Showing 3854 items matching "institutions"
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Australian White Ibis, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Australian White Ibis is commonly known by the colloquial names "bin chicken" and "tip turkey" in Australian culture. These nicknames have arisen based on the presence of this bird at garbage locations where it is often seen rummaging through the waste. The Yindjibarndi people of the central and western Pilbara call this species mardungurra. This bird is located throughout the wetlands of eastern, northern and south-western Australia. Initially, it was not seen in urban areas, however, the species has been able to adapt and reduce fear of humans due to the lure of food found in human garbage. They commonly feed on terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates alongside human scraps. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Australian White Ibis has white and cream plumage on its body and a black neck, head, bill and legs/feet. The bill on this particular species has a distinctive long shape which is down-curved. It is a fairly large variety of the Ibis species. This specimen has been stylised in a standing position and is positioned on a wooden platform. 5 C. / White Ibis / See catalogue / Page 32 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, ibis, bin chicken, white ibis, australian birds, australian white ibis -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Pacific Black Duck, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Pacific Black Duck is also known as the Grey Duck in New Zealand. Despite these names, the plumage of the bird is brown in colour with the occasional cream and small amount of black. This species of Duck is located in all of Australia with the exception of the most arid zones. They can also be found throughout the Pacific region. The Pacific Black Duck resides in a range of different habitats that have some sort of water. These birds feed on aquatic plants, crustaceans, molluscs and aquatic insects. To catch their food, these birds plunge their heads and necks under the water with their rear raising above the top of the water. This technique is termed "dabbing". This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.Despite its name, the Black Duck is largely brown in colouring. It has a mixture of light brown and cream plumage on the neck, face and stomach. The wings and rear of the duck are a darker brown. Each brown feather is bordered with a cream colour which separates the feathers from each other. The top of the head is also dark brown and there is a darker stripe of black colour horizontally on either side of the eye. The specimen has two brown and black glass eyes and a black bill. The legs and webbed feet are a dark brown and black colour. Tied around the left leg is a paper identification tag. The number 134 is inscribed on the left side of the wooden platform on which the bird is standing. This specimen is stocky.3a. / Australian Wild Duck / See Catalogue, Page 38. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, duck, pacific black duck, grey duck, australian duck -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Belted King Fisher, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Belted Kingfisher is commonly seen near bodies of water or coasts in Canada, Alaska and the United States. During migration periods these birds may stray far from their usual habitat. Interestingly, the female of this species, as is the case for this specimen, is often larger than the male. They are also more brightly coloured. This species feed on amphibians, small crustaceans, insects, small mammals and reptiles. They lie await perched on a tree located close to water and remain there watching until they see their prey. When they have located their prey, the Belted Kingfisher plunges its head into the water and catches its food. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Belted Kingfisher stands upon a wooden perch with a light brown paper tag attached to leg. This specimen has pale cream/white and slate grey/blueplumage. The head and back are coloured the blue-grey while the neck and stomach are cream/white. The bird has a black ring around its upper chest. The stomach has a chestnut brown band which identifies this particular specimen as female. The bill is long and pointed and the eyes and legs black. The bird is small and stocky with a large head and a square-tipped tail.95.a / Belted / Kingfisher / Catalogue page, 25 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, kingfisher, small birds, belted kingfisher, king fisher, female bird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red Necked Avocat, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This particular species is native to Australia and can be located throughout the mainland, preferably in the south-western interior. It is known for its distinctively upturned bill, the males of this species have a slightly more upturn to their bill than the female. This style of bill is unusual among birds and is used to assist them forage in the water of shallow wetlands. These birds feed on aquatic insects, crustaceans and seeds. The name of this species is derived from the distinctive chestnut brown/red colouring of the head and neck. Interestingly, the call of this bird has been described as a "yapping" sound which is similar to the sound of dogs barking when performed by a flock in flight. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Red Necked Avocat specimen is stylized in a standing position upon a wooden platform. There is a pale brown identification tag tied around its left leg. The bird has long pale grey coloured legs and a characteristic long, thin and black upturned bill. The plumage of this species is largely white. It has a chestnut brown/red coloured head which is where this species gets its name. The wings are white with black tips.25c. / Avocet / Catalogue, page, 36. / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, large bird, red necked avocat, avocat -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red-Necked Avocat, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This particular species is native to Australia and can be located throughout the mainland, preferably in the south-western interior. It is known for its distinctively upturned bill, the males of this species have a slightly more upturn to their bill than the female. This style of bill is unusual among birds and is used to assist them forage in the water of shallow wetlands. These birds feed on aquatic insects, crustaceans and seeds. The name of this species is derived from the distinctive chestnut brown/red colouring of the head and neck. Interestingly, the call of this bird has been described as a "yapping" sound which is similar to the sound of dogs barking when performed by a flock in flight. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Red Necked Avocat specimen is stylized in a standing position upon a wooden platform. There is a pale brown identification tag tied around its left leg. The bird has long pale grey coloured legs and a characteristic long, thin and black upturned bill. The plumage of this species is largely white. It has a chestnut brown/red coloured head which is where this species gets its name. The wings are white with black tips.24c. / Avocat / Catalogue, page, 36. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, large bird, red necked avocat, avocat -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Book - Handbook, VIOSH: BCAE Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management; ES Risk Engineering, Derek Viner,1986
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. "It is always better as a matter of principle to remove the hazard from a design rather than subsequently develop safeguards for the design". This may not always be possible. This book looks at safeguard designs and applications, specifically in Engineering. Checklists for various situations are enclosed. This book has been written by Derek Viner - Engineering Department at BCAE and Consultant VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. A4 size book of 105 printed pages - spiral bound. Divided into seven sections by yellow paper. Yellow cover.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ballarat college of advanced education, graduate diploma in occupational hazard management, es472 risk engineering, derek viner, safeguard designs, applications, checklists -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Course Outline, VIOSH: Ballarat College of Advanced Education; General Information - Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management, c1986
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders in the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Document is General Information on the Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management. Sections are from a larger fully detailed document. Outlines the structure of the course, Unit Descriptions, Staff, Student Workloads. Student Enrolment Statistics for 1979 to 1985 show the numbers from each state and overseas, employments areas such as government, industry, manufacturing, health, and associations, plus the total applications and enrolments. Thirteen A4 sheets - typed on both sides.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ballarat college of advanced education, graduate diploma in occupational hazard management, pg1, objectives of course, admission requirements, structure of course, unit descriptions, student workloads, assessment methods, k brown, dennis else, r gillis, tom norwood, max brooke, r kemp, j harvey, p kelly, l roberts, m torode, derek viner, eric wigglesworth, g fernandez, b lees, r maud, p swan, j blitvich, g bradley, j castleman, r lang, j lowinger, p reid -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionManual - Manual - Fire Protection, VIOSH: Munich Reinsurance Company of Australia Limited; Tertiary Education for Fire Protection
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders in the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Manual was sent to Derek Viner. It has an introductory section telling the development of the program and outside providers. Detailed section on the Proposed Curriculum. There are various courses related to Fire Detection, Fire Prevention, Fire Protection and protection Design. Manual has notations supporting and disagreeing with areas that could be incorporated into the programs at Ballarat College of Advanced Education. Forty A4 pages in glossy card cover. Blue and orange bands at bottomOn orange section at bottom: Munich Re of Australia Munich Re Group Symbol viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ballarat college of advanced education, munich reinsurance company of australia, tertiary education for fire protection, fire detection, fire prevention, fire protection, design, derek viner -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, VIOSH: Certificate Course in Occupational Health and Safety; Fijian Department of Labour and Industrial Relations, 23 September - 19 October 1996
