Showing 1572 items matching "blades"
-
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Blade, Laryngoscope, Macintosh, Circa 1943
"First described by professor R. R. Macintosh in the Lancet of February 13th, 1943, this design is now the acknowledged leader throughout the world." (PENLON, 1969) Reference: PENLON. 1969. Anaesthetic Equipment - Longworth Scientific Instrument Company LTD. Abingdon, Berkshire, England. January 1969. Macintosh semi curved blade designed in a baby size, with an unfitted light bulb attached. Minor scratches and some slight hit marks over the piece surface caused by its previous use. It has the manufacturer name and the place where it was made along with the owner’s name engraved at the back of the blade. Engraved at the back of the blade near light bulb the owner details: R.C.H. / O.P.T. Stamped at the back blade base into metal the manufacturer's name and place: Longworth / MADE IN ENGLAND Stamped on light bulb base serrated surface, HEINE XHL / #059 2,5v paediatric blades, royal children's hospital, macintosh, light bulb, longworth, blade, laryngoscope -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchWeapon - Kukri Knife, Circa 2000s
Kukri knife as used by Ghurka soldiers in Burma. Curved steel blade with bone handle. Leather sheath with steel tip. Bone handle decorated with ivory dots and brass pins. Missing the two smaller knives.Blade adorned with intricate scroll and flower etching and the word INDIA . -
 Warrnambool RSL Sub Branch
Warrnambool RSL Sub BranchCut Throat or Straight Razor, Max Voos, Germany, 1930's-1940's
Curved Acrylic (probably) or tortortoise shell handled cutthroat/straight razor with steel blade. Two handle pieces known as 'scales'. Blade hinged through handle with rivet at one end. Thumb notch as part of blade continues past hinge. Two more rivets attach two pieces of handle together; 1st rivet with spacer 4cm from hinge rivet, 2nd rivet at opposite end to hinge. Handle:Gold decorative writing-Flic R with 'REGD' enclosed below on one side approx 9 cm from hinge. 2nd side no inscriptions. Blade: Side 1- FLIC enclosed in rectangular parrallelagram next to hinge. Etched 'gold' decoration and inscription along back edge. Inscription reads 'FLIC GOLD'. Blade: Side 2- Near Hinge- MADE IN GERMANY FROM BEST FLIC SILVER STEEL. Blade: Back edge- Serrations for 5cm from hinge. -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchWeapon - Sword
WW2 Sword Donated by Mr Peter CottonWWII Sword metal with metal handle and hilt with clip that scures it in Scabbard when sheathed. Metal handle has xxx pattern. D shaped hilt. Refer 0063-02 (Scabbard)) Hilt extends out 3mm from the rear of the blade to protect the users hand and fingers.Number 74428 recorded on blade near handle. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Spokeshave, Mathieson and Son, 1860 to 1910
A spokeshave is a hand tool used to shape and smooth woods in woodworking jobs such as making cart wheel spokes, chair legs, paddles, bows, and arrows. The tool consists of a blade fixed into the body of the tool, which has a handle for each hand. Historically, a spokeshave was made with a wooden body and metal cutting blade. With industrialization metal bodies displaced wood in mass-produced tools. Being a small tool, spokeshaves are not suited to working large surfaces. The name spokeshave dates back to at least the 16th century, though the early history of the tool is not well documented. The name spokeshave reflects the early use of the tool by wheel wrights. The first spokeshaves were made of wood usually beech with steel blades, before being largely superseded by the development of metal-bodied spokeshaves in the latter half of the 19th century, though many woodworkers still use wooden spokeshaves. Due to their widespread use and versatility vintage wooden spokeshaves remain commonly available and relatively low in price. Spokeshaves consist of a blade or iron secured to the body or stock of the tool, which has two handles – one for each hand. The bottom surface of the tool is called the sole. The blade can be removed for sharpening, and adjusted to vary the depth of the cut. An early design consisted of a metal blade with a pair of tangs to which the wooden handles were attached, as with a draw knife. Unlike a draw knife, but like a plane, spokeshaves typically have a sole plate that fixes the angle of the blade relative to the surface being worked. There are a wide variety of different types of spokeshave, suited to different trades and applications. Company History: The firm of Alexander Mathieson & Sons was one of the leading makers of hand tools in Scotland. Its success