Showing 257 items
matching may 1942
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Scrapbook, Ballarat School of Mines Scrapbook, 1936-1948, 1936-1948
The Ballarat School of Mines was the first school of mines in Australia.Exercise books of newspaper clippings relating to the Ballarat School of Mines. Clippings include: 12 Feb 1936 - State Scholarships 12 March 1936 - Dr J.R. Pound 19 March 1936 - MacRobertson Scholarship 23 March 1936 - gift to the museum - Wardle and Jermyn donate timber specimens 11 May 1935 - A.W. Steane 13 June 1936 - Frederick Longhurst appointed art instructor 27 July 1936 - Ballarat Junior Technical School Reunion 11 Sept 1936 - Wiltshire Poster Competition 30 Oct 1936 - Dressmaking classes 20 NOv 1936 - Nornie Gude NOvember 1936 - Ballarat School of Mines Reunion 16 March 1937 - Oval for Ballarat Junior Technical School - White Flat 11 Nov 1937 - Poster competition - Betty Brown and Albino Paganetti 08 Feb 1938 - Frederick J. Martell obituary 07 July 1938 - Henry Kum-Yuen 14 July 1938 - Red Cross Competition for Women 06 Aug 1938 - School Pine Plantation at Vale Park 19 Aug 1938 - Memorial trees planted at Ballarat Junior Technical School to the memory of Cliff Ellis and Ken Butler 06 March 1939 - Ballarat School of Mines Reunion 16 May 1939 - Ballarat School of Mines Battery 19 April 1940 - Progress of Technical Education - New Engineering workshop opended by Sir John Harris 03 June 1940 - W.H. Middleton obituary 16 July 1940 - Training munition workers 30 May 1941 - Lady Tracers 19 Oct 1942 - War Poster competition 24 February 1944 - Ballarat School of MInes Record Enrolments Feb 1944 - D.F.C. for Ballarat Airman H.J. Trevenen 11 Feb 1945 - Harold Herbert Obituary 14 Oct 1945 - Technical Schools in Wartime 23 Feb 1946 - Molasses and Chaff for SMB Initiates 06 June 1946 - Plans for Victory Ball 13 Sept 1946 - Ken Walker sculpts Prime Minister Chifey's bust 23 Aug 1946 - Edgar McConnon obituary 24 Oct 1946 0 Retirement of A.F. Heseltine 25 Nov 1946 - Army huts for classrooms 12 Dec 1946 - Proposed New Theatre for Ballarat by Geoff Richards 16 Dec 1946 - Ballarat Junior Technical School Old Boys who served in armed forces during World War Two 28 July 1947 - Pottery section at Ballarat School of Mines 31 July 1947 - Red Cross Hut removed to the Ballarat School of Mines 10 March 1948 - Guncotton Factory buildings to become nurses quarters 18 March 1948 - Samuel Mayo Obituary ballarat school of mines, ballarat techncial art school, swimming shield, ballarat school of mines museum, ballarat war museum, sydney pern, t.m. pescott, c.w. brazenor, victory ball, w. rowe, joan walker, graeme dowling, ken walker, prime ministers' avenue, ben chifley, amalie feild, amalie colquhoun, h.h. smith, portrait, girls' preparatory classes, world war two, w. williams, raaf, w.s. williams, william william, william williams, new workshops, herbert j. trevenen, harold herbert death, les crouch, swimming, ballarat city baths, heather scott, clunes hospital nurses' quarters, ballarat ladies' art association scholarships, samuel henry mayo, samuel mayo death, girls preparatory classes, w. william, pilot, killed in action, education reform, ballarat schoool of mines museum, h.j. trevenen, world war ii, world war 2, ballarat junior technical school war service, nurses quarters, guncotton factory building, s. mayo death, initiation, ballarat school of mines scrapbook, newsclippings, j.r. pound, macrobertson scholarship, a.w. steane, ballarat junior technical school, wiltshire's poster competition, ballarat junior technical school old boys' association, ballarat junior technical school old boys' reunion, nornie gude, a. nye, albino paganettu, betty brown, dorothy woolcock, jean coates, jack hewitt, hazel robinson, gilda gude, white flat oval, gauge tower demolition, a.f. hesiltine, darwin, victor greenhalgh, frederick martell, memorial trees, cliff ellis, valda king, pharmacy, reunion, engineering workshops, thomas k. sim, daylesford, battery, h.h. smith reunion, ballarat technical art school reunion, w.h. middleton obituary, munition makers, plumbers, pottery industry, girls education, munition trainees, lady tracers, waterloo prize money, war museum, art as vocation, art education, nine-inch telescope, returned soldiers' league, repatriation classes, pinkertson scholarship, amel robert gordon, projector, pethard cup, ballarat food appeal for britain, queen mary, ballarat swimming pool, ballarat school of mines initiation, swimming carneval, prime ministers avenue, edgar mcconnon, community theatre project, world war two service, john l. burt, hockey, pottery, ceramics, ballarat school of mines coat of arms, coat of arms, k. bremner, red cross hut, s.m.b. follies, ken palmer, s. mayo, chinese, albert steane, university women, a.f. heseltine, student activity, swimming sports, albino pagnetti, w.h. middleton death -
 Red Cliffs Military Museum
Red Cliffs Military MuseumLetter
Letter written from (unknown) POW imprisioned by the Japanese on Morotai Island from 1942 - 1945 to (unknown) friend. Descriptive of life and treatment in POW camp. The island was captured by the Japanese in early 1942. Morotai's southern plain was taken by American forces in September 1944 during the Battle of Morotai, and used as a staging point for the Allied invasion of the Philippines in early 1945, and of Borneo in May and June of that year. Japanese soldier Teruo Nakamura was discovered in the Morotai jungle in 1974, as one of the WWII Japanese soldiers who held out subsequent to the Japanese military's surrender.Photocopy of letter, 4 pages, originally written in ink on (unofficial) Australian Red Cross form.Added to head of letter at a later date is inscription ' First letter written home for 3 1/2 years'.Top left hand- FOR SAFETY/ IN YOUR LETTERS DO NOT REFER TO:-/ The name of your ship or other ships in the convoy, or its escorts./The date of sailing, ports of call, or probable destination./ The description of troops, their loca-/tion or any other information/ which, if intercepted, would be of/ value to the enemy. In your Top right hand- Australian Red Cross Society/ (UNOFFICIAL)/ 25-8-45/ (added at later date 'Morotri Island')/ Alex, Have witten this especially/ as i don't wish our women folk to know the tougher side of life./Well Alex for the first/ 2 1/2 years as POWs we lived reasonably/ well, but the last 15 months was like /hell. Heres the worst lot of b-s/ you could find on earth, they worked /us from 7AM till 6 PM, & fed/ us on muck you wouldn't feed to/ Pigs. I'm nothing at all they would 2, pow, morotri island, morotai island, world war, prisoner of war, australian red cross society -
 Australian Commando Association - Victoria
