Showing 348 items
matching apparatus
-
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumFunctional object - Yarn Spinner and Accessories, John Nesbitt, 19th Century
Nino Corda was a Geelong based textile designer who worked at various textile mills between 1957 & 2003. He travelled the world in search of the latest fashions and techniques and developed timeless designs that were much loved by Australians. These items are on rotational display at the National Wool Museum’s ‘In the Factory’ exhibition. For many years, Nino also worked as part of the Honorary Staff of the National Wool Museum. His passion for the world of textiles provided energy and knowledge to the visitors and staff of the museum. Although Nino has now retired from his honorary position and has hung up his Australian Tartan vest, these items will continue to serve the community in sharing the stories of Australian Textile design.Custom made wooden hinged box with a hook latch. Brass yarn spinner, attached to a mahogany wood plinth base, which spins fibre into cord/yarn/thread. It has dials to set the rate that it spins. Metal plaque with black inlaid enamel lettering. Small cork inlay. Brass rod with hinge and wingnut, and ball at end. Ball at end has an adjustment mechanism. Rod also has an adjustable circular collar. Pair of curved tweezers. Circular magnifying glass on long thin handle. Glass has two concave lenses. Weaving sample in shades of blue, green and brown. Twill weave. Alternate pattern samples separated by red thread.Brass plaque on base of spinner: 42 MARKET St / John Nesbitt / REGd TRADE MARK / LIMd / MANCHESTER Underside of wooden plinth: 4976apparatus, textile, testing, spinning, nino corda, magnifyer, tools, brass, mahogany, tweezers, yarn, spinner, design, john nesbitt, manchester, england, 19th century, engineering, manufacturing -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryOrmsby's Inhaler, 1877
Lambert Ormsby was a New Zealand surgeon who migrated to Ireland. He described his inhaler in a letter to the Lancet in 1877.Ormsby listed the advantages of his inhaler as simple, inexpensive, small quantity required to produce sleep, prevents evaporation of ether, portable and small (can be carried in pocket), short time to complete anaesthesia (two minutes) and safe. Disadvantages of this apparatus were that it had to be removed in order to recharge the sponge with ether or when anaesthesia becomes too deep. Considerable carbon dioxide accumulation developed and there would also be some oxygen lack. In thirty years of use, Ormsby's Inhaler underwent certain modifications, an exhalation valve was fitted to the mask and device for recharging the sponge with ether was later added. The Ormsby inhaler was modified by Carter Braine in 1898 with the aim of making it easier to clean. Essentially it is very similar except there is no net around the bag.The inhaler consists of an india-rubber flexible bag enclosed within a net bag to limit expansion. There is a soft metallic mouthpiece with india-rubber tubing around the edge. The tubing had to be purchased separately from the manufacturer. The body contains a wire cage with a similarly shaped hollow sponge into which ether was poured.Maker's details inscribed into metal ring around the bore: Barth Co. London.ormsby, new zealand, carbon dioxide, carbon accumulation, carter braine, portable -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Foot Bellows, Fletcher Russell & Co. Ltd, c1895
FLETCHER RUSSELL & CO. LTD/ WARRINGTON MANCHESTER & LONDON Thomas Fletcher (1840-1903) had established a gas appliance manufactory in Thynne Street, Warrington by the 1880s. By 1895 the company had become Fletcher Russell and Co Gas Engineers, his firm having merged with Alexander and William Russell of Pendleton Iron Works. In 1950, the firm merged into Radiation Ltd which was later acquired by 'TI New World. In the early 1880s Thomas Fletcher was a registered dentist who went on to found a dental apparatus manufacturing business. He later diversified into producing equipment for blacksmiths, foundries, forging and other sectors. The company had grown to 900 employees in 1914. These foot-operated bellows were for pumping gas to keep the patient relaxed while the dentist worked on their teeth. They were later modified for a variety of uses where a continual flow of air was needed.These bellows are representative of a range of devices developed in the late 19th Century to assist in manufacturing. They were donated to our collection by a Wodonga resident.A set of foot bellows made from timber, metal and leather. The bellows were activated by pressing up and down on the metal step-shaped lever at the front. The air outlet on one side would have a hose attached to it to direct the air current to wherever it was needed. The bellows are made from leather. The manufacturers mark is attached to the top within a metal circle.On top of Bellows in a circle: "FLETCHER RUSSELL & CO./ WARRINGTON/ MANCHESTER / LONDON"foot bellows, fletcher russell & co. ltd. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, C. French, A Handbook of the Destructive Insects of Victoria, Part One, 1891 (exact)
Purple hardcovered book153 pages plus 20 figures. Contents inlcude: Introduction to Entimology, classification of insects, quarantine rules, Woolly Aphis, Codlin Moth, Curve-winged Apple moth, Apple-tree borer, Apple-bark Scale, Apple Beetle, Red Spider, Harlequin Fruit Bug, Pear and Cherry Slug, Rutherglen Fly-pest, Cherry borer, Pear Phytoptus. Coloured plates (by C. Brittlebank)of insects and figures (by Hart Vonarx) include the Knowles' Pump, Charnwood Spray, Danks' Lever Spray Pump, Spawn's Climax Spray, Apparatus for Sparying Orange Trees, Strawsonizer, French Portable Hand Spraying Machine, Lowe and Park's Insect Exterminator, Greenhill Codlin Moth Lamp, Wolfskill Fumigator, Tutus Fumigator, Oliver Fumigator, Agitator Spray PumpBookplate - Ballarat School of Mines Ballaarat No 1201. Presented by Secretary for Agriculture, Melbourne, 14th July 1891 insects, pumps, c brittlebank, hart vonarx, c french -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Marvels of Heat, Light and Sound
Blue hard covered book with gold writing and illustrations on front cover, illustrations, 196 pages. Targetted to the general reader of the scientific principles of heat, light and sound topics include heat; light (including reflection and refraction); vision (including vision and optical illusions, the eye, chromatic aberration, spinning tops); optical illusions (including occular estimation, zollner's designs, the thaumatrope, phenakistoscope, zootrope, praxinoscope, the dazzling top); optical illusions cont. (including the talking head, ghost illusions); optical apparatus (including the eye, the streoscope, spectrum analysis, the spectroscope, the telescope and microscope, photography, dissolving views, luminous paint); spectral illusions (including a spectre, ghosts); acoustics (including the harmonograph); acoustics cont (including the topophone, the megaphone, the autophone, the audiphone, the telephone, the phonograph, the microphone). non-fictionscience, science class, scientific recreation series, light, heat, sound, ballarat ironworkers & polytechnic association -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Magazine - THE AUSTRALIAN STANDARD NOVEMBER 2002 VOL 23 NO 10
Magazine titled 'The Australian Standard'. Dated November 2002 Volume 23 Number 10. Contains new and revised Australian Standards, publications and projects. Front cover has a part sketch of the Beehive Building, home of the Bendigo Stock Exchange, in Sandhurst (now Bendigo). Above and below the sketch is a part coloured picture of a fireman at a fire. An article mentions that on 25 August 1871, 18 year old Edward Hope Kirkby, watched the burning of the Beehive Building, home of the Bendigo Stock Exchange, this may have been his motivation to become one of the most prolific inventors of communication apparatus and fire protection equipment in Australia. Has a small full picture of the Burning of the Beehive Stores and Chambers, Sandhurst and picture of the E H kirkby Fire Alarm System.magazine, organization, standards australia, the australian standard november 2002 volume 23 number 10, felicity pontoni, tom godfrey, mark elder, pmp print, beehive building, bendigo stock exchange, edward hope kirkby, la trobe picture collection, state library of victoria, barry lee oam, brian kirkby, david michel -
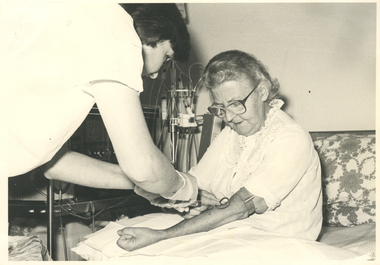 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 1978
