Showing 2931 items matching "late victorian"
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, Border Morning Mail newspaper, 14/5/2979
This photograph is recorded as depicting the presentation by Mr Alan Dunlop to Cr Val Mason, Shire President, of a 2.86-gram solid gold nugget found in the area more than 100 years ago, at the Burke Museum. The gold is reported as attached to a small amount of milk quartz mounted onto a tie pin. The photo and an article about the donation appeared in the Border Morning Mail on Friday 14th May, 1979. Alan Dunlop, pictured, was Sir Edward 'Weary' Dunlop's older brother. The tie pin artefact being donated in this photo is entered into the Victorian Collections database as follows: 'This nugget was found on the Beechworth Goldfield in the late 1800s by Mr Fred McIntosh (Alan & Edward Dunlop's Uncle by marriage, husband of Elizabeth (Bessie) Dunlop), who had made it into a tie pin and presented it to the Dunlop family'. Furthermore, Val Mason was the first female president of the former Beechworth Shire for two terms and a councillor for nine years. This photograph is of historic significance as it depicts known individuals who have connections to key Australian figures. Alan Dunlop is the brother of famous war doctor Edward 'Weary' Dunlop, and both men are Beechworth locals. The object Alan holds is a tie pin made from gold found by the Dunlops' uncle. It's also significant as it documents visually the origin of the tie pin artefact in the Burke Museum collection, via donation by Alan Dunlop. In addition, it depicts Val Mason, the first female president of the former Beechworth Shire for two terms and a councillor for nine years. It is of social significance as it depicts two well-known and respected Beechworth locals handling a key artefact of significance to the Beechworth Goldfields, and therefore Beechworth local history. It also shows the Burke Museum in 1979, providing research potential for those interested in the history of the development of the museum's collection.Black and white, rectangular photograph printed on paper.Obverse: (lllegible) Reverse: A02653weary dunlop, gold, beechworth, val mason, tie pin, jewellery, goldfield, beechworth goldfield, fred mcintosh, bessie dunlop, elizabeth dunlop, dunlop, border morning mail, victorian collections, donation, burke museum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, 1990s--estimated
Taken in 1990, this photograph depicts a row of shops in Beechworth, with the shopfront of watchmaker and jewellers, William Turner and C.F. Falck, in the foreground, and newsagent and bookseller James Ingram's shop in the background.This photograph is of social significance to the Beechworth community in depicting the Street of Shops, the creation of curator, Roy Harvey, which opened in 1979 at Burke Museum. According to the Indigo Shire Council webpage for Burke Museum, this addition 'began a new period of collecting with Roy Harvey calling to the community for donations. The response resulted in an influx of material adding to the town history/ development and local identities collections. The Shops and their contents reflect another period in museology.' The historic shopfronts in this image portray those of local settlers, William Turner and CF Falck's Watchmaker and Jeweller store, and James Ingram's news agency and bookshop. William Turner was originally a goldfields official who became a commissioner on the Ovens goldfield, and later a resident warden, at times performing magisterial duties and chairing the Local Court. Charles Frederick Falck, born in Korlin, Germany, in 1833, a skilled watchmaker and jeweller, ran the jewellery business from 1862. Along with William Turner and Melbourne barrister, George Milner Stephen, he prepared a dazzling display of gems and jewellery from Beechworth for the Royal Society's Exhibition in Melbourne in 1865. This act signposted Beechworth's progress as a nineteenth-century gold rush town with a population of around 3000. In the mid-1850s, newsagent James Ingram established a newsagency and supplied papers and stationary to the goldfields. He and bookseller R.T. Vale stocked a wide range of literary, historical and religious works, textbooks, periodicals and newspapers, as well as hosting a reading and writing room on Camp Street{?}. James Ingram was a 'devoted instigator and supporter of the town's welfare institutions', who raised funds for to establish a hospital, primary school and benevolent asylum, and assisted people who'd fallen on hard times with his wife. He was also a mainstay of the early Baptist church, holding meetings in his house. He died in 1928, six weeks short of his 100th birthday. Ingram's Rock, north-west of Beechworth near where he lived in later life, was named after him. Colour rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper.Obverse: FALCK 1880 / maker & Jeweller/ WARDENS OFFICE/COACHING OFFICE/ EST. ??55/ ????ON HOUSE/ JAMES INGRAM/ NEWS?????? AND BOOKSELLER/ TOYS visible above shopfront in left foreground. Reverse: Catalogue item number 3305 pencilled in top right-hand corner.beechworth, beechworth historic shops, william turner, cf falck, james ingram, turner and falck watchmaker and jeweller, james ingram newsagent and bookseller, burke museum, promoting settlement, marketing and retailing, living in country towns, making regional centres, preserving traditions and commemorating, beechworth founders, victorian gold rush towns, beechworth pioneers, ingram's rock, 1860s beechworth, street of shops, roy harvey -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1970
... and nearly a year later, was appointed to senior inspector ...Historical photograph taken of the frontage of the Burke Museum in Beechworth. As Australia’s oldest regional museum, the building used for the Burke Museum was originally built as the Beechworth Athenaeum, and was later dedicated as a museum in memorial to the explorer Robert O’Hara Burke, who died on the Burke and Wills expeditions in 1861. The Burke and Wills exhibitions were a significant colonial event that was memorialised in paintings, buildings, monuments, and statues. The photograph has historical significance, connecting with various themes such as exploring, establishing pathways, and significant colonial events or persons. The photograph depicts the frontage of the Burke Museum, which was dedicated as a memorial to the explorer Robert O’Hara Burke, who died on the Burke and Wills expeditions in 1861. Robert O’Hara Burke was a significant person who was connected to both Beechworth and to an important colonial event, the Burke and Wills expeditions. Born in Ireland, Burke migrated to Australia in 1853 and nearly a year later, was appointed to senior inspector at Beechworth. Described as quick-tempered yet generous, Burke later joined an expedition to explore the interior of the Victorian colony, which was later termed the Burke and Wills expeditions. While the expeditions generated a significant amount of interest, the objectives of the Burke and Wills expeditions were hazy, as was its planned route, leading to disaster on the trip as group infighting, poor provisions, and a lack of clear instructions ultimately resulted in Burke’s death. Regardless, the Burke and Wills expeditions promoted discovery and endures today in popular memory.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on paper.Obverse: 1856/ BEECHWORTH/ PUBLIC/ LIBRARY/ BURKE/ MUSEUM/ BURK MUSEUM/ (parking signs illegible) Reverse: BMM 84-2-1/ A02989 1997 2696/ BMM 84-2-3burke museum, beechworth, beechworth athenaeum, athenaeum, memorial, robert o'hara burke, robert burke, burke and wills exhibitions -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Basalt (igneous-volcanic) containing Olivine, unknown
