Showing 1536 items
matching flowers street
-
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Shields (pair of curtains), 1965
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Periwinkle
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Fabric piece, framed
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Victorian Villa, High Street, c.1922
Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence of the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold on which a built structure was subsequently constructed as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.An old inscription on this photograph identifies it as ‘an elegant timber villa in High Street. It occupied part of Lot 91, bought by Edward Glyn in the land sale of 16th October 1851, and run as a flower farm’. The subdivision called the ‘Flower Farm Estate’ in East Kew occurred in 1922. [The subdivision plan is on the reverse of this photo.] The Estate included 61 lots on either side of Boorool Road between High Street and Harp Road. In the MMBW Detail Plan 2017 of 1926, a number of these new villas had already been built. Matching houses with MMBW maps can always be a challenge, however if this house was near the corner of Boorool Road and High Street, it seems to fit the profile of a house called ‘Maxton’ (demolished).Photographer's name on photograph, lower right, and stamp on mount lower right: "A. Aberline, Glenferrie".houses - maxton - high street - kew (vic.), violet farm estate, subdivisions - kew (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Black Chiffon Scarf with Multicoloured Silk Embroidery, c. 1926-1931
An item forming part of a collection of costumes, photographs and documents relating to the Weir family who lived in the mansion originally named Illapa, 84 Princess Street, Kew, from c.1917 to 1950. This historically significant collection includes items relating to both George Weir (1866-1937) and his wife Edith Mary Weir (1867-1948). George Weir attained national prominence in the mining industry, becoming General Manager of the North Broken Hill Silver Mining Company in 1903 (later renamed North Broken Hill Mining Company 1905-12, and North Broken Hill Ltd 1912-1988), and subsequently President of the Mine Owners Association. He was to remain General Manager of North Broken Hill Ltd until his retirement in 1926.This scarf is part of a 30-piece collection of women’s clothing owned by Edith Mary Weir (nee Betteridge), who was born in Clare, South Australia in 1867 and who died in Kew at the age of 81 in 1948. The items of clothing in the collection date from the 1880s to the 1940s and constitute outstanding examples of dressmaker’s skills from each of these decades. The collection includes day dresses, evening dresses, evening coats, capes, shoes and undergarments. As the wife of a mining engineer, and later mine manager, Edith Weir’s clothing has historic significance as examples of clothing worn by upper middle class Australian women in domestic circumstances and at social and civic events. The costumes in the collection represent the periods when Edith Weir lived in Broken Hill, New South Wales, and in Kew, Melbourne. A number of the costumes from the 1920s to the 1940s are of a particularly fine quality, being both rare, representative and intact examples of Australian fashion of the period. The garments in the Weir Collection were donated to the Kew Historical Society by the granddaughter of Edith Weir in 2017Very long, doubled chiffon evening scarf with a silk tassle at one end and multicoloured hand embroidered flowers at the other. The scarf was owned by Edith Mary Weir.edith mary (betteridge) weir, 84 princess street -kew, australian fashion, scarfs -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Peel Street Health Centre : Official Opening, 1930
The North Kew Centre was the third established at North Kew. It followed a lease of a house at 50 Willsmere Road. The Peel Street building was designed by Mr Chipperfield. Messrs McIntosh and Taylor were the successful tenderers, the price being 1,240 pounds. The North Kew Baby Health Centre was finally opened on 18 June 1930 in the presence of the mayor, councillors and citizens of Kew, and representatives of the Infant Welfare Council. A report in The Age of 19 June described the opening in detail as well as the features of the new Centre. These included: "The rooms ... filled with flowers, pink and mauve hydrangeas and native heath, and the walls are adorned, with a charming frieze, representing windmills, flocks and a fairy tale goose girl. On the walls are hygiene editions of the funniest of Belloc's "Cautionary Tales" revised as posters, Outside there is promise of a gay garden, and a lovely view of green fields sloping to a shining bend of the river." Early photographic record of the opening of an early baby health centre in Kew.