Showing 5098 items
matching wells street
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, 1973
Taken in 1973, this photograph features 13 men in suits, most of whom are council members of the United Shire of Beechworth, as well as a secretary and engineer. The photo is taken in a formal setting, suggesting there may have been an occasion at this time (potentially surrounding or related to the August council meeting). Previously a district (1856), then a borough (1863) and separate shire (1866) at this time the Local Government Area (LGA) had been known by this name for approximately two years, after having amalgamated with the still-existing borough. Beechworth amalgamated with Rutherglen and Chiltern Yackandandah to become the Indigo Shire Council in 1994. Little has been found about the men in the photograph, however this was at also around the time that women were becoming more widely accepted into positions on Victorian council (such as Valerie Mason, who was elected the first President of the United Shire of Beechworth council 6 years after this photograph.) The photograph has been taken in front of the Beechworth Shire Hall. The Hall was designed by architects J.J. Coe and Thomas Dalziel and is dated to 1859. Originally the building was used as the Shire Offices but also doubled as a fire station and a courthouse, with still surviving cells underneath. The Town Hall is now home to the Visitor Information Centre, is the starting point for historical Precinct walking tours and is available for hire for events or community meetings.The Beechworth Town Hall is one of five distinctive granite buildings on Ford Street that comprise the Justice Precinct, and is listed on the Victorian Heritage register. This photograph captures the ongoing importance and use of the Beechworth Town Hall and its ties to Council operations in the 1970s.Black and white rectangular photograph print matt photographic paperReverse - written in pencil upper right corner: 1997.2602; stamped in black ink across centre margin: Beechworth shire council Aug.1973/ Crs.H.H.Warner, H.C.Lucas, L.W. Powell, L. Leentjes, R.C. Sewell, T.J. Carroll/ G.Gray (Secry), Crs.R.P. O'Connor, D. Nankervis, D. McKenzie-McHaig, J.J. Macaulay, H.R. Sinclair/ D.Pope (Engineer), Absent Cr.J.V.Diffey; written in pencil in cursive lower left margin: Absent J Diffey; written in pencil bottom right edge: BMMA02602beechworth shire council, crs.h.h.warner, h.c.lucas, l.w. powell, l. leentjes, r.c. sewell, t.j. carroll, g.gray (secry), crs.r.p. o'connor, d. nankervis, d. mckenzie-mchaig, j.j. macaulay, h.r. sinclair, d.pope (engineer), cr.j.v.diffey, beechworth town hall -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Photographs, c1900
Both of these stereoscopic images depict a man standing by Lake Kerferd in Beechworth. The boathouse is located behind him. Lake Kerferd is significant because it was created in 1862 and Beechworth's main water supply. These images depict how Lake Kerferd was once used for boats because of the boathouse shown in the background of the image. However this boathouse appears to be in poor condition. This could give an indication that either boating was not a popular activity or that this boathouse in particular was not well looked after. Black and white photograph mounted on cardA03074.2 obverse: Lake Kerferd/ Beechworth/boathouse, lake, lake kerferd, man, stereoscopic, beechworth lake, beechworth, victoria, trees, boat, wooden house -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
The photograph depicts two young men standing atop a prominent outcrop at Lake Sambell, with buildings visible on the further shore. The present day park and reserve occupies the site of the former Rocky Mountain Mining Company, an open-cut sluice mine that began operations in the mid-Nineteenth Century and operated until the early 1900s, through the peak of Victoria’s Gold Rush. It was converted into a park and leisure area in the 1920s. Lake Sambell was formally opened to the public on Friday 5th October 1928 and was opened by the Victorian Government’s Minister of Lands, Mr Bailey, as part of initiatives to boost the economies and development of country towns. The lake was named after Mr L.H. Sambell, a shire engineer and secretary of the Forward Beechworth Committee who was involved in promoting the transformation of the mining site and promoting plantation forestry and tourism as alternative industries. £300 to begin the process was provided by Mr J. McConvill, a former resident of Beechworth, who is remembered in a street name adjacent to the lake. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser on Saturday, 5th May, 1917, gives some insight into issues in the Rocky Mountain Mining Company’s final years. The writer details the 1917 annual meeting of the Rocky Mountain Mining Company, stating that locals present appeared ‘well pleased this important local industry is in such a prosperous condition and that future prospects are so encouraging’. The author describes plans to give workers a bonus as evidence of profit-sharing that would ‘bridge the gulf between capital and labour’. The article concludes, however, with the statement that ‘there is a little arithmetical puzzle in the report in connection with the dredging operations I have been unable to solve.' The photograph is significant as it contributes to knowledge about how Beechworth reinvented itself after the Gold rush period, and more broadly how country towns repurpose and redevelop infrastructure and facilities to meet the present needs of their population. Sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper. Obverse: nil. Reverse: 3471 / Velox (paper mark)beechworth, beechworth lake, lake sambell, l.h. sambell, mcconvill, rocky mountain mining company, rocky mountain mining co, minister of lands, forward beechworth committee, wallace park-lake sambell development scheme, wallace park lake sambell development scheme, lake, sambell, j. mcconvill, recreation, reserve, park, transformation, repurposed, redeveloped -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Actionlite and Pyrite
