Showing 3190 items
matching thermometer-medical
-
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAward - MEDAL SET & BADGE, Post WW1
Francis John WILLIAMS No 7326 enlisted on 22.9.1916 in the 24th reinforcements 8th Batt AIF aged 18 years 1 month. Embarked for England 19.2.1917, embarked fro France 18.10.1917, WIA 9.8.1918 GSW to right shoulder. Promoted Temp Sergeant 1.6.1919, discharged from the AIF on 11.7.1920 medically unfit not due to misconduct. Pre War he had 3 years in Snr Cadets. Refer Reg No's 66 & 68P. .1) Medal & ribbon set, court mounted - British War medal 1914-1919. Ribbon on own is for the Victory medal. .2) Badge, copper coloured - Returned from Active Service WW1..1) Engraved: 7326 T-SGT F.J.WILLIAMS-8BN-AIF .2) Engraved on rear: 117672awards, numismatics - medals, metalcraft, military history -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDVD - Tawonga Hospital, early 2000's
This DVD of the development of the Tawonga and Mount Beauty General Hospital covers the time period 1949 to 1996. It was a period of intense evolution of both the expansion in population and the increase in the medical facilities provided by a once slightly remote rural hospital to that of one of a regional and alpine advanced hospital. The population expansion of the region during this period was due to the greater growth of local (Kiewa Hydro Scheme) and tourism population provided the need of advancement in the modus operandi of hospital treatments.This DVD details the medical evolution in rural areas and the greater availability of medical professionals to rural areas. The relative isolation of the Kiewa Valley before transport and communications were greatly advanced in the mid to late 1900's resulted in not only increases in population but also the tourism trade. These two important factors required the degree of professionalism for the hospital and with an increasing aged population the diversity into aged care.This DVD has a coloured photograph of the Tawonga District Hospital as a background drop. Printed in black on the front 'An Historical Record / Tawonga District General Hospital / 1949 - 1996.'On the DVD label "An Historical record" below this "Tawonga District General Hospital" below this "1946-1996"hospital dvd, tawonga, mount beauty hospital, specialised treatments -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryResuscitator, Ambu, c.1961
In 1937, the engineer Holger Hesse founded Testa Laboratory, which later became Ambu. Hesse developed products that made a difference to patients and doctors. The real breakthrough came in 1956 when the Ambu ventilation bag reached the market, developed together with anaesthetist Henning Ruben. It was the world’s first self-inflating resuscitator and a major milestone in emergency medical equipment. The Ambu bag became a permanent part of hospital and emergency services product ranges. Brown rubber bag with a round metal filter at one end and a connector tube at the other. There is a blue plastic connector between the rubber bag and the metal tube.Moulded into blue plastic connector: AMBU-INTERNATIONAL / Ruben-Resuscitator Stamped into filter: Ambu logo - large capital A with AUER inside the legs of the Aambu, ruben, self-inflating, resuscitator, emergency, henning, ruben -
 Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Education kit - Sisters of Charity Miniature Doll, Nursing Through the Ages
Sisters of Charity St Vincent de Paul. In 1638 St Vincents de Paul and Mademoiselle de Gras taught simple nursing procedure to young peasant women. They worked in the home hospital and battlefield. Their duties were arduous no pain relief was known and they were exposed to infection. In the 20 century the sisters of St Vincents De Paul are working worldwide nursing teaching caring for orphans the aged lepers. They shared in advances in medical science.30cm Miniature Doll dressed in bright blue shimmering dress with matching capeName tag Sisters of Charitynursing history, nursing uniforms, northern district school of nursing, miniature dolls -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, Home and surgery of Dr William Langley Carrington, 174 Union Road, 1935
The building was erected in c 1913 as a home / surgery for Dr James L Blakie (1868-1937), who originally lived / practised across the road. It was designed by architect Arthur William Plaisted (1890-1965) and is an early example of attic-style Californian bungalow style. Dr Carrington ( 1900-1970) succeeded Dr Blakie and practised at 174 Union Road from 1930-1970. Now known as the Surrey Hills Medical Centre.Black and white photo of the surgery and home of Dr and Mrs William Langley Carrington at 174 Union Road on the corner of Guildford Road, Surrey Hills.. The exterior of the building is decorated with paper lanterns around the windows and veranda for the Empire Day celebrations in 1935. The building is 2 storey, of brick construction with a tiled roof and front porch. It has a bay window front right. Shadows indicate the photo was taken early morning in winter.medical services, guildford road, union road, dr william langley carrington, mr arthur plaisted, dr james landells blakie, californian bungalow, dr bill carrington -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, Private William Stanley Paull, 1915
W S Paull was born 12/01/1893 and was known as Stan. His name is listed on The Shrine in the Surrey Gardens. He was severely wounded at the Gallipoli landing on 25/04/1915. He was repatriated to Malta, spent time in 8 different hospitals in England, returned to Australia on 8/10/1915 and discharged medically unfit. He died 19/04/1949. The photo was possibly taken in England and sent home to family.Sepia studio photo of Private William Stanley Paull, No 431 of the 7th Battalion. He is wearing WW1 army uniform with the jacket buttoned to the collar and a peaked hat with a rising sun badge. There are 2 similar badges on the point of each collar. The (brown and red) patch of the 7th Battalion is visible on his right shoulder. He is standing 'at ease'.armed forces, world war, 1914-1918, uniforms, surrey gardens, shrine of remembrance, 7th battalion, monuments and memorials, stan paull, william stanley paull -