[Badly damaged] black and white photograph of the opening of the North Kew Baby Health Centre in Peel Street. The photo is mounted on card, and shows mothers and their children on the veranda, and officials at right. The latter includes the Mayoress and probably Vera Scantlebury. All mothers wear hats as do most of the children. [When the photograph was presented to the Society in 1979, it was described in the first Acquisitions Register as framed. Some time after that it was removed from its frame and badly broken. A separate photocopy of the original photograph is also held in the collection.]Earliest inscription: "Peel Street Health Centre / Official Opening 1930 / donated by Sr Costello and Sr Bewish [sic] 1979 / Copy purchased by ..... for Centre". Old Accession number in Texta: "KH-133 Kew Historical Society". Separate later label: "Opening North Kew Baby Health centre 1930". north kew baby health centre, peel street (kew), baby health centres - kew (vic) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, Façade of ‘Southesk', Cotham Road, 1970
Colour enlargement of a photograph (slide) of Southesk (formerly Ordsall) in Cotham Road, Kew (demolished 1970).Colour photograph of the front lawn and façade of ‘Southesk’ (formerly ‘Ordsall’, built for John Halfey in 1882). The house was located on the corner of Cotham Road and Charles Street, Kew. The Italianate mansion was built in the Renaissance villa style on a bluestone plinth. Two balustrades surrounded the parapet of the roof and ran between the groups of pillars on either side of the entrance porch. The verandah was tiled and wide and Corinthian columns supported its roof. When the house passed into the hands of the City of Kew in 1948, the landscaping and formal flower beds were removed and replaced by lawns.The house was demolished in 1970.david carnegie, john halfey, southesk - cotham road - kew (vic), ordsall - cotham road - kew (vic) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Ceiling fresco, Ballroom, ‘Southesk’, Cotham Road, Stewart West, 1970
Colour enlargement of a photograph (slide) of Southesk (formerly Ordsall) in Cotham Road, Kew (demolished 1970).The ceilings of and architraves of Ordsall were painted by artists employed by the decorating company, Cullis Hill & Co. The frescos, of which fragments survive, were some of the most important murals used as elements of interior decoration in Melbourne during the Boom Period of the 1880s. These photographs were taken immediately prior to the demolition of the house, and are the best examples of the murals.The most significant decorative aspects of Southesk (formerly ‘Ordsall’) were the murals in the front two rooms. An article in the Melbourne Argus in 1882 records that Mr Vandenbrandt and Signor Rizzi created these under the supervision of Cullis Hill. This fresco from the ceiling of the ballroom is believed to depict two of the Seasons. Signor Rizzi was a renowned painter of flowers. He is credited with painting these parts of the murals. Examples of his floral paintings can still be seen at Villa Alba in Walmer Street.david carnegie, john halfey, southesk - cotham road - kew (vic), ordsall - cotham road - kew (vic) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, J F C Farquhar, A View in Studley Park Road, 1891
At the beginning of the 1890s, the Kew businessman and Town Councillor, Henry Kellett, commissioned J.F.C. Farquhar to photograph scenes of Kew. These scenes included panoramas as well as pastoral scenes. The resulting set of twelve photographs was assembled in an album, Kew Where We Live, from which customers could select images for purchase.The preamble to the album describes that the photographs used the ‘argentic bromide’ process, now more commonly known as the gelatine silver process. This form of dry plate photography allowed for the negatives to be kept for weeks before processing, hence its value in landscape photography. The resulting images were considered to be finely grained and everlasting. Evidence of the success of Henry Kellett’s venture can be seen today, in that some of the photographs are held in national collections.It is believed that the Kew Historical Society’s copy of the Kellett album is unique and that the photographs in the book were the first copies taken from the original plates. It is the first and most important series of images produced about Kew. The individual images have proved essential in identifying buildings and places of heritage value in the district.This is the earliest known photograph of the exterior of Byram (later Tara Hall). It shows the original red brick fence, its asymmetrical gate and gateposts, with a large terra cotta gargoyle surmounting the higher of the two. The architect, Edward Kilburn designed Byram in the Arts & Crafts style for the industrialist George Ramsden. Construction began in 1888 and was reputed to have lasted three years. The mansion had frontages to Studley Park Road and Stevenson Street, including gardens laid out with great taste, including pleasure grounds, tennis lawn, fruit and flower garden, and paddock. The size of many of the trees in the garden indicate that many survived from the garden of Clifton Villa, the previous single-storeyed house built on the site by the Stevenson brothers. Byram had views to Melbourne and Port Phillip Bay. The house was demolished in 1960, despite opposition from the National Trust (Victoria), and its gardens subdivided into residential allotments.A View in Studley Park Roadkew illustrated, kew where we live, photographic books, henry kellett, byram, tara hall, goathlands -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncContainer - MacRobertson's Toffee Tin, MacRobertson's Confectionery, 1955-65
