Showing 872 items matching " cooking"
-
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Leisure object - Toy Enamelled Pot
Blue enamelled toy cooking pot with pouring lip and two handles. White enamel inside.toys, general -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Domestic object - Pot
Large cast iron cooking pot with spout and handle. Suitable for use over open fire.domestic items, food preparation -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Domestic object - Kitchen Equipment, 'Brockoff' SR flour bag
Circa early 1900s. Flour was a staple ingredient of bread, as well as being used for general cooking. This 7lb bag of flour would have been purchased for domestic use by a housewife living in the Moorabbin district. Used bags were often made into shade blinds, underwear, sleepwear, aprons by the industrious early settlers who could not afford to waste any material.This flour bag is typical of the type that would have been found in every housewives' kitchen in the Moorabbin district. It recalls the fact that flour was being made in Melbourne. Unbleached, cotton bag., with faded black lettering. Bag held 7lbs of flour.A.F.BROCKOFFS / 7 LBS / coat of arms – spread eagle with flags - /Trade mark / SELF FLOURS/ RAISING/ FACTORIES / MELBOURNE / SYDNEY AND FREMANTLE flour, cooking, kitchen, moorabbin, housewife, housewives. -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyArticle - Imber, Doris
An article from ‘The Age’ dated 21 October 1980 describing Breadmaker Mrs Doris Imber who ran her Doris’s Dough Cooking School from the kitchen of her North Caulfield home. There is a photograph of her in the article.imber doris, doris’s dough cooking school, north caulfield, bread, cooking demonstrations, kitchens, bakers, cooking, home units -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyBook, Robertson & Mullens, Mrs Floate's Secret of Success Cookery Book, Vol. 2, 1950
On the page following the title page is the following information: "Mrs. Dorothy Floate's Cookery Book Presented to the Queen. Authoress Honored. On the occasion of the visit of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II. to Australia, Mrs. Dorothy Floate's now famous "Secrets of Success" Cookery Book was presented to Her majesty as a gift from the Authoress. It was duly accepted and gratefully acknowledged by Her Majesty." On the following pages are photographs of Mrs Floate with trophys and other awards received for competitive cooking, as well as a certificate received from the Royal Agricultural Society of Victoria at the Melbourne Centenary Royal Show in 1934.Paperback cookery book, cover printed in green background, title printed in white on a brown background, volume no and price shown in white on red background. Black and white photo of author on cover. 160 pagesdorothy floate, cooking, cookery, recipes -
 Broadmeadows Historical Society & Museum
Broadmeadows Historical Society & MuseumPhotograph, Gulcan Cooks Up a Treat, 3 February 1998
This item is part of a series of images regarding social housing in Broadmeadows. Titled "Gulcan Cooks Up a Treat Public Housing" / "Broadmeadows 1998," the photograph features a woman standing at a stove, cooking in a house within the Banksia Gardens estate. This image captures a moment of daily life and highlights the personal and communal aspects of living in public housing. It provides a glimpse into the domestic environment and the social fabric of the community during that period, emphasizing the importance of home and family within the context of social housing.The photograph titled "Gulcan Cooks Up a Treat Public Housing" / "Broadmeadows 1998" holds significant historical and cultural value. It features a woman, Gulcan, standing at a stove and cooking in a house within the Banksia Gardens estate. This image is part of a series documenting social housing in Broadmeadows and provides a poignant glimpse into the everyday lives of residents. It highlights the personal and communal aspects of living in public housing, emphasising the importance of home, family, and community. The photograph captures the essence of domestic life and the social fabric of the community during that period, offering valuable insights into the lived experiences of those in social housing.A black and white photograph on glossy photographic paper of a woman in a kitchen."Gulcan Cooks Up a Treat Public Housing"/"Broadmeadows 1998"broadmeadows, social housing, cooking, banksia gardens, 1998 -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPie Iron Camping, circa mid to late 1900s