Actinolite is usually found in metamorphic rocks, such as contact aureoles surrounding cooled intrusive igneous rocks. It also occurs as a product of the metamorphism of magnesium-rich limestones. Pyrite is usually found with other sulfides or oxides in quartz veins, sedimentary rock, and metamorphic rock, as well coal beds, and as a replacement mineral in fossils. Actinolite is an amphibole silicate mineral. It is named after the Greek word "aktinos" meaning “ray” in allusion to the mineral's fibrous nature. Fibrous actinolite is a type of asbestos and was once mined along Jones Creek at Gundagai, New South Wales. Pyrite or "Fool's Gold" is the most common sulfide mineral. It is named after the Greek "pyr" meaning "fire" because it can be used to create sparks needed for a fire if struck against metal or a hard surface. Due to its gold colour, pyrite can be mistaken for gold and often forms alongside it, causing small amounts of gold to be present in rocks containing pyrite. Most importantly, pyrite is an ore of gold. Pyrite is sometimes used as a gemstone but is not great for jewellery as it easily tarnishes. In some fossils of ammonites – shelled cephalopods that died ~66 million years ago – pyrite also replaces the shell. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A small-medium-sized solid specimen with the minerals actinolite (dark green fibrous) and pyrite (brassy) with shades of brown, black/grey, and white. Actinolite is an amphibole mineral in the tremolite-actinolite series of calcium, magnesium, and iron silicates. Pyrite is an iron disulfide mineral.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, geological, mineralogy, pyrite, actinolite, victoria, sewyln, alfred selwyn -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Malachite, unknown
Malachite is a water soluble, crystalline, triphenyl methylene chloride salt. It has a close relationship to copper because it is common for Malachite and copper to come from the same ore. Malachite often has shades of green, making it also known as Malachite Green. As a result of it's colour, it is known for being a dye and has been used in the dye industry, the textile industry and in medical fields. Cobar in New South Wales is well known for it's mining. This is because of the number of important deposits present in the area and include three important mining belts where most of the materials are found. These are the 'Cobar belt', the 'Canbelego belt' and the 'Girilambone belt'. The 'Cobar belt' runs underneath the main town. Copper was first discovered in Cobar in 1869 and since then, many deposits of other materials have been found, including Malachite.This specimen is significant because it comes from Cobar, NSW and represents the many deposits of materials found there. Cobar has a long history of mining and is a source of Australia's copper minerals. Malachite is often found in copper deposits meaning that it is representative of Cobar's copper production. Malachite is known for it's vivid green colour and as a result, has many uses, such as meaning used as a dye. This makes it a valuable material and highly significant. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized mineral with shades of brown , white and light green throughout.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, malachite, copper, water soluble, cobar, cobar mines, cobar mining, cobar nsw, nsw, new south wales, mining belts, ore, copper ore, malachite green, dye, green, dye industry, textile industry, desposits, canbelego, girilambone, alfred selwyn -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Fluorite (purple)
Fluorite comes in a variety of natural colours and crystal formations and glows under ultraviolet light (the word 'fluorescence' comes from the same etymological source). In its pure form, calcium fluoride, it is a colourless combination of the elements calcium and fluorine, but gains its colour from trace elements that infiltrate or replace calcium within its crystal structure during its formation. Although fluorite crystals polish well and can achieve a high level of lustre, the mineral is very soft (4 on MOHS hardness scale) so it is unsuitable for use in rings and must be handled and stored carefully if used in other forms of jewellery. Most crystals of the mineral are too coarse for decorative purposes but have been mined under the name fluorspar for a variety of commercial and industrial purposes. These include the production of hydrofluoric acid, smelting metal alloys, producing glazes and ceramic finishes and use in medical and dental products. An existing label for this specimen indicates that its origin or collection-point was 'probably USA.' Fluorspar, the form of fluorite used commercially and industrially, was mined