee Ponds where the children attend Bank Street School, Ascot Vale. The children developed diphtheria Mary and Bon were transferred to Fairfield Hospital. March 1919 the family returned to live at Melton at the time of the outbreak of the Spanish influenza. Mary, Bon, and Edgar returned to Melton School. Following the death of CEB in a car accident in 1931 she was left to bring up her children on her own; the youngest Jim, aged 9 and eldest Mary, aged 24. Jessie left ‘Darlingsford’ in 1946 when her sons had safely returned from WW II. She stayed at Yarram for a time where her married twin daughters lived when more grandchildren were born and spent the remainder of her life living with various family members. SUMMARY - Dr Ian Robinson OAM Born 26th June 1931 Parents – Keith John Robinson of “Creighton” Melton Mary nee Barrie of “Darlingsford” Melton The family lived at “Heatherdale” Toolern Vale. Their 3 children, Ian the first followed by daughters, Ena May and Mary Elizabeth (Beth) Ian and Ena attended Toolern Vale State School. No 946 The family later moved to Columban Ave Strathmore. During 1942 the children stayed their grandmother’s house at “Darlingsford” Melton. They enrolled at Melton State School No 430 on the 13/3/42 after attending State School No 483 Raleigh Street Essendon. They left Melton School on the 31/7/42 returning to Essendon. Ian attended Geelong College as a boarder after completing his schooling he entered University to study Medicine. His early General Practice was in Melbourne. In 1972 he joined the Royal Flying Doctor at Mount Isa, North West Region of Queensland. The region covered an area larger than the British Isles. He was on call 24 hours for emergencies. He spent three weeks away with calls and in the fourth week attended Aboriginal Reserves. Ian took two Queensland Governors and their wives to spend three nights at the Clinic. Sir Colin and Lady Hannah are still their friends. Area Co-ordinator Ian was awarded the Royal Humane Society Medal along with his pilot when they risked their lives landing on flooded land to save a patient. Ian remained a loyal contributor to the Royal Flying Doctor Service until 1997 He met Queen Elizabeth 2nd in Cairns, and also met Prince Phillip and Prince Andrew in Brisbane. Townsville – Locum Beenleigh – General Practice Open 7 Days 198? -2002 Aspects of his work covered the following – Police Work State Commonwealth Medical Officer TEYS COMPANY Q FEVER. Q Fever presents with flu like symptoms. The 1st Test always came back Negative BUT 2nd Test always positive. Ian lectured other Medicos re Q Fever Council Immunization in schools Covered boxing bouts Large Practice In 2002 Ian retired but continued house calls for older patients. Information from Anne to Beth received by Wendy October 2013 Wendy Elizabeth Barrie Jessie May Lang [Barrie] and Ian Keith Robinson standing in front of a carlocal identities -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Chiltern Pharmacy, now called Dow's Pharmacy, opened in 1859 at a time when the township of Chiltern was experiencing a second-wave gold rush that redistributed the balance of commercial and social activity in the region. David McEwan, father of Prime Minister John McEwan, was one of the first pharmacists practicing at the business. It was purchased in 1929 by pharmacist Hilda Dow who ran the business with her apprentice and husband, Roy Dow, until they closed the business in 1968. In 1988, after founding the North East branch of the National Trust, the Dows donated the premises with its entire fittings and stock. Some of the more than 4,000 items in stock at the time of closure in 1968 were present in the shop when the Dows took charge in 1929 and date to the late Nineteenth Century (around the time this image was taken). Hilda Dow (nee Grey) was born in 1897, the daughter of a police magistrate. She enrolled to study at the Victorian College of Pharmacy in 1919 and worked initially for Poynton's Pharmacy in Morwell before purchasing the Chiltern Pharmacy that was later named after her. She was a member of the Pharmaceutical Society of Victoria, a hospital committee and Board, the Red Cross and the Infant Welfare Association and held office for the Chiltern branch of the Country Women's Association. Her sister Helene Grey received an OBE for her work as Lady Superintendent of the Royal Melbourne Hospital. Although Hilda Dow was not Australia's first female pharmacist (this was Caroline Copp in 1880) the preservation of the pharmacy and the stories it presents sheds light on the general issue of recognition for female medical pioneers in Australia. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This image is significant as it provides insight into social and commercial infrastructure available in the North-East region of Victoria in the late Nineteenth and early Twentieth Centuries. The business pictured is also associated with a Prime Minister of Victoria and some of Victoria's first female medical and pharmaceutical practitioners. Thin translucent sheet of glass with a circular image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metals strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, hilda dow, roy dow, chiltern pharmacy, dow's pharmacy, chiltern, indigo shire, north east victoria, history of pharmacies, women in pharmacy, women in medicine, women in business, david mcewan, john mcewan, national trust, national trust victoria, north-east victoria national trust, heritage buildings, industrial heritage, helene grey, pharmaceutical society of victoria, victorian college of pharmacy, country women's association, caroline copp, royal melbourne hospital, red cross, infant welfare association -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Miners from Snake Valley lobbied the Victorian Government in 1855 to make land available for sale for farming purposes as an alternative occupation and income for people who wished to stay in the region but move away from gold mining. A secondary motivation was to increase the supply of fresh produce and decrease prices of items that otherwise needed to be transported from Melbourne or other regions. Forty-three country lots were initially offered in the Three Mile area, ranging in size from two to ninety acres and costing from £1 to £3 per acre. An additional eighty-five country lots were auctioned later in the year, in addition to many smaller suburban lots. More lots were offered than sold, initially, but this represented conditions of sale requiring the total purchase cost up front which many people interested in purchasing could not afford, especially as land purchased for farming would accrue substantial additional costs for clearing and labour before becoming productive. Further lobbying activities and the election of parliamentary members sympathetic to the cause took place through the 1850s. Ovens Parliamentary Member, Daniel Cameron, was re-elected in 1856 on a platform of surveying the land for public selection with deferred payment options. Land reform remained an issue in the area through the 1850s and early 1860s, impacting broader decisions in the new State of Victoria relating to voting rights, use of Crown land and the farming of land that wasn't always suitable for the purpose. This photograph depicts Beechworth in approximately 1900, after several waves of land sales resulted in increasingly levels of development. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is significant because it provides insight into Beechworth's built environment and infrastructure in the early Twentieth Century, around the time of Australia's Federation. It is also an example of an early photographic and film-making technology in use in regional Victoria in the time period.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a square-edged image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, indigo shire, north-east victoria, farming, squatters, miners, agriculture, land-clearing, land reform, daniel cameron, land sales, three mile, snake valley, tarrawingee -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Pudding Mould
One of the first documented mentions of pudding can be found in Homer's Odyssey where a blood pudding roasted in a pig's stomach is described. This original meaning of a pudding as a sausage is retained in black pudding, which is a blood sausage originating in the United Kingdom and Ireland made from pork or beef blood, with pork fat or beef suet, and a cereal. Another early documented recipe for pudding is a reference to asida, found in a tenth century Arabic cookbook by Ibn Sayyar al-Warraq called Kitab al-Ṭabīḫ (Arabic: كتاب الطبيخ, The Book of Dishes). It was described as a thick pudding of dates cooked with clarified butter (samn). A recipe for asida was also mentioned in an anonymous Hispano-Muslim cookbook dating to the 13th century. In the 13th and 14th centuries, in the mountainous region of the Rif along the Mediterranean coast of Morocco, flour made from lightly grilled barley was used in place of wheat flour. A recipe for asida that adds argan seed oil was documented by Leo Africanus (c. 1465–1550), the Arab explorer known as Hasan al-Wazan in the Arab world. According to the French scholar Maxime Rodinson, asida were typical foods among the Bedouin of pre-Islamic and, probably, later times. In the United Kingdom and some of the Commonwealth countries, the word pudding can be used to describe both sweet and savoury dishes. Unless qualified, however, the term in everyday usage typically denotes a dessert; in the United Kingdom, pudding is used as a synonym for a dessert course. Puddings had their 'real heyday...', according to food historian Annie Gray, '...from the seventeenth century onward'. It is argued that 'the future of the boiled suet pudding as one of England's national dishes was assured only when the pudding cloth came into use' and although puddings boiled in cloths may have been mentioned in the medieval era, one of the earliest mentions is in 1617 in a recipe for Cambridge pudding, a pudding cloth is indicated; 'throw your pudding in, being tied in a fair cloth; when it is boiled enough, cut it in the midst, and so serve it in'. The pudding cloth is said, according to food historian C. Anne Wilson, to have revolutionised puddings. 'The invention of the pudding-cloth or bag finally severed the link between puddings and animal guts. Puddings could now be made at any time, and they became a regular part of the daily fare of almost all classes. Recipes for them proliferated.' https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PuddingPuddings and pudding making have evolved over the years, and continue to do so. White ceramic pudding bowl with fluted decoration on the outside.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, puddings, ceramics -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Functional object - Kitchen Equipment, Coolgardie Safe, c1900
