Showing 544 items matching "size 6"
-
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAdministrative record - COMPENDIUM WW1 - WW2, 4) A H Pettifer, Government Printer et al, 2) 14.2.1946; .3) 1.3.1919; .4) 30.11.1954 .5) 24.11.19? - WWI; .6) 31.10.1917; .7) 12.6.1917; .8) Page 1: 20.12.1915, Page 2: 10.12.1915, Page 6: 19.1915; .9) 10.9.1918; .10) 18.4.1919; .11) c.2.3.19?; .12) 18.9.1920; .14) post WWI; .15) 24.4.1920; .17) 18.4.1942; .18) 19.6.1943; .19) 18.3.1947; .20) 1944; .21) 1944; .23) 22.10.1941; .26) 13.9.1944; .27) 1.1944; .30) 7.3.1950; .31) 31.7.1944; .32) 16.4.1942; .33) 13.6.1946; .34) 6.5.1946; .36) a) & b) 3.11.1947; .37) 24.10.1951; .38) 24.9.1957; .39) 9.10.1957; .40) 19.2.1958; .41) 26.2.1958; .42) 1.3.1958; .43) & .44) 7.3.1958; .45) 25.2.1958; .46) 3.1.1948; .47) 26.2.1948; .48) 22.4.1958; .49) 24.2.1958; .50) 12.3.1958; .51) 6.1958; .52) c.Mar/Apr 1958; .53) 5.4.1958; .54) c.end WWII; .55) a.b. 13.6.1967; .56) 26.5.1967; .57) 18.2.1954
Herbert Trangmar Allan, refer 2755.4 for his extensive service history and wards. .2) Details gifting of a pair of Japanese binoculars to Col H T ALLAN by Pacific Island Regiment. .3) Certificate issued by Winston Churchill, Secretary of State for War (The War of 1914-1918), awarded to Capt H T ALLAN MC. .4) Herbert Trangman ALLAN born 5.1.1895 at Woolwich, NSW. Middle name misspelled, should be Trangmar not Trangman. .6) Congratulating H T ALLAN on receiving the Military Cross award for leading 2 companies which had lost officers during action on Passchendaele Ridge on 9.10.1917. .7) Describes life behind the lines whilst H T ALLAN's battalion has been resting for a month. Daily life consisted of training drills, sport & entertainment. Writer takes time to describe the countryside & weather. .8) Relate to H T ALLAN's military exam results & his promotion to 2nd Lieutenant in 1915. .9) To Herbert Allan's father, Mr P Allan detailing the citation for awarding of the Military Cross to Herbert ALLAN. Original citation appeared in the London Gazette,5.4.1918. .10) Form addressed to Capt H ALLAN MC, 17th Battalion stating his period of enlistment in the 1st AIF was to expire 26.5.1919. .11) Letter from Lord BIRDWOOD (General) to Herbert ALLAN in response to a letter received 19.11.19?. General BIRDWOOD expresses his opinions on difficulties the allied troops face in their fight against the Japanese. .12) Letter to Capt H T ALLAN advising of MID oak leaves sent to him. Details guidelines for attaching oak leaves to both the larger Victory Medal & the small service dress medal. .13) Form details H T ALLAN's WWII Army No, Rank, Unit & Decorations & Medals held. The form has not been signed & dated. .14) Details service record of Lt Col H T ALLAN NX12229. Includes military service from 1912 - 1944, schools & courses attended, decorations, promotions & overseas service. .16) Form issued to H T ALLAN on 15.12.1939 granting permission to leave New Guinea for Australia & return within a period of 12 months. Issued by Customs Office in Salamaua. Lists H T ALLAN's age as 44, height 5' 10" & occupation. .17) Letter from Major General MORSHEAD GOC, AIF (ME) to Major H T ALLAN, OBE, MC congratulating him on being awarded the OBE for outstanding service at Tobruch. .18) Letter from Major General MORSHEAD to Major H T ALLAN, OBE, MC replying to ALLAN's letter of 15.6.1943. MORSHEAD is congratulating ALLAN on his appointment to New Guinea Force, also acknowledges his excellent service record. .19) Letter acknowledges H T ALLAN's resignation from the Office of Production Member of the Australian New Guinea Production Control Board, effective from 28.8.1946. .20) Major General WINDEYER commanded the 20th Brigade from 1942-1946. .22) Card sent from the CO of the 3rd Australian Anti-Tank Regiment. .23) Menu for Farewell Dinner held in the Officer's Mess of the 20th Infantry Brigade, Tobruch on 22.10.1941. .24) Menu & Toast list for Farewell Dinner to Brigadier J J MURRAY DSO MC VD. Attended by H T ALLAN & held in the Officers Mess, 2/17 Australian Infantry Battalion on 22.12.1941. .25) Invitation to Col H T ALLAN by Lady Gowrie (wife of Governor General Baron Gowrie) to attend a Luncheon at Government House, Canberra, ACT. .26) Letter to Major (T/Lt Col) H T ALLAN from Major W A JENNER advising him of his secondment to 2/17 Australian Infantry Battalion & appointment to command 5 Aust Base Sub Area. .27) Application for Africa Star with Eighth Army Clasp signed by H T ALLAN & approved by Lt Colonel of 2/17 Australian Infantry Battalion. H T ALLAN held the rank of Major (substantive) at the time of qualification, 1.3.1942 - 11.1942. He held the rank of Lt Colonel at the time of application in 2.1944. .28) Detailing changes in command & promotions including that of Lt Col H T ALLAN, dated 1.4.19? .29) For Lt Col H T ALLAN detailing movements required by First Australian Army command. .30) Acknowledgement & confirmation of Col H T ALLAN's application for campaign awards for WWII. .31) Letter addressed to Lt Col H T ALLAN from Lt Gen Stanley Sauige requesting information on New Britain for a forthcoming visit. .32) Certificate was presented to H T ALLAN on 16.4.1942 when he was awarded an OBE by King George VI. .33) Document details H T ALLAN's relinguishing of Command of the HQ of Pacific Islands Regiment. ALLAN also relinguished the rank of temporary Colonel & was transferred to the Reserve of Officers with rank of substantive Lt Colonel. .35) Official letter to Colonel H T ALLAN from Joseph Francis, Minister for the Army. The letter acknowledges Col ALLAN's long & distinguished career during both peace & wartime. .36) a) & b) From H T ALLAN (assumed) to Prime Minister J B CHIFFLEY referring to the production of copra in New Guinea, the actions of the Commonwealth Bank in relation to planters & the collaboration of New Guinea natives with the Japanese. Assumed to be a copy of original. .37) Letter to H T ALLAN indicating he had been placed on the Retired List with the rank of Honorary Colonel. .38) Letter invites H T ALLAN to officially open the State Conference in Lae in late March or early April 1958. Invitation was extended due to H T ALLAN for distinguished service in PNG. .39) Letter to H T ALLAN thanking him for accepting the invitation to open the Papua & New Guinea State Conference in late March or early April 1958. .40) Letter from H T ALLAN to Lt Gen Sir Henry WELLS, Chief of the General Staff, Victoria Barracks, Melbourne. ALLAN requests permission to wear his uniform for official engagements during his upcoming visit to New Guinea. ALLAN also offers advice on how to deal with native troops including serving time with them, learning their language & studying their customs. He suggests that this would help quell & dissent & revolt. .41) Reply from Major General DALY to HT ALLAN thanking him for his offer to spend time with the CO of the Pacific Island Regiment to address concerns with that unit. This meeting would coincide with ALLAN's upcoming visit to PNG. .42) HT ALLAN's reply to Major General T J DALY's letter of 26.2.1958. ALLAN requests an opportunity to discuss PIR issues with Major General DALY prior to his visit to PNG. .43) Major General T J DALY's reply to HT ALLAN's request for a meeting to discuss ongoing issues with the Pacific Island Regiment. .44) Letter from HT ALLAN to Brigadier D M CLELAND notifying him that he will be staying in Port Moresby on his way to the RSS&AILA Congress in Lae. .45) Lieutenant Colonel MCGUINN writes to invite Colonel ALLAN to visit the PIR during his visit to New Guinea at the end of March of the beginning of April 1959. .46) Letter of appreciation to H T ALLAN thanking him for his efforts in presenting the case for the Territory of New Guinea during the post WWII transition period. .47) Letter to H T ALLAN from New Guinea Citizens Association, Lae Branch, thanking him for his service on behalf of the people of the Territory of New Guinea. The association offered to send ALLAN a suitable present in recognition of his service. .48) Major General T J DALY's reply to HT ALLAN's suggestions for handling disquiet amongst the native troops in the Pacific Island Regiment. .49) Reply from Lieutenant General WELLS to H T ALLAN granting him permission to wear his uniform on his forthcoming visit to New Guinea. WELLS also notes that he has passed other requests made by ALLAN to Major General DALY. .50) Copy of H T ALLAN's reply to Lieutenant General WELL's letter of 24.2.1958 [.49)]. .51) A written account of Colonel H T Blue ALLAN's visit to New Guinea in 3.1958. Article appeared on p.65 & 67 of the 6.1958 edition of Pacific Islands Monthly. .52) Newspaper account of Colonel H T Blue ALLAN's opening of the Rabaul Branch of the Native Ex Servicemen's Association. Colonel ALLAN spoke of the involvement of the Pacific Islands Regiment during WWII. .53) The Rabaul Times account of Colonel H T Blue ALLAN's opening of the Rabaul Branch of Native Ex Servicemen's Club. Featured on p1, concluded p3. .54) Biographical account of Colonel H T ALLAN's service in WWI & WWII. In addition an account of his success in New Guinea between the wars is included. .55) a.b. Biography of Colonel H T ALLAN written by R W Robson who was the founder of the Pacific Islands Monthly. Article was written following ALLAN's death on 23.5.1967 aged 72. This item is a pre publication copy of Robson's article which appeared in the Pacific Islands Monthly. .56) Text of a valedictory given at the funeral of Colonel Herbert Trangmar ALLAN OBE, MC, ED, NX12229 held 26.5.1967 following his death on 23.5.1967. The speech summarized his life in both wars & civilian life. 57) Invitation issued to Colonel H T & Mrs ALLAN to attend a Garden Party at Government House on 18.2.1954. At this function Colonel H T & Mrs ALLAN were to be presented to her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II.Herbert T ALLAN Collection. The contents are all of various size, the Album is the size documented. .1) Large teal green album containing 16 plastic pockets each with white card insert. Various documents & photos contained in each pocket. .2) Typed letter, black type on cream paper. .3) Certificate mounted on fawn card backed with dark brown veneer. Presented to Capt H T ALLAN MC for being mentioned in despatches on 7.11.1917. .4) New South Wales Birth Certificate extract, printed on pink paper with watermark. .5) Telegram on tissue paper to a sheet of cream paper. Pin located top L corner. Requests the attendance of Lt Herbert ALLAN, Russell Hotel, Russell Square. .6) Typed letter mounted on grey cardboard. .7) 2 page letter on foolscap paper, secured by pin top L corner. Written from France by Herbert (Bert) ALLAN & addressed to his father. .8) 11 pages secured with a clip top L corner. 1st document typed, 2nd handwritten, remainder printed. Relate to H T ALLAN's military exam results. .9) Typed letter from Department of Defence Base Records Office to P ALLAN. .10) Document, printed form to inform the recipient that their period of enlistment in the 1st AIF had expired. .11) 4 page handwritten letter on 2 sheets of paper. 1st page has a printed letterhead. .12) BR Form No 20. Typed formal letter from AIF Base Records Office to accompany Mentioned in Despatches oak leaves sent to the recipient. .13) Form AAFA36 used for recommending the awarding of an Efficiency Decoration. Form details service record & details of a serving soldier. .14) 1 large / 1 small page, numbered, detailing the service record of Lt Col H T ALLAN. Black type on cream paper. 2 pages are loose but evidence of attachment visible. .15) Bachelor of Arts Degree Certificate (testamur) granted by the University of Sydney, awarded to Herbert Trangmar ALLAN. Printed on cream parchment. .16) Proforma document issued by the Territory of New Guinea permitting leave & return to the Territory. Printed 2 sides, black type on cream paper. .17) Letter on Australian Imperial Force letterhead from Major General MORSHEAD to Major H T ALLAN. .18 Letter on HQ2 Aust Corps letterhead from Major General MORSHEAD to Major H T ALLAN. .19) Typed letter on External Territories letterhead from J R Halligan to H T ALLAN. .20) Cream Christmas card folded in 2, sent to H T ALLAN. On front in black lettering is HQ 20th Australian Infantry Brigade below black Rising Sun emblem. Inside in black lettering is With Best Wishes for Christmas and New Year. Christmas 1944. .21) Cream card folded in 2. Front illustration depicts a devil figure riding a platypus & carrying a pennant with 2/13 on it. The devil is depicted attacking a German & Japanese soldier. Below the devil is a boomerang with Greetings Xmas 1944 printed on it. Illustration is in green & black. Inside on LHS is a message from 2/13 Battalion. On RHS is a list of 2/13 battle honours from 1940-1943. On back in black print is 1944-1945 New Guinea Australia. .22) Cream Christmas card folded in 2. Front illustration in brown with word Greetings in green. RHS inside printing in green & brown letters. Artillery badge on back in brown. .23) Cream card folded in 2. Typed menu on cream paper attached inside. Front cover illustrated with 20th Infantry Brigade colour patch & a rat over a scroll with words - So What? .24) Cream card folded in 2. On front black printing accompanied by 2/17 Battalion colour patch that is black over green diamond shape. Inside a list of Toasts & Dinner Menu printed in black. Back page for autographs. .25) Cream invitation card. Black cursive script printing below gold crown on