 Brighton Historical Society
Brighton Historical SocietyDress, 1920s
This dress belonged to Christina Barclay 'Ina' Strahan (nee Guinn, 1889-1974), the mother of donor Sheila Alston (1911-2008). Ina married medical practitioner Dr Septimus Strahan in 1909 and the family lived in a stately home in Moonee Ponds from 1912 until Septimus' untimely death at 56 in 1933. Ina later moved to Sandringham, where her daughter Sheila also settled after her marriage to Peter Alston.Black chiffon and lace dress with long sleeves, scooped neckline. Lozenge shaped lace pattern; machine top-stiched chiffon panels.Label, woven, blue on cream cotton, centre back: MADE IN FRANCElace, christina barclay strahan, 1920s -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumX-ray Tube, Machlett
This X-ray tube was designed to provide electrostatic protection for the filament (cathode) so as to permit long life to be achieved at operating voltages in the range 100-300kV. It is not certain whether the tube was in use within the School by Professor Laby’s X-ray group or whether it was presented to the School by a medical user. It would be somewhat surprising if it fitted into this School of Physics Research Program at a date as late as 1933 when tubes with demountable anodes were in use.Glass bulbous X-ray tube attached at either end to metal electrodes. Mounted for demonstration on a wooden base. Dated1937On glass bulb: “Machlett Patent 1954016” -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Artefact, G.W.Scott & Sons, Picnic Case, 1930s
This is a car picnic set made by the English firm of G. W. Scott and Sons who were producers of wickerwork crafts, basketry and luxury leather goods. The business was founded in 1661 and ceased operations in 1967. The picnic set belonged to Dr Horace Iles Holmes (1877-1959) who was born and educated in Tasmania and completed a medical degree at Melbourne University. He commenced a practice in Warrnambool in 1906 and was the Honorary Medical Officer at the Warrnambool Hospital and Warrnambool’s Health Officer. His practice was at ‘Ierne’ at the corner of Spence and Kepler Streets. He was an early member of the Royal Australian College of Surgeons and was prominent in Warrnambool community affairs (Foundation President of Warrnmbool Rotary Club, a member of the local Masonic Lodge for over 50 years, Warrnambool Hospital Committee member, long-term Trustee of the Warrnambool Methodist Church and President of the Lyndoch Hostel for the Aged Committee). Dr Holmes also had agricultural interests and enjoyed fishing, golf and bowls. He also had a motor car and this picnic set would have been used for family picnics. This picnic set is of considerable significance because: 1. It is a good example of the luxury picnic sets owned by more affluent people in the 1930s and 40s. 2. It has important local provenance as it belonged to Horace Holmes, a doctor associated with the professional and community life of Warrnambool for over 50 years. This is a rectangular wooden box with a leather covering. It has metal hinges on the corners of the box and two two metal catches on the side with a leather belt and metal buckle on one of these catches with one leather belt missing on the other side. These leather straps were to attach the picnic box to the running board of the car. There are also two metal catches or locks on the front of the box. Inside the box there is a white lining with a plaited wickerwork insert containing spaces for the following: 1. large china container with a silver top 2. smaller metal container with a silver lid 3. small rectangular metal tin with a silver lid. This container still has some loose tea leaves inside 4. four china cups 5. two circular china dishes for jam and butter 6. four china saucers 7. one glass bottle with a silver top 8. one metal phial, silver-coloured 9. one amber-coloured glass bottle (probably not an original) 10. four nickel silver spoons 11. three metal forks 12. three white enamel plates, blue edged Numbers 10,11 and 12 are held in place by leather straps on the inside of the lid of the box 13. two loose metal straps 14. one metal kettle with a handle with cane strapping, a brass lid, a brass spout with an end chain and a metal inscription 15. The kettle is sitting in a metal tray which has a lighting mechanism to heat the water The picnic set has some rusted metal catches on the exterior of the box and the leather is very stained and torn in places. ‘Remove screw before lighting G.W.S. & S ‘ ‘Coracle brand’ antique luxury picnic set, dr horace holmes, history of warrnambool -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyPhotograph - Digital image, Marilyn Smith, Old Ely House in Greensborough 2010, 03/07/2010
Recent photograph of one of the older houses in Greensborough. This house is in Grimshaw Street Photo taken at the very beginning of the construction of the Watermarc precinct. This house at 49 Grimshaw Street, along with the one next door at 47 Grimshaw Street were built by John Ely, son of Frederick Ely. John and his wife Melinda(Iredale), lived in Main Street (where is father Fred lived), then Grimshaw Street, John a labourer, later an assistant. John owned land in Grimshaw Street, where he built their home, he subdivided the land, this was when Eldale Avenue came to be, a combination of John’s and Melinda’s surnames. He sold a block of land, to Dr. E.R. Cordner, this is where the Cordner house, “Ashmead” was built. John and Melinda’s house later (mid 1970's) became a 'Ely House Medical Centre' owned by Drs. Myerscough and Hugh T McDonald . Alan (John's son) and Maisie’s a Physiotherapy Centre. Later Drs Stephen Hanslow and Dr. Eastern operated the medical centre. The house at 47 Grimshaw Street was demolished in 2017.Digital copy of colour photograph.grimshaw street greensborough -