in significant quantities in the counties of Hardin and Pope in South-Eastern Illinois throughout the Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries. Fluorite was made Illinois' state mineral in recognition of its contribution to the state's identity and economy. The specimens are significant as examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century.The specimen is a piece of purple shaded fluorite (also known as fluorspar), the mineral form of calcium fluoride. The unpolished specimen presents a dark purple interior with a substantial dark grey crust representing the matrix from which the specimen was obtained. Existing label: Flourite / (purple) / probably / USA / BB /burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, fluorite, flourite, calcium fluoride, hydrofluoric acid, jewellery, indigo shire, north-east victoria, mining, illinois, usa, united states, fluorine, gemstones, purple stones -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Bituminous Coal, Unknown
Bituminous coal is the most common type of coal, abundantly found in ancient coal deposits which can be dated back millions of years. Often referred to as soft or black coal, this specimen exhibits a high carbon content, ranging from 76-86%. It also holds a relatively high energy density (27 MJ/kg) meaning that it releases significant amounts of energy when burned. Bituminous coal is most commonly used for electricity generation, as well as in the production of steel. This particular piece of coal was collected as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria in the nineteenth century. It originates from Cape Paterson, a seaside village located in South Gippsland, Victoria (located on Bunurong Country). The discovery of bituminous coal in this locality was first made in 1826 by explorer William Hovell. More discoveries were gradually made over the following decades and in 1859 the Victorian Coal Company commenced the first active coal mining operations in the state by sinking a number of shafts and bores near the area of Cape Paterson. Evidence of this coal-focused past can be found today at the State Coal Mine Museum in the nearby town of Wonthaggi. This specimen is significant as it was collected from the locality of Cape Paterson in Victoria, an area that has since become historically instrumental in the mining of coal and other substances in the state of Victoria. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A solid hand-sized piece of bituminous coal with a shiny black-grey surface and jagged edges.Existing Label: BITUMINOUS COAL / Locality: Cape / Patterson, VIC. burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, state coal mine museum, wonthaggi coal mine, victorian coal company, bituminous coal, coal victoria, coal energy generation, william hovell, cape paterson, coal specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Laterite
Laterite refers to both a rock and a soil type that is rich in clay, as well as Iron and Aluminium. It is created during a process that is called laterization, where high heat and seasonal heavy rainfall cause there to be wet and dry periods, which over time hardens the soil into rock. Because of this, most laterite is formed between tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. The iron oxide in laterite is what gives it it’s orange-red colouring. The largest religious complex in the world, Angkor Wat in Cambodia, is partially constructed of laterite, particularly its foundations, as laterite is porous and allows rainwater to drain. This specimen of laterite was collected from the Democratic Republic of Congo while it was colonised by Belgium in the 19th century. Laterite forms in many parts of the world, particularly between the tropics. It is used both for ore and as a building material, and comparing specimens from different parts of the world allows us to document the different compositions that this mineral can have when formed at different locations. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.a palm-sized solid iron-aluminium oxide mineral specimen in shades of brown, orange and greyburke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, laterite, laterite specimen, geology -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a type of clay composed of aluminium silicate that forms very small particles that are not well-bonded to one another. This is why it is so soft. When in the presence of water, all types of clay swell. Montmorillonite swells even more than most types of clay, which is why it is often chosen over other types of clay in its practical uses. Montmorillonite has many different practical uses, including in the mining industry, as a soil additive, as a sealant, as a desiccant to draw water out of the air, to clean ponds, to make kitty litter and in cosmetics. Montmorillonite is a common mineral and, despite being named after Montmorillon, France, can be found all over the world, including many deposits in Australia. It is not known where this particular specimen originates from. Montmorillonite is an economically and socially significant material with a wide variety of uses. Having samples of common and important minerals allows collections, like the Burke Museum, to have a more complete view of the land on which they are located, and therefore a more complete view of heritage. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid tennis-ball sized chunk of aluminium silicate clay. It is primarily white, accented with orange and brown.burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, clay, montmorillonite -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Cassiterite