went hand in hand with the growth of the shipbuilding industries on the Firth of Clyde in the nineteenth century and the emergence of Glasgow regarded as the "second city of the Empire". It also reflected the firm's skill in responding to an unprecedented demand for quality tools by shipyards, cooperage's and other industries, both locally and far and wide. The year 1792 was deemed by the firm to be that of its foundation it was in all likelihood the year in which John Manners had set up his plane-making workshop on Saracen Lane off the Gallowgate in the heart of Glasgow, not far from the Saracen's Head Inn, where Dr Johnson and James Boswell had stayed on their tour of Scotland in 1773. Alexander Mathieson (1797–1851) is recorded in 1822 as a plane-maker at 25 Gallowgate, but in the following year at 14 Saracen's Lane, presumably having taken over the premises of John Manners. The 1841 national census described Alexander Mathieson as a master plane-maker at 38 Saracen Lane with his son Thomas Adam working as a journeyman plane-maker. In 1849 the firm of James & William Stewart at 65 Nicolson Street, Edinburgh was taken over and Thomas was put in charge of the business, trading under the name Thomas A. Mathieson & Co. as plane and edge-tool makers. Thomas's company acquired the Edinburgh edge-tool makers Charles & Hugh McPherson and took over their premises in Gilmore Street. The Edinburgh directory of 1856/7 the business is recorded as being Alexander Mathieson & Son, plane and edge-tool makers at 48 Nicolson Street and Paul's Work, Gilmore Street. The 1851 census records indicate that Alexander was working as a tool and plane-maker employing eight men. Later that year Alexander died and his son Thomas took over the business. Under the heading of an edge-tool maker in the 1852/3 (Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory) the firm is now listed as Alexander Mathieson & Son. By the early 1850s, the business had moved to 24 Saracen Lane. The directory for 1857/8 records that the firm had moved again only a few years later to East Campbell Street, also off the Gallowgate, and that through further diversification was also manufacturing coopers' and tin men's tools. The ten-yearly censuses log the firm's growth and in 1861 Thomas was a tool manufacturer employing 95 men and 30 boys; in 1871 he had 200 men working for him and in 1881 300 men. By 1899 the firm had been incorporated as Alexander Mathieson & Sons Ltd, even though only Alexander's son Thomas appears ever to have joined the firm.A vintage tool made by a well-known firm made for other firms and individuals that worked in wood. The tool was used to shape various items mainly in use by wheel wrights. A significant vintage item from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how trade people predominately worked materials such as wood by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsman's art of the time. Spokeshave with blade 4 inches wide.Mathieson and Son Glasgow. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, spokeshave, mathieson and son, carpentry tools, wheel wright tools -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Page Turner, Unknown
Page turners were used in churches and synagogues to read Holy books, to turn pages in huge manuscripts and books (and later newspapers) as well as open double pages without a sharp knife (letter openers). This was from the home of W.J. Sebire in Wandin.A highly polished cream coloured long vintage celluloid page turner used for reading. It has a curved round ended long smooth blade which is paler than the darker short round pointed handle. Both sections have small dark brown fine floral designs on one side. There is a 3mm crack all round near where the handle meets the blade. On one side only are small dark brown floral patterns on the handle and one on the blade.page turners, holy books, celluloid -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Compass Saw, Mid to late 20th Century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone.The subject item is believed to date from around the mid to late 20th century and is regarded as a modern item. The maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture.Compass saw with wooden handle and metal blade. Small teeth. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood cutting, wood saw, cross cut saw, cabinet makers tools, wood working tools, tool, compass saw -
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionWeapon - Sword, patt 1896, infantry officer w/ leather scabbord, 1896