 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental Collection
8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental CollectionFunctional object - water bottle
This water bottle was carried by stretcher bearers in the Light Horse Field Ambulance. The cup/cap was used to give a drink to a wounded soldier who could not hold a water bottle to his lips. A light horse field ambulance was an Australian World War I military unit whose purpose was to provide medical transport and aid to the wounded and sick soldiers of an Australian Light Horse brigade. Typically a Lieutenant Colonel commanded each ambulance. All officers of the ambulance were medical doctors or surgeons. Dental units were often attached to the ambulance as well. A Field Ambulance consisted of two sections, the Mobile and the Immobile. The Mobile Section travel with its brigade into combat, where it would establish a Dressing Station. It use stretchers or carts to retrieve the wounded and transport them to the Dressing Station. The Immobile Section established and operated a Receiving Station, which received the wounded the Dressing Station sent on. The ambulance's surgeons would operate on the wounded at the Receiving Station. From the Receiving Station, the sick and wounded would go first to the Casualty Clearing Station and ultimately to a Base Hospital. Representative of a water bottle which differed from the regular water bottle and was used for a specific purpose.Water bottle, felt coated, with small metal cup over spout, all held in leather carrier. Strapped to a wooden stand.military, water, medical, light horse, ambulance, stretcher bearer -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Syringe set, 20th century
Whether it’s an anaesthetic, blood test, insulin, vitamin shot or vaccination, at a base human level something feels instinctively wrong about having a long thin piece of metal stuck deep into your flesh. And yet, in allowing physicians to administer medicine directly into the bloodstream, the hypodermic needle has been one of the most important inventions of medical science. In the beginning… Typically, it was the Romans. The word ‘syringe’ is derived from Greek mythology. Chased to the edge of a river by the god Pan, a rather chaste nymph by the name of Syrinx magically disguised herself as water reeds. Determined, Pan chopped the hollow reeds off and blew into them to create a musical whistling sound, thereby fashioning the first of his fabled pipes. Taking that concept of ‘hollow tubes’, and having observed how snakes could transmit venom, the practice of administering ointments and unctions via simple piston syringes is originally described in the writings of the first-century Roman scholar Aulus Cornelius Celsus and the equally famous Greek surgeon Galen. It’s unclear if the Egyptian surgeon Ammar bin Ali al-Mawsili was a fan of either of their scribblings, but 800 years later he employed a hollow glass tube and simple suction power to remove cataracts from his patients’ eyes – a technique copied up until the 13th century, but only to extract blood, fluid or poison, not to inject anything. Syringes get modern Then, in 1650, while experimenting with hydrodynamics, the legendary French polymath Blaise Pascal invented the first modern syringe. His device exemplified the law of physics that became known as Pascal’s Law, which proposes “when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container.” But it wasn’t until six years later that a fellow Renaissance man, the English architect Sir Christopher Wren took Pascal’s concept and made the first intravenous experiment. Combining hollow goose quills, pig bladders, a kennel of stray dogs and enough opium to fell a herd of elephants, Wren started injecting the hapless mutts with the ‘milk of the poppy’. By the mid-1660s, thinking this seemed like a great idea, two German doctors, Johann Daniel Major and Johann Sigismund Elsholtz, decided to try their hand at squirting various stuff into human subjects. Things didn’t end well, and people died. Consequently, injections fell out of medical favour for 200 years. Let's try again… Enter the Irish doctor Francis Rynd in 1844. Constructing the first-ever hollow steel needle, he used it to inject medicine subcutaneously and then bragged about it in an issue of the Dublin Medical Press. Then, in 1853, depending on who you believe, it was either a Frenchman or a Scot who invented the first real hypodermic needle. The French physician Charles Pravaz adapted Rynd’s needle to administer a coagulant in order to stem bleeding in a sheep by using a system of measuring screws. However, it was the Scottish surgeon Alexander Wood who first combined a hollow steel needle with a proper syringe to inject morphine into a human. Thus, Wood is usually credited with the invention. Sharp advancements Over the following century, the technology was refined and intravenous injections became commonplace – whether in the administering of pain relief, penicillin, insulin, immunisation and blood transfusions, needles became a staple of medicine. By 1946, the Chance Brothers’ Birmingham glassworks factory began mass-producing the first all-glass syringe with interchangeable parts. Then, a decade later, after sterilisation issues in re-used glass syringes had plagued the industry