The invention of the Coolgardie Safe is credited to Arthur Patrick McCormick, a contractor in Coolgardie, and later the Mayor of Narrogin. Coolgardie is in the Eastern Goldfields region of Western Australia. Gold was first discovered there in 1892; the townsite became a municipality in 1894, and by 1898 its population of 15,000 made it the third largest town in Western Australia after Perth and Fremantle. In the last decade of the 19th century, Coolgardie was the capital of the West Australian goldfields. Being 180 kilometres from the nearest civilisation, food supplies were initially scarce and expensive. As fresh food was a valuable commodity there was incentive to preserve it, and keep it out of reach of scavengers such as birds, dingos, dogs, ants, and flies. It was in an effort to do this, in the extreme heat of the Australian Interior, that McCormick came up with his design for the Coolgardie Safe. McCormick noticed that a wet bag placed over a bottle cooled its contents. He further noted that if this bottle was placed in a breeze, the bag would dry out more quickly, but the bottle would get colder. What McCormick had discovered was the principle of evaporation: ‘to change any liquid into a gaseous state requires energy. This energy is taken in the form of heat from its surroundings.’ Employing this principle, McCormick made a box for his provisions which he covered with a wet hessian bag. He then placed a tray on top, into which he poured water twice daily. He hung strips of flannel from the tray so that water would drip down onto the hessian bag, keeping it damp. As the water evaporated, the heat dissipated, keeping the food stored inside cool and fresh. The success of McCormick’s invention would not have worked without a steady supply of water. Fresh water was scarce in the eastern goldfields at this time but the demand for water from a steadily growing population encouraged innovation. The solution was to condense salt water. Heating salt water in tanks produced steam that was condensed in tall cylinders, cooled and then collected in catchment trays. By 1898 there were six companies supplying condensed water to the goldfields, the largest company producing 100,000 gallons of water a day. In the early 20th century, Coolgardie Safes were also manufactured commercially. These safes incorporated shelving and a door, had metal or wooden frames and hessian bodies. The feet of the safe were usually placed in a tray of water to keep ants away. (MAV website) The early settlers of Moorabbin Shire depended on this type of Food Safe to protect their food from flies and vermin as they established market gardens in the fertile area around the notorious Elster Creek A metal framed, 4 sided structure standing on 4 legs with 2 hinged doors on one side, a metal tray at base of food safe and a metal cover over top. Ridges on which to rest trays carrying food are inside safe. The Safe is enclosed by fly-wire mesh.'...IN.....GEELONG' A manufacturer's oval metal plate is embossed on one side of Safe but it is illegible.elster creek, moorabbin, brighton, dendy's special survey 1841, market gardens, infant mortality, disease, cemeteries, fruit, vegetables, pioneers, coolgardie safe, mccormick arthur patrick, dendy henry, vaccination, jones martha, jones ethel may -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Poster - Poster, Information Board, 5 RAR 1966 - 1967 (1st Tour)
An Poster, Information Board of 5 RAR 1966 to 1967 (tst Tour). The 5th Battalion Royal Australian Regiment ("Battalion") were the leading element of the First Australian Task Force (1 ATF) and stationed in Vietnam from 1966 to 1967. The Battalion's task was to break Viet Cong control over the central region of Phuoc Tuy Province - an area that communists had freely operated in since 1945. Commencing of the 24th May 1966, the Battalion conducted its first operation codenamed "Hardihood". Their objective was to sweep and clear areas to the north and east of Nui Dat to a distance of 5000 meters, then create a defensive position to enable 1 ATF to establish an operation base. The Battalion conducted eighteen full-lenght operations as well as numerous day and night cordon and search, search and destroy, ambush and clearing patrols conducted at company, platoon and section levels. the Battalion achieved considerable success during Operations Canberra and Queanbeyan in October 1966 when it swept and cleared the Nui Thi Vai mountain. A Viet Cong base consisting of training facilities, a hospital, booby trap factory and several tonnes of rice was located and destroyed. during phase two (Operation Queanbeyan) the battalion discovered complex cave and tunnel systems along with other fixed installations that were vigorously fought for and destroyed by the battalion. Not only di the caves contain large quantities of weapons, equipment and documents but the 274 VC Regiments deputy commanders radio complex. For bravery and leadership, three Military Crosses, one Military Medal and one Mentioned in Dispatches were awarded. The last was awarded posthumously. However, at the completion of the battalion's first tour, the 274 and 275 Viet Cong Regiments remained functional. While the enemy retained the capacity to inflict serious casualities on smaller allied forces, the Battalion and other elements of the 1 AFt were successful in denying the enemy their previous gains. This enabled the South Vietnamese Government to re-establish control of over 96 per cent of the Phuoc Tuy Province during Australia's involvement. Source O'Neill, RJ Vietnam Task, the 5th Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment 1966/67, Melbourne. Cassell Australia Ltd, 19685 rar, 1st tour 1966 - 1967, operation hardihood, 1st atf base, poster, information board, nui dat, nui thai vai mountains, operation canberra, operation queanbeyan, viet cong, 274 vc regiments -
 Plutarch Project
Plutarch ProjectTrireme Replica, Paralos, circa 2005
The name Trireme comes from its distinct three rows of oars/oarsmen. The first tier of rowers were known as the Thranites, translating to Thrones. They were the most prestigious, and worked the hardest because their oars were furthest away from the water and therefore had to work harder. They were usually younger and they were paid one and a half drachma per day, half a drachma more than the other two tiers of rowers who were paid one drachma per day. After a few years working as Thranites, each was moved down into the second tier, the Zygites. Zygites derives from the word balance, as the second tier was balanced in the middle. After more years again, oarsmen were moved down into the third and final tier, known as the Thalamites. The Thalamites were consistently wet due to the proximity of their tier to the water. The water would leak through the gaps where the oars entered the ships despite the leather skins used to close the openings.This is a unique specimen made by D. Paraskevatos, in that it is the only one of its kind in the world that has been built to the exact specifications of the Athenian vessel. It was built in Melbourne and it also has historic and artistic valueWooden replica model ship that is an exact replica of the ancient Athenian trireme making it unique in the world since there's no other such replica made. Great care was exercised to ensure that it will include all functionality and detail of the ancient ship used to by the Athenians to fight in the Sea battle of Salamis and beyond. Mr Denis Paraskevatos constructed the Paralos Trireme over a period of eighteen months. Mr Paraskevatos relayed the history of his Trireme. The first Trireme was constructed in Greece by the shipbuilder Aminoklis in 704BC, originating from Corinth. The first four Triremes he constructed were ordered by a Poliykrates from Samos, thus the ships were known as Samines. Poliykrates realised he would be able to use the Triremes for his own benefit against invading pirates, as well as to engage in activities of piracy himself. The Athenians built 200 Triremes for the battle of Salamis, all constructed over a period of eighteen months. This was a huge feat, on average a new ship was build every second day. Triremes were primarily used in sea battles, however there were two unique Triremes, the Salaminia and the Paralos, which were considered Holy and only used for Ambassadors and Consulates on overseas trips. Mr Paraskevatos’ Trireme is the Paralos. The term Paralos derives from the Greek social class from the shores, or the merchant classes. Greece was divided into three basic social classes. The mountain region, the plateaus or fields bound to agriculture, and those from the shores. Paralia translates to from the shore. The Paralia were an important class in influencing the democracy. They were divergent group who would deliberately vote on the contrary to everyone else. This is how the Trireme was born. Every Trireme held between 20-50 soldiers, and either 170 or 174 oarsmen. Mr Paraskevatos’ Trireme is a 174 oarsmen ship. The role of the oarsmen was difficult and specialised. When engaged in sea battle and the wind was not enough, the navy would remove the masts and leave them on shore and solely use the oarsmen, leaving the deck clear. However when there were sufficient winds and both the sails and oars were in use the oarsmen had to show great skill in manoeuvrability. When the oarsmen were not needed to manoeuvre the ship they also engaged in battle. model, replica, paraskevatos, plutarch, ship, trireme, παρασκευάτος, πανομοιότυπο -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MERLE HALL COLLECTION: ARTS BENDIGO, VARIOUS SUNDRY DOCUMENTS
Merle Hall Collection - Arts Bendigo, Various sundry documents- a. One-page notice (''To All Teachers of Piano in the Bendigo Area'') of visit to Bendigo of former Bendigo student Tony Gray, notice date March 1993 - concert in the Banquet Room, Capital Theatre 14/3/1993; b. One-page notice of visit of Russian pianist Elisio Virsaladze and ''Moving Harps'' (trio) for October dates Year??; c. A5 brochure of information and dates for 1985 ''for many of the local and visiting arts-associated functions''. (3 pages of functions with dates, summary of performance and location of show; d. Single-page sheet of ''Arts Bendigo Activities Oct. '84 - Sept. '85 with paragraphs of ''Major Achievements'' and ''Disappointments'' and ''Thanks''. Also - ''Just Happened of Still To Come''; d. Six paged listing of 'Bendigo Subscribers' List 1979'' (Arts Council of Australia) with * annotations of being ''Financial'' - mostly personal names/addresses but some organizations. Approx 150 entries; e. two-paged list of ''Arts Bendigo Members July 1985'' with annotations of s= Single and F = Family members - approx 65 names; f. one-page Brief Report of Program Subcommittee June 1982, with rough analysis of attendance figures for recent shows; g. 3-page report of AB Development Sub-Committee meeting of 25/2/1985; h. two-paged report on ''Possible rehearsal and performing spaces in Bendigo area as known at June 1988 by Merle Hall, Secretary - brief details of 7 facilities and a number of ''Other'' facilities, with a final section on ''The Grand Vision''; i. One-page ''Proposals from Development Sub-committee'', prepared by Ellis C Blainer 3/3/87 - eight proposals in small detail; j. Bi-fold flyer ''Membership Information'' with description of AB activities and membership details/application form (not dated); k. A5 invitation of 'parchment' paper to ''25 Years of Achievement in the Arts'' (27/101995) - a brief AGM with a Social Evening from 8 pm; l. one-page invitation note accompanying the formal invitation to the special evening for 25th celebration of working with the arts in the Bendigo region. -
 Tarnagulla History Archive
Tarnagulla History ArchiveSet of Maps (Mining & Local Area), various