Straight Blade, fuller edge side , 3/4 hand guard "GVR" cypher, ray skin grip - wire bound, sword knot, leather scabbard with chrome around mouth. Scabbard markings "6MD 107" "PW" on opposite side outer hand guard "6MD 106" blade M5850. Scabbard markings "6MD 107" "PW" on opposite side outer hand guard "6MD 106" blade M5850. regimental property, sword, cermonial, king george v, infantry -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, steel hacksaw 'Marples', 20thC
A hacksaw is a fine-toothed saw, originally and principally for cutting metal. They can also cut various other materials, such as plastic and wood; for example, plumbers and electricians often cut plastic pipe and plastic conduit with them. On hacksaws, as with most frame saws, the blade can be mounted with the teeth facing toward or away from the handle, resulting in cutting action on either the push or pull stroke. In normal use, cutting vertically downwards with work held in a bench vice, hacksaw blades should be set to be facing forwards. Joseph Marples & Son Pty Ltd Traditional Craftsmans Hand Tools made in Sheffield. The finest quality hand made tools, backed by over 170 years of manufacturing heritage. .In the 1840’s Joseph Marples was one of several ‘Marples’ (most of which were related) in Sheffield manufacturing joiners tools, such as brass inlaid rosewood & ebony braces, boxwood spokeshaves, beech planes, gauges and squares. The business has remained within the family to this date, and has been based in Sheffield since those early days. Although modern technology has been used in some instances, many of the traditions of manufacturing fine hand tools has remained the same using selected materials and hand finishing, indeed the same threads are used in the gauges as were used over 100 years ago. A steel hacksaw. 'Marples' with bladeMARPLEStools, woodwork, metalwork, carpentry, pioneers, market gardeners, early settlers, moorabbin, cheltenham, bentleigh, ormond, joseph marples & son pty ltd, sheffield , england, -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Compass Saw, Mid to late 20th Century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone.The subject item is believed to date from around the mid to late 20th century and is regarded as a modern item. The maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture. Compass saw with wooden handle broken and metal blade. Small teeth.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood cutting, wood saw, cross cut saw, cabinet makers tools, wood working tools, tool, compass saw -
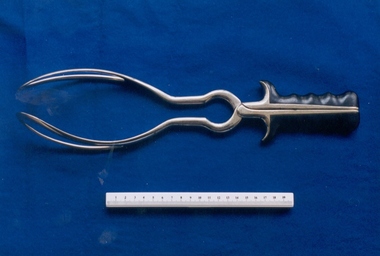 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Barnes-type obstetrical forceps with Simpson style handles, c. 1849-1962, J. Grey & Son, Sheffield, U.K
Neville Barnes obstetric forceps have a cephalic and pelvic curve and are used for delivery of babies presenting as occipitoanterior. The left blade is put on first, followed by the right blade – the baby is then pulled down until the occiput is under the symphysis, then pulled around. This particular set of Barnes forceps is unusual because it has handles/grips associated with Simpson type obstetrical forceps, making it a combination of styles. These forceps are similar in appearance to a style of 19th century forceps known as Hensoldt's forceps, made by Jetter and Scheerer, c. 1899. These are pictured as Fig. 771 in the Sir Kenardatth Das catalogue (see references). J. Gray & Son, Sheffield, were in operation from 1849 to 1962, so these forceps date from this time period.Set of obstetric forceps. Consists of a set of stainless steel blades, with black bakelite hand grip attachment. Forceps are engraved with the text 'J.GREY & SON" and "SHEFFIELD". The number '4' is engraved on the inner aspect of the blade, at the join point.'J.GREY & SON/SHEFFIELD'obstetric delivery -
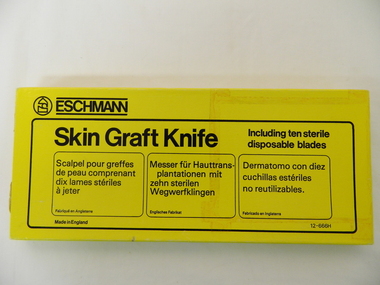 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySkin Graft Knife
This medical / hospital equipment was used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was built in the 1950s specifically for the increase in population due to the Kiewa Hydro Scheme.Historical: Shows the development of scientific hospital equipment. Provenance: Used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was remote and therefore required good equipment.In yellow cardboard box with black writing. Hollow (loop) handle. Pivot is a screw so that the blade can be taken out. Blade has a hole for the screw. Has a shorter straight side and a longer side with teeth like a saw. It fits in a cavity shaped for the knife. Another cavity is next to it but is empty.Box: Eschmann Skin Graft Knife / Including ten sterile disposable blades. Followed by 3 other languages. Made in England hospital equipment. medical instrument. tawonga. mt beauty. knife. skin graft -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionObject, Boxed Pewter Keris Letter Opener
