Showing 1380 items
matching quick
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino arriving in port, taken 1930-1932. Decks are laden with men and women , crowd of waving people along the river bank, smoke coming from funnel. Warehouse and homes in the background. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, forecabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade in along the West Coast of Victoria. (Belfast is the original name for Port Fairy, South West Victoria. The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, whose had a hay and corn store and shipping agency was on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, then Captain Middleton then took command 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers . Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life through shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection show S.S. Casino underway in heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy). This photograph is significant because of its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino 1882-1932 and its significance to trade along Victoria's West Coast in the late 19th and early 20th century. The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck under State and Commonwealth Law in the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino arriving in port, taken 1930-1932. Decks are laden with men and women , crowd of waving people along the river bank, smoke coming from funnel. Warehouse and homes in the background. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, saltau and osburne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino taken 1930-1932. The Casino is berthed at the Warrnambool Breakwater, either loading or unloading. A person is attending a container at the bottom of a ramp between ship to Breakwater. People are sitting or standing on the Breakwater. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, forecabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade in along the West Coast of Victoria. (Belfast is the original name for Port Fairy, South West Victoria. The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, whose had a hay and corn store and shipping agency was on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, then Captain Middleton then took command 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers . Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life through shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection show S.S. Casino underway in heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy). This object is significant because of its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino 1882-1932 and its significance to trade along Victoria's West Coast in the late 19th and early 20th century. The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck under State and Commonwealth Law in the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino taken 1930-1932. The Casino is berthed at the Warrnambool Breakwater, either loading or unloading. A person is attending a container at the bottom of a ramp between ship to Breakwater. People are sitting or standing on the Breakwater.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, saltau and osburne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBarometer, 1858-1869
The barometer was either made or sold by T. Gaunt & Co. of Melbourne, a manufacturer, importer and retailer of a wide variety of goods including jewellery, clocks and watches, navigational and measuring instruments, dinnerware, glassware and ornaments. Thomas Gaunt photograph was included in an album of security identity portraits of members of the Victorian Court, Centennial International Exhibition, Melbourne, 1888. (See below for further details.) Admiral Fitzroy Pattern Barometer History: The stick mercury barometer was named after Admiral Robert Fitzroy of the Royal Navy (1805-1865) for his detailed instructions on how to interpret the weather, which were included with the instrument. Fitzroy was the captain of the HMS Beagle, also a weather forecaster to Charles Darwin and the second Governor of New Zealand. He developed many different types of barometers and was the first person to introduce the science of weather forecasting to the British Isles. A local manufacturer of scientific instruments, Thomas Gaunt, produced the barometer that was adapted for the southern hemisphere by Robert Ellery, the State Astronomer based at the Melbourne Observatory. In the original sale catalogue for Gaunt's, the item is described as "Gaunt's Fitzroy Barometers" and it was priced from 25/- to ₤9.9s. History of Thomas Gaunt: Thomas Gaunt established Melbourne's leading watchmaking, optical and jewellery business during the second half of the 19th century. Gaunt arrived in Melbourne in 1852, and by 1858 had established his own business at 14 Little Bourke Street. Around 1869 he moved to new premises in Bourke Street on the corner of Royal Arcade. Gaunt's shop quickly became a Melbourne institution. Gaunt proudly advertised that he was 'The only watch manufacturer in the Australian colonies'. While many watches and clocks may have had Gaunt's name on the dial, few would have been made locally. Gaunt did make some watches for exhibitions, and perhaps a few expensive watches for wealthy individuals. Gaunt's received a telegraph signal from Melbourne Observatory each day to correct his main clock and used this signal to rate and repair ship's chronometers and good quality watches. His main horological manufacturing was directed at turret clocks for town halls, churches and post offices. These tended to be specific commissions requiring individualised design and construction. He made the clock for the Melbourne Post Office lobby, to a design by Government Astronomer Robert Ellery, and won an award at the 1880-81 Melbourne International Exhibition for his turret clock for the Emerald Hill Town Hall. He became well known for his installation of a chronograph at Flemington Racecourse in 1876, which showed the time for the race, accurate to a quarter of a second. The firm also installed the clockwork and figures for Gog and Magog in the Royal Arcade. Thomas Gaunt also developed a department that focused on scientific instrumentation, making thermometers and barometers (from imported glass tubes), telescopes, surveying instruments and microscopes. Another department specialised in electroplating for trophies, awards and silverware, and the firm manufactured large amounts of ecclesiastical gold ware and silverware, for the church including St Patrick's Cathedral. There are no records that disclose the number of employees in the firm, but it was large enough for Gaunt to hold an annual picnic for the watchmakers and apprentices at Mordialloc from 1876; two years previously they had successfully lobbied Gaunt to win the eight hour day. Gaunt's workforce was reportedly very stable, with many workers remaining in the business for 15 to 30 years. Gaunt's wife Jane died on September 1894, aged 64. They had one son and six daughters, but only three daughters survived to adulthood. Two became nuns at the Abbotsford Convent and one daughter, Cecelia Mary Gaunt (died 28 July 1941), married William Stanislaus Spillane on 22 September 1886 and had a large family. Gaunt died at his home in Coburg, Victoria, leaving an estate valued at ₤41,453. The business continued as T. Gaunt & Co. after his death. The barometer is historically significant as an example of the work of Melbourne’s leading scientific instrument maker, Thomas Gaunt. The barometer has social significance as an example of the type of scientific equipment that Thomas Gaunt expanded his horology business into producing. Further social significance lies in the fact that Robert Ellery, the Government Astronomer who designed the local version of the barometer, had a direct connection with the Melbourne Athenaeum founded in 1839 as the Melbourne Mechanics' Institution. Its purpose was "the diffusion of literary, scientific and other useful information". There are also records of a T Gaunt as a subscription and committee member of this the Athenaeum organisation during the 1870s and 1880s which may be Thomas Gaunt, unfortunately still unverified.Stick mercury barometer known as the Admiral Fitzroy Barometer. It comprises an oblong wooden case with glass front panel, ornate pediment, barometer with bulb cistern (empty of fluid), cleaning brush with printed instructions for interpreting information given by the gauge affixed to left and right face of instrument. Includes a thermometer. The barometer appears to be intact. Adapted to the Southern Hemisphere. Special remarks by Admiral Fitzroy. Made by Thomas Gaunt, Melbourne. Manufacturer's details are on back of wooden casing. Rear has upper and lower brass screw plates for securing to vertical surface."Manufactured by Thomas Gaunt, 14 Little Bourke Street, Melbourne. "flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, barometer, admiral fitzroy, thomas gaunt, thomas gaunt of melbourne, clockmaker, admiral fitzroy barometer, barometer instructions, gaunt’s fitzroy barometer, gaunt’s of melbourne, gog and magog designer, horological manufacturer, meteorological instrument, melbourne athenaeum, melbourne mechanics' institution, melbourne observatory time signal, robert ellery government astronomer, scientific instrument, stick mercury barometer, thermometer, weather forecast, t gaunt & co -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCopper Sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or "Muntz metal" - 60% copper and 40% zinc, used to line the hull of the Schomberg to prevent shipworm infestation. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. There are 11 irregular shaped small pieces. Verdigris, nail holes and slight encrustation.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCopper Sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or "Muntz metal" - 60% copper and 40% zinc, used to line the hull of the Schomberg to prevent shipworm infestation. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. Folded, with verdigris, marine growth and slight encrustation. Irregular shaped 2' 2" long by 2' 1" wide.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing, ca 1855
This sheet of copper sheathing or Muntz metal has been recovered from the sea at the wreck-site of the ship SCHOMBERG. . It has been damaged by the reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and has other damage that has caused the edges to break away or fold over. Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in seawater and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUTH THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its dayCopper sheathing or Muntz metal recovered from the shipwreck Schomberg. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, coppper sheathing, ship building, sea worm -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCopper Sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or "Muntz metal" - 60% copper and 40% zinc, used to line the hull of the Schomberg to prevent shipworm infestation. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. With verdigris, marine growth and slight encrustation. Irregular shaped 1' 2½" Wide by 2' 7" long.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCopper Sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Piece of rectangular Muntz metal from the wreck of the Schomberg. Metal has been bent back on itself at one end. Evidence of nail holes. Metal has verdigris and marine encrustation. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Australian Commando Association - Victoria
Australian Commando Association - VictoriaBook, A history of the 2nd Independent Company and 2/2nd Commando Squadron