front. .26) Typed letter on cream paper. .27) Typed foolscap application form to claim the Africa Star. .28) & .29) Message form filled with typed orders. .30) Typed letter acknowledging an application for campaign medals & listing eligible awards. .31) Typed letter on bond paper. .32) Certificate on cream parchment. Black print in cursive script. Text details the awarding of an OBE to the recipient. .33) Typed text on Australian Military Forces letterhead. Cream paper. .34) Typed text. Temporary note for H T ALLAN's discharge from AMF. .35) Typed letter on Commonwealth of Australia, Minister for the Army letterhead. .36) a) & b) 2 page letter in black type on cream paper. Pages are loose, letter unsigned. .37) 1 page typed letter on Australian Military Forces letterhead. .38) & .39) 1 page typed letter on Return Sailors, Soldiers & Airmen's Imperial League of Australia, Papua & New Guinea Branch letterhead. .40) 1 page typed letter, unsigned. .41) Single sided typed letter on Australian Military Forces letterhead on cream paper. .42) 1 page typed letter, unsigned on cream paper. .43) Single sided typed letter on Australian Military Forces, Northern Command, Victoria Barracks, Brisbane letterhead on cream paper. .44) Single sided typed letter on cream paper. .45) 2 page typed letter on folded cream paper bearing the letterhead of the Pacific Islands Regiment. .46) 1 page typed letter on cream, lined paper. .47) 1 page typed letter on cream paper. .48) 1 page typed letter on Australian Military Forces, Northern Command Headquarters, Victoria Barracks, Brisbane letterhead on cream paper. .49) 1 page typed letter on Chief of General Staff, Australian Military Forces, Army Headquarters, Victoria Barracks, Melbourne letterhead on cream paper. .50) 1 page copy of an unsigned letter on cream paper. .51) Magazine article: Building a New Nation in New Guinea : Some advice from Colonel Blue ALLAN. Black & white article with a 2nd small section stapled to the main page. Large page features a black & white captioned photo of a group listening to a uniformed Officer deliver a speech. Also features advertising front & back. .52) Newspaper article: Official Opening of Native Ex Servicemen's Club. Black & white typed newspaper article featuring a captioned black & white photo of a uniformed Australian Officer & a group of New Guinea Ex Servicemen. .53) a. b. c. Newspaper article: Master Blue Came Back to the Islands: 4000 Attend Club Opening. 3 Section article cut from a newspaper. One part is the banner of the newspaper with date published. Other sections contain the text of the article. The larger section features a black & white photo of an Australian Army Officer in uniform. .54) Newspaper article, untitled. Black & white typed newspaper article with black & white caricature of an Australian Army Officer featured. .55) a. b. Magazine article: The Story of a Big Man who Loved Soldiering. 2 page black & white typed article with sub headings. .56) Text of a Speech. 2 page typed text written for a valedictory given at a funeral. Pages connected with a staple in the top L corner. .57) Printed, cream card invitation to a Garden Party for the recipient to meet Queen Elizabeth II & The Duke of Edinburgh. Text is in cursive script under the Coat of Arms of Her Majesty. .2) Signature ? Capt S C PIR. .4) Date of issue typed: 30.11.1954 Name of recipient: Herbert Trangman Allan Stamped: T Wells, Registrar General NSW .5) Handwritten: To Lt Herbert Allan, Russell Hotel, Russell Square. Typed: Buckingham Palace OHS. Your attendance is required at Buckingham Palace on Wednesday next the Twentyeighth inst (28.11.19?) at ten o'clock am service dress please telegraph acknowledgement Lord Chamberlain London. Stamped: Central District 24 NO 19. .6) Signed in pencil: W Birdwood. In pencil on back: 15 x 12. .8) p1: Handwritten signature. Copy dated 29.12.1915. p2 Handwritten in ink: P Allan Esq, Mount Hunter Hill. Military Examination. Copy dated 29.12.1915. Handwritten in pencil: Results: H T Allan. Tactics - Distinction 92% HE Barff p3 Underlined in ink: 38th Infantry Herbert Trangmar Allan to be 2nd Lieutenant (provisionally). Dated 16 June 1914. p5 Handwritten: Total 139. Lieut Allan tied with 15 others for 20 place. p7, 9, 10 & 11underlined in ink: H T Allan. p8 Underlined in ink: Allan HT. .9) & .10) Signature in black ink. .12) Handwritten signature in black ink: On back handwritten signature in black ink: Clive Wilkinson, Buddong, Robinson St, Chatswood. Also ? Rd, Cremorne Pt. .13) Handwritten in black ink: Details of HT Allan's Commission Service from 16.6.1914 - 18.2.1946. .15) Handwritten signature of the University Chancellor, Dean of Faculty of Arts & Registrar. Handwritten name of recipient. Seal of the University of Sydney imprinted bottom LHS. .16) Handwritten in black ink: Details of recipient. Stamped in red ink: New Guinea Customs. Stamped in blue ink: H M Customs, Cooktown, dated 17.12.1939. Handwritten on reverse: Signature. Stamped on reverse in red ink: New Guinea Customs, dated 15.12.1939. .17) & .18) Handwritten signature: Major General Morshead. .19) Handwritten signature in black ink: J R Halligan. .20) Handwritten inside in blue ink: Lt Col Allan. Good wishes from your many friends here. Signed by Major General Windeyer. .21) Inside LHS handwritten in blue ink: Lt Col Allan & an indecipherable signature. .22) Inside RHS handwritten: To Major (Blue) Allan OBE MC from Lt Col? .23) On front handwritten in blue ink: H T Allan?. Inside in black ink & pencil are 19 signatures. .24) On front: 3 signatures in black ink & pencil. On back: 36 signatures in black & blue ink & pencil. .25) On back handwritten in black ink: Colonel H T Allan OBE MC, with 3 ink lines below name. .26) Handwritten in blue/black ink: Signature. Handwritten in blue pencil top R corner: A32/3477. Handwritten in black ink bottom L corner: Cond (?) 15/9A. Handwritten in black ink: Signature. .27) Stamped top R corner: 2/17 Bn Received 9.2.1944. Signature in black ink: H T Allan. Signature in black ink: ? Lt Col 2/17 Aust Inf Bn 10.2.1944 Page bottom in pencil: Blue will keep 1 1/4 for you? .30) Handwritten: Details of eligible medals. Handwritten signature: J C K Miller Capt 7.3.50. Handwritten bottom L corner: Col H T Allan Bottom R corner: OBE, MC, 1914-19, Victory, ED, MID 1914-18, MID 1939-45 On back: Steak & Kidney Morris ) Clark ) Vowood ) 10/- 70215 Maughan ) Allan ) .31) Top of page: Imprinted Coat of Arms Top LHS in black ink: TOP SECRET AND PERSONAL Handwritten signature: Stanley Sauige .32) Embossed top L corner: Seal of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire. Handwritten: Mary R. .32) Signed: Queen Mary, mother of George VI. .33) Handwritten signature. .34) Handwritten in blue ink: HERBERT TRANGMAR ALLAN 6 MAY 46 Handwritten signature. .35) Handwritten signature in blue ink: Joseph Francis, Minister for the Army. .37) Handwritten signature. .38) & .39) Handwritten signature: J W Knight. .41), .43) & .45) Handwritten signature in blue ink. .46) & .47) Handwritten signature in black ink: Henry G Eckhoff. .48) Handwritten signature in blue ink: With best wishes Yours sincerely T J Daly. .49) Handwritten signature in black ink: Yours sincerely H Wells. .57) Handwritten in black ink: Colonel & Mrs H T Allan.certificates, records, awards, administrative, compendium -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - TIN & PHOTOGRAPHS WW2, c.WWII