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders in the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry.. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. VIOSH conducted a Certificate Course in Occupational Safety and Health for the Fijian Department of Labour and Industrial Relations in 1996. The course was held in the Government Training Centre Fiji. The group was made up of Labour and Factory Inspectors. Steve Cowley led this program. It was from 23 September to 18 October, 1996. A graduation ceremony held at end of course.Colour photographs.Photographs 26814.28 to 26814.47 have stamp for CAINES JANNIF PTE of Victoria Parade Suva, Figi on backviosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, certificate course, government training centre fiji, fiji, labour and industrial relations, factory inspectors, september to october 1996, steve cowley -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionArticle - Article - Women, Ballarat College of Advanced Education: Anne Stewart; Librarianship Storyteller
Anne completed her secondary education at Presentation College Windsor. She left Melbourne to study Librarianship at Ballarat College of Advanced Education and completed a Graduate Diploma of Librarianship in 1981 and a Graduate Diploma of Education in 1986. During her studies Anne E. Stewart produced weekly shows on 3BBB Community Radio Ballarat, `As the assistant children's librarian at Geelong in 1987 Anne E. Stewart drove the Jolly Jumbuck storytelling van to various local sites, gathered the children and told a story. A keen community player Anne E. Stewart has fulfilled a number of pro bono roles such as the President of the Australian Storytelling Guild (Vic Branch), and Council President of the Daylesford Primary School. Anne E. Stewart is a senior writer for the 'Swag of Yarns' and has worn the prestigious storytellers Cape at Dromkeen, an institution that nurtures and develops children's literature. Returning to her alma mater in 2007 Anne E. Stewart developed a ghost tour through the historic Ballarat School of Mines (SMB) campus. Established in 1870, and incorporating a former gaol, the SMB ghosts came to life as she enthralled numerous groups visiting the campus on Open Day 2007, 2008 and 2009. In 2009 Anne E. Stewart was a principal teller at the Scottish International Storytelling Festival at Edinburgh.women of note, ballarat college of advanced education, anne stewart, presentaion college windsor, librarianship, graduate diploma of librarianship, graduate diploma of education, community radio, geelong library, jolly jumbuck van, storytelling, australian storytelling guild, daylesford primary school, swag of yarns, cape at dromkeen, children's literature, ghost tours, school of mines ballarat -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, VIOSH: Occupational Hazard Management Dinner and Presentations, 2002
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Photographs taken at the OHM Dinner and Presentation in 2002. Students attended the University of Ballarat to complete the VIOSH Occupational Hazard Management Course. Oliver Footwear Solution Award and Shared Solution Award were presented. Male student was presented with the "Rae Epthorp Human Factors Prize" and the "National Safety Council of Australia Perpetual Trophy".Thirty-eight colour photographs with matte finish; Twelve colour photographs with high gloss finishviosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ballarat university, david boyce, dulcie brooke, andrew oliver, nsca, national safety council of australia, perpetual trophy, john knowles, rae epthorp human factors prize, oliver footwear solution award, oliver footwear shared solution award, dennis else, steve cowley, john culvenor, university women -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, VIOSH: Certificate in Occupational Health and Safety, extended to include environmental management, Graduation, April 1998
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. This was a customised version of the VIOSH Certificate in OH&S extended to include environmental management. It included on-campus time plus approximately 24 months practical work, starting April 1996 and finishing in April 1998. Participants were from BP Oil. It was held at University of Ballarat. Graduating students shown in grounds of the University.Colour photographviosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, university of ballarat, bp oil, environmental management, graduation -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionProgramme, Invitation and Programme for the Naming Ceremony South Wing of the Education Building T Ian Gordon, 1995, 1995
Ian Gordon played a prominent part in both the development of the Mt Helen Campus and in the progress the Institution made prior to becoming a University on 01 January 1994; In 1973 he was appointed President of the Council of hte newly created State College of Victorian at Ballarat (SCVB) which absorbed the former Ballarat Teachers' College. As President, he led the merger of the SCVB with Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE), the tertiary division of the School of Mines and Industries, Ballarat. Out of the merger the Ballarat College of Advanced Education (BCAE) was established on 01 July 1976. Ian Gordon, a partner in the Ballarat law firm Heinz and Gordon, became the first Vice-President of the new Council and was involved with the plan to transfer the former SCVB to the Mt Helen site. In June 1981, Ian Gordon became President of the Council of BCAE and held that position until June 1989. He remained a member of the Council of the BCAE (later Ballarat University College) unti l31 December 1993, the eve of the creation of the University of Ballarat. He was the only person to remain a member of the BCAE and the BUC Councils for the whole of their existence. Mt Helen T Building wzs erected to house the major part of teh State College of Victorian at Ballarat when it moved to the Mount Helen Campus.Folded programme and invitation for the Naming Ceremony of the South Wing of the Education Building T "Ian Gordon".ian gordon, ballarat college of edvanced education, state college of victoria at ballarat, t building, ballarat institute of advanced education, david james, verna barry, building name, mt helen campus -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Report, VIOSH: A Review of Occupational Safety and Health in the Antarctic Division and A.N.A.R.E.; August 1990 and Agreement with Commonwealth of Australia to perform review
