Showing 2602 items matching " parts of buildings or structures"
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Zig-Zag Bridge, 1924
Henry Beater Christian (1886-1962) , was a descendant of one of the earliest settler families in Kew. Employed at the Kew Asylum as a 'public servant', he was a skilled amateur photographer, photographing numerous scenes in Kew and on his travels around Victoria. The majority of his photographs date from 1916 to 1929. His finest photographs are housed in two photograph albums. Digital copy of a photograph from page 8 of the 47-page photograph album containing 261 gelatinous silver images, loaned by Diane Washfold with permission given to digitise and hold a copy in our collection. This photograph reveals how the photographer, Henry Christian, positioned himself to take the photograph from the angle in which he was interested. A skilled canoeist, an empty canoe is on the left of the photo that he apparently he used to access his vantage point. His subject, the Zig-Zag Bridge linked the grounds of the Yarra Bend and Kew Asylums. The wooden bridge was constructed in the 1870s and lasted through numerous floods until its destruction in 1929. A horizontal structure, one climbed steps to reach the higher Yarra Bend bank. At the Studley Park end, the bridge descended via a staircase to reach the much lower bank. "Zig-Zag Bridge"henry beater christian (1886-1962), landscape photography, kew (vic.) — yarra river, christian-washfold collection, photograph albums, zig-zag bridge -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Zig-Zag Bridge, 1924
Henry Beater Christian (1886-1962) , was a descendant of one of the earliest settler families in Kew. Employed at the Kew Asylum as a 'public servant', he was a skilled amateur photographer, photographing numerous scenes in Kew and on his travels around Victoria. The majority of his photographs date from 1916 to 1929. His finest photographs are housed in two photograph albums. Digital copy of a photograph from page 8 of the 47-page photograph album containing 261 gelatinous silver images, loaned by Diane Washfold with permission given to digitise and hold a copy in our collection. This photograph reveals how the photographer, Henry Christian, positioned himself to take the photograph from the angle in which he was interested. A skilled canoeist, an empty canoe is on the left bank that he apparently he used to access his vantage point. His subject, the Zig-Zag Bridge linked the grounds of the Yarra Bend and Kew Asylums. The wooden bridge was constructed in the 1870s and lasted through numerous floods until its destruction in 1929. A horizontal structure, the walkway was reached via a wooden staircase on the Studley Park end. The steps were requires due to the different levels of the banks on this stretch of the river. "Zig-Zag Bridge"henry beater christian (1886-1962), landscape photography, kew (vic.) — yarra river, christian-washfold collection, photograph albums, zig-zag bridge -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Zig-Zag Bridge, 1924
Henry Beater Christian (1886-1962) , was a descendant of one of the earliest settler families in Kew. Employed at the Kew Asylum as a 'public servant', he was a skilled amateur photographer, photographing numerous scenes in Kew and on his travels around Victoria. The majority of his photographs date from 1916 to 1929. His finest photographs are housed in two photograph albums. Digital copy of a photograph from page 8 of the 47-page photograph album containing 261 gelatinous silver images, loaned by Diane Washfold with permission given to digitise and hold a copy in our collection. This photograph reveals how the photographer, Henry Christian, positioned himself to take the photograph from the angle in which he was interested. A skilled canoeist, an empty canoe is on the left bank that he apparently he used to access his vantage point. His subject, the Zig-Zag Bridge linked the grounds of the Yarra Bend and Kew Asylums. The wooden bridge was constructed in the 1870s and lasted through numerous floods until its destruction in 1929. A horizontal structure, the walkway was reached via a wooden staircase on the Studley Park side. The steps were requires due to the different levels of the banks on this stretch of the river. "Zig-Zag Bridge"henry beater christian (1886-1962), landscape photography, kew (vic.) — yarra river, christian-washfold collection, photograph albums, zig-zag bridge -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Sunnyside and Mt Wills, c.1926
Henry Beater Christian (1886-1962) , was a descendant of one of the earliest settler families in Kew. Employed at the Kew Asylum as a 'public servant', he was a skilled amateur photographer, photographing numerous scenes in Kew and on his travels around Victoria. The majority of his photographs date from 1916 to 1929. His finest photographs are housed in two photograph albums. Digital copy of a photograph from page 35 of the 47-page photograph album containing 261 gelatinous silver images, loaned by Diane Washfold with permission given to digitise and hold a copy in our collection. John Chapman has written in 'Bushwalking Clubs - A Brief History', about the establishment in Victoria of the first bushwalking club in 1888, and the popularisation of bushwalking during the interwar period. Henry Christian's 'walks' appear to have been undertaken solely or with a companion/s. This black and white photo is part of a group of photos taken in the Victorian High Country. The page is labelled 'Mt Wills / Sunnyside' and includes photos of landscapes and built structures. Mt Wills and Sunnyside were at the time goldfields north of Omeo. This small black and white point-of-view photograph shows the photographer, Henry B Christian, staring across a treed landscape to Mt Wills in the distance."MT WILLS / SUNNYSIDE"henry beater christian (1886-1962), landscape photography, christian-washfold collection, photograph albums, bushwalking, northeast victoria, victorian high country, mt wills, sunnyside -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - BENDIGO GOLDFIELD VERTICAL PROJECTIONS