The keris is a dagger unique to the Malay cultures of Southeast Asia, with renderings depicting the weapon dating to 825 CE. Asymmetry is this ancient weapon’s distinguishing feature and, although different styles exist, it is the wavy blade that is instantly recognisable. Today, the keris is a potent symbol of the history and culture of the Malay world.A boxed pewter letter opener, in the form of a wavy-bladed keris, in satin finish pewter. Thank you Professor Kerry O. Cox Vice-Chancellor University of Ballarat for gracing the graduation ceremony hosted by Regions College 10th October 2005international visitors, international visits, souvenirs, gifts, malaysia, keris, blade, knife -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumFret Saw, 1940
Made by internee at camp 3 tatura, used as a handtool. blade made from steel,(stays from a ladies corset)Handmade wooden saw varnished frame, turned handles ( either end)with supportin centre struts & metal serrated cutting blade with adjustable metal rod.RH ( on adhewsive tape)tatura -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Australian Army Issue Clasp Knife
Australian manufactured clasp knives were a standard issue to Australian Military Forces during World War 2. The most commonly encountered knife was an all metal model with a canoe shaped body. This knife was a Whittingslowe first pattern clasp knife which included a blade, a tin opener and a marline spike as well as screw driver and shackle to attach the knife to a lanyard or belt clip. These knives were given a dull Nickel plating to protect them. William Thomas Whittingslowe was born in Wales in 1888, he was educated in England and at 18 migrated to Canada and then to Australia, arriving in about 1912. After working in various states, he settled in South Australia and in the 1920s set up his own business, Whittingslowe Engineers Limited. He specialised in ironworking and knife manufacturing. His firm produced a large amount of blade ware during World War 2. He also designed and built manufacturing equipment for General Motors Holden. He died at Murray Bridge (SA) in 1956.This item is significance because it was donated by a member of the community of Wodonga which has a strong connection to Australian military history.A clasp knife made completely from metal with nickel plating. The accessories all fold into a canoe-shaped body. It included a knife, can opener and marlin spike.On knife blade: WE over a broad arrow/I\australian army equipment ww2, thomas whittingslowe, australian army -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, Knife, curved, Sheffield c1900, 20thC
John Oxley was a shoe and butchers’ knife manufacturer, who was listed in Whitecroft UK in 1822 . By 1825, he was based in Hollis Croft. John apparently died in about 1837. He had two sons – George (1808-1879) and James (1811-1881) who took over the business. George moved to Indianna, USA and in 1868 James continued to manufacture 'Cooks’ and palette knives and steels" Oxley’s trade mark was a butcher’s knife crossed with a sharpening steel (and the letters ‘JO’). The firm stayed in the family until 1960. Early settlers were self reliant and repaired their own equipment for kitchen,dairy, farm, horses, carts using various tools . This strong steel knife is typical of the type used by early settlers in Moorabbin Shire c1900Heavy duty curved steel knife with a wide blade encased in 2 thick leather straps secured with steel rivets Blade ; James Oxley with Trade Mark - a butcher’s knife crossed with a sharpening steel (and the letters ‘JO’). scratched into leather handle ; J EVANSknives, sheffield steel, oxley james ltd. , leatherworkers, saddles, horses, bootmakers, shoes, boots, builders, carpenters, early settlers, market gardeners, blacksmiths, tools, building equipment, hammers, moorabbin shire, bentleigh, mckinnon, highett, cheltenham,mcewan james pty ltd, melbourne, bunnings pty ltd, -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Small Personal Corn Razor and box- Arthur Lock collection