.1) Tin that held photos, orange. .2) Black / white portrait photo of an Australian soldier wearing slouch hat, brim down & a khaki shirt. .3) Black / white portrait photo of an Australian Sergeant wearing slouch hat & at least 4 medal ribbons. .4) Collection of 145 photos subjects including Middle East, soldiers, trains & bridges. Photos are various sizes..1) On front: “MacRobertson's OLD STYLE BUTTER SCOTCH, Richest Quality 6 oz. Nett” .2) On front: “Yours sincerely Greg” On back: “G W Gregory 16 Millet Street Hurstville” .3) On front: “Yours truly Harry (? illegible)” .4) On back: “Various inscriptions”photos, middle east -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPHS PRE WW2, 1937 - 1939
Photos relate to James Lyle Truscott No.1842 RAAF. Refer to Cat. No.4040.8P .1) On rear in pencil: "No.21 (City of Melbourne) Squadron Laverton 1937. SQD LDR Charles EATON DFC F/O Bobby Hitchcock." .2) On rear in pen: "21 SQD Laverton Vic 1937" .3) On rear in pen: "A Flt 21 SQD". There are also 19 names on rear out of the 21. Lyle Truscott is centre row, 2nd from right. .4) On rear in pen: "Laverton 29-6-39 No12 GP SQUADRON ADVANCE PARTY JUNE 1939 - Melbourne." The names are also listed underneath. Lyle Truscott is on the right front row. This group moved to Parap NT soon after..1) Photo, black & white. large group of airforce personnel in four rows outside a hangar. .2) Photo, black & white. large group of RAAF personnel outside a brick building. .3) Photo, black & white. group of RAAF personnel outside a brick building. .4) Photo, black & white. group of RAAF personnel in work dress. All slightly different in size.photographs, raaf, laverton -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPHS WW2, C.WW2
Collection relates to Harold Johnson TX3956. Refer to Cat. No. 4053.3 for service details..1) Photo, black & white, harbour scene showing two ships, one at lean, buildings and timber on wharf. Hand writing on rear. .2) Photo, black & white, view over Jerusalem towards hills. .3) Photo, black & white, close up of a mosque with one person in front. .4) Photo, black & white, bombed wreckage of a gun emplacement overlooking a harbour. .5) Photo, black & white, air strip with covering and a plane coming into land, background appears to be jungle. .6) & .7) Photo, black & white, Japanese surrender being conducted aboard a ship. Photos are various sizes. .1) On rear in pencil "Close up of the wreck, Love Hal xxx" .2) On rear in pencil "View of Jerusalem from YMCA" .3) On rear in pencil "Mosque of Omah Jerusalem Love Hal xxx"photographs, jerusalem -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPHS WW1, 1917 - 1919
.1) James Worland MILLS; .2) & .3) James Worland MILLS 1st on L; .4) James Worland MILLS 2nd on L front row; .6) James Worland MILLS on R in rickshaw. James Worland MILLS No 3441 59th Battalion. Refer Cat No 169P for his service details..1) Photo, sepia, showing a soldier in uniform standing outside a tent. .2) Photo, sepia, showing 5 soldiers, 4 standing, 1 kneeling. .3) Photo, black / white, showing 6 soldiers standing in a wood. .4) Photo, sepia, showing a soldier sitting with 3 stripes on arm & no hat. .5) Photo, sepia, showing 8 soldiers on deck of a ship. .6) Port card photo, black / white, showing 8 soldiers standing with a native & a rickshaw. Average size listed..6) On rear in black pen: “Taken at Durham 11.8.17 while on leave from Troopship A16 Port Melbourne”photographs, 59th -
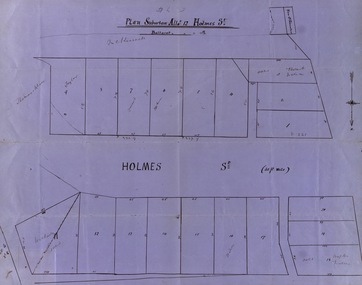 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMap, Plan subdivision: Allotment 12 Holmes Street, Ballarat
The Allotments drawn in Holmes Street appear to be hand drawn and showing one of the first subdivisions in Ballarat. This was begun in the 1860s. Some names are marked on the blocks - Taylor (9), Holmes (6), Robert Watson (3), Watson (16), Walter (18),Wetherly (11), Vacant (7)Blue paper with black ink showing the land blocks either side of Holmes Street Each block is numbered - 20 in all Names on some blocksNorth indicated with arrow Sizes of blocks - depth and width holmes street, subdivision, allotment 12, holmes, taylor, robert watson, watson, wetherly, vacant -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, VIOSH: Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management - Intake 6, 1984
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. viosh, victorian institute of occupational hazard management, ballarat college of advanced education, graduate diploma, peter bishop, warwick bratby, graham cross, bruce daff, adrian glumart, harold halloran, ivan miller, ulrich ojczyk, john oldfield, alwyn piggott, john rowan, george white, allan wright -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPostcard - POSTCARDS WW1, 1) 19.1.17 .2) 31.7 .15
Robert Charles NORMAN No 1560 enlisted in the AIF in 1st reinforcements 21st Batt on 10.4.1915 age 24 years 6 months. Embarked for Eygpt 28.6.1915, embark for Gallipoli 29.8.1915, embark for France 26.3.1916, WIA 31.7.1916 GSW to right shoulder and head severe, embark for Australia 13.2.1917 for 3 months change but was discharged medically unfit on 1.6.1917. A typying error on one post card states 10th reinforcements, 1st reinforcements as per his enlistment papers.Two post cards on an A4 size paper attached Via photo corners. The left had brown one is a " Field Service postcard." the right one is a Post card scene with Egypt and Pyramids." the attached writings under both pertain to this card. the field service card on rear is printed so that any details are added by the writer.documents - postcards, military history -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumUniform - UNIFORM AIF WW1, 4) Hat - Akubra et al, c.2000