This photograph is showing a procedure performed by an RDNS Sister in the home of an elderly lady.Education was an integral part of Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) from its inception in 1885, later called Royal District Nursing Service, (RDNS). Only Trained Nurses were employed by the Society, and on visits to patients they taught the necessity of hygiene and cleanliness, as well as the need for a good diet, to bring about good health. Doctor’s lectures were later given at the MDNS home to instruct patients and their families on prevention of disease. Education to patients continued throughout the years regarding health care and the use of equipment in the home. In 1961 Education programs commenced at MDNS with Sisters receiving In-service education. Staff could also apply for scholarships to further their education outside of RDNS. At RDNS many programs were run, including: a Post Basic Course, Cardiac Rehabilitation Nursing, Haematology/Oncology Nursing, Palliative Care program, Diabetic Stabilization Program, Leg Ulcer Management Program, HIV/AIDS Nursing Care, Cystic Fibrosis Home Support, Veterans Home Care Program, Breast Cancer Support Program, Continence Management Program, Stomal Therapy Program, In-Home Lactation Support Program and a Community Nursing Education Program extended to student nurses from hospitals and to other nursing organizations. RDNS staff attended several hospitals to observe and learn special care needed to some clients, e.g. to the Austin Hospital to learn the care required for paraplegic and quadriplegic clients at home and to Mount Royal Hospital to observe the care of clients in the rehabilitation ward.This Black and white photograph is showing Sister Liddalow, of the Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), linking up a home dialysis unit into the left arm of an elderly lady. The lady who wears glasses and has wavy hair, is wearing a white nightdress with lace at the neck and down the centre front. Her left arm is resting on top of a surgical cover and she is clenching her left fist and has a tourniquet above her elbow. She is sitting against a flower patterned pillow on her bed watching the procedure. Sister Liddalow has short dark hair and is wearing a white gown over her uniform. She has a glove on her right hand and a syringe in her hand. In the left rear IV apparatus, with two syringes and a trolley on which a machine can be seen.date of photographroyal district nursing service, rdns, patient care - home dialysis, sister liddalow, -
![The Erskine River Waterfall / [by] Nicholas Caire, circa 1876](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/57831695d0cdd1176c4f24d8/item-media/57831701d0cdd1176c4f989a/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, Anglo-Australasian Photographic Company, The Erskine River Waterfall, c. 1876
Nicholas Caire was born on Guernsey in the Channel Islands in 1837. He arrived in Adelaide with his parents in about 1860. In 1867, following photographic journeys in Gippsland, he opened a studio in Adelaide. From 1870 to 1876 he lived and worked in Talbot in Central Victoria. In 1876 he purchased T. F. Chuck's studios in the Royal Arcade Melbourne. In 1885, following the introduction of dry plate photography, he began a series of landscape series, which were commercially successful. As a photographer, he travelled extensively through Victoria, photographing places few of his contemporaries had previously seen. He died in 1918. Reference: Jack Cato, 'Caire, Nicholas John (1837–1918)', Australian Dictionary of Biography.An original, rare photograph from the series 'Views of Victoria: General Series' by the photographer, Nicholas Caire (1837-1918). The 60 photographs that comprise the series were issued c. 1876 and reinforced a neo-Romantic view of the Australian landscape to which a growing nationalist movement would respond. Nicholas Caire was active as a photographer in Australia from 1858 until his death in 1918. His vision of the Australian bush and pioneer life had a counterpart in the works of Henry Lawson and other nationalist poets, authors and painters.‘The Erskine River waterfall’ : Views of Victoria (General Series) No.52 : Albumen silver photograph | Photo on card with Title and Description on reverse | Mounted 24 x 30 cm; Photo 12 x 17 cm.On Reverse: ‘The River Erskine, which empties itself into Loutitt Bay, is noted for the grandeur of its scenery. Its sources, owing to the impenetrability of the bush and the mountainous nature of the country, are unknown. They may eventually be traced a long way into the Cape Otway Ranges. An idea of the difficulty with which the present very beautiful illustration was obtained may be gained from the fact that it took our assistants, several days to convey the apparatus a distance of six miles and back. The depth of the fall is 150 feet. The foliage as seen comprises the very rare staghorn tree, the myrtle, the dogwood tree, and ferns.’nicholas caire (1837-1918), lorne (vic), erskine river (vic), landscape photography -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Bottle, H London Chemist & Dentist, Early 20th century