This Pie Iron was used in the mid to late 1900's when stock, both cattle and sheep, were grazed on the Bogong High Plains. Providing meals for stockmen over open fires, even in log cabins in the Victorian Alpine region, was usually by a "camp cook" or a stockman designated "cook" from the Valley station/property. The use of "camping cooking utensils were a necessity and not a "weekend" affair. Stockmen could spend up to six weeks on the plains and all their cooking needs required had to "pack horsed" from the valley below. A scientific study started in 1947, to study the impact of grazing cattle on the natural Alpine and sub Alpine vegetation found grazing cattle had an adverse affect on the natural Alpine and sub alpine vegetation, and grazing on the plains was stopped by the Victorian Government in 2005.This item is highly significant to the Kiewa Valley as it demonstrates the kind of cooking utensils that were required for camp drafts in the Bogong High Plains environment. As the control of cattle and sheep in the High Plains was very demanding upon horse and rider, good "tucker" was a pre- requisite for a successful operation. As the time spent in this remote location was governed by the climatic condition maximum utilisation of the very good pastures in the High Plains was crucial to a successful and profitable season.This pie iron has two pie forms in horizontal configuration and both top and base rounded forms are connected at one end (Top) with pop rivet application. This application allows for the "opening" up of the two halves. The bodies are made from cast iron in a "cup" form and a metal rod and wooden handle extend to permit the opening of the two sides. The inner side of the "cups" are smooth which relates to pie requirements and not the jaffle/sandwich irons. A clasp metal "D" ring is installed at the end of one wooden handle (to keep the iron in the close/cooking position).camp fire cooking utensils, hot plate, cast iron cooking appliances, pie irons, jaffle irons, drovers kitchen -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CASTLEMAINE GAS COMPANY COLLECTION: PHOTO BOX
Photo of a carton box with the words ''Modern maid and staff top 4 low profile cooking top''Kodakbusiness, retail, gas and fuel -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumPhotograph, 1942
Handcrafts of Camp 3 interneesColour photograph of dolls house furniture consisting of bath, wardrobe, stove with cooking utensils are main pieces. camp 3, templer society -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Book, c1950
These books were being used in schools during the 1950s.Soft covered cream book with illustration of woman on apron holding pie with cooking utensils in front of her.books, cookery -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncLeisure object - Toys, Miniature Kitchen Equipment, 1970s
The Kew Historical Society’s collection includes a wide range of leisure objects. Many of the items are European-made, generally of British origin, however there are a number that were made for the Australian market by Australian manufacturers. There were clearly a huge range of toys produced for the Australian and International children’s market in the Nineteenth and Twentieth centuries. The examples of toys in the collection include examples of alphabet toys, arcade toys, baby toys, construction toys, dolls, doll accessories, educational toys, soft toys, tin toys, toy animals, toy blocks, toy machines, toy typewriters, etc. Miniature kitchen stove, cooking utensils and implements. Made of metal and enamel. Orange and black. Eight pieces.miniature toys, toy kitchen equipment, functional toys -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaPhotograph - Image, Two female residents eating lunch in dining room at Elanora, 1983-1990
Three women sit around a table eating a warm lunch. Two of them are more viewable to camera. It is unknown where these images were taken, however assumed to be at Elanora in 1999 due to the processing imprint on the back (Hampton). Four strips of negatives include these images and others taken at that time.4 colour photographs of women eating a cooking lunch and 4 strips of negatives, some of other peopleelanora home (brighton), association for the blind -
 Ithacan Historical Society
Ithacan Historical SocietyPhotograph, IPS barbecue, c 1980s
The photo is taken at the North Balwyn home of Jim and Leah Kandiliotis who were hosting an IPS barbeque luncheon. The cooks on the right are Chris Lourantos (foreground) and Spero Defteros both wearing white aprons, whilst Bill Benias on the left is offering advice.Informal social gatherings with family and friends where food is also served is a very popular form of relaxation in the Ithacan community. A coloured photograph of three men cooking meat on a barbecue outside a house while other people are in the background. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fire poker