This specimen is Cassiterite in Quartz. Cassiterite is a tin oxide metal that forms in thin crystals which can have a beautiful lustre. Quartz is made of silicon dioxide, also known as silica, and is one of the most common minerals on earth. Cassiterite has been a fundamental source of tin ore for humans throughout history, including today. Tin is an important metal that has a wide variety of human uses in different areas, from dying fabric, to making mirrors, and their most well-known use ‘tin’ cans. Tin cans are primarily made of steel and are coated with tin in order to take advantage of tin’s property of being non-corroding. This is a massive step in the history of food preservation. Tinned food first reached Australia in 1815 with early settlers, and it began to be manufactured here in the 1840s. It was incredibly popular, and was a highly exported product, which would be a contributing factor to the ‘tin mining boom’ of the early 1880s. This specimen was collected at Jingellic, New South Wales, in about 1852. Although the Goldfields of the 1800s are much more well-known, tin mines existed alongside the gold mines which began in the mid 19th century and extended almost one hundred years, to the mid 20th century. Specimens like this would have been used as evidence to justify tin mining operations in the region as an investment. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. The Geological Survey of Victoria was headed by British geologist, Alfred Richard Cecil Selwyn (1824-1902), who was responsible for issuing over 60 geological maps during his 17 years as director. These maps were all hand-drawn and coloured and became the benchmark for accuracy for geological mapping. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A fist-sized solid geological specimen made on one half of tin oxide, which is dark grey, and on the other side of silica, which is brown and cream.burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen -
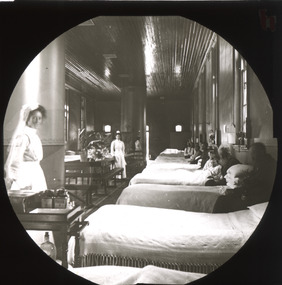 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
This glass slide captures a scene from a male hospital ward at Mayday Hills Mental Asylum. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum, Mayday Hills was officially opened on the twenty-fourth of October 1867 and was commissioned following lobbying from Beechworth Municipal Council concerning a need for better living conditions for individuals confined to the town's gaol. These individuals, as well as many others who were brought from surrounding institutions, exhibited behaviours that were deemed to be unfit for mainstream society. At its peak, the asylum consisted of sixty-seven buildings and housed over twelve-hundred patients and five-hundred staff. At the time of Australian Federation in 1901 - just a year after this photograph was taken - the patient population numbered six-hundred and seventy-four. The asylum was officially closed in 1996. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being architecturally significant. The extensive complex of buildings are examples of Italianate-style, which is strongly associated with asylums of the 1860s - the period in which construction of this particular asylum began. Today the asylum offers tours to visitors, including daytime history tours and night-time ghost tours. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is socially and historically significant as it is representative of the lives of the nurses and patients at Beechworth Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century. It is also historically significant as it is representative of the changing style of treatments and attitudes towards mental illness. Thin translucent sheet of glass with a circular image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.Obverse: h /lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, mayday hills, mayday hills hospital, mayday hills asylum, beechworth lunatic asylum, beechworth mental asylum, psychiatric hostpital, beechworth, burke museum, beechworth municipal council, beechworth patients, psychiatric patients, victorian heritage register, 1900, 1900 mayday hills, italianate style, 19th century asylums, asylums victoria, male ward mayday hills -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
This glass slide presents an image of the Old Beechworth Post Office and was taken in the year 1900. The building displayed within the image is not that of the post office in its original form; the post office originally consisted of only a simple wooden building. With the establishment and growth of new towns across Victoria, as well as an increased need for more consistent communications with the City of Melbourne, this modest building was soon deemed inadequate. In 1858 it was brought into the style of the changing times, with the tall clock tower added in 1865. This transition aligned with a pattern of refurbishment and conversion of many Beechworth buildings (which could be seen during the 1860s-70s), aiding in the growth and prosperity of the town. Early makeshift homes were turned into more substantial dwellings, featuring elements such as weatherboard, brick, and granites materials, and gabled or hipped roofs with iron lacework fringing the verandah. These refurbishments were temporarily halted in March of 1867 when a fire swept through the town, damaging many buildings including the post office. This led to further reconstructions on the building, including heightening of the clock tower, and in 1870 the two-storey Italianate style building was completed. The Old Beechworth Post Office itself also holds significance due to its connection with one of Australia's most infamous families. It reportedly played an important role in communicating the news of the 1880 murders of police at Stringybark Creek by the Kelly Gang. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques. This glass slide captures social and historical significance as it displays the Old Beechworth Post Office in 1900, a building that demonstrates the prosperity and growth of Beechworth as a town during this time period. This slide also holds a level of aesthetic significance due to the Italianate style building that is featured in its image; a style that became very popular during the nineteenth-century. Thin translucent sheet of glass with a square image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.Obverse: x / burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, beechworth post office, beechworth post office kelly gang, 1900, 1900 beechworth, growth of beechworth, 1867 beechworth fire, old beechworth post office, beechworth post office reconstructions, italianate style, italianate style buildings, italianate style beechworth post office -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Taken in approximately 1900, this glass slide captures an image of a Mayday Hills Mental Asylum nurse. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum, Mayday Hills was officially opened on the twenty-fourth of October 1867 and was commissioned following lobbying from Beechworth Municipal Council concerning a need for better living conditions for certain individuals confined to the town's gaol. These individuals, as well as many others who were brought from surrounding institutions, exhibited behaviours that were deemed to be unfit for mainstream society. At its peak, the asylum consisted of sixty-seven buildings and housed over twelve-hundred patients and five-hundred staff. At the time of Australian Federation in 1901 - just a year after this photograph was taken - the patient population numbered six-hundred and seventy-four. The designated site of the institution was chosen due to its scenery and altitude. It was argued that these picturesque surroundings would assist in curing the hospital's patients of their ailments. The asylum was officially closed in 1996. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being architecturally significant. The extensive complex of buildings are examples of Italianate-style, which is strongly associated with asylums of the 1860s - the period in which construction of this particular asylum began. Today the asylum offers tours to visitors: both daytime history tours and night-time ghost tours. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is socially and historically significant as it is representative of the lives of the nurses who worked at Beechworth's Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century. Thin translucent sheet of glass with a portrait image printed on the front. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, mayday hills, mayday hills mental asylum, beechworth asylum, beechworth asylum nurses, psychiatric nurses, psychiatric care, 1900 mayday hills, victorian heritage register, italianate style, 19th century asylums, asylums victoria -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Taken in approximately 1900, this glass slide captures an image of two Mayday Hills Mental Asylum nurses. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum, Mayday Hills was officially opened on the twenty-fourth of October 1867 and was commissioned following lobbying from Beechworth Municipal Council concerning a need for better living conditions for certain individuals confined to the town's gaol. These individuals, as well as many others who were brought from surrounding institutions, exhibited behaviours that were deemed to be unfit for mainstream society. At its peak, the asylum consisted of sixty-seven buildings and housed over twelve-hundred patients and five-hundred staff. At the time of Australian Federation in 1901 - just a year after this photograph was taken - the patient population numbered six-hundred and seventy-four. The designated site of the institution was chosen due to its scenery and altitude. It was argued that these picturesque surroundings would assist in curing the hospital's patients of their ailments. The asylum was officially closed in 1996. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being architecturally significant. The extensive complex of buildings are examples of Italianate-style, which is strongly associated with asylums of the 1860s - the period in which construction of this particular asylum began. Today the asylum offers tours to visitors: both daytime history tours and night-time ghost tours. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is socially and historically significant as it is representative of the lives of the nurses who worked at Beechworth's Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a portrait image printed on the front. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, 1900 mayday hills, mayday hills, beechworth mental hospital, beechworth mental asylum, beechworth asylum nurses, psychiatric nurses, psychiatric care, victorian heritage register, italianate style, 19th century asylums, asylums victoria -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybellows, late 19th century-early 20th century
