Showing 2487 items
matching act
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the ship tilting towards port side and the bow dipping. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued, transferring from one vessel to another, which is likely to be the HMAS Swan II. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Survivors are helped from one vessel to another by seamen. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney, 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows injured men being assisted onboard a vessel at sea. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Image shows men in a lifeboat beside men in a ship, at sea. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued, transferring from a lifeboat to the ship. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows men being taken onboard a ship from a small boat. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. Figures can be seen on deck. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the damaged and listing ship in the sea with figures on deck. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time. "HMAS Warrnambool being sunk by mine", "sunk in Queensland waters 13 September 1947"flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPoster, There's a new name in education, and you're part of it, 2013
Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat had a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is Australia’s newest public University. Headquartered in Ballarat, Victoria, the University offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. With campuses from Horsham in the west of the state, to Churchill in the east, the name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses contributing to a new and different Australian university. Poster advertising new name of University of Ballarat incorporating Monash Gippsland Campus.colored posterprinted "There's a new name in education and you're part of it....Federation University"poster, federation university, monash gippsland campus, university of ballarat, gippsland campus -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - colour, Clare Kathleen Gervasoni, Federation University Gippsland Council Room, 2013, 29/10/2013
The campus at Churchill became a part of Federation University Australia on 01 January 2014. Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat had a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is Australia’s newest public University. Headquartered in Ballarat, Victoria, the University offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. With campuses from Horsham in the west of the state, to Churchill in the east, the name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses contributing to a new and different Australian university.Photograph of a timber lined Council Room at Federation University Gippsland campus. This campus was formerly a campus of Monash University, and their logo has not been removed from thr wall in this photograph.federation university, gippsland campus, monash university, churchill, gippsland, board room, council room, gippsland campus collection -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Monash University College Gippsland Handbook, 1991-3
Legislation passed in State Parliament in May, 1990, formalised the merger of the Gippsland Institute of Advanced Education and Monash University. From 01 July 1990 the Gippsland Institute became the Monash College Gippsland. Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat had a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is Australia’s newest public University. Headquartered in Ballarat, Victoria, the University offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. With campuses from Horsham in the west of the state, to Churchill in the east, the name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses contributing to a new and different Australian university..1) Pink covered Monash University College Gippsland Handbook 1991 .2) Gold and blue covered Monash University College Gippsland Handbook 1992 .2) Gold and blue covered Monash University Gippsland Handbook 1993monash university college gippsland, churchill, gippsland, federation university australia -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Letter Scale, Late 19th Century
Before 1851, letters sent through the mail were charged by the number of sheets it contained and the distance it travelled. For example, a letter consisting of one sheet of paper was charged the single rate; a double letter, that is two sheets, was charged double the single rate, a treble letter, was charged three times the single rate, and so on. In other words, each additional sheet of paper increased the charge by one rate. In Great Britain. Sealing a letter in an envelope effectively put an end to postal clerks' ability to count the number of sheets in a letter and an alternative method of determining the postage had to be found. Overweight mailings had previously required the items to be weighed but with the introduction of the Uniform Penny Postage act of 1839, the public could mail a letter not exceeding a half-ounce in weight within the United Kingdom for one penny if prepaid, or two pence if paid on delivery. At about the same time that the adhesive postage stamps and envelopes made their appearance, postal administrations began to experiment with strategically placed street letter boxes, known as pillar boxes because of their round, pillar-like shape, that permitted the public to mail letters from a place other than from a post office. For all these reasons, the use of postal scales became the nucleus of every post office. Scales had been in use since ancient Egyptian times so their use for everyday commerce was not unusual in the 1800s. What was new in 1840 was their ubiquitous use throughout the postal system. No post office could function effectively without one. Although the earliest scales used in post offices did not differ markedly from the ones in general use as time went on they were adapted specifically for postal use. For example, a paper sleeve, also known as a weight sticker, was attached that showed the applicable rate of postage for any given weight. This innovation was quite a time saver as postal clerks no longer needed to weigh the item first and then refer to a separate chart to determine the required postage for that particular weight. Victorian postal scales were used in village Post offices in the late 19th century, of which there are many examples today for sale. No maker can be attributed to the manufacture of the item. Postal scales with weights,. Balance scale has brass fittings and is mounted on a rectangular wooden stand, with depressions for brass weights; which measure 1/2oz, 1oz, 2oz, "Young Aton REL., C.N.0.9."flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, scales and weights, balancing scales, postal scales, letter scale -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Speaking Tube, Morts Dock & Engineering Co. Ltd, circa 1941