A complete replica uniform set of clothing and all items that were or could be worn by a first AIF soldier.Light horse brigade .1) Jacket, 100% wool with cotton lining. 7th Battalion AIF colour patches with a brass A signifying original ANZAC on both sleeves. Right sleeve has sergeant's stripes & 5 blue & 1 red chevron stripes. Left sleeve has 3 brass bars re WIA 3 times. Rising Sun badges on each collar & Australia badges on shoulder straps. Belted at waist. .2) Jodphurs, khaki corded wool. Brass button up fly. .3) Braces, red, white & blue oblique striped. .4) Hat, size 57, khaki Akubra with felt pugaree, leather chin strap, & blackened brass Rising Sun badge on upturned rim. .5) & .6) Puttees, pair, khaki wool felt with khaki cotton tapes. .7) & .8) Boots, pair, size L, tan coloured leather with dark brown leather laces, leather soles with metal reinforcing on heels..1) & .2) Makers labels. .4) Hat: Akubra, Made in Australia; On badge: Australian Commonwealth Military Forces. on hat: "5.7 Akubra Made in Australia"uniforms-army, costume - male footwear, costume - male headwear -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumClothing - VEST WW2, Department of Defence, c.1946
Department of Defence brown, lined, leather, buttoned, with khaki wool & 4 buttons down front“G H ALLISON 1946” Jerkin leather Size No 1 Wearers height 5' 3" to 5' 6" Wearers breast over jacket 34 " to 41"uniforms - army, costume - male uniform, vest, -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Information, VIOSH: Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management - Intake 6, 1984, Information Letter to students
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Information letter sent to those in Intake 6 of the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management Course, 1984. It outlines the timetable for subjects and times at the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. Include in the package is a form that must be completed and returned ASAP. Residences are provided and items included are listed. Transport for those coming from interstate can be arranged. Derek Viner is the Course Co-ordinator.Twenty-three A4 pages, typed with diagrams, mapsHand written note in blue pen on map. Letter head of Ballarat College of Advance Education on some pages. Signature of Derek Viner, Course Co=ordinator.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, derek viner, course co-ordinator, occupational hazard management, residence, timetable, ballarat college of advanced education -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour - Framed, VIOSH: Occupational Health and Safety Certificate Course; Intake 6, January 1995
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Framed photograph of Occupational Health and Safety Certificate Course students, Intake 6, 1995Framed colour photographh with grey mounting. Black frameLabel of framer - Artafact, Ballaratviosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, intake 5 1995, mark bartlett, bryan colburn, kelvin denford, ken fuhrmeister, paul mckinn, garth palmer, john preston, ken schmid, linda smith, ian terry, sean turner -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Syllabus, Education Department: Technical Schools Syllabus, 1921
A syllabus for each subject taught in Technical Schools that was provided by the Education Department of Victoria. .1: Syllabus for Heat Engines - side 1, Grade 1; side 2, Grade 2 .2: Syllabus for Refrigeration - Grade 1 and Grade 2 on side 1. .3: Syllabus for Farm Irrigation and Irrigation Engineering - side one, Farm Irrigation; side 2, Irrigation Engineering. .4: Mechanics and Mechanics applied to Mining - 4 pages covering Mechanics (Applied) Grade 1, Grade 2, Mechanics (Applied) Structures, Grade 3, Mechanics (Applied) Machines, Grade 3; Mechanics Applied to Mining and Theoretical Mechanics .5: Syllabus for Mechanics and Heat - First Grade Mechanics students will be required to know the general principles and formulae of the science, apparatus used method of using and to verify formulae experimentally. Second Grade course includes all subjects for Grade 1 plus Newton's proof of the parallelogram of forces, rotation round fixed axis, laws of rotary motion of a body, resistance, harmonic motion, friction,impulsive forces, barometer corrections and Heat and thermodynamics. Third Grade students, an intimate knowledge of the courses for first and second grades plus remaining portions of thermodynamics. A special course for Evening Students in Mechanics and Heat outlined. .6: Syllabus for Electricity - covers the requirements for First Grade, Second Grade and Grade 3. Areas covered are Magnets and Magnetism, Electroscopes and Electrification, Electronic Fields, Voltaic Electricity, Measurement of Current, Electromagnetism, Amperemeters, Resistance, Electrical Technology,A5 size pages, typed. Some are doubled sided.education department victoria, technical schools, syllabus, 1921, heat engines, refrigeration, farm irrigation, irrigation engineering, mechanic, mechanics applied to mining, mechanics and heat, electricity -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchPocketbook, National Bible Press, New Testament & Psalms, US Armed Forces, 25/1/1941 (estimated); Date from introductory letter from "The White House, Washington"
Pocket size book of New Testament & Psalms issued to U S Armed Forces from "The Gideons" International. With introduction page from The White House, Washington & Franklin D Roosevelt dated January 25, 1941. A title page headed "A Sacred Token" gives name of Private A.(Arthur) D.(Dean) Campbell. He was born at Melbourne on 31 March, 1917. it also provides his unit, being 2/55 Aust L.A.D. (Light Aid Detachment), AIF Australia and dated 3/6/1945A title page headed "A Sacred Token" gives name of Private A.(Arthur) D.(Dean) Campbell. He was born at melbourne on 31 March, 1917. it also provides his unit, being 2/55 Aust L.A.D. (Light Aid Detachment), army, ww2, new, testament, us, issue -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchBoots, GP
pair general purpose black boots, size 8, ankle height leather uppers, rubber soles, with lacespluss 50 under instep, R60 8/6 Cblack leather general purpose boots -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchMedal Set (set of 6), As Issued
Pilot Officer Ernest Williams LIns. Was 42 years of age on enlistment. Gold framed mounted medal set consisting of six full size and six miniature medals. The medals are 1939-45 Star, Africa Star, Italy Star, Defence medal, British War Medal, Australian Service Medal 1939-45These medals are impressed with 254290 LINS.EW. medals -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Screwdriver Set, 1930-1955's