The history of the No. 2 Independent Commando Company and 2/2 Commando Squadron during World War II – scarce as a 1st edition dated 1986. Having completed its training at Foster, on Wilson’s Promontory, Victoria, the 2nd Independent Company was raised and travelled north to Katherine, in the Northern Territory. However, following Japan’s entry into the war, as with the other independent companies that were sent to the islands off Australia, the 2nd was sent to Timor, where it joined the 2/40th Battalion and the rest of Sparrow Force. Sparrow Force divided itself between west Timor, part of the Netherlands East Indies, and east Timor, which belonged to Portugal. The 2/40th Battalion defended the capital of west Timor, Koepang, and the airfield at Penfui. Most of the independent company moved to the airfield at Dili, in east Timor, and the nearby mountains. Portugal was opposed to the stationing of a Dutch or Australian garrison in case this provoked the Japanese, but despite this opposition, on 17 December 1941, elements of the 2nd Independent Company and Dutch troops landed near Dili. On 20 February 1942 the Japanese invaded the island, attacking east and west Timor simultaneously. The 2/40th Battalion held out for three days, but were overrun and were killed or captured. Similarly, the 2nd could not hold the airfield and were also driven back. But they were not captured and instead retreated to the mountains where they conducted a very successful and pursued a guerrilla war against the Japanese which lasted for over a year. Following the capture of Timor, the 2nd occupation the company was listed as “missing”, the company’s signallers were able to build a wireless transmitter, nicknamed ‘Winnie the War Winner’, and on 18/19 April were able to contact Darwin. At the end of May RAN vessels began landing supplies for the Australians on the south coast of east Timor. These supply runs were very dangerous but they allowed the Australians on Timor to continue fighting. In September the guerillas were reinforced with the 2/4th Independent Company. However, this could not go on indefinitely. In August the Japanese lunched a major offensive against the guerrillas and Japanese reprisals against the civilian population of east Timor reduced their support for the Australians. The 2nd (now named the 2/2nd Independent Company) and 2/4th were withdrawn in December and January 1943 respectively. Although the 2/2nd Independent Company is best known for its time on Timor, it also saw extensive service in New Guinea and New Britain. The independent company reformed at the army’s training centre at Canungra, Queensland, where it was reinforced and reequipped. The company then moved to the Atherton Tableland, where it briefly became part of the 2/6th Cavalry (Commando) Regiment. Due to this reorganisation, in October, the 2/2nd Independent Company was renamed the 2/2nd Cavalry (Commando) Squadron. This name was later simplified to just commando squadron. When this happened though, the 2/2nd was back in action. In June 1943 the 2/2nd sailed from Townsville for Port Moresby and was subsequently flown to Bena Bena, in the Bismark Range in New Guinea’s highlands. Here they supported the 2/7th Independent Company in patrolling the Ramu River area. In the second week of July the 2/2nd moved into position, with its headquarters at Bena Bena and with its platoons’ occupying neighbouring positions. By the end of the month their patrols were skirmishing with the Japanese. The 2/2nd remained in New Guinea until October 1944. After 90 days leave, the squadron reformed at Strathpine in Queensland before sailing to New Britain in April 1945. The 2/2nd landed at Jacquinot Bay on 17 April. The squadron then moved to Wide Bay, in order to support the 13th Brigade of the 5th Division, and was based at Lamarien. Following Japan’s surrender and the end of the war, the ranks of the squadron thinned quickly as men were discharged or transferred to other units. For those who were left, they returned to Australia and in early 1946 the 2/2nd Commando Squadron was disbanded. Includes Nominal Roll Soft Cover without Dust Jacket – 270 pages -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Line throwing pistol, 1925-1945
This is a SPRA, or Schermuly’s Pistol Rocket Apparatus. The large firearm type pistol would have been used to throw a line between ships, usually in the event of saving lives. The line throwing pistol consists of a long barrel with handle attached, a pistol grip and trigger, which fires a short blank cartridge. Accessories for the pistol included: flares, 12 gauge adaptor (to shoot 12 gauge flares), a wood plunger, and boxes of faked line. The stamp on the handle, Crown over "NP" is a Birmingham Proof House mark that dates the pistol between 1904 and 1954. However Schermuly's line throwing pistol was invented in the 192s and used on British Naval Ships from 1929. The serial number '22507' is only 806 numbers later than one on sale as a British Military WWII issue SRPA '21701'. This pistol appears to be made 125-1945. The apparatus was used as a life saving device for crew and passengers on vessels in distress that were only a few hundred metres from shore, often eliminating the need to launch a boat and risk lives to go out to the vessel in dangerous conditions. It could also be used from ship to ship rescue. The pistol would launch a line from shore to the vessel. The line would be attached to the vessel, then shore crew would send out equipment, including a breeches buoy, in which the stranded people could be pulled to shore. It has saved many lives at sea. The cartridge is loaded into the breech of the pistol and the rocket is inserted into the muzzle. On pulling the trigger, the gases generated by the fired cartridge eject the rocket on its correct line of flight, and at the same time, burst through the waterproof disc and ignite the propellant mixture, which carries the rocket and line on the remainder of the flight. The rocket consists of a weldless steel case filled with propellant mixture sealed in by a waterproof disc. Fixed to the rocket case is a direction bridle, to the end of which a short length of flexible steel wire is attached, this in turn being connected to the end of the line to be thrown. A complete rocket set, or line throwing kit. would include a wood carrying case, two coils of faked line in separate compartments, three rockets and a can of six cartridges. William Schermuly (1857 – 1929) - Founder of the Schermuly business. In 1897 he invented a trough-fired, line throwing apparatus. In 1920 he and his third son, Alfred James Schermuly, invented the pistol rocket apparatus and promoted this overseas during the 1920s. The system was approved by the British Navy in 1929 through an Act of Parliament, which made it compulsory for ships over 500 tons to carry this equipment. The company, Schermuly Pistol Rocket Apparatus Ltd., grew quickly during and after World War II but business eased off during the 1970s before it eventually closed in the 1990s. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. This line-throwing pistol is part of he Rocket Launching Equipment used to perform life-saving rescue at sea from the 1920s. It is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Pistol, line-throwing, SPRA (Schermuly's Pistol Rocket Apparatus). This line throwing pistol has a wooden pistol grip, brass trigger mechanism, and a long, wide, steel barrel with Bakelite handle attached to the top. Inscriptions are stamped onto the pistol.Stamped on handle: "5" and "[symbol of a Crown] above NP" , "22507", "[within oval] SPRA" Stamped on barrel: "L22507".gun, pistol, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, line throwing, line throwing pistol, spra, schermuly's pistol rocket apparatus, sea rescue, pyrotechnicks, marine technology, schermuly pistol rocket apparatus ltd., william schermuly, alfred schermuly, pistol line thrower, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime village, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, beach rescue set, rocket set, schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, pistol rocket apparatus, line throwing cartridge, line-throwing rocket, firearm, life saving, lsrc -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePrint - Vessel - Steamship, A.V. Gregory, SS Casino off Point Lonsdale, ca. 1899-1932
Print of a picture of the S.S. Casino, This print is from an original painting by the Australian marine artist A V Gregory (1867-1957), also known as Arthur Victor Gregory. Gregory lived and worked in South Melbourne. He took over the Gregory Studio owned by his father, George Frederick Gregory, painting actively between 1899 and 1932. He usually signed his works as ‘A V Gregory’. Some of his original works have been sold for thousands of dollars. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and a depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, a fore cabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade along the West Coast of Victoria. (The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, who had a hay and corn store and shipping agency on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her from 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, and then Captain Middleton then took command from 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers. Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life in a shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century, the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection shows S.S. Casino underway in the heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy).This print of the S.S. Casino is of significance for its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino. The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck under State and Commonwealth Law in the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). The detailed image of the vessel depicted in this print shows one of the many sail and steam vessels painted by the renowned Victorian marine artist A V Gregory, whose original works are highly valued today by marine collectors.Print with hand-painted watercolour highlights depicting the port side steamship SS Casinounderway in a heavy sea, merchant flag flying at the stern. Mounted in a decorative wooden frame behind glass. The original painting was by A V Gregory. The title of the picture is repeated in handwritten words on the matte below the artist's signature on the print.Signed "A V Gregory" Hand painted title "SS Casino off Point Lonsdale"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, saltau and osburne, a v gregory, arthur victor gregory, melbourne artist -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel, The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company's S.S. "Casino, 425 Ton, Late 19th to early 20th centuries
This black and white photograph shows the image of the coastal trading vessel S.S. Casino, with both sail masts and steam funnel. Men in hats are clearly visible on deck. The ship is in calm water and only light rigging is on the masts. Other vessels are in the background. Photograph is taken 1882-1932. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, forecabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade in along the West Coast of Victoria. (Belfast is the original name for Port Fairy, South West Victoria. The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, whose had a hay and corn store and shipping agency was on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, then Captain Middleton then took command 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers . Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life through shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection show S.S. Casino underway in heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy). This photograph is significant because of its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino and its significance to trade along Victoria's West Coast in the late 19th and early 20th century. It was taken 1882-1932 The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck under State and Commonwealth Law in the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Photograph, black and white, taken 1882-1932. Foreground is vessel SS Casino, the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company's coastal trading ship. The ship, in calm water, has light rigging on its masts and also a steam funnel. One lifeboat is visible. People are on the deck. The background shows other vessels.Under the photograph "The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company's S.S. "Casino," 425 Tons"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, saltau and osburne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing, ca. 1855
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three-masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the cover and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its dayCopper sheathing or "Muntz metal" - 60% copper and 40% zinc, used to line the hull of the Schomberg to prevent shipworm infestation. The sheet was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. It is irregular in shape with nail holes and slight encrustation.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building, late 19th century sailing ships -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or Muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by the reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and has other damage that has caused the edges to break away or fold over. Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in seawater and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day This Muntz sheet was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. It has been folded, bent and wrinkled. It has nail holes, Verdigris, marine growth and slight encrustation. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCraft - Ship Model, S.S. Casino
Ship model of coastal trader SS Casino in glass fronted case with stained wood frame. Ship has both steam and sail. Background of lighthouse on cliff, sea and sky. Ship painted green, 3 flags flying. Details (incorrect) of ship painted in white across top frame of case. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, forecabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade in along the West Coast of Victoria. (Belfast is the original name for Port Fairy, South West Victoria. The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, whose had a hay and corn store and shipping agency was on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, then Captain Middleton then took command 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers . Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life through shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection show S.S. Casino underway in heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy). This ship model is significant because of its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino 1882-1932 and its significance to trade along Victoria's West Coast in the late 19th and early 20th century. The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck under State and Commonwealth Law in the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Ship model SS Casino in glass fronted case with stained wood frame. Ship has both steam and sail. Background of lighthouse on cliff, sea and sky. Ship painted green, 3 flags flying. Details of ship painted in white across top frame of case. NOTE: Correct details for shipwreck is 10 July 1932, at Apollo BayPainted in white on wood across top of case "SS CASINO WRECKED AT APOLL BAY JUNE 10 10 LIVES LOST".flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, ship model s.s. casino, saltau and osburne -