This particular geological specimen was found in Mount Franklin or Lalgambook in Djadjawurrung, located between Daylesford and Newstead, approximately ninety minutes drive from Melbourne. The mountain is an example of a breached scoria cone (a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments) which was created by a volcanic eruption about 470,000 years ago, a date which may indicate the age of this geological specimen. The volcanic eruptions of Mount Franklin were most likely witnessed by members of the Dja Dja Wurrung Aboriginal tribe, who referred to this country as the 'smoking grounds'. Mount Franklin and the surrounding area appears to have been a place of considerable religious significance to Aboriginal people, there is evidence which indicates that frequent large ceremonial gatherings took place in the area. Basalt is the most common rock on Earth’s surface, more than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Basalt is an aphanitic extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. Specimens are black in colour and weather to dark green or brown. Basalt is rich in iron and magnesium and is mainly composed of olivine, pyroxene, and plagioclase. Olivine is the name of a group of rock-forming silicate minerals with compositions ranging between Mg2SiO4 and Fe2SiO4. Unlike other minerals, Olivine has a very high crystallisation temperature which makes it the first of the minerals to crystallise from magma. As magma cools, the crystals begin to form and settle on the bottom of the lava and form basalts that are abnormally enriched in olivine in the lower part of lava flows. According to H. M. King (on geology.com) "Olivine is thought to be an important mineral in Earth's mantle. Its presence as a mantle mineral has been inferred by a change in the behaviour of seismic waves as they cross the boundary between Earth's crust and mantle". Lava from Mount Franklin and other volcanoes in the area filled valleys and buried the gold bearing streams that became the renowned ‘deep leads’ of the gold mining era. In 1852, as part of the Victorian gold rush, gold was discovered in the immediate area, this gold was created by lava flows during the Newer Volcanic period, which were mined intensively during the nineteenth century. Around 1865 the presence of a deep lead in Mount Franklin was established. Deep lead mining was initially unsuccessful, and it was not until the late 1870s that the Franklinford Gold Mining Company mined at Mount Franklin on a significant scale. A few years later the Mount Franklin Estate Gold Mining Company also struck gold, followed by the Shakespeare and Great Western companies in the mid-1880s. By the late 1880s, however, deep lead mining had ceased in the area. Soon after gold was discovered in 1851, Victoria’s Governor La Trobe wrote to the Colonial Office in London, urging ‘the propriety of selecting and appointing as Mineral Surveyor for this Colony a gentleman possessed of the requisite qualifications and acquaintance with geological science and phenomena’. Alfred Selwyn was appointed geological surveyor in Australia in 1852 which began the Geological Survey of Victoria. In 1853-69 the Geological Survey issued under Selwyn's direction sixty-one geological maps and numerous reports; they were of such high standard that a writer in the Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London bracketed the survey with that of the United States of America as the best in the world. During his years spent in Australia, Selwyn collected numerous significant geological specimens, examples of which are held in collections such as the Burke Museum.This geological specimen is an example of basalt and olivine which shows the volcanic lava activity and geographical specific nature of Mt Franklin as a significant volcanic site. According to Agriculture Victoria 'The crater is one of the deepest in the Central Highlands area. It is a major megacryst site with some of the largest known Victorian examples of megacrysts of augite and an orthoclase. The small parasitic mound of Lady Franklin on the western flanks adds to the geological interest of the site'. This specimen also highlights the locality as a significant place for both indigenous activity and Victorian gold rush era mining practices. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.An angular, solid hand-sized piece of grey volcanic Basalt with green/brown Olivine phenocrysts along one flat edge.Olivine in basalt / - label is probably / correct. / C. Willman / 15/4/21burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, basalt, igneous rock, igneous-volcanic, volcanic geology, volcanic, olivine, olivine specimen, basaltoid -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mrs Vanessa McDonald, 9 November 2000
Mrs. Vanessa McDonald was born in Beechworth in 1917. Christened, Agnes Bertha Collins, Vanessa changed her name in 1960. Mrs. McDonald's family's connection with gold mining in the district reach back to the first of Beechworth's gold rushes, when her great grandfather, a Dutchman who adopted the name Charles Collins, arrived in 1851-1852. Mrs. McDonald spent her childhood in the isolated hamlet of Stanley, in the area known as 'Little Scotland', where she recalls helping her mother to raise younger siblings, picking apples and walnuts on the family farm, and roaming the hills for wildflowers. As a young woman Mrs. McDonald attended religious and social gatherings in the local community. In 1940 she went to Melbourne to work as a mothercraft nurse during the Second World War. She met her husband at a Beechworth football match and was married at the Stanley Methodist Church in 1941. The gold diggings known as the 'Nine Mile' became the hamlet of Stanley, after the British Prime Minister, Lord Stanley, in 1858. By the late 1850s, Stanley boasted schools, an athenaeum, a church, a weekly newspaper and several hotels and other civic infrastructure to cater for a growing population. The area attracted large numbers of Chinese miners, whose presence was frequently resisted. Like other early Victorian mining settlements, Stanley was a hotbed of political and racial tensions during the gold rush. One side of the Nine Mile Creek was known as 'Little Scotland’, the other, 'Little Ireland'. A number of Christian denominations built congregations and churches in Stanley, including the Church of England, Methodist Church, the Catholic Church, and Presbyterian Church. Stanley became part of the United Shire of Beechworth in 1871. By 1880 timber was being cut and two sawmills were established by 1887. River-dredged gold mining consumed vast amounts of timber from the forests in the area, and in 1931 the first of several softwood plantations began. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth'. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Following the decline in the mining and associated industries during the early-mid-twentieth century, the Beechworth district experienced a period of general economic decline. On the east side of the Dingle Range, Mrs. McDonald's father, William Henry Collins, felled timber and the family were pioneer apple orchardists. The establishment of apple orchards in Stanley reflects changes to how land was used and contributes to our understanding of the historical development of rural communities following the gold rush. Mrs. McDonald's recollections are significant for understanding family and social life in a small rural town in years leading up to the Great Depression and prior to the Second World War. This oral history recording may be compared with other oral histories and items in the Burke Museum's collection. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mrs Vanessa McDonald /listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, emigration, gold rush immigration, victorian gold rush, mining families, apple orchard, forestry, forest plantation, little scotland, stanley, twentieth century history, regional australia, rural australia, farming, harvest festival, great depression, dingle range, the nine mile, australian wildflowers, high country wildflowers, mothercraft nurse, rural and regional women, social history, collins, mrs. vanessa mcdonald, building community life, shaping cultural and creative life, fruit growers, family history, changes to land use in regional victoria -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Chiltern Pharmacy, now called Dow's Pharmacy, opened in 1859 at a time when the township of Chiltern was experiencing a second-wave gold rush that redistributed the balance of commercial and social activity in the region. David McEwan, father of Prime Minister John McEwan, was one of the first pharmacists practicing at the business. It was purchased in 1929 by pharmacist Hilda Dow who ran the business with her apprentice and husband, Roy Dow, until they closed the business in 1968. In 1988, after founding the North East branch of the National Trust, the Dows donated the premises with its entire fittings and stock. Some of the more than 4,000 items in stock at the time of closure in 1968 were present in the shop when the Dows took charge in 1929 and date to the late Nineteenth Century (around the time this image was taken). Hilda Dow (nee Grey) was born in 1897, the daughter of a police magistrate. She enrolled to study at the Victorian College of Pharmacy in 1919 and worked initially for Poynton's Pharmacy in Morwell before purchasing the Chiltern Pharmacy that was later named after her. She was a member of the Pharmaceutical Society of Victoria, a hospital committee and Board, the Red Cross and the Infant Welfare Association and held office for the Chiltern branch of the Country Women's Association. Her sister Helene Grey received an OBE for her work as Lady Superintendent of the Royal Melbourne Hospital. Although Hilda Dow was not Australia's first female pharmacist (this was Caroline Copp in 1880) the preservation of the pharmacy and the stories it presents sheds light on the general issue of recognition for female medical pioneers in Australia. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This image is significant as it provides insight into social and commercial infrastructure available in the North-East region of Victoria in the late Nineteenth and early Twentieth Centuries. The business pictured is also associated with a Prime Minister of Victoria and some of Victoria's first female medical and pharmaceutical practitioners. Thin translucent sheet of glass with a circular image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metals strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, hilda dow, roy dow, chiltern pharmacy, dow's pharmacy, chiltern, indigo shire, north east victoria, history of pharmacies, women in pharmacy, women in medicine, women in business, david mcewan, john mcewan, national trust, national trust victoria, north-east victoria national trust, heritage buildings, industrial heritage, helene grey, pharmaceutical society of victoria, victorian college of pharmacy, country women's association, caroline copp, royal melbourne hospital, red cross, infant welfare association -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Miners from Snake Valley lobbied the Victorian Government in 1855 to make land available for sale for farming purposes as an alternative occupation and income for people who wished to stay in the region but move away from gold mining. A secondary motivation was to increase the supply of fresh produce and decrease prices of items that otherwise needed to be transported from Melbourne or other regions. Forty-three country lots were initially offered in the Three Mile area, ranging in size from two to ninety acres and costing from £1 to £3 per acre. An additional eighty-five country lots were auctioned later in the year, in addition to many smaller suburban lots. More lots were offered than sold, initially, but this represented conditions of sale requiring the total purchase cost up front which many people interested in purchasing could not afford, especially as land purchased for farming would accrue substantial additional costs for clearing and labour before becoming productive. Further lobbying activities and the election of parliamentary members sympathetic to the cause took place through the 1850s. Ovens Parliamentary Member, Daniel Cameron, was re-elected in 1856 on a platform of surveying the land for public selection with deferred payment options. Land reform remained an issue in the area through the 1850s and early 1860s, impacting broader decisions in the new State of Victoria relating to voting rights, use of Crown land and the farming of land that wasn't always suitable for the purpose. This photograph depicts Beechworth in approximately 1900, after several waves of land sales resulted in increasingly levels of development. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is significant because it provides insight into Beechworth's built environment and infrastructure in the early Twentieth Century, around the time of Australia's Federation. It is also an example of an early photographic and film-making technology in use in regional Victoria in the time period.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a square-edged image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, indigo shire, north-east victoria, farming, squatters, miners, agriculture, land-clearing, land reform, daniel cameron, land sales, three mile, snake valley, tarrawingee -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyhandkerchief, c. 1899
The Daily Mail printed this handkerchief to raise funds for the "Soldiers' Families Fund" after the outbreak of the Second Boer War (1899-1902. (The Daily Mail, devised by Alfred Harmsworth (later Lord Northcliffe) and his brother Harold (later Lord Rothermere), was first published on 4 May 1896 and was an immediate success.) Patriotic handkerchiefs were popular during the Victorian era and this one featuring a popular song and well-known people was probably the most popular.This handkerchief was produced to raise funds for the families of soldiers involved in the Second Boer War. This fund, The Soldiers' Families Fund was the first such charitable effort for a war. The handkerchief and other related items raised more than 250,000 pounds.A white linen man's handkerchief. It is printed in blue. It has a map of the South African Republic and the music and words of The Absent Minded Beggar - music by Arthur Sullivan, words by Rudyard Kipling. There is a picture of Lord Roberts, the British Commander in Chief, in the top left corner with the British flag and a picture of Queen Victoria in the bottom right corner.handkerchief souvenir boer-war -
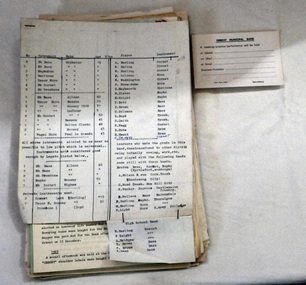 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societydocuments, 1970's
The first Orbost Brass Band was formed in 1889. Around 1908 the town band split and the Orbost Workers' Band was formed. Eventually the two bands merged in 1913 to reform as the Orbost Municipal Band under conductorship of Charles Spink. The band continued for many years but was later disbanded and again reformed. This was to happen a number of times, the last time being in 1961 and continuing through to the late 1970's. Further info and Ref: In Times Gone By - Deborah HallThe brass bands of Orbost in their various forms provided entertainment to the Orbost community as well as benefits to the many members.Miscellaneous documents from the Orbost Municipal Band. These include; meeting notice registration cards; players list for VBL; a brief history of the band; constitution; directory of Victorian music organisations; list of attendees; attendance book-1976-1977brass-band orbost-municipal-band music entertainment -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societydocuments, 1977-1978
The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's.Target shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. One of the most important adjuncts to the militia system from 1903 to the re-organisation of 1912 was the role played by the Rifle Club movement in Australia. At the time, these clubs were seen as the reservoir of manpower for a potential guerrilla force should any invasion occur. For Australia, the invasion fear was uppermost in the minds of the population. So important were the rifle clubs for the defence of Australia that the Commonwealth provided the training staff, rifles and ammunition so the clubs could function. Members were drilled, wore uniforms and practised all the basic skills of soldiering as well as target shooting. The Orbost Rifle Club was active during this period.Nine envelopes containing correspondence sent to Mr D. Thexton, Secretary of Orbost Rifle Club in 1977-1978. Some are from the Victorian Rifle Association.orbost-rifle-club shooting -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyprograms, 1967-1970