David Gordon Collection. A set of mining documents, maps and plans: 1. Dunolly Deep Leads - showing location and names of deep lead gold deposits in region around Dunolly including at Tarnagulla and Newbridge. Geological Survey of Victoria, Department of Minerals and Energy. Bulletin No. 62, Map No. 4 Dunolly (770 x 485 mm). 2. Poseidon Lead (Facsimile) 3. Nick O Time Lead (Facsimile) 4. Happy Go Lucky Mine prospectus and plan (colour copy) 5. Jones Creek GM Co. (Raven & Gourlay's) Waanyarra - Prospectus (colour copy) 6. Poseidon Area Plan (colour copy) and Poseidon Area map (B&W copy). 7. Cross-section diagram of Spread Eagle Reef 8. New Birthday Gold Mine - area map (colour copy) and mine cross-section ( (colour copy). 9. Cross section of Poverty Reef, by Department of Mines (B&W copy, 2 parts on A2 paper) 10. Time-Lease Graph for Watts Reef, Specimen Reef, Stony Reef, Poverty Reef (second page in detail), created by Eric WIlkinson for Ref Mining NL, 1995 11. 1859 Plan of the Gold Workings & Township of Sandy Creek, Shewing the Mining Leases, Extended Claims & Machinery by R.J. McMillan, Mining Surveyor (B&W copy) 12. Longitundinal and Transverse Vertical Sections of Poverty Reef, Sandy Creek 1859, by R.J. McMillan, Mining Surveyor (B&W copy) 13. Tarnagulla Locality Plan (B&W copy) 14. Universal Grid Reference Map (Topographic) for Laanecoorie North (2 copies) 15. Universal Grid Reference Map (Topographic) for Inglewood South 16. Poverty Reef, Plan showing shafts and early tenements, created by Eric WIlkinson for Ref Mining NL, 1995 17. Locality Map of mining leases in Tarnagulla 18. Plan and Elevation of part of Poverty Reef, Sandy Creek, showing the claims and positions of the shaft. by R.J. McMillan, Mining Surveyor (Facsimile, composed of taped together components) 19.Plan and Elevation of part of Poverty Reef, Sandy Creek, showing the claims and positions of the shaft. by R.J. McMillan, Mining Surveyor (Facsimile, composed of taped together components) -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
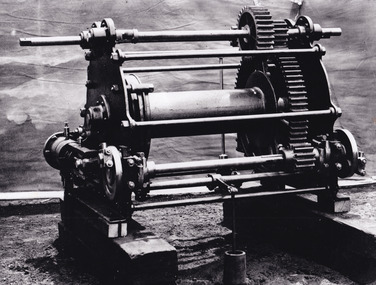
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Photograph - Reproduction, c.1870s
This photograph shows a piece of gold mining equipment identified as a mine winch, possibly an air winch cylinder of 1870s RG Ford's Patent design. Throughout the history of mining for gold and other precious materials, the windlass or winch (pictured) was used to bring up buckets full of soil from the bottom of a mine. This soil was then searched for gold/metals before being relocated to a different area. Due to the size and complexity of this particular piece of equipment, this winch may have been used to raise and lower mine carts to the entrance of the mine (often used in coal mining) and could have been used in raising cages up and down (acting as elevators) containing miners if the mine was particularly deep. The actual use of this particular item in the Beechworth locality is undocumented but these are some possibilities based on the use of these pieces of equipment in other mining locations. Mining can have a largely detrimental impact to the environment and therefore, the study of machinery like the one depicted in this photograph can help researches to reconstruct the methods and technologies used in the late 1800s and early 1900s. This particular item appears to have been removed from it's original site where it would have been used to assist with mining. It is possible that this photograph has been taken for recording purposes or as part of a machinery exhibition. Prior documentation records that this piece of equipment had connections to the Rocky Mountains Mining Company. Today, the Rocky Mountains Gold Mining company is famous in Beechworth for having been instrumental in the creation of the Rocky Mountain tunnel. Construction for this tunnel began in 1859 when a group of 12 men blasted a 400ft long tailrace though the rock beneath the town of Beechworth. Today, the 800ft tunnel, completed in 1871, is a popular tourist attraction but during the decades of gold mining, the purpose of this tunnel was to divert water away from the main sluicing operations so miners could better access gold and precious materials. The tunnel was used for this purpose for many years, later becoming useful for the Zwar Brother's tannery and currently as an outfall drain for Lake Sambell. This area continued to be mined until the early 1900s. The period when this item was in use is unclear but it is estimated to have been in the 1870s based on the design and appearance of the image. The gold works at the Rocky Mountain Tunnel closed in the early 1920s but the impact of mining remains in Beechworth today and therefore the study of photographs like this one which contain mining equipment can further understanding of mining in this region.This photograph has historic and research potential for study on the gold mining of the Beechworth region and types of equipment used to locate gold after the initial gold rush of 1853-1854 which resulted in the discovery of the surface gold and required miners to dig deeper to access precious metals. The clarity of the photo, and its good preserved condition, means it can continue to be used for research. This photo is part of a collection of six photos all within the Burke Museum Collection which depict mining equipment.Square black and white photograph on card.7793.1beechworth, mining, goldmining, goldmining equipment, beechworth burke museum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
This lantern slide shows the Ovens District Hospital (also called the Ovens Goldfields Hospital) in Beechworth in approximately 1900. The Hospital was built as part of a community push to develop the infrastructure needed for a permanent town in the 1850s. At the time there was no hospital located between Melbourne and the NSW town of Goulburn and it was recognised that the nature of mining and agricultural work predisposed people to serious injury. The community voted in 1853 to raise funds for a hospital and a voluntary committee elected from people who contributed £2 or more annually determined the organisation's management policies, which aimed to provide care for poor people at rates levied according to the person's means. Ongoing operations of the hospital were primarily supported by Government grants, however. The foundation stone was laid at a site in Church Street at a ceremony held 1st September 1856 which was attended by 2000 people using a locally crafted trowel with a tin ore handle and pure gold blade. The hospital, which was designed by J.H. Dobbyn, cost £2347. The hospital had two wards, a dispensary, apartments for a resident surgeon and the matron, an operating theatre and a board room. Further medical facilities including services to meet the cultural and health needs of the local Chinese community were later added, in addition to a Palladian-style cut-granite face built in 1862-63. It functioned as the region's primary hospital until surpassed by the Wangaratta Hospital in 1910. In the 1940s much of the building materials were salvaged and repurposed, with the exception of the facade which was restored in 1963 by the Beechworth Lions Club and still stands today. The facade featured on the covers of local history volume 'Beechworth: a Titan's Field' by Carole Woods and heritage-focused travel guide the 'Readers Digest Book of Historic Australian Towns'. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is significant because it provides insight into Beechworth's built environment and infrastructure in the early Twentieth Century, around the time of Australia's Federation. It is also an example of an early photographic and film-making technology in use in regional Victoria in the time period.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a round-edged square image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.Obverse: Y /burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, ovens district hospital, indigo shire, north-east victoria, hospital, palladian architecture, granite, community fundraising, community infrastructure, j.h. dobbyn, beechworth lions club, ovens goldfields hospital, chinese community -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Anchor, John Trotman, 1852 to early 1900s
This Trotman’s pattern stock anchor is the southernmost anchor on display at Flagstaff Hill’s Anchor Graveyard. This large Trotman design anchor was patented in 1852 by John Trotman and was widely used on merchant ships. On April 15th 2001 around midday this anchor was raised from the seabed of Lady Bay, Warrnambool, by the crew from Birdon Dredging, who had been hired to dredge the Harbour. The spokesperson Steve Walker, who worked for the firm, said that the anchor and long chain were found after the chain became tangled in the cutter blade of the dredging equipment. The anchor was lifted from the water and onto the Breakwater then a front-end loader placed it onto a truck that then delivered it to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum & Village. Howard Nichol, Museum Manager at the time, had estimated the anchor to be up to 130 years old. The previous Museum Manager, Peter Ronald, who was also a diver, had identified the anchor as a Trotman’s type and similar to those used on some of the major wrecks in the region. According to Nicholl, Museum staff believed it was possible that the anchor is one of two used as a mooring line that had been used to catch driving vessels and prevent ships from washing aground on the sand bar. The mooring line was shown as a dotted line on the 1890 chart of Lady Bay, approved by Lieutenant Stanley of the British Admiralty. by Lieutenant Stanley [British Admiralty]. The location of the anchor corresponds to a point on that map and the length of the chain supports that theory. “The map is quite a detailed survey of the Bay and it shows two anchors with buoys on the ends with probably about 100 yards of chain stretched between them. The ships would drop anchor and was the chain as a snag because this was a treacherous bay before the Breakwater was built and this was a way to eliminate that problem, "said Nichol. The mooring chain was put in place to catch drifting vessels during wild stormy weather. It was identified. ABOUT TROTMAN’S ANCHORS- The British Admiralty wanted an anchor design that had more holding power. The Committee of 1852 on Anchors was appointed to assess and report on the qualities of various anchors including Trotman’s anchors. Trotman’s pattern anchor received the highest score. The anchor is similar to the Admiral’s design but features arms that pivot when the anchor settles and the upper fluke moves to rest against the shank. The anchor then sits lower, which in turn greatly reduces the chances of the anchor’s chain, cable or rope getting tangled. The top of the shank has a fitting that allows a quick release of the anchor’s chain if this becomes necessary. This Trotman’s anchor is significant as a part of the maritime history of the Port of Warrnambool regardless of whether it belonged to one of the 29 ships that were stranded or wrecked in Lady Bay. The anchor is connected to the many attempts to maintain Warrnambool as a safe and manageable port, including the various plans for the construction of the Breakwater.Anchor: an iron Trotman’s pattern style with a rectangular-section shank that is wider in the middle and has a base that extends on two opposite sides in a ‘fork prong’ manner. A crescent-shaped, double-ended arm is fitted into the base of the shank with a bolt, enabling it to pivot. Each arm has a fluke in the shape of an upward palm with an attached metal plate that forms a horn at the back of the palm. A long, round-section pipe is fitted to the top of the shank at 90 degrees to the arms; one side has an elbow bend parallel to the arms, and both ends have an attached metal sphere. The pivoting ring at the top of the shank can be lifted for a quick release of the chain.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, anchor, mooring, trotman, lady bay, breakwater, admiralty, ship equipment, stock anchor, john trotman, 1852 patent, 2001, birdon dredging, steve walker, howard nichol, peter ronald, british admiralty, lieutenant stanley, committee of 1852 on anchors -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayGreenbat Battery Loco, Greenwood & Batley ltd