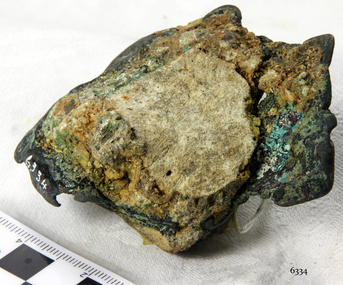 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCopper sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or Muntz metal in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, The Robins, 13 Kangaroo Ground-Warrandyte Road, North Warrandyte, 2 March 2008
Built by noted artist Theodore Penleigh Boyd, father of architect Robin Boyd. Covered under National Estate, National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Local Significance and Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p111 The Robins at Warrandyte,* was once home to a member of a famous family and is also one of the first reinforced concrete houses in Victoria. The builder, Theodore Penleigh Boyd, born in 1890, was a talented painter1 noted for his works of the Warrandyte bush. He was the father of architect Robin Boyd, author of the Australian Ugliness and the uncle of painter, Arthur Boyd. Penleigh Boyd’s great grandfather was Sir William A’Beckett, Victoria’s first Chief Justice. Penleigh Boyd is considered by some to be an ‘unsung hero’ overshadowed by more famous members of his family. Mornington Gallery Director Andrea May said many believed Boyd ‘had never received the national acclaim that he deserved’.2 Classified by the National Trust3 and part of the Australian National Heritage,4 The Robins is set well back near the end of Kangaroo Ground – Warrandyte Road, unobserved by passers-by. Built in 1913, The Robins has some Art Nouveau influences and is a descendant of the Queen Anne style. It is covered in stucco and has a prominent attic, which Boyd used as a studio. Some parts of the house are up to 33 centimetres thick and built in part with pisé (rammed earth) and in part with reinforced concrete. Amazingly, Boyd built The Robins without an accessible driveway, and only a narrow track along which he had to cart building materials. The journey was uphill and Boyd terraced the land with Warrandyte rock5 without the aid of machinery. At only 33 years, Boyd was killed in a car accident in 1923. He was buried in Brighton near the home of his parents. Several people have since owned the house, including political journalist, Owen Webster. Boyd was born at Penleigh House, Wiltshire, and studied at Haileybury College, Melbourne and The Hutchins School, Hobart. He attended the Melbourne National Gallery School and in his final year exhibited at the Victorian Artists’ Society. He arrived in London in 1911 and his painting Springtime was hung at the Royal Academy. He painted in several studios in England and then worked in Paris.6 There he met painter Phillips Fox through whom he met artists of the French modern school and also his wife-to-be, Edith Anderson, whom he married in Paris in 1912. After touring France and Italy, the couple returned to Melbourne. In 1913 Boyd held an exhibition and won second prize in the Federal Capital site competition, then the Wynne Prize for landscape in 1914. In 1915 Boyd joined the Australian Imperial Force, and became a sergeant in the Electrical and Mechanical Mining Company. However he was severely gassed at Ypres and invalided to England. In 1918 in London Boyd published Salvage, writing the text and illustrating it with 20 black-and-white ink-sketches of army scenes. Later that year he returned to Melbourne, and, despite suffering from the effects of gas, he held several successful one-man shows, quickly selling his water-colour and oil paintings. In his short career Penleigh Boyd was recognized as one of Australia’s finest landscape painters. He loved colour, having been influenced early by Turner and McCubbin. His works are in all Australian state galleries, the National Collection in Canberra as well as in regional galleries.7 His wife Edith was also an artist having studied at the Slade School, London, and in Paris with Phillips Fox. After her marriage she continued to paint and excelled in drawing. In later years she wrote several dramas, staged by repertory companies, and radio plays for the Australian Broadcasting Commission, in which she took part. She was the model for the beautiful red-haired woman in several of Phillips Fox’s paintings and the family hold three of his portraits of her. *Possibly named after the Aboriginal words warran, meaning ‘object’ and dyte, meaning ‘thrown at’.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, kangaroo ground-warrandyte road, north warrandyte, the robins -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Craft book, Norma Benporath, Tatting, circa 1940's
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doilies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. This book has photographs and detailed instructions for a wide range of tatted edgings and insertions suitable for household linens such as towels, doilies and tablecloths as well as patterns for whole mats. Stanley E. Mullen (a businessman) developed Semco Pty Ltd which began as a Melbourne based importation company in 1907. The first three letters of Semco's name were his initials. In 1915 it began manufacturing women's apparel, whitework and transfer patterns. In 1924 the company moved to Black Rock, Victoria and continued to produce an extensive range of needlework patterns and handcraft instruction booklets, threads etc. up until the late 1970's. Semco had a staff that included many young women. It was noted by E.J. Trait (editor of the local newspaper "Standard News") that the firm provided them with good working conditions and the correct rate of pay for women in a time of war - the starting rate for 15 year olds, mainly girls at Semco was 25 shillings per week. During World War 2, Manpower Regulations could be used to coerce workers to move into jobs that supported the war effort, but Trait argued that being employed at Semco could make this unlikely as the firm made some goods essential for the war effort. He even suggested that women be encouraged to produce needlework items (and play a part in the war effort) by sending them as presents, to the troops up north. He also heaped praise on the Semco workplace - noting that no Saturday work was the norm, allowing employees to shop and have "hair-do's" before enjoying a relaxing weekend! Semco also had a female cricket side in the women's Saturday association. After the war the firm stayed in production until the early 1990's when it was taken over by Coates-Paton Pty Ltd. Norma Benporath (1900 - 1998) was an expert in tatting techniques and taught and published extensively on the subject. She was born in New Zealand with impaired sight but cataract surgery restored 50% vision to one eye. She was inspired to learn tatting whilst watching her aunt tat and being told that tatting did not require as much sharp vision as embroidery. She quickly learnt to design her own patterns and published over 1000 tatted lace patterns between 1929 and 1952. She became a regular contributor to magazines (such as Home Beautiful) and newspapers across Australia. Her designs were also published in New Zealand, South Africa as well as the U.K. and U.S.A. When Semco, a thread manufacturer, noticed a rise in the sale of fine crochet threads, they realized they had an untapped market to explore. Norma designed a collection of tatting patterns for Semco that were used to help promote their threads. Norma also worked with Semco to produce a line of threads and shuttles specifically suited to tatting. In 1997, Norma was inducted into the "Order of Australia" for "Service to the craft of tatting as a designer and through the international publication of her patterns".This item is an excellent example of the needle work being enjoyed by women in the 1940's in Australia and the skills of the Australian designer, Norma Benporath. It is also an example of the trend that emerged for craft companies such as Semco to publish pattern books in order to advertise their own materials.A 32 page soft cover instruction book with green front and back covers showing two tatted doily designs. The book includes black and white photographs and written patterns by Norma Benporath.Front cover - "TATTING" "For / EXPERTS/ and / BEGINNERS" "By/Semco" "SEMCO INSTRUCTION BOOK" "No. 16" "WITH ILLUSTRATIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS" "9" Back cover - "FOR INSTRUCTIONS FOR WORKING SEE PAGE 22" "Published by Semco Pty. Ltd." "BLACK ROCK, 29, VIC"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, tatting, tatting instruction book, tatting patterns, tatting shuttle, semco, semco pty ltd, norma benporath, needlework, handcrafts, household linen, craftwork -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Rod, Approx. 1871
This rod was salvaged from the American three-masted wooden clipper ship, Eric the Red, named after the Viking discoverer, Eric the Red. The ship first traded in coal between America and Britain and later traded in guano nitrates from South America. In 1879 its hull was re-metalled and the vessel was in first class condition. On 10th June 1880 Eric the Red departed New York under the command of Captain Z Allen, with 24 crew plus two passengers. It was heading for Melbourne and then Sydney. The ship was commissioned by American trade representatives to carry a special cargo of 500 American exhibits for the U.S.A. pavilion at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition. The items included furniture, ironmongery, wines, chemicals, dental and surgical instruments, paper, cages, bronze lamp trimmings, axles, stamped ware, astronomical and time globes, and samples of corn and the choicest of leaf tobacco. Also on board was general merchandise such as cases of kerosene and turpentine, brooms, Bristol's Sarsaparilla, Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, Wheeler’s thresher machine, axe handles and tools, cases of silver plate, toys, pianos and organs, carriages and Yankee notions. The ship had been at sea for 85 days when, on 4th September 1880, it hit the Otway Reef on the southwest coast of Victoria and was quickly wrecked. Captain and crew ended up on floating parts, or in the long boat or the sea. He was amongst the 23 battered and injured men who were rescued by the steamer Dawn and later taken to Warrnambool, where they received great hospitality and care. Four men lost their lives; three crew and one passenger. Captain Allen took the train back to Melbourne and then returned to America. The captain and crew of the Dawn were recognised by the United States Government in July 1881 for their humane efforts, being thanked and presented with substantial monetary rewards, medals and gifts. The salvaging ship Pharos collected Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, nests of boxes, bottles of Bristol’s sarsaparilla, pieces of common American chairs, axe handles, a Wheelers’ Patent thresher and a sailor’s trunk with the words “A. James” on the front. A ship’s flag board bearing the words “Eric the Red” was found on the deckhouse; finally, those on board the Pharos had found the name of the wrecked vessel. The government steamer Victoria and a steamer S.S. Otway picked up flotsam and wreckage. A whole side of the hull and three large pieces of the other side of the hull, with some of the copper sheathing stripped off, had floated onto Point Franklin. Some of the vessel's yards and portions of its masts were on shore with pieces of canvas attached, confirming that the vessel had been under sail. On shore were many cases of Diamond Oil kerosene labelled R. W. Cameron and Company, New York. large planks of red pine, portions of a small white boat and a large, well-used oar. There were sewing machines, some consigned to ‘Long and Co.”, and notions, axe and scythe handles, hay forks, wooden pegs, rolls of wire, some branded “T.S” and Co, Melbourne”, and kegs of nails branded “A.T. and Co.” from the factory of A. Field and Son, Taunton, Massachusetts. Other cargo remains included croquet balls and mallets, buggy fittings, rat traps, perfumery, cutlery and Douay Bibles, clocks, bicycles, chairs, a flywheel, a cooking stove, timber, boxes, pianos, organs, wooden clothes pegs and a ladder. There were three cases of goods meant for the Exhibition Other items salvaged from amongst the debris floating in the sea were chairs, doors, musical instruments, washing boards, nests of trunks and flycatchers. Most of the goods were saturated and smelt of kerosene. A section of the hull lies buried in the sand at Parker River Beach. An anchor with a chain is embedded in the rocks east of Point Franklin and a second anchor, thought to be from Eric the Red, is on display at the Cape Otway light station. A life belt was once on the veranda of Rivernook Guest House in Princetown with the words “ERIC THE RED / BOSTON”. Parts of the ship are on display at Bimbi Park Caravan Park and Apollo Bay Museum. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village also has several artefacts from the wreck. There seemed to be no personal luggage or clothing. “The Eric the Red is historically significant as one of Victoria's major 19th century shipwrecks. (Heritage Victoria Eric the Red; HV ID 239) The wreck led to the provision of an additional warning light placed below the Cape Otway lighthouse to alert mariners to the location of Otway Reef. The site is archaeologically significant for its remains of a large and varied cargo and ship's fittings being scattered over a wide area. The site is recreationally and aesthetically significant as it is one of the few sites along this coast where tourists can visit identifiable remains of a large wooden shipwreck, and for its location set against the background of Cape Otway, Bass Strait, and the Cape Otway lighthouse.“ (Victorian Heritage Database Registration Number S239, Official Number 8745 USA)Iron rod with flat lugged washer. The rod is made of a heavy metal with encrustations and signs of rusting on the surface. It is stepped down in diameter mid-shaft and is slightly bowed on the narrower end. The narrow end flares out slightly in the last few centimetres with a burred foot and has a circular head on the wider end. The washer on the narrower end cannot move past the centre or the narrow end of the rod. The washer is a different metal from the rod and has a small lug jutting out along the circumference in one position. The rod was recovered from the wreck of the ship the Eric the Red.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, rod, iron-rod, eric the red, steamer dawn, cape otway reef, 1880, captain allen, usa pavillion, melbourne exhibition, melbourne international exhibition, captain jones, medal, united states government, pharos, a. james, flag board, steamer victoria, steamer otway, diamond oil, r w cameron and company, long and co., t s and co melbourne, a. field and son, taunton, massachusetts, ketch apollo, ship nail -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper sheathing, c. 1855