This fire poker is a basic design that has been used throughout the centuries to attend to a fire for cooking, heating, firing a boiler and similar domestic activities.This object is significant as an example of an item in common use in the 19th and early 20th centuries and is still in use today.Fire poker; a flat metal bar shaped with ring at one end and a right angle bend at the base. It is painted black.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, poker, fire poker, fire iron, heating, cooking, laundry, tending a fire -
 Wangaratta Urban Fire Brigade
Wangaratta Urban Fire Brigadephotograph
colour photograph of members and families having a picnic .3 Joan Rosser in centre (white skirt, blue top)4 x colour photographs of members and families having a picnic in what looks like Merriwa Park (the park below and behind the Ely St Station) No.7 in a circle - centre(.1) (social committee) in a circle - below the above(.2) .4 Allan Mills cooking the bbqjoan rosser, allan mills, 1970 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Cooking pot and lid, T & C Clark, 1880-1910
T & C Clark & Company Limited, based at Shakespeare Foundry, was founded in 1795 by Thomas and Charles Clark and grew to be one of the largest iron foundries in Wolverhampton. The firm was the pioneers of Enamelled Cast ironware and the founder Charles Clerk went on to became mayor of Wolverhampton in 1860 after also serving as a Councilor, Alderman, and later Chief Magistrate. The company exhibited many products at the International Exhibition of 1862 at South Kensington, alongside the gardens of the Royal Horticultural Society. The company was also awarded the silver medal for its products at the International Paris Exhibition in 1878. The company's product range included thousands of items, both domestic and industrial. T & C Clark pioneered the use of enamelled cast ironware, after taking out a patent in 1839 guaranteed to be free of lead or arsenic. In the late 1940s and 1950s the company produced acid-resisting enamelled cast iron boiling pans; steam-jacketed pans; stills; square and rectangular tanks; open and closed mixing vessels; flanged pipes; bends and tees; laboratory equipment; small scale plant; evaporating bowls; beakers; sulphonates; and glass-lined mild steel tanks for beer, mineral water, and food. The company is listed as enamelled chemical plant manufacturers in Kelly's 1962 Wolverhampton Directory, but within a few years, the company had ceased trading.The item is significant as it was used as a domestic kitchen or camp fire item used to cook food safely without the concern that the metal may contain lead or arsenic as earlier cooking utensils had. T C Clark innervates the first manufacturing process of cast iron cook ware to have enamel lining in his products to alleviate the possibility of lead or arsenic contamination of food.Oval cast iron boiler or cooking pot, with lid, pot is oval shaped lid is dented and handle buckled.Inscription on base "Clark & Co Patent", "Best Quality", "9 Gallons" and a Trade Mark of a "C" inside two triangles to side of potflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, cooking pot, stew pot, food, kitchen utensil, shakespeare foundry, tc clark -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Leisure object - Toy Cooking Utensil
Round toy cooking utensil - painted yellow with a pattern of colourful roosters . Frying pan and pot. 4 piecestoys, general -
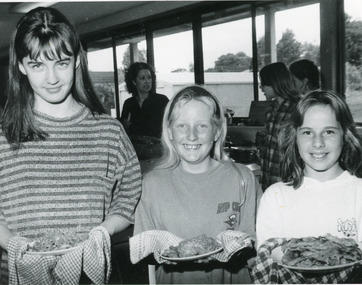 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Lakes Entrance Secondary School, 1993
Black and white photograph three named students Secondary College in Japanese cooking class. Lakes Entrance Victoriaschools, activities -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Fireplace Crane, Unknown
In the late 1800's and early 1900's kitchens were built separate from the main house for safety, as the open fire was used daily for all cooking, washing and heating of water. This very heavy strong fireplace crane could support several items such as cast iron kettles, pans and boilers which were hung on the hinged swing-arm, known as a “crane”. The metal arm was swung out from the fireplace to access the hot water in a kettle relatively safely. A black cast iron fireplace crane with a supporting pole bolted to the wall in the side of the brick open fireplace. It has a swinging handle with a rectangular hand grip at the end to move it over or away from the fire. The metal arm was swung out from the fireplace to access the hot water in a kettle relatively safely. There are holes in the bar for hanging hooks which kitchen cooking pots may be hung. Two small hooks are welded to the bar and there are two small removable hooks and two long ones. architectural elements, fireplaces, fireplace accessories, heating equipment, fireplace crane -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: COOKING