MacRobertson's confectionery was founded by Macpherson Robertson in the 1880s, and later sold to Cadbury's. The tin has local significance as Sir Macpherson Robertson was a resident of Sackville Street, KewOctagonal celadon and pink coloured tin, originally holding confectionary manufactured by MacRobertson. The lid of the tin features an image of roses, while the sides portray other flowers."MacRobertson"confectionery, sir macpherson robertson, containers, macrobertson's confectionery -
![Architectural Moulding: Fragment of plaster and cement cornice from Southesk [Ordsall]](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/66b185bc235bc2950ebe8440/item-media/66b197c7235bc2950ec38cc7/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncArchitectural Moulding, Fragment of plaster and cement cornice from Southesk [Ordsall], 1870-80
'Ordsall', renamed 'Southesk' in the 20th century was built for John Halfey in or before 1865. The house was rebuilt in the 1870s to designs by architect Michael Hennessy. In 1882 the house was redecorated by the firm of Cullis Hill & Co., who hired the artists 'Mr Vandenbrandt' and 'Signor Rizzi" to paint the ceilings of the ballroom and the drawingroom. The artistic triumph was described in detail in The Argus, 30 October, 1882. In 1947, Southesk was purchased by the Kew City Council. For 23 years it was used as a meeting place for community groups. The house was then demolished in 1970 to make way for a new Town Hall.Rare, and possible unique fragment of a plaster cornice from one of the most architecturally distinctive houses in Kew, demolished 1970.Section of plaster cornice removed from Southesk on the corner of Charles Street and Cotham Road, Kew, when it was demolished in 1970 by the City of Kew. The cornice has a narrow layer of previously coloured plaster which is now overlaid with a grey distemper. The foundation of the cornice is moulded cement. Remnant flowers moulded in the central band of the cornice include a rose and a sunflower. The plaster decoration was probably located in the entrance hall, dining room or ballroom, all of which were created in the 1870s by Michael Hennessy and decorated by the firm of art decorators, Cullis Hill & Co in 1882.Nilordsall, south esk, cullis hill, plasterwork, cornices, victorian interiors -
![Central Avenue, Fitzroy Gardens / [by] Nicholas Caire, circa 1876](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/57773e53d0cdd10a5c0ccd3b/item-media/57773f3fd0cdd10a5c0d358d/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, Anglo-Australasian Photographic Company, Central Avenue, Fitzroy Gardens, c. 1876
Nicholas Caire was born on Guernsey in the Channel Islands in 1837. He arrived in Adelaide with his parents in about 1860. In 1867, following photographic journeys in Gippsland, he opened a studio in Adelaide. From 1870 to 1876 he lived and worked in Talbot in Central Victoria. In 1876 he purchased T. F. Chuck's studios in the Royal Arcade Melbourne. In 1885, following the introduction of dry plate photography, he began a series of landscape series, which were commercially successful. As a photographer, he travelled extensively through Victoria, photographing places few of his contemporaries had previously seen. He died in 1918. Reference: Jack Cato, 'Caire, Nicholas John (1837–1918)', Australian Dictionary of Biography.An original, rare photograph from the series 'Views of Victoria: General Series' by the photographer, Nicholas Caire (1837-1918). The series of 60 photographs that comprise the series was issued c. 1876 and reinforced a neo-Romantic view of the Australian landscape to which a growing nationalist movement would respond. Nicholas Caire was active as a photographer in Australia from 1858 until his death in 1918. His vision of the Australian bush and pioneer life had a counterpart in the works of Henry Lawson and other nationalist poets, authors and painters.Albumen Silver Photograph, mounted on Board.printed in ink on support l.c.: CENTRAL AVENUE, FITZROY GARDENS / COPYRIGHT REGISTERED. printed in ink on support reverse c.: VIEWS OF VICTORIA. / (GENERAL SERIES.) / No. 2. / CENTRAL AVENUE, FITZROY GARDENS. / The Fitzroy Gardens have, for several years past, become one of the most popular places for public resort- / attributable, no