This object is a piece of Muntz or copper sheathing, a sheet of metal used for lining a ship's hull as protection from sea worm or muntz worm. It has been salvaged from the Schomberg ship wreck. The muntz has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea. It also has encrustations from the sea such as sand. Other damage, such as movement of the sea or objects in the sea, has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ The hulls of early timber sailing ships had a problem of being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries ships were built with their hulls sheathed in sheets of copper or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing remained effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. This piece of muntz sheathing is representative of building methods and materials used in late 19th and early 20th century ship building. The munts is also significant for its association with the Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or Muntz metal in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, copper sheathing, muntz, muntz metal, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building, 19th century sailing ships -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesDocument, Service of Celebration and Thanksgiving for the life of Ernest Wesley Barrie (Bon) 1909-1985, 1985
SUMMARY - Ernest W (Bon) Barrie, 1909 – 1985 Profile Melton Mechanics Institute Member 1935 - 1982i Trustee 1952 - 1982 Life Member 1968 Years of service – 47 years He constructed and provided a public address system which was used at Melton and district halls and sports grounds for a wide variety of community events including school sports, gymkhanas, theatrical productions and processions. Fire Brigade Melton Fire Brigade (and predecessor Bush Fire Brigade) Apparatus Officer, 1945 - 1953 Captain, 1951 - 1965 Mt Cotterill Fire Brigades’ Group Elected Group Officer, on the formation of the Group, 1967. As Group Communications Officer he operated the VL3 LY base radio station from home on a 24 hour basis for fire brigades of Melton, Rockbank, Sydenham, Diggers Rest, Toolern Vale, Truganina and Werribee. With his brother Edgar, he built the first Melton Fire Truck. It was housed on the family property until a fire station was constructed in the Melton township. Recipient of the Queens Medal, 1979 Recognised for 44 years of service on the Melton Fire Brigade Memorial Wall Plaque, dedicated May 2013 Melton State School, no 430 Committee – School Correspondent (secretarial and financial role) 34 years of Service Provided his Amplifier Equipment for events and the annual district School Sports from 1939-1973. Donated the House Athletic Shield Melton and District Historical Society 1968 – 1985 President and foundation member Willows Historical Park – supported the establishment of the park and contributed many volunteers hours in the construction and landscaping of the precinct Member, Western Metropolitan Groups of Historical Societies, 1980s Shire of Melton Councillor South Riding, 1969-1971 Member of the Water Trust Melton Uniting Church Melton Uniting Church (and its predecessors the Methodist, Methodist-Presbyterian churches). A lifetime association which extended from childhood when he attended Sunday school until his death in 1985. Member of the Presbyterian Board of Management for more than 25 years in which he held positions of Honorary Secretary and Treasurer, Board member of the Parish Council and Member of the Committee of Management. He was a Sunday school teacher 1933. Community development With Mr RC Butler met with Shire Council in 1937 to canvass residents to ascertain prospective Electric consumers in the district. Electricity was subsequently turned on at dusk on 20th December 1939. Melton Progress Association, including Melton Musical, Elocutionary and Vocal Competitions, Vice President 1939 1940 Melton Development Association, 1960s Volunteer Air Observers Corps (VAOC)ii Carried out plane spotting at Shire Office and spotting tower in Melton and later from home until 1944/45. Agriculture and farming Progress and Better Farming Association, Melton. Honorary Secretary, 1935 Member, Agricultural Engineering Society Australia c1960-1985 A successful grower of wheat, oats and barley, he planted experiment plots and held Field Days on the “Darlingsford” property. He later diversified into other grains and sheep (wool and meat). He took a enthusiastic interest in agricultural engineering and was keen to introduce innovative ideas that improved the productivity of farms and farming practices. In the mid 1950 he conducted trials during harvest on the family property of the original mechanical hay fork built on a British Bedford truck by Bill Gillespie. This design was further refined in collaboration with the Gillespie brothers and resulted in the construction the hydraulically operated tractor mounted hay fork. The innovative design of the hay fork created interest from far and wide and was quickly taken up by farmers because it significantly reduced hand labouring of loading sheaves of hay with a pitch fork. His father established chaff mills in Melton, Rockbank, Parwan, Diggers Rest in the first decade of 1900 and in 1915 went into partnership with JR Schutt to establish the Schutt & Barrie Pty. Ltd. Chaff Cutting and Flour Mill in West Footscray. When it ceased trading in 1968 the directors were: Ernest W Barrie and Thomas L Barrie, R, A, and M Schutt. Awards Queens Medal, 1979 Rotary Award for Community Service, 1980 Victoria 150th Anniversary Celebrations contributions, 1985 Service held at Melton Uniting Church local identities -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Bon Barrie, c.1940, Unknown
SUMMARY - Ernest W (Bon) Barrie, 1909 – 1985 Profile Melton Mechanics Institute Member 1935 - 1982i Trustee 1952 - 1982 Life Member 1968 Years of service – 47 years He constructed and provided a public address system which was used at Melton and district halls and sports grounds for a wide variety of community events including school sports, gymkhanas, theatrical productions and processions. Fire Brigade Melton Fire Brigade (and predecessor Bush Fire Brigade) Apparatus Officer, 1945 - 1953 Captain, 1951 - 1965 Mt Cotterill Fire Brigades’ Group Elected Group Officer, on the formation of the Group, 1967. As Group Communications Officer he operated the VL3 LY base radio station from home on a 24 hour basis for fire brigades of Melton, Rockbank, Sydenham, Diggers Rest, Toolern Vale, Truganina and Werribee. With his brother Edgar, he built the first Melton Fire Truck. It was housed on the family property until a fire station was constructed in the Melton township. Recipient of the Queens Medal, 1979 Recognised for 44 years of service on the Melton Fire Brigade Memorial Wall Plaque, dedicated May 2013 Melton State School, no 430 Committee – School Correspondent (secretarial and financial role) 34 years of Service Provided his Amplifier Equipment for events and the annual district School Sports from 1939-1973. Donated the House Athletic Shield Melton and District Historical Society 1968 – 1985 President and foundation member Willows Historical Park – supported the establishment of the park and contributed many volunteers hours in the construction and landscaping of the precinct Member, Western Metropolitan Groups of Historical Societies, 1980s Shire of Melton Councillor South Riding, 1969-1971 Member of the Water Trust Melton Uniting Church Melton Uniting Church (and its predecessors the Methodist, Methodist-Presbyterian churches). A lifetime association which extended from childhood when he attended Sunday school until his death in 1985. Member of the Presbyterian Board of Management for more than 25 years in which he held positions of Honorary Secretary and Treasurer, Board member of the Parish Council and Member of the Committee of Management. He was a Sunday school teacher 1933. Community development With Mr RC Butler met with Shire Council in 1937 to canvass residents to ascertain prospective Electric consumers in the district. Electricity was subsequently turned on at dusk on 20th December 1939. Melton Progress Association, including Melton Musical, Elocutionary and Vocal Competitions, Vice President 1939 1940 Melton Development Association, 1960s Volunteer Air Observers Corps (VAOC)ii Carried out plane spotting at Shire Office and spotting tower in Melton and later from home until 1944/45. Agriculture and farming Progress and Better Farming Association, Melton. Honorary Secretary, 1935 Member, Agricultural Engineering Society Australia c1960-1985 A successful grower of wheat, oats and barley, he planted experiment plots and held Field Days on the “Darlingsford” property. He later diversified into other grains and sheep (wool and meat). He took a enthusiastic interest in agricultural engineering and was keen to introduce innovative ideas that improved the productivity of farms and farming practices. In the mid 1950 he conducted trials during harvest on the family property of the original mechanical hay fork built on a British Bedford truck by Bill Gillespie. This design was further refined in collaboration with the Gillespie brothers and resulted in the construction the hydraulically operated tractor mounted hay fork. The innovative design of the hay fork created interest from far and wide and was quickly taken up by farmers because it significantly reduced hand labouring of loading sheaves of hay with a pitch fork. His father established chaff mills in Melton, Rockbank, Parwan, Diggers Rest in the first decade of 1900 and in 1915 went into partnership with JR Schutt to establish the Schutt & Barrie Pty. Ltd. Chaff Cutting and Flour Mill in West Footscray. When it ceased trading in 1968 the directors were: Ernest W Barrie and Thomas L Barrie, R, A, and M Schutt. Awards Queens Medal, 1979 Rotary Award for Community Service, 1980 Victoria 150th Anniversary Celebrations contributions, 1985 Photographs of Bon Barrielocal identities, pioneer families -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Gordon Ford's Garden, 'Fulling', Pitt Street, Eltham, 10 November 2006
