Showing 1450 items matching "water victoria"
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - STATE RIVERS AND WATER SUPPLY COMMISSION : 1964-1965 A YEAR OF ACHIEVEMENT, 30/05/1965
... State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria....State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. Small... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. State Rivers and Water ...State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. Small brochure titled '1964-1965 A Year of Achievement'. Contains information headed 'Rural Water Assets as at 30th June, 1965' and 'Highlights of 1964/5'. Also contains information about the purpose and work of the Commission as well as an answer to the question - Why do you pay rates? People mentioned in the brochure : The Minister - the Hon. T. A. Darcy, M.L.A.; The Commission - A.L. Tisdall, Chairman; R.A. Horsfall, Deputy Chairman; K.D. Green, Commissioner; The Secretary - G. W. V. Lewis.state infrastructure, water supply, coliban system, state rivers and water supply commission of victoria. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
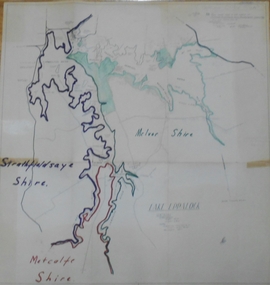
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - STATE RIVERS AND WATER SUPPLY COMMISSION : LAKE EPPALOCK
... State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria...State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. Coliban System ...State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. Coliban System. Lake Eppalock. Map of Lake Eppalock foreshore area. Colour is used to delineate the areas of the Lake included in the three councils - McIvor Shire, Metcalf Shire and Strathfieldsaye Shire. Scale is 1 inch = 40 chains. Various notations in pencil have been added, with 'Coliban Office Plan' written and circled in the top right corner. A coloured (green) area is scaled as 'fore shore area in the charge of Derrinal Recreational Area Management Committee'. Individual leasing details have been added. state infrastructure, water supply, coliban system, state rivers and water supply commission of victoria. coliban system. lake eppalock. -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Work on paper - Letter, Henry Watts, Letter written 1859
... was the author of "On the Fresh-water Algae of Victoria " (Trans. Roy... of "On the Fresh-water Algae of Victoria " (Trans. Roy. Soc. Vict., 1861-4 ...Henry Watts (1828_1889) Died at Melbourne, 16th December, 1889. He was a good microscopist. His botanical studies were chiefly devoted to algae, both fresh-water and marine, and while living for many years at Warrnambool he was a contributor of algae to Harvey, who figured Wrangelia wattsii, Harv., and Crouania wattsii, Harv., in his “Phycologia Australica " He was the author of "On the Fresh-water Algae of Victoria " (Trans. Roy. Soc. Vict., 1861-4, 67) ; .also a paper "On Fossil Polyzoa" (ib.. 82); "A Trip to Mt. Macedon in Search of Fresh-water Algae" (Wing's S. S. Record, iii., 252); "On a Species of fresh-water Algae from Victoria" (Vict. Nat., i., 21); "Some Recent Additions to our Knowledge of Microscopic Natural History" (ib., iii., I33) (includes lists of fresh-water algae and Desmidieae ), First librarian (1881-2), also a vice-president of the Field Naturalists' Club of Victoria. He is further commemorated by Acacia wattsiana. F. v. M. www.anbg.gov.au/biography/watts-henry.html . Henry Watts worked as a bootmaker in Timor and Liebig streets Warrnambool in the 1860’s but it was as an amateur scientist that Watts gained public notice.For an exhibiton in Melbourne in 1861 Henry Watts prepared a collection of over 100 different species of seaweed from the Warrnambool district. It is recorded in the Examiner in 1863 that he had been elected as an honorary member of the Bristol Microscopical Society of England He was a member of the Warrnambool Horticultural society and in 1865 he opted to become a flower distiller.At the 1866 MelbourneExhibition, Henry Watts exhibited 44 bottles of his perfumes. He had a keen interest in microscopes and microscopic organisms.He spent many hours combing the caves and examining the guano of local bats. This letter is written to Professor Quekett advising him that he has sent a collection of packets of samples of diatomaceae asking him to examine and name the same.. Professor Quekett was a famous microscopist of the Victorian era with the Quekett microscopist club one of the oldest in the world dedicated to the use of the microscope and its discoveries. Henry Watts was one of Warrnambool’s first botanists and marine scientists. He also established a flower distilling and perfume manufacturing business in Warrnambool. In 1861 he sent a collection of over 100 species of seaweed to the Melbourne Exhibition.Framed, handwritten letter, ink on blue paper. Transcript of letter is typed black on white paper. Five small numbered pieces of paper containing specimens of diatomaceae collected from marine and fresh water areas around Warrnambool.Names Henry Watts, Professor Quekett. Handwritten along the bottom of the frame, “The above was bought at a London Auction for $12-10-00 by Miss Eddey a Melbourne Book shop Proprietress and recently presented to the W.F.N. Club.: warrnambool, henry watts, watts henry, botanist,microscope, microscopic, quekett, john thomas quekett -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - DRAINAGE PROBLEMS - BAILING OPERATIONS