Map of Bendigo Gold Field in two sections showing 'vertical projections along several anticlinal axial planes showing pitch, stratigraphical zones, faultlines, shafts and etc.'. Bulletin No 47 written top left hand side. Lines of reef described: Christmas line Lancashire line Nell Gwynne line New Chum line Hustlers line Garden Gully line Sheepshead line Mines along the reef lines are listed. This map forms part of the Geological Survey of Victoria, Structure of Bendigo Goldfield report, No. 47, 1923. H.Herman, late Director of Geological Survey. On bottom of second section : Prepared in the Geological Survey Office, Bendigo, under the direction of H. Herman, late Director of Geological Survey, from surveys by H.S. Whitelaw, Field Geologist, assisted by E.S. Usher, A.J.J. Moore and R.A. Keble.Geological Survey of Victoriabendigo, gold mining, reef lines -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, "Report by Administrators", March to June 2003
Set of two "Report by Administrators" concerning the receivership of National Express prepared by Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu for distribution to creditors. .1 - Report - A4 - 52 pages + card covers stapled with black binding strip on the left hand side dated 17/3/2003 with table of contents giving the background, corporate structure, financial performance, directors reasons for company failure, possible offences, legal issues, meeting of creditors, deeds and administrators opinion and remuneration. .2 - Report - A4 - 28 pages + card covers, perfect bound, dated 12/6/2003, with table of contents, giving an executive summary, liability for insolvent trading, director's statement of claim, arrangements, meeting of creditors, deeds and administrators opinion and remuneration and draft proposal for a deed of company arrangement. See Reg Item 1332 for other related documents.trams, tramways, national express, meetings -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPamphlet, Minister of Transport, "Transport Safeguards", "New Guarantees for Public Transport Passengers effective mid 1999", "A New Partnership - Reforming Victoria's trains and trams: what it means for public transport employees", 1998 - 1999
Set of three items related to the decision to franchise the public transport in Melbourne during late 1998. Items are related to Reg Item 2830. a report titled "A system into a Service" by the Victorian Government late 1998. .1 - photocopy of a newspaper article in The Age 30/10/1998 titled "Transport Safeguards" written by Lyall Johnson giving details of the Passenger Charter, guarantees, quotes Robin Cooper, Minister for Transport. Has a cartoon by Tandberg. .2 - Pamphlet - 4 fold DL titled "New Guarantees for Public Transport Passengers effective mid 1999" detailing the Passenger charter. .3 - Pamphlet - 3 fold DL titled "A New Partnership - Reforming Victoria's trains and trams: what it means for public transport employees", outlining the corporate structure, franchising and private ownership, guarantees for employees and passengers. Not dated.trams, tramways, public transport, franchising, ptc, privatisation, passengers, minister for transport, cartoons, passenger services -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPamphlet, Minister of Transport, "Transport Victoria", 1977 and 1978
453.1 - Sixteen page, full colour printed on glossy paper, centre stapled pamphlet, titled "Transport Victoria", with part of the Harold Freedman on the front cover, detailing the structure and the authorities of the Ministry of Transport, c1977. Foreword by Hon. J. Rafferty Transport Minister (1976 to 1978 - State Parliament website biography). Provides information on: MMTB Victorian Railways - VicRail Railway Construction Board Melbourne Underground Rail Loop Authority - MURLA Country Roads Board - CRB Transport Regulation Board - TRB Westgate Bridge Authority and who's who in the transport in Victoria - Board members - with photos. 453.2 - as above but with foreword by Robert Maclellan MLA as minister (see image 9) and revision of the "Who's who" on page 15 - see image 10. Maclellan was the Minister was 1978 to 1982 - parliamentary web site. Not imaged..trams, tramways, mmtb, minister for transport, vicrail, crb, murla -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyBooklet, City of Ringwood 1988 Community Information Guide, 1988
Community information booklet issued by City of Ringwood for 1988 - covering the facilities and activities of the Ringwood Council and other local organisations and associations. Cover photographs: Front - Floral displays at Clock Tower and a scene at Council nursery; Back - Activities at Ringwood Festival held at Ringwood Lake in April each year.CONTENTS: (page no.) After School Activities Programme 23 Aged Services 21 Bicentennial 15 Building Information 29 By-Laws and Traffic Regulations 31 Caravans/Mobile Homes 31 Chief Executive's Message 10 Children's Services 22 Churches 40 Civic Centre 4 Committees of Council 5 Community Plan 15 Community Services 35 Corporate Management Structure 11 Council Meeting Dates 4 Council Representatives 8 Councillors 6 & 7 Disabled Persons Facilities 42 Dogs 31 Domiciliary Care 24, 25 & 26 Elderly Day Care 44 Elderly Persons Units 29 Emergency Telephone Numbers 53 Employment Opportunities in Ringwood 26 European Wasps 28 Family Day Care 22 Finances 17 Fire Hazards 31 Future Leaders 16 Golf Course 34 Home Handyman Services 25 Home Help 26 Immunisation Programme 27 Incinerators 32 Knaith Road Child Care Centre 22 & 23 Library 30&31 Maternal & Child Health Centre 30 Mayoral Message – Cr. John R. Caffyn 3 Meals on Wheels 24 Members of Parliament 9 Playgroups 33 Pre-Schools 53 Primary Arterial Road Network in Ringwood 13 Rates—New Collection Service 18 & 19 Ringwood Aquatic Centre 14 & 15 Ringwood Bypass Road 12 Ringwood Convention & Performing Arts Centre 33 Ringwood District Centre Structure Plan 12 Rubbish Collection Service 35 & 36 Schools 56 Youth Outreach Worker 20 rinx -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, July 1922