The Victorian Rifle Association governs the operation of rifle ranges and target shooting clubs throughout Victoria. The Association was formed in 1860 and held its first individual competition at the end of that year. These programs were used by C. Curtis of the Orbost Rifle Club.The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's. It had a substantial membership.Four programs for the Victorian Rifle association Annual Prize Meeting. 2090.1 has a pink cover -1967. 2090.2 has a pale green cover -1968. 2090.3 has a yellow cover -1969. 2090.4 has a pale green cover-1970. Inside 2090.4 is a newspaper cutting.orbost-rifle-club shooting victorian-rifle-association -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Orbost Rifle Club, Match Record Book, 5th January, 1974 ; 13th May, 1978
Cec, Curtis was a member of the Orbost Rifle Club. He was a cycle trader with a business in Lind Lane, Orbost. The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's.Target shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. One of the most important adjuncts to the militia system from 1903 to the re-organisation of 1912 was the role played by the Rifle Club movement in Australia. At the time, these clubs were seen as the reservoir of manpower for a potential guerrilla force should any invasion occur. For Australia, the invasion fear was uppermost in the minds of the population. So important were the rifle clubs for the defence of Australia that the Commonwealth provided the training staff, rifles and ammunition so the clubs could function. Members were drilled, wore uniforms and practised all the basic skills of soldiering as well as target shooting. The Orbost Rifle Club was active during this period A light blue covered book with a bright red spine. It contains hand-written records of the shooters who were members of the Orbost Rifle Club. Inside are seven letter heads of CED. CURTIS - 9 LIND ST ORBOST and a newspaper cutting ( date unknown). orbost-rifle-club shooting -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Match Record Book, 13.1.1965 - 12.5. 1973
The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's.Target shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. One of the most important adjuncts to the militia system from 1903 to the re-organisation of 1912 was the role played by the Rifle Club movement in Australia. At the time, these clubs were seen as the reservoir of manpower for a potential guerrilla force should any invasion occur. For Australia, the invasion fear was uppermost in the minds of the population. So important were the rifle clubs for the defence of Australia that the Commonwealth provided the training staff, rifles and ammunition so the clubs could function. Members were drilled, wore uniforms and practised all the basic skills of soldiering as well as target shooting. The Orbost Rifle Club was active during this period A grey cardboard covered book with a red spine. It contains hand-written match records of the members of the Orbost Rifle Club.records orbost-rifle-club shooting -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Handicaps, 1968
The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's.Target shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. One of the most important adjuncts to the militia system from 1903 to the re-organisation of 1912 was the role played by the Rifle Club movement in Australia. At the time, these clubs were seen as the reservoir of manpower for a potential guerrilla force should any invasion occur. For Australia, the invasion fear was uppermost in the minds of the population. So important were the rifle clubs for the defence of Australia that the Commonwealth provided the training staff, rifles and ammunition so the clubs could function. Members were drilled, wore uniforms and practised all the basic skills of soldiering as well as target shooting. The Orbost Rifle Club was active during this period. A green Universal exercise book which contains hand-written handicap record of the Orbost Rifle Club. On front cover - handwritten - Handicap Recordsorbost-rifle-club shooting records -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyinventory book, 1950-1970
The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's.Target shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. One of the most important adjuncts to the militia system from 1903 to the re-organisation of 1912 was the role played by the Rifle Club movement in Australia. At the time, these clubs were seen as the reservoir of manpower for a potential guerrilla force should any invasion occur. For Australia, the invasion fear was uppermost in the minds of the population. So important were the rifle clubs for the defence of Australia that the Commonwealth provided the training staff, rifles and ammunition so the clubs could function. Members were drilled, wore uniforms and practised all the basic skills of soldiering as well as target shooting. The Orbost Rifle Club was active during this period. A plain grey covered indexed book with a light blue cloth spine. It has a yellow label on the front cover. It appears to be a record of individual results for the Orbost Rifle Club.On label - printed - ORBOST RIFLE CLUB 211orbost-rifle-club shooting records -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyminute book, 8.6.1961 - 15.2.1978
The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's.Target shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. One of the most important adjuncts to the militia system from 1903 to the re-organisation of 1912 was the role played by the Rifle Club movement in Australia. At the time, these clubs were seen as the reservoir of manpower for a potential guerrilla force should any invasion occur. For Australia, the invasion fear was uppermost in the minds of the population. So important were the rifle clubs for the defence of Australia that the Commonwealth provided the training staff, rifles and ammunition so the clubs could function. Members were drilled, wore uniforms and practised all the basic skills of soldiering as well as target shooting. The Orbost Rifle Club was active during this period. A plain light blue minute book with a cloth brown spine. It has a white label on the front cover.On label- Orbost Rifle Clubminutes orbost-rifle-club shooting -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, Wood, 1901
This photograph appears to have been taken during the construction of the rifle range just north of the Orbost township. "The photo shows the range stop butt being formed by the scoops being pulled by the horses. It appears that the rear of the mound there is a wall of logs lining it, most likely to help with being eroded or washed away. They haven’t yet formed the mantlet and target machines." ( Info, from Victorian Rifle Association) The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's.Target shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. After Federation in 1901, rifle clubs came under army control, but in 1921 they were reconstituted as a civilian organisation, which they have remained ever since. After World War I a system of national training was embodied in the Defence Act and the rifle clubs reverted to their purely sporting role. A black / white photograph of four men and four horses standing an a soil bank with another man, a lady and a small girl at the base of the hill. It is in a clearing in forest. It appears to have a row of targets set at the edge of the bank. The photograph is mounted on a very mouldy cream coloured buff card.on front - "Wood" ; "Rifle Range - 1901" ; "Orbost 1901"sport-shooting orbost-rifle-range -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, late 19th century