This item belonged to Arthur Lock. During the late 1800's cutlery firms manufactured these uniquely styled razors. The Corn razor was much smaller than an average razor, and was used to remove corns from the feet. Corn razors came with many different handle designs. The hollow ground process produces a much thinner blade with more flex.This item is part of a collection of items owned by Athur Lock, a member of the 2/23rd Battalion, an all-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force which served as part of the garrison during the Siege of Tobruk, then at El Alamein, New Guinea and Borneo. It has particular local significance as the battalion was know as "Albury's Own" because a large majority of the battalion's initial intake of volunteers came from the Albury–Wodonga region. A small corn razor and box showing manufacture detailsOn blade "Kutwell" On Box "Kutwell" /Hollow Ground/ Corn Razorworld war 11, rats of tobruk, tobruk, corn razor -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Adenoid curette associated with Dr Felix Meyer, Medical Supply Depot
Adenoid curettes are used to remove infected or inflamed adenoids. Their sharp inner blade removes the adenoid in an atraumatic manner without causing harm to the surrounding tissues.This is one of a collection of items associated with Dr Felix Henry Meyer (1858-1937). Meyer was a very prominent early obstetrician and doctor, playing a part in the establishment of the role of the chair of obstetrics at the University of Melbourne in 1929. He was also a foundation member of the Royal Australian College of Surgeons.Metal curette (surgical scraping tool). Consists of a handle section with divots for ergonomic finger grip, and a straight, thin metal shaft which forks into two small arms with a cutting blade between them at the tips. The arms at the end of the shaft are curved so that the blade is perpendicular to the shaft of the instrument. Shaft of the curette is engraved with the text 'MEDICAL SUPPLY DEPOT''MEDICAL SUPPLY DEPOT'surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Saw, Mid to late 20th century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone. The subject item at this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, as the maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture around the mid to late 20th century.Wood hand saw with wooden handle attached to saw by 4 rivets. No blade markings Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, handsaw, wood saw, carpenders tools, cabinet makers tools, wood cutting -
 Geelong RSL Sub Branch
Geelong RSL Sub BranchGunto (military sword), Circa 1935
The shin gunto was used by non-commissioned officers the design resembled the officer's shin gunto but were a cheaper quality.These swords are originals of their time and would have belonged to non-commissioned officers.2 x Gunto Japanese Swords, both swords have a curved steel blade, one sword has a metal scabbard, one has a leather scabbard. One sword has a brown tassle indicating the rank of sergeant and three cherry blossoms on the grip, one has three cherry blossoms on the grip however the tassle is missing.The blade of the sword with the metal scabbard has the number - 101657.japanese, sword, non-commissioned officers -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumMat cutter
Purchased in Illinois, USA, in the 1950s. Comes with instruction manual and additional blades, all of which appear unused. Made by Logan brand who are still in operation today. This is model 401 which is not manufactured currently.Black plastic and yellow plastic box with white foam-core base and side walls. Mat cutter is a black metal base/frame with horizontal ruler attached within. Steel handle at front with mounting area for blade. Blade is stored flat within base but can be turned to protrude through the bottom of the frame which allows it to cut carpet. 4 additional unused blades stored in small brown paper envelopes. Faded cream coloured single page paper folded instruction manual. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tool - Tools, Saw double sided pruning 20thC, 20thC
Among the early settlers in Moorabbin Shire were blacksmiths who made tools for the other settlers who were establishing the homes, market gardens, farms, orchards and various businesses. Early settlers were self reliant and repaired their own equipment for kitchen,dairy, farm, horses, carts using various tools . This is a double sided pruning saw with tapering blade used by orchardists and farmers This pruning saw is typical of the type used by early settlers in Moorabbin Shire c1900A steel saw with double sided tapering blade and wood handle for pruning trees. saws, pruning saws, orchardists, fower gardens, fruit trees, early settlers, market gardeners, blacksmiths, tools, building equipment, hammers, moorabbin shire, bentleigh, mckinnon, highett, cheltenham,mcewan james pty ltd, melbourne, bunnings pty ltd, -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Joiner or Jack Plane, Late 19th to first quarter of the 20th century