A new bridge over the Snowy River at Orbost was opened for traffic on June 20th 1922. It was designed for future joint use by road and railway traffic, but it was only used for road traffic. During the last few years the condition of an old suspension bridge [the 1893 bridge] which was the only vehicular crossing between the town of Orbost and the railway station, caused much concern. The structure was of timber, except for the wire suspension cables of its central span of about 100 feet. A design was prepared in 1914 for a permanent bridge with five spans of 85 feet composed of plate girders on concrete piers. With great increase in the price of steel work during the war, the cost of this design became prohibitive, and the need for a new structure becoming urgent, alternative proposals were investigated. As a result the present design was adopted as providing a sem-permanent bridge at moderate cost. The new bridge spans the river about 160 feet upstream from the old bridge on a slight skew, the piers being at an angle of 80 degrees with the centre line of the bridge. It has a camber of about 2 feet 5 inches in its total length of 527 feet. ( information from Newsletter March 2014 - Lois Crisp) The photograph shows Mrs James Cameron cutting the ribbon at the opening of the Orbost Pile Bridge in 1922. This second bridge, was built by the Victorian Railways and the Country Roads Board. Constructed at a cost of 35,000 pounds and used second-hand girders from the Flinders Street- Spencer Street viaduct. On July 4 1922 it was officially opened by Mrs James Cameron. Unfortunately, her husband, who had long championed the building of the bridge so that it would be ready for the railway to continue to the border, was too ill to attend the ceremony. In fact, James Cameron died on July 13 after a long and severe illness (ref. S.R.M. 20.7.1922). There is a section of this ribbon in the collection - Registration No. 366. This is a pictorial record of a significant event in Orbost's history.A black / white photograph of a pile bridge with a suspension bridge behind it. There are many people standing on the bridge.on back - "Opening of Pile Bridge - 1922"snowy-river-bridge ceremonies cameron-mrs -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncSlide, Maroondah Aqueduct, Research, Victoria, 22 Mar. 1981
An inspection tour of the Maroondah Aqueduct was undertaken by the Shire of Eltham Historical Society on Sunday, March 22nd, 1981, commening where the aqueduct crosses Main Rd., Research, just below Eltham College. The Maroondah Aqueduct was part of Melbourne’s water supply system. It carried water over the 66 km from the Maroondah Reservoir on the Watts River at Healesville to the Preston Reservoir. Of this length, 41 km were open channel, 10 km, tunnel through hills and 15 km in 14 inverted siphons across stream valleys. The route of the aqueduct is north of Tarrawarra and Yarra Glen, along the Yarra escarpment south of Christmas Hills and crossing Watsons Creek into the present Shire of Eltham near Henley Rd. The eastern part of the route lies entirely within the former boundaries of the shire. The aqueduct passes south of Kangaroo Ground to Research and crosses the Diamond Creek by siphon at Allendale Rd., Eltham North. It then extends to Reservoir via St. Helena, Greensborough North and Bundoora. Water first flowed through the aqueduct in February 1891 when it was fed by a diversion weir on the Watts River. Records of the building of the aqueduct indicate that it was a significant construction achievement. The present Maroondah Reservoir was completed in 1927 and the aqueduct was enlarged at that time to take increased flows. About 1971 the section of the aqueduct through and north of Research was replaced by a large pipe and that section of the channel is now unused. The channel has remained largely intact (unlike sections at Greensborough and Bundoora where long lengths of the disused aqueduct have been demolished or filled in). The M.M.B.W. relinquished control of the disused aqueduct reserve which is crown land and the Shire of Eltham took control of this section of the reserve as a linear park. The Maroondah Aqueduct is considered to be an important historic structure, not just to the local area but to the metropolitan area generally. It is considered important to preserve substantially intact long lengths of the disused aqueduct, together with its bridges and other associated structures. 35 mm colour positive transparency (1 of 5) Mount - Agfachrome Agfa CS System black 8 dotsactivities, heritage excursion, maroondah aqueduct, research (vic.), shire of eltham historical society -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncSlide, Maroondah Aqueduct, Research, Victoria, 22 Mar. 1981