for years, a Kiwi inventor called Colin Murdoch applied for a patent of a disposable plastic syringe. Several patents followed, and the disposable syringe is now widespread. https://www.medibank.com.au/livebetter/be-magazine/wellbeing/the-history-of-the-hypodermic-needle/ This syringe set was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Syringe set (5 pieces) in container, from W.R. Angus Collection. Rectangular glass container with separate stainless steel lid, syringe cylinder, end piece and angle-ended tweezers. Container is lined with gauze and fabric. Scale on syringe is in "cc". Printed on Syringe "B-D LUER-LOK MULTIFIT, MADE IN U.S.A." Stamped into tweezers "STAINLESS STEEL" and "WEISS LONDON"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, syringe, b d syringe, luer-lok multifit, weiss london, surgical tweezers, hypodermic syringe, injections -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Syringe set, c. 1940s
Whether it’s an anaesthetic, blood test, insulin, vitamin shot or vaccination, at a base human level something feels instinctively wrong about having a long thin piece of metal stuck deep into your flesh. And yet, in allowing physicians to administer medicine directly into the bloodstream, the hypodermic needle has been one of the most important inventions of medical science. In the beginning… Typically, it was the Romans. The word ‘syringe’ is derived from Greek mythology. Chased to the edge of a river by the god Pan, a rather chaste nymph by the name of Syrinx magically disguised herself as water reeds. Determined, Pan chopped the hollow reeds off and blew into them to create a musical whistling sound, thereby fashioning the first of his fabled pipes. Taking that concept of ‘hollow tubes’, and having observed how snakes could transmit venom, the practice of administering ointments and unctions via simple piston syringes is originally described in the writings of the first-century Roman scholar Aulus Cornelius Celsus and the equally famous Greek surgeon Galen. It’s unclear if the Egyptian surgeon Ammar bin Ali al-Mawsili was a fan of either of their scribblings, but 800 years later he employed a hollow glass tube and simple suction power to remove cataracts from his patients’ eyes – a technique copied up until the 13th century, but only to extract blood, fluid or poison, not to inject anything. Syringes get modern Then, in 1650, while experimenting with hydrodynamics, the legendary French polymath Blaise Pascal invented the first modern syringe. His device exemplified the law of physics that became known as Pascal’s Law, which proposes “when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container.” But it wasn’t until six years later that a fellow Renaissance man, the English architect Sir Christopher Wren took Pascal’s concept and made the first intravenous experiment. Combining hollow goose quills, pig bladders, a kennel of stray dogs and enough opium to fell a herd of elephants, Wren started injecting the hapless mutts with the ‘milk of the poppy’. By the mid-1660s, thinking this seemed like a great idea, two German doctors, Johann Daniel Major and Johann Sigismund Elsholtz, decided to try their hand at squirting various stuff into human subjects. Things didn’t end well, and people died. Consequently, injections fell out of medical favour for 200 years. Let's try again… Enter the Irish doctor Francis Rynd in 1844. Constructing the first-ever hollow steel needle, he used it to inject medicine subcutaneously and then bragged about it in an issue of the Dublin Medical Press. Then, in 1853, depending on who you believe, it was either a Frenchman or a Scot who invented the first real hypodermic needle. The French physician Charles Pravaz adapted Rynd’s needle to administer a coagulant in order to stem bleeding in a sheep by using a system of measuring screws. However, it was the Scottish surgeon Alexander Wood who first combined a hollow steel needle with a proper syringe to inject morphine into a human. Thus, Wood is usually credited with the invention. Sharp advancements Over the following century, the technology was refined and intravenous injections became commonplace – whether in the administering of pain relief, penicillin, insulin, immunisation and blood transfusions, needles became a staple of medicine. By 1946, the Chance Brothers’ Birmingham glassworks factory began mass-producing the first all-glass syringe with interchangeable parts. Then, a decade later, after sterilisation issues in re-used glass syringes had plagued the industry for years, a Kiwi inventor called Colin Murdoch applied for a patent of a disposable plastic syringe. Several patents followed, and the disposable syringe is now widespread. https://www.medibank.com.au/livebetter/be-magazine/wellbeing/the-history-of-the-hypodermic-needle/ This syringe set was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Syringe set (8 pieces),part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Pocket syringe kit in oval stainless steel container with separate lid. Container holds syringe cylinder, plunger, 2 needles, blade and cap. Printed on syringe cylinder "FIVEPOINT BRITISH" and symbol of a red star. One needle stamped "22"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, medical education, medical text book, fivepoint syringe, general surgical co., injections -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumSouvenir - SKETCH, MEN of TOBRUK, C.1941