'Fulling', the half-hectare property at Pitt Street, Eltham was the home of landscape designer Gordon Ford and his wife Gwen. Ford bought the property in 1948, originally part of an orchard. The garden encapsulates the major trends of Australian garden design in the second half of the 20th century. The garden design is based on mass (plants) and void (paths and pools), textures and forms. It epitomises the Eltham style because of its relaxed informality and attraction to native wildlife. The mud brick house and designed and built by Ford commenced in 1948. Several extensions were added up to 1970 and were built by Graham Rose (Source: information panel for exhibition, n.d.) Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p147 A narrow timber gate opens onto a garden that has had a huge impact on natural garden development in Australia since the 1950s.1 Fulling, the half-hectare property at Pitt St, Eltham, was the home of the landscape designer, Gordon Ford, who died in 1999. The garden ‘encapsulates the major trends of Australian garden design in the second half of the 20th century...and epitomises the Eltham style of garden’.2 It in turn, was influenced by several Victorian major landscape designers of the mid 20th century – Ellis Stones, Peter Glass and Edna Walling. The gate opens onto a sandy gravel path, one of several, which wind around dramatic pools and what appear to be natural bush, but on close inspection are carefully integrated native, indigenous and exotic plantings. Retaining walls and steps of rock through the garden link different terrace levels. Lichen-covered boulders serve as steps across a pool, leading to the triple level mud-brick house. Ford bought the property, which was originally part of an orchard, in 1948. As the son of a Presbyterian minister, Ford received a good education, which included learning Latin. This was advantageous when he worked in plant sales for the Forestry Commission, before the Second World War. In the late 1940s, however, Ford turned to building and landscape gardening. He worked on the Busst house, an early mud-brick building designed by Alistair Knox and at the same time, Ford was employed by Ellis Stones. Knox described Ford as, ‘one of the funniest men of the district. ...Rocky’s (Ellis Stones) Depression stories and Gordon’s memory and quick tongue made the jobs the most enjoyable of all those hysterical times that made Eltham the centre of the eternal laugh, between the years of 1945 and 1950’.3 Ford’s house, like so many after the war, was built progressively, as more space was needed and formerly scarce materials became available. It began with an army-shed of timber-lined walls, now used as the kitchen. Ford then built what is now the lounge room, and the house grew ‘like topsy and on a shoestring,’ says his widow Gwen. A lot of second-hand materials such as window frames were used, a style made famous particularly with their extensive use at Montsalvat, the Eltham Artists’ Colony. The house was constructed as a joint venture with friends, including artist Clifton Pugh, who built Ford’s bedroom for £10. The polished floorboards and solomite (compressed straw) ceilings, interspersed with heavy beams, exude warmth. The result is a home of snug spaces, with soft light and garden vistas. Several other mud-brick buildings were constructed as needed, including a studio and units for bed-and-breakfast clients. The garden, which has been part of the Open Garden Scheme since the mid 1980s, is based on a balance of mass (plants) and void (paths and pools), textures and forms. It epitomises the Eltham style because of its relaxed informal ethos and attracts native animals. Wattlebirds, scrub wrens, pardalotes, currawongs, owls and even kangaroos, have been seen at Fulling. Gwen, a former English teacher who has worked on the garden since around 1970, urged and helped Ford write his book, The Natural Australian Garden.4 Several of Ford’s favourite trees are in the garden, including the native Casuarina or She-Oak. In spring, the garden is dusted with the purple Orthrosanthus multiflorus or blue native irises and rings with the calls of birds attracted to plants like the callistemons, correas and grevilleas.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham, fulling, gordon ford garden, pitt street, eltham mud brick buildings, mud brick house -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Wycliffe Centre, Graham Road, Kangaroo Ground, 2008
Wycliffe translates the Bible for people around the world. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p171 The peace and beauty of Australia’s Wycliffe Centre reflects what it aims to bring to thousands of people around the world. Kangaroos calmly feed, accompanied by bird song, near the mud-brick buildings set amongst Kangaroo Ground’s rolling hills. On 11 hectares off Graham Road, the centre aims to transform people’s lives by giving groups around the world, with no written language, help with literacy and Bible translation into their own tongue. Associate Director, Harley Beck, says reading the Bible (probably history’s most influential collection of books),1 in one’s own language, provides a strong moral basis, helping people withstand exploitation and escape poverty. One of Wycliffe’s field partners, SIL (formerly Summer Institute of Linguistics) Papua New Guinea, has won two UNESCO awards, and SIL branches in many other countries have won international and national awards. The translators are modern heroes. They undertake hardships, forsaking for years, sometimes decades, a salary and the soft western lifestyle, to face loneliness and primitive conditions that most of us would not even contemplate. No staff is paid a salary. An example is the first Australian Director and former International President, David Cummings, who for 50 years has depended on donations from supporters and churches. Students of all ages at the EQUIP Training School on the site come from all walks of life. They train in linguistics and learn how to communicate in a way that is sensitive to other cultures. Spiritual resilience is encouraged, enabling people to persist until the job in the field is done, which takes on average ten to 15 years. Courses range from a few weeks to a year. The Wycliffe concept was born in the 1920s when American missionary, Cameron Townsend, found a Spanish Bible was inadequate to evangelise the Cakchiquel people of Guatemala. When a Cakchiquel man challenged: ‘If your God is so great, why doesn’t he speak my language?’ Townsend decided to translate the Bible into all languages! He founded a linguistics training school in 1934, naming it after 14th century theologian John Wycliffe, the first to translate the Bible into English.2 The first Wycliffe Bible was completed in 1951 in the Mexican San Miguel Mixtec language. In May 2007 after 30 years of work, Wycliffe Australia, with other organisations, completed the first Bible for indigenous people in the Kriol* language, for about 30,000 people in northern Australia.3 Wycliffe Australia began in 1954 in the Keswick Bookshop basement, Collins Street, Melbourne. As the organisation grew, its quarters became so cramped that Director Cummings at times interviewed potential recruits in his car! The development of the Kangaroo Ground property is a story of faith and generosity. In 1967 Cummings proposed moving to a larger property despite having no funds. Within a month Wycliffe received a $20,000 donation and a gift of land towards a national centre. An earlier owner of the Kangaroo Ground property, Mrs Elsie Graham, would have been delighted, as she had wanted her land to be used for ‘God’s service’. Mud-brick architect and Christian, Alistair Knox, offered to design the centre at no charge. Despite a drought, straw was donated to make bricks. Many volunteers helped with the building, including church youth groups who made mud-bricks.4 Volunteers planted thousands of native plants, watered by recycled water from the site’s dam. Building began in 1968 and in 1983 the South Pacific SIL School (now EQUIP Training) followed. Wycliffe, the world’s largest linguistic organisation, and other organisations, have translated the Scriptures into more than 2000 languages. But another 2000 languages still lack any portion of the Bible. However translations are now completed more quickly, because of new computer programs and as education spreads, more speakers of the local language can assist.5 Despite the growth of secularisation, Beck says support for Wycliffe Australia, which has offices in all states and the ACT, is stronger than ever. * Kriol is a Pidgin language, which has become a speech community’s prime language.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, graham road, kangaroo ground, wycliffe centre -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - First Aid Case, Thomas Urquhart & Son Pty Ltd (Thos. Urquhart), 1930-1939
This small, portable 1930s Sanax First Aid Case has been strongly constructed, with corners reinforced with metal to take knocks and bumps, so it could be quickly transported to the site of an emergency. Having these supplies organised into a kit made them easily accessible and reduces time to take them to the site of the accident. It was possibly designed for use in factories because the booklet in the case states that the kit complies with “Part 1, Victorian Factories Regulations”. The text of the printed brand “Sanax First Aid Case” is right-way up when the case stands vertically on its hinged side. In modern times people are well aware of the importance of quick treatment when accident and injury occur. However, before the first commercial First Aid Kit was made by Johnson & Johnson in 1888, people had little knowledge about treating injuries and lacked information about suitable supplies to keep on hand for emergencies. They were often unaware of how to help in that critical time before the doctor or other assistance arrived, a particularly important time for the many people living in remote areas. A quote from Johnson’s & Johnson’s 1888 price list explains “It is a fact, which is everywhere being recognized, that many lives are lost and much suffering entailed in such accidents on account of the lack of the simple but necessary articles required to afford prompt assistance to the wounded.” One example of the value of First Aid assistance to community groups is shown in an article from the Weekly Times, 29th November 1930. It records a report from the Annuello Branch of the Younger Set (a Country Women’s Organisation), telling that on Armistice Day their president Mrs Jamieson, presented the Annuello School with the gift of a Sanax Red Cross First Aid outfit, which was accepted as being “of great practical use to the scholars.” (Annuello is a remote wheat growing area in the Mallee region of North Western Victoria, which became a soldier settlement area after World War I. There is a strain of wheat named ‘Annuello’ due to its suitability for that area. ) The Sanax Case in our Collection contains instructions, equipment and medical items suitable for use in emergency situations. The Case was one of 42 patterns available from Sanax that conformed to ‘Part 1, Victorian Factories Regulations’. It includes items made by Sanax Company and by Burroughs Wellcome & Co. (Australia) Ltd., Sydney, NSW. A quote at the back of the First Aid Emergency Instructions booklet says: “Sanax products are made in Australia by or under the supervision of qualified chemists, from the highest quality materials. They are dependable for the purposes written on labels.” BOOKLET included in First Aid Case: “SANAX” First-Aid Emergency Instructions has orange cover and white pages, joined in the centre by two staples. Booklet contains First Aid Instructions for general events listed in alphabetical order. It also contains an indexed sections headed “Poisoning, and what to do” written by S.A. Burrows, Ph.C., Vuc and N.Z. There are instructions and diagrams on how to perform Artificial Respiration. There are advertisement for Sanax products throughout the booklet that include; - Sanax Ambulance Stretcher for timber mills, mines, ships and quarries - Saw dust masks (porous rubber) for workers in dust, paint or duco sprayers Inside cover lists Sanax’s Australian made products including - tablets and powders for headaches, neuralgia, influenza, colds - snuff for Catarrh that is “quite harmless” - First Aid Cases that come in a range of 42 patterns - sunburn preventatives and treatments - healing salve for carbuncles, pock, pimples, boils, varicose ulcers etc. - snake bite outfits and kits LEAFLETS included in First Aid Case: (1) Tannafax Tannic Acid Jelly. Tannafax should be kept at hand in every home. It should be applied direct from the tube and used with neither oil nor grease. Where a large area has to be covered the clamped end may be torn or cut off to give a wider mouth to the tube. Collapsible tubes of different sizes. Made in Australia. Burroughs Wellcome & Co. (Australia) Ltd. (Incorporated in England). Sydney, NSW. Assorted Houses, London, New York, Montreal, Cape Town, Milan, Bombay, Shanghai, Buenos Aires. Copyright A. 1817, J. 9463 (2) Tabloid. The strong thing is the just - - . Tabloid marks the wor - - Burroughs Wellcome & Comp. The use of the word is to enab – the prescriber, dispenser and patient to get the right thing with one short word, instead of the firm’s long name. If another maker apply the word to his product, the act is unlawful. Tabloid is our trade mark and brand. If a vendor disregard it in dispensing or selling, the act is unlawful for the same reason. We prosecute both offenders rigorously, in the interest of prescribers, dispensers, patients and the owners of the trade mark. Please inform us of any instance of either offence. Burroughs Wellcome & Co. (Australia) Ltd. (Incorporated in England). Telephone Number - M 4184 (4 lines) All communications to G.P.O. Box No. 1185 DD. Copyright Sy. 20. & J 9894. Medicines and Equipment included in First Aid Case: - Absorbent Cotton, Sanax, for absorbing blood or drying a wound. As a swab for washing wounds; to place above a compress to keep the heat in: or as a pad to protect wounds or fractures. The Sanax Co. Manuf. Chemists, Melbourne. Regd. Office: 5 Brunswick St, Fitzroy. N.6. - ACHE tablets, Sanax, for all aches, pains, fevers etc. Dose: 2 to 3 tablets with a draught of water, every 3 hours. Children in proportion. For influenza or colds, take the bedtime dose with a hot lemon drink or toddy. Recommended for Headaches, Colds, Influenza, Fevers, Neuralgia, Rheumatism, Nerve Pains, Sleeplessness, and Seasickness. Three Sanax Ache tablets equals one Sanax Ache powder. Each tablet contains 1.75grs. each Phenacotinum and Acety acSzilcyl, and .75grs Ammon Brom. Etc.. Sanax brand specialties are prepared by highly qualified pharmaceutical chemists and may be accepted as safe and effective for the purpose indicated on the label. The Sanax Co. Melbourne - Eye lotion, Sanax, “in eye bath full strength or diluted with equal parts of water. Sanax Co. Brunswich St, Fitzroy, Melbourne. - Iodine, Sanax, POISON, with instructions for what to do if swallowed. - Kuraburn, Sanax, Applied to the burn and allowed to dry, the pain and heat instantly disappear, and blistering is prevented. If necessary, apply again in an hours. To safeguard against burning when sunbathing, apply before exposure to the sun. If already sunburnet, use Kuraburn as directions above. Safe and