An inspection tour of the Maroondah Aqueduct was undertaken by the Shire of Eltham Historical Society on Sunday, March 22nd, 1981, commening where the aqueduct crosses Main Rd., Research, just below Eltham College. The Maroondah Aqueduct was part of Melbourne’s water supply system. It carried water over the 66 km from the Maroondah Reservoir on the Watts River at Healesville to the Preston Reservoir. Of this length, 41 km were open channel, 10 km, tunnel through hills and 15 km in 14 inverted siphons across stream valleys. The route of the aqueduct is north of Tarrawarra and Yarra Glen, along the Yarra escarpment south of Christmas Hills and crossing Watsons Creek into the present Shire of Eltham near Henley Rd. The eastern part of the route lies entirely within the former boundaries of the shire. The aqueduct passes south of Kangaroo Ground to Research and crosses the Diamond Creek by siphon at Allendale Rd., Eltham North. It then extends to Reservoir via St. Helena, Greensborough North and Bundoora. Water first flowed through the aqueduct in February 1891 when it was fed by a diversion weir on the Watts River. Records of the building of the aqueduct indicate that it was a significant construction achievement. The present Maroondah Reservoir was completed in 1927 and the aqueduct was enlarged at that time to take increased flows. About 1971 the section of the aqueduct through and north of Research was replaced by a large pipe and that section of the channel is now unused. The channel has remained largely intact (unlike sections at Greensborough and Bundoora where long lengths of the disused aqueduct have been demolished or filled in). The M.M.B.W. relinquished control of the disused aqueduct reserve which is crown land and the Shire of Eltham took control of this section of the reserve as a linear park. The Maroondah Aqueduct is considered to be an important historic structure, not just to the local area but to the metropolitan area generally. It is considered important to preserve substantially intact long lengths of the disused aqueduct, together with its bridges and other associated structures. 35 mm colour positive transparency (1 of 5) Mount - Agfachrome Agfa CS System black 8 dotsactivities, heritage excursion, maroondah aqueduct, research (vic.), shire of eltham historical society -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncSlide, Maroondah Aqueduct, Research, Victoria, 22 Mar. 1981
An inspection tour of the Maroondah Aqueduct was undertaken by the Shire of Eltham Historical Society on Sunday, March 22nd, 1981, commening where the aqueduct crosses Main Rd., Research, just below Eltham College. The Maroondah Aqueduct was part of Melbourne’s water supply system. It carried water over the 66 km from the Maroondah Reservoir on the Watts River at Healesville to the Preston Reservoir. Of this length, 41 km were open channel, 10 km, tunnel through hills and 15 km in 14 inverted siphons across stream valleys. The route of the aqueduct is north of Tarrawarra and Yarra Glen, along the Yarra escarpment south of Christmas Hills and crossing Watsons Creek into the present Shire of Eltham near Henley Rd. The eastern part of the route lies entirely within the former boundaries of the shire. The aqueduct passes south of Kangaroo Ground to Research and crosses the Diamond Creek by siphon at Allendale Rd., Eltham North. It then extends to Reservoir via St. Helena, Greensborough North and Bundoora. Water first flowed through the aqueduct in February 1891 when it was fed by a diversion weir on the Watts River. Records of the building of the aqueduct indicate that it was a significant construction achievement. The present Maroondah Reservoir was completed in 1927 and the aqueduct was enlarged at that time to take increased flows. About 1971 the section of the aqueduct through and north of Research was replaced by a large pipe and that section of the channel is now unused. The channel has remained largely intact (unlike sections at Greensborough and Bundoora where long lengths of the disused aqueduct have been demolished or filled in). The M.M.B.W. relinquished control of the disused aqueduct reserve which is crown land and the Shire of Eltham took control of this section of the reserve as a linear park. The Maroondah Aqueduct is considered to be an important historic structure, not just to the local area but to the metropolitan area generally. It is considered important to preserve substantially intact long lengths of the disused aqueduct, together with its bridges and other associated structures. 35 mm colour positive transparency (1 of 5) Mount - Agfachrome Agfa CS System black 8 dotsactivities, heritage excursion, maroondah aqueduct, research (vic.), shire of eltham historical society -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncSlide, Maroondah Aqueduct, Research, Victoria, 22 Mar. 1981
An inspection tour of the Maroondah Aqueduct was undertaken by the Shire of Eltham Historical Society on Sunday, March 22nd, 1981, commening where the aqueduct crosses Main Rd., Research, just below Eltham College. The Maroondah Aqueduct was part of Melbourne’s water supply system. It carried water over the 66 km from the Maroondah Reservoir on the Watts River at Healesville to the Preston Reservoir. Of this length, 41 km were open channel, 10 km, tunnel through hills and 15 km in 14 inverted siphons across stream valleys. The route of the aqueduct is north of Tarrawarra and Yarra Glen, along the Yarra escarpment south of Christmas Hills and crossing Watsons Creek into the present Shire of Eltham near Henley Rd. The eastern part of the route lies entirely within the former boundaries of the shire. The aqueduct passes south of Kangaroo Ground to Research and crosses the Diamond Creek by siphon at Allendale Rd., Eltham North. It then extends to Reservoir via St. Helena, Greensborough North and Bundoora. Water first flowed through the aqueduct