A punt crossed the Snowy River at Orbost from 1884. A bridge was constructed in 1893, but was soon damaged by a huge flood. Flooding was a regular occurrence, the worst inundations being in 1870, 1893, 1925, 1934, 1952 and 1971. Over the years major flood protection works have been implemented. The Princes Highway, which passes Orbost, now crosses the flood plain on raised concrete supports. (info, from Victorian Places Orbost)This item is associated with the Snowy River and its history. It is a pictorial record of transport in the late 19th century.A black / white photograph (copy) of a punt loaded with people and a horse-drawn carriage making its way across a river.on front at bottom - "Snowy River Punt"snowy-river-orbost transport shipping -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This photograph, taken by Courtney’s Thelma Studios in Wangaratta, depicts Sergeant Arthur Loftus Maule Steele standing in the regalia of the Masonic Lodge. Before his death, Steele was a long term member of the St John’s Lodge of Masons where he was a Past Master and held office of treasurer for over thirty years. He was also a dedicated member of the Church of England and was an Electoral Inspector for Wangaratta. Steele was Sergeant of Police in Wangaratta for much of his life. He was one of 17 children born to Captain Robert Ball Steele and Mary Babington in Tours, France, in 1839. His parents were travelling at the time and soon after settled in Donegal, Ireland. At the age of 12, Steele was sent to the Military Academy of Dublin where he passed his examinations and prepared to enter the British Army. Steele met a bother of Robert O’Hara Burke and was advised to travel to Australia and join as a police cadet. Steele took the advice and travelled to Australia, arriving in Melbourne at the age of 17. He spend some time in a variety of employment including working as a clerk for the White Star Line. He entered the Victorian Police force in 1856. By 1864, Steele married Ruth Ingram Ballinger at Snowy Creek and worked at Omeo until being promoted to the mining centre of Beechworth, taking charge of the Yackandandah Station. Steele and Ballinger had ten children. Steele is well known in Victorian history for a variety of reasons, the most famous being the role he played in capturing Edward “Ned” Kelly at Glenrowan on the 28th June 1880. He also arrested Frank Neville (for the murder of a local resident Mr Nicholls) and Patrick Sheehan (first person to be executed in the Beechworth Gaol 1865 for the murder of James Kennedy at Rowdy Flat Yackandandah). He later worked on the case of Bridget Mepham (charged with the murder of her sister) at Wangaratta and retired from the Police force on the 1st of August 1896. In this retirement, Steele was a keen horticulturalist who enjoyed observing the habits and growth of new varieties cared for in his conservatory. Steele passed away in February 1914. This image has the potential to support current research on Sergeant Steele, the Masonic Lodge and photography during the c.1890s. Sergeant Steele is a well-researched member of the Victorian Police force and is known primarily for his involvement with the Kelly Gang. Therefore, depictions of Steele through photography can help to provide essential information about Steele outside of the Police force. This image has the capacity to inform about Steele’s involvement with the Masonic Lodge in Wangaratta. Therefore, it is important for what it can reveal regarding historic and social aspects. The Burke Museum is home to a large collection of Kelly centred photographs. The study of these photographs in connection to those in other museums have the ability to further current understanding on important figures and events in this historic occasion.Black and White rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper and mounted on an oval boardObverse: Courtney's Thelma Studios/ Wangaratta Reverse: 2747portrait, ned kelly, uniform, policeman, wangarratta, sergeant, steele, 1880, photograph, oval, black and white, sergeant steele, arthur loftus maule steele, arthur steele, wangaratta, beechworth -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
In this image a Colt 1855 Revolving Rifle is placed upon a sign detailing an £8,000 reward for robbery and murder. Writing on the rear of the photograph identifies the rifle as having belonged to Joe Byrne. In colonial Victoria, the Colt brand firearm was highly popular. They began their popularity in the goldfields of the early 1850s. Individuals, particularly those coming to Victoria with prior experience in the goldfield, brought with them a means of self-defence because of the prevalence of assault and robbery on the goldfields. In the 1860s, the Colt firearm became popular among the Victorian Police force. It was decided in June 1864 by Chief Commissioner of Police, Frederick Standish that the Colt revolvers were far more practical, being of simpler construction and therefore, more easily cleaned and less dangerous than the revolvers used prior to this: the Adams and Kerr firearms. The Colt revolver remained in use in regional districts of Victoria as late as the early 1880 when they were used at the Kelly siege at Glenrowan. The £8,000 reward was issued in 1879 after the Kelly Gang committed numerous bank robberies at Euroa and Jerilderie. In the year prior, the Kelly Gang murdered three policemen at Stringybark Creek. This resulted in the creation of the “Felon’s Apprehension Act 1878” which enabled an individual, whether a part of the Police force or civilian, to shoot a declared outlaw on sight. After the bank robberies, the Police force of NSW and Victoria increased the existing reward to this £8,000 amount.This photograph is significant for what it can potentially reveal about the Kelly Gang and firearms made in this period. The rifle in the image is a Colt Revolving Rifle which was known to have been used by the Victorian Police force from the early 1850s to the late 1880s. It is also known that the Kelly Gang stole police rifles which they used to practise with and so the identification of the rifle as having belonged to Joe Byrne is of significant importance to researchers studying the firearms of the Kelly Gang. More research is needed to solidify the connection of this particular weapon to Byrne other than the handwritten note on the back of the photograph. The Burke Museum Beechworth is home to a significant collection of photographs connected to Ned Kelly and the Kelly Gang. Photographs like this one are valuable for what they can potentially reveal about the Kelly Gang and the Police force during this period. Alongside the study of the other images, photographs from this collection have the ability to further expand current knowledge on this period of Australian history. There is also the capability to provide an analysis of how these firearms and Kelly memorabilia have been received in the past. It could be beneficial to undertake a close study of the use history and reception of these artefacts within the museum context.Black and white rectangular reproduced photograph printed on matte photographic paperReverse: 10268 / Joe Byrne's / Riflekelly album, ned kelly, kelly gang, joe byrne, rewards, outlaw, criminals, bushrangers, colt, police, firearm, beechworth, reward, felon's apprehension act 1878, 1880, glenrowan, colt revolver, revolving rifle, 8000 pound reward, jerilderie, euroa, beechworth goldfield -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, George Rose, c.1945