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. An Agreement between the Commonwealth of Australia and Doctors Else and Cowley of VIOSH was made in relation to Consultancy Services for a review of Occupational Safety in the Antarctic Division and on Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions. It was signed by Commonwealth representative, Mr B R Dixey and by Dr D Else and Dr S Cowley of VIOSH on 21 November 1989. The completed Review was signed off in August 1990..1 consists of twelve sheets printed on one side. .2 consists of thirty sheets printed on one side..1 Hand written note on first sheet. Date and signatures to agreement on last page - B R Dixey (for the Commonwealth), D Else and S P Cowley (for VIOSH). Signed on 21/11/1989viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, commonwealth of australia, agreement, review of occupational safety, antarctic division, australian national antarctic research expeditions, casey station, macquarie island, voyage 4 -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Report, VIOSH: BCAE;, Special Inspection Report prepared for The Sovereign Hill Park Association; 1980
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. This special report was prepared by Neville Betts, Occupational Hazard Management student at Ballarat College of Advanced Education in 1980. It was to provide comment and recommendations aimed towards improving the standards of both occupational health and safety and general public safety at Sovereign Hill, Ballarat. Interviews with those at Sovereign Hill and external public officials - fire brigade, police, ambulance contributed to the report.Twenty-eight A4 pages - typed document. Photographs included showing various safety concerns. Small holes down left side from binding which has been removed.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ballarat college of advanced education, bcae, occupational hazard management, sovereign hill, general public safety, fire brigade, police, ambulance, inspection report, neville betts, student -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Information, VIOSH: Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management - Intake 6, 1984, Information Letter to students
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Information letter sent to those in Intake 6 of the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management Course, 1984. It outlines the timetable for subjects and times at the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. Include in the package is a form that must be completed and returned ASAP. Residences are provided and items included are listed. Transport for those coming from interstate can be arranged. Derek Viner is the Course Co-ordinator.Twenty-three A4 pages, typed with diagrams, mapsHand written note in blue pen on map. Letter head of Ballarat College of Advance Education on some pages. Signature of Derek Viner, Course Co=ordinator.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, derek viner, course co-ordinator, occupational hazard management, residence, timetable, ballarat college of advanced education -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Book - Handbook, VIOSH: Chemicals and the Artist; A health and safety handbook for students, teachers and artworkers by Bob Hall
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Book outlines the requirements to be considered - chemicals, conditions re ventilation, protective clothing such as respiratory devices, gloves and eye and face protectors. An understanding of the effects of various chemical solutions. A detailed Glossary of health and safety terms is included. Alternative options for solvents etc is also given. The importance of a safety hazard audit register for hazardous substances is detailed. Glued and cloth bound book of 161 pages. Cover light fawn with black print and binding.viosh, safety and health, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, art facilities, chemicals, ventilation, safety audits, hazardous chemicals and substances, protective clothing, bob hall -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Book - Handbook, VIOSH: BCAE, Readings in Occupational Hazard Management, 1981
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. The handbook provides students with the reading resources appropriate for tutorials in Occupational Hazard Management at Ballarat College of Advanced Education. Articles are from a wide range of resources and by a number of authors in the field. One of interest was a Report of the Committee 1970-72 by Chairman Lord Robens. It was presented to Parliament by Command of Her Majesty, July 1972.Spoiral bound book of 234 A4 Pages. Cream cover - slightly dirty.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, occupational hazard management, tutorials, readings, occupational accidents, road safety, strategies, sociological problems, dimensions of the problem in australia, s p barker, w hadden, k g jamieson, eric wigglesworth, j s robertson, d klein, e suchman, d f jones, lord robens, o woodhouse, j m henderson, j a walker, p z barry, j c lane, j w anderson, s lancer, r g sell, s k mckenzie -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Magazine - Safety, VIOSH: Australian Safety News, July-August 1983. Official Occupational Safety and Health Journal of the National Safety Council of Australia