doubt, to the great variety of picturesque scenes they contain. Shrubs and flower plants, of almost / every description, can be seen growing in rich profusion within the enclosures, studded here and there with choice / pieces of statuary. The subject of the present illustration is but one of the many to be found within their precincts. / The distance of these gardens from the Melbourne Post Office is about one mile. printed in ink on support reverse l.c.l.: J.W. FORBES, Agent, printed in ink on support reverse l.c.: ANGLO-AUSTRALASIAN PHOTOGRAPHIC COMPANY, MELBOURNE. printed in ink on support reverse l.c.r.: 10 Temple Court, Collins Street West.nicholas caire (1837-1918), landscape photography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncDecorative object - Velvet mantel hanging embroidered with chenille thread, c. 1890
Variably described as mantel hangings, pelmets or valances, these became a common form of Victorian interior decoration in the second half of the 19th century. The hanging uses arrasene embroidery which was introduced for artistic embroidery c.1883. Arrasene embroidery was a variation of chenille embroidery and was mainly used for curtain borders, mantel hangings and screens. When used to embroider flowers on velvet or plush, it was sewn upon the surface without being ‘drawn through’. Madonna lilies, irises, daffodils and narcissi were commonly used in designs of mantel hangings.Velvet mantel hanging embroidered with chenille thread. The scalloped edge of the pelmet is bordered by multicoloured silk cording. This example was owned by Netty Cornish of 15 Peel Street, Kew, and donated by her daughter, Mrs F Plumridge in 1980. The embroidered flowers in this example include narcissi and roses.mantel pelmet, peel street, kew, nettie cornish, mary plumridge -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Harrison-Balfour Wedding Party, 1905
This wedding photograph is an illustration of the intermarriage of notable Victorian (and Kew) families. The parents of the groom were the Hon. James Balfour MP., and his wife, Frances Charlotte (Henty) [the eldest daughter of James Henty] who married at Hawthorn in 1859. The Balfour lived at 'Windella' in Studley Park Road. Henry Rairey (Harry) Balfour was the youngest son of Mr & Mrs Balfour who married Katie Harrison of 'Horley' in Molesworth Street, Kew. Miss Harrison's father was the T.S. Harrison (merchant and importer, b. Banbury, Oxon, 1829, d. Melb 1901). Portrait of the wedding party in the garden of Horley in Molesworth Street, following the marriage of Elizabeth Kate (Katie) Harrison to Henry Rairey (Harry) Balfour at the Kew Presbyterian Church in 1905. The outfits worn by the women were reported in Punch, on 9 February 1905]. The bride wore a frock of ivory white satin, with bertha of duchesse lace and a yoke of ruched chiffon. The bridesmaids … wore white muslin dresses, inserted with Valenciennes, made in early Victorian style. The white straw hats were trimmed with lace and blue hydrangea, and their flowers were blue hydrangea, delphiniums and cornflowers. … The bride’s mother [right] wore a well-cut dress of black silk. The bridegroom’s mother [left] wore a gown of black silk voile, and smart black bonnet grouped with roses. L. to R. Christian Balfour, Jean Mackintosh, Mrs James Balfour (nee Henty), Bridegroom, Bride, Dr. Lewis Balfour, Genevieve Harrison, Hon. James Balfour, Henry Harvey, Marion Harrison (nee Borodin) [Married by Mr Alec Scholes at Kew Presbyterian Church] .Individuals identified in ink on reverse plus donor name and date.balfour, henty, harrison, horley, molesworth street, kew -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Grace Tabulo, 'Fairyland', 57 Malmsbury Street, c.1963
Mr. and Mrs. Tabulo, who owned the house between 1945 and 1965, created Fairyland in the 1940s. Fairyland was open to the public, especially children, who were invited to write their names in visitors’ books. These are now in the possession of the Kew Historical Society. Following the sale of the house after Mrs. Tabulo’s death, the garden and content of the house was cleared of its previous adornments. Grace Tabulo died in 1965. "CHILDREN LIVING IN THE ONE STREET soon find out which house will welcome them and which house to avoid. Few children in few streets have ever had such a find as those who live in Malmsbury st, Kew. At 56 Malmsbury st they all belong. It is their house. There are no young children who are actual residents, but they are to be found there all day long. Mrs J. Tabulo is chatelaine of 56, but few children know her by this name. To them she she is the Fairyland Lady. In her pocket handkerchief front garden there are few flowers; there isn't room, for it has been turned into a children's dream. Cement, tiles, old broken pieces of priceless china, miniature bottles, leadlights, and strange and beautiful little statues have been welded into a grotto which Mrs Tabulo says is only appreciated and understandable