Australian Commando Association - VictoriaBook, The Private War of the Spotters: A history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company, February 1942-April 1945
... the three years of its existence. In May 1942 a network was set up ...The history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company. This reprinted version contains a map of the dispositions of Spotting Stations August 1943, additional MID awards listed and some additions to the nominal roll. The New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company was formed in Port Moresby in late January 1942 and was granted “Separate Independent Establishment” status in October 1943. The company’s “founding father” was Major Don Small, who had witnessed Japanese air raids on Rabaul and realised that having lacked an effective early-warning system around New Britain meant that the defenders were taken by surprise. At the time, gaps had also appeared in the coast-watching communications network because the territory administration ordered the withdrawal of civilian wireless operators when Japan entered the war. The first influx of men into the company consisted largely of volunteers from the 39th Infantry Battalion, which was stationed at Port Moresby. Initial training was rudimentary, hasty, and was sometimes even carried out on en route to a new station. The first party of company personnel, or “spotters”, left Port Moresby as early as 1 February 1942, bound for the strategically important Samarai area, at the tip of Papua. In the first month of the company’s existence 16 spotter stations were established on the coast of Papua and in the mountains around Port Moresby. At the end of 1942 there were 61 operational stations being run by 180 men. The company’s high-water mark was in late 1944, by which time over 150 stations had been set up in Papua and New Guinea behind enemy lines. On 3 February 1942 the company issued its first air warning in Papua, when spotters at Tufi saw Japanese aircraft about to attack Port Moresby for the first time. The following month the company was responsible for the first Japanese killed in action in Papua by Australian ground forces, when spotters from Gona engaged the crew of a downed Japanese bomber. And in July 1942 the station at Buna signalled Port Moresby with news of the Japanese landings in Papua, marking the beginning of the Kokoda campaign. The dangers involved in the company’s work had also been made clear by this time. In July 1942 a party of spotters attempting to set up a station at Misima Island, off Milne Bay, was intercepted by a Japanese destroyer, resulting in the company’s first operational losses. Anticipating the direction of the campaign as a whole, the company’s focus moved north and north-west over the three years of its existence. In May 1942 a network was set up in the Wau area in association with the activities of Kanga Force. As part of the Wau network, spotter Ross Kirkwood audaciously constructed an observation post overlooking the Japanese airstrip at Salamaua. Kirkwood’s position was photographed by Damian Parer on the understanding that the pictures would not be published. They nevertheless appeared in a Sydney newspaper. The day after the publication of the photographs the observation post was attacked by the Japanese and Kirkwood was lucky to escape. In June 1944 the company’s headquarters were moved to Nadzab. By that time, spotter stations existed behind Japanese lines, as far north as Hollandia, and the company began to train Americans to perform similar work in the Philippines. In early 1945 the company moved to Balcombe, Victoria, where its members were posted to other units of the Australian Corps of Signals.gray plasticnon-fictionThe history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company. This reprinted version contains a map of the dispositions of Spotting Stations August 1943, additional MID awards listed and some additions to the nominal roll. The New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company was formed in Port Moresby in late January 1942 and was granted “Separate Independent Establishment” status in October 1943. The company’s “founding father” was Major Don Small, who had witnessed Japanese air raids on Rabaul and realised that having lacked an effective early-warning system around New Britain meant that the defenders were taken by surprise. At the time, gaps had also appeared in the coast-watching communications network because the territory administration ordered the withdrawal of civilian wireless operators when Japan entered the war. The first influx of men into the company consisted largely of volunteers from the 39th Infantry Battalion, which was stationed at Port Moresby. Initial training was rudimentary, hasty, and was sometimes even carried out on en route to a new station. The first party of company personnel, or “spotters”, left Port Moresby as early as 1 February 1942, bound for the strategically important Samarai area, at the tip of Papua. In the first month of the company’s existence 16 spotter stations were established on the coast of Papua and in the mountains around Port Moresby. At the end of 1942 there were 61 operational stations being run by 180 men. The company’s high-water mark was in late 1944, by which time over 150 stations had been set up in Papua and New Guinea behind enemy lines. On 3 February 1942 the company issued its first air warning in Papua, when spotters at Tufi saw Japanese aircraft about to attack Port Moresby for the first time. The following month the company was responsible for the first Japanese killed in action in Papua by Australian ground forces, when spotters from Gona engaged the crew of a downed Japanese bomber. And in July 1942 the station at Buna signalled Port Moresby with news of the Japanese landings in Papua, marking the beginning of the Kokoda campaign. The dangers involved in the company’s work had also been made clear by this time. In July 1942 a party of spotters attempting to set up a station at Misima Island, off Milne Bay, was intercepted by a Japanese destroyer, resulting in the company’s first operational losses. Anticipating the direction of the campaign as a whole, the company’s focus moved north and north-west over the three years of its existence. In May 1942 a network was set up in the Wau area in association with the activities of Kanga Force. As part of the Wau network, spotter Ross Kirkwood audaciously constructed an observation post overlooking the Japanese airstrip at Salamaua. Kirkwood’s position was photographed by Damian Parer on the understanding that the pictures would not be published. They nevertheless appeared in a Sydney newspaper. The day after the publication of the photographs the observation post was attacked by the Japanese and Kirkwood was lucky to escape. In June 1944 the company’s headquarters were moved to Nadzab. By that time, spotter stations existed behind Japanese lines, as far north as Hollandia, and the company began to train Americans to perform similar work in the Philippines. In early 1945 the company moved to Balcombe, Victoria, where its members were posted to other units of the Australian Corps of Signals.world war ii, special operations, new guinea, new guinea air warning wireless company -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyDocument - Folder, Landata Certificates - Part of Crown Portion Six, (Lots 1-4 and numbers 70-90) Maroondah Highway, Parish of Ringwood, Victoria