A jack plane (or fore plane) is a general-purpose woodworking bench plane, used for dressing timber down to the correct size in preparation for truing and/or edge jointing. It is usually the first plane used on rough stock, but in exceptional cases can be preceded by the scrub plane. Jack planes are 300–460 mm long and 64–76 mm wide, with wooden-stocked planes sometimes being slightly wider. The blade is 44–57 mm wide that is often slightly convex (or ground with rounded corners) to prevent digging in to or marking the work. The cut is generally set deeper than on most other planes as the plane's purpose is to remove stock rather than to gain a good finish (smoothing planes are used for that). In preparing stock, the jack plane is used after the scrub plane and before the jointer plane and smoothing plane. The carpenters' name for the plane is related to the saying "jack of all trades" as jack planes can be made to perform some of the work of both smoothing and jointer planes, especially on smaller pieces of work. Its other name of the fore plane is more generally used by joiners and may come from the fact that it "is used before you come to work either with the Smooth Plane or with the Jointer". Early planes were all wood, except for the cutter, or combined a wood base with a metal blade holder and adjustment system on top. Although there were earlier all-metal planes, Leonard Bailey patented many all-metal planes and improvements in the late 19th century. A jack plane came to be referred to as a "No. 5" plane or a "Bailey pattern No. 5" at the end of the 19th century. A vintage tool made by an unknown company, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could remove large amounts of timber. These jack or dressing planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a flat and even finish to timber surfaces before the use of smoothing planes and came in many sizes. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that is still in use today with early models sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other finishes were created on timber by the use of cutting edged hand tools. Tools that were themselves handmade shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative or even finish that was needed for the finishing of timber items. Jack or Fore plane with blade and wedge. Marked "D Morris" (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, plane, fore plane, d morris, jack plane, wood working tools -
 Charlton Golden Grains Museum Inc
Charlton Golden Grains Museum IncDomestic object - Razor Strap
Item used to sharpen cut throat razor bladesDouble layered razor Strap . Leather joined at one end to form a handle and at the other to house a hanging attachment. Top layer is green and black leather and the bottom layer is natural. The item was used to sharpen cut throat razor blades.The words 'SPECIAL' and 'Soft Finish' are in gold lettering on the front straprazor strap, razor sharpener -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRazor, Early 1900's
This cut-throat razor was originally owned by the father of Dr. W.R. Angus' wife Gladys. Her ,maternal father's name was William Lawrence Forsyth. The razor was inherited by Gladys and is now part of the W.R. Angus Collection, which was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. The “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Cut-throat razor, part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Razor in dark green cardboard box. Razor has bone handle with arrow-head shaped end; blade swings inside the handle. The razor is a design called The Abbott and was made by J & J Maxfield of Sheffield in the early 1900's. It once belonged to William Lawrence Forsyth. Written in pencil script on lid: "W. L. Forsyth". Stamped into box and on steel blade "The Abbott". Blade also inscribed "J & J MAXFIELD / SHEFFIELD" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, william lawrence forsyth, j and j maxfield sheffield, cut-throat razor 1900's, personal effects 1900's, grooming equipment 1900's, hair cutting equipment 1900's -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, Mid to late 19th century