This brass speaking tube or voice pipe was used by the crew to communicate within the ship. It was recovered from the wreck of the Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool in 1948. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941 and was. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This speaking tube is an example of communication used in the mid-1900s on board a vessel. It is significant is significant for its association with Royal Australian Navy and its vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWIISpeaking tube or voice pipe, brass, conical shape, broken off at base. Wide end has a rolled edge. Recovered from HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, ship’s bell, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, speaking tube, voice pipe, communication on ship, marine technology, marine equipment, minesweeper -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionNotes, Kath Cunningham, Ballarat Teachers' College Creative Activities Notes, 1962, 1962
Ballarat Teachers' College notes on teaching Creative Studies and Needlework to primary school children. Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat has a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. In 2016, Federation University Australia announced plans to take possession, over a two-year period, of Monash’s Berwick Campus in the south-east corridor of Melbourne. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is headquartered in Ballarat and offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. The name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses.A number of notes relating to teaching creative activities to primary school children. Includes needlework samples. education, creative activities, art, needlework, samples, apron -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionInvitation, City of Ballarat Reception Invitation to Mark the 140th Anniversary of the University of Ballarat, 2010, 27/04/2010
Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat has a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. In 2016, Federation University Australia announced plans to take possession, over a two-year period, of Monash’s Berwick Campus in the south-east corridor of Melbourne. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is headquartered in Ballarat and offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. The name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses. The reception was attended by Clare Gervasoni, the University's Curator: Art & Historical Collections.City of Ballarat invitation to a civic reception celebrating 140 years of technical educatoin by the University of Ballarat. The reception was held in the Ballarat Town Hall. invitation, anniversary, city of ballarat, city of ballarat reception, judy verlin, university of ballarat, ballarat school of mines, 140th anniversary, ballarat school of mines 140th anniversary, ballarat town hall, city of ballarat logo, clare gervasoni -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, James Baker, Ballarat School of Mines Collector, James Baker, 1870, 1870
Information related to the establishment of the Ballarat School of Mines, the first of its kind in Australia. Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat has a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. In 2016, Federation University Australia announced plans to take possession, over a two-year period, of Monash’s Berwick Campus in the south-east corridor of Melbourne. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is headquartered in Ballarat and offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. The name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses.Copy of a letter signed by James Baker outlining that he had been appointed Collector to the proposed Ballarat School of Mines, and requested co-operation and pecuniary assistance torwards the establishment and maintenance of the new school. School of Mines for the COlony of Victoria Ballarat, 1870 Sir,- Having been appointed to the Trustees of this proposed Institutin, I have the honor to request your co-operatoin and pecuniary assistance towards its establishment and maintenance. Your attention is respectfully requested to the appended outline of the Institution, with the names of gentlemen who have accepted provisional offices. The object sought to be obtained is the cobinatin of the highest scientific with the most practical training for all men engaghed in the enterprise of mining in its various branches, whether so engaged as mining managers, engineers, surveyors, mechanists, working miners, directors or promoters of companies. Hitherto, in this Colony, no means of scientific educatin, in this most important occupation has been provided. The result has been an enormous waste of captial, time, and labor. Indeed, it may be fairly stated that the persent depression in the mining market and the distrust of mining property as an inverstment may in great part be traced to the numerous failures of enterprises either ignorantly entered upon or unscientifically, pursued. The scientific education of those engaged in mining pursuits would, it is believed, not merely render gold mining a safe and generally more productive speculation, but would bring into profitable prominence and activity many branches of mining now wholly neglected, or distrustfully, and consequently unsuccessfully, pursued. The Government has so far recognised the attempt to estalish this, so much wanted, Institution as to grant a ease, at a nominal lease, of the old Court-house in Lydiard street : and steps are being taken to put the building in repair and adapt it to the requirement so fhte proposed School. You will see from the appended Outline that L600 at least much be subscribed before the School can be opened. Towards thos sum several public bodies and private persons have given subscriptions; either as Life Governors, Annual Governors, or Donors, by whose liberality the Institution may be not only opened, but permanently maintained in the highest state of efficiency. I trust therefore that you will pardon my earnestly requesting your assistance, which many be effectually rendered by your returning to me one of the enclised forms, signed by you either as a Life Governoe (L50), and Annual Governor (L3 3s), or simply as a Donor of any sum which you may see fit to give. I have the honor to be, Sir, Your most obedient Servant, James Baker, Collector to School of Mines.ballarat school of mines, ballarat school of mines establishment, balalrat school of mines collector, james baker -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionCertificate, Clemente: Celebrating 10 Years in Australia, 2013, 2013