"Terry Toone" is actually Frederick John Toone NX55874 J Section Workshops, 9th Div Supply Column. Enlisted 2.7.1940 age 36 years 6 months, appointed L/Cpl 12.8.1940, embark for the Middle East 27.8.1940, serves in Seige of Tobruk, he spends time in Hospital, embarks for Australia 2.4.1942 and is discharged Medically unfit on 29.9.1942. Item in the collection re Ron Bollard VX14150, refer Cat No 5919P for his service details.Sketch on card, B & W drawing of a soldier on left, heading is "Men of Tobruk" followed by a central scroll with a poem hand written in pencil, behind main cartoon shows a town "Tobruk" with aeroplanes, at bottom shows a town with civilians. On rear in black pen are details re copyright and who item returned to, either direct to him (T Toone) or his wife in East St Kilda Melbourne.On front at bottom in pencil, "Terry Toone Tobruk 15.9.41", On rear signed in black pen, "F.J. (terry) Toone 15.9.41"sovenir, tobruk -
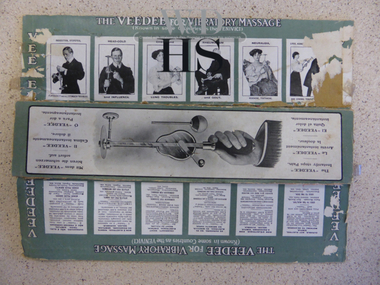 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Packaging, Box, Early 20th century
The box pieces belong to a VeeDee Massager that has been in the Historical Society collection for several years. It is an interesting example of the dubious medical aids used by 19th century and early 20th century people who resorted to this sort of appliance to try to find relief for many ailments. The box lists the ailments that the massager claims to be able to treat effectively. These include rheumatism, lung troubles, sciatica, insomnia, kidney disease, paralysis, constipation, deafness, bowel complaints and tumours. These box pieces are kept because they have much information on them regarding the use of the VeeDee massager, with a list of the ailments and medical conditions that are claimed to be cured or aided by the use of massager. The information is of use when researching social and medical history and tells us much about the primitive knowledge of ailments and illnesses in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The massager is a medical curiosity of much interest to people today and is a valuable and fascinating display piece. These are the remains of a box that contained a VeeDee massager. There are two pieces - a flattened piece of cardboard that once formed the base and sides of the box and another cardboard piece that was the top of the box. The two small ends of the original box are missing. The inside of the box is red and the base and the sides are green and white with illustrations and descriptive material in black printingThe box pieces have much printed material on them in six languages, but the main heading is ‘THE VEEDEE FOR VIBRATORY MASSAGE’warrnambool, allied health -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumPhotograph, No 28 Camp Hospital staff, Original 1942, copy 1989
Nursing staff and senior medical officer of No 28 camp hospital (Waranga Hospital) at Tatura 15 June 1943. Back row (l to r): Sister L G W Anderson, Sister D A McLeod, Sister A I Barden, Sister I A Paterson. Middle row (l to r): Sister B Moore, Major J Morlet, Sister D J Steed. Front: Sister M W Trott and Sister K Heaphy. Black and white photograph of 4 female nursing staff standing, 2 female nursing staff and male Army officer seated and 2 female nursing staff seated on ground. Tree directly behind them. Hut nearby to the right.internment camps, tatura internment camps, internment camp hospitals, internment camp hospital staff, captain morley, sister beatrice moore, waranga hospital, sister l g w anderson, sister d a mcleod, sister a i barden, sister i a paterson, sister b moore, major j morley, sister d j steed, sister m w trott, sister k heaphy -
 Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Education kit - Hygeia - Miniature Doll, Nursing Through the Ages
Miniature Doll Hygeia - The ancient Greeks, Egyptians, Romans believed gods directed physical welfare. Temples were built for priests - physicians. In Greece temples remains of "Asklepios" provided hostels, hospital wards, bath houses, gymnasia. Hygeia symbolized health and panacea. Hippocrates born in 460BC was a great physician and held ideals of ethical conduct and practice. Todays medical students still adhere to this oath when graduation and also laid the foundations of scientific medicine.Miniature Doll - Dressed in Blue Dress with Silver Trim 30 cm tall with name tag. Name Tag Hygeianursing history, nursing education equipment, miniature doll -
 Otway Districts Historical Society
Otway Districts Historical SocietyBook, Colac & District Family History Group Inc, Pioneering days: a woman's life, 2013
This is a collection of stories and newspaper clippings that relate to the women of the Colac district during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Over 300 women, some with a lot of information, others only covering a few lines, have been recorded. Many often would have had overwhelming issues to face in their day-to-day lives, with loneliness, lack of close communication and medical help, bad or unmade roads and harsh living conditions, ensuring that their children were fed. Pioneering days: a woman's life. Colac & District Family History Group Inc (comp.). 1st ed. Colac (Vic); Colac & District Family History Group Inc; 2013. vi, 284 p.; illus. ISBN 978 0975 0679 1 8 Soft cover.colac; otways; families; articles; -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPamphlet, Legacy. An outline of the facilities offered to the dependants of deceased ex-servicemen, 1961
A brochure explaining Legacy's work and the facilities they provide. It is aimed at the widows to inform them of what is available to them and it outlines the times for classes for the children. 'Melbourne Legacy offers friendship and help to the dependants of our departed comrades.' Headings included: Help and advice to mothers or guardians; Mothers' Club; Senior Widows' Club; Housing and repairs; Legal advice; Medical, dental and optical care; Education, Employment, Camps and holidays, Christmas party, Residences, Junior Legacy groups. A record of how Legacy portrayed itself to the widows and children in 1961 and 1962.Black and white brochure x 6 pages made of white paper, folded into a 6 page booklet from June 1961 and another from October 1962. Black printed text. legacy promotion, fundraising -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Smoker's Cabinet, 1927