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden objects. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear-resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmaker's shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other workers to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. This item may be a one off item made by a cabinet maker for a particular project as the plane is not marked resulting in no history or manufacturing provenance available.A vintage tool made by an unknown maker, this item was made commercially and by individual cabinet makers for particular furniture projects that could produce an ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into regular use after World War l l, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims, etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant early tool that today is quite rare and sought by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item.Plane, wooden, narrow blade. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, wooden plane, wood working tool, boat building tool, tool, woodwork tool, plane -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Smoothing Wood Plane, John Welsh & Co, 1845-1850
A vintage tool made by a obscure early 19th century woodworking Scottish tool maker. This item would have been made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a flat smooth finish to timber. These tools were used before routers and spindle moulders came into use in the late 19th and early 20th centuries before this time to produce a decorative moulding or to smooth a piece of furniture timber, door trims etc. had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. The subject item is a smoothing plane Known as a Coffin Plane due to its shape. Traditionally wood planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding or had a flat blade use for achieving a flat and smooth finish to timber. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile or for smoothing and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding and flat bladed planes for a full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about John Welsh is that he was a tool maker and possibly a retailer that operated a business in Dundee Scotland between 1845-1850. This is the only record we have to date that he existed and is from the Master Catalogue of Scottish woodworking tool makers. His tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools due to their rarity. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves handmade shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Wood Plane Rounded base, blade attached. Owner J Huband Marked J Welsh, Dundee maker and "J Huband" (Owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, plane, compass plane, j welsh, j huband -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumFolding knife
Slightly curved, folding knife, serrated blade. Some kind of yellow material forms the handle (possibly ivory/bone) . Two metal pins hold the two sides of handle together.Barely legible: side A Made in ..... Germany, with further writing further up blade? Side B Wald .........Soligen -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchCutlass chrome pair of, 1804 Chromed cutlass pair
Windlass, an ISO accredited sword maker and official supplier to MOD UK and the RN.good example of Navy cutlass swords2 x British Naval Cutlass 1804 - Chromed These highest quality blades are manufactured by Windlass, an ISO accredited sword maker and official supplier to MOD UK and the RN. Each blade is fold forged from a single billet of high-carbon steel, then hardened and tempered. Hand assembled and ground, each is then fully chrome plated for a mirror finish. 1. Blade near the hilt has on one side crossed sword and scabbard, obverse has a J. On the basket are N an arrow WD followed by an L. 2. Blade near the hilt has on one side crossed sword and scabbard, obverse has a inscribed 9 and stamped C6. On the basket are N an arrow WD followed by an L.navy, cutlass -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionTool - Joiner or Jack Plane, c.mid to late 1900
A timber plane , or jack plane (or fore plane) is a carpenters or cabinet makers tool that is used for dressing timber down to the correct size in preparation for truing and/or edge jointing.A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that is still in use today. It gives context of how furniture and other finishes were created on timber by the use of cutting edged hand tools. Tools that were themselves handmade shows the craftsmanship of the era but also highlights craftsmanship needed to produce a even finish.Carpenters Plane also referred to a Joiner or Jack Plane. Long rectangular shaped timber block with carved timber grip handle, timber block support and blade. Square shaped opening Infront of block and blade, tapers to a small slot to the bottom to allow for the timber shaving to fall through. Stamp mark on metal plane blade: MITCHLL A........(Unable to distinguish further writing) Stamp is in a horse shoe shape with the Mitchll curving around the stop and the word starting with 'A' along the bottom.capenter, wood work, construction, box plane, cabinet maker