The Clemente Australia Program enables people to embark on a transformational education journey. Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat has a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. In 2016, Federation University Australia announced plans to take possession, over a two-year period, of Monash’s Berwick Campus in the south-east corridor of Melbourne. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is headquartered in Ballarat and offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. The name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses.Certificate presented to the University in recognition for their support of the Clemente Australia Program. The certificate is signed by Peter Howard (National Leader, Clemente Australia); Ann Gervasoni (Chair, Ballarat Clemente Steering Committee and Letitia Medwell (ACU Program Co-ordinator)clemente australia, anniversary, university of ballarat, letitia medwell, peter howard, ann gervasoni, john mcdonald -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayZeehan & North East Dundas Tramway Bogie 1896, wagon bogie, 1896
Zeehan & North East Dundas Tramway Bogie 1896 The North East Dundas Tramway (NEDT) was a 2 ft (610 mm) narrow gauge tramway on West Coast Tasmania that ran between Zeehan and Deep Lead (now Williamsford). It was part of Tasmanian Government Railways. The line was opened in 1896 to carry ore from the Williamsford mines to Zeehan where it would be loaded onto another train for shipment to Burnie. The narrow-gauge (2 ft) was chosen because of the extremely difficult terrain that the railway crossed, requiring several big trestle bridges, including one at the foot of Montezuma Falls. After some rain the engine and carriages would get soaked by spray from the falls. There was a break-of-gauge with the mainline 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) system at Zeehan. The railway was closed in 1932. The rolling stock for the Tramway was built in the Launceston Railway workshops, and comprised twenty five eight-wheel low-side trucks, tare 3 tons 1 cwt. 1 qr., load 10 tons; six eight-wheel flat trucks, tare 2 tons 18 cwt. 1 qr., load 10 tons; two four-wheel bolster trucks, for carrying long timber, tare 1 ton 19 cwt., load 5 tons; and four passenger cars, each with six cross-seats with reversible backs, to carry eighteen passengers, also a locker for mails and parcels. All trucks and cars have cast-steel wheels 21 inches in diameter and are fitted with automatic vacuum brakes. The trucks have side levers and the cars have hand-screw brakes. The vacuum brake can be worked from the engine or from the passenger cars, which act as brake vans. When this brake was introduced, one effect was to accelerate the journey speed by about 10 minutes owing to more even running on down gradients. Historic - Industrial Narrow Gauge railway - Bogie used on the Zeehan & North East Dundas Tramway, Tasmania, Australia Bogie made from steel, iron and wrought ironZN & NTDS ML TRAM 1896 Griffinpuffing billy, bogie, zeehan & north east dundas tramway bogie, zeehan & north east dundas tramway, industrial narrow gauge railway, gauge: 2' (610 mm) -
 Glen Eira City Council History and Heritage Collection
Glen Eira City Council History and Heritage CollectionBooklet, "AVENUES OF HONOUR The Councils of the Municipalities of the CITY OF CAULFIELD TOWN OF BRIGHTON acting in conjunction PUBLIC DEMONSTRATION SAT 3rd AUG. 1918 AT 3oCLOCK"
Souvenir Programme from the Councils of the Municipalities of the City of Caulfield and the Town of Brighton for a Public Demonstration to be held on Sat 3rd August 1918 at 3 o'clock for the proposed Avenues of Honour to be planted in memory of fallen WWI soldiers. From Honour Roll Display 2019 interpretation panel - Brighton-Caulfield Avenue of Honour It is hard to imagine but a grand arboreal Avenue of Honour once lined parts of North Road, McMillan Street and Point Nepean Road (now Nepean Highway). The Avenue of Honour was a distinctly Australian phenomenon with hundreds being constructed throughout Australia during and following World War One, most of these in Victoria. Consisting of tree lined streets with each tree representing a solider, the Avenue of Honour signalled a more egalitarian approach to commemoration where rank was not a consideration. Arguably the most famous Avenue of Honour in Victoria still exists at Ballarat. Stretching for nearly 22 kilometres, the entrance to the Avenue is marked by the imposing Arch of Victory. Smaller in scale, the Brighton-Caulfield Avenue of Honour was dedicated to the ‘memory of (Brighton and Caulfield’s) kith and kin who came from (the) district and who died in the Great War’. A joint project between the neighbouring Councils, the idea was first reported in The Argus on 1 July 1918. Plans moved along quickly and on 3 August 1918 the Governor of Victoria Arthur Stanley planted the first Australian flowering gum. The next of kin were then invited to plant trees for lost sons, brothers, uncles, nephews and husbands. In all, over 400 trees were planted. Intensely personal, the Avenue also acted as a focus of grief and remembrance for the wider community. For many years, the annual civic Anzac Day service was held at the Avenue on Point Nepean Road, near Glen Huntly Road, Elsternwick. The service was moved to Caulfield Park upon the completion of the Cenotaph in 1930. Due to road widening and disease the last original tree was replaced in the 1980s, however a plaque in Caulfield Park records the Avenue’s plantation. Commemorative booklet, grey cover with text printed on the grey textured paper cover and an image of four trees and a wreath. Image of a kookaburra on the back. Inside, 28 numbered pages with b/w text and photographic images including a transparent paper representation of the proposed Avenues of Honour on Brighton Road and Point Nepean Road. Souvenir programme for a Public Demonstration for the Avenues of Honour as detailed on the front.city of caufield, world war one, first world war, anzac, remembrance, town of brighton, brighton, caulfield, avenue of honour -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionManual, Post Master General's Department, Telegram Delivery Instructions, 1967
Electrical telegraphs were point to point text messaging systems primarily used from the 1840's until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and were sent by an operator or telegrapher using Morse code. Social telegrams were also encouraged and special pictorial forms and envelopes were designed such as the special purple form and envelope which was used when conveying condolence details during World War 2.