This bottle was used in the pharmacy of Harry London of Warrnambool. Born in England, Harry London arrived in Victoria in 1883 and worked as a chemist in Ballarat and Euroa. In 1891 he went back to England where he studied dentistry. In 1891 he came to Warrnambool where he bought the pharmacy business of the late William Nettleton. He occupied the Nettleton building in Liebig Street (95 Liebig Street today) until 1896 when he erected new premises at the south west corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets. At that time he was the only chemist in Warrnambool using a Pasteur filter for water to make up his medicines. In his dentistry business he used gas, chloroform and cocaine as anaesthetics. The making of dentures was his speciality. In 1904 he was the owner of the only set of Rontgen X Ray apparatus in Warrnambool. In 1905 his shop was the first in Warrnambool to have electric lighting installed. This item is a valuable one as it has local provenance. It came from the pharmacy business of Harry London, a prominent Warrnambool chemist in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Harry London mementoes such as this are comparatively rare. This is a chemist’s glass bottle with a rectangular body, a circular neck and a rounded top. There is no stopper and the bottle is empty. The top has a small chip. The name of the chemist is embossed on the front of the bottle in an indented section of the glass. The bottle is slightly scratched and discoloured from the original contents. On front of bottle: ‘H. London Chemist & Dentist Warrnambool’ On base: ‘M’ On the body of the bottle: ‘31’ harry london, chemist, warrnambool chemists, history of warrnambool -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyMeter Volt, mid to late 1900's
This analog voltmeter is quite a large (industrial type) apparatus which permits the easy monitoring of electrical variations within the large SEC Victoria Hydro Scheme's electrical generators. These generators are powered by the hydro force of "stored" water at a higher altitude. The establishment of both the NSW and Victorian Hydro schemes was achieved from the mid 1900's to the 1960's. At this point in time the need for additional power sources to quench both an industrial and domestic demand for electricity was purely an economic and not and environmental (carbon reduction) factor. This hydro scheme was instigated by "the Government of the day" as a bold move and was the major force of the World War II refugee and "technical" workforce inclusion of skilled and unskilled migration into the Australian environment. Although this mass "invasion" of workers with families was thought of in some circles as intrusive, the expansion of population post war years and its integration into the Australian rural sector, produced the multi- lingual multi-cultural diversity of later years. This voltmeter is very significant to the Kiewa Valley as its use was introduced during the Kiewa Hydro Scheme. Although only a small apparatus it was part of the explosion of human resources into the valley. This influx of population transformed the region from that of a basically quiet rural region to one which evolved into both an industrial and a larger residential community. This evolution in the valley created a change, not only in the "physical" landscape but also the socio-economic expansion which permitted other "tourist" based industries into the valley. This analog volt meter has two metal rods protruding from the "back" of instrument with screw on points for the negative and the positive leads allowing the "current" to flow across the calibrated resistors to indicate on the "face" side the strength of the voltage "power". The "face" of the instrument has a zero point and then five evenly graduated marks from Zero to the "100, 200 and 300" marked points of measures. A large "V" below these pointers indicates that they represent levels of voltage. Three small screws hold the "face" in place. At the back of the meter is an aluminium "clasp" with three protruding screws (positioning fasteners) and a a screw tightening fixture for the correct fastening of the "clasp" into the correction location on the meter "board".Manufacturer's logo "CSG" underneath "ITALIA"kiewa valley tourism, victorian alps, alternate energy supplies, alpine population growth -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDrill Auger, Circa early 1900s