in February 1891 when it was fed by a diversion weir on the Watts River. Records of the building of the aqueduct indicate that it was a significant construction achievement. The present Maroondah Reservoir was completed in 1927 and the aqueduct was enlarged at that time to take increased flows. About 1971 the section of the aqueduct through and north of Research was replaced by a large pipe and that section of the channel is now unused. The channel has remained largely intact (unlike sections at Greensborough and Bundoora where long lengths of the disused aqueduct have been demolished or filled in). The M.M.B.W. relinquished control of the disused aqueduct reserve which is crown land and the Shire of Eltham took control of this section of the reserve as a linear park. The Maroondah Aqueduct is considered to be an important historic structure, not just to the local area but to the metropolitan area generally. It is considered important to preserve substantially intact long lengths of the disused aqueduct, together with its bridges and other associated structures. 35 mm colour positive transparency (1 of 5) Mount - Agfachrome Agfa CS System black 8 dotsactivities, heritage excursion, maroondah aqueduct, research (vic.), shire of eltham historical society -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyFour photographs of the Blue Duck Hotel and two Photos of the Glen Wills area, c1920 Post cards, c1949/50 small photographs
The Blue Duck Hotel stands at the confluence of 3 trout rivers - Cobungra, Bundarra and Mitta Mitta, called Angler's Rest. The original 1900's building was of slab construction and operated as a butcher shop, servicing miners on the track from Omeo to Mt. Wills. In 1912 it was purchased by a miner, Billy O'Connell, and he obtained a hotel license. In the early 1920's he transported 2 houses from Omeo on Horse drays. One is the main building of the Blue Duck and the other was a residence where Billy and his wife raised their nine children. The small log structure behind the pub is State School No.4286 where the children attended school. A teacher was shared with Glen Wills. By the late 1920's the hotel was discovered and patronized by keen anglers. Sir Harold Clapp (head of the railways) was one and he had the bronze blue duck cast and presented to the owners in the 1930's. This stands at the entrance to the premises.These photographs are of a building, in a remote area, that has provided a service to miners, anglers and travellers for over 100 years and continues to do so today. It also played a vital role in the history of the Mt. Wills/Omeo gold mining days.3 Post cards, Black and White photographs. 3 small black and white photographsPost Card No. 1 - "Blue Duck Hotel- Omeo-Glen wills road Ray Love Series No.2"(written on lower front) Post Card No. 2- "Looking towards Bogong High Plains. Omeo-Glen Wills road"(front, bottom, L hand) Ray Love Series No. 18 (front, lower R hand corner) On both of above photos, centre back, is stamped POST CARD and underneath this is printed "A GENUINE PHOTOGRAPH'/ Post Card No. 3 - Bottom L hand corner "Mystic Sea Australian Alps". R hand corner "(Bulmer Copyright)". Each small photograph, handwritten on back "Blue duck Hotel". All have circular stamp with "Print by Wilson White Albury" blue duck hotel; anglers rest; omeo highway; fishing; mining -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPamphlet - An Introduction to Topographic Mapping, C 1991
This pamphlet was published by the Army Survey Regiment as an overview of the Royal Australian Survey Corps (RASvy), its role and unit structure circa 1991, prior to RASvy’s disbandment in 1996. The pamphlet comprehensively detailed the eight steps of topographic map production: Establish Survey Control, Aerial Photography, Aerotriangulation, Stereoplotting, Field Verification, Cartography, Printing and Storage/Map Distribution. Leading technologies used by RA Svy in 1991 included GPS control surveys, 5 colour printing on the Speedmaster offset press and bulk map packaging using the Map Handling Station (with guillotine). Digital map production was operating on the AUTOMAP 2 system, before the “Newheart” system upgrade two years later. Printed on the pamphlet cover was a portion of the plane tabled “four inches to a mile” map of Newcastle. This was compiled and surveyed in 1910 by LCPL A. Barrett, a member of the RAE Detachment, as part of the first major topographic mapping effort of Australia.This is a Royal Australian Survey Corp pamphlet with a historical map printed in colour on cardboard on both sides of the cover. There are 16 pages printed in colour on gloss paper, with photos, diagrams and descriptions. The pamphlet is bounded by two staples on its spine. Each of the 17 images were scanned at 300 dpi in JPEG (.jpg) format and stored on the attached 16 Gb USB memory stick. The images have been converted into MPEG-4 (.mp4) video format, 4Mb in size and runs for 2:16 minutes and is also stored on the memory stick.royal australian survey corps, rasvy, fortuna, army survey regiment, army svy regt, asr -
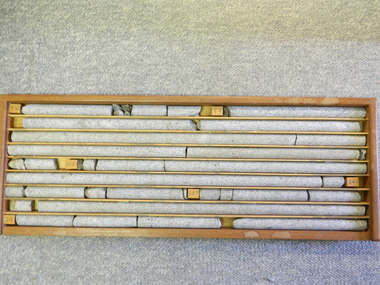 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyCore Rock Samples