(fn. Powerhouse https://collection.powerhouse.com.au/object/163103). There was a brief resurgence in telegraphy during World War I but the decline continued as the world entered the Great Depression years of the 1930s. Although telegraph lines continued to play an important part in distributing news feeds from news agencies post World War 2, the rise of the internet in the 1990s and the widespread installation of the telephones in homes saw the need for telegrams to greatly decline. When the Commonwealth Post and Telegraph Act was passed in June 1902, and a national Postmaster General's Department (the PMG) was established the responsibility for the nation's mail and telephone services fell on Post Offices. The Bendigo Post Office, built in 1887 and situated on Pall Mall was the central distribution centre for receiving and delivering telegrams and continued to deliver communication and postal services until 1997. Now a Visitor Centre, dedicated volunteers at the Post Office continued to demonstrate and educate the public about telegraphic services and the development of this unique form of communication up until 2019 when Covid 19 disrupted every day life, coupled with the death Ted Rankins (the last Post Master and a long term telegraph volunteer at the Post Office). This book was issued to Junior Postal Workers in Bendigo to guide them in the delivery of telegrams and designed to fit into their delivery satchels and carried while on the job. In the early years telegrams were delivered by bicycle and this manual is part of the postal collection donated by the Rankins family in memory of Ted. Small, blue, vinyl covered manual. Contains thirty printed pages covering all aspects of how to correctly deliver telegrams. Topics include 'Loss of telegram', 'Undelivered Telegram', 'special Delivery' and 'Beware of Dogs'. Bound with two ring metal clip. Front cover; Australian Post Office / Telecommunications Division / Telegram / Delivery / Instructions / Headquarters / 1962 Various annotations and updates throughout. ted rankins collection, bendigo post office, bendigo tourism, city of greater bendigo tourism, post office collection -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph, Hibernian Hall, 30/6/1947
A photo of the first property owned by Legacy, at 342 Swanston Street. After receiving money in memory of David H Dureau to purchase premises, Legacy purchased the old Hibernian Hall. However there were many issues with the property, including its suitability and the inability to gain vacant possession from the existing tenants. So eventually the property was sold and the money used to buy the current Legacy House, still formally known as the David H Dureau Memorial Building as per the bequest instructions. The notes on the back of the photo say it was sold to Sir Bernard Evans and then to RMIT and it was renamed Storey Hall. The full story of the donation has been pieced together from several sources. Part of the story of the donation towards Dureau House. BG Corporation in New York used 'Brown and Dureau' as agents in Melbourne for their spark plug manufacturing (for the American aircraft based in Australia during the war). A royalty of two shillings and sixpence was agreed. The entrepreneur President of BG Corporation was Richard Goldsmith. L/ Grat Grattan had a friend Mr Edwards who was managing director at Brown and Dureau and heard of the desire by Mr Goldsmith to leave a permanent memorial to ex-servicemen in Australia (Children's Hospital was considered). L/ Grattan took Mr Edwards to Market St (where Legacy was situated at the time) and showed him the inadequacy of the building. It was agreed if Melbourne Legacy could come up with a purchased building in 10 days they would get the money needed and the building was to be named in memory of David H Dureau, who had died at sea during the war. The donation was £27,059. The property purchased was 'Hibernian Hall' in Swanston St (later called Storey Hall when it was acquired by RMIT). After the war it turned out not to be suitable and a new building was required. An act of parliament was required to enable the sale (01262) and consent from the donor was also sought before the sale (document still to be catalogued). Money raised from the sale was used to purchase 293 Swanston St.A photo of the first property purchased by Legacy as a result of a generous donation.Black and white photo of the old Hibernian Hall in Swanston Street.Handwritten on back 'The old Hibernian Hall purchased by Melbourne Legacy and later sold because of inability to secure vacant possession from tenants. Sold to Sir Bernard Evans then to RMIT and named 'Storey House', in pencil. Stamped '30 Jun 1947' in purple inkproperties, dureau house, swanston st -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Glass plate, circa 1866
This glass plate photograph shows good detail of members of the Warrnambool Garrison posing for their photograph in front of a young township. There are other well-dressed citizens behind them. The three men with frogging on their sleeves were commanders were likely to be commanders. The men are facing north with Cannon Hill and the fortification area in the background. It dates from the 1860s. The firearms held appear to be 1853 pattern Lee Enfield muskets used by the British army in Crimea at this time and in Australia, rather than the later Martini Henry cartridge rifles. The uniforms match other photos of the Warrnambool Garrison Militia and Band in our Collection, taken up until the 1880s. The three storey building in the photograph is likely to be the Manifold & Bostock flour mill, built in 1854 near the ‘cutting’ in Merri Street, which was one of the main streets at the time; if one faced the building’s front from a vantage point and looked south to south-east, the hills around Flagstaff Hill and Cannon Hill would be behind that mill, and the Harbour behind the hills. This is the area of the Fortifications. The glass plate method of photography was widely used during the mid-19th to early-20th century. The donor and maker of the photograph are unknown. Around this time the citizens of Victoria were prospering from the gold rush but felt isolated and uneasy about their security in the colony. In 1854 the Volunteer Act was passed to provide some military defence. In 1858 the Warrnambool Volunteer Rifle Corps was established, disbanded in 1863, then a new Warrnambool Detachment was formed in September 1866. Legislation was passed in 1884 that replaced the volunteers’ corps with a partly paid, permanent Militia Defence Force. The batteries manning the coastal forts of Victoria were termed Garrison Artillery Companies. When the Army was federated in 1901 there were eight Militia Companies in Victoria. Warrnambool and Port Fairy together were known as 8 Coy AGA (Australian Garrison Artillery). Changes to formation and name continued into the 20th century.This photograph is a record of the very early local defence force, circa 1866. The photograph signifies the connection of the colony in Victoria to the growing need for security due to the unrest in Europe at that time. The photograph is also locally significant to the industry of the young township of Warrnambool, showing what is likely to be one of the first flour mills in the town. The photograph is also the only example of the early methods of glass plate photography in our collection. Photograph, rectangular glass plate, positive sepia image. Photograph has brass framed edges that fold over to the back, with mitred corners. The front edges are pressed with a decorative floral pattern. The photograph shows a group of thirty military men, standing or kneeling, in dark uniforms with pillbox forage caps, round-collared jackets with light buttons, light sashes worn from top left shoulder to bottom right side of waist belt, and long, straight-legged trousers. Three of these men have light braid around the buttons on the front of their jackets, light frogging on their sleeve cuffs and stripes on the outside seams of their trousers. The other twenty-seven men have plain uniforms and are holding firearms in their right hands, steadied with their left hands. Other figures are standing behind this group of soldiers, including three or four men wearing top hats, jackets and ties. In the background is a row of buildings. The central building is three stories high. Bare hills are in the far background. The foreground is uneven ground with patches of short grass. Photographer looking towards the south east and Cannon Hill, with the Warrnambool Garrison facing north, ca.1860s.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, glass plate, photography 19th century, colonial forces, military defence, volunteer act 1854, volunteer rifle, garrison artillery, volunteer corps, militia, militia garrison band, pillbox forage caps, helpmann, manifold and bostock, 1853 lee enfield musket, tintype, warrnambool garrison, 1860s, cannon hill, manifold & bostock, flour mill, 3-storey building -