These bellows are from the Lynn property at Jarrahmond and were used in the blacksmith's shop. It was common for rural properties to have , of necessity, their own blacksmithing facilities.These bellows are from the Lynn property at Jarrahmond and were used in the blacksmith's shop. It was common for rural properties to have , of necessity, their own blacksmithing facilities. The Lynn family settled in Orbost circa 1890 and is well known in the Orbost area.Wood and leather bellows with metal studs. The frame and handle were constructed by Graham Fall c.2009 and are not original. The handle is attached by a chain. This was probably used on the Lynn property at Jarrahmond in the blacksmith's shop.blacksmith bellows tools -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Elizabeth and Philip, January 1, 1947
This is a short study of Princess Elizabeth and Lieutenant Philip Mountbatten, written expressly to coincide with their wedding. It tells some of the stories behind the Royal romance as well as sketching the personalities and characters of the young Royal couple. The book probably belonged to Mary Gilbert, a prominent member of the Orbost community - a teacher and historian who was the first curator of the Orbost Museum. This book is a useful reference tool.A 64 pp dark blue hardback book with gold print on the cover - ELIZABETH and PHILIP and underneath a gold line - LOUIS WULFF, M.V.O. It contains b/w photographs and stories of Princess Elizabeth and Lieutenant Philip Mountbatten. It is authored by Louis Wulff, M. V. O.Inside front cover - in brown pencil - Gilbertsroyal-family princess-elizabeth gilbert-mary -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyframed photographs, 2420.1 : WW1 2420.2 : late 1970's
Ormond Andrews (b 1894 d 1987) was an original ANZAC who enlisted from Orbost. He lived at 19 McLeod Street in Orbost and opened Andrews Mensland in Nicholson Street, Orbost. From Allan McKenzie - "The other person in the photograph with Orme is my grandfather, George Piper from North Fitzroy Vic who was a pilot with the RAAF in WW1. Orme and George were very good friends in later life."This item is a reminder of a well-known Orbost identity.Two framed b/w photographs of Orme Andrews. 2420.1 is a photograph of two airmen in uniform - one standing (most likely George Piper). Orme Andrews is sitting. The frame is painted wood. The photo is inset with an embroidered mount and has a hanging wire. 2420.2 is a wooden framed photograph of Orme Andrews as an older man. He is wearing a suit and has an air force badge on the lapel of the jacket. It has a stand.2420.1 - has label written in pen -Mr Orme Andrews 2420.2 - has label - Mr Orme Andrews 1894-1973andrews- orme -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societymagazine, Woman and Home, September 1940
Women’s magazines during WWII played a “reflecting role,” meaning they cooperated with government agendas while still including topics of readers’ interests Women’s employment rate skyrocketed during WWII. However, even though the number of women working outside the home grew rapidly most of them were still engaged entirely in homemaking. Therefore women’s magazines centered mostly on the stresses and shortages of wartime. Articles as well as advertisements presented information on “product rationing, tips on keeping the family healthy, guidelines for thrifty shopping and advice on how to look good through it all.This is an example of an English women's magazine published during WW11.It gives practical advice on needlework / knitting and evidences the widespread interest in contemporary fashion. In doing so it shows what were the fashionable, but broadly affordable, women's and children's clothing styles of their day. These magazines also reflect women's interests.A 64 pp magazine, titled Woman and Home and Good Needlework Magazine. The front cover has a a coloured picture of a man in a uniform and woman sitting at a round table drinking tea and photographs of knitted jumpers, the patterns of which are inside the magazine.Handwritten on front cover in pencil -Mehlert -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societymagazine, Woman and Home, October 1951
Women’s magazines just after WWII played a “reflecting role,” meaning they cooperated with government agendas while still including topics of readers’ interests Women’s employment rate had skyrocketed during WWII. However, even though the number of women working outside the home grew rapidly most of them were still engaged entirely in homemaking. Therefore women’s magazines centered mostly on the stresses and shortages of wartime. Articles as well as advertisements presented information on “product rationing, tips on keeping the family healthy, guidelines for thrifty shopping and advice on how to look good through it all.This is an example of an English women's magazine published post WW11.It gives practical advice on needlework / knitting and evidences the widespread interest in contemporary fashion. In doing so it shows what were the fashionable, but broadly affordable, women's and children's clothing styles of their day. These magazines also reflect women's interests.A 64 pp magazine, titled Woman and Home and Good Needlework Magazine. On the front cover is a coloured drawing of a fashionably dressed and made-up woman with red hair and holding a bunch of similarly coloured flowers (gerberas?) At the bottom left are knitted baby clothes - pattern inside - as well as a man and woman wearing fashionable clothing - suggesting patterns are inside the magazine. The magazine cost 1/6 and is dated October 1951.magazine-woman-and-home -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societymagazine, The Australian Woman's Mirror, September 1945