harmless. Sole makers, The Sanax Co. Brunswick St. - - Vic. - Sal Volatile, Sanax, - - stimulant for - - nervous aches - - or as smelling salts Dose - - - - Solution of A- - - 5%, . The Sanax Co. Brunswick St, Melbourne. - Tannafax, Burroughs Wellcome & Co. Australia Ltd. Sydney, N.S.W., 20gm. Approx., Tannic Acid Jelly, (Tannic Acid with 0.5% Phenol in a water-soluble base) for burns and scalds. A.N. 15050, p188, logo of a unicorn. Apply lightly, allow to dry, and bandage loosely. Do not apply oil or grease. - bottle wrapped in brown paper, unknown contents, paper adhered to bottle. - dish, kidney shaped, metal, white enamel with black rim - eye bath, green, plastic or Bakelite SANAX COMPANY The Sanax Company was at the address of 5 Brunswick Street, Fitzroy [Melbourne] at least as early as November 1924, as shown by its advertisement of Ache Powder in the Weekly Times, 8th November 1924. It was still at this address in September 1951, when it advertised First Aid outfits and components in the Post Master General’s section of the Commonwealth of Australia Gazette. REFERENCES: Annuello, Victoria; Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Annuello,_Victoria Annuello Younger Set, Branch Activities and Local Reports, Country Women’s Organisations, Weekly Times, 29 November 1930, Trove http://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/224921009?searchTerm=%22sanax%22%20and%20%22melbourne%22&searchLimits=# Commonwealth of Australia Gazette, Issue 32, 24th April 1915, https://www.legislation.gov.au/file/1915GN32 [Johnson & Johnson Price List, September 1, 1888, p. 20. From our archives], Celebrating the 125th Birthday of the First Aid Kit , The Story of Johnson & Johnson, , http://www.kilmerhouse.com/2013/06/from-1888-to-2013-celebrating-the-125th-birthday-of-the-first-aid-kit/ Post Master General’s section of the Commonwealth of Australia Gazette, Issue No. 73, Thursday 27th September 1951 http://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/232185299?searchTerm=%22sanax%22%20and%20%22fitzroy%22&searchLimits= Sanax First Aid Emergency Instructions, by S.A. Burrows, publisher Sanax Ltd. Fitzroy, Victoria, 1930-1939 English, book, Illustrated edition, Trove http://trove.nla.gov.au/version/40948895 Access to emergency medical help in early settlement days of Victoria could take quite some time, especially in remote areas. From 1888 First Aid Kits and instructions became available for work sites, offices, community groups and individuals, helping to bridge the gap between the accident and the arrival of medical assistance. This portable Sanax First Aid Case is an example of portable medical equipment made in Melbourne, Australia, in the 1930’s and available to the public. It contains a range of items plus information to be used in a variety of injuries and emergencies in in factories, households, businesses and local communities, and instructions on their use. First Aid Case, portable, Sanax First Aid Case. First Aid kit in strong black cardboard carry case with metal reinforced corners, metal hinges on lid, metal catch and leather carry handle. Inside lid is a vertical strap with narrow gap behind it. Base is divided into two compartments. Manufactured by Sanax, Fitzroy, Melbourne, C. 1930-1939 Contents include "Sanax" First Aid instructions booklet, 2 leaflets, metal kidney dish enamelled in white with black trim on edge, green plastic or Bakelite eye bath, eye lotion, Tannafax tannic acid jelly, Sal Volitile, Kuraburn, Iodine, Argyrol, ACHE tablets, absorbent cotton in cardboard box, gauze bandage, and UNKNOWN wrapped bottle. Printed in gold on lid of case “SANAX” FIRST AID CASE. Most of the contents, as well as the case, show the “SANAX” brand. Some contents are inscribed Burroughs Wellcome & Co. (Australia) Ltd., flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, first aid items, first aid kit, emergency first aid, medical emergency kit, home emergency kit, industrial emergency kit, sanax company fitzroy melbourne, burroughs wellcome & co. (australia) ltd, thos. urquhart & son pty. ltd. melbourne, sanax first aid case, sanax first-aid emergency instructions, part 1 victorian factories regulations, tabloid medical supplies -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - TOWN HALL, THE BENDIGO CHORAL SOCIETY, 27 July, 1921
Town Hall, The Bendigo Choral Society. Season 1921, Second Concert. Seventh Grand Concert. Wednesday, July 27th, 1921. Artists: Miss Ivy Taylor, L.A.B. Miss Winnie Mayberry, Mr L Hattenbach. Conductor: Mr W C Frazier, A.R.C.O. Acting Conductor: Mr H W Gregory, L.T.C.L. Pianiste: Miss Eileen Hains, A.T.C.L. Patron: His Worship the Mayor (Cr. D Andrew. President: Mr H M Leggo. Vice presidents: Sir John Quick, Hon. D Smith, M.L.A., Cr. J H Curnow, Cr. J E Holland, Mr Oscar Flight, Mr E S Cahill, Dr. W J Long, Dr. O Penfold, Mr A L Bolton, O.B.E., Mr G E Bolton, Mr D Berriman, Mr Alf E Wallis, Mr J G Oliphant, Mr Arthur Whitehead, Mr W Watts, Mr A E Sayer, Mr William Wright, Mr Magnus Cohn, Mr R H S Abbott, Mr Geo. Mackay, Mr Barkley Hyett, Mr A G Finster, Mr W E Bradshaw, Mr W J Campbell. From the performing members: Mr E H Collett, Mr A W McGibbony. Conductor: Mr W C Frazier, A.R.C.O. Acting Conductor: Mr H W Gregory, L.T.C.L. Sub Conductor: Mr E A Miller. Pianiste: Miss Eileen Hains, A.T.C.L. Treasurer: Mr D H Holden. Librarians: Mr: Mr R J Duguid, Mr H Veale, Mr W Mansell, Mr A Ditchburn. Auditors: Mr H T Bayton, A.A.I.S., L.I.C.A., and Mr Harold Walker. Committee: Office Bearers, with Mesdames T Scott, Chisholm, and Misses Colgan, Gall Field, Lethlean, and Messrs Sleeman, Jeffery, McLure, Carwardine, F J Walker and Wittscheibe. Subscribers may book at Flights on and after July 21st. Box Plan opens at 10am. Holders of 2/6 tickets may also book without extra fee. Holder of 1/6 tickets may book by paying the difference (1/-) Admission: 2/6/ Reserved, 1/6 Ordinary: including Tax. Hon Sec. J Hudspeth (85Wills St.) Z S Martin (66 McKenzie St.) Programme. Concert to commence at 8pm. Doors closed during each item. God Save the King. Part Song: Hymn to Music, Weary Wind of the West, Vagabonds, Soft, Soft Wind, A Song of the Sea, Moonlight. Song: Jeanne d Arc, Ombra ma Fui, My Ships, Broken Vase. Cello Solo: Fantasie et Variationes Brilliante, Adagio, Gavotte, Berceuse Slave, Mazurka. Other Artists: Choral Society, Ladies of the Choral Society. God Save the King. Subscribers and Patrons will, we are sure, be equally gratified, with the Committee, at the great artistic success which the Society achieved in the colloboration with the Verbrugghen orchestra in the memorable performance of ''The Messiah.'' The great praise which Mr Verbrugghen bestowed on the tone quality of the vocalists and of their exceptionally clear enunciation and fine English was indeed very pleasing to all concerned, and was ample and full justification of Mr Frazier's methods and patient care in training the Choir in these particular points. Nor must Mr H W Gregory, the Acting Conductor's part be forgotten. He worked assiduously and earnestly, doing all possible to keep up the high standard of the Society's work. The programme presented to-night is also the result of his interpretation of the descriptive works of these modern composers, In bidding farewell to him at this Concert the Committee and members desire to express their thanks for the energy with which he has carried out the duties of Acting Conductor. We expect, at a very early date to the return of Mr W C Frazier to Bendigo. He is bringing, with him a choice of selection of the very latest and best of English and other part songs (both of the earlier composers and of the ultra-modern school) and patrons can look forward to a fine series of programmes. It is particularly cheering to inform you that, as a result of the visit of the Society to Castlemaine last year, a strong Choral Society has formed there with promises to . . . . . 4 pagesBolton Bros. Pty Ltd, Printcottage, miners, town hall, the bendigo choral society. season 1921, seconed concert. seventh grand concert. wednesday, july 27th, 1921. artists: miss ivy taylor, l.a.b. miss winnie mayberry, mr l hattenbach. conductor: mr w c frazier, a.r.c.o. acting conductor: mr h w gregory, l.t.c.l. pianiste: miss eileen hains, a.t.c.l. patron: his worship the mayor (cr. d andrew. president: mr h m leggo. vice presidents: sir john quick, hon. d smith, m.l.a., cr. j h curnow, cr. j e holland, mr oscar flight, mr e s cahill, dr. w j long, dr. o penfold, mr a l bolton, o.b.e., mr g e bolton, mr d berriman, mr alf e wallis, mr j g oliphant, mr arthur whithead, mr w watts, mr a e sayer, mr william wright, mr magnus cohn, mr r h s abbott, mr geo. mackay, mr barkley hyett, mr a g finister, mr w e bradshaw, mr w j campbell. from the performing members: mr e h collett, mr a w mcgibbony. conductor: mr w c frazier, a.r.c.o. acting conductor: mr h w gregory, l.t.c.l. sub conductor: mr e a miller. pianiste: miss eileen hains, a.t.c.l. treasurer: mr d h holden. librarians: mr: mr r j duguid, mr h veale, mr w mansell, mr a ditchburn. auditors: mr h t bayton, a.a.i.s., l.i.c.a., and mr harold walker. committee: office bearers, with mesdames t scott, chisholm, and misses colgan, gall field, lethlean, and messrs sleeman, jeffery, mclure, carwardine, f j walker and wittscheibe. subscribers may book at flights on and after july 21st. box plan opens at 10am. holders of 2/6 tickets may also book without extra fee. holder of 1/6 tickets may book by paying the difference (1/-) admission: 2/6/ reserved, 1/6 ordinary: including tax. hon sec. j hudspeth (85wills st.) z s martin (66 mckenzie st.) programme. concert to commence at 8pm. doors closed during each item. god save the king. part song: hymn to music, weary wind of the west, vagabonds, soft, soft wind, a song of the sea, moonlight. song: jeanned arc, ombra ma fui, my ships, broken vase. cello solo: fantasie et variationes brilliante, adagio, gavotte, berceuse slave, mazurka. other artists: choral society, ladies of the choral society. god save the king. subscribers and patrons will, we are sure, be equally gratified, with the committee, at the great artistic success which the society achieved in the collobration with the verbrugghen orchestra in the memorable performance of ''the messiah.'' the great praise which mr vergrugghen bestowed on the tone quality of the vocalists and of their exceptionally clear enunciation and fine english was indeed very pleasing to all concerned, and was ample and full justification of mr frazier's methods and patient care in training the choir in these particular points. nor must mr h w gregory, the acting conductor's part be forgotten. he worked assidously and earnestly, to keep up the high standard of the society's work. the programme presented to-night is also the result of his interpretation of the descriptive works of these modern composers. in bidding farewell to him at this concert the committee and members desire to express their thanks for the energy with which he has carried out the duties of acting conductor. we expect, at a very early date to the return of mr w c frazier to bendigo. he is bringing, with him a choice of selection of the latest and best of english songs. as a result of the visit of the society to castlemaine, a choral society was formed -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ROYAL PRINCESS THEATRE COLLECTION: EIGHT FIRST BIRTHDAY SOUVENIR PROGRAMME, c1955
Royal Princess Theatre Eight First Birthday Souvenir Programme, 31st August, 1955. 1874 - 1955. Manager: Don Vincent. Price - Sixpence. Proceeds: Cinematograph Trade Benevolent Fund. The Royal Princess Theatre. In May, 1874, the late John Crowley, at a cost of 12,000 pounds the Royal Princess Theatre. It was opened on 31st August, 1874, on which occasion the 'Grand Duchess of Gerolstein' was performed. It was in January, 1904, that the Theatre was closed until April, 1905, for re-construction at a cost of 5,000 pounds. Further alterations were made I 1936 when the old circle and the gallery was converted into the present circle and loge, the cost on this occasion was 14,000 pounds. At the Royal Princess has been seen every form of entertainment known in the world. Operas, including Gilbert and Sullivan, Shakespearean plays, Minstrels, Pantomime, Circus (Wirth's making their first appearance in1887), Drama, Revues, Magicians, and the latest medium of entertainment Ice Revue. Of the many shows presented on stage of the theatre, I feel none has survived as long, or as well, as 'Charley's Aunt.' The companies to present their performances have been many and varied, but among an imposing list, the names of Charles Holloway, The Royal English Opera Company, J. C. Williamson Co., and Royal Comic Opera Coy., will long be remembered. The line of notable personalities who have appeared on the stage is long also, and includes such names as John McCormack, Clara Butt, Harry Lauder, Peter Dawson and more recently Jessie Mathews and John Calvert. But of all these and many others, I am sure none can ever compare with the wonderful performances by the late Dame Nellie Melba, who gave her farewell performance in September, 1921. It is interesting to note that Dame Nellie Melba, gave two farewell performances. The first was in February, 1886, when she made a last appearance as Mrs Armstrong, to later become Madame Melba. The first competition of the Austral Society was held in the Theatre in May, 1897, and the first living pictures were seen in August, 1899. The London Bioscope Co. presented 'Struck Oil,' with Maggie Moore, in February, 1901 (Maggie Moore had appeared in the stage play or the same name many times earlier). However, it was not until 1910 that the Royal Princess was mainly used for pictures, and of course, since that year, that has been the principle form of entertainment presented. It was Easter, 1930, that the first talkie, 'The Desert Song,' was screened and then followed coloured films, and now in 1955 the latest in film development - Cinemascope has been installed. This installation caused, for the first time in many years, alterations to the back stage to enable the large 30ft. Screen to be quickly removed ready for any 'live' performances. In 1937 the Royal Princess came under the Management of Northern Amusements Pty. Ltd., a unit of the Woodrow Corporation Ltd., whose policy it is to bring in entertainment to Bendigo, and I, as their representative will carry on the traditions of the past, and make the Royal Princess truly a Home of Entertainment. Don Vincent, Manager. Wednesday, 31st August, 1955 on the stage. Eagelhawk Brass Band. Official cutting of the Bithday Cake and its presentation to the Matron of the Benoevolent Home by His Worship the Mayor of Bendigo (The cake kindly donated by Friedrich & Bassemir). Presentation of the Travel Voucher for a 10 day Luxury Coach Tour on behalf of Pioneer Coaches Ltd., to the licky couple winning the recent 25th Wedding Anniversary Contest, by His Worship the Mayor of Eaglehawk. 