... .. Instructions for use are on label. Ratchet screwdriver plus 6 drill...“WITH 6 DRILL POINTS / SIZES, 1/16 TO 11/64 includes... of the sea Ship model Hobby Ship model tool “WITH 6 DRILL POINTS ...This Yankee spiral-ratchet Screw Driver (screwdriver) set was a hand tool with drills, used in the making of components for the ship model Sovereign of the Seas. It is part of a collection of objects used by Jim Williams, maker of fine ship models from about 1930-1955. Most of the components for the models, as well as many of the tools, were handmade by Jim Williams. Jim’s family has donated the ship model “Sovereign of the Seas” and many tools, accessories and documents used in the making of this and other ship models have been donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. Ship model of HMS Sovereign of the Seas, scale model of 17th Century English war ship, was handmade and carved from plans, enclosed in airtight glass case. All components of that model, including even the smallest pulleys, were hand crafted using tools designed and made by Jim. Outstanding details include functional rigging and moving cannons. Please see our record 3732 of the mode Sovereign of the Seas for further details of the ship and the maker. This set is connected with the hobby and skill of ship model making that has been crafted as a leisure activity for many generations. The hobby is often chosen by serving and retired mariners who appreciate the connection with maritime history. This set was used by local Warrnambool man, Jim Williams, who was employed at Cramond and Dickson clothing store, and then at Fletcher Jones menswear for 27 years. It was used in making components for the model of the historic ship, the Sovereign of the Seas. The Sovereign of the Seas was a historic 17th century English war ship with important maritime heritage. Spiral-Ratchet Screw Driver set, also called an ‘American drill’ or hand drill. 9 parts, Yankee brand, No. 31 set. Made by North Bros. Mfc Co. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S.A.. Instructions for use are on label. Ratchet screwdriver plus 6 drill bits - sizes 1/16th to 11/64th - contained in a small round wooden tube with lid, label on outside. This Screw Driver set is part of a collection of tools and accessories once used by Jim Williams, maker of a series of ship models 1930-1955 including “HMS Sovereign of the Seas”. “WITH 6 DRILL POINTS / SIZES, 1/16 TO 11/64 includes - - with - - / “Yankee” Spiral-Ratchet Screw Driver No. 31 / Made by NORTH BROS. MFG. CO. PHILADELPHIA P [A?]- / Directions for use – First Insert Drill Point In - / Drill Chuck, and turn the – in Chuck of Screwdriver U.S.A.”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, jim williams, james bernard williams, ship model hobby, ship model tools, ship model making equipment, ship model making accessories, wood working tool, model making tool, screwdriver set, spiral ratchet screwdriver set, yankee screwdriver set, spiral-ratchet screw driver set, american drill, ratchet drill set, ratchet hand drill, ratchet screwdriverset, north bros. mfc co philadelphia pa, tool, sovereign of the sea, ship model, hobby, ship model tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Bottle, c. 1850's - 1900's
This is one of four bottles in our Collection that were recovered by a local diver from the quarantine area just inside the Port Phillip Heads. Ships were required to pull into this area to check for diseases etc before they could head up to Melbourne. Quite often they would drink and throw the bottles overboard. Handmade glass bottle, manufactured in 1850's - 1900's. Glass bottles and glass jars are in many households around the world. The first glass bottles were produced in south-east Asia around 100 B.C. and the Roman Empire around 1 AD. America's glass bottle and glass jar industry were born in the early 1600s when settlers in Jamestown built the first glass-melting furnace. The invention of the automatic glass bottle blowing machine in 1880 industrialized the process of making bottles. In 2019, plans were made to re-introduce milk glass bottle deliveries to Auckland in early 2020 The earliest bottles or vessels were made by ancient man. Ingredients were melted to make glass and then clay forms were dipped into the molten liquid. When the glass cooled off, the clay was chipped out of the inside leaving just the hollow glass vessel. This glass was very thin as the fire was not as hot as modern-day furnaces. The blowpipe was invented around 1 B.C. This allowed molten glass to be gathered at the end of the blowpipe and blown into the other end to create a hollow vessel. Eventually, the use of moulding was introduced, followed by the invention of the semi-automatic machine called the Press and Blow. In 1904 Michael Owens invented the automatic bottle machine. Before this time most glass bottles in England were hand blown. This is one of four bottles in our Collection that were recovered by a local diver from the quarantine area just inside the Port Phillip Heads. Ships were required to pull into this area to check for diseases etc before they could head up to Melbourne. Quite often they would drink and throw the bottles overboard. Handmade glass bottle, manufactured in the 1850s-1900s. The bottle gives a snapshot into history and a social life that occurred during the early days of Melbourne's development and the sea trade that visited the port in those days. Bottle, opaque brown glass, concave base, tapering slightly wider towards shoulder then inwards towards neck; ring of glass just below opening. Base is blown glass; pontil mark on base. "STUBBY 1850-1900 SMALL SIZE", ENGLISH 3 PIECE MOULD, HAND MADE TOP", "PAPER LABEL, CORK & WIRE SEAL $6flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, brown glass bottle, handmade glass bottle, handmade beer bottle, handmade late 19th century bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1819
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1819, the year before King George III died. There were over 7 million of these coins minted. King George III succeeded his grandfather, King George II, on the throne in 1760. He reigned until his death on 29th January 1820. The shield in the centre of the reverse of the coin is the Hanoverian Shield, showing that the House of Hanover was elected to the crown rather than taking the crown as a victory. This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - The 6 pence coin is 19mm - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) - The Half Crown is 32mm British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George III by the Grace of God, King of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was Benedetto Pistrucci. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated "Evil to him who evil thinks” The engraver of the reverse image was Thomas Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time Australia became a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation, the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling, 1819. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George III head, looking right. Reverse; crown on top of quartered shield, 2 diagonally opposite quarters both show 3 lions, another quarter has a rampant lion, another quarter has a harp; in the centre of the shield is a small crowned shield with 3 symbols that appear to be lions. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEOR . III D . G . BRITT . REX F . D .” and “1819” Reverse “HONI . SOIT . Q [UI obscured] . MAL . Y . PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1819, king george iii currency, colonial australia currency, benedetto pistrucci, thomas wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1819