Greenbat Battery Loco Built by Greenwood & Batley Ltd Builders No. 420363/2 This Greenbat Battery Loco has been loaned to the Museum by the Walhalla Goldfields Railway, who had acquired it in 2013 along with a large quantity of narrow gauge trollies and light rail from Orica’s now closed munitions factory in Melbourne’s western suburbs. The trolley on display was one of two in use from the 1970s. Orica - Deer Park Munitions factory Orica Deer Park in Melbourne’s west has been used since circa 1875 for various forms of manufacturing and storage of chemicals. Although the site is bounded by Ballarat Road, Station Street, Tilburn Road and the Western Ring Road, the current entry point for industrial operations is situated at Gate 6 off Tilburn Road. Operations include: • a specialty chemicals facility producing products for mining services operations • quarry services • other chemical manufacture activities. The Deer Park factory complex is of historical significance as the location of the first plant for the manufacture of high explosives in Australia and has been, for its entire history, the most important, if not only, commercial manufacturer of high explosives in Australia. It commenced operation under the importer Jones Scott and Co, and then the Australian Lithofracteur Company (Krebs Patent), a rival to Nobel's dynamite patent. The factory was producing nitro-glycerine based explosives in Australia only a couple of years after Nobel's Ardeer factory began operating in Scotland. The explosives factories complex is of historical significance for the association with the Australian Lithofracteur Company, Australian Explosives and Chemicals, the Nobel company and later ICIANZ, which grew to become one of the largest explosives, chemical and plastics manufacturers in Australia. It was the pioneer of the industry and retained its dominance through monopolistic practices, taking over most of its competitors in the Australasian region. Substantial parts of the pre-Second World War layout of the site remain which, with a number of significant buildings dating back to the 1920s and '30s, indicate past and present processes of manufacturing, the necessary safety measures required and the integrated nature of the explosives and chemical industry. The narrow gauge tramway, which ran through the explosives section, was a rare survivor of nineteenth century materials-handling methods into the 21st Century. Greenwood & Batley were a large engineering manufacturer with a wide range of products, including armaments, electrical engineering, and printing and milling machinery. They also produced a range of battery-electric railway locomotives under the brand name Greenbat. The works was in Armley, Leeds, UK. Greenbat was the trade name for the railway locomotives built by Greenwood & Batley. The company specialised in electric locomotives, particularly battery-powered types for use in mines and other hazardous environments. Historic - Industrial Narrow Gauge Railway - Battery Locomotive - Orica - Deer Park Munitions factory - Deep park, Victoria, Australia Battery Locomotive - made of iron puffing billy, greenbat battery loco, battery locomotive, industrial narrow gauge railway, orica - deer park munitions factory -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kenneth Darnton Watson - Community Leader
Kenneth Darnton Watson was born at Bendigo on 24 May 1893 to George Darnton Watson and Adelaide Nora Holmes. He was educated at Melbourne Church of England Grammar School, being selected as School Captain in 1913 and a member of the Head of the River rowing team. After finishing school, he worked as a jackaroo on Wanganella Station and later at Mt. Widderin, Skipton, Victoria. When WW1 was declared, Kenneth enlisted and after initial training at Maribyrnong, Victoria he left Australia as 2nd Lieutenant with 7th Australian Field Artillery Brigade, to disembark at Plymouth on July 10, 1916. He took part in the Battles of Messines, Menin Road, Polygon Wood and Passchendaele Ridge in 1917. For his efforts in Passchendaele Ridge on 17th December he was awarded the Military Cross "for conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty." In 1918 he took part in the Battles of Villers-Bretonneux, Hamel and Amiens. He returned to Australia in November 1919 and was discharged on 20th January 1920. In 1922, Kenneth Darnton Watson came to Wodonga where he purchased de Kerilleau, consisting of 2,500 acres, from Mr George Gordon. The two storey brick homestead had been built by William Huon in 1870. On 30th May 1924, he married Phyllis Emily Lenore Austin and they had four children, Ian Darnton 1925, Robert Darnton 1926 Rosemary McPherson 1929 and Faith Holmes 1931. On the land he worked hard, building fences, cattle, sheep and horse yards, and farmed Corriedale sheep, Shorthorn cattle and horses. Mr Watson was an innovative farmer, introducing modern methods of top dressing at de Kerilleau by means of an aircraft. He was also a dedicated community man. He was a member of both Albury and Wodonga Show Committees, Murray Valley Development League, No.1 Region, Graziers' Association of Southern Riverina, Albury Legacy Club, Wodonga RSL, and Wodonga Turf Club including terms as President on several of these organisations. Kenneth was also a Warden of St. Luke's Church of England, Wodonga. Kenneth served as Wodonga Shire President from 1929 to 1931, and was again elected to Council from 1943 to 1945. A most respected and valued member of the local community, Kenneth Darnton Watson died on the 4th of October 1951, aged 58. Lenore Watson lived at de Kerilleau until her death on 15th June 1984. Both are buried in Wodonga.These images are significant because they record the service of a prominent member of the Wodonga community.A collection of black of white images of Kenneth Darnton Watson of Wodonga.kenneth darnton watson, watson family wodonga, wodonga community members -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Cigarette Case - K. D. Watson, Wodonga, 1919
This cigarette case was owned by Kenneth Darnton Watson and carried into battle during World War I. Kenneth Darnton Watson was born at Bendigo on 24 May 1893 to George Darnton Watson and Adelaide Nora Holmes. He was educated at Melbourne Church of England Grammar School, being selected as School Captain in 1913 and a member of the Head of the River rowing team. After finishing school, he worked as a jackaroo on Wanganella Station and later at Mt. Widderin, Skipton, Victoria. When WWI was declared, Kenneth enlisted and after initial training at Maribyrnong, Victoria he left Australia as 2nd Lieutenant with 7th Australian Field Artillery Brigade, to disembark at Plymouth on July 10, 1916. He took part in the Battles of Messines, Menin Road, Polygon Wood and Passchendaele Ridge in 1917. For his efforts in Passchendaele Ridge on 17th December he was awarded the Military Cross "for conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty." In 1918 he took part in the Battles of Villers-Bretonneux, Hamel and Amiens. He returned to Australia in November 1919 and was discharged on 20th January 1920. In 1922, Kenneth Darnton Watson came to Wodonga where he purchased de Kerilleau, consisting of 2,500 acres, from Mr George Gordon. The two storey brick homestead had been built by William Huon in 1870. On 30th May 1924, he married Phyllis Emily Lenore Austin and they had four children, Ian Darnton 1925, Robert Darnton 1926 Rosemary McPherson 1929 and Faith Holmes 1931. On the land he worked hard, building fences, cattle, sheep and horse yards, and farmed Corriedale sheep, Shorthorn cattle and horses. Mr Watson was an innovative farmer, introducing modern methods of top dressing at de Kerilleau by means of an aircraft. He was also a dedicated community man. He was a member of both Albury and Wodonga Show Committees, Murray Valley Development League, No.1 Region, Graziers' Association of Southern Riverina, Albury Legacy Club, Wodonga RSL, and Wodonga Turf Club including terms as President on several of these organisations. Kenneth was also a Warden of St. Luke's Church of England, Wodonga. Kenneth served as Wodonga Shire President from 1929 to 1931, and was again elected to Council from 1943 to 1945. A most respected and valued member of the local community, Kenneth Darnton Watson died on the 4th of October 1951, aged 58. Lenore Watson lived at de Kerilleau until her death on 15th June 1984. Both are buried in Wodonga.This item is significant because it was owned by a decorated Australian serviceman and prominent member of the Wodonga community.A silver cigarette case owned by Kenneth Darnton Watson of Wodonga. The inside contains straps to hold the cigarettes in place. Both the front and back have been engraved.On front: KDW On back: 1919kenneth darnton watson, watson family wodonga, wodonga community members -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Silver Mug - K. D. Watson, Wodonga