The core samples in the display cabinet were obtained from the various sites at which drilling into the rock surface was carried out (under the control of design and structural engineers of the SEC Kiewa Hydro Scheme - late 1940's). This function was a precursor to the decision where to locate, in this case, the McKay Creek Power Station. The information gained by structural engineers from the core samples would be used also for the placements of underground tunnels entry and exit points and the overall effective size of the generator plant. This would have included drill and blast techniques (rock characteristics play an import part of explosion control), requirements for support structures and reinforcing cement/steel forms. The use and replenishment of diamond drill bits(the strongest available, see KVHS 0280) was dependent on the "type" of rock found (harder rock required greater numbers of drill bits). Support beams for reinforced ceilings and floors was also a necessity.These rock core samples are very significant in the formulation and placement of the underground Power Stations and their maze of tunnels (in and out) for a successful implementation of the Hydro Scheme. The amount of pre-planning and engineering studies required for such a large scheme must be undertaken to ensure that a "white elephant" was not the result.There are nine columns of rock cores, each 30mm in diameter, set in a wooden display rack. A clear plastic (slide out) protective panel is installed to the front section. Within each column are block details of the depth from which that section was brought from. See KVHS for the appropriate sketch details.Depth levels (retrieved from) are shown for each section on wooden Blocks: 1st Block: "7'10" (seven feet, ten inches), 2nd Block:"9'4" (nine feet, four inches), 3rd Block: "19'3" (nineteen feet, three inches), 4th Block: "24'2" (twenty four feet, two inches), 5th Block: "25'7"( twenty five feet, seven inches) and last block: "30' (thirty feet)"alternate energy supplies, alpine feasibility studies temperature, rainfall, sec, kiewa hydro scheme, electricity -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyPhotograph, Dalny Road, 5-17 Rear, Murrumbeena, 2001
Originally labelled "Beauville Estate, Established 1936, Still Thriving 65 years on, 10th March 2001", the Beauville Estate Album contains colour photographs of houses in the Estate. They were taken around the time of the Beauville Estate’s 65th Heritage Celebration held on 10/03/2001 and donated to the Caulfield Historical Society shortly afterwards. Photographer unknown. From Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan by Andrew Ward (1996) Vol 2 p78: "Beauville Avenue is unusual in that it is terminated in a cul-de-sac (see Section 3.9.2) whilst the design of the estate may well be unique for its time in that the houses back onto 6 tennis courts for public use. St. Patrick's Church, which adjoins the estate is a comparatively recent structure whilst the school has one building erected in 1930 and prior to the release of the Beauville lots." It also notes that St.Patrick's Church and School now run the tennis courts. The Beauville Historic Area is important at the State level as the first large housing estate undertaken by the AV Jennings Construction Co, later Jennings Group Limited, Victoria’s largest home builder. It is important also as a very early estate development incorporating a range of features other than houses and including made roads, shops and recreation facilities. In this respect it was the forerunner of the comprehensively planned housing estate of the post war era. The estate is distinguished by its aesthetic values, as is the earlier and comparable Hillcrest Estate, which are formed by a combination of restrained diversity in house styles, with the exception of no. 30 in the emerging International style, and by a landscaped garden environment. See Significance Statement in Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan by Andrew Ward (1996) Vol 2 p.79. Available from https://www.gleneira.vic.gov.au/media/4779/heritage_management_plan_volume_2.pdf (Note see p.84 of pdf)Colour photograph of a playground on the Beauville Estate. murrumbeena, houses, 1930's, a.v. jennings, av jennings, jennings, beauville estate, playgrounds, parks and reserves, sir albert victor jennings, a v jennings construction co, beauville estate heritage area, glen eira city council, jennings group limited, land subdivision, gardens, beauville historic area, st patrick's church, st patrick's school, dalny road -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyPhotograph, Dalny Road, 5-17 Rear, Murrumbeena, 2001
Originally labelled "Beauville Estate, Established 1936, Still Thriving 65 years on, 10th March 2001", the Beauville Estate Album contains colour photographs of houses in the Estate. They were taken around the time of the Beauville Estate’s 65th Heritage Celebration held on 10/03/2001 and donated to the Caulfield Historical Society shortly afterwards. Photographer unknown. From Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan by Andrew Ward (1996) Vol 2 p78: "Beauville Avenue is unusual in that it is terminated in a cul-de-sac (see Section 3.9.2) whilst the design of the estate may well be unique for its time in that the houses back onto 6 tennis courts for public use. St. Patrick's Church, which adjoins the estate is a comparatively recent structure whilst the school has one building erected in 1930 and prior to the release of the Beauville lots." It also notes that St.Patrick's Church and School now run the tennis courts.City of Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan Vol 2 p79 (this is p84 of the pdf version) – HO12 Beauville Estate and environs, Murrumbeena: The Beauville Historic Area is important at the State level as the first large housing estate undertaken by the AV Jennings Construction Co, later Jennings Group Limited, Victoria’s largest home builder. It is important also as a very early estate development incorporating a range of features other than houses and including made roads, shops and recreation facilities. In this respect it was the forerunner of the comprehensively planned housing estate of the post war era. The