The Rose Stereograph Company first began producing postcards, identified as the 'P' series (like this particular example) in 1913 and continued in this business until 1967 after which they switched to machine manufactured colour postcards printed by an external company. These were produced by Victorian-era photographer George Rose (1861-1942) often reputed as one of the best photographers in Australia during the later 19th Century and early 20th Century. Rose was born in 1861 in Clunes and began his photography business in 1880 when he founded the Rose Stereograph Company. He later switched to producing postcards after stereographs lost popularity in the early 1920s. The Mayday Hills Hospital was one of these locations photographed by George Rose and published as a postcard. Beechworth's Mayday Hills was chosen as the site of Victoria's newest asylum, at the time, due to the landscape and altitude. The hilltop atmosphere and the native fauna, it was argued, would assist in the cure of the patients kept at the hospital (Wood 1985, 122). The positioning of the hospital had a beneficial effect on the rural town. A pamphlet published by James Ingram and Son (1849) reveal that famous landmarks in Beechworth which included the Post Office, Gaol, Courthouse and Asylum "demonstrate the appreciation of Beechworth by the Government not only as as important district center, but also as a site unrivaled as a sanitarium". There were other locations in contention at the time, but ultimately Beechworth was chosen (Craig 2000,33). Prior to the creation of the Asylum in Beechworth, those charged with having mental illnesses or, as it was termed, "insanity" were unable to be properly cared for in the Gaol (which is where they were often sent). John Buckley Castieau wrote, in 1861 for the Ovens and Murray Advertiser, that the Gaol was unable to properly care for those classified then as "insane" but that they would endeavor to treat them above the other inmates (which he notes is not always the case in other establishments). Castieau wrote this in favour of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth. It was stated that at the time the Mayday Hills Hospital was built, there were 83 prisoners kept in the Gaol who were to be rehoused to the Hospital on the grounds of "insanity". The classification as someone as "insane", in this period of time is a reflection on the inability to cure and understand illnesses of the mind during the mid to late 1800s. Opening on the 24th of October 1867, the Mayday Hills Hospital was originally named the "Ovens Lunatic Asylum", a title which is very much a product of its time. Whilst controversial, changes to the name is part of the history of the Hospital and can provide much insight into the understanding of mental illness throughout history and the use/disuse of this term provides information into the reception/changing opinions of mental illness in society. The Hospital would later become known as the "Mayday Hills Asylum" and/or "Mayday Hills Hospital" with the latter being the most commonly used title. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser notes that on the 7th of March 1865, the foundation stone of the Hospital was laid (it would officially open in 1867) and that it was such a moment of accomplishment and joy for Beechworth that a letter to the editor even suggested that there should be a holiday dedicated to the day the foundation stone as laid. This reveals an extent to which the townspeople of early Beechworth valued the construction of the Hospital in their town. It provided the town with a sense of prestige and honour. At first glance, the remains of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth, Victoria, inspire tragedy, trauma and beauty. The buildings themselves, with their Italianate style Renaissance architecture designed by J.J. Clark (Craig 2000, 49 & Smith 2016, 203) reflect a bygone period of European and Australian history. The gardens provide a sense of tranquility and beauty. The experience of those within these walls remains a valuable area of study to provide a more complete understanding. This particular hospital is considered the fourth of its like and one of three identified as the largest of their kind. The Mayday Hills Hospital is a sister to the Kew and Ararat Asylums in Melbourne which are both located in relative proximity. Understanding the role of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth history is integral to understanding the development of the goldfields town, but also for providing important information as to the history of caring for, and the reception of, mental illnesses in Australian and wider European history. Mayday Hills provides a case study which can be researched through oral history, an analysis of the grounds/buildings and through images like this postcard which portray the structure in a highly deliberate manner. Images like this depict the strong façade of the Hospital and provide a glimpse into the tranquility of the gardens. This has been done deliberately to provide a sense of comfort and healing about the building to those looking from the outside. Further research into the importance of the Hospital in Beechworth and it's connection to the town will be supported through images like these kept in the Mayday Hills photo album in the collection of the Burke Museum.Pale sepia toned rectangular postcard printed on matte card.Obverse: THE ROSE SERIES P. 4689 / COPYRIGHT / ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICES, MENTAL HOSPITAL, BEECHWORTH, VIC / Reverse: Published by the Rose Stereograph Co. / Armadale, Victoria / POST CARD / THE "ROSE" SERIES / DE LUXE / A REAL PHOTOGRAPH / PRODUCED IN AUSTRALIA /mayday hills, asylum, mental hospital, hospital, beechworth -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This photograph depicts Camp st in Beechworth looking east. This postcard is part of the Rose Series produced by Victorian photographer George Rose’s business, the Rose Stereograph Company. George Rose (1861-1942), is considered one of Australia's best photographers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Rose Stereograph Company was founded in 1880 and became famous for producing stereographs, or stereoviews, which gave the illusion of being in 3D when seen through a hand-held viewer, a big craze of the era. As stereographs lost popularity in the 1920s, Rose switched to production of postcards and decorative cards, and he and the photographers who followed took thousands of scenes around Victoria as well as interstate that became iconic images of Australian life.Black and white rectangular photograph (copy) printed on gloss photographic paper. Obverse: The Rose Series P.3469 Copyright FORD STREET Reverse: BMM7744 PH150 1998.00059 beechworth, ford street, rose series, photograph, post card, black and white -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1940
This copy of a postcard depicts Ford Street in Beechworth looking North. This postcard is part of the Rose Series produced by Victorian photographer George Rose’s business, the Rose Stereograph Company. George Rose (1861-1942), is considered one of Australia's best photographers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Rose Stereograph Company was founded in 1880 and became famous for producing stereographs, or stereoviews, which gave the illusion of being in 3D when seen through a hand-held viewer, a big craze of the era. As stereographs lost popularity in the 1920s, Rose switched to production of postcards and decorative cards, and he and the photographers who followed took thousands of scenes around Victoria as well as interstate that became iconic images of Australian life.Black and white photograph (copy) on gloss photographic paper. Obverse: THE ROSE SERIES P.3481 COPYRIGHT FORD STREET, LOOKING NORTH, BEECHWORTH, VIC Reverse: BMM7743 PH 149 1998.00059beechworth, ford street, rose series, postcard, photograph, black and white, burke museum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This copy of a postcard from the Rose series depicts Camp Street looking East. This postcard is part of the Rose Series produced by Victorian photographer George Rose’s business, the Rose Stereograph Company. George Rose (1861-1942), is considered one of Australia's best photographers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Rose Stereograph Company was founded in 1880 and became famous for producing stereographs, or stereoviews, which gave the illusion of being in 3D when seen through a hand-held viewer, a big craze of the era. As stereographs lost popularity in the 1920s, Rose switched to production of postcards and decorative cards, and he and the photographers who followed took thousands of scenes around Victoria as well as interstate that became iconic images of Australian life.Black and white photograph (copy) on gloss photographic paper.Obverse: THE ROSE SERIES P.3459 COPYRIGHT CAMP STREET, LOOKING