to children. It started off in a small way three years ago with a few odd statuettes, but with a street full of children ready and eager to build, it now has hardly room for even a miniature. Like the children, the Fairyland Lady knows and values each mosaic-like piece. Many a wedding present, succumbed at last to the ravages of time, holds a vantage spot in the grotto. The children bring along their broken bits and each is found a spot and cemented into the fairy story picture. In the cottage itself the children are also welcome. There is no spot, from skirting board to ceiling, that is not crowned with some gem or another. Fans, plaques, and china, some of it more than 300 years old, is handled daily by tiny but careful hands. "Children," said Mrs Tabulo, "should be allowed to love and handle beautiful things. They are much more careful than adults. Bless them!" -H.S (The Argus, 22 January 1949)A photograph of Mrs. Grace Tabulo in the garden of ‘Fairyland’ in 57 Malmsbury Street, Kew. fairyland, malmsbury street, kew, tabulo, grace tabulo -
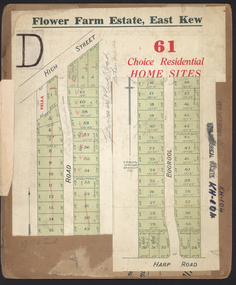 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Flower Farm Estate, East Kew, 1922
... The subdivision called the ‘Flower Farm Estate’ in Kew East... on the reverse. subdivision plans - east kew flower farm estate High ...Pru Sanderson, in her groundbreaking ‘City of Kew Urban Conservation Study : Volume 2 - Development History’ (1988), summarised the periods of urban development and subdivisions of land in Kew. The periods that she identified included 1845-1880, 1880-1893, 1893-1921, 1921-1933, 1933-1943, and Post-War Development. These periods were selected as they represented periods of rapid growth or decline in urban development. An obvious starting point for Sanderson’s groupings involved population growth and the associated economic cycles. These cycles also highlighted urban expansion onto land that was predominantly rural, although in other cases it represented the decline and breakup of large estates. A number of the plans in the Kew Historical Society’s collection can also be found in other collections, such as those of the State Library of Victoria and the Boroondara Library Service. A number are however unique to the collection.The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. The subdivision called the ‘Flower Farm Estate’ in Kew East occurred in 1922. It included 61 lots on either side of Boorool Road between High Street and Harp Road. In an advertisement in The Argus in the same year, the proximity of the estate to the newly erected shops at the corner of Harp Road and High Street is noted. The Flower Farm Estate and similar subdivisions in Kew East were assisted by the extension of the High Street tramline in 1924.subdivision plans - east kew, flower farm estate, high street - kew east (vic.), boorool road -- kew east (vic.), harp road -- kew east (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, Kew Light Opera Company, Marion Tilley in The Maid of the Mountains, 1956
The Kew Light Opera Company was formed in 1952, and mounted a number of musical and variety productions each year until it was subsumed in the "Q" Theatre Guild in 1957. A partial record of performances by the company includes: 1952 Florodora, 1953 The Cingalee - San Toy or The Emperor's Own, 1954 While the Sun Shines - A Country Girl - Our Miss Gibbs, 1955 The Toreador - The Arcadians, 1956 The Maid of the Mountains - Whiteoaks - Goodnight Vienna!, 1957 A Country Girl. Most of the Company's performances took place in the Kew Recreation Hall in Wellington Street, Kew. The scrapbook of annotated photographs, programmes, and newspaper reviews of which this item is a part was assembled by Marion Tilley, wardrobe mistress for, and performer in, productions by the Kew Light Opera Company and the "Q" Theatre Guild. It is significant as a remarkably complete document of theatre performances in Kew, Victoria during the 1950s and 1960s. The scrapbook, and the items individually catalogued within it, have artistic and aesthetic significance within the history of performing arts in Victoria in the middle of the 20th Century. They have social significance in that they reveal socio-cultural values and preoccupations during the period. The records also act as a history of arts activities in the Kew Recreation Hall and later in the Kew City Hall as entertainment and community arts and music precincts.Sepia toned photograph of Marion Tilley, one of the 'Fisher Folk' in the production. Marion Tilley was the creator of the scrapbook from which the photo is drawn. Here she stands at the end of the performance with a bouquet of flowers.marion tilley, kew light opera company, kew recreation hall -- wellington street -- kew (vic.), performing arts -- kew (vic.), theatre memorabilia -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Black Silk & Chantilly Lace Evening Dress, 1920s