This smoker’s cabinet is a very decorative and clever version of the item that was a novelty piece of furniture that appeared before the First World War. The contents of the cabinet are cleverly hidden behind a tambour roller door. The door slides down into the cabinet when the bottom drawer is unlocked and pulled forward, revealing two more drawers and a shelf. The bottom drawer is fitted with its own removable ashtray and a match striker. The smoker’s cabinet was a popular piece of personal furniture from the 1900s to the 1930s. The cabinet was usually designed so that its purpose was hidden. Behind the door would be a place to store all manner of things associated with smoking, such as pipes, cigars or tobacco, a removable ashtray, matches and perhaps cigar trimmers. The small cabinet was presented to Dr Angus in March 1927 by patients of the Mira hospital in Nhill, Victoria, to show their appreciation for his care. It may have been chosen as something suitable for Dr Angus to take with him when shortly afterwards sailed overseas to study at the London University College Hospital and at the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary. In 1928 he became a Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh, before returning to Australia. He and his wife and their young family settled in the Nhill district until moving to Warrnambool in 1939. His family donated this smoker’s cabinet, along with many other historic items, and it is now part of the W.R. Angus Collection. W.R. Angus Collection- The W R Angus Collection spans from 1885 to the mid-1900s and includes historical medical and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward and Thomas Ryan of Nhill, Victoria. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. He and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the part-time Port Medical Officer responsibility and was the last person appointed to that position. Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the early planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill, where they contributed to the layout of the gardens. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This smoker’s cabinet is significant as an unusual and rare piece of personal vintage furniture. The tambour roller door is seldom seen on this type of cabinet. The smoker’s cabinet is connected to the history of Warrnambool, as it was owned by Dr W. R. Angus and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection, which is notable for still being located at the site connected to Doctor Angus, Warrnambool’s last Port Medical Officer. It is also connected to the history of western Victoria through its origin, being a gift from the patients of the Mira Hospital in Nhill to Dr Angus, who was the local doctor there in the 1920s and 1930s. Smoker’s cabinet; a stained and lacquered Rosewood tabletop cabinet with a tambour cover. The cabinet is lockable. The tambour shutter door rolls downwards as the bottom drawer is opened, revealing the top two drawers and shelf. The bottom drawer is divided into compartments and has a fitted metal bowl with a bar across it to use as an ashtray and an attached striking surface for lighting matches. The cupboard had decorative silver metal swinging handles on the drawers and sides. The underside of the cabinet is painted crimson. A shield-shaped silver metal commemorative plaque is attached to the top. The cupboard was a gift to Dr W R Angus on March 7th 1927 from the patients of the Mira Hospital in Nhill, Victoria, and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.Inscription on the plaque: “Dr W.R. ANGUS, A Token of Appreciation from the Patients of “Mira” Hospital, Nhill, Victoria, March 7th 1927.”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr roy angus, dr ryan, smoker’s cabinet, smoker’s cupboard, tambour door, smoking stand, smoking accessory, novelty furniture, tobacco storage, tabletop cabinet, patients’ gift, mira hospital, nhill hospital, w.r. angus, doctor angus, dr angus, march 7th 1927, w.r. angus collection -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Cachet Machine, Christy & Co, Early 20th Century
Cachets Unpalatable drugs were cached using gelatine or a similar compound. The standard cachet machine consisted of three metal plates drilled with holes of different diameter for the size of the cachet used. The first half of the cachet was then fitted in the base plate. The centre plate was then used to mask the rims of the cachets to prevent powder deposit. Funnels were then used to deposit an appropriate dose of the powdered drug into the lower part of the cachet. Tampers were used if the drug had to be compressed. When the cachets were filled, moisture was applied to the rims of the cachet halves in the top plate. The centre plate was then removed and the two cachet halves brought together. After a few minutes the cachets were dry and could be removed. Capsules Another option was to use capsules. Again mechanisation supplanted the earlier models. The early models however are still used in clinical studies using the “double blind” method, where neither the clinician or the patient are aware which capsule contains the active agent or the placebo, as identical capsules are used for both. Each machine consists of two plates with openings to fit the capsules. The two levers at the front allow the upper plate to be raised or lowered. In the first instance the upper plate is raised half way and the empty lower halves of the capsules are inserted. This allows the operator