'Progress of Fashion by Bendigo Fashion House including A Tableaux of 7 Bridal Ensembles. Miss 1874 Gertrude Perry, Misses 1955 Rosemary Lorenz, Lorraine Foley, Joan Pinder, Pauline Kim, Shirley Morgan, Pat Ferrari, Wilma Breerton. Make - up by Helen Lang Beauty Salon. 81st Birthday Performance on the screen. Newsreels, Cartoons, Shorts, Seven Brides for Seven Brothers. Photograph: The Staff of the Royal Princess, under the Management of Mr Don Vincent, who are at your service. Hearing Aids are now installed in all parts of the Theatre, Doctors or Nurses on call may leave their names at the pay-box. Advertisements for Bendigo businesses: Radio Taxis, Kings Dry Cleaners, John V. Schenck Art Florist, Morley Johnsons everything for the home, Ron Meurer fridges, The Melody Bar, music. Program comprises of two sheets of paper.program, theatre, royal princess theatre, royal princess theatre eight first birthday souvenir programme, 31st august, 1955. 1874 - 1955. manager: don vincent. price - sixpence. proceeds: cinematograph trade benevolent fund. the royal princess theatre. in may, 1874, the late john crowley, at a cost of 12, 000 pounds the royal princess theatre. opened on 31st august, 1874, 'grand duchess of gerolstein' was performed. 1904, the theatre was closed until 1905, for re-construction. further alterations 1936 when the old circle and the gallery was converted into the present circle and loge, 14, 000 pounds. seen every form of entertainment known in the world. operas, including gilbert and sullivan, shakespearean plays, minstrels, pantomime, circus (wirth's making their first appearance in1887), drama, revues, magicians, and the latest medium of entertainment ice revue. 'charley's aunt.' the companies have been many and varied, charles holloway, the royal english opera company, j. c. williamson co., and royal comic opera coy., john mccormack, clara butt, harry lauder, peter dawson and more recently jessie mathews and john calvert. dame nellie melba, who gave her farewell performance in september, 1921. it is interesting to note that dame nellie melba, gave two farewell performances. the first was in february, 1886, when she made a last appearance as mrs armstrong, to later become madame melba. the first competition of the austral society was held in the theatre in may, 1897, the first living pictures in august, 1899. the london bioscope co. presented 'struck oil, ' with maggie moore, in february, 1901 (maggie moore had appeared in the stage play or the same name many times earlier). by1910 that the royal princess was mainly used for pictures, has been the principle form of entertainment presented. it was easter, 1930, that the first talkie, 'the desert song, ' was screened and then coloured films, now 1955 the latest in film development - cinemascope has been installed, alterations to the back stage to enable the large 30ft. screen to be quickly removed 'live' performances. in 1937 the management of northern amusements pty. ltd., a unit of the woodrow corporation ltd., 1955. eagelhawk brass band. official cutting of the bithday cake and its presentation to the matron of the benoevolent home by his worship the mayor of bendigo (the cake kindly donated by friedrich & bassemir). presentation of the travel voucher for a 10 day luxury coach tour on behalf of pioneer coaches ltd., to the licky couple winning the recent 25th wedding anniversary contest, by his worship the mayor of eaglehawk. 'progress of fashion by bendigo fashion house including a tableaux of 7 bridal ensembles. miss 1874 gertrude perry, misses 1955 rosemary lorenz, lorraine foley, joan pinder, pauline kim, shirley morgan, pat ferrari, wilma breerton. make - up by helen lang beauty salon. 81st birthday performance on the screen. newsreels, cartoons, shorts, seven brides for seven brothers. photograph: the staff of the royal princess, under the management of mr don vincent, who are at your service. hearing aids are now installed in all parts of the theatre, doctors or nurses on call may leave their names at the pay-box. advertisements for bendigo businesses: radio taxis, kings dry cleaners, john v. schenck art florist, morley johnsons everything for the home, ron meurer fridges, the melody bar, music. royal princess theatre eight first birthday souvenir programme, 31st august, 1955. 1874 - 1955. manager: don vincent. price - sixpence. proceeds: cinematograph trade benevolent fund. the royal princess theatre. in may, 1874, the late john crowley, at a cost of 12, 000 pounds the royal princess theatre. opened on 31st august, 1874, 'grand duchess of gerolstein' was performed. 1904, the theatre was closed until 1905, for re-construction. further alterations 1936 when the old circle and the gallery was converted into the present circle and loge, 14, 000 pounds. seen every form of entertainment known in the world. operas, including gilbert and sullivan, shakespearean plays, minstrels, pantomime, circus (wirth's making their first appearance in1887), drama, revues, magicians, and the latest medium of entertainment ice revue. 'charley's aunt.' the companies have been many and varied, charles holloway, the royal english opera company, j. c. williamson co., and royal comic opera coy., john mccormack, clara butt, harry lauder, peter dawson and more recently jessie mathews and john calvert. dame nellie melba, who gave her farewell performance in september, 1921. it is interesting to note that dame nellie melba, gave two farewell performances. the first was in february, 1886, when she made a last appearance as mrs armstrong, to later become madame melba. the first competition of the austral society was held in the theatre in may, 1897, the first living pictures in august, 1899. the london bioscope co. presented 'struck oil, ' with maggie moore, in february, 1901 (maggie moore had appeared in the stage play or the same name many times earlier). by1910 that the royal princess was mainly used for pictures, has been the principle form of entertainment presented. it was easter, 1930, that the first talkie, 'the desert song, ' was screened and then coloured films, now 1955 the latest in film development - cinemascope has been installed, alterations to the back stage to enable the large 30ft. screen to be quickly removed 'live' performances. in 1937 the management of northern amusements pty. ltd., a unit of the woodrow corporation ltd., 1955. eagelhawk brass band. official cutting of the bithday cake and its presentation to the matron of the benoevolent home by his worship the mayor of bendigo (the cake kindly donated by friedrich & bassemir). presentation of the travel voucher for a 10 day luxury coach tour on behalf of pioneer coaches ltd., to the licky couple winning the recent 25th wedding anniversary contest, by his worship the mayor of eaglehawk. 'progress of fashion by bendigo fashion house including a tableaux of 7 bridal ensembles. miss 1874 gertrude perry, misses 1955 rosemary lorenz, lorraine foley, joan pinder, pauline kim, shirley morgan, pat ferrari, wilma breerton. make - up by helen lang beauty salon. 81st birthday performance on the screen. newsreels, cartoons, shorts, seven brides for seven brothers. photograph: the staff of the royal princess, under the management of mr don vincent, who are at your service. hearing aids are now installed in all parts of the theatre, doctors or nurses on call may leave their names at the pay-box. advertisements for bendigo businesses: radio taxis, kings dry cleaners, john v. schenck art florist, morley johnsons everything for the home, ron meurer fridges, the melody bar, music. -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumSlide - 35mm slide/s - set of 32, Noel Simons, 25/02/1971 12:00:00 AM
Set of 31 transparencies taken on 25/2/1972 on Kodak mounts. 1201.1 - Bendigo No. 26 in Bond St. just after leaving Long Gully en route for Quarry Hill. Has Norris Supermarket in background. Has two SEC roof ads. 1201.2 - No. 26 climbing View St. from Charing Cross en route to Eaglehawk. Has ANZ bank and AMOCO service station in background. 1201.3 - as for 1201.3, but after tram has passed photographer. Has buildings west of Mackenzie St. in photograph. 1201.4 - Tram stop and centre of the road pole with two "CARS STOP BY REQUEST" signs mounted on pole at the corner of Mackenzie St. 1201.5 - same position as for 1201.3, but with No. 5 descending the street. 1201.6 - same position as for 1201.2, but with No. 5 descending the street. Photo taken after tram has passed photographer. 1201.7 - No. 7 in Nolan St. from across the park at Lake Weeroona. 1201.8 - No. 7 entering McCrae St from Nolan St. - distant view. Note "TRAM "sign on left hand side under tree and overhead in McCrae St. from former track that once was in this street. 1201.9 - No. 7 in High St. with Cathedral in background. Tram en route to North Bendigo. Note scaffolding around Cathedral main spire area. 1201.10 - No. 7 crossing Bendigo Creek bridge in High St. near Golden Square. Has a Caltex Service station in the background. 1201.11 - No. 7 at Golden Square terminus with Sunburst Fruit Juices and a Peters Ice cream delivery vans alongside. 1201.12 - as for 1201.11 but photo taken from behind tram, with the end of the rails in the photograph. 1201.13 - No. 7 and 21 in Pall Mall at Charing Cross with No. 5 in the background. Taken some distance away from the location. 1201.14 - No. 7 at Golden Square terminus, taken a short distance from the tram terminus. Shows Milk Bar on right hand side and the hotel on the left hand side. Taken from the south side of the roadway. 1201.15 - as from 1201.14 but taken from the north side of the roadway. 1201.16 - No 5 waiting at California Gully loop. Distant photo showing surrounds 1201.17 - No. 5 en route for Quarry Hill crossing No. 26 at California Gully. 1201.18 - No. 26 at Eaglehawk terminus with Eaglehawk Town Hall and Post Office in background. 1201.19 - No. 21 arriving at Charing Cross en route to North Bendigo. Has Alexandra Fountain in the background, ANZ bank RACV building, and other buildings on the north side of Pall Mall or Nolan St. 1201.20 - No. 26 en route for Quarry Hill at Charing Cross, with crew standing by front door. Has Colonial Mutual life building, Armstrong Tyre Service (Firestone) and a sign for Cohns Drinks in the background. 1201.21 - as for 1201.20 but with No. 5 en route to Eaglehawk now in photograph. 1201.22 - No. 26 at Quarry Hill terminus. 1201.23 - No. 26 at Quarry Hill terminus, view of front portion of tram only from a gate at the Bendigo cemetery. 1201.24 - Track at the end of the Quarry Hill line showing the point blades of the former "Y" terminus and the overhead for this. 1201.25 - No. 2 at the Quarry Hill terminus, looking along the former Trackwork. 1201.26 - as for 1201.25 1201.27 - number not used. 1201.28 - Golden Square terminus from some distance from the actual terminus, showing the Warning sign "TRAM" for motorists from the south. No. 7 at the terminus. 1201.29 - No. 7 passing through the Golden Square shopping centre. Numerous cars and pedestrians. Tram en route for North Bendigo. 1201.30 - No. 7 in High St. Golden Square, en route for North Bendigo. Photo taken after tram has passed photographer. 1201.31 - No. 7 in High St. just past Wattle St. with the Cathedral in the background. Tram has two SEC roof ads good side on photo, 'Everything's fine in my all electric kitchen' and 'Electrical cooking - clean, quick, economical'. 1201.32 - No. 7 in High St. nearing Wattle St. Has Cathedral in the background. Photo taken after tram has passed photographer.Information written on in black ink and date stamped on purple ink. 1201.1 - "No. 26 in Bond St just after leaving Long Gully" 1201.2 - "No. 26 climbing View St. from Charing Cross" 1201.3 - "No. 26 ascending View St. from Charing Cross (At Mackenzie St.)" 1201.4 - "View St. & Mackenzie St." 1201.5 - "No. 5 in View St. near Mackenzie St." 1201.6 - "No. 5 in View St. nearing Charing Cross." 1201.7 - "No. 7 in Nolan St. seen from Lake Weeroona Park." 1201.8 - "No. 7 entering McRae St. from Nolan St. Note "TRAM" warning sign on left. 1201.9 - "No. 7 in High St. passing Short St." 1201.10 - "No. 7 crossing Bendigo Creek bridge in High St. near Golden Square." 1201.11 - "No. 7 at Golden Square terminus" 1201.12 - "No. 7 at Golden Square terminus" 1201.13 - "No 7, 21 and 5 at Charing Cross" 1201.14 - "No. 7 at Golden Square terminus" 1201.15 - "No. 7 at Golden Square terminus" 1201.16 - "No 5 waiting at California Gully loop." 1201.17 - "Nos. 5 and 26 crossing at California Gully loop" 1201.18 - "No. 26 at Eaglehawk terminus" 1201.19 - "No. 21 arriving at Charing Cross from Golden Square" 1201.20 - "No. 26 at Charing Cross" 1201.21 - "Nos. 5 and 26 at Charing Cross." 1201.22 - "No. 26 at Quarry Hill terminus" 1201.23 - "No. 26 at Quarry Hill terminus seen through the gates of the Bendigo Cemetery." 1201.24 - "Quarry Hill terminus showing remains for former double track layout abandoned before 1964." 1201.25 - "No. 2 at Quarry Hill terminus" 1201.26 - "No. 2 at Quarry Hill terminus" 1201.28 - "The Southern approach to Golden Square with No. 7 standing at the terminus, "TRAM" warning sign on the left. 1201.29 - "No. 7 passing through Golden Square Shopping Centre" 1201.30 - "No. 7 in High St. Golden Square" 1201.31 - "No. 7 in High St. passing Wattle St." 1201.32 - "No. 7 in High St. nearing Wattle St."tramways, trams, bendigo, bond st., view st., nolan st., high st., eaglehawk, california gully, charing cross, quarry hill, trackwork, tram 2, tram 5, tram 7, tram 21, tram 26 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Clock, c. 1860s