 Seaworks Maritime Museum
Seaworks Maritime MuseumDocument
Large paper document including colour illustrations of Melbourne Harbor Trust shield and other shields. Includes three wax seals attached to document with blue ribbon."To All and Singular to whom these presents shall come, Sire Anthony Richard Wagner/ Knight Commander of the Royal Victorian Order Garter Principal King of Arms. Sir John Lunamace Heaton Arm/ Strong Knight, Member of the Royal Victorian Order. Clarenceux King of Arms an Aubrey John Toppin Esquire/ Commander of the Royal Victorian Order. Norroy and Ulster King of Arms Send Greeting! Whereas Victor/ George Swanson. Esquire upon whom has been conferred the Australian Efficiency Decoration Chairman of the Melbourne Harbor/ Trust Commissioners hath represented unto The Most Noble Bernard Marmaduke, Duke of Norfolk, Knight of the Most/ Noble Order of the Garter Knight Grand Cress of the Royal Victorian Order, Earl Marshal and Hereditary Marshal of/ England and one of Her Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council that the Melbourne Harbor Trust Commissioners is a body/ corporate with perpetual succession and a Common Seal duly constituted by Act of Legislature of the Colony of Victoria number/ DLII bearing date Twenty second day of December 1876 the said Act having been amended from time to time and various Acts passed consolidating such amendments that under the said/ Act the exclusive management and control of the port and the preservation and improvement of the port generally as vested in the said Commissioners. That the Melbourne Harbour Trust/ Commissioners being desirous of having Armorial Bearings, Supporters and a Device or Badge duly assigned under lawful authority and he hath therefore requested the favour of His Grace's/ Warrant for Ouigranting and assigning such Armorial Ensigns and in the same Patent such Supporters and such Device or Badge as may be proper to be borne and used by the Melbourne/ Harbor Trust Commissioners on Seals otherwise accoding to the Laws of Arms. And forasmuch as the said Earl Marshal did by warrant under his hand and Seal bearing date the Sev-/ enth day of March 1962 authorize and direct Us to grant and assign such Armorial Ensigns and such Supporters and such Device or Badge Accordingly. Know ye therefore that we/ the said Garter Clarenceux and Norroy and Ulster in pursuance of His Grace's warrant and by virtue of the Letters of Patent of Our several offices to each of us respectively granted do/ by these Presents grant and assign unto the Melbourne Harbor Trust Commissioners the Arms following that is to say: Azure a representation of the constellation of the Southern Cross/ Argent on a Chief enarched on five Pallets of the first. And for the Crest Out of a Coronet composed of eight Masts each with sail set and upon Rim Or in front of a Bollard proper/ two Anchors in saltire Azure Mantled figure doubled Argent as the same are in the margin here of more plainly depicted. And by the Authority aforesaid We do/ further grant and assign the following Device or Badge that is to say: Two Anchors in saltire Argent as here depicted And by the Authority aforesaid the said Garter/ do by these Presents further grant and assign unto the Melbourne Harbor Trust Commissioners the Supporters following that is to say : On either side a Sea Horse/ (Hippocampus) or collared and lined Gules in front of a representation of the Melbourne Harbour front proper as the same are also in the margins here of more/ arms plainly depicted the whole to be borne and used forever hereafter by the Melbourne Harbour Trust Commissioners on seals otherwise according to the laws of/ Arms. In witness whereof we the said Garter Clarenceux and a Norroy and Ulster Kings of Arms have to these presents subscribed Our names and affixed the seals/ Of our Several offices this fith day of March in the Twelfth Year of the reign of our Soveriegn Lady Elizabeth the Second by the Grace of God of the United Kingdom of Great/ Britain and Northern Ireland and of Her other Realms and Territories Queen head of the Commonwealth Defender of the Faith and in the years of Our Lord One Thousand nine/ hundred and sixty three" "Prosperity Through Service" -
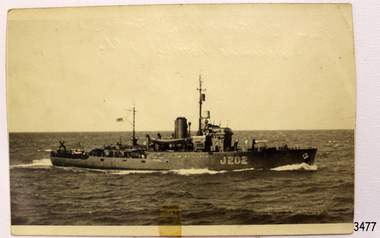 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel, H.M.A.S. Warrnambool J202, Between 1941-1947
This photograph is connected to the first HMAS Warrnambool (J202), which was one of 60 Bathurst class corvette vessels built during World War II by Mort's Dock & Engineering Co Ltd of Sydney under the commission of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). It was the namesake of the City of Warrnambool in Victoria. The armed minesweeper was 57 metres long and could had a complement of 85 personnel. Its armament included 1 × 4 inch Mk XIX gun, 1 × 40 mm Bofors AA gun (installed later), 3 × 20 mm Oerlikon guns (1 later removed), machine guns and depth charge chutes and throwers. It was launched in Sydney in May, 1941. The HMAS Warrnambool began service with patrols off Bass Strait in 1941. In December the ship docked in Warrnambool Harbour and the crew marched in a parade along Timor Street. The ship’s crew received a donation of 110 books from the Warrnambool Patriotic Fund, and a plaque of the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms presented by the Mayor, Cr. John R Astbury. In September 1942 a Dutch East Indies family, Samuel and Annie Jacob and seven of their eight children, was rescued by the HMAS Warrnambool and evacuated to Darwin. The family settled in Melbourne, then in 1944 Samuel tragically died. After the war ended the family was threatened with deportation under Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (known also as the White Australia policy). Annie married her landlord, John O’Keefe but was still issued a deportation order in 1949. The family appealed to the High Court and the case became famous for being the first successful legal challenge to the Act. The HMAS Warrnambool was in Darwin during the time it was bombed, attacked by the Japanese while rescuing 73 crew from a merchant vessel that had also been attacked. The ship was involved in several other rescues and carried troops to New Guinea. Other events included escort and patrol duties on Australia's east coast, then at Fremantle and back to Darwin. When the Japanese surrendered on