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. The magazine is the Official Occupational Safety and Health Journal of the National Safety Council of Australia. It provides information on various aspect of safety plus equipment and clothing suitable for different situations. Pages 38 and 39 outlines the VIOSH course at Ballarat College of Advanced Education - Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management. The Pamphlet included is a detailed explanation of the course.Magazine:Sixty-four pages plus cover - stapled together. Colour and black and white Pamphlet: Foldout with yellow front - A4 folded in threeviosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, national safety council of australia, graduate diploma in occupational hazard management, safety news, journal -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Transcript of presentation, VIOSH: Presentation to the Third World Conference, Melbourne February 1983; "Post Graduate Course Development in the Cooperative Mode"; Derek Woolley
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Derek Woolley was a speaker at the Third World Conference on Cooperative Education, held in Melbourne, 21-25 February 1983. This model of education was the basis for the VIOSH program at Ballarat College of Advanced Education. Tables of statistics were included to support the course development. Page 4 has a Bibliography, List of the External Advisory Panel and Seminars and Short Courses attended - 1977-1980. Four A4 pages type written - top section hand written. Two columns per page.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, third world conference on cooperative education, melbourne, ballarat college of advanced education, external advisory panel, seminars and short courses, occupational hazard management, derek woolley, head of school of engineering, derek viner -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Memo, VIOSH: Ballarat College of Advanced Education; AIDAB Training Course, 1983
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Memo to Derek Woolley from Dennis Else about information from Melbourne Regional Office about course to be run at Ballarat. No final decision has been made in Canberra as yet. Nominations from India have come and the Indian Government very keen for the course to take place. See photograph 26735 See also document 26687Two A4 pages. One typed memo, one shows advertisement re training courses availableSignature of Dennis Elseviosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, dennis else, derek woolley, aidab, australian international development assistance bureau, indian government, canberra, melbourne regional office, graham ward -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Correspondence, VIOSH: Ballarat College of Advanced Education; Training Course in Factory Inspection, 1983
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Letters from Dennis Else, Eric Wigglesworth, Richard Gillis and Derek Woolley organizing the course and timetable for the Training Course in Factory Inspectors that would come under Australian International Development Assistance Bureau (AIDAB) funding. See photographs 26735 See also documents 26686 and 26687 See Booklet re Training Course written by BCAE - 26850Four A4 pages, typedLetterheads for Ballarat College of Advanced Education, The Menzies Foundation and Altona Petrochemical Company Ltd.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ballarat college of advanced education, dennis else, eric wigglesworth, richard gillis, derek woolley, gayle richards, the menzies foundation, altona petrochemical company ltd, letterheads, factory onspection, environmental health advisor -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Life Jacket, General Naval Supply G.N.S.), 1940
This life jacket was issued by the Australian Government's General Naval Store in N.S.W.. It was inspected in 1940. Life Jackets - Life jackets were part of the equipment carried by the Life Saving Rescue Crew of South Western Victoria, including Warrnambool, from around 1858 until the 1950s. The purpose of a life jacket is to keep the wearer afloat until he or she is rescued from the water. Life jackets were first invented in 1854 by Captain Ward of the Royal National Lifeboat Institution in Britain. The early life jackets were filled with cork, which is very buoyant. However, many times he cork caused the jacket to rise up quickly with a force that caused unconsciousness, sometimes turning the person face down in the water , causing them to drown. After the tragic loss of the ship RMS Titanic in 1912 and the lost lives of those onboard, a woman named Orpheus Newman designed the Salvus life jacket (Salvus means safe), which was filled with kapok instead of cork. Kapok comes from seed pods of the Ceiba Pentandra tree and is waterproof as well as buoyant. These Salvus jackets were used by the Royal Navy until new synthetic materials became available around the time of World War II.This life jacket is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Life jacket, canvas covered, with two padded compartments filled with kapok. Designed to slip over the head. it has shoulder straps and straps for tying under the arms. An inscription and symbol is stamped on one shoulder strap. The life jacket was supplied by the General Naval Store, Defence Department, N.S.W., and inspected in in 1940.Inscription "G.N.S. [crown symbol] N.S.W / 12 JUN 1940 / INSPECTED".flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, g.n.s., general naval store, 1940s life jacket, captain ward, royal national lifeboat instution, cork, kapok, life jacket, orpheus newman, salvus jacket, life saving, rescue, rescue crew, l.s.r.c., life saving equipment, marine technology, lifeboat, shipwreck victim, vintage -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayVictorian Railways Saucer Plate, May 1954 "5-54" = "month-year"