The clock was either made or sold by T. Gaunt & Co. of Melbourne, a manufacturer, importer and retailer of a wide variety of goods including jewellery, clocks and watches, navigational and measuring instruments, dinnerware, glassware and ornaments. Thomas Gaunt photograph was included in an album of security identity portraits of members of the Victorian Court, Centennial International Exhibition, Melbourne, 1888. Thomas Gaunt History: Thomas Gaunt established Melbourne's leading watchmaking, optical and jewellery business during the second half of the 19th century. Gaunt arrived in Melbourne in 1852, and by 1858 had established his own business at 14 Little Bourke Street. Around 1869 he moved to new premises in Bourke Street on the corner of Royal Arcade, Gaunt's shop quickly became a Melbourne institution. Gaunt proudly advertised that he was 'The only watch manufacturer in the Australian colonies'. While many watches and clocks may have had Gaunt's name on the dial, few would have been made locally. Gaunt did make some watches for exhibitions, and perhaps a few expensive watches for wealthy individuals. Gaunt's received a telegraph signal from Melbourne Observatory each day to correct his main clock and used this signal to rate and repair ship's chronometers and good quality watches. His main horological manufacturing was directed at turret clocks for town halls, churches and post offices. These tended to be specific commissions requiring individualised design and construction. He made the clock for the Melbourne Post Office lobby, to a design by Government Astronomer Robert Ellery, and won an award at the 1880-81 Melbourne International Exhibition for his turret clock for the Emerald Hill Town Hall. He became well known for his installation of a chronograph at Flemington Racecourse in 1876, which showed the time for the race, accurate to a quarter of a second. The firm also installed the clockwork and figures for Gog and Magog in the Royal Arcade. Thomas Gaunt also developed a department that focused on scientific instrumentation, making thermometers and barometers (from imported glass tubes), telescopes, surveying instruments and microscopes. Another department specialised in electroplating for trophies, awards and silverware, and the firm manufactured large amounts of ecclesiastical gold ware and silverware, for the church including St Patrick's Cathedral. There are no records that disclose the number of employees in the firm, but it was large enough for Gaunt to hold an annual picnic for the watchmakers and apprentices at Mordialloc from 1876; two years previously they had successfully lobbied Gaunt to win the eight hour day. Gaunt's workforce was reportedly very stable, with many workers remaining in the business for 15 to 30 years. Gaunt's wife Jane died on September 1894, aged 64. They had one son and six daughters, but only three daughters survived to adulthood. Two became nuns at the Abbotsford Convent and one daughter, Cecelia Mary Gaunt (died 28 July 1941), married William Stanislaus Spillane on 22 September 1886 and had a large family. Gaunt died at his home in Coburg, Victoria, leaving an estate valued at ₤41,453. The business continued as T. Gaunt & Co. after his death. Post Office and Clock History: Warrnambool’s Post Office has been in existence since 1857, when it was originally situated on the corner of Timor and Gilles Street. In March 1864 the Warrnambool Borough Council purchased this clock from Henry Walsh Jnr. for the sum of £25, “to be put up in front of the Post Office”. Henry Walsh Jnr was the eldest son of Melbourne’s Henry Walsh, maker and retailer of clocks, watches, thermometers and jewellery. In 1854 Henry Walsh Jnr. began business in Warrnambool as a watchmaker and jeweller later becoming a Councillor with now a local street named after him. The Post Office was extensively remodelled in 1875-76. Early photographs of this building show that the clock was installed on the northern outside wall, Timor Street, under the arches and between the 2 centre windows, where it could be seen by passers-by. Although spring loaded clocks date back to the 15th century, and fob and pocket watches evolving from these date to the 17th century, personal pocket watches were only affordable to the very fortunate. Public clocks such as this Post Office clock provided opportunity for all to know the time, and for those in possession of a personal watch to check and set their own timepieces to the correct time. During post office reservations during the 1970s the clock was removed and was eventually donated to the Flagstaff Collection. The Clock’s maker Thomas Gaunt, is historically significant and was an established and well renowned scientific instrument and clock maker in Melbourne during the 1860s. He was at that time the only watchmaker in the Australian colonies. In the 1870’s and 1880’s he won many awards for his clocks and was responsible for sending time signals to other clocks in the city and rural areas, enabling many businesses and organisations to accurate set their clocks each day. Warrnambool Borough Council purchased this clock from Henry Walsh Jnr. for the sum of £25 and the clock used to stand in front of the Warrnambool post office to allow ordinary citizens to set their time pieces as they walked by. The item is not only important because it was made by a significant early colonial clock maker and retailed by a locally known clock maker and jeweler but also that it was installed in the Warrnambool Post Office a significantly historical building in it's own right. Built in 1857 and regarded as one of the oldest postal facilities in Australia, with a listing on the National Heritage Database, (ID 15656). This 1864 hall clock originates from the Warrnambool Post Office. The clock glass is hinged to the top of the clock face and has a catch at the bottom. The metal rim of the glass is painted black. The clock face is metal, painted white, with black Roman numerals and markings for minutes and five minutes. The tip of the small hour hand is shaped like a leaf. "T. GAUNT / MELBOURNE" is printed in black on the clock face. The winding key hole is just below the centre of the clock face. The key winds a fusee chain mechanism, attached to the brass mainspring barrel that powers the pendulum with an 8-day movement. The speed of the clock can be adjusted by changing the position of the weight on the pendulum, lengthening or shortening the swing; raising the pendulum shortens its swing and speeds up the clock. The metal fusee mechanism has an inscription on it. The rectangular wooden casing is with a convex curve at the bottom that has a hinged door with a swivel latch. The original stained surface has been painted over with a matte black. There are two other doors that also allow access to the clock’s workings. The case fits over the pendulum and workings at the rear and attaches to the clock by inserting four wooden pegs into holes in the sides of the case then into the back of the clock. A flat metal plate has been secured by five screws onto the top of the case and a hole has been cut into it for the purpose of hanging up the clock. There is a nail inside the case, possibly used for a place to the key."T. GAUNT MELBOURNE" is printed on the clock face. “6 1 3” embossed on the back of the fusee mechanism behind the clock. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, clock, warrnambool post office, fusee, henry walsh jnr, thomas gaunt, t gaunt & co, post office clock -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Isaac Butt, c1864, 1864
An Irish barrister, politician, Member of Parliament (M.P.), and the founder and first leader of a number of Irish nationalist parties and organisations, including the Irish Metropolitan Conservative Society in 1836, the Home Government Association in 1870 and in 1873 the Home Rule League. (Wikipedia) After being called to the bar in 1838, Butt quickly established a name for himself as a brilliant barrister. He was known for his opposition to the Irish nationalist leader Daniel O'Connell's campaign for the repeal of the Act of Union.[4] He also lectured at Trinity College, Dublin, in political economy. His experiences during the Great Famine led him to move from being an Irish unionist and an Orangeman[5] to supporting a federal political system for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland that would give Ireland a greater degree of self-rule. This led to his involvement in Irish nationalist politics and the foundation of the Home Rule League. Butt was instrumental in fostering links between Constitutional and Revolutionary nationalism through his representation of members of the Fenians Society in court. (Wikipedia) He began his career as a Tory politician on Dublin Corporation. He was Member of Parliament for Youghal from 1852 to 1865, and for Limerick from 1871 to 1879 (at the 1852 general election he had also been elected for the English constituency of Harwich, but chose to sit for Youghal). The failed Fenian Rising in 1867 strengthened Butt's belief that a federal system was the only way to break the dreary cycle of inefficient administration punctuated by incompetent uprisings.[6] In 1870 he founded the Irish Home Government Association. This was in no sense a revolutionary organisation. It was designed to mobilise public opinion behind the demand for an Irish parliament, with, as he put it, "full control over our domestic affairs."[6] He believed that Home Rule would promote friendship between Ireland and her neighbour to the east. In November 1873 Butt replaced the Association with a new body, the Home Rule League, which he regarded as a pressure-group, rather than a political party. In the General Election the following year, 59 of its members were elected. However, most of those elected were men of property who were closer to the Liberal cause.[7] In the meantime Charles Stewart Parnell had joined the League, with more radical ideas than most of the incumbent Home Rulers, and was elected to Parliament in a by-election in County Meath in 1875.[8] Butt had failed to win substantial concessions at Westminster on the things that mattered to most Irish people: an amnesty for the Fenians of '67, fixity of tenure for tenant-farmers and Home Rule. Although they worked to get Home Rulers elected, many Fenians along with tenant farmers were dissatisfied with Butt's gentlemanly approach to have bills enacted, although they did not openly attack him, as his defence of the Fenian prisoners in '67 still stood in his favour.[9] However, soon a Belfast Home Ruler, Joseph Gillis Biggar (then a senior member of the IRB), began making extensive use of the ungentlemanly tactic of "obstructionism" to prevent bills being passed by the house. When Parnell entered Parliament he took his cue from John O'Connor Power and Joseph Biggar and allied himself with those Irish members who would support him in his obstructionist campaign. MPs at that time could stand up and talk for as long as they wished on any subject. This caused havoc in Parliament. In one case they talked for 45 hours non-stop, stopping any important bills from being passed. Butt, ageing, and in failing health, could not keep up with this tactic and considered it counter-productive. In July 1877 Butt threatened to resign from the party if obstruction continued, and a gulf developed between himself and Parnell, who was growing steadily in the estimation of both the Fenians and the Home Rulers.[10] The climax came in December 1878, when Parliament was recalled to discuss the war in Afghanistan. Butt considered this discussion too important to the British Empire to be interrupted by obstructionism and publicly warned the Irish members to refrain from this tactic. He was fiercely denounced by the young Nationalist John Dillon, who continued his attacks with considerable support from other Home Rulers at a meeting of the Home Rule League in February 1879. Although he defended himself with dignity, Butt, and all and sundry, knew that his role in the party was at an end.[11] Butt, who had been suffering from bronchitis, had a stroke the following May and died within a week. He was replaced by William Shaw, who in turn was replaced by Charles Stewart Parnell in 1880. (Wikipedia)Image of a man known as Isaac Butt.