This item wasused before diesel, electric and battery drilling apparatus were used by farmers, and other trades requiring a portable yet reliable method of drilling holes. As this item is a 3/4 inch hole drill it would be suitable for fencing and providing holes for structural studs. As with all outdoor farm equipment, man power was required (be it the farmer or farm hands). Fitness of the operator was at a high standard but protective gloves were not highly thought of as it was before occupational, health and safety regulations became mandatory over all manual handling activities, be they on rural properties or town/city factories. This period was one where the male ego was at its pinnacle i.e. the harder the tasks the more of a man was required. Hard manual work was not only the "way to go" but also a necessity. Evolution of cheap portable electric/battery powered tools opened up a more efficient method available, especially to those with less muscle strength. This item personifies the rugged environment of the rural workplace. The Kiewa Valley with its main emphasis on farming and grazing provided ample opportunity to use this construction implement. The manufacturer being a Scottish tool company is very significant in the era when this hole maker was in high demand. British steel products were of high grade and had a good record of reliability. The reliability of any tool was a solid factor for farmers and tradesmen in this semi-isolated region (Circa early 1900s) within the Kiewa Valley and its regional area. This factor,although not as crucial, post 1960s, when Asian manufacturers entered the market place and produced cheaper tools and transportation and supplies was more frequent and reliable, the need for the more expensive British made tools diminished considerably. After the influx of tradesmen from war torn Europe (post 1945) and the increased availability of tradesmen in the Kiewa Valley and its region the price of tools was and still is not as crucial and the cost of all required tools has become a minimal part of the equation. It is only with the emerging younger trades person, farmer and grazier, who have more, "one eye on production costs" and no "old ties to the motherland" inert mind set that quality tools such as this auger and other hand tools "must be made to last a life time" is no longer part of the modern work environment.This cast iron, hand operated Auger has a short barrel shaped cylinder at one end (known as the "Eye") and at the other end a Helical screw blade (screws the cutting edge into wooden material, thereby creating a hole 3/4 inch diameter in the wood) . The barrel section at the top permits a metal or wooden leverage plank to be inserted. The main rod has a 180mm long cutting/screw blade running from the bottom up towards the "eye" end. From the end of the screw blade to the handle is 380mm and cylindrical, but this changes at 550mm from the "eye" end to a 14mm x 10mm rectangular shape shaft.This shaft end is welded to the "Eye".On the shaft below the "eye" is stamped " MATHESON GLASGOW" on the front side and a spade (cards) symbol on the back.auger, hand drill, fencing, tool, rural trades, brace & bit -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDrill Auger, Circa early 1900's
This item was before diesel, electric and battery drilling apparatus were used by farmers, and other trades requiring a portable yet reliable method of drilling holes. As this item is a 3/4 inch hole drill it would be suitable for fencing and providing holes for structural studs. As with all outdoor farm equipment, man power was required (be it the farmer or farm hands). Fitness of the operator was at a high standard but protective gloves were not highly thought of as it was before occupational, health and safety regulations became mandatory over all manual handling activities, be they on rural properties or town/city factories. This period was one where the male ego was at its pinnacle i.e. the harder the tasks the more of a man was required. Hard manual work was not only the "way to go" but also a necessity. Evolution of cheap portable electric/battery powered tools opened up a more efficient method available, especially to those with less muscle strength.This item personifies the rugged environment of the rural workplace. The Kiewa Valley with its main