This cup was awarded to Kenneth Darnton Watson when he was a boarder and competitive rower whilst completing his secondary education. Kenneth Darnton Watson was born at Bendigo on 24 May 1893 to George Darnton Watson and Adelaide Nora Holmes. He was educated at Melbourne Church of England Grammar School, being selected as School Captain in 1913 and a member of the Head of the River rowing team. After finishing school, he worked as a jackaroo on Wanganella Station and later at Mt. Widderin, Skipton, Victoria. When WW1 was declared, Kenneth enlisted and after initial training at Maribyrnong, Victoria he left Australia as 2nd Lieutenant with 7th Australian Field Artillery Brigade, to disembark at Plymouth on July 10, 1916. He took part in the Battles of Messines, Menin Road, Polygon Wood and Passchendaele Ridge in 1917. For his efforts in Passchendaele Ridge on 17th December he was awarded the Military Cross "for conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty." In 1918 he took part in the Battles of Villers-Bretonneux, Hamel and Amiens. He returned to Australia in November 1919 and was discharged on 20th January 1920. In 1922, Kenneth Darnton Watson came to Wodonga where he purchased de Kerilleau Homestead, consisting of 2,500 acres, from Mr George Gordon. The two storey brick homestead had been built by William Huon in 1870. On 30th May 1924, he married Phyllis Emily Lenore Austin and they had four children, Ian Darnton 1925, Robert Darnton 1926 Rosemary McPherson 1929 and Faith Holmes 1931. On the land Kenneth worked hard, building fences, cattle, sheep and horse yards, and farmed Corriedale sheep, Shorthorn cattle and horses. he was an innovative farmer, introducing modern methods of top dressing at de Kerilleau by means of an aircraft. He was also a dedicated community man. He was a member of both Albury and Wodonga Show Committees, Murray Valley Development League, No.1 Region, Graziers' Association of Southern Riverina, Albury Legacy Club, Wodonga RSL, and Wodonga Turf Club including terms as President on several of these organisations. Kenneth was also a Warden of St. Luke's Church of England, Wodonga. Kenneth served as Wodonga Shire President from 1929 to 1931, and was again elected to Council from 1943 to 1945. A most respected and valued member of the local community, Kenneth Darnton Watson died on the 4th of October 1951, aged 58. Lenore Watson lived at de Kerilleau until her death on 15th June 1984. Both are buried in Wodonga.These images are significant because they record the service of a prominent member of the Wodonga community.A silver mug awarded to K D Watson as a rowing trophy in April 1909. It features the shield of Melbourne Church of England Grammar School (M.C.E.G.S.), as well as his name and the event for which it was awarded.View 1: M.C.E.G.S. April 1909 Regatta View 2: Crest of MECEGS featuring motto "Ora et Labora" View 3: BOARDERS FOUR K. D. WATSON 3kenneth darnton watson, watson family wodonga, wodonga community members -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - PETER ELLIS COLLECTION: NEWSPAPER ARTICLE, 23rd May, 2015
Colour photocopy of article from Bendigo Advertiser. Dated Saturday, May 23, 2015. FAREWELL, MA.. When Peter received his Order of Australia Medal it was one of his proudest moments. He couldn’t resist wearing it on every occasion. FROM - PREVIOUS PAGE The Emu Creek Bush Band has performed at National Folk Festivals in four states and numerous times at the National Folk Festival in Canberra. They have also been mainstays of the Maldon Folk Festival for most of its history as well as doing dance programs for the Port Fairy Folk Festival on two occasions. Peter wrote and published many books related to traditional music and dance. These include: Three volumes of 'Collector's Choice' which is musical notations for bush dances coupled with much dance history which would have been lost without Peter's efforts, are 'Two Hundred Dancing Years- How to run a Colonial Ball' (Co-authored with Shirley Andrews (AM), 'Music Makes Me Smile- The Music of the Nariel Valley' (Co-authored with Harry Gardner), and his last completed book is titled 'The Merry Country Dance' with over 300 pages.. .. .. Grant. The first edition sold out in only a few weeks. Peter taught old time musicianship, accomplished as he was on the concertina and button accordion, tin whistle, and harmonica, as well as the Swanee whistle, piano and ukulele. In demand for workshops in music and dance at National Folk Festivals in Perth, Alice Springs, Maleny, Melbourne, Adelaide, Kuranda and more recently at several Canberra National Folk Festivals, he was a hit at festivals across the country. As a trained ballroom dancer, with many gold medals to his name, Peter passed on his knowledge every time he trained debutante sets in the Bendigo region. As an early environmentalist, he was a life member of the Bendigo Field Naturalists Club, secretary in the 1970's and actively involved in campaigns to save Lake Pedder and establish the Whipstick and Kamarooka State Parks (now part of the Bendigo National Park). He has discovered and named new plant species in the Whipstick Forest and propagated many Australian plants. Peter took regular guided tours through the Whipstick each spring, on wildflower educational tours. He was a keen and gifted photographer of local plant species. When Peter received his Order of Australia Medal it was one of his proudest moments. He couldn’t resist wearing it on every occasion. Funeral details. Family, friends and his supporters will farewell Peter.. .. .. ..person, individual, peter ellis oam -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesPeriodical, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, Australian Aboriginal studies : journal of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, 2008
1. Rock-art of the Western Desert and Pilbara: Pigment dates provide new perspectives on the role of art in the Australian arid zone Jo McDonald (Australian National University) and Peter Veth (Australian National University) Systematic analysis of engraved and painted art from the Western Desert and Pilbara has allowed us to develop a spatial model for discernable style provinces. Clear chains of stylistic connection can be demonstrated from the Pilbara coast to the desert interior with distinct and stylistically unique rock-art bodies. Graphic systems appear to link people over short, as well as vast, distances, and some of these style networks appear to have operated for very long periods of time. What are the social dynamics that could produce unique style provinces, as well as shared graphic vocabularies, over 1000 kilometres? Here we consider language boundaries within and between style provinces, and report on the first dates for pigment rock-art from the Australian arid zone and reflect on how these dates from the recent past help address questions of stylistic variability through space and time. 2. Painting and repainting in the west Kimberley Sue O?Connor, Anthony Barham (Australian National University) and Donny Woolagoodja (Mowanjum Community, Derby) We take a fresh look at the practice of repainting, or retouching, rockart, with particular reference to the Kimberley region of Western Australia. We discuss the practice of repainting in the context of the debate arising from the 1987 Ngarinyin Cultural Continuity Project, which involved the repainting of rock-shelters in the Gibb River region of the western Kimberley. The ?repainting debate? is reviewed here in the context of contemporary art production in west Kimberley Indigenous communities, such as Mowanjum. At Mowanjum the past two decades have witnessed an artistic explosion in the form of paintings on canvas and board that incorporate Wandjina and other images inspired by those traditionally depicted on panels in rock-shelters. Wandjina also represents the key motif around which community desires to return to Country are articulated, around which Country is curated and maintained, and through which the younger generations now engage with their traditional lands and reach out to wider international communities. We suggest that painting in the new media represents a continuation or transference of traditional practice. Stories about the travels, battles and engagements of Wandjina and other Dreaming events are now retold and experienced in the communities with reference to the paintings, an activity that is central to maintaining and reinvigorating connection between identity and place. The transposition of painting activity from sites within Country to the new ?out-of-Country? settlements represents a social counterbalance to the social dislocation that arose from separation from traditional places and forced geographic moves out-of-Country to government and mission settlements in the twentieth century. 3. Port Keats painting: Revolution and continuity Graeme K Ward (AIATSIS) and Mark Crocombe (Thamarrurr Regional Council) The role of the poet and collector of ?mythologies?, Roland Robinson, in prompting the production of commercial bark-painting at Port Keats (Wadeye), appears to have been accepted uncritically - though not usually acknowledged - by collectors and curators. Here we attempt to trace the history of painting in the Daly?Fitzmaurice region to contextualise Robinson?s contribution, and to evaluate it from both the perspective of available literature and of accounts of contemporary painters and Traditional Owners in the Port Keats area. It is possible that the intervention that Robinson might have considered revolutionary was more likely a continuation of previously well established cultural practice, the commercial development of which was both an Indigenous ?adjustment? to changing socio-cultural circumstances, and a quiet statement of maintenance of identity by strong individuals adapting and attempting to continue their cultural traditions. 4. Negotiating form in Kuninjku bark-paintings Luke Taylor (AIATSIS) Here I examine social processes involved in the manipulation of painted forms of bark-paintings among Kuninjku artists living near Maningrida in Arnhem Land. Young artists are taught to paint through apprenticeships that involve exchange of skills in producing form within extended family groups. Through apprenticeship processes we can also see how personal innovations are shared among family and become more regionally located. Lately there have been moves by senior artists to establish separate out-stations and to train their wives and daughters to paint. At a stylistic level the art now creates a greater sense of family autonomy and yet the subjects link the artists back in to much broader social networks. 5. Making art and making culture in far western New South Wales Lorraine Gibson This contribution is based on my ethnographic fieldwork. It concerns the intertwining aspects of the two concepts of art and culture and shows how Aboriginal people in Wilcannia in far western New South Wales draw on these concepts to assert and create a distinctive cultural identity for themselves. Focusing largely on the work of one particular artist, I demonstrate the ways in which culture (as this is considered) is affectively experienced and articulated as something that one ?comes into contact with? through the practice of art-making. I discuss the social and cultural role that art-making, and art talk play in considering, mediating and resolving issues to do with cultural subjectivity, authority and identity. I propose that in thinking about the content of the art and in making the art, past and present matters of interest, of difficulty and of pleasure are remembered, considered, resolved and mediated. Culture (as this is considered by Wilcannia Aboriginal people) is also made anew; it comes about through the practice of artmaking and in displaying and talking about the art work. Culture as an objectified, tangible entity is moreover writ large and made visible through art in ways that are valued by artists and other community members. The intersections between Aboriginal peoples, anthropologists, museum collections and published literature, and the network of relations between, are also shown to have interesting synergies that play themselves out in the production of art and culture. 6. Black on White: Or varying shades of grey? Indigenous Australian photo-media artists and the ?making of? Aboriginality Marianne Riphagen (Radboud University, The Netherlands) In 2005 the Centre for Contemporary Photography in Melbourne presented the Indigenous photo-media exhibition Black on White. Promising to explore Indigenous perspectives on non-Aboriginality, its catalogue set forth two questions: how do Aboriginal artists see the people and culture that surrounds them? Do they see non-Aboriginal Australians as other? However, art works produced for this exhibition rejected curatorial constructions of Black and White, instead presenting viewers with more complex and ambivalent notions of Aboriginality and non-Aboriginality. This paper revisits the Black on White exhibition as an intercultural event and argues that Indigenous art practitioners, because of their participation in a process to signify what it means to be Aboriginal, have developed new forms of Aboriginality. 