... Progress. Water at the Victoria Quartz lowered 139 ft for the week... - A Week's Progress. Water at the Victoria Quartz lowered 139 ft ...Handwritten extracts from the Bendigo Advertiser 17/8/1910 Col. 2. Extract mentions Bailing Operations - A Week's Progress. Water at the Victoria Quartz lowered 139 ft for the week. Bailing carried out at Lansell's 180, Lazarus, New Chum Consolidated and New Chum Railway Mines. Cost of bailing about 200 pound per week and the Government is contributing half. The balance is being found from the Victoria Quartz, Victoria Consols, Ironbark, Hercules and Energetic and Lansell's Estate. Expenditure over 6 weeks has amounted to over 1200 pounds. ''Mr McBride, Minister for Mines,said work was to be continued for the present at all events. Mr Merrin, Chief Inspector of Mines, said the Dept's aim was to keep the whole of contributing mines on the New Chum line unwatered, and also to enable the Victoria Quartz to go on with its sinking. It was not however intended to introduce a pumping system for the present.''document, gold, drainage problems, drainage problems, bendigo advertiser 17/8/1910 page 3 col 2, victoria quartz, lansell's 180, lazarus, new chum consolidated, new chum railway, victoria consols, ironbark, hercules and energetic, lansell's estate, mr mcbride, mr merrin, new chum line -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - The Hume Dam: 100 Questions for a Centenary, Howard C Jones, 2019
... Department of Public Works and the State Rivers and Water Supply... Department of Public Works and the State Rivers and Water Supply ...A booklet describing the history of the Hume Dam in question-and-answer format, illustrated by photographs from the Albury City Collection and other sources. This booklet was produced to accompany the exhibition "Turning the sod: building the Hume Dam", on display at Lavington Library from 21 December 2019 -1 March 2020."non-fictionA booklet describing the history of the Hume Dam in question-and-answer format, illustrated by photographs from the Albury City Collection and other sources. This booklet was produced to accompany the exhibition "Turning the sod: building the Hume Dam", on display at Lavington Library from 21 December 2019 -1 March 2020." hume dam, dams -- new south wales, hume dam history, dams -- new south wales -- design and construction -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBooklet - Victoria's Upper Kiewa Valley, State Electricity Commission, C. 1984
... The Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme is the largest water power... The Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme is the largest water power ...This booklet is one of several publications from the State Electricity Commission during the period it was responsible for the running of the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme. It promotes tourism and depicts key features of the region in the 1980s.non-fictionThis booklet is one of several publications from the State Electricity Commission during the period it was responsible for the running of the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme. It promotes tourism and depicts key features of the region in the 1980s.victoria. kiewa valley, kiewa river valley (vic.) -- description and travel., kiewa hydro -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, Unknown c.1930s
... . The State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria and the New.... The State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria and the New ...This image shows Bethanga Bridge, which was constructed between 1927 and 1930 in Albury, NSW. The bridge was a necessity due to the building of the Hume Dam (Wier), 1919-1936. Bethanga Bridge is a long, nine-span, riveted-steel, variable depth, Pratt Truss road bridge of nine principal spans of 82 metres and a total length of 752 metres over the flooded valley of the Murray River, now part of Hume Reservoir. Because of its unique location, over the waters of a dam with the border running down the centre of the body of water, the Bethanga bridge is the only built structure shared by both New South Wales and Victoria. It was built 1.6 kilometres upstream of the dam and in 1961 was raised 300mm, with a concrete deck replacing the original wooden deck. The State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria and the New South Wales Department of Public Works were responsible for the construction works for the Hume Weir under the River Murray Waters Agreement. It is apparent that a similar joint arrangement was made for the construction of the Bethanga Bridge as part of the Hume Weir works.This photograph of the Bethanga Bridge is of historical significance as it showcases the architectural skills of Percy Allen and Vincent Packer. Additionally, it reveals the environmental landscape of the 1920s-1930s, is linked to the Hume Dam and both New South Wales and Victorian heritage. Unmounted black and white rectangular photograph. Reverse: 1997.3196 84-20-3bethanga, bethanga bridge, hume dam, pratt truss, murray river, hume weir, transportation -
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub BranchPropeller from HMAS Bayonet, Walkers Ltd