emphasis on farming and grazing provided ample opportunity to use this construction implement. The manufacturer being a Scottish tool company is very significant in the era when this hole maker was in high demand. British steel products were of high grade and had a good record of reliability. The reliability of any tool was a solid factor for farmers and tradesmen in this semi-isolated region (Circa early 1900s) of the Kiewa Valley and its regional area. This factor,although not as crucial, post 1960s, when Asian manufacturers entered the market place and produced cheaper tools and transportation and supplies was more frequent and reliable, the need for the more expensive British made tools diminished considerably. After the influx of tradesmen from war torn Europe (post 1945) and the increased availability of tradesmen in the Kiewa Valley and its region the price of tools is not as crucial and the cost of all required tools has become a minimal part of the equation. It is only with the emerging younger trades person, farmer and grazier, who have more, "one eye on production costs" and no "old ties to the motherland" inert mind set that quality tools such as this auger and other hand tools "must be made to last a life time" is no longer part of the modern work environment.This cast iron hand operated drill, has a short barrel-shaped cylinder, known as "the eye" welded across the main rod and is 30mm in circumference. It also has a hole drilled to allow a screw to be fastened onto the hand stock ( not available).The main rod is solid for 400mm and then has been flattened and coiled (Helical screw blade) for another 200mm. At the end of the larger screw blade there is a smaller gauged starter blade with a pointer thread 15mm long. This Auger produces a 1/8th inch hole (metric measurement not used at time of manufacture) See KVHS 0469 for 3/4 inch hole and KVHS 0471 for another 1/8th inch hole.A number 5 stamped on the flat sideauger, hand drill, fencing, tool, rural trades, brace & bit -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDrill Auger, Circa early 1900's
This item was before diesel, electric and battery drilling apparatus were used by farmers, and other trades requiring a portable yet reliable method of drilling holes. As this item is a 3/4 inch hole drill it would be suitable for fencing and providing holes for structural studs. As with all outdoor farm equipment, man power was required (be it the farmer or farm hands). Fitness of the operator was at a high standard but protective gloves were not highly thought of as it was before occupational, health and safety regulations became mandatory over all manual handling activities, be they on rural properties or town/city factories. This period was one where the male ego was at its pinnacle i.e. the harder the tasks the more of a man was required. Hard manual work was not only the "way to go" but also a necessity. Evolution of cheap portable electric/battery powered tools opened up a more efficient method available, especially to those with less muscle strength.This item personifies the rugged environment of the rural workplace. The Kiewa Valley with its main emphasis on farming and grazing provided ample opportunity to use this construction implement. The manufacturer being a Scottish tool company is very significant in the era when this hole maker was in high demand. British steel products were of high grade and had a good record of reliability. The reliability of any tool was a solid factor for farmers and tradesmen in this semi-isolated region (Circa early 1900s) of the Kiewa Valley and its regional area. This factor,although not as crucial, post 1960s, when Asian manufacturers entered the market place and produced cheaper tools and transportation and supplies was more frequent and reliable, the need for the more expensive British made tools diminished considerably. After the influx of tradesmen from war torn Europe (post 1945) and the increased availability of tradesmen in the Kiewa Valley and its region the price of tools is not as crucial and the cost of all required tools has become a minimal part of the equation. It is only with the emerging younger trades person, farmer and grazier, who have more, "one eye on production costs" and no "old ties to the motherland" inert mind set that quality tools such as this auger and other hand tools "must be made to last a life time" is no longer part of the modern work environment.This cast iron hand operated drill, has a short