7. Culture production Rembarrnga way: Innovation and tradition in Lena Yarinkura?s and Bob Burruwal?s metal sculptures Christiane Keller (University of Westerna Australia) Contemporary Indigenous artists are challenged to produce art for sale and at the same time to protect their cultural heritage. Here I investigate how Rembarrnga sculptors extend already established sculptural practices and the role innovation plays within these developments, and I analyse how Rembarrnga artists imprint their cultural and social values on sculptures made in an essentially Western medium, that of metal-casting. The metal sculptures made by Lena Yarinkura and her husband Bob Burruwal, two prolific Rembarrnga artists from north-central Arnhem Land, can be seen as an extension of their earlier sculptural work. In the development of metal sculptures, the artists shifted their artistic practice in two ways: they transformed sculptural forms from an earlier ceremonial context and from earlier functional fibre objects. Using Fred Myers?s concept of culture production, I investigate Rembarrnga ways of culture-making. 8. 'How did we do anything without it?': Indigenous art and craft micro-enterprise use and perception of new media technology.maps, colour photographs, b&w photographswest kimberley, rock art, kuninjku, photo media, lena yarinkura, bob burruwal, new media technology -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesPeriodical, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, Australian Aboriginal studies : journal of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, 2010
Mediating conflict in the age of Native Title Peter Sutton (The University of Adelaide and South Australian Museum) Mediators have played roles in managing conflict in Aboriginal societies for a long time. This paper discusses some of the similarities and differences between older customary mediator roles and those of the modern Native Title process. Determinants of tribunal outcomes for Indigenous footballers Neil Brewer, Carla Welsh and Jenny Williams (School of Psychology, Flinders University) This paper reports on a study that examined whether football tribunal members? judgments concerning players? alleged misdemeanours on the sporting field are likely to be shaped by extra-evidential factors that disadvantage players from Indigenous backgrounds. Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australian Football League (AFL) players, matched in terms of their typical levels of confidence and demeanour in public situations, were interrogated in a mock tribunal hearing about a hypothetical incident on the football field. The specific aim was to determine if the pressures of such questioning elicited behavioural differences likely to be interpreted as indicative of testimonial unreliability. Mock tribunal members (number = 103) then made judgments about the degree to which a number of behavioural characteristics were evident in the players? testimonies. Under intense interrogation, Indigenous players were judged as presenting less confidently and displaying a greater degree of gaze aversion than non-Indigenous players. These behavioural characteristics are commonly ? and inappropriately ? used as cues or heuristics to infer testimonial accuracy. The paper discusses the implications for Indigenous players appearing at tribunal hearings ? and for the justice system more broadly. Timothy Korkanoon: A child artist at the Merri Creek Baptist Aboriginal School, Melbourne, Victoria, 1846?47 ? a new interpretation of his life and work Ian D Clark (School of Business, University of Ballarat) This paper is concerned with the Coranderrk Aboriginal artist Timothy Korkanoon. Research has uncovered more about his life before he settled at the Coranderrk station in 1863. Evidence is provided that five sketches acquired by George Augustus Robinson, the former Chief Protector of Aborigines, in November 1851 in Melbourne, and found in his papers in the State Library of New South Wales, may also be attributed to the work of the young Korkanoon when he was a student at the Merri Creek Baptist Aboriginal School from 1846 to 1847. Developing a database for Australian Indigenous kinship terminology: The AustKin project Laurent Dousset (CREDO, and CNRS, Ecole des Hautes Etudes en Sciences Sociales), Rachel Hendery (The Australian National University), Claire Bowern (Yale University), Harold Koch (The Australian National University) and Patrick McConvell (The Australian National University) In order to make Australian Indigenous kinship vocabulary from hundreds of sources comparable, searchable and accessible for research and community purposes, we have developed a database that collates these resources. The creation of such a database brings with it technical, theoretical and practical challenges, some of which also apply to other research projects that collect and compare large amounts of Australian language data, and some of which apply to any database project in the humanities or social sciences. Our project has sought to overcome these challenges by adopting a modular, object-oriented, incremental programming approach, by keeping metadata, data and analysis sharply distinguished, and through ongoing consultation between programmers, linguists and communities. In this paper we report on the challenges and solutions we have come across and the lessons that can be drawn from our experience for other social science database projects, particularly in Australia. A time for change? Indigenous heritage values and management practice in the Coorong and Lower Murray Lakes region, South Australia Lynley A Wallis (Aboriginal Environments Research Centre, The University of Queensland) and Alice C Gorman (Department of Archaeology, Flinders University) The Coorong and Lower Murray Lakes in South Australia have long been recognised under the Ramsar Convention for their natural heritage values. Less well known is the fact that this area also has high social and cultural values, encompassing the traditional lands and waters (ruwe) of the Ngarrindjeri Nation. This unique ecosystem is currently teetering on the verge of collapse, a situation arguably brought about by prolonged drought after decades of unsustainable management practices. While at the federal level there have been moves to better integrate typically disparate ?cultural? and ?natural? heritage management regimes ? thereby supporting Indigenous groups in their attempts to gain a greater voice in how their traditional country is managed ? the distance has not yet been bridged in the Coorong. Here, current management planning continues to emphasise natural heritage values, with limited practical integration of cultural values or Ngarrindjeri viewpoints. As the future of the Coorong and Lower Murray Lakes is being debated, we suggest decision makers would do well to look to the Ngarrindjeri for guidance on the integration of natural and cultural values in management regimes as a vital step towards securing the long-term ecological viability of this iconic part of Australia. Hearts and minds: Evolving understandings of chronic cardiovascular disease in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations Ernest Hunter (Queensland Health and James Cook University) Using the experience and reflections of a non-Indigenous clinician and researcher, Randolph Spargo, who has worked in remote Aboriginal Australia for more than 40 years, this paper tracks how those at the clinical coal-face thought and responded as cardiovascular and other chronic diseases emerged as new health concerns in the 1970s to become major contributors to the burden of excess ill health across Indigenous Australia. The paper cites research evidence that informed prevailing paradigms drawing primarily on work in which the clinician participated, which was undertaken in the remote Kimberley region in the north of Western Australia. Two reports, one relating to the Narcoonie quarry in the Strzelecki Desert and the other concerning problematic alcohol use in urban settings.maps, b&w photographs, colour photographs, tablesstrzelecki desert, native title, timothy korkanoon, merri creek baptist aboriginal school, austkin project, coorong, lower murray lakes district, south australia, indigenous health -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPamphlet - Promotional brochure, Bachelor of Visual Arts, Graphic Design/Multimedia, c1999
Promoting the Graphic Design/Multimedia program being offered by the University of Ballarat at the Mt Helen Campus. Promoted course as "one of the smallest and arguably the best three year programs of its kind in Australia and the South Pacific region." The brochure lists student awards received including Platinum and Gold in the AGFA International Young Designer Contest, 1999; two meritorious awards in The Art Directors Club Student Awards, New York, USA 1999; Graphis New Talent 1999; two Gold in Souther Cross Packaging Awards, 1998. At time of publication, the School of Arts, Visual Arts reportedly had 210 students with majors in Graphic Design/Multimedia, Ceramics/3D, Painting, Drawing, and Multidiscipline. Minors studies included Printmaking, Photography, 3D, 2D, and Graphic Communication. ___ Course aimed to train "independent, flexible thinkers". The course promised to "Promote creativity, originality and imaginative thinking; Develop self-directed learners, displaying initiative in the formation of ideas and the confidence to construct personal responses; Develop appropriate conceptual, technical and professional skills; Develop the student's critical process: ability to undertake research, and to make informed decisions; Clarify thinking, concepts and understanding and deep knowledge, attitudes and skills enabling the designer to respond to community needs." Studio and working environment described as "one open space with working facilities for approximately 75 students across 3 year levels. The area is divided up into work stations where 1st, 2nd and 3rd year students intermix, allowing a natural interaction. These workstations are configurations of six, consisting of two students from each year level. This reinforces the area's ongoing development with an open ethos and cross-level delivery and learning. This maximises the use of information in order for it to be applied throughout all levels of the learning process, whilst allowing a natural mentor arrangment to be developed for all first year students, " "The open ethos approach also encourages students and staff to freely express their opinions in relation to design via cross-level critiques, whilst allowing for a liberal arts approach and structure to the development of the creative process." "Emphasis is placed on experimentation, innovation, expression and the development of the individual's design philosophies, concepts and style." Also notes the 24 hour access Macintosh laboratory, with 34 Power Macintosh computers, ratio of one for every 2.5 students. Each with a Fujitsu Dyna Magneto Optical drive for file storage and transport. Two Sharp scanners, Phaser Dye-Sublimation Extra Tabloid colour printer and Ricoh A3 colour printer. Two large format printers. Digital and video cameras. Software: Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Acrobat; QuarkXpress; Macromedia Freehand; Pagemaker; Premier; Director; 3D Extreme; Sound Eidt, Shockwave, Infinite 3D and After Effects. Approx 4.5 staff, "all of whom are practicing designers. They have a full understanding of industry requirements and trends which assists in the development of industrial contacts when specialists are required." Prospective students interviewed in late Nov/ early Dec, face to face. Present a "comprehensive folio of work", academic records, references. "Selection is determined by the perceived potential of the student, their motivation and reason for study within the field as well as their previous experience in the Visual Arts. Folio work should be representative of the individual's ideas and abilities. Qualities of importance are: originality, innovation, imagination, experimentation and a competent display of the basic skills associated with visual arts [evidence of drawing skills should be included]." Demonstration of GD/MM computer skills an advantage. Students also asked to bring sketch books. Promotional brochure for prospective students. 8pp Double fold brochureuniversity of ballarat, federation university, graphic design, multimedia, bachelor, degree -