... maritime services on 21 September 1999 in 82 m of water off Torquay... maritime services on 21 September 1999 in 82 m of water off Torquay ...Bayonet was one of 20 Attack class patrol boats built for the Royal Australian Navy between 1967 and 1969 by Walkers Ltd of Maryborough Qld . In the 1960s, Australia became more closely involved in events in the Asia-Pacific region. This led to improved surveillance and control of our enormous coastline, especially the northern approaches. Patrol boats controlled illegal fishing, smuggling and immigration, search and rescue, and occasional inshore survey work. Her hull is steel and the superstructure is aluminium. It is armed for small-scale encounters, with one 40-mm Bofors gun and two 0.5-inch Browning machine guns to fire warning shots across the bow of a suspect vessel. She was 32.6 m long and 6.1 m wide, 150 tons, powered by two paxman diesel engines and capable of about 24 knots. . A sister ship featured in the popular ABC-TV series Patrol Boat. The Bayonet conducted patrol duties around Australian waters until her scuttling by defence maritime services on 21 September 1999 in 82 m of water off Torquay in Victoria. propeller, hmas bayonet -
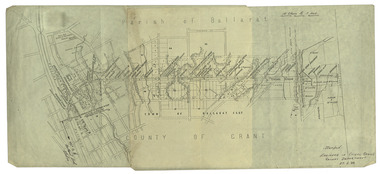 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan, Ballarat Railway Plan, 1888, 27/02/1888
... Street, Scott Parade, Ross Street, Chamberlain Street, Victoria..., Chamberlain Street, Victoria Street, Water Street. Allotments owned ....1) Copy of a Ballarat Railway Plan, running along Belford Street, from the Engineer in Chief's Office, Railway Department. It shows bridges, diversions, culverts and the following streets: Joseph Street, Lal Lal Street, Clayton Street, Belford Street, Rodier Street, trench Street, Stawell Street, Rodier Street, Belford Street, George Street, Eureka Street, Queen Street, Otway Street, Scott Parade, Ross Street, Chamberlain Street, Victoria Street, Water Street. Allotments owned by Tulloch and McLaren, J. Wilson, J. McCarthy, Mrs P. Glynn, E. Ratcliffe, soap works, Orphan Asylum .2) Copy of a plan relating to the construction of the Ballarat Railway Line. It includes shafts for the following companies: South Extended Co, Black Hill; Parade Co.; Black Hill Co.; Spanhake Co. Shaft; Black Hill South Co.; Wellingtonia Gigantiea Co., and the old workings of the Welllingtonia Gigantea Co,ballarat railway plan, belford street, lal lal street, clayton street, rodier street, trench street, south extended co., black hill, parade co., spanhake co. shaft, black hill south co., wellingtonia gigantiea co, railway -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Beechworth FCV District office sign
... ), Parks Victoria, Melbourne Water, Alpine Resorts Commission...), Parks Victoria, Melbourne Water, Alpine Resorts Commission ...This sign proudly hung outside the Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Beechworth office which is now site of the Forestry Heritage Museum. The granite building in the Beechworth's historic precinct was once the Gold Warden's Office and is one of the town's original buildings. The FCV was the main government authority responsible for management and protection of State forests in Victoria between 1918 and 1983. The Commission was responsible for ″forest policy, prevention and suppression of bushfires, issuing leases and licences, planting and thinning of forests, the development of plantations, reforestation, nurseries, forestry education, the development of commercial timber harvesting and marketing of produce, building and maintaining forest roads, provision of recreation facilities, protection of water, soils and wildlife, forest research and making recommendations on the acquisition or alienation of land for forest purposes″. The Forests Commission had a long and proud history of innovation and of managing Victoria's State forests but in September 1983 lost its discrete identity when it was merged into the newly formed Victorian Department of Conservation, Forests and Lands (CFL) along with the Crown Lands and Survey Department, National Park Service, Soil Conservation Authority and Fisheries and Wildlife Service. After the amalgamation the management of State forests and the forestry profession continued but the tempo of change accelerated, with many more departmental restructures occurring over the subsequent four decades. Responsibilities are currently split between the Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action (DEECA), Forests Fire Management Victoria (FFMV), Parks Victoria, Melbourne Water, Alpine Resorts Commission, the State Government-owned commercial entity VicForests and the privately owned Hancock Victorian Plantations (HVP).Large office sign. Hand painted in traditional FCV mission brown and gold colour scheme.forests commission victoria (fcv), forest signs -
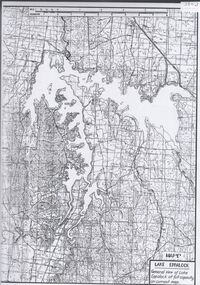 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Laminated map of Lake Eppalock at full capacity. Map 'E'
... by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam...map eppalock water dam reservoir John Perry Collection ...John Perry Collection. Laminated map of Lake Eppalock at full capacity. Black and white. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, eppalock, water, dam, reservoir -
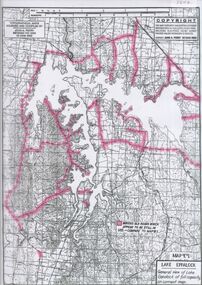 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Laminated map of Lake Eppalock at full capacity
... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall...map water dam reservoir eppalock John Perry Collection ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of map of Lake Eppalock at full capacity. Had highlighter markings of old roads which appear to be still in use. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, water, dam, reservoir, eppalock -