Victorian Railways Saucer Plate - Red & White Supplier to Victorian railways : Loftus Moran, Melbourne: Mr Loftus Henry Moran was well known in the tea trade. Originally employed by Griffiths Bros Ltd, he started his own business, Loftus Moran Pty Ltd, in 1909 In 1913 he purchased the tea business of McIntyre Bros, and later, that of Steele Bros, and absorbed them in his own company. He had a wide business connection among hotels and guest houses for supplying crockery and other supplies. Ref: DEATH OF MR LOFTUS MORAN (1944, May 27). The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1957), p. 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article11809686 1st Advertisement of the Plates in the papers: CHIPPED CROCKERY. Nothing is more objectionable than chipped crockery--besides its use is illegal. DURALINE Plates, manufactured by The Grindley Hotel Ware Co., are tough as raw-hide. This is why they are used by practically every hotel and institution in Australia. Obtainable only from LOFTUS MORAN PTY. LTD., Hotel Supply Specialists, 131 Queen's Bridge Street, Melbourne South Advertising (29 March 1933, ). The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. ), p. 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article4726734Historic - Victorian Railways - Refreshment Services crockery - plateCeramic Victorian Railways Saucer Plate - Red & White Victorian Railways ( in Red on fount of plate ) "DURALINE" ( in Black on back of plate ) super Vitrified GRINDLEY HotelWare Co England Loftus Moran Pty Ld Melbourne 5 -54 puffing billy, victorian railways, crockery, plate -
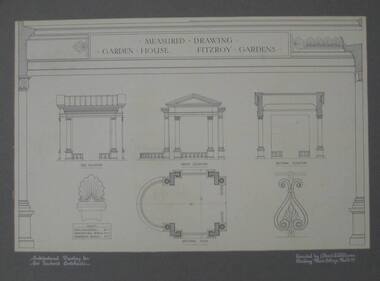 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionArchitectural Drawing, Measured drawing ornament House Fitzroy Gardens by Albert E. Williams, c1920, c1920
Albert E. Williams first studied art under Fred Foster after being awarded a scholarship to the Ballarat East Art School. In 1913 he became one of the first intake of 83 students to study the Merit Certificate at the newly opened Ballarat Junior Technical School. Williams was the second person to receive a certificate from that institution. He then studied under H.H. Smith for the Art Teachers’ Certificate at the Ballarat School of Mines Technical Art School between 1915 and 1920. Williams joined the staff of the Ballarat Junior Technical School in 1921, teaching sign writing, ticket writing and house decoration. He taught in other technical schools between 1923 and 1928, returning to Ballarat in that year to fill a vacancy left by John Rowell . Williams continued his teaching career at both the Ballarat School of Mines Technical Art School and the Junior Technical School until 1942. He taught in various other technical schools from 1943, retiring as Headmaster of the Brighton Technical School in 1964. Albert E. Williams continued producing artwork throughout his career, and was responsible for the education of generations of artists and art teachers. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Pen and ink measured drawing showing side elevation, front elevation, sectional elevation and scales.art, artwork, williams, albert e. williams, ballarat technical art school, architecture, art teachers' certificate -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionPhotograph, Frank Golding, 'Three-quarter Time' - by Frank Golding, 2001
Frank Patrick Golding (1938 - ) This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007. Frank Golding is an author, researcher, historian, consultant: Honorary Senior Research Fellow at Federation University in Victoria, Australia. His formal qualifications are TPTC (Ballarat), BA (Melb), BEd (Melb), Dip MT (UNE), MA (Hons) (London). He has taught English and History in several schools. Frank Golding was employed as Principal at three schools including a multi-site English language centre for refugees and other new arrivals. Later he taught in and managed curriculum and equity programs in education departments and universities. Finally he is the author of 12 published books including a memoir, An Orphan’s Escape: Memories of a Lost Childhood (Lothian, 2005) which describes his childhood as a Ward of the State of Victoria in the ‘care’ of three foster mothers and three institutions. Golding lived in the Ballarat Orphanage from 1943 to 1953. It is his childhood experiences that underpin Golding's active involvement in ‘care’ leaver issues as an advocate and lobbyist. Golding is a Life Member of CLAN (Care Leavers of Australasia Network) the peak body of Care Leavers for Care leavers run by Care Leavers.Image of bird on 1/2 orange citrus fruit - a play on childhood memory of oranges at 3/4 timeSignature on label on backart, artwork, frank golding, bird, federation college, photography, colour photography, alumni -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Brown Goshawk Juvenile, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This specimen is a Brown Goshawk juvenile. The Brown Goshawk is widely distributed across Australia, Wallacea, New Guinea, New Caledonia, Vanuatu, and Fiji. In Australia, it predominantly inhabits eucalypt forests, woodlands, farmland, and