September 11, 1945, at the end of World War II, the ship was at Timor. It performed mine clearance work around the Solomon Islands and New Guinea after the war. On 13th September 1947 the ship was sent to lead a flotilla at the Great Barrier Reef, off the Queensland coast. The mission was to clear the defensive British mines that were laid during1941-43 to protect Australia’s boarders. The HMAS Warrnambool hit a mine near Cockburn Reef, exploded and sank shortly afterwards. One of the 70 or so men on board was killed at the time and thirty-two men were badly injured; three of these also lost their lives. The four deceased were Victorian seamen. The wounded men were transferred by boats to the nearby HMAS Swan II, where the Swan’s and the Warrnambool’s doctors cared for them. The HMAS Swan II took the survivors to Cairns, and from there the men were flown by RAAF to either Brisbane or Sydney hospitals. The HMAS Warrnambool was the only RAN ship to be sunk by a mine, and the four who lost their livers were the last naval casualties from World War II. The ship’s wartime service was recognised by three honours. In May 1948 a number of items were recovered by Navy divers from the wreck of HMAS Warrnambool. The items included the ship’s bell (inscribed HMAS Warrnambool 1941) and the round plaque with the Seal of the Warrnambool City Council. In 1949 the plaque was returned to the Council, and the bell was donated to the Australian War Memorial. Further objects were recovered by the new owners of the wreck, Southern Cross Diving and Salvage, in 1972-75. A memorial plaque, honouring the memories of all those who served on the HMAS Warrnambool until is sunk on September 13 1947, was erected in Warrnambool on September 13, 1995. NOTE: (1)- The second HMAS Warrnambool (FCPB204), also the namesake of the City of Warrnambool, was built in 1980 in Cairns, one of fifteen Fremantle Class Patrol Boats ordered by the RAN. It was just over 41 metres long with a compliment of 22 personnel. It patrolled Australia’s northern waters for illegal fishing vessels. This vessel was decommissioned in 2005. (2)- There was also a steam and sail ship named the S.S. Warrnambool, built in 1892 in London and broken up in 1926.This photograph is significant for its association with Royal Australian Navy and its vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (j202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWIIBlack and white photograph of vessel H.M.A.S. Warrnambool J202 on an open sea. The identifying number is painted on the hull. The ship is flying a white ensign. A lifeboat is suspended near the centre of the ship. Figures can be seen on deck. Hand written inscription on the reverse side. On ship's hull "J202" On reverse of photo "From P.O. FRED MATTHEWS. 23378. R.A.N." "MARIBYRNONG MAIDSTON RSL" "H.M.A.S. WARRNAMBOOL"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, photograph, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, ship’s bell, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, sinking ship, sunk ship, immigration restrictions act 1901, white australia policy, samuel and annie jacob, john o'keere, minesweeper -
 Red Cliffs Military Museum
Red Cliffs Military MuseumCertificate, Certificate of Promotion in Rank, 5/12/1923 (exact)
This certificate and 5 other documents from the Walter Thomas West Collection, are in a frame 90.40cm x 66.50cm, which has non reflecting glass.Official Australian Government Certificate.Possibly written in old English script and carries the Royal Seal.Main face of Certificate. "His Excellency the Right Honorable Henry William Baron Forster a member of his Majesty's Most Honorable Privy Council Knight Grand Cross of the most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George, Governor General and Commander In Chief of the Commonwealth of Australia. To Walter Thomas West Greeting: By virtue of the provisions of the Defence Act 1903 - 1918 and of all the other powers me enabling I, Henry William Baron Forster, the Goveneror General a foresaid acting with the advice of the Federal Executive Council, do gereby appoint you to be an officer of the Military Forces of the Defence Force of the Commonwealth from the First Day of January 1920. And I direct you diligently to discharge your duty as such officer in the rank of Lieutenant or in any higher rank to which the Governor General is pleased to promote or appoint you. Given under my hand and the seal of the Commonwealth this first day of October One Thousand Nine Hundred and Twenty Three. By the Excellency's Command. (signed) E.K. Bowden" Left Hand side Margin: Entered on record by me, in Register of Patents No 40 Page 2 this 5th day of December, One Thousand Nine Hundred and Twenty Three.of, ww1, walter, thomas, west, mm, mc, photo, register, patents, no40, page, 2, , 1923, collection -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - THE MAYORAL AUXILIARY, 25 Sept. 1947
The Mayoral Auxiliary. Entertainment arranged by The Mayoral Auxiliary in aid of The Food For Britain Appeal. 25 Sept., 1947. Part 1 - Musical Programme. 1.Piano & Violin: Misses Leggo & McNair. Vocal Solo: Mr Arthur Nicholls. Trio: Mesdames Ennor & Lober & Miss Pianto. Dramatic Scene, Song & Dance: Miss Janice Morgan. Vocal Solo: Mr Beckwith. Specialty Act: Miss Gladys Brown. Vocal Solo: Mrs Ennor. Part 2 - Dramatic Entertainment. Dramatic Personage: Dreamer: Mr Jack Hocking. Grandparents: Mr Mac Walker & Mrs Oliver. Suitors: Messers Beckwith & Harvey. Daughter: Miss Letty White. Dancer: Miss Eileen Clarke. Sports Girl: Miss Mary Stanistreet. Marie & Mary: Misses A Taylor. The Cook & the Lady: Misses Dorothy Farmer & Helen Sargeant. Widow: Miss Beverly Dyer. Sister: Miss Judy Edwards. Bride: Miss Phyllis Farmer. Nanny & the Children: Mrs T O Hunter, Misses Janice Morgan & Gladys Brown. Nurses: Misses D Farmer & Helen Sargeant. Orchestra: Misses Leggo (Piano); McNair (Violin) & Kerr (Viola). Costumieres: Mr & Mrs L V Lansell. Cake Stall: Mesdames Amer, Bryenton & Poulston. Sweets: Mesdames Chellew & Guthery. Sellers: Girls School Students. Doorkeepers: Mesdames Anderson and Streader. Sweets supplied by Girls School, High School, Mr Wilkinson, Mrs Body, Misses Burgess & Weller. Tickets donated by Mr Albert Matthews. Stage Manager: Mrs T O Hunter. Compere: Mess L MacGillivray. Assistant: Mr L M Green. 3 copies of program 4268 a,b,c. 4 pages.entertainment, theatre, the mayoral auxiliary, the mayoral auxiliary in aid the food for britain appeal. 25 sept., 1947. piano & violin: misses leggo & mcnair. vocal solo: mr arthur nicholls. trio: mesdames ennor & lober & miss pianto. dramatic scene, song & dance: miss janice morgan. vocal solo: mr beckwith. specialty act: miss gladys brown. vocal solo: mrs ennor. dramatic personage: dreamer: mr jack hocking. grandparents: mr mac walker & mrs oliver. suitors: messers beckwith & harvey. daughter: miss letty white. dancer: miss eileen clarke. sports girl: miss mary stanistreet. marie & mary: misses a taylor. the cook & the lady: misses dorothy farmer & helen sargeant. widow: miss beverly dyer. sister: miss judy edwards. bride: miss phyllis farmer. nanny & the children: mrs t o hunter, misses janice morgan & gladys brown. nurses: misses d farmer & helen sargeant. orchestra: misses leggo (piano); mcnair (violin) & kerr (viola). costumieres: mr & mrs l v lansell. cake stall: mesdames amer, bryenton & poulston. sweets: mesdames chellew & guthery. sellers: girls school students. doorkeepers: mesdames anderson and streader. sweets supplied by girls school, high school, mr wilkinson, mrs body, misses burgess & weller. tickets donated by mr albert matthews. stage manager: mrs t o hunter. compere: mess l macgillivray. assistant: mr l m green. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MCCOLL, RANKIN AND STANISTREET COLLECTION: NEW STAR GOLD MINE HARRIETVILLE NL, 1935