to ensure that all the openings contain empty capsule halves. The upper plate is then raised to the maximum and the well is filled with a previously determined dose of the drug. A similar technique is used for the placebo. The upper plate is then lowered to half way, and the empty top half of the capsule is inserted in order to close and seal the previously filled half of the capsule. The upper plate is then lowered fully and the capsules can then be removed. https://www.samhs.org.au/Virtual%20Museum/Medicine/drugs_nonsurg/capsule/capsule.htm This cachet machine was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI store is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.Cachet machines were in widespread use in earlier days when doctors would make their own cachets and capsules. Cachet machine for making Cachets or Koseals of pharmaceuticals such as quinine or sulphanol. Materials contained in wooden box. Manufactured by Thos Christy & Co, Old Swan Lane, Upper Thames Street London.Metal plague on inside of lid reads: ‘Morstadt Cachets Improved & patented Christy & Co Old Swan Lane EC’. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, medical equipment, tablet making set, cachet machine, pharmaceuticals, chemist equipment, medication -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Chronometer or Marine Clock, ca. 1935 to 1975
This chronometer was made around 1936 and has been on display at Flagstaff Hill for over 40 years as part of the exhibit of the ‘Reginald M’, an Australian-built, 19ss, coastal trader vessel. A chronometer is an accurate mechanical instrument used for measuring time. It is constructed carefully to remain stable even under the changing conditions of seafaring life such as temperature, humidity and air pressure. The Master or Navigator of a ship could use the chronometer and the positions of celestial bodies to calculate the ship’s latitude at sea. In 1905 the business Chronometerwerke GmbH was formed in Frankfurt, Germany, to supply the country with high-quality mechanical chronometers and ship clocks for their maritime trade, making the country independent of other international suppliers such as those in England. In 1938 the firm was renamed Wempe Chronometerwerke. The business continues today. Its products now include its well-known chronometers, battery-powered ship clocks, ship’s bell clocks, barometers, barographs, thermometers, hygrometers, comfort meters to measure temperature and humidity, and wristwatches. The company also performs chronometer testing facilities for the State’s Weights and Measures office. The article written by Givi in July 2022 “The Basics of Marine Meteorology – a Guide for Seafarers” refers to the weather’s signs and patterns being repeated over and over, and the recording of these observations helps forecasters predict changes in the weather. The chronometer is an example of a mechanical navigational marine instrument in use in the early to the mid-20th century. The maker is significant as part of a German government initiative to be self-sufficient in the production of good quality marine technology. This chronometer is significant as part of the exhibit, the Australian-built vessel, 1922 coastal trader ‘Reginald M’, listed on the Australian Register of Historic Vessels and on display for over 40 years.Marine chronometer or marine clock, brass case, glass cover, Roman numerals, 24-hour numbers beside them. Two black hands, a keyhole for winding and ventilation holes in the side. The base has a collar with four machined mounting holes. Inscriptions are on the clock’s face."Made in Germany"" and ""WEMPE / CHRONOMETERWERKE / HAMBURG"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, marine meteorology, horology, chronometer, marine technology, latitude, marine navigation, mechanical instrument, scientific instrument, ship clock, chromometerwerke gmbh, wempe chronometerwerke, marine clock -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Glass, Pharmacy beaker, c1950
Otto Schott, a chemist and glass engineer, had the vision of uniform production ie making glass items that would resemble one another. At the end of the eighteenth century, with most glass items still created by hand, the quality of output was still a guessing game. Schott was the first to render this an industrial certainty. 1884 Otto Schott, Ernst Abbe and Carl and Roderich Zeiss found the Schott & Associates Glass Technology Laboratory in Jena, Germany. Glastechnisches Laboratorium Schott & Gen was born. Production started in 1886. Original products included optical and thermometer glasses. The following year, a crucial discovery was made: borosilicate, a heat and chemically resistant glass. By it’s 25th year anniversary, the company had grown from an experimental glass factory into an internationally renowned manufacturer of optical and industrial glasses. Soon to be added was fiolax, tube-shaped glass used for vials, ampoules and syringes thus allowing the company to play a significant role in supplying Europe's nascent pharmaceutical industry. Post WW2 USA Army opens new factory in Mainz, West Germany and factory in Jena , East Germany taken over by the DDR State both using same trade name. Legal action for 30 years resolved in 1980 - split name. Berlin Wall 1989, Factories reunited 1991A pharmaceutical clear glass beaker with graduation 100ml -300ml DURAN 50Front : DURAN 50 / SCHOTT & GEN / MAINZ / JENA (ER) GLAS 300 Back : PYREX 300pharmacy, medications, medicines, glass manufacturing, glass works, early settlers, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, jenaer glaswerk schott & gen company, west germany, east germany, berlin wall, ww2 1939-45, schott otto, zeiss roderich -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPhotograph, 'First council meeting in new Ringwood chambers, 1928