An item forming part of a collection of costumes, photographs and documents relating to the Weir family who lived in a mansion, originally named Illapa, at 84 Princess Street, Kew, from c.1917 to 1950. This historically significant collection includes items relating to both George Weir (1866-1937), his wife Edith Mary Weir (1867-1948) and their children. George Weir attained national prominence in the mining industry, becoming General Manager of the North Broken Hill Silver Mining Company in 1903 (later renamed North Broken Hill Mining Company 1905-12, and North Broken Hill Ltd 1912-1988), and subsequently President of the Mine Owners Association. He was to remain General Manager of North Broken Hill Ltd until his retirement in 1926.This garment is part of a collection of women’s clothing, owned and worn by Edith Mary Weir (nee Betteridge) - born in Clare, South Australia 1867, died Kew 1948 - and also by her daughter. The garments date from the 1880s to the 1930s. The collection includes day dresses, evening dresses, evening coats, capes, and undergarments. As the wife and daughter of a mine manager, the collection includes representative examples of clothing worn by upper middle class Australian women in domestic circumstances, and at social and civic events. A number of the costumes from the 1920s to the 1930s are of a particularly fine quality, being both rare, representative and intact examples of Australian fashion of the period. The garments in the Weir Collection were donated to the Kew Historical Society by a granddaughter of Edith Weir in 2017.Long black silk waisted dress, gathered at the waist with and featuring a full skirt. The short-sleeved bodice has a high round neck with a small amount of embroidery at the front in the form of abstract flowers. The skirt features an additional Chantilly lace overskirt that is scalloped at the hem. edith mary weir (nee betteridge), 84 princess street - kew, australian fashion, women's clothing, costumes, coats -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Silk Georgette, Floral Chiffon & Velvet Dress, c. 1926-28
An item forming part of a collection of costumes, photographs and documents relating to the Weir family who lived in a mansion, originally named Illapa, at 84 Princess Street, Kew, from c.1917 to 1950. This historically significant collection includes items relating to both George Weir (1866-1937), his wife Edith Mary Weir (1867-1948) and their children. George Weir attained national prominence in the mining industry, becoming General Manager of the North Broken Hill Silver Mining Company in 1903 (later renamed North Broken Hill Mining Company 1905-12, and North Broken Hill Ltd 1912-1988), and subsequently President of the Mine Owners Association. He was to remain General Manager of North Broken Hill Ltd until his retirement in 1926.This garment is part of a collection of women’s clothing, owned and worn by Edith Mary Weir (nee Betteridge) - born in Clare, South Australia 1867, died Kew 1948 - and also by her daughter. The garments date from the 1880s to the 1930s. The collection includes day dresses, evening dresses, evening coats, capes, and undergarments. As the wife and daughter of a mine manager, the collection includes representative examples of clothing worn by upper middle class Australian women in domestic circumstances, and at social and civic events. A number of the costumes from the 1920s to the 1930s are of a particularly fine quality, being both rare, representative and intact examples of Australian fashion of the period. The garments in the Weir Collection were donated to the Kew Historical Society by a granddaughter of Edith Weir in 2017.Cocktail dress of an overall muted pink colour, with an outer layer of multi-coloured pink silk georgette patterned all over with small flowers. Below the waist the georgette is formed into separate hemmed floating panels. Pink velvet is used on the square neckline and on the cuffs of the sleeves. The same velvet fabric is used in the separate pink velvet headband with feathers. edith mary weir (nee betteridge), illapa -- 84 princess street -- kew (vic.), women's clothing, weir collection, dresses, fashion -- 1920s -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Cream crocheted bodice, c. 1891-98