estate is distinguished by its aesthetic values, as is the earlier and comparable Hillcrest Estate, which are formed by a combination of restrained diversity in house styles, with the exception of no. 30 in the emerging International style, and by a landscaped garden environment. Colour photograph of a tennis club house and a park on the Beauville Estate. murrumbeena, houses, 1930's, a.v. jennings, av jennings, jennings, beauville estate, jennings albert victor, parks and reserves, sports and recreations establishments, clubhouses, tennis clubs, beauville tennis courts, st patrick's tennis club, sir albert victor jennings, a v jennings construction co, beauville estate heritage area, glen eira city council, architectural features, jennings group limited, land subdivision, gardens, beauville historic area, dalny road -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyPhotograph, Dalny Road, 5-17 Rear, Murrumbeena, 2001
Originally labelled "Beauville Estate, Established 1936, Still Thriving 65 years on, 10th March 2001", the Beauville Estate Album contains colour photographs of houses in the Estate. They were taken around the time of the Beauville Estate’s 65th Heritage Celebration held on 10/03/2001 and donated to the Caulfield Historical Society shortly afterwards. Photographer unknown. From Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan by Andrew Ward (1996) Vol 2 p78: "Beauville Avenue is unusual in that it is terminated in a cul-de-sac (see Section 3.9.2) whilst the design of the estate may well be unique for its time in that the houses back onto 6 tennis courts for public use. St. Patrick's Church, which adjoins the estate is a comparatively recent structure whilst the school has one building erected in 1930 and prior to the release of the Beauville lots." It also notes that St.Patrick's Church and School now run the tennis courts.City of Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan Vol 2 p79 (this is p84 of the pdf version) – HO12 Beauville Estate and environs, Murrumbeena: The Beauville Historic Area is important at the State level as the first large housing estate undertaken by the AV Jennings Construction Co, later Jennings Group Limited, Victoria’s largest home builder. It is important also as a very early estate development incorporating a range of features other than houses and including made roads, shops and recreation facilities. In this respect it was the forerunner of the comprehensively planned housing estate of the post war era. The estate is distinguished by its aesthetic values, as is the earlier and comparable Hillcrest Estate, which are formed by a combination of restrained diversity in house styles, with the exception of no. 30 in the emerging International style, and by a landscaped garden environment. Colour photograph of tennis courts and surrounding mesh fencing on the Beauville Estate. murrumbeena, houses, 1930's, a.v. jennings, av jennings, jennings, beauville estate, parks and reserves, sports and recreations establishments, tennis courts, sportsgrounds, sir albert victor jennings, a v jennings construction co, beauville estate heritage area, glen eira city council, architectural features, jennings group limited, land subdivision, gardens, beauville historic area, tennis clubs, beauville tennis courts, st patrick's tennis club, dalny road -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyPhotograph, Dalny Road, 5-17 Rear, Murrumbeena, 2001
Originally labelled "Beauville Estate, Established 1936, Still Thriving 65 years on, 10th March 2001", the Beauville Estate Album contains colour photographs of houses in the Estate. They were taken around the time of the Beauville Estate’s 65th Heritage Celebration held on 10/03/2001 and donated to the Caulfield Historical Society shortly afterwards. Photographer unknown. From Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan by Andrew Ward (1996) Vol 2 p78: "Beauville Avenue is unusual in that it is terminated in a cul-de-sac (see Section 3.9.2) whilst the design of the estate may well be unique for its time in that the houses back onto 6 tennis courts for public use. St. Patrick's Church, which adjoins the estate is a comparatively recent structure whilst the school has one building erected in 1930 and prior to the release of the Beauville lots." It also notes that St.Patrick's Church and School now run the tennis courts. City of Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan Vol 2 p79 (this is p84 of the pdf version) – HO12 Beauville Estate and environs, Murrumbeena: The Beauville Historic Area is important at the State level as the first large housing estate undertaken by the AV Jennings Construction Co, later Jennings Group Limited, Victoria’s largest home builder. It is important also as a very early estate development incorporating a range of features other than houses and including made roads, shops and recreation facilities. In this respect it was the forerunner of the comprehensively planned housing estate of the post war era. The estate is distinguished by its aesthetic values, as is the earlier and comparable Hillcrest Estate, which are formed by a combination of restrained diversity in house styles, with the exception of no. 30 in the emerging International style, and by a landscaped garden environment. Colour photograph of tennis courts with lights on the Beauville Estate. murrumbeena, houses, 1930's, a.v. jennings, av jennings, jennings, beauville estate, parks and reserves, sports and recreations establishments, tennis courts, sportsgrounds, sir albert victor jennings, a v jennings construction co, beauville estate heritage area, glen eira city council, architectural features, jennings group limited, land subdivision, gardens, beauville historic area, tennis clubs, beauville tennis courts, st patrick's tennis club, dalny road -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratBook - Contemporary Labor Economics, Second Edition (D.J. Spiers Collection), McConnell, Campbell R. et al