McColl Rankin & Stanistreet, New Star Gold Mine Harrietville NL. a/ Agreement to purchase the mining operations and land at Black Snake Creek, Dargo, Mining District of Gippsland. For Mining Leases numbers 5187 & 5195, 31 acres. The purchaser Company is to be called Kong Meng Gold Reefs NL. Dated: 16/2/1935. Signed: J A Michelsen?, C Kingsley?, J Stanistreet, E R Grelis & ??? Inscriptions: Signed sealed and delivered by the said Ronald Alexander Rankin in the presence of E R Grelis. b/ Leasehold. Transfer of Land situated in the Parish of Dargo County of Dargo Mining District of Gippsland from New Star Gold Mine Harrietville NL to Kong Meng Gold Reefs NL. Dated: 12/3/1935. Signed: G ??, Geo ??, Stanistreet, G ??, Jamie Jeps ? Markings: pencil line through Gold Mining Lease No. 5187 change to a Leasehold Estate, line through January to be changed to March. c/ Indenture (copy of b/ with adjustments made) New Star Gold Mine Harrietville NL with Kong Meng Gold Reefs NL. Dated 13/3/1935. Signed: G ??, Geo ??, Stanistreet, G ??, Jamie Jeps ?, Stanistreet. d/ Carbon copy of a/. Signed: J A Michelsen?, C Kingsley?, J Stanistreet, E R Grelis & ??? Inscriptions: Signed sealed and delivered by the said Ronald Alexander Rankin in the presence of E R Grelis, J Stanistreet. e/ Indenture, agreement between New Star Gold Mining Harriet NL and Kong Meng Gold Reefs NL, was on the 9/3/1935 registered and Incorporated under the Companies act 1928 Part 2. Signed: E R Grelis, J Stanistreet, G ??, Geo ??, Stanistreet, G M?, Stanistreet. Dated: 12/3/1935.organization, business, gold mine, mccoll rankin & stanistreet new star gold mine harrietville nl black snake creek parish of dargo county of dargo mining district of gippsland mining leases numbers 5187 & 5195 kong meng gold reefs nl 1935 -
 Plutarch Project
Plutarch Project16mm Portable Optical & Magnetic Sound Projector, circa 1950's
One of the three projectors used in every trip was this 16mm Portable Projector, which was used taken to about 60 towns and cities around Australia, as Mr Yiannoudes states. This projector is in working condition serviced by Mr Yiannoudes himself regularly. It is an optical and magnetic sound projector, a rare one of its type.Primary historic significance as well as rarity significanceFrom January 1959 and until 1982, “Cosmopolitan Motion Pictures”, owned by Mr Peter Yannoudes (Παναγιώτης Γιαννούδης) and Mr Stathis Raftopoulos (Στάθης Ραφτόπουλος) travelled around Australia to entertain the Greek, Turkish, Indian and Yugoslav speaking population of Australia and provide a significant cinema culture. They travelled as far as Perth in WA, Adelaide in SA, Tasmania, Darwin in Nt, Canberra in ACT and Sydney and NSW. However they found themselves also in places like Berri and Renmark in NSW, where concentrations of migrants lived and thrived during the period. Initially they were travelling by train, carrying all their equipment by hand and placing them in boxes and suitcases. However after 1962 when they acquired their first automobile, travelling became less of a burden, nevertheless cumbersome and laborious. They carried with them initially two portable projectors (second one as a backup) and at times travelled with a third in order to ensure that technology will not be letting them down at the time of film projection. At times the films were projected onto a white sheet of cloth because there was no proper screen to project it on at the venue they were using. One of the three projectors used in every trip was this 16mm Portable Projector, which was used taken to about 60 towns and cities around Australia, as Mr Yiannoudes states. This projector is in working condition serviced by Mr Yiannoudes himself regularly. It is an optical and magnetic sound projector, a rare one of its type. Apart from this projector these items were taken on each trip. -a- 3 projectors in total -b- 2 tripod stands -c- 1 20 feet x 10 feet screen -d- 6 projector lamps and 2 exider lamps for sound -e- 2 extra lamps per film to be shown -f- 1 film rewinder (see rewinder in same collection)Siemensprojector, film, magnetic, sound, optical, language, greek, siemens, german, γιαννούδης, προβολέας, yiannoudes, plutarch -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MELBOURNE SYMPHONY ORCHESTRA, CAPITAL THEATRE, BENDIGO
Melbourne Symphony Orchestra, Capital Theatre, Bendigo. Tuesday 16th August, 8pm. The Australian Broadcasting Commission presents Sir Bernard Heinze. These concerts are arranged by the Australian Broadcasting Commission in conjunction with the Government of Victoria. Rogramme: Fifteen Cents. Articles with photos of on Sir Bernard Heinze and Wayne Rapier. Annotations. Geelong A.B.C. Subscribers' Committee Members 1966. President: Mr J A Brockman. Secretary: Mr J E McClellend. Committee: Miss A France, Miss E Sheridan, Mrs G Brook, Mrs W G L Cartwright, Mrs HC Fallaw, Mrs R H Hoe, Mrs H G Marfell, Mrs G Pennan, Mr & Mrs D O Davey, Mr C P S Billot, Mr Mervyn Callaghan, Mr E A Goding, Mr J L Grant, Mr R Heagney, Mr P H Larsen, Mr F Loxley, Mr N G Schultz, Mr J Phemister, Miss J Cullen. Australian Broadcasting Commission Constituted under the Broadcasting and Television Act, 1942-1965. Commissioners: J R Darling, E R Dawes, A G Lowndes, H B Halvorsen, J T Reid, Mrs. Dorothy Edwards, General Manager: T S Duckmanton. Manager for Victoria: E A Whiteley. Melbourne Symphony Orchestra (Season of 1966). Leader of Orchestra: Leonard Dommett. First Violins: Bertha Jorgenson, Paul McDermott, Leon La Gruta, Milton Holden, Brian Beatty, Ronald Layton, Rudolf Osadnik. Second Violins: William Glassford, Alex Burlakov, Chrles Reither, Ivan Pietruschka, Robert Pattison, Percy Pledger. Violas: Marston Bate, Henry Wenig, -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ROYAL PRINCESS THEATRE COLLECTION: MAJORIE IN WONDERLAND, 12 Aug 1916