An item forming part of a collection of costumes, photographs and documents relating to the Weir family who lived in a mansion, originally named Illapa, at 84 Princess Street, Kew, from c.1917 to 1950. This historically significant collection includes items relating to both George Weir (1866-1937), his wife Edith Mary Weir (1867-1948) and their children. George Weir attained national prominence in the mining industry, becoming General Manager of the North Broken Hill Silver Mining Company in 1903 (later renamed North Broken Hill Mining Company 1905-12, and North Broken Hill Ltd 1912-1988), and subsequently President of the Mine Owners Association. He was to remain General Manager of North Broken Hill Ltd until his retirement in 1926.This garment is part of a collection of women’s clothing, owned and worn by Edith Mary Weir (nee Betteridge) - born in Clare, South Australia 1867, died Kew 1948 - and also by her daughter. The garments date from the 1880s to the 1930s. The collection includes day dresses, evening dresses, evening coats, capes, and undergarments. As the wife and daughter of a mine manager, the collection includes representative examples of clothing worn by upper middle class Australian women in domestic circumstances, and at social and civic events. A number of the costumes from the 1920s to the 1930s are of a particularly fine quality, being both rare, representative and intact examples of Australian fashion of the period. The garments in the Weir Collection were donated to the Kew Historical Society by a granddaughter of Edith Weir in 2017.Ornamental cream crocheted bodice of ribbing, flowers and leaves.edith mary weir (nee betteridge), illapa -- 84 princess street -- kew (vic.), women's clothing, weir collection, bodices -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncHeadwear - Navy Straw & Silk Sun Hat, R & M Dower, 1949
R&M Dower was a major millinery partnership located at 146 High Street, Kew in the 1940s and 1950s. Examples of this millinery firm's hats are in other major public collections, including the National Gallery of Victoria.The Kew Historical Society’s fashion and design collection is comprised of costumes, hats, shoes and personal accessories. Many of these items were purchased or handmade in Victoria; some locally in Kew. The extensive hat collection comprises items dating from the 1860s to the 1970s. While most of the hats in the collection were created by milliners for women, there are a number of early and important men’s hats in the collection. The headwear collection is particularly significant in that it includes the work of notable Australian and international milliners.Wide brimmed navy blue fine straw woman’s hat retailed by R & M Dower of High Street, Kew, with red, white and apricot coloured fabric flowers surrounding the crown of the hat.Label: R & M Dower 146 High St., Kew. Phone WM 8527r & m dower, milliners, hats, australian fashion, women's clothing -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncHeadwear - Multicoloured Silk Floral Hat, R & M Dower, 1960s
R&M Dower was a major millinery partnership located at 146 High Street, Kew in the 1940s and 1950s. Examples of this millinery firm's hats are in other major public collections, including the National Gallery of Victoria.The Kew Historical Society’s fashion and design collection is comprised of costumes, hats, shoes and personal accessories. Many of these items were purchased or handmade in Victoria; some locally in Kew. The extensive hat collection comprises items dating from the 1860s to the 1970s. While most of the hats in the collection were created by milliners for women, there are a number of early and important men’s hats in the collection. The headwear collection is particularly significant in that it includes the work of notable Australian and international milliners.Small brimless woman’s hat retailed by R & M Dower of High Street, Kew. The structure of the hat is made of stiffened net, covered with multicoloured flowers, leaves and a purple ribbon.Label: R & M Dower, 146 High St., Kew. Phone WM 8527.r & m dower, milliners -- kew (vic.), women's clothing -- hats, headwear -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncHeadwear - Purple Raffia Sun Hat, Latiners, 1934-1945
Latiners was a Melbourne millinery company owned by Rupert Vincent Kirsch during the 1930s and 1940s. Originally located at 310 Flinders-lane, in 1934 the company shifted to 20 Dawson Street Brunswick. An article in the Melbourne Age newspaper recorded that the (illustrated) extensive factory was nearlng completion.(The Age, 10 July 1934). As well as producing hats in the factory, Latiners also imported hats into Australia. The Dawson Street factory is now listed on the Victorian Heritage Database as 'Of regional significance as one of the largest hat manufacturing businesses in Melbourne and architecturally important for its bold use of rendered forms.'The Kew Historical Society’s fashion and design collection is comprised of costumes, hats, shoes and personal accessories. Many of these items were purchased or handmade in Victoria; some locally in Kew. The extensive hat collection comprises items dating from the 1860s to the 1970s. While most of the hats in the collection were created by milliners for women, there are a number of early and important men’s hats in the collection. The headwear collection is particularly significant in that it includes the work of notable Australian and international milliners.Deep purple coloured straw girls’ hat retailed by Latiners featuring a maroon ribbon at the base of the crown and a multicoloured fabric posy of flowers on the rim. The straw hat is irregularly layered to give the impression of folds.Label: Latinerslatiners -- 310 flinders lane, latiners - dawson street -- brunswick, rupert vincent kirsch, women's clothing -- hats -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Teal Blue Rayon Dress, Cann’s, 1950s