27 A4 pages of colour photocopied certificates with typewritten summaries, including Certificate of Title Vol 1156 Fol 231096, 8th March 1880. Certificate of Title Vol 1440 Fol 930, 14th March 1883. Certificate of Title Vol 8487 Fol 090, 28th January 1964. Certificate of Title Vol 9019 Fol 634, 5th December 1973. Certificate of Title Vol 3711 Fol 742129, William John Harnwell, 1st August 1913. Certificate ot Title Vol 6552 Fol 1310305, 5th June 1942. Certificate of Title Vol 5282 Fol 1056207, Arthur Clifton Beilby, 19th July 1927. Certificate of Title Vol 6573 Fol 1314497, Florence Beatrice McGoldrick, Lot 4 on Subdivision 14786, Whitehorse Road, Ringwood, 18th August 1942. Proprietors and transferees include: William Astley of Richmond, Compositor, Marianne Thomson of Jolimont, Spinster, Margaret McGillivray of Ringwood, Spinster, George Frederick Burgess Wilsmore of Ringwood, Railway Employee, Leslie Wilsmore, John Wilsmore, Lionel Wilsmore, 90 Whitehorse Road Ringwood, B.T. Building Aust P/L, Lot 1 of subidivision 35788, Whitehorse Road Ringwood, Maliblue P/L 33-35 Ruthven Way Ringwood East, Hesketh Motor Cycles P/L, 70 Maroondah Highway Ringwood, Arthur Clifton Beilby of Ringwood, Storekeeper, Florence Beatrice McGoldrick and Oscar Edward John McGoldrick of "Carrum", Whitehorse Road Ringwood, Elsie May McGoldrick, 82 Whitehorse Road Ringwood, Douglas Murray and Ronald Arthur Mason, H.W.P Tortice and D.M. Tortice, V.B. Rowe. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Leather, luggage straps and labels c1916, 20thC
Leather straps were commonly used to secure cases and other forms of luggage when traveling. The labels enabled easy identification when collecting luggage from transport carriages, coaches, buses and trains. 10th Field Company, Australian Engineers WW1 1914-18. The 10th Brigade was an infantry brigade of the Australian Army. Originally formed in 1912 as a Militia formation, the brigade was re-raised in 1916 as part of the expansion of the Australian Imperial Force following the end of the Gallipoli campaign. It subsequently saw service on the Western Front in France and Belgium during the First World War. After the war it was disbanded but was re-raised in 1921 as a part-time formation based in the state of Victoria. During the Second World War the brigade was used in a garrison role in Australia before being disbanded in 1942.These leather straps and labels were attached to the luggage of an Australian soldier during early 20th C who may have been a resident or relative of a resident in City of MoorabbinLeather luggage straps with metal buckles and 3 luggage address labels attached.Label 1 - L.D.McCallum Sgt / 10th Fd Coy AE Label 2 - Healesville Label 3 - Maryborough leather, straps, belts, luggage labels, tools, saddles, wallets, personal effects, horses, drays, world war 1 1914 -18, world war 2 1939-45, army, 1st aif, military, 10th field company australian engineers, western front, france, belgium, -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CABINET PORTRAIT OF A BOY & GIRL
Cabinet Portrait of a boy and a girl. The girl, Ivy May Muriel Dower (Born 1891 Bendigo, Died 1980.), is seated on a wicker couch and holding a doll. The boy Jack is John Adrian Dower, (Born 1893 Rochester, Died 1952 Paynesville) is standing to the front of the couch and holding a bat? On the back is written: To Grandma (Elizabeth Dower (Born 1833) from Ivy & Jack. Parents of Jack and Ivy are (James Martin Dower Born 1859, Fryers Creek, Victoria and Died 11th October 1942 at Brighton. Mother was Florence Amy Chalmer, Born 1867, Sandhurst, Vic, Died 13th August , Brighton Vic.1953). Dowar, Dunstan and Opie names are related and are associated with Bendigo district. The photo is part of an album with other members not identified as yet. Coincidentally Neville Davies from the BHS has this photo in his family history photographs. Contact Neville for details of who Ivy and Jack and Grandma actually are. Neville Davies provided information for the above.Alan Spicer, Bendigophotograph, portrait, dower family, cabinet portrait of a boy & girl, alan spicer bendigo, dower, dunstan and opie families related. part of an album. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - COHN BROTHERS COLLECTION: ENVELOPE ADDRESSED TO COHN'S SECRETARY
... and Shipping re Crown Seals 1942. Return furnished May 1943. [b... to Cohns Secretary dated 21st Oct 1942. Handwritten caption ...[a] Manilla envelope addressed to Cohns Secretary dated 21st Oct 1942. Handwritten caption 'The Department of Supply and Shipping re Crown Seals 1942. Return furnished May 1943. [b] Pinned documents enclosed pertaining to above.bendigo, industry, cohn bros brewery -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - CARWARDINE COLLECTION: INFORMATION RE COLLECTION
Handwritten note from Tim Gibson, a descendant of the original Cawardine family, has donated the items in the Carwardine Collection (Cat No. 3401). CARWARDINE, Walter Henry Walter Henry Carwardine Groom: Walter Henry CARWARDINE. Bride: Elizabeth Arnold THORPE. Year married: 1863. Place: Victoria, Australia. Walter died 1923 in Caulfield, Victoria. Age: 89 years. Parents named as John CARWARDINE and Charlotte WILCOX. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon G1. Grave number: 21110. Service date: 03 June 1923. Elizabeth Arnold Carwardine (Thorpe) Died 1911 in Bendigo, Victoria. Age: 70 years. Parents named as Joseph THORPE and Jane ARNOLD. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon G1. Grave number: 21110. Service date: 19 May 1911. Eleven children located Victorian records for Walter and Elizabeth. 1. Henry Thorpe CARWARDINE. Born: 1864 Dunolly, Victoria. Birth recorded under CAWARDINE. Died: 1916 Bendigo, Victoria. Age: 52 years. Married: Jessie Mary Jean BURNS. Year: 1891. Place: Victoria. See Post: CARWARDINE Henry married Jessie BURNS 1891 2. Hugh Wilcox CARWARDINE. Born: 1866 Dunolly, Victoria. Died: 1952 Bendigo, Victoria. Age: 86 years. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon G1. Grave number: 21110. Service date: 22 May 1952. 