Royal Princess Theatre - Majorie in Wonderland. Saturday, 12 August, 1916. Price of Program, One Penny. Australian Children's Pantomime. Matinee Performance. In Aid of Fruit and Vegtable Fund For Our Soldiers in The Trenches. Produced by Miss Girlie Mackay. Children's Vocal Training by Madame Rossow. Dialogue by Miss Eileen O'Keefe. Musical Director, Mr Stanley Upton. Stage Manager, Mr J Dunphy. Lighting Effects Mr W Wenborn. Theatre kindly lent by W Crowley, Esq. Hon. Sec., Norman Howell. Prologue. The curtain rises showing the flowers asleep. The fairies, summoned by daylight, entre and sing, awakening the flowers, and leave. Then Puck entres, followed by the Blue Wrens, singing, and after them the Bunnies, who are all . . . Sale of Sweets supervised by Miss Nita Weller and Assistants. Novelties by Mrs Julius Cohn. Dresses designed and made by Mrs McQuie, Mrs Marc Cohn, Miss Lena Weller, and Miss Girlie Mackay, assisted by Mrs Balsillie, Mrs Ralph Ross. Mrs Robert Makayand the Misses Gladys McQuie, Norma Moorhead, Carola Iser, and Hilda Meurer. Program: Songs sung throught Performance. Act I. 1 Chorus-Fairy Song. 2 'Bunnies' Adventure' by the Bunnies. 3 Chorus-Holiday Song. 4 Bell Bird Duett-Jean & Jim Walker. 5 Sailor's Hornpipe-Crissie Cravino. 6 'Marjorie Sunbeam'-Myrtle Glanville. 7 'As I went o'er the Paddock'-Jean Walker. 8 Chorus'Billy Tea. 9 Song-'Possum'-Bertie Barkell. 10 'Bogie Man'-Stella Coghlan. 11 'Kookooburra'-Mel Wearne. 12 Chorus-'Winter Bells'. Act II. 1 Chorus-'Autumn Winds'. 2 'Stay Little Wave'-Jean Walker. 3 'Southern Cross'-Rose Murphy. 4 Song-'Kangaroo'-Brownies. 5 'Pixie Man'-Ruthie Murphy. 6 Chorus-'Wattle'. 7 'Grow Little Mushroom'-Stella Cook. 8 'Cooee'-Myrtle Glanville & Marie Hamilton. 9 Butterfly Dance-Sheila Shannon.10 'King Billy & Black Mary'-Ken McQuie. 11 Boomerang Song-Ken McQuie. 12 Final Chorus-'To the Fairies', 'Good Night'. God Bless Our Splendid Men. Cast of Characters:Marjorie & Jean Walker, Myrtle Glanville, Ruthie Murphy, Marie Hamilton, Thelma Thomas, Stella Coghlan, Jim Walker, Jim Long, Bertie Barkell. Fairies:-Mary Hunter, Lily Brown, Una Grelis, Biddie Bulley, Rosa Dyring, Ellie Colcough, Ida Collins. Puck:-Una Leggo. Butterfly:-Sheila Shannon. Brownies:-Tom Green, Douglas McQuie, Hunphrey, Gill, Mel Wearne, Laurence Skewes. Aboriginal:-Ken Mquie. Frog:-Sid Whitelaw. Native Bear:-Ken Moore. Blue Wrens:- Alma Jorgenson, Doris Reed, Geoff Schultz, Jean Cahill. Flowers. Orchids:- Joyce Ross, Margaret Long, Dorothy Thomas, Margaret McQuie, Mollie Roberts, Rose Murphy. Pink Gums:-Lorna Weddell, Minnie Hartley, Isola Woodward, Jean Moran, Decima Holtorf, Merle Nagel. Flannel Flowers: Gwen Hunter, Nancy Tatchell, Catherine Green, Mary Rymer, Thelma Cairns, Cecil Gleeson. Poppies:-Lorna Cattran, Alice Murphy, Maisie O'Grady, Eileen Coglan, Alma McWilliams, Jean Miller. Blue Bells:-Mavis Tozer, Vivian Reed, Monnie Fattorini, Gwennie Seely, Alice Evans, Lily O'Conner. Southern Cross:-Eileen Martin, Jean Murdoch, Effie Williams, Verna Mayne, Minnie Hartley, Mollie Martin.Cambridge Press, Print.program, theatre, royal princess theatre, royal princess theatre - majorie in wonderland. 12 august, 1916. program, one penny. australian children's pantomime. matinee performance. in aid of fruit and vegtable fund for our soldiers in the trenches. produced by miss girlie mackay. children's vocal training by madame rossow. dialogue by miss eileen o'keefe. musical director, mr stanley upton. stage manager, mr j dunphy. lighting effects mr w wenborn. theatre lent by w crowley, esq. hon. sec., norman howell. prologue. the curtain rises showing the flowers asleep. the fairies, summoned by daylight, entre and sing, awakening the flowers, and leave. then puck entres, followed by the blue. . . sale of sweets supervised by miss nita weller and assistants. novelties by mrs julius cohn. dresses designed and made by mrs mcquie, mrs marc cohn, miss lena weller, and miss girlie mackay, assisted by mrs balsillie, mrs ralph ross. mrs robert makayand the misses gladys mcquie, norma moorhead, carola iser, and hilda meurer. program: songs sung throught performance. act i. 1 chorus-fairy song. 2 'bunnies' adventure' by the bunnies. 3 chorus-holiday song. 4 bell bird duett-jean & jim walker. 5 sailor's hornpipe-crissie cravino. 6 'marjorie sunbeam'-myrtle glanville. 7 'as i went o'er the paddock'-jean walker. 8 chorus'billy tea. 9 song-'possum'-bertie barkell. 10 'bogie man'-stella coghlan. 11 'kookooburra'-mel wearne. 12 chorus-'winter bells'. act ii. 1 chorus-'autumn winds'. 2 'stay little wave'-jean walker. 3 'southern cross'-rose murphy. 4 song-'kangaroo'-brownies. 5 'pixie man'-ruthie murphy. 6 chorus-'wattle'. 7 'grow little mushroom'-stella cook. 8 'cooee'-myrtle glanville & marie hamilton. 9 butterfly dance-sheila shannon.10 'king billy & black mary'-ken mcquie. 11 boomerang song-ken mcquie. 12 final chorus-'to the fairies', 'good night'. god bless our splendid men. cast of characters:marjorie & jean walker, myrtle glanville, ruthie murphy, marie hamilton, thelma thomas, stella coghlan, jim walker, jim long, bertie barkell. fairies:-mary hunter, lily brown, una grelis, biddie bulley, rosa dyring, ellie colcough, ida collins. puck:-una leggo. butterfly:-sheila shannon. brownies:-tom green, douglas mcquie, hunphrey, gill, mel wearne, laurence skewes. aboriginal:-ken mquie. frog:-sid whitelaw. native bear:-ken moore. blue wrens:- alma jorgenson, doris reed, geoff schultz, jean cahill. flowers. orchids:- joyce ross, margaret long, dorothy thomas, margaret mcquie, mollie roberts, rose murphy. pink gums:-lorna weddell, minnie hartley, isola woodward, jean moran, decima holtorf, merle nagel. flannel flowers: gwen hunter, nancy tatchell, catherine green, mary rymer, thelma cairns, cecil gleeson. poppies:-lorna cattran, alice murphy, maisie o'grady, eileen coglan, alma mcwilliams, jean miller. blue bells:-mavis tozer, vivian reed, monnie fattorini, gwennie seely, alice evans, lily o'conner. southern cross:-eileen martin, jean murdoch, effie williams, verna mayne, minnie hartley, mollie martin. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Gippsland Institute (Affiliated with Monash University) Handbook, 1990, 1990
The Councils of Monash University and Gippsland Institute of Advanced Educaiton agreed to the Gippsland Institute becoming an affiliated institution of Monash University. This was the first step in a process where the Gippsland Institute was to become a constituent of the university, the establishment of which was subject to amending legislation. Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat had a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is Australia’s newest public University. Headquartered in Ballarat, Victoria, the University offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. With campuses from Horsham in the west of the state, to Churchill in the east, the name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses contributing to a new and different Australian university.grey and red soft covered book.gippsland institute of advanced education, monash university, churchill, federation university, t. kennedy, b.g. bremner -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Gippsland Institute Information for Prospective Students, c1989
Aqua soft covered book relating to the Gippsland Institute. The contents include Aboriginal Studies, Accounting, Administration, Applied Science, Business, Computing, Engineering, Nursing, Psychology, Primary Teaching, Secondary teaching, Social Sciences, Visual Arts and Welfare.non-fictiongippsland institute, monash university gippsland, gippsland university college, churchill, gippsland, computing, computers, teacher education, engineering, gippsland campus, gippsland campus collection