The Australian Woman's Mirror, was an Australian weekly women's magazine published by The Bulletin magazine in Sydney, between 1924 and 1961.Women's magazines reflect class and family structures as well as contemporary women’s role in society. A 32 pp magazine, titled The Australian Woman's Mirror. The magazine's contents include recipes, knitting patterns and articles about fashion, holiday destinations and household tips.It also contains short stories, poems, and a serialised novel. On the front cover is a b/w photograph of a woman wearing a knitted jerkin indicating that the pattern is inside the magazine. The magazine cost 3d and is dated Tuesday, Sept. 4 1945.magazine-the- australian-woman's-mirror literature -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societynewspaper articles, Dramas of a Real Country Practice, September 1987
David Hollands is a country doctor who has had a lifelong passion for birds and bird photography. Born and educated in England he arrived in Australia 1961 with his wife Margaret.Together they were in practice in Orbost from 1963 - 2000.Dr's David and Margaret Hollands have made a significant contribution to the Orbost district with their service to medicine as well as their documentation off its history. These articles are useful research items.Original plus a copy of a newspaper article titled, Dramas of a Real Country Practice. It is from the Herald newspaper of September 9, 1987. The article pertains to the life and practice of Dr David Hollands of Orbost. 2454.1 is the original and 2454.2 is a copy.hollands-david medicine -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyjacket, first half 20th century
This jacket was made for Marjorie Burton by her mother who was a milliner and an excellent dressmaker who worked from home. She made all of Marjorie's clothes, hats and outfits. as a result, Marjorie was always well-dressed in stylish clothing.. This item is an example of a handcrafted item and reflects the handcraft skills of women during the first half of the twentieth century.A hand-sewn short-sleeved velvet jacket. It has fur cuffs. It is lined with a cream coloured satin-like material which has been used to make a narrow collar.jacket hand-sewn burton-marjorie needlecraft -
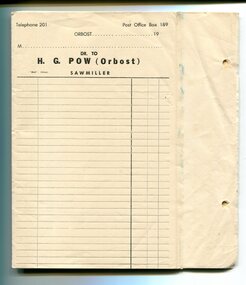 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyinvoice forms, Snowy River Mail as "Mail" Print, 19th century
These invoice forms were to be used by Hector G. Pow's Sawmiller Company in Newmerella ( Henty's & Pow). Pow's had a mill at Cabbage Tree as well. The mill is currently owned by Mectec.Orbost has historically been based on the timber industry, but that industry has declined considerably over the last 20 years. The number of locals involved in the timber industry has declined and many of the mills have closed. This item reflects a time when that industry was a significant contributor to the economy of the district.Unused invoice forms for H.G.Pow Orbost Sawmillers. They are white paper with black print and lines. On the right hand side are two small holes for filing. The page is perforated with carbon underneath to provide two copies - one for filing and one for the customer. At the top of each page is "Telephone 201 Post Office 189 Orbost" and a line for the date. Below this is a line for the customer's name and "Dr to H.G. Pow (Orbost) Sawmiller". There are columns for item descriptions and costs.h.g.pow sawmills timber-orbost -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, E-Gee Printers, Middleton & Manning's Gippsland Directory 1884-5, 1983
The 1884-1885 Directory was the first year of publication for the Middleton and Manning's Gippsland Directory. It was first published by Ale Middleton and Francis Beresford Manning. Beginning with advertisements from local businesses of the time, this is followed by a short gazetteer of places around the region, as well as general information on the districts of Gippsland. The main part of the Directory consisting of about 100 pages, is the Alphabetical Directory. Listed alphabetically by surname under each region, this lists heads of household (mostly male but there are a few females mentioned), together with their occupation and address.The list includes farmers, labourers, coach painters, dairywoman, teacher, saddler, brickmaker, merchant, laundress, hotel keeper, minister of religion, dressmaker, grocer, grazier, gasfitter, seedsman, coachbuilder, engineer, auctioneer, upholsterer, fowler, journalist, surveyor, musician, traveller, watchmaker, solicitor, restaurant keeper, blacksmith and miner. It is not just "business owners" mentioned in this directory it is everyone. (ref Gen E Books)This is a useful reference tool.A 135 pp soft covered book with an orange/brown cover. On the front cover in black print is a range of advertisements or local businesses. It contains a short gazetteer of places in the region as well as general information on the districts of Gippsland. The main part of the directory is an alphabetical list of the household , with occupations and addresses. This is a reprint of the original.directory-gippsland book-middleton-manning-1884-5 -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Brown, Prior & Co, In the Dawning of the Day, 1916