 Department of Health and Human Services
Department of Health and Human ServicesPhotograph, Berry Street Kindergarten
In 1877 the Victorian Infant Asylum was founded in Kew. In 1881, the asylum relocated to Berry Street in East Melbourne. By 1908, it was called the Foundling Hospital and Infants Home. It was non-denominational and controlled by a committee of management. By 1956, Berry Street consisted of a Mothercraft Training Centre and two main residential units: Berry Street for infants aged zero to 18 months, and Vale Street for toddlers aged zero to two years old. In August 1956, Berry Street was declared an approved category 2 Children's Home. In 1960, Vale Street was converted to an adult nursing home. In 1964, the name was changed to Berry Street Babies Home and Hospital. Berry Street was also an approved adoption agency. By 1968, Berry Street comprised the Training School for Mothercraft Nurses, the adoption agency, an infant life-protection house, a long-stay home for children to three years of age (the toddlers’ wing) and a small house for unmarried mothers. The home's infant life-protection work was seen as a critical agency function, particularly where family illness was putting pressure on mothers and Berry Street was able to provide respite and support. By the late 1960s, 30–40 adoptions annually were being arranged from Berry Street. By 1974 the home's orientation had shifted. Four family group homes had been established (two in Burwood, one in Ashburton and one in St Kilda), the mothercraft training function had been phased out, the toddlers wing converted to day care, and the main building (containing the nursery, administration, kitchen, dining room and single mothers accommodation) was demolished in favour of four home units, which housed 24 children, supervised by cottage parents. Berry Street provided short term, emergency and residential care for 'protection of infant' cases and state wards. Two flats were also established for short-term family accommodation. The nurses’ home was converted to house the home’s administration function and a social work service. The social work service coordinated family aid and family counselling services, and a neighbourhood house. In 1975 Berry Street also provided short-term care for 42 Vietnamese children brought to Australia in the official government-sponsored airlift. In 1976 Berry Street made application to change its category 2 Children's Home classification to category 1, as it was now catering for a wider range of children. It had ceased to be a babies’ home and hospital, and had started providing child and family care, including residential care. In 1977 Berry Street to established a family group home in Richmond to house children affected by the closure of St Cuthbert's Children's Home in Colac. Berry Street changed its name to Berry Street Child and Family Care in 1977. In 1978, the range of services provided by Berry Street Child and Family Care consisted of a social work counselling service, a financial aide, a family aide program using volunteers, two temporary accommodation units each housing eight children, an information and referral service, a neighbourhood house in Richmond, a day care centre for 36 children, and four family group homes. In 1980–81 the family group homes in Burwood were sold and the resources moved to the Richmond area. In 1994, Sutherland Youth and Family Services Inc. amalgamated into Berry Street Inc. During the 1990s, Berry Street combined with the Sutherland Community Resource Centre in Watsonia in Melbourne’s northern region. The agency operates today as Berry Street Victoria and has service centres across metropolitan and country Victoria. https://www.findingrecords.dhhs.vic.gov.au/CollectionResultsPage/BerryStreet -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncFolder, Eltham's new library opened 1994; local issues involved
Contents 1 Hand written note on cost of planning appeal 2 Determination re Appeal 1992/39742 by Rosalind Harris, Sigmund Jorgensen and Claire Fitzpatrick against granting of permit E92/481, 6 pages, 27 Jan 1993 3 Submission to the Appeal 1992/39742 by H. Gilham 4 Independent planning assessment for Appeal 1992/39742 by Tract Consultants, 13 pp including appendices, Jan 1993. 5 Letter from three ratepayers protesting against the siting of the proposed new library, 21 Jan 1993. 6 Statement of protest against library site by Claire Fitzpatrick, undated. 7 Impact study of proposed new library building by D.V.Bick, conservation architect, 2 October 1992. 8 assessment of impact of new library on historic significance of Shillinglaw Cottage, by National Trust of Australia, 22 October 1992. 9 Newspaper clipping, The Age, 2 Aug 1992, Scramble to revive capital works plans. 10 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 24 May 1988, New Angle to library funding 11 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 24 May 1988, Committee wants library views 12 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 24 May 1988, Library services in cash struggle 13 Library survey by Vic Ministry for the Arts, 14 December 1992 14 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 3 Aug 1992, Libraries in crisis 15 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 3 Aug 1992, Library funding editorial 16 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 7 Sept 1992, Library windfall 17 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 10 Aug 1992, Letters, Shire relies on rates to provide services, Cr J. Cohen 18 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 26 Oct 1992, Shire defends library plans. 19 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 26 Oct 1992, Letters, Library benefits whole community, J.Ilian, H. Gilham, R Harris 20 Letter to DV News by H. Gilham 20 October 1992, re library 21 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 19 October 1992, Letters, T. Malseed, Funds for region's jobless hijacked. 22 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 19 October 1992, Funds approved to build new library. 23 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 12 October 1992, Letters, Does Eltahm need a new mausoleum, M. Walker. 24 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 2 Nov 1992, Library project not haphazard. 25 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 9 Nov 1992, Letters, Library chose best architect for new project, Cr J. Cohen 26 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 16 Nov 1992, AAT to deal with library objections 27 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 30 Nov 1992, Public Notice, Registration for building trades 28 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 7 Dec 1992, Public Notice, Registration for building trades 29 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 7 Dec 1992, Letters, Find better site for library, S. Jorgensen, G.Verall 30 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 8 Feb 1993, Library given AAT aproval, and Extra funds should help make new facility more versatile 31 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 25 Jan 1993, Public Notice, Quotations invited for worls associated with new library 32 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 3 Feb 1993, Public Notice, Registration for building trades 33 Newspaper clipping, DV News, 4 January 1993, Letters, Bemused over library, C Fitzpatrick, R Henry 34 Newsletter Yarra Plenty RLS, Vol1, No 1, Your Public LibraryFolder/Booklet of various documents, mainly A4 size photocopiesHG Booklet 2administrative appeals tribunal, appeal, appeal 1992/39742, application e92/481, c. fitzpatrick, d. bick, diamond valley news, eltham library, eltham shire, g. verall, h. mccorkell, harry gilham, harry gilham collection, j. ilian, john cohen, m. walker, national trust (i. wight), r. harris, r. henry, s. jorgensen, shillinglaw cottage, parkland, rosalind harris, sigmund jorgensen, claire fitzpatrick -
 Halls Gap & Grampians Historical Society
Halls Gap & Grampians Historical SocietyMap - Coloured
Background on Bridle Path up Stony Creek Gorge Pre 1840 C. B. Hall, squatter on Mokepilly Run 1841-1842, first European to discover the Fyans Creek valley, the entrance of which became known as Hall's Gap. He later recorded that he followed a number of tracks which he assumed had been made by the Aboriginies and described one as "leading up a wild romantic glen and over on to the source of the Glenelg River". This could well have been the route taken up Stony Creek gorge by the first timber-cutters in this part of the Grampians to the saddle between the Wonderland and Mt. Difficult ranges known as Valley Gap 1850s/60s Timber cutters and shingle splitters were reported to be moving into the eastern side of the Grampians and by the mid 1860s there were a number of families connected to the supplying of timber to Pleasant Creek living in the "Hall's Gap ranges". John Wakeham, the first store owner in Pleasant Creek in 1854, established a timer-mill in upper Stony Creek Gorge in the late 1850s. Wakeham is credited for the clearing and levelling of the first bridle-path up the gorge. 1870s By the mid 1870s the track had been extended over Valley Gap to the Victoria Forest (the upper region of the Victoria Valley). McKeon's bullock team was known to have hauled red gum from the Valley to Stawell in the late 1870s and the 1880s. 1880s In 1887 an article in the Pleasant Creek news describes the Stony Creek Gorge track as "being a ledge alongside the mountain range, formed in the early days with the aid of earth and timber, along which the bullock teams used to travel to Horsham and plains of the Wimmera beyond." 