barrel-shaped cylinder, known as "the eye" welded across the main rod and is 30mm in circumference. It also has a hole drilled to allow a screw to be fastened onto the hand stock ( not available).The main rod is solid for 400mm and then has been flattened and coiled (Helical screw blade) for another 200mm. At the end of the larger screw blade there is a smaller gauged starter blade with a pointer thread 15mm long. This Auger produces a 1/8th inch hole (metric measurement not used at time of manufacture) See KVHS 0469 for 3/4 inch hole and KVHS 0470 for another 1/8th inch hole.auger, hand drill, fencing, tool, rural trades, brace & bit -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionLetter, Richard W. Richards et al, Correspondence with Dick Richards, 1956-7
Dick Richards joined the Ballarat School of Mines in 1914, and soon afterwards was granted leave to join an expedition to Antartica. In 1915 he sailed from Australia with the Antarctic Exploration Expedition, led by Sir Ernest Shackleton. Prime Minister Bob Hawke wrote in 1984 'Your incredible journey of almost 2000 miles across the Antarctic Wastelands - involving some 9 months in the field with makeshift equipment - and you're adherence to duty in the face of enormous difficulty, suffering from scurvy, and the death of comrades, will; be an inspiration to your countrymen of the future as it is to us today." After returning to Australia Dick Richards resumed his work at SMB as Lecturer in Physics and Mathematics, and developed many pieces of experimental equipment. During World War Two he acted as a scientific adviser in the production of optical apparatus in Australia. In 1946 he was appointed Principal and twelve years later he retired after a total of 44 years service.Correspondence .1) Dick Richards to the Ross Sea Committee, 06/06/1957 .2) Letter from Wilis N. Tressler to Dick Richards, 21/12/ .3) Letter from Dick Richards to Willis N Tresslerdick richards, r.w. richards, willis tressler, cape evans, mcmurdo sound, u.s.s. glacier agb-4, lettherhead, antarctica, ballarat school of mines principal, captain mackintosh, spencer-smith, hayward, cape royds, mortimer mccarthy -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, W. B. Macdonald, The Ballarat School of Mines, Industries and Science, Annual Report 1890, 1890
The Ballarat School of Mines Annual Report 1890. Annual Report, Crown Grant, Affiliation Statute, Constitution, Examination Statutes, Associateship of The School, Department of Agriculture, Certificates Granted by Council, Fees, Form of Bequest, Gauge-Testing Apparatus, General Balance Sheet and Liabilities and Assets, Honorary Correspondents, Life Governors, Meteorological Observations, Number of Students attended The School of Mines, Office Bearers, Report of the Professor of Mineralogy and Geology and Curator of the Museum, Report of the Superintendent of Laboratories, Report of the Lecturer on Engineering and Surveying, Report of the Lecturer on Geometrical and Freehand Drawing, Report of the Lecturer on Telegraphy, Report of the Lecturer on Botany, Report of the Lecturer on Materia Medica and Physiology, Report of University Classes, Examinations Held, Scale of Charges for Assays and Analyses, Statement of Receipts and Expenditure for the year 1890 and Special Trust Funds, Statistics - Students attending Lectures, Subjects and Examiners, Subscriptions and Donations from 1st January to 31st December 1890, Time TableThe Ballarat School of Mines annual Report, 1890. Cover is browning around the edges, back cover partly detached and is torn, 184 pages. ballarat school of mines, annual report, andrew anderson j.p. - president (acting) and vice president, rivett henry bland - trustee, the hon. sir w. j. clarke - trustee, the hon. john warrington rogers - trustee, james oddie - trustee, the hon. henry cuthbert - honorary solicitor, i. j. jones - honorary treasurer, chas. kent - auditor, andrew berry - registrar, f. m. krause - professor of mineralogy and geology, and curator of the museum, alf. mica. smith - superintendent of laboratories, mr e. wattis - manager, mining laboratory, j. h. horwood - lecturer on engineering and surveyin, h. j. hall - lecturer geometrical and free-hand drawing, george day - botany, j. f. usher - materia medica and physiology, miss bella guerin - university classes, charles kent - auditor, henry krone - assistant registrar of titles, henry b. loch, d. e. martin - secretary for agriculture, r. hedger wallace - department of agriculture -