Bendigo Advertiser "The way we were" from 1999. Cooking: Grimsby Roller Flour Mills, Wills Street, Sandhurst.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Stove, c1947
This unit was constructed by Mr. John Phillip Bennett( Sec Barbara Gardiner's uncle) to provide a small convenient stove when he and his wife were camping.Two single kerosene stove s installed in a fabricated container to give a level cooking surface and adequate wind deflector.On stove on the label|BLUE ACE Pat No. 527455 British Made No. 1940.recreations, camping -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Men cooking
1. The first Apex Club was formed in Geelong in 1931 as a service club responding to conditions during the depression. It was soon followed by a club in Ballarat and then in Bendigo. It is aimed at 18-35 year olds and has the motto "Service, Citizenship and Fellowship" 2. Ron Barker(1913-23/6/1997) married Verna Clarke in 1948 3. Laurence William Pocock (1913 - 27/6/1989) married Mena Irene Bailie in 1941 4. Austin Gant (1917-1988) was a dentist who served as a Captain in the AIF Dental corps during WW2. He married Clarice Bryce in 1939.Black and white photograph of six men in white aprons cooking a barbecue. The date is unknown. Part of the Barker's family collection.On the back: the warmest job in Bgo today. Apexians cook the grill and hamburgers. Apex Club Bendigo L -R: Ron Barker, Laurie Pocock, maybe Austin Gart.apex club, bendigo, bbq -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fire screen
This decorative fire screen is placed in front of an open fireplace to prevent hot sparks and ash from causing damage. Open fires were common in Australia in the 19th and early 20th century, for both cooking and heating.Fire screen, crescent shaped, brass pressed sheet, with a ship motif within a rectangular area. Ship is a 3 masted sailing vessel, a Spanish galleon. Made in England, c. 1930.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fire screen, fire guard, domestic item, heating, cooking -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CASTLEMAINE GAS COMPANY COLLECTION: PHOTO PEOPLE, 1987
1987 Cooking school's competition - a school team standing in front of table prepared with flowers and food. Location Unknown. A19 on the back.Kodakevent, entertainment, school's cooking competition -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CASTLEMAINE GAS COMPANY COLLECTION: PHOTO TABLE, 1987
1987 Cooking school's competition - Table set for 4, flowers in a vase and bottle of water in the middle, . Location Unknown. A8 on the back.Kodakevent, entertainment, school's cooking competition -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CASTLEMAINE GAS COMPANY COLLECTION: PHOTO TABLE, 1988
Photo of a table with several packages and a vase of white flowers. The sign ''Welcome to the 1988 Gas Cooking Competition for Schools'' above the tableKodakevent, entertainment, school's cooking competition -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Magazine, 24/02/1978 12:00:00 AM
Family Circle Magazine, special cooking features, craft, sewing, needlework, health and beauty, gardening, home companion and family health.Family Circlebooks, magazines -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Lions Club, Lakes Post Newspaper, 1994
Black and white photograph, David Wright cooking fish and chips at the Lions Club Fish Tasting, on Esplanade Lakes Entrance Victoria volunteering, lions club -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - MESS SET, DIXIES, C.1960’s
Items issued to Malcolm Stuart Angus No 3112710.Two Aluminium Cooking Utensils with Handles, small utensil fitting inside larger utensil, both utensils have collapsible handles.military equipment - mess utensils, metalcraft - aliminium, dixies -
 Anglesea and District Historical Society
Anglesea and District Historical SocietyCan - Pennant Kerosene, The Shell Company of Australia Ltd, Probably 1948-1955 (when logo changed)
Pennant kerosene tin with large tapering top and screw on pouring spout. Cylindrical part of can painted red with yellow Pennant flag on pole.PENNANT KEROSENE / FOR LIGHTING, COOKING & HEATING Black band: HOUSEHOLD KEROSENE A SHELL PRODUCT (Shell logo) / THE SHELL COMPANY OF AUSTRALIA LTD.household kerosene, pennant, the shell company of australia