EAST, BEECHWORTH, VIC Reverse: BMM7743 PH 149 1998.00059beechworth, rose series, camp street, burke museum, black and white -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This copy of a postcard from the Rose series depicts Ford Street looking South. This postcard is part of the Rose Series produced by Victorian photographer George Rose’s business, the Rose Stereograph Company. George Rose (1861-1942), is considered one of Australia's best photographers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Rose Stereograph Company was founded in 1880 and became famous for producing stereographs, or stereoviews, which gave the illusion of being in 3D when seen through a hand-held viewer, a big craze of the era. As stereographs lost popularity in the 1920s, Rose switched to production of postcards and decorative cards, and he and the photographers who followed took thousands of scenes around Victoria as well as interstate that became iconic images of Australian life.Black and White photograph (copy) on gloss photographic paper. Obverse: THE ROSE SERIES P.10544 COPYRIGHT FORD STREET, BEECHWORTH, VIC Reverse: BMM7746 PH 147 1998.00059beechworth, rose series, ford street, burke museum, postcard -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1940
Taken in Beechworth, this photograph depicts Ford Street looking North. This postcard is part of the Rose Series produced by Victorian photographer George Rose’s business, the Rose Stereograph Company. George Rose (1861-1942), is considered one of Australia's best photographers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Rose Stereograph Company was founded in 1880 and became famous for producing stereographs, or stereoviews, which gave the illusion of being in 3D when seen through a hand-held viewer, a big craze of the era. As stereographs lost popularity in the 1920s, Rose switched to production of postcards and decorative cards, and he and the photographers who followed took thousands of scenes around Victoria as well as interstate that became iconic images of Australian life. Black and White photograph on gloss photographic paper. Obverse: THE ROSE SERIES P.2749 COPYRIGHT FORD STREET, LOOKING NORTH, BEECHWORTH, VIC Reverse: 7739 PH 152 1998.00059beechworth, rose series, ford street, george rose, burke museum -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Works of Alfred Lord Tennyson
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually, the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower areas of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave from 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However, he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL MECHANICS’ INSTITUTE Warrnambool's Mechanics' Institute (or Institution as it was sometimes called) was one of the earliest in Victoria. On 17th October 1853, a meeting was held where it was resolved to request the Lieutenant Governor of the Colony to grant land for the erection of a Mechanics' Institutes building. A committee was formed at the meeting and Richard Osburne chaired the first meeting of this committee. The land on the North West corner of Banyan and Merri Streets was granted but there were no funds to erect the building. The Formal Rights of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute's encompassed its aims and these were officially adopted in1859; "This Institution has for its object the diffusion of literary, scientific, and other useful knowledge amongst its members, excluding all controversial subjects, religious or political. These objects are sought to be obtained by means of a circulating library, a reading room, the establishment of classes, debates, and the occasional delivery of lectures on natural and experimental philosophy, mechanics, astronomy, chemistry, natural history, literature, and the useful and ornamental arts, particularly those which have a more immediate reference to the colony." The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute opened its first reading room in November 1884 in the National School building at the corner of Banyan and Timor Streets. The Institute was funded by member subscription, payable on a quarterly, half-yearly or yearly basis. Samuel Hannaford, the Manager of the Warrnambool Bank of Australasia, was the first Honorary Secretary of the Mechanics' Institutes, and an early President and Vice-President. He also gave several of the early lectures in the Reading Room. Another early Secretary, Librarian and lecturer was Marmaduke Fisher, the teacher at the National School. Lecture topics included The Poets and Poetry of Ireland', 'The Birth and Development of the Earth', 'The Vertebrae - with Remarks on the pleasures resulting from the study of Natural History' and 'Architecture'. In 1856 the Reading Room was moved to James Hider's shop in Timor Street, and by 1864 it was located in the bookshop of Davies and Read. In the 1860's the Mechanics' Institute struggled as membership waned but in 1866, after a series of fundraising efforts, the committee was able to purchase land in Liebig Street, on a site then called Market Square, between the weighbridge and the fire station. A Mechanics' Institute building was opened at this site in August 1871. The following year four more rooms were added to the main Reading Room and in 1873 the Artisan School of Design was incorporated into the Institute. The same year Joseph Archibald established a Museum; however, it deteriorated when he was transferred to Bendigo in 1877. In 1880, with Archibald's return to Warrnambool, the Museum was re-established, and in 1885 a new building was built at the back of the Institute to accommodate the re-created School of Design, the Art Gallery and the Museum. In 1887 the Museum section was moved to the former courthouse in Timor Street (for some time the walls of the building formed part of the TAFE cafeteria but all is now demolished)). In 1911 the Museum was transferred back to the original building and the management of the Mechanics' Institute was handed over to the Warrnambool City Council. The Museum and Art Gallery became one and housed many fine works of art, and the Library continued to grow. The building was well patronised, with records showing that at the beginning of the 20th century there were between 500 and 800 visitors. During World War One the monthly figures were in the thousands, with 3,400 people visiting in January 1915. The Museum was a much-loved Institution in Warrnambool until the contents of the Museum and Art Gallery were removed to make room for the Warrnambool City Council Engineers' Department. The contents were stored but many of the items were scattered or lost. When the original building was demolished the site became occupied by the Civic Centre, which included the new City Library. (The library was temporarily located in the old Palais building in Koroit Street.) In the process of reorganisation the Collection was distributed amongst the community groups: -The new City Library took some of the historical books and some important documents, historic photographs and newspapers. -The Art Gallery kept the 19th Century art collection and some of the artefacts from the museum. -The Historical Society has some items -The State Museum has some items -Some items were destroyed -Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village has old newspapers, Government Gazettes, most of the Mechanics' Institute Library, ledgers and documents connected to the Mechanics' Institute Library, some framed and unframed artworks and some photographs. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Library book collection is deemed to be of great importance because it is one of the few collections in an almost intact state, and many of the books are now very rare and of great value. The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Works of Alfred Lord Tennyson Author: Alfred, Lord Tennyson - Poet Laureate Publisher: Macmillan And Co Date: 1892The label on spine cover has typed text PAT 821 TEN Pastedown front endpaper has a sticker from Warrnambool Mechanics Institute and Free Library Front loose endpaper has a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Corangamite Regional Library Service Flyleaf has a stamp from Warrnambool Public Museumshipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, warrnambool, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, the works of alfred lord tennyson, alfred, lord tennyson, poet laureate, alfred tennyson -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White photograph of vessel S.S. Casino in calm water, taken 1882-1932. The coastal trader has light rigging and steam funnel, lifeboat on side, two men on deck. Background shows other ships. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, forecabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade in along the West Coast of Victoria. (Belfast is the original name for Port Fairy, South West Victoria. The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, whose had a hay and corn store and shipping agency was on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, then Captain Middleton then took command 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers . Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life through shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection show S.S. Casino underway in heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy). This photograph was taken 1882-1932. It is significant because of its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino and its significance to trade along Victoria's West Coast in the late 19th and early 20th century. The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck under State and Commonwealth Law in the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Black and White photograph of vessel S.S. Casino in calm water, taken 1882-1932. The coastal trader has light rigging and steam funnel, lifeboat on side, two men on deck. Background shows other ships.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, saltau and osburne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino arriving in port, taken 1930-1932. Decks are laden with men and women , crowd of waving people along the river bank, smoke coming from funnel. Warehouse and homes in the background. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, forecabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade in along the West Coast of Victoria. (Belfast is the original name for Port Fairy, South West Victoria. The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, whose had a hay and corn store and shipping agency was on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, then Captain Middleton then took command 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers . Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life through shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection show S.S. Casino underway in heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy). This photograph is significant because of its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino 1882-1932 and its significance to trade along Victoria's West Coast in the late 19th and early 20th century. The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck under State and Commonwealth Law in the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino arriving in port, taken 1930-1932. Decks are laden with men and women , crowd of waving people along the river bank, smoke coming from funnel. Warehouse and homes in the background. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, saltau and osburne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino arriving in Port. Taken 1930-1932. People on the deck and on the river banks waving. Smoke coming from funnel. The S.S. Casino was a passenger and freight steamer built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1882 for the Newcastle and Hunter River Steam Navigation Company of N.S.W. She weighed 425 tons gross with a length of 160.4 feet, beam of 24.1 feet and depth of 10.2 feet. She had saloon accommodation for 35 people, forecabin for 25 more people, and she carried 300 tons of cargo. While on her delivery journey on May 30th 1882 the S.S. Casino called in at the Port of Warrnambool for coal ., narrowly escaping going ashore in gale force winds due to the quick action of the pilot. At that time, still at anchor, she impressed the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company so much that they bought her immediately; she was ideal for trade in along the West Coast of Victoria. (Belfast is the original name for Port Fairy, South West Victoria. The Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company was first managed by Messers. Saltau and Osburne and after the passing of Mr. Osburne, by produce merchants Messers H. Sautau and Sons, whose had a hay and corn store and shipping agency was on the corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets in Warrnambool. ) The S.S. Casino became “the most famous steamer to operate in Victorian waters along the West Coast” by author Jack Loney. Captain Boyd was her first Master, followed by Captain Chapman, who stayed with her 1890 until 1924. Captain W. Robertson followed for a short term, then Captain Middleton then took command 1925 - 1932. The S.S. Casino had several mishaps during her life. One was on 3rd January 1898 when she collided with the S.S. Flinders in Apollo Bay with minor damage. Another was on 24th October 1924 when she grounded on a reef at Point Hawdon near Grey River and most of her cargo (of Christmas goods) had to be dumped into the sea. Then in February 1929 she was ‘holed’ when she struck a submerged object as she entered Lady Bay, Warrnambool. On the morning of 10th July 1932, after attempting to berth at Apollo Bay jetty in heavy seas, Captain Middleton decided to take her out into the bay and wait until the seas abated. It was not realised that the anchor used to steady her as she manoeuvred to her berth had pierced her hull. She put about and headed for the beach but sank. Captain Middleton and nine others lost their lives; nine people were rescued including the two female passengers . Captain Middleton had been in charge of the S.S. Casino for seven years. He was the first ship’s Master to lose his life through shipwreck in the West Coast trade. In the years following the turn of the century the S.S. Casino remained the only regular trader with normal passenger accommodation along the West Coast. From 1882 she had made at least 2,500 voyages on the one run. Flagstaff Hill’s collection has a photograph of a portrait of Captain Chapman, , a ship model of the S.S. Casino that shows both forms of power under which she sailed, steam and sail. The ship is painted green and flies three flags. The inscription across the case of the ship model, incorrectly dated, tells the sad story of the wreck of the ship and the loss of lives on July 10th 1932 at Apollo Bay. A print in the Collection show S.S. Casino underway in heavy sea off Point Lonsdale, another two photographs show her at the Port of Warrnambool, leaving from the Breakwater in Lady Bay and another identifies the S.S. Casino as a ship from the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company. (Belfast is the original name for the township of Port Fairy). This photograph is significant because of its association with the coastal trader S.S. Casino 1930 -1932 and its significance to trade along Victoria's West Coast in the late 19th and early 20th century. The wreck of the S.S. Casino is considered an important part of Victorian and Australian cultural heritage and as such has been declared and protected as an Historic Shipwreck Black and White Photograph of S.S Casino arriving in Port. Taken 1930-1932. People on the deck and on the river banks waving. Smoke coming from funnel.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, newcastle and hunter river steam navigation company, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, h. sautau and sons, s.s. casino, west coast trader s.s. casino, victorian coastal trader, captain boyd, captain w. robertson, captain chapman, captain middleton, apollo bay shipwreck, s.s. casino at lady bay warrnambool, saltau and osburne