urban areas, while in the Pacific, it is primarily associated with rainforest environments. Historically, it was also present on Norfolk Island until around 1790, potentially representing an undescribed subspecies. However, the limited material available—consisting of a single historical skin and nine subfossil bones—precludes confirmation through scientific analysis. This specimen was originally identified as a Nankeen Kestral and is catalogued as such in the original Public Library and Burke Museum catalogue. The specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen exhibits distinctive plumage compared to its adult counterparts. It has a streaky appearance, with a buff to pale rufous base color on its underparts adorned with bold, dark brown streaks. The upperparts are brown, with a slightly mottled or scalloped effect due to pale feather edges. Its eyes are yellow and legs are a pale yellow. The wings are broad and rounded, and the tail is long and barred. Identification swing tag with catalogue page number reads: 4. / Nankeen Kestrel - / See Catalogue,/ Page 2. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, birds of prey, goshawk, ornithological, nankeen kestral -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Australian Magpie, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Australian magpie is a passerine native to Australia and southern New Guinea. Renowned for its black and white plumage and distinctive song, the Australian magpie has also established populations in New Zealand and on the Fijian island of Taveuni, where it was introduced during the 19th century. Previously classified as three distinct species, it is now recognized as a single species comprising nine subspecies. Belonging to the family Artamidae, the Australian magpie is the sole member of the genus Gymnorhina and shares its closest relation with the black butcherbird (Melloria quoyi). Unlike the Eurasian magpie, it is not part of the Corvidae family. This specimen was originally misidentified as a white winged chough and is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen an Australian Magpie with black and white plumage over the body, mounted on a cedar stand. The specimen has a large straight beak and is in an unusual pose for a magpie, compressing the white patch on the back of the neck. The beak has turned yellow where originally grey, potentially leading to a previous misidentification as a white-winged chough.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian magpie, ornithological, ornithology, white winged chough -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Krefft's glider, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Krefft's glider (Petaurus notatus) is a small, nocturnal, arboreal marsupial known for its ability to glide. It is native to much of eastern mainland Australia and has also been introduced to Tasmania. The classification of Petaurus populations from New Guinea and Indonesia, previously assigned to P. breviceps, remains under review. The American Society of Mammalogists tentatively includes these populations within P. notatus, though they may represent a complex of distinct species. Notably, most captive gliders referred to as "sugar gliders" in the United States are believed to originate from West Papua, suggesting they may actually be Krefft's gliders, though this classification is still under study. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. The specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia's fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental, climate and conservation research.Small sized glider with a pointed head, curved body, bushy tail, and curved claws perched on a wooden mount. The pelage is thick, long and silky in pale caramel and tan shades. The head is small with two pointed ears, two glass eyes, and about five teeth.On wooden mount: BMM5895 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, flying fox, fruit bat, burke museum, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, natural history, animal, krefft's glider, glider, arboreal -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncAudio - Audio Recording, Audio Recording; 2019-10-09 Andrew Lemon; Heritage Advocacy - the role of historical research and historical societies, 9 Oct 2019
October Meeting (Newsletter No. 248, Oct. 2019) It was intended that Dr. Andrew Lemon AM would be our guest speaker at our last meeting on Wednesday 14th August 2019, to talk about Heritage Advocacy - the role of historical research and historical societies. Unfortunately, due to a clash of commitments Andrew apologised for not being able to attend and we are delighted he will now be our speaker at our next meeting on Wednesday 9th October. As mentioned in our last newsletter, this presentation was very well received when Andrew was the keynote speaker at the recent Regional Conference of the Association of Eastern Historical Societies. Andrew is an independent professional historian who has published many commissioned local and institutional histories since his first book, Box Hill, forty years ago. He has now written sixteen books, four of which have won prizes, on subjects ranging from local history, sport, education and biography. Andrew received his doctorate of letters from the University of Melbourne in 2004 because of the excellence of a body of work, not one single piece, as in a thesis. He has been a consistent supporter of our Society and a long term member, who has spoken at a number of our meetings, over many years.1:20:57 duration Digital MP3 File 27.7 MB andrew lemon, audio recording, eltham, eltham district historical society, heritage advocacy, meeting, society meeting