Written on back of photograph, 'First council meeting in new chambers, 1928. 1924 Foundation Council. Mayor Cr. A.T. Miles, Town Clerk, A.F.B. Long, Engineer, F.R. Lucas, R???? MR. Gill and Mr. Ostrom, Rate collector, W.T. Jenkins, Architect, A.C. Leith, Councillors, J.K. McCaskill, R. Wilkins, A. Blood, W. McKinlay, J.B. McAlpin. Medical officer, Dr. Langley (absent). -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumMEDICAL ITEM
Red circular tin complete with Elastoplast bandage insideLid: "S&N" Side: Elastoplast trade mark/Elastic Adhesive/Bandage/B.P.C. with porous adhesive/British Patent No. 713 838/for the medical profession/Directions for use enclosed/width 3in (7,6cm) Length unstretched 3yd (2.70m)/Length stretched 5/6yd (450/550m) Order No. 1003 Made in England by T.W. Smith & Nephew ltd., Hall & Welwyn Garden City. Keep in a cool place bandage, medical item -
 Friends of Westgarthtown
Friends of WestgarthtownBottle
Clear glass bottle oval shaped. Embossed on back J. Bosisto Richmond. Paper label on front reads "Bossisto's Parrot Brand Oil of Eucalyptus".Paper label on front of bottle reads " A valuable external remedy for rheumatism lumbago, sciatica, sprains, chilblains, whooping cough, Croop, asthma, bronchitis, sore throat and all other painful afflictions whenever stimulating applications is required. The oil taken internally in five to six drop doses on loaf sugar and inhaled over hot water is recognised as many medical authorities as almost a specific in the treatment of common cold and influenza. A few drops sprinkled on a cloth and suspended in a sick room renders the air refreshing. Rubbed lightly on the face and hands it prevents attacks from mosquitoes. Full directions for use on full wrapper around bottle. Bosistos Eucalyptus Oil is the genbuine essence of the Tree distilled from E. Ihumosa and other speicies best known to contain the medicial purposes of the oil in the most perfect combination for general medical use. Embossed on back of bottle reads J. Bosisto Richmond.medicine, first aid, bosisto, richmond, eucalyptus, domestic, remedy, oil. -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Document - National Service Selection for Service Card, NS 69(Rev 1/68) with envelope, 1960s
Perforated pro-forma call-up card from Department of Labour and National Service : National Service Registration Office addressed to Mr N E Swainston, 37 Leamington St, Reservoir Vic, dated 01/10/70 with Registration Number 21765955. Specific details are typed in black ink, and the document is signed by registrar W K Allen. Back of card advises recipient that he will be given at least 7 days' notice of the time and place for the medical, and that it is his responsibility to notify changes in marital status or address. Envelope is marked O.H.M.S, National Service Registration Papers and torn open at bottomnational service - australia, conscription, call-up, swainston collection -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Bisque porcelain figurine of a doctor
Bisque porcelain figurine of a male doctor holding a medical instrument. The doctor has grey hair and is in surgical attire, with white gown, gloves, surgical hat and mask. The cuffs of his brown trousers, and his black shoes, are visible below the gown. The doctor is wearing glasses on the end of his nose, and holds a surgical tool in his right hand. The figurine is standing on a base with a painted green stripe across the centre, and is supported by a pillar at the back which is decorated with decorative orange and black squiggly lines. Orange and black squiggly lines also feature on the front of the base. Handwritten lettering on a sticker on underside of base reads 'FF'. -
 Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and Archives
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and ArchivesMemorabilia - Thai- Burma Dog Spike and sleeper
Built in 1942-1943, the Thai-Burma Railway was a 415 kilometre stretch of railway between Ban Pong, Thailand and Thanbyuzayat in Burma. It was constructed by the Japanese using civilian labourers and prisoners-of-war. It is estimated that 90,000 labourers and more than 12,000 POW’s died during construction of the railway.This is a commemorative object highlighting the role of medical personnel during the war and its impact on them personally and preofessionallyThis dogspike and its attached sleeper came from the Thai-Burma Railway. A dogspike is a rail fastening with a pointed end and a ‘plate holding’ head, giving the impression of a dog’s head. Built in 1942-1943, the Thai-Burma Railway was a 415 kilometre stretch of railway between Ban Pong, Thailand and Thanbyuzayat in Burma. It was constructed by the Japanese using civilian labourers and prisoners-of-war. It is estimated that 90,000 labourers and more than 12,000 POW’s died during construction of the railway. The dogspike was donated by Bill Sharp in 2014. It commemorates the Australian Medical personnel who became prisoners-of-war. they are listed on the plaque behind the spike.thai-burma, japanese, 1942-43, commemorative gift -
 Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - Medical Reference Books
1. Surgical Nursing by J.E.Whiteside F.C.N.A. Belonged to Marion Dunn 'Pilot' NDSN 24/2/75 2. Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine and Nursing by Benjamin F Miller, M.D. and Claire Brackman Keane, R.N., B.S. Belonged to Marion Symes (nee Dunn) N.D.S.N. 17-3-7 3. Medical-Surgical Nursing and Related Physiology by Jeannette E. Watson, R.N., M.Sc.N. Belonged to Marion Symes (nee Dunn) 4. Basic Physiology and Anatomy by Ellen E. Chaffee and Esther M. Greisheimer Belonged to Marion Dunn NDSN, 37 Rowan St, Bendigo, 14/2/741. surgical nursing, medicine, physiology, anatomy