3 Guy CARWARDINE. Born: 1867 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 1942 Cohuna, Victoria. Age: 74 years. Married: Minnie LANSELL. Year: 1892. Place: Victoria. Minnie was born 1863 in Sandhurst, Victoria. Parents named as William LANSELL and Jane Crouch ANDERSON. Minnie died 1954 in Cohuna, Victoria. Age: 91 years. Parents named as William LANSELL and Jane Crutch ANDERSON. 4. Mary Charlotte Arnold CARWARDINE. Born: 1869 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 1942 Bendigo, Victoria. Age: 72 years. Married: Luther Edwin Goldsmith BRIGHT. Year: 1891. Place: Victoria. Luther was born 1865 in Ballarat, Victoria. Parents named as Alfred Goldsmith BRIGHT and Sophia JACOBSON. Luther died 1892 in Prahran, Victoria. Age: 26 years. Parents named as Alfred Goldsmith BRIGHT and Siphia Goldsmith JACOBSON. 5. John CARWARDINE. Born: 1871 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 1871 Sandhurst, Victoria. Age: 02 days. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon C4. Grave number: 3881. Service date: 17 April 1871. 6. Thomas Brunsdon CARWARDINE. Born: 1872 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 1876 Sandhurst, Victoria. Age: 03 years. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon C4. Grave number: 3881. Service date: 07 April 1876. 7. Rose Elizabeth CARWARDINE. Born: 1874 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 09 October 1963, Ravensthorpe, Western Australia. Age: 89 years. Buried: Karrakatta Cemetery, Western Australia. Area: Anglican. Section: ZU. Gravesite: 0356. Grantee: Muriel Carwardine ARCHER. Married: Arthur Sydney CHAMBERS. Year: 1905. Place: Ravensthorpe, Western Australia. Arthur died 1950, Williams district, Western Australia. 8. Walter Henry CARWARDINE. Born: 1876 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 1937 Bendigo, Victoria. Age: 60 years. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon H6. Grave number: 30803. Service date: 11 February 1937. Married: Flora Constance HILL. Year: 1906. Place: Victoria. Flora was born 1876 in Bendigo, Victoria. Parents named as Frederick HILL and Mary Ann KERSHAW. Flora died 1959 in Bendigo, Victoria. Age: 84 years. Parents named as Frederick HILL and Mary Ann KERSHAW. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon H6. Grave number: 30803. Service date: 13 October 1959. 9. James Arnold CARWARDINE. Born: 1878 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 1947 Heidelberg, Victoria. Age: 69 years. Cremated: Fawkner Memorial Park, Victoria. Service date: 06 September 1947. Cremated remains location: Not recorded. First World War Embarkation Roll. Name: James Arnold CARWARDINE. Service number: 4158. Rank: Private. Roll title: 6 Infantry Battalion - 13 to 18 Reineforcements. (Dec 1915 - July 1916) Conflict: First World War, 1914-1918. Date of embarkation: 29 December 1915. Place of embarkation: Melbourne. Ship embarked on: HMAT Demosthenes. Ship number: A64. Married: Frances Georgina TURNER. Year: 1919. Place: Victoria. Frances was born 1875 in Eaglehawk, Victoria. Parents named as James Perriman TURNEER and Caroline GORDEN. Frances died 1956 in Brighton, Victoria. Age: 76 years. Father named as James TURNER. Mother unknown. Cremated: Fawkner Memorial Park, Victoria. Service date: 29 November 1956. Cremated remains location: Rose Garden 02. 10. Albert Augustus Arnold CARWARDINE. Born: 1880 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 1885 Sandhurst, Victoria. Age: 05 years. Buried: Bendigo Cemetery, Victoria. Area: Mon C4. Grave number: 3881. Service date: 18 July 1885. 11. George Frederick Brunsdon CARWARDINE. Born: 1888 Sandhurst, Victoria. Died: 02 August 1916, France. First World War Embarkation Roll. Name: George Frederick CARWARDINE. Service number: 3794. Rank: Acting Sergeant. Roll title: 24 Infantry Battalion - 9 to 12 Reinforcements. (Feb-April 1916) Conflict: First World War, 1914-1918. Date of embarkation: 08 February 1916. Place of embarkation: Melbourne. Ship embarked on: HMAT Warilda. Ship number: A69. First World War Roll of Honour. Name: George Frederick Brunston CARWARDINE. Service number: 3794. Rank: Private. Unit: 24th Battalion. (Infantry) Service: Australian Army. Conflict: 1914-1918. Date of death: 02 August 1916. Place of death: France. Cause of death: Killed in action. Cemetery or memorial details: Villers-Bretonneux Memorial, France. Sources: Registry of Births, Deaths and Marriages Victoria. Registry of Deaths and Marriages, Western Australia. Bendigo Cemetery Records, Victoria. Fawkner Memorial Park Cemetery Records, Victoria. Karrakatta Cemetery Records, Western Australia. First World War Embarkation Rolls. AWM145 Roll of Honour cards, 1914-1918 War, Army.bendigo, business, carwardine soap and candle -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ARMY HEADQUARTERS SURVEY REGIMENT, BENDIGO, 10 May, 1964
Army Headquarters Survey Regiment, Bendigo. Public Inspection at 'Fortuna', 10 May 1964. Donation 2/-. Includes photos of the Entrance Hall, Music Room and Villa. 3 army photos. In 1942 the mansion was occupied by the Australian Survey Corps and 'Fortuna' became the site of the base map production plant of the Australian Army for the remainder of the war years. During this period approximately sixteen million maps of Australian Territories and theatres of operation in the South West Pacific Area, were produced for use by the Allied Services. This function was continued as a peace time role in the post war years, and in 1951 ''Fortuna'' was purchased by the Commonwealth Government. As the largest unit of the Royal Australian Survey Corps, AHQ Survey Regiment carries out mapping in all parts of the Commonwealth and Territories including Papua and New Guinea. The Regiment is not only capable of doing its own field surveys but is responsible for the drawing and printing of map compilations from Royal Australian Survey Corps units in all States. . . . Includes map of grounds.buildings, residential, fortuna villa, army headquarters survey regiment, bendigo. public inspection at 'fortuna', 1964. photos of the entrance hall, music room and villa. mansion was occupied by australian survey corps and 'fortuna' site of the base map production plant australian army war. sixteen million maps australian territories and theatres of operation in the south west pacific area, were produced for use by the allied services. 1951 ''fortuna'' was purchased by the commonwealth government. royal australian survey corps, ahq survey regiment mapping commonwealth and territories including papua and new guinea. royal australian survey corps units in all states. map of grounds -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPhotograph - School photos
Photocopy of 3 small black and white photos, school photos 1. - Nott Street, 1427, 1941 2. - Kingsville 3988, grade 11, 1938 (may not be relevant to Port melb) 3. Nott St 1427, 1942 Grade V1Beducation - primary schools, nott street state school, kingsville primary school -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyFinancial record - Wage rates, Waterside Workers, 1942
Waterside Workers Wage Rate Book, 1942piers and wharves - waterside workers, percy allan may -
 Tramway Heritage Centre
Tramway Heritage CentrePhotograph Album (part of), Ray Pearson's Photo Album - Trams of Victorian Railways, Ballarat, Bendigo, Geelong
Page 3 of Ray Pearson's Photo Album. Brown card page with two metallic look postcards (landscape format) placed on page using clear plastic photo corners. Both postcard images depict trams in Ballarat. The bottom postcard has come loose of two of it's photo corners (top and bottom on the right) and is not secure on the page. A hand written inscription is written in pencil behind the bottom photograph.Hand written inscription in pencil behind postcard at base of page: W.4. Printed text to left of image on bottom postcard: BALLARAT TRAMS / 1887 to 1971 / A series of four postcards. / NO. 3 LATER ELECTRIC TRAM SYSTEM / In 1934 the State Electricity / Commission took over the Bal- / larat trams from the Electric / Supply Company of Victoria. / During 1935-37 the whole sys- / tem was reconditioned by the / Commission. / For the Coronation of King / George VI, No. 28 was decor- / ated for the occasion. It ran / for three days – 12th, 13th / and 14th May, 1937, and was / painted red and cream. / During the Coronation cele- / brations of Queen Elizabeth II, / the trams carried two flags / mounted vertically fore and aft / on the roof. / Some huge loads were / carried during the second / World War period and owing / to man power shortages, con- / doctresses were employed / from September, 1942 to July, 1946. At one time, the total / reached 23. Printed text to back of bottom postcard: BALLARAT TRAMS / 1887 to 1971 / A series of four postcards. / In the early fifties, loading / on the trams was heavy. When / the lag in housing was over- / taken, however, breadwinners / started to leave the trams and / travel to work in cars. Increas- / ing affluence in the sixties ac- / centuated the trend. Soon the / trams were running with mount- / ing annual losses. Most of the / passengers travelling in these / times were concession holders: / students, pensioners, deserted / wives and T.P.I.'s A fine printed vertical line runs down the centre of the blank writing space to the left of the body text. Above is written: POSTCARD postcard, coronation, ray pearson, vintage trams, ballarat tramway, tram postcard, female conductors, suttons, ballarat tram -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Fremantle Arts Centre Press, The Cocos Islands mutiny, 2001
... A significant World War Two mutiny took place on the night of 8 May 1942 ...A significant World War Two mutiny took place on the night of 8 May 1942 in a lonely atoll in the Indian Ocean in a setting of intrigue, rebellion and the blood and tears of war. Japanese naval forces were at the peak of their southward thrust." "While the battle of the Coral Sea raged, gunners of the Ceylon Garrison Artillery on the Cocos (Keeling) Islands off Australia's north-west coast attempted to arrest their British commanding officer and compel him to surrender to the Japanese. One soldier was killed and another wounded, but the mutiny failed and seven men were condemned to death. Ultimately three soldiers were hung, becoming the only Commonwealth troops to be executed for mutiny in World War TwoBib, ill, maps, p.248.non-fictionA significant World War Two mutiny took place on the night of 8 May 1942 in a lonely atoll in the Indian Ocean in a setting of intrigue, rebellion and the blood and tears of war. Japanese naval forces were at the peak of their southward thrust." "While the battle of the Coral Sea raged, gunners of the Ceylon Garrison Artillery on the Cocos (Keeling) Islands off Australia's north-west coast attempted to arrest their British commanding officer and compel him to surrender to the Japanese. One soldier was killed and another wounded, but the mutiny failed and seven men were condemned to death. Ultimately three soldiers were hung, becoming the only Commonwealth troops to be executed for mutiny in World War Twomutiny, world war 1939-1945 - sri lanka -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Photograph: CTS Boxing team c1940s, Photograph of Collingwood Technical School Boxing team 1940s
Photograph of Collingwood Technical School Boxing team. Undated. Collingwood won the trophy in 1932, 1933, 1934, 1939, 1942-1947. Estimate this photo may be in the 1940s.collingwood technical school, students, staff, nmit, -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MCCOLL, RANKIN AND STANISTREET COLLECTION : EAST CLARENCE GOLD MINING CO NL, 1934
McColl Rankin & Stanistreet, East Clarence Gold Mine Company NL, The Bank of England Scottish Australian Bank Ltd Pass Books a/ dated Aug 10, 1934 to May 15, 1940. Inscriptions: East Clarence Gold Mining Coy No Liability Bendigo page 53 789. b/ May 16, 1940 to January 17, 1942. Inscriptions: East Clarence Gold Mining Co NL. c/ Jan 20. 1942 to June 30, 1944. Each has green fabric cover tho a/ appears to have a wax coating.organization, business, gold mine, mccoll rankin & stanistreet, east clarence gold mine nl pass book the australian scottish & australian bank bendigo -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Australian Broadcasting Corporation, P.O.W. : prisoners of war, 1985
Within three months of the Japanese entering World War II on December 8, 1941 over 22 000 Australians had become prisoners-of-war. They went into camps in Timor, Ambon, New Britain, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Singapore and Malaya, and a few were scattered to other points in what was briefly part of the Japanese empire. Later most of the prisoners were to be shifted further north into South-east Asia, Formosa, Korea, Manchuria and Japan itself. They were captives within lands and cultures and to experiences alien to those known to all other Australians. At the end of the war in August 1945, 14315 servicemen and thirty service women were alive to put on new, loose-fitting uniforms and go home. One in three of the prisoners had died. That is, nearly half of the deaths suffered by Australians in the war in the Pacific were among men and women who had surrendered. Another 8174 Australians had been captured in the fighting in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa: but of these men only 265 died as a result of wounds, disease or execution.By any quantitative measure the imprisonment of so many Australians is a major event in Australian history. For many soldiers it was living --and dying --in captivity which made World War II different from that of World War I. But the prisoners have received no permanent place in Australian history. Their story is not immediately recalled on celebratory occasions. In a general history of the nation in which a chapter is given to the war the prisoners might be mentioned in a sentence, or part of a sentence. Where the horror, stoicism and gallantry of Gallipoli have become part of a common tradition shared by all Australians, the ex-prisoners are granted just the horror. The public may be sympathetic; but the horror is for the prisoners alone. To make another comparison: in five months of fighting on the Kokoda Trail in 1942 the Australians lost 625 dead, less than the number who died on Ambon. Yet the events on Ambon are unknown to most Australians. There were no reporters or cameramen on Ambon and, for the 309 who defended Ambon's Laha airfield, no survivors. How many of them died in battle or died as prisoners will never be known. But there are more than just practical reasons why the record of the prisoners of war is so slight and uneven in the general knowledge of Australians. They have not tried to find out. No historian has written a book to cover the range of camps and experiences, and only in specialist medical publications has anyone investigated the impact of prison life on subsequent physical and mental health. The complexity of the experience and its impact on particular lives have not been expressed in a way to give them significance for other Australians.Index, bib, ill, maps, p.224.Within three months of the Japanese entering World War II on December 8, 1941 over 22 000 Australians had become prisoners-of-war. They went into camps in Timor, Ambon, New Britain, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Singapore and Malaya, and a few were scattered to other points in what was briefly part of the Japanese empire. Later most of the prisoners were to be shifted further north into South-east Asia, Formosa, Korea, Manchuria and Japan itself. They were captives within lands and cultures and to experiences alien to those known to all other Australians. At the end of the war in August 1945, 14315 servicemen and thirty service women were alive to put on new, loose-fitting uniforms and go home. One in three of the prisoners had died. That is, nearly half of the deaths suffered by Australians in the war in the Pacific were among men and women who had surrendered. Another 8174 Australians had been captured in the fighting in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa: but of these men only 265 died as a result of wounds, disease or execution.By any quantitative measure the imprisonment of so many Australians is a major event in Australian history. For many soldiers it was living --and dying --in captivity which made World War II different from that of World War I. But the prisoners have received no permanent place in Australian history. Their story is not immediately recalled on celebratory occasions. In a general history of the nation in which a chapter is given to the war the prisoners might be mentioned in a sentence, or part of a sentence. Where the horror, stoicism and gallantry of Gallipoli have become part of a common tradition shared by all Australians, the ex-prisoners are granted just the horror. The public may be sympathetic; but the horror is for the prisoners alone. To make another comparison: in five months of fighting on the Kokoda Trail in 1942 the Australians lost 625 dead, less than the number who died on Ambon. Yet the events on Ambon are unknown to most Australians. There were no reporters or cameramen on Ambon and, for the 309 who defended Ambon's Laha airfield, no survivors. How many of them died in battle or died as prisoners will never be known. But there are more than just practical reasons why the record of the prisoners of war is so slight and uneven in the general knowledge of Australians. They have not tried to find out. No historian has written a book to cover the range of camps and experiences, and only in specialist medical publications has anyone investigated the impact of prison life on subsequent physical and mental health. The complexity of the experience and its impact on particular lives have not been expressed in a way to give them significance for other Australians.world war 1939 – 1945 - prisons and prisoners – japanese, world war 1939-1945 - personal narrativies - australia -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (item) - CAC Documents Various Refer Description for further details
CAC Letter from Qantas Empire Airways relating to efficiency of Pratt & Whitney engines manufactured by CAC. CAC Copy of letter from Lord Hives relating to Australian visit 22.03.1946. CAC First Annual Report on Operations at Lidcombe NSW for 12 months ending March 1942. CAC Combined Unions Shop Committee. 27.03.43. CAC Financial Statements as at 30th September 1961. CAC Report On The Possible Future Development OF CAC Pty Ltd Fishermans Bend Melbourne May 1969. -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway5A Number Plate
Historic - Victorian Railways Locomotive Number Plate used on Steam Locomotive 5A Loco: 5A In service Saturday, 23rd March 1901 Scrapped Monday, 7th July 1958 Livery Black Owner VR Gauge 762 Status Scrapped Service History : Mar 1901 Colac - initial allocation of a new locomotive Mar 1901 - Feb 1902 Colac Dec 1902 - Oct 1908 UFTG. Nov 1908 - Oct 1912 Colac Nov 1912 - May 1913 Other Jun 1913 - Jun 1915 UFTG. Sep 1915 - Sep 1920 Moe Oct 1920 - Nov 1921 UFTG. Mar 1922 - Jan 1927 Colac Mar 1927 - Aug 1927 Moe Oct 1927 - Jan 1928 UFTG. Feb 1928 - Dec 1934 Colac Jan 1935 - Mar 1935 Moe Apr 1935 - Sep 1942 Colac Mar 1943 - Mar 1949 Moe Apr 1949 - Nov 1957 Colac Dec 1957 Colac - Stored. Feb 1958 - Jul 1958 Workshops - ScrappedHistoric - Victorian Railways Locomotive Number Plate used on Steam Locomotive 5AVictorian Railways produced 5a number plate. made of cast iron5a5a, puffing billy, victorian railways -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchMedal - Framed Medals, Lt Allan R Stewart, Unknown
... Hospital Enlisted 23rd October 1942 Discharged 15th May 1946... October 1942 Discharged 15th May 1946 Two metal medals with ribbon ...Two service medals awarded to Lt Allan Robert Stewart VX114312 of 124 Aust. Special Hospital Unit. He was born on 29/5/1906 at Hamilton and enlisted at Ballarat. Military service records not available/examined.Two metal medals with ribbon above black engraved plaque mounted on timber framed red felt Plaque: VX 114312 Lt Allan R Stewart 124 Aust. Special Hospital Enlisted 23rd October 1942 Discharged 15th May 1946allan robert stewart, ww2, service medals, 124 aust. special hospital unit -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook, Bank Book, 1940's