Chapter titles: Chapter 1: Labor Economics Introduction and Overview -- Chapter 2: The Theory of Individual Labor Supply -- Chapter 3: Population, Participation Rates, and Hours of Work -- Chapter 4: Labor Quality: Investing in Human Capital -- Chapter 5: The Demand for Labor -- Chapter 6: Wage Determination and the Allocation of Labor -- Chapter 7: Alternative Pay Schemes and Labor Efficiency -- Chapter 8: The Wage Structure -- Chapter 9: Mobility, Migration, and Efficiency -- Chapter 10: Labor Unions and Collective Bargaining -- Chapter 11: The Economic Impact of Unions -- Chapter 12: Government and the Labor Market: Employment, Expenditures, and Taxation -- Chapter 13: Government and the Labor Market: Legislation and Regulation -- Chapter 14: Labor Market Discrimination -- Chapter 15: Job Search: External and Internal -- Chapter 16: The Distribution of Personal Earnings -- Chapter 17: Labor Productivity: Wages, Prices, and Employment -- Chapter 18: Employment and Unemployment.Relevance to union business.Book; paper.Front cover: authors' names and titles.btlc, ballarat trades and labour council, economics - labor, unions, collective bargaining, wealth distribution, employment -
 Otway Districts Historical Society
Otway Districts Historical SocietyBook, Annie Notley, History of the Gellibrand Hotel, June 2014
In 1884 Frank Ball erected a house and general store beside the Gellibrand River at Gellibrand. These buildings were burnt in the 1886 bushfires so Ball rebuilt a large weatherboard building with accomodation rooms for guests. In the same year he also acquired a Roadside Victuallers Licence. From the purchase of the hotel by Mark Marks in 1895 the hotel passed through the publicans' hands of Joe Marks (who replaced the original hotel with a grand masonry structure), Henry Wills, Ellen Pathe, another Marks licensee, Charles Sharp (adding a new accomodation wing and tennis court), Ray Stewart, Arthur McKenzie, Jim Fry from Beech Forest, and Colin and Noeline Sinclair. There have been several owners and licensees since then, the last co-owners being Dylan Kane and Michael Elton with the licensee being Annie Notley. While not strictly hotel business there are also pieces about the Gellibrand School, timber processing, sports and churches.History of the Gellibrand Hotel: a work in progress. Annie Notley. 1st ed. Annie Notley; Gellibrand (Vic); 2014. 120p.; illus, maps. Hard cover.gellibrand; gellibrand hotel; wonga hotel; schools; football; -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMAMixed media, Inga Hunter, The Forest People - Three Quivers, 1986-1989
"The Forest People use poison on their darts, and on some of their arrows, to stun or kill small prey. Poison Brewers distil the venom, which is obtained from roots, bark, leaves, and the skin of a certain frog-like creature. Alchemancers distribute the venom to hunters and healers. Poison-impregnated darts are kept in special pouches or quivers, blessed by the Alchemancer or the Guardian with special spells and incantations to prevent accidents and the perversion of the tools by evil spirits. Each of these quivers carries amulets of protection. The quivers themselves, were made by a specially trained craftsman who is able to sing incantations into the actual structures themselves, ensuring double and sometimes treble protection from danger, as well as increased effectiveness, sureness of flight, efficacy of the poison etc. Quivers such as these are kept on the belt, on the side away from the dominant hand, to ensure considered, careful use, and to prevent the wrongful use of poison when a simple arrow would be sufficient." - Inga Hunter -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionLa Perruque, 2018
Laresa KOSLOFF Laresa Kosloff makes performative videos, Super-8 films, hand-drawn animations, sculpture, installations and live performance works, all linked by an interest in the body and its agency within the everyday. Recurrent themes include humour and tension between received cultural values, individual agency and free will. La Perruque won the 2018 Guirguis New Art Prize. ‘Laresa is a worthy winner having been dedicated to her practice over many years and creating a work that is intelligently structured and steeped in satire, epitomising what we all either know or experience at work or in office life. By her clever collaging of characters, editing and story adaptation, Laresa has created an impressive fictional and insightful work that by way of its very construction cleverly illustrates and articulates aspects of Australian culture,’ (Shelley Hinton, Curator Federation University’s Post Office Gallery)A USB and a portable hard drive in a black archival box with a signed certificate. Her short film La Perruque is made entirely out of commercial stock footage, generic material produced for corporate advertising, which is strangely artificial, simplistic and loaded with images of success and productivity. Kosloff uses this footage to tell the tale of an office worker who is secretly trying to write a novel during work hours. The silent footage has been dubbed using voice actors and assembled into a story that subverts commercial representations of office life. The title refers to a French term that translates into 'wearing the wig', used to describe a situation of secretly working on personal projects during work time.guirguis new art prize, video -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic