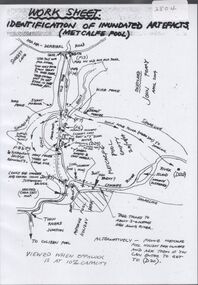 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Laminated worksheet - identification of inundated artifacts at Lake Eppalock
... . The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of worksheet identifying inundated artifacts at Lake Eppalock when at 10% capacity. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, artifacts, eppalock, reservoir -
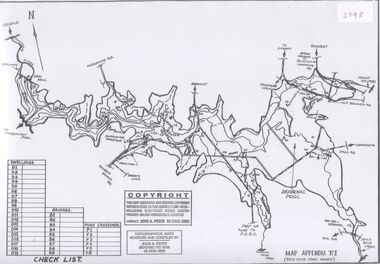 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Black and white map pertaining to Lake Eppalock
... crossings. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply... by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of map pertaining to Lake Eppalock. Gives details of dwellings, bridges and ford crossings. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.eppalock, map, water, dam, reservoir -
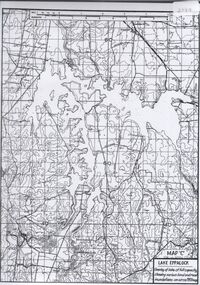 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Map of overlay of lake Eppalock at full capacity. Map 'C'
... was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 ...John Perry collection. Map 'C'. Laminated map of overlay of Lake Eppalock at full capacity. Circa 1951. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, water, eppalock, dam, reservoir -
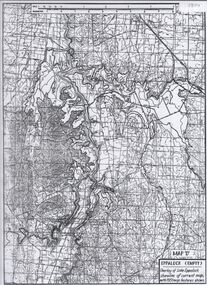 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Laminated map of Lake Eppalock empty. Map 'D'
... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall...map water dam reservoir eppalock John Perry Collection ...John Perry Collection. Laminated map of Lake Eppalock empty. Map 'D'. Circa 1951. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, water, dam, reservoir, eppalock -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
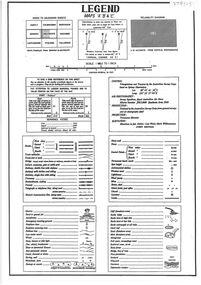
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - Legend to maps A, B and C for Lake Eppalock
... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall ...John Perry Collection. Laminated 'legend' for Maps A, B and C for Lake Eppalock also in this collection. Black and White definitions and descriptions of objects and markers found on maps. Circa 1951. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, water, dam, reservoir, eppalock -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - Collection of photographs from newspaper on a single page
... . The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of page from 'Weekly Times' newspaper, February, 1962. Nine images relating to establishing and building Eppalock Reservoir, 15 miles from Bendigo. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system. dam, engineering, water, eppalock -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
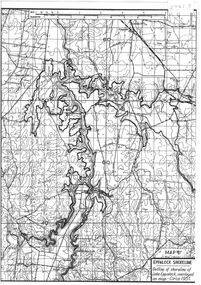
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Black and White map. Outline of Lake Eppalock. Map 'B'
... 1951. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply... by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy black and white map. Map 'B'. Outline of Lake Eppalcok, overlayed on map. Circa 1951. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, water, dam, reservoir, eppalock -
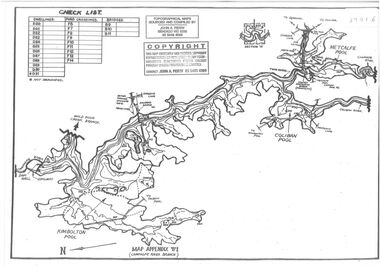 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Black and white map pertaining to Lake Eppalock
... . The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of map relating to Lake Eppalock. Lists dwellings, ford crossings and bridges. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, water, dam, reservoir, eppalock -
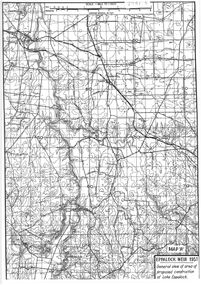 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - General view of area of proposed construction of Lake Eppalock. Map 'A'
... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45... by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam ...John Perry Collection. Laminated map of proposed construction of Lake Eppalock. Map 'A'. Black and white map in laminate. Circa 1951. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, dam, water, weir, eppalock -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - Black and white laminated photo of flow of water from Lake Eppalock. 1964
... by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of photo of crowd watching flow of water from the opened valve at the wall of Lake Eppalock during its commissioning. March, 1964. Lake Eppalock was created by flooding to town of Wild Duck. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.water, dam, reservoir, eppalock, wild duck -
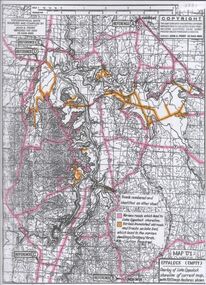 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Map of Lake Eppalock shoreline when empty
... was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of map detailing Lake Eppalock shoreline when empty. Circa 1951. Has colored highlighter lines following roads leading to lake shoreline and various inundated old roads and tracks on lakebed. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.map, eppalock, reservoir, lake, water -
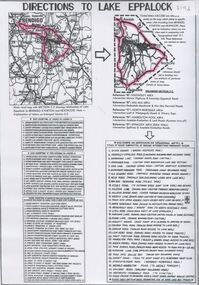 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - Directions to Lake Eppalock with road descriptions and map
... Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall...water dam directions eppalock John Perry Collection ...John Perry Collection. Laminated copy of 'Directions to Lake Eppalock'. Gives directions in relationship of Lake Eppalock to Bendigo, Kyneton and Heathcote. Undated. Gives basic descriptions of bridges on lakebed, ford crossings on lakebed and inundated dwellings on lakebed. The dam was built by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. The dam wall height is 45 metres (148 ft) and the main embankment is 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) long. At 100% capacity the dam wall was designed to hold back 304,651 megalitres (6.7014×1010 imp gal; 8.0480×1010 US gal) of water. The surface area of Lake Eppalock is 3,011 hectares (7,440 acres) and the catchment area is 2,124 square kilometres (820 sq mi). The controlled spillway is capable of discharging 8,040 cubic metres per second (284,000 cu ft/s). Lake Eppalock supplies both stock and domestic water to the Campaspe irrigation district. It also serves as a water supply to Bendigo and Heathcote and, in more recent times, Ballarat. The lake is a major attraction for those engaging in watersports, with a number of tourist parks and accommodation facilities available. Permissible activities on the lake include high-speed boating, water skiing, sailing, canoeing, fishing and swimming. The lake's water levels were low for approximately eight years between 2002 and 2010 during a prolonged drought, which restricted the amount of recreational activity until rainfall in the latter half of 2010 returned the lake to 100 percent capacity. Built between 1961 and 1964, Lake Eppalock remains the only water storage on the Campaspe River system.water, dam, directions, eppalock -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Diamond Creek, Barak Bushlands, Eltham, 2008
... . The Friends also received grants from Melbourne Water and Parks.... The Friends also received grants from Melbourne Water and Parks ...A habitat corridor and it strengthens the community. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p185 Barak Bushlands lie west of the Diamond Creek on the corner of Falkiner Street and busy, noisy Main Road. They form part of an important habitat corridor linking the Yarra River to the Kinglake National Park.1 Manna Gums, tawny frogmouths and platypuses are some of the indigenous plants and animals that have made their home there. The bushlands are the result of more than nine years of hard work by the local community with the Nillumbik Council, to transform a degraded flood plain into this refuge of natural beauty. In 1997, shortly after moving into the new Riverside Estate on Falkiner Street, Eltham, several residents noticed the sorry state of the Diamond Creek and surrounding area. Part of it was used as a cow paddock and although small patches of vegetation survived, the area was infested with weeds, rabbits, rubbish and drainage from the housing estate. At various times the 4.4 hectares had been used as a market garden and for shire stock piles. The residents began to restore the area by revegetating land along the Diamond Creek. In 1998 they established the Friends of the Diamond Creek Falkiner Street Reserve2 and 35 families joined from the 90-house Estate. Carolyn Mellor, as the Friends’ Land Manager, undertook a four-year horticulture course to guide this massive project for a volunteer organisation. Since 1999, she has been the Friends’ President. In 1999 the Friends urged the Nillumbik Council to undertake a feasibility study into establishing a wetland system and urban forest. Work began in 2002 with Nillumbik Council funding the project, supplemented by government grants. The Friends also received grants from Melbourne Water and Parks Victoria. Aided by the Friends and other community members, the Council created the Barak Bushlands consisting of a forest, a wetland, a bridge, a path and open space. The beautiful wetland treats most of the estate’s stormwater runoff. Storm water is filtered through plants in the wetland ponds then is released slowly into the billabong, before flowing into the Diamond Creek. The wetland also helps to minimise flooding and the improved water quality provides a flora and fauna habitat. The Friends and other volunteers planted more than 27,000 plants, more than one third of which they grew from seeds they collected at Lower Eltham and Wingrove Parks. Eltham High School students planted thousands of these through a Year Eight program introduced for this purpose. Other groups who assisted were: Green Corps, local Scouts and Guides – 2nd Montmorency, 1st Diamond Creek and 1st Eltham Cub Packs, Eltham College students, Eltham East Primary School, Landcare members, Eltham Lions Club and the Eltham Baptist Church. To maintain enthusiasm for the mammoth task, the Friends and other volunteers ‘adopted’ trees to water and wrote their names on the stakes. In 2004, to recognise the area’s original occupiers, the reserve was named Barak Bushlands. William Barak, who lived from 1824 to 1903, was the last chief of the Yarra Yarra tribe of the Wurundjeri-willam people. Traces of these original inhabitants remain in scar trees (bark sections removed to make a shield or canoe). That same year the Friends’ group was a finalist in the prestigious Federal Government, Banksia Environmental Awards. The Friends have also participated in Clean Up Australia, removing tonnes of rubbish and regularly testing the billabong, wetland and creek, for pollutants. For years the Friends, together with the Australian Platypus Conservancy, have tagged, measured and checked the health of platypuses from the Diamond and Mullum Mullum Creeks. With Latrobe University the Friends have conducted night walks to view owls, possums, bats and sugar gliders. Challenges for the council and the Friends continue with a large rabbit population, some vandalism, weed eradication and maintenance. However, thanks to this community effort, locals can now escape confined urban living on small blocks of land and enjoy the beauty of indigenous plants and animals. Working together has also strengthened the local community,This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, barak bushlands, diamond creek (creek), eltham -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Detail plan and explanation, Department of Public Works, N.S.W, 1927
... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria who are the Constructing... and Water Supply Commission of Victoria who are the Constructing ...This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.2. Detail Plan and Section. Starting from the New South Wales and there will be an earthen embankment 430 feet 6 inches long which is retained by the North Wing Wall. Then come the sluice section 284 feet 3 inches long, the spillway 720 feet long and the South Wing Wall, making a total length of 1,042 feet 6 inches of concrete wall. Beyond the South Wing Wall is earth embankment again to a length of 3,827 feet. The Full Supply Level is R.L.626.00 and allowance has been made for a surcharge of 9 feet. A road will run along the top of the dam at R.L.642.00. The sluice section contains seven offlets, the three nearest the north wing wall being 13 feet in diameter for hydro-electric purposes and the other four 9 feet in diameter for regulation purposes only. There are to be stony sluice gates on the upstream ends of the outlets and needle valves on the downstream ends. The shock of the discharged water will be taken by a stilling pool. Trash racks will protect the intake ends of the outlets. Next comes the spillway section, which is curved on the downstream face, and carried up to within 15 feet of the full supply level. Above that will be a series of piers between which will be the flood gates and on top of which the roadway will be carried. The gates will be 20 feet wide and 15 feet high and will be 29 in number. They will slide down the face of the wall when opened for the escape of the water. The investigation of the control of this cascade of water was made by means of a model and as a result the form of “bucket” or energy dissipater shown on the section of the spillway was decided upon. The earth embankment in Victoria is being constructed by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria who are the Constructing Authority for that State under the River Murray Waters Agreement. The core of the embankment is of concrete 6 feet wide at the base tapering to 2 feet at the top end and is reinforced with steel rods from the level of the decomposed rock upwards. On the downstream side, at about natural surface level, is a tunnel for drainage and inspection purposes. Above the tunnel is a vertical layer of large stones to drain any seepage to the tunnel. Against the core wall is packed selected material of as impervious a character as can be got locally and beyond that the bank is carefully built up in horizontal layers by means of horses and wheel scoops. The upstream slope is 3-to-1 hardening to 2½-to-1 at the top and the downstream slope is 2½-to-1 hardening to 2.07-to-1 at the top. The thrust of the upstream toe is taken by a mass of granite blocks, and this face is protected by concrete laid in situ. The width of the bank at base is 650 feet and at top 32 feet.hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume weir diagrams, hume plan details -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c.1870
This photograph was taken in approximately 1870 and depicts four male miners standing in mining sluice at the Three Mile Goldfields. These men are wearing typical attire for 1870s gold miners. They wear white shirts, tan coloured pants with water proof shoes and most of the men are wearing an apron to prevent their clothing from becoming too dirty from the mud. Each man is wearing a wide brim hat and hold large wooden tools used for sorting through the sluice. Three of the four men have full beards. The photograph was donated to the Burke Museum by R. Ziegenbein before 2001 but the photographer and the individuals captured in the photo are unknown. The image depicts the landscape of the Three Mile Goldfields during a period when open cut sluicing was undertaken to reach gold. Open cut sluicing is a method used to extract gold and other precious metals from beneath the surface of the earth. This technique involved the use of high-powered hoses which broke down the soil enabling miners to come along and search this soil for gold. After the gold rush of the early 1850s, diggers had to enlist the assistance of heavy machinery and techniques like hydraulic sluicing in order to reach gold because the surface alluvial gold had already been discovered and removed. This heavy machinery was not used until after 1853. The Three Mile Goldfields was a site of rich alluvial gold deposits located about 5 km south of Beechworth in Victoria. Today, the location of this gold deposit is called Baarmutha. It was a popular area for gold mining in the 1850s but became largely abandoned by the following decade. In 1865, a man named John Pund recognized that the area could be potentially rich if a better water supply could be obtained. He secured a 15 year license with three other miners. Within the next five years, these men had constructed 19 km of water race going from Upper Nine Mile Creek to Three Mile Creek. By 1881, these four men had delivered 950,000 gallons to the Three Mile Sluicing area which is depicted in this photograph. Pund was later go into partnership with John Alston Wallace who would become owner of the Star Hotel in Beechworth. The Three Mile sluicing location continued to be operational until 1950. Sluice box workers were a vital part of gold mining regardless of how inefficient they were in the recovery of gold. After using hydraulic sluicing to cut away the earth, miners would use the big wooden boxes depicted in the image to catch the earth which would then be sifted for gold. However, accidents would occur often which would result in the gold washing away and unable to be recovered. It was not a very efficient system because the gold, which was alluvial and thus very fine, would often pass through the sluice box undetected.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one which portray an open cut sluicing site can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. This image is of important historical significance for its ability to convey information about sluicing and the methods used to find gold in the late 1800s and early 1900s. It also shows a location where sluicing was undertook which provides insight into the impact of sluicing on the environment at a time when it was done. Images, like this one, of Australian gold rush history can reveal important information about the social and environmental impact of this period. This image depicts diggers standing in a mining location and therefore, this image has the capacity to reveal or support significant information for researchers studying the fashion and social status of diggers in Australia in approximately 1870. It can also provide information on the landscape of Australia in this period and the impact of mining for gold on both society and the Australian landscape. The Burke Museum is home to a substantial collection of Australian mining photographs which can be used to gain a deeper understanding into life on the gold fields, technology used in mining, the miners themselves and the impact of the gold digging on the environment.Sepia toned rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper and mounted on board.[illegible] about 1870 / 97 2514.1 / 2594 30three mile goldfields, goldfields, 1870, 1870 gold, australia, australian landscape, miners, gold miners, diggers, gold diggers, beechworth, victoria, sluice box workers, sluicing, sluice, mining -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Photograph - Reproduction, W. D. Gibbon, Early 1900s
This photograph was taken in 1911 at Three Mile Creek, about five kilometers south of Beechworth town. Significant digging took place at this location from late 1855, which led to a flood of workers and stores to follow, though daily earnings were slim compared to the nearby Woolshed site. This remained the case even after workers at Three Mile Creek attempted to protest around Beechworth during an election in November 1855. Three Mile Creek was one of seven significant divisions of the Beechworth Mining District formalised by the Governor-in-Council in 1858, though by the time this photograph was taken, the boundaries of the original seven districts had shifted to create seventeen divisions. The Three Mile Goldfields was a site of rich alluvial gold deposits located about 5km south of Beechworth in Victoria. Today, the location of this gold deposit is called Baarmutha. It was a popular area for gold mining in the 1850s but became largely abandoned by the following decade. In 1865, a man named John Pund (a man second from the left in the back row of this photograph shares this surname) recognized that the area could be potentially rich if a better water supply could be obtained. He secured a 15 year license with three other miners. Within the next five years, these men had constructed 19 km of water race going from Upper Nine Mile Creek to Three Mile Creek. By 1881, these four men had delivered 950,000 gallons to the Three Mile Sluicing area which is depicted in this photograph. Pund would later go into partnership with John Alston Wallace who would become owner of the Star Hotel in Beechworth. The Three Mile sluicing location continued to be operational until 1950. The eleven miners in this photograph are: Back row: Led Guthrie, P. Pund, F. Beel, [Unknown] Miller Front row: Paddy McNamara, J. King, W. Beel, [Unknown] Garland, J. Clarke, J. Ryan, H. Bartsh In the background of the photograph is a huge dirt wall that appears to suffer damage caused by hydraulic sluicing. Hydraulic sluicing is a specialised mining technique that involves directing high pressure water flows at dirt to uncover gold. The technique played a significant role in shaping Beechworth's landscape during the gold rush to create the topography seen today.