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1819, the year before King George III died. There were over 7 million of these coins minted. King George III succeeded his grandfather, King George II, on the throne in 1760. He reigned until his death on 29th January 1820. The shield in the centre of the reverse of the coin is the Hanoverian Shield, showing that the House of Hanover was elected to the crown rather than taking the crown as a victory. This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - The 6 pence coin is 19mm - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) - The Half Crown is 32mm British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George III by the Grace of God, King of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was Benedetto Pistrucci. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated "Evil to him who evil thinks” The engraver of the reverse image was Thomas Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling, 1819. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George III head, looking right. Reverse; crown on top of quartered shield, 2 diagonally opposite quarters each show 3 lions, another quarter has a rampant lion, another quarter has a harp; in the centre of the shield is a small crowned shield with 3 symbols that appear to be lions. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEOR . III D . G . BRITT . REX F . D .” and “1819” Reverse “HONI . SOIT . Q [UI obscured] . MAL . Y . PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1819, king george iii currency, colonial australia currency, benedetto pistrucci, thomas wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Crucible, The Patent Plumbago Crucible Company, circa 1878
This crucible was raised from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It is one of six similar relics, in a range of sizes, now in the Flagstaff Hill collection. All bear markings to indicate their manufacture by the Morgan brothers of Battersea, trading as the Patent Plumbago Crucible Co. A crucible is a container used for purifying and melting metals so that they can be cast in a mould to a predetermined shape and use. They must withstand extremely high temperatures, abrupt cooling, and shed their contents with minimal adherence. The addition of graphite to the traditional firing clays greatly enhanced the durability of industrial crucibles in mid-Victorian Britain, a significant technological advance at a time of great activity in foundries and expansion of demand for refined metals. The Morgans first noticed the advantages of graphite crucibles at the Great Exhibition held in London in 1851. Initially they contracted to be sole selling agents for the American-made products of Joseph Dixon and Co. from New Jersey, but in 1856 they obtained that firm’s manufacturing rights and began producing their own graphite crucibles from the South London site. The Morgans imported crystalline graphite in 4-5 cwt casks from the British colony of Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) and mixed it with conventional English (Stourbridge) clays to be fired in kilns. Their products were purchased by the Royal Mints in London and India, and exported to official mints in France and Germany. They were successful exhibitors of their crucibles and furnaces at the London Exhibition held in 1861 (Class 1, Mining, quarrying, metallurgy and mineral products, Exhibit 265, Patent Plumbago Crucible Co). The range of sizes represented by the six crucibles retrieved from the LOCH ARD, suggest they may have been part of a sample shipment intended for similar promotion in the Australian colonies ― at Melbourne’s International Exhibition to be held in 1880. The summary of cargo manifest, by Don Charlwood in ‘Wrecks and Reputations’ does not mention any crucibles, implying that they were not a large consignment of uniform items. A newspaper account of an 1864 tour of the Morgan brothers’ ‘Black Potteries’ at Battersea indicates: “All the pots were numbered according to their contents, each number standing for one kilogram, or a little over two pounds; a No. 2 crucible contains two kilogrammes; a No. 3, three kilogrammes, and so on.” These numbers are obscured by marine sediment on three of the crucibles in the Flagstaff Hill collection, but those legible on the remaining three are 5, 6, and 8. None of the six are of the same size from a visual appraisal.The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Register S417A large crucible, or fluxing pot, for heating and pouring molten metal. It was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The clay fired vessel rises from circular flat base to a larger rim with pouring lip. It is stained a rust colour and bears some sedimentary accretion. Half of its loose fitting lid with central knob has also survived. Markings on the artefact indicate it is a Morgan’s crucible, made with graphite to prevent cracking in the furnace and provide a smooth (non-adhesive) inner surface. On base: “…RGAN’S PATENT CRUCIBLE”. On rim: “MORGAN’S PATENT P…” Below top edge "BAK"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, graphite crucible, plumbago crucible, morgans crucible company, loch ard, fluxing pot, crucible -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Crucible, The Patent Plumbago Crucible Company, circa 1873