The Fashion & Design collection of the Kew Historical Society includes examples of women’s, men’s, children’s and infants’ clothing from the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries. Items in the collection were largely produced for, or purchased by women in Melbourne, and includes examples of outerwear, protective wear, nightwear, underwear and costume accessories.Dark blue green rayon dress self patterned with small flowers of a lighter colour. The short sleeved high waisted dress is fastened with a zip at back.Label: Cann’s, Swanston Street, Melbournecann's, georgina cann, women's clothing, day dresses, australian fashion - 1950s -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, 'Goathland', The Residence of Sir Malcolm D McEacharn, 1901-1911
The architect, Edward Kilburn designed Byram in the Arts & Crafts style for the industrialist George Ramsden. Construction began in 1888 and was reputed to have lasted three years. The mansion had frontages to Studley Park Road and Stevenson Street, including gardens laid out with great taste, including pleasure grounds, tennis lawn, fruit and flower garden, and paddock.The size of many of the trees in the garden indicate that many survived from the garden of Clifton Villa, the previous single-storeyed house built on the site by the Stevenson brothers. Byram had views to Melbourne and Port Phillip Bay. The house was demolished in 1960, despite opposition from the National Trust (Victoria), and its gardens subdivided into residential allotments.An early photograph of Goathland (also known as Byram, Lowan and Tara Hall). The photo shows the front of the building during the period of Sir Malcolm McEacharn’s occupation of the house (1901-11). Edward George Kilburn, of Ellerker & Kilburn, had originally designed the house for the industrialist George Ramsden in 1888. When Sir Malcolm McEacharn purchased Byram, he was to rename it as Goathland. This has led to some confusion, as Goathland was also the name used for McEacharn’s other home in St. Kilda. The period of McEacharn’s ownership represented the high point of the mansion’s history. 'Lost Glories: a memorial to forgotten Australian buildings' was published by David Latta in 1986. It tells the story of a number of significant Australian buildings that had previously been demolished. A chapter in the book was devoted to Goathland, later known as Tara Hall. To supplement the text, he sourced photographs from a range of suppliers, chiefly the Royal Women's Hospital which had once owned Tara Hall, but had sold it in 1960. This is one of the photographs donated to KHS by the author."'Goathland', The Residence of Sir Malcolm D McEacharn"byram, goathland, tara hall, lowan, studley park road -- kew (vic.), melbourne mansions, e g kilburn - architect -
 Expression Australia
Expression AustraliaAdvertising Card, Cut Flowers - Deaf Mutes' Flower Farm, Blackburn
The Australian Deaf and Dumb Society of Victoria purchased and developed land at Blackburn Lake as a flower farm, the idea being to provide light occupation for the deaf and dumb unable to follow other regular employment, A home for aged and infirm deaf was also erected on the property.A rare example of advertising produced by the Adult Deaf and Dumb Society of Victoria for its Flower Farm at BlackburnSize 15.5cmHx21cmWlake park, blackburn, flower farm, deaf -
 Expression Australia
Expression AustraliaAdvertising Booklet, Lake Park Blackburn - The Idael Place for Pic-Nics
The Australian Deaf and Dumb Society of Victoria purchased and developed land at Blackburn Lake as a flower farm, the idea being to provide light occupation for the deaf and dumb unable to follow other regular employment, A home for aged and infirm deaf was also erected on the property.A rare booklet advertising Lake Park Blackburn as an ideal public picnic spot.Size 12cmHx15cmW; 12 pages -
 Expression Australia
Expression AustraliaPhotograph - c 1900s, The "Power House" on the Lake
An early colour photograph of the pumping station at Blackburn Lake which drew water from the lake for the Lake Park Flower Farm run by the Adult Deaf and Dumb Society of Victoria.This is significant as an early photograph of the pumping station at Blackburn Lake.Colour photograph, 25cmHx22cmWblackburn lake, lake park flower farm, pumping station -
 Queen Victoria Women's Centre
Queen Victoria Women's CentreNewspaper exerpt, κεντρο γυναικειων το queen victoria, 27 November 1996
Greek community newspaper. Black and white photograph of a woman sitting with a flower vase.greek community -
 Magnet Galleries Melbourne Inc
Magnet Galleries Melbourne Incsoldiers in field of wild flowers
wild flowers, field, soldiers, horses, aif, a.i.f, ww1, world war 1