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one which portray an open cut sluicing site can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. This image is of important historical significance for its ability to convey information about sluicing and the methods used to find gold in the late 1800s and early 1900s. It also shows a location where sluicing was undertook which provides insight into the impact of sluicing on the environment at a time when it was done. Images, like this one, of Australian gold rush history can reveal important information about the social and environmental impact of this period. This image depicts diggers standing in a mining location and therefore, this image has the capacity to reveal or support significant information for researchers studying the fashion and social status of diggers in Australia in approximately 1911. It can also provide information on the landscape of Australia in this period and the impact of mining for gold on both society and the Australian landscape. The Burke Museum is home to a substantial collection of Australian mining photographs which can be used to gain a deeper understanding into life on the gold fields, technology used in mining, the miners themselves and the impact of the gold digging on the environment.Black and white / sepia rectangular reproduced photograph printed on glossy photographic paper mounted on board.beechworth, beechworth museum, mining, mining team, three mile creek, sluicing, hydraulic sluicing, photography, gold sluicing, gold mining, pund mining -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, est. 1860-1875
In 1875, the Rocky Mountain Extended Gold Sluicing Company Ltd was created, utilising the previous Rocky Mountain claim for the area near Lake Sambell. The company employed A.L Martin to survey an area for a tunnel underneath Beechworth and Johnson Stephens to dig it. The tunnel was built at a rate of 40 feet a month and eventually measured 800 metres. The tunnel was a true accomplishment both in the present and during the 19th century. It was considered to be a marvelous engineering feat. Beechworth is renowned for its hydraulic sluice method of mining. This involved soil being exposed to torrents of water from high-pressure hoses. From 1876 until its closure in 1921, the mine produced an astounding 47,926 ozs of gold. Companies like this were the source of income for many Chinese gold-diggers who sought to make their fortune on the goldfields of Beechworth. During the height of the rush, the town had around 7,000 Chinese inhabitants living on the outskirts of town as they were not permitted to live within Beechworth itself.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one which portrays an open-cut sluicing site can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. This image is of important historical significance for its ability to convey information about sluicing and the methods used to find gold in 1910. It also shows a location where sluicing was undertaken which provides insight into the impact of sluicing on the environment at a time when it was done. This image of the Rocky Mountain mine is historically significant as the mining complex is now non-existent, with the only remains being the tunnel built in 1880 by the company, which was considered one of the greatest engineering feats of the time. The image also provides a first-hand look into the social and cultural networks at play during the 19th century with racial segregation of the Chinese at the 'Chinese Camp', as well as an insight into Beechworth's origins during the Gold Rush.A sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper as a postcardReverse: Historic Beechworth / 7792.1 / ROCKY MOUNTAIN MINE / Viewed from the “Chinese Camp”, shown partly in the foreground, we see the central plant of the famous Rocky Mountain Mining Company. This extensive complex, of which nothing remains, was situated between Silver Creek and the present Lake Sambell area. The company was responsible for a tunnel cut through solid bedrock underneath the town of Beechworth and surfacing near the keystone bridge on the Wangaratta side. Completed in 1880 it was declared to be one of the greatest engineering feats in Australia. The tunnel is still basically intact today. / Series by Wooragee Graphics: Historic Beechworth. / COPYRIGHT BURKE MUSEUM / No.72 beechworth, rocky mountain mine, sluicing, gold rush, mining, gold -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Pink-Eared Duck, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Pink-eared Duck can be found throughout Australia, commonly in locations that are timbered and near water. This species of Duck prefers to reside in areas which are shallow, temporary waters and on occasion may venture into open wetlands if with a large flock; however, this species is highly dispersive and often nomadic. The special bill of this Duck is designed to enable the bird to catch their food. The bill is fringed with grooves which filter out microscopic plants and animals from the water which makes up the birds diet. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Pink-Eared Duck is named for the small pink spot of feathers which feature on the sides of the drake's head. Another name for this bird is Zebra Duck because of the striking bold black and white striped plumage which decorates the duck's neck, breast and stomach. The bill is spoon shaped and the eyes are made of dark coloured glass and surrounded by brown colouring. The bird has brown wings and light coloured legs with webbed toes. This particular specimen stands on a wooden square platform. There are signs of damage on the platform and a wooden identification tag is tied to the upper right leg of the bird.6a./ Pink-eyed Duck / See Catalogue, page 39 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, duck, pink-eyed duck, pink-eared duck