This crucible was raised from the wreck of the Loch Ard. It is one of six similar relics, in a range of sizes, now in the Flagstaff Hill collection. All were manufactured by the Morgan brothers who founded the Patent Plumbago Crucible Company in 1856, making crucibles in a small factory in Battersea London. A crucible is a container used for purifying and melting metals so that they can be cast in a mold to a predetermined shape and use. They must withstand extremely high temperatures, abrupt cooling, and shed their contents with minimal adherence. The addition of graphite to the traditional firing clays greatly enhanced the durability of industrial crucibles this technique was pioneered by the Morgan Bros thereby making a significant technological advance in foundry technology and metallurgy. The Morgans first noticed the advantages of graphite crucibles at the Great Exhibition held in London in 1851. Initially, they contracted to be sole selling agents for the American-made products of Joseph Dixon and Co. from New Jersey, but in 1856 they obtained that firm's manufacturing rights and began producing their graphite crucibles from the South London site. The Morgans imported crystalline graphite in 4-5 cwt casks from the British colony of Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) and mixed it with conventional English (Stourbridge) clays to be fired in kilns. Their products were purchased by the Royal Mints in London and India and exported to official mints in France and Germany. They were successful exhibitors of their crucibles and furnaces at the London Exhibition held in 1861 (Class 1, Mining, quarrying, metallurgy and mineral products, Exhibit 265, Patent Plumbago Crucible Co). The range of sizes represented by the six crucibles retrieved from the Loch Ard suggests they may have been part of a sample shipment intended for similar promotion in the Australian colonies or at Melbourne's International Exhibition to be held in 1880. A newspaper account of an 1864 tour of the Morgan brothers' 'Black Potteries' at Battersea indicates: "All the pots were numbered according to their contents, each number standing for one kilogram, or a little over two pounds; a No. 2 crucible contains two kilograms; a No. 3, three kilograms, and so on." These numbers are obscured by marine sediment on three of the crucibles in the Flagstaff Hill collection, but those legible on the remaining three are 5, 6, and 8. None of the six is of the same size. (For more information on the Loch Ard wreck see note sec this document) The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the crucible is a small part. The collections objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.A medium size crucible, or fluxing pot, for heating and pouring molten metal. The container rises in a slight curve from a smaller flat base to a wider open top with a lip for pouring. It was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The crucible has a coating of sediment that obscures its numerical specifications of size and capacity. The markings that remain visible indicate it is a Morgan’s crucible, made with graphite to prevent cracking and provide a smooth non-adhesive inner surface. .On base: “…ORGAN’S …ENT”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, graphite crucible, plumbago crucible, morgan's crucible company, loch ard, morgan potteries, crucible, fluxing pot -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyPoster, Banyule City Council, Statement of commitment to Indigenous Australians 2009: Banyule City Council, 2009
... Poster, folded in 6 to pamphlet size. Text and colour... wurundjeri willam Poster, folded in 6 to pamphlet size. Text ...A brief history of Banyule Council's commitment to Indigenous Australians and the 2009 statement of commitment.Poster, folded in 6 to pamphlet size. Text and colour images.indigenous australians, banyule council, wurundjeri willam -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaFurniture - Volum Medicine chest
This chest is the typical mid-18th century model. Thought to have belonged to captain James Volum.A medicine chest was a necessity for all sea journeys. Sometimes surgeons were onboard ships if there were passengers but on merchant ships, the captain had to be able able to look after his crew. A medium size mahogany cabinet with four protruding feet, small free hinged handles on left and right sides which are positioned approximately 5/8ths up from the bottom of the item, these handles can hinge 100 degrees upwards. The front and back 6/8ths of the cabinet can hinge open, as can the top of. Both front and back doors can be locked closed with their own respective hook latch which is on both sides of the cabinet. The top lid can be locked by interacting with a metallic keyhole which is present on the front of the cabinet close to the top. Revealed by opening the top lit is storage location with two rows of three storage spaces and one row of four. Revealed by opening the front door, is a single shelf with six divided locations for an equal number of glass containers, though only five remain in complete form. Below this self are three rows of drawers of differing dimensions, each with a small white knob. There are two drawers of equal width in the first row. Each drawer has four equally divided sliding pieces on its top face. When removed, these lids reveal a respective small space. Present on small paper labels on each of these lids are identifiers of the material which was stored. There are three equally sized drawers in the second row, which are less wide than the previous row. Only two of the drawers in this row have lids, of which each only have a single lid which covers a single compartment, each of these have a single label on them. The middle drawer contains a small glass mortar and pestle which are restrained by small wooden fixtures within the drawer. There are two drawers of equal width and greater height than any of the previous drawers in the third row. The first drawer has a single compartment containing multiple vials of varying dimensions, some of which feature a paper label with a respective inscription. Some of these vials are broken. In the second drawer has no lid which covers its four equally sized glasses. These are restricted by a wooded piece with four circular cut-outs. Revealed by opening the back door are two equally sized and spaced shelves which both have four divided locations which are filled by eight respective glass containers. These glass containers are of similar design to those in the front compartment but are larger. Some of these glass jars have paper labels like those found on previous glass containers.Label on top lid:volum collection, medecine chest, portable furniture, geelong, peterhead, scotland, captain, seafaring, whaling, london, bishopsgate, old gravel lane, london docks, tobacco dock, james burrows -
 Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub Branch
Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub BranchHeadwear - Hat, Utility, Camouflaged (Auscam)
DCPU is a five colour camouflage pattern developed by the Australian Defence Force and tested during Auscamthe late 1970s. DCPU has been replaced in the Australian Army by Australian Multicam Camouflage Uniform (AMCU) Soft round 'giggle' hat with 6 cm stitched brim. Fabric loops for inserting Camouflage materials. Fabric is Disruptive Pattern Camouflage Uniform (DCPU) nicknamed Auscam or Jelly Bean Camo. JOHN STAR P/L NSW 02 9669 1066 SIZE: 60CM 100% COTTONauscam cammo, uniform, australian armed forces