Many of the poems contained in this book were written by Burns while at school and first appeared in "The Scotch Collegian" which he edited in 1913-1914. Four of his editorials are included. Prose and verse tributes by former schoolmates and fellow soldiers are included, as well as an essay on Burns by the headmaster of Scotch College, W.S. Littlejohn. James Drummond Burns was born in Geelong in 1895. James was the first of eight children born to Hugh and Mary and while he was born at Geelong the family had moved to Bairnsdale by 1905. As Methodist minister, Hugh had accepted the posting to Bairnsdale where the family stayed till about 1913. He died in Gallipoli on September 18 1915. James was a student when he enlisted on 2 February 1915 at Lilydale, Victoria. He served in the 21st Battalion with the rank of Corporal. His Regimental Number was 805. (ref. Scotch College World War I Commemorative Website) This book is a tribute to a WW1 soldier and contains contemporary writing which can be used in research. A thin 32 pp paper back book with a brown cover. On the cover is the title, "In the Dawning of the Day: in Memoriam, J. D. Burns", in black print inside a rectangular red/gold/black line frame. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societywages sheets, 1.7.1970 - 30.6.1988
These forms were used by Hector G. Pow's Sawmiller Company in Newmerella ( Henty's & Pow). Pow's had a mill at Cabbage Tree as well. Hec Pow and his father sold the Newmerella mill to Henry Silverberg and Les Grace. The mill is currently owned by Mectec.Orbost has historically been based on the timber industry, but that industry has declined considerably over the last 20 years. The number of locals involved in the timber industry has declined and many of the mills have closed. This item reflects a time when that industry was a significant contributor to the economy of the district.Thirty dark green hard-backed folders with black spines and silver metal fastenings, containing wages sheets for employees of POW's Sawmills P/L. All have labels with "POW's Sawmills P/L" and dates of wages sheets included. They are hand-written. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybottle, 1930's
T. C. W. CO. is a trademark belonging to the T. C. Wheaton Company--a glassware manufacturer most well-known for their medicine bottles. this small bottle may have contained serum used for animal medication on a local farm.This small bottle is an early example of a glass container used to hold veterinary medicine.A small clear glass bottle with a seal -possibly cork with a metal top.on base - TCW Co 5?0 USAbottle t.c.wheaton container -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societycertificate, 1st March 1907
The Lynn family is well-known in the Orbost area. Ethel Lynn is believed to have been working at Bairnsdale in 1924. Ethyl Lynn was the only child of Samuel James Lynn and Elizabeth Jane Lynn ( nee Warren). Samuel Lynn (1865-1949) was a farmer and grazier at Jarrahmond and bred ClydesdalesThis item is a part of the educational history of the Orbost district.A black / white certificate of merit from the Education Department, Victoria for Ethel Lynn. The certificate is 20969. It is dated at Jarrahmond State School No. 2745 on the 1st march 1907 and certifies that Ethel Lynn has passed in all subjects of instruction for the Sixth Class. It has been signed by E.R. Davey, Inspector of Schools.education jarrahmond lynn-ethel -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societydocuments, originals - late 19th - early 20th centuries
Archie Munro was a well-known Orbost identity who first operated a boot shop in Cameron's barn. He was also active in the promotion of the first brass band in Orbost. He was the son of Hector Munro.Archie Munro was a well-known Orbost identity who first operated a boot shop in Cameron's barn. He was also active in the promotion of the first brass band in Orbost. A collection of photocopied documents. The originals are from the writing desk of A.D. Munro ( Reg. 368).munro-archie dcouments -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyaccount, November 29 1911
This account was sent fro H. James & Co to Robert Pullar Cameron. Henry James (1860-1932) was a well-known identity in the Orbost district. He was a stock agent and auctioneer who helped to establish the seed bean industry in Orbost. He was the second secretary of the Snowy River Shipping Co. as well as a shire councillor and prominent member of MUIOOF. Robert Pullar Cameron was a Shire Councillor for many years. He married Penuel Hossack and had a family of James, Flora, Penuel and Alex. Henry James (1860-1932) was a well-known identity in the Orbost district. This item is an example of a hand-written document used by an early Orbost business. It is a useful research tool.Two white paper accounts , red lines and black print. It is from H. James & CO - Freighters to R. Cameron.james-henry cameron-robert-pullar account