1890s Gold was discovered in the catchment area of Stony Creek and by the end of the 1890s a new track was built from "near the junction of Fyan's and Stony Creeks, up the gorge to the diggings settlement. The mining Department had paid L300 for its construction and, when completed, the track was "three miles and 30 chains in length, the side cuttings at the narrowest part being 10 feet between" and "the watercourses which cross the track at various points" having been "filled up with rocks rolled down the sides of the hills, and consequently there can be no damage caused by bushfires which destroyed the former wooden bridges erected on the old track to Wakeham's saw-mill, the remains of which are still to be seen at the side of the diggings" The article goes on to further describe the track as one which "can with ease travel with a two horse conveyance either up or down" and that the workmen engaged in the construction of the track would be attending "a ball that night at McKeon's farm near the mouth of the gap to celebrate the successful completion of the undertaking". 1900s At what time the bridle path was extended beyond Valley Gap to the Wartook basin on the Mt. Difficult Range has not yet been determined. However, it is known that, by the turn of the century, people were travelling between Halls Gap and the caretakers' residence at Wartook Reservoir along what was now known as the "Bluff Road. Wartook's embankment had been constructed in 1887 and at that time there was already a track from Rosebrook Station homestead (near the present day Wartook Pottery) to the reservoir. Philip Rose owned both Rosebrook and Wartook Stations from the mid 1840s to the late 1850s and had regularly leased the Wartook basin to Cobb & Co. to rest horses there. 1920s Following the war of 1914-1918, tourism really took off in the Grampians, and Halls Gap rapidly grew. People would travel as far as they could on the many tracks then hike to the many lookouts being discovered by local tour guides. This led to the need for access across the range so that horse riders and the increasing number of vehicles could travel between Horsham and Halls Gap. To this end, the Bluff Road was improved and extended on 1929 and at its opening in March, 1930, by Lady Somers it was renamed the Mt. Victory Road.Map of Mt Victory Road and othersaccess routes, mt victory rd, bridle path, roads -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayV. R. Krupp 1888. IV. Rail, 1888
60lbs rail that was used throughout the Victorian rail network. In 1887 Gibbs, Bright and Co. had a contract with Victorian Railways for railway and canal construction and supply of Krupp Rails. Gibbs, Bright and Co were merchant bankers and shipping agents and merchants who where also Directors of the GWR ( Great Western Railway ) and the Ship The "Great Britain" in England Gibbs, Bright and Company had principally been involved in shipping and trading, mainly in the West Indies, but following the discovery of gold in Victoria they established an office in Melbourne and soon became one of the leading shipping agents and merchants in the Colony. They expanded into passenger shipping and soon established offices in Brisbane, Sydney, Newcastle, Adelaide and Perth as well as launching passenger services between England, Mauritius and New Zealand. Gibbs, Bright also held a number of financial agencies from British mortgage, finance and investment companies as well as representing several British insurance companies in Australia. In addition they conducted a growing import business as well as an export business that included livestock, dairy produce, wool and flour. Also the company played a substantial part in the development of Australia's mineral resources, starting with lead in 1895, and later venturing into tin, gold, copper, cement and super phosphates. In Australia, after WWI, many of the larger companies were managing their own import and export so Gibbs, Bright and Company tended to focus its Agency business on smaller companies while expanding their interest into other markets such as timber, wire netting, zinc, stevedoring, road transport, marine salvage, gold mining as well as mechanical, structural, electrical and marine engineering. The Company's shipping interests continued to grow as well and still formed a major part of its business. In 1948 the parent company in England took the major step from tradition when they changed the business from a partnership into a private limited company. The name was the same, Antony Gibbs and Sons Limited, and in practice the effect of the change was very little. Some of the firm's branches and departments had already become limited companies and the formation of a parent company simplified the structure. The Australian operation was in time changed to Gibbs Bright & Co Pty Ltd in 1963. In 1848 Alfred Krupp becomes the sole proprietor of the company which from 1850 experiences its first major growth surge. In 1849 his equally talented brother Hermann (1814 - 1879) takes over the hardware factory Metallwarenfabrik in Berndorf near Vienna, which Krupp had established together with Alexander Schöller six years earlier. The factory manufactures cutlery in a rolling process developed by the brothers. Krupp's main products are machinery and machine components made of high-quality cast steel, especially equipment for the railroads, most notably the seamless wheel tire, and from 1859 to an increased extent artillery. To secure raw materials and feedstock for his production, Krupp acquires ore deposits, coal mines and iron works. On Alfred Krupp's death in 1887 the company employs 20,200 people. His great business success is based on the quality of the products, systematic measures to secure sales, the use of new cost-effective steel-making techniques, good organization within the company, and the cultivation of a loyal and highly qualified workforce among other things through an extensive company welfare system. From 1878 August Thyssen starts to get involved in processing the products manufactured by Thyssen & Co., including the fabrication of pipes for gas lines. In 1882 he starts rolling sheet at Styrum, for which two years later he sets up a galvanizing shop. The foundation stone for Maschinenfabrik Thyssen & Co. is laid in 1883 with the purchase of a neighboring mechanical engineering company. In 1891 August Thyssen takes the first step toward creating a vertical company at the Gewerkschaft Deutscher Kaiser coal mine in [Duisburg-]Hamborn, which he expands to an integrated iron and steelmaking plant on the River Rhine. Just before the First World War he starts to expand his group internationally (Netherlands, UK, France, Russia, Mediterranean region, Argentina). info from The company thyssenkrupp - History https://www.thyssenkrupp.com/en/company/history/the-founding-families/alfred-krupp.htmlHistoric - Victorian Railways - Track Rail - made by Krupp in 1888Section of VR Krupp 1888 Rail mounted on a piece of varnished wood. Rail made of ironpuffing billy, krupp, rail, victorian railways -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Retirement of Alan Sonsee, 1976, 08/1976
Born in 1911, Cecil Alan Sonsee lived at Springmount near Creswick, and taught natural history at the Ballarat Teachers' College for 30 years. His teaching career stretched over a 48 year period. He spent six years as a student teacher before reaching the position of first class teacher. He had the distinction of never attending a teachers' college, but spending half his teaching career training students to become teachers. At the time of his retirement Mr Sonsee said during his years at the college, "the training had changed from a one year course to a two year course, followed by a three year course, and now a four year course was offered." He recalled "in the early days all country schools had eight grades and a child finished with a merit certificate. Today [1976], children went to high schools from sixth grade and most of the country schools had disappeared.' Alan Sonsee spent 10 years on a television program on BTV6 answering questions sent by viewers regarding aspects of plant and animal live. Mr Sonsee was a life member of both Creswick and Ballarat Field naturalists Clubs. Alan Sonsee died in 1985.1) Foolscap Department of Victoria Ballarat newsletter titled Education 'Regional Views'. The newsletter depicts an image of Alan Sonsee and outlines his career at the time of his retirement on 20 July 1976. The author of the newsletter is unknown. .2) newspaper article on the retirement of Alan Sonsee dated 25 August 1976 (probably from the Ballarat Courier).1) Mr "Nature Man" Retires After a quiet celebration, Mr C.A. Sonsee, a well-known staff member at Ballarat State College, retired from the Victorian Education Department on 20th July, 1976. Alan was the longest serving primary teacher seconded to the State College (Formerly the Ballarat teachers' College), probably the best known and certainly one of the most highly respected educationalists in this region. Leaving Ballarat high School in 1927, he spent the following years teaching at Smeaton, Willowvale, Lawrence (originally called Jerusalem) and Kooroocheang primary schools. However, during the last twenty-nine years, his fame and his influence spread further and further afield. From 1947 to 1976, under a number of principals, Alan endeared himself to thousands of students undergoing their tertiary preparation for teaching. And thousands is the word! Hundreds and hundreds of practising teachers of all ages came to this great teacher again and again for assistance in understanding natural phenomena, a broad field in which he is an acknowledged expert. What undoubtedly made him so accessible to the young and the no-so-young alike was his ready willingness to share with them is rich experience. The warmth of his nature, his kindliness, his dry humour enriched and enlivened the gifts he lavished liberally on all who needed help. Nor did he spare himself in the process. During his ling period of service to teachers, students and some two generations or so of school children, Field Naturalists also, within and well beyond Ballarat, profited from his participation and guidance. A car trip from Ballarat to Lancefield was made unforgettable by Alan's running and lively commentary; the time spent with him viewing and fossicking in an aboriginal flint area is still vivid, thouhg many moons have waxed and waned since then. And who can ever forget his palcid, home;y handling of "Mr nature Man" programmes on BTV 6 for over ten years? his name became a hose-hold word over an existence viewing area in Western Victoria - as his mail bag showed. Mr T. Turner was closely associated with C.A.S. for some twenty-three years as colleague and college principal. Recently tome said, "Alan was highly esteemed by staff and students, When I saw him lecturing I would be struck by the depth and breadth of his knowledge, and by the smooth, almost deceptively simple way he shared what he knew with others. I remember, too, his consideration for the views and the feelings of others; for the tolerance and range of his understanding of human nature. But, above all else, I remember him as a friend." All who know him in any way at all will want to say, "Thanks you, Alan, for everything you did for us. Thank you, Alan for what you are."alan sonsee, ballarat teachers' college, ballarat state college, education, teaching, ballarat field naturalists, creswick field naturalists, aborigines, lancefield flint, smeaton primary school, willowvale primary school, lawrence primary school, jerusalum primary school, kooroocheang primary school, nature studies, mr nature man