The McHugh brothers were Wood and Chaff Cutters. The books were used from March 1942 to December 1946 and December 1946 to May 1952.2 x Maroon covered bank books. A buff coloured sticker on front with the words "In Account Current with The Commercial Bank of Australia Limited. Page ........) Mr LJP McHugh. (the owner of the two bank books.)commercial bank of australia, bank books, mchugh brothers, wood and chaff cutters in tatura, tatura businesses -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook - Autobiography, Detained by the Enemy, 1942-1945, 1987
Personal history written by Bill Anderson of his experiences in the Australian Army in WW2. He volunteered at the age of 18 years after Japan entered the war, as an Ally to Germany and Italy, the aggressors. Taken prisoner by the Japanese and held in camps in Malaya and Singapore, enduring previously untold horrors at the hands of the Japanese captors. Written for his grandchildren to read and perhaps understand.Burgundy hard covered book with printed title in gold, containing photocopied handwritten material and printed material.Two photos and descriptions of the author, and his record of his Army Service. 1 - Bill Anderson aged 20 years and 10 months (May 1941); 2 - Bill Anderson aged 66 years and 10 months (May 1987). Service record. These items inside front cover of book.documents, reports, bill anderson, australian army, australian army personnel -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumArtwork, other - Fujitsu, Sei
Sia Fujitsu, the son of Jiroguma Fujitsu was born on 27 May 1926 in Yamaguchi-Ken, Japan. His trade is listed as Employee of Culture and his religion is Buddhist. He was captured at Tawao, North Borneo on 27th January, 1942 and was interned in Loveday South Australia until he was repatriated to Japan on 21st February, 1946. Kurt Winker was born in Germany in 1902 and was a survivor of the "Arandora Star". He was sent to Australia on the "Dunera" where he was interned at Tatura 1940-1945.SiaPhotocopy of a pencil and ink Portrait of a Japanese youth Short black hair, dark eyes and pink lips. He is wearing a jacket that appears to be too large for him and white collar and beige coloured tie. There is light blue shading around is head and shoulders. Japanese lettering in black ink on the left of the picture translates to his name "Sia FUJITSU". Signed in black ink by artist Kurt Winkler, Loveday, 1942.Kurt Winkler LOVDAY 1942 -
 Anglesea and District Historical Society
Anglesea and District Historical SocietyBullet Shell - Exploded, 1941
Artillery shell (exploded) may? have been used in the M10 Hellcat Tank made in the U.S.A., (M18 Gun Motor Carriage Tank Destroyer). Although the date on the shell is 1941 and the Hellcat was under developent during that year.Bottom: 75mm M18 / LOT 5898-27 & FA 1942 Centre: M22A2 1942 / 1-23230-1artillery shell -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph
The Battle of Tarakan was the first stage in the Borneo campaign of 1945. It began with an amphibious landing by Australian forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended with success for the Allied forces over the Japanese defenders, this victory is generally regarded as having not justified its costs. 225 Australian soldiers of the 26th Brigade, 9th Division, 2nd Australian Imperial Force were once buried here. They were killed in the Battle of Tarakan (1 May - 21 June 1945) or died due to their wounds until 15 August 1945.The 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of a monument/cenotaph and lawn grave sites with white crosses.Handwritten on rear - Tarakan Cemetery2/24th battalion, wangaratta, tarakan -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph
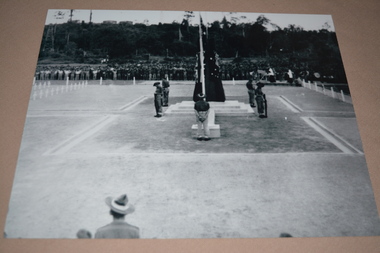
September 30,1945 - The official dedication service and unveiling of the Cenotaph at Tarakan War Cemetery The Battle of Tarakan was the first stage in the Borneo campaign of 1945. It began with an amphibious landing by Australian forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended with success for the Allied forces over the Japanese defenders, this victory is generally regarded as having not justified its costs. 225 Australian soldiers of the 26th Brigade, 9th Division, 2nd Australian Imperial Force were once buried here. They were killed in the Battle of Tarakan (1 May - 21 June 1945) or died due to their wounds until 15 August 1945.The 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of monument/cenotaph and catafalque party2/24th battalion, tarakan, cenotaph -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, c1941
Black and white image of large sign in the desert/barren location. Sign reads DO NOT LEAVE YOUR VEHICLE UNATTENDED IN ALEXANDRIA, OR IT MAY BE STOLEN.The 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of large warning sign in English in open barren landscape.2/24th battalion, ww2, middle east, alexandria -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, c1945
Prior to the Second World War Tarakan Island was part of the Dutch East Indies and an important oil-producing centre. In early 1942 it was occupied by the Japanese. The primary objective for the Allied attack on Tarakan (code-named "Oboe One") was to secure and develop the island's airstrip so that it could be used to provide air cover for subsequent landings in Brunei, Labuan and Balikpapan. The secondary objective for the operation was to secure Tarakan's oilfields and bring them into operation as a source of oil for the Allied forces. As part of the 26th Brigade the 2/24 Battalion landed at Tarakan on May1 1945. The task of capturing Tarakan's airstrip was assigned to the 2/24th Battalion. The Battalion's initial attack on the airstrip on the night of 2 May was delayed when the Japanese set off large explosive charges, and the airstrip was not secured until 5 MayThe 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of metal pylon structures with man standing in bombed foreground Handwritten on rear - Oil wells on Tarakan2/24th battalion, tarakan, ww2 -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph
James Legge was born of Scots parentage at Dunolly, Victoria on 2 July 1873. He was educated at Scotch College Melbourne, and at the University of Melbourne. He worked as a teacher before starting the Theological course at Ormond College. He completed his theological training in 1902, and was appointed by the Home Mission Committee to the parish of Boort, where at Durham Ox he was ordained and inducted in May 1903. He married Susan Ison at the Collins St. Independent Church on 11 September 1907. Legge was called to Clunes (1907), Preston (1917), Mildura (1920), Dandenong (1924), and Kew (1926). Demitted 1942. Home Mission appointment Mitcham 1946. Died October 21 1951B & W waist length photo enlargement of Rev James Legge B.A. printed on buff card.Rev. James Legge, B.A. 1926 - 1942james legge, presbyterian, minister, scotch college, university of melbourne, ormond college, kew -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white prints and negatives, Athol Shmith Studio Illustrative Photography, Les Provan Collection, 1922-1946
Photographs donated by James Leslie (Les) Provan. (1) Note by T.H. Kneen 6 May 1992, "James Leslie Provan went to Melbourne University - graduated B. Agr. Sc-and later 1942 became Principal Burnley and 1946 Principal Dookie Agricultural College."Black and white photographs and negatives. (1) 2 photographs and negative. Les Provan reclining on the ground infront of a Kentia palm and part of the pavilion behind. (2) Includes negative. Les Provan and another male student seated on the lawn. (3) Note attached, "English lad, Fred ?, ?, Jack Allen." 4 male students seated on the lawn in front of the Pavilion. (4) Male student with calf. (5) 3 male students squatting on the lawn in front of the pavilion, one holding a football. Note by E.B. Littlejohn 6 May 1992, "Student on left is R. Fred Gillespie ? Jack Allen (centre) was later on staff as an Instructor. (6) Mrs Kneen and two children walking through the Administration Building under construction. (7) 4 men standing next to Dahlias judging them. (8) Student walking along path between ponds and Pavilion.(1) On reverse, "Student Les Provan 1922 &1923. Dux 1923. Background is Kentia Palm & the Chemistry classroom of the old Pavilion. (2) On reverse, "Les Provan & ? 1923." (3) On reverse, "Group of male students 1922 or 1923." (4) On reverse, "? name an English lad, student 1922 or '23." (5) On reverse, "The Football Team L to R. Fred---Jack Allen & ? 1923." (6) On reverse, "The new College building in course of construction early 1946. Mrs. Kneen & children." (7) On reverse,"Judges in trial Dahlias Burnley 1943. Left to right Jack Reid, Castell, Charlie Stone, Geo. Russ, Norm Scable." (8)) On reverse, "June Bishop-student," and, "Athol Shmith Studio Illustrative Photography 125 Collins Street, Melbourne C.1. Cent. 27. No 10383 Position J." Note by E.B. Littlejohn 4 March 1992, "June Bishop standing at junction of paths one of which leads to main entrance to Pavilion."les provan, kentia palm, chemistry classroom, pavilion, james leslie provan, dookie agricultural college, jack allen, r. fred gillespie, dahlias, jack reid, castell, charlie stone, geo. russ, norm scable, june bishop, cows, student group 1922-1923, football team 1922-1923, administration building construction, mrs kneen, kneen children, athol shmith, garden view, dux, calf, main building construction -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumProgram, Dennys Lascelles Limited: Staff Reunion at the National Wool Centre 1988
A copy of both the ‘Dennys Lascelles Limited 1857-1957: Annual Wool Report & Centenary Review’ & ‘Staff Reunion Souvenir Programme, 1988’ was donated to the museum in 2021. These were duplicate items so only their story was retained in addition to the image of Rita located in Multimedia. “Enclose two items which may be of interest to add to your collection. They belonged to my mother, Rita Sedgwick (nee Glenn), who died earlier this year in April. She worked for Dennys Lascelles in two separate periods. First as a young girl, who had finished her schooling, at Morongo Presbyterian ladies College, having been sent as boarder there by her parents from their farm at Mathoura (just north of Echuca). This period was from 1942 — 1947. It was her second job out of school having worked first at the then Geelong Telephone Exchange. She would commute daily to work on a bicycle from where she was then living in Drumcondra. She had the front office role of receptionist and telephonist driving an old manual switchboard. The old front desk was her domain. She departed in 1947, shortly after she was married in late 1946. She spoke fondly of her times at the company as a young girl in her late teens and early twenties. Her second stint was much later, but again as the front-desk telephonist and receptionist commencing in 1972, ending 11 years later in 1983. This was a period when Sir Henry Bolte was on the Board, Don Urqhuart was MD, Ray Hobson was General Manger, Cliff Bone the company Secretary, Peter Keys the CFO and Jim Hay was also on the Executive team. While there were some 25 years between her periods of service, she welcomed the chance to re-join the company. Again, it was a time of hard work, and good friends. The busy times were the wool auctions, when the Firm would be visited by representatives of the big Japanese trading houses such as Mitsui, and Kanematsu. The Chief Auctioneer, Mr. Reeves (I can't recall his first name), would hold court at the now demolished Geelong Wool Exchange — I saw him in action once — what a sight. The huge show floors in the Denny's building would be full of open bales and samples for the buyers to inspect, and for mum days would start at 0800, and finish at 1800 or later. In quieter times over summer, it was reported that the empty show floor would provide an excellent arena for the more enthusiastic cricketers to get in a bit of practise with a tennis ball at lunch and after closing time! Dennys was a full-service firm for wool growers, with branches all over the Western Districts as far afield as Mt Gambier, but through Timboon, Warrnambool, and the like, as I am sure you are aware. She also saw the merger of Dennys and Strachan to create DSM, and later the amalgamation with AML&F to create Dennys AML (I think). She saw the change from the old manual switch board to the then latest of PABX technologies and was part of the team the relocated from the original offices to the new address on the south side of Brougham Street. Along with the shift from the large show floor-based sales of the past. She retired from fulltime work in mid-1983, again with fond memories and friendships that lasted a lifetime. I found these two items among her things recently, and felt that given her connection to the industry, and the place in which the Museum now resides you may like to add them to the collection. I hope you can find a home for them, and that they might add a little to the story that the wool museum now houses and curates.” Program 12pp: soft pale grey cover, contians brief history of the company , the buildings and at the last page is a list of acceptances for the reunion, 2nd October, 1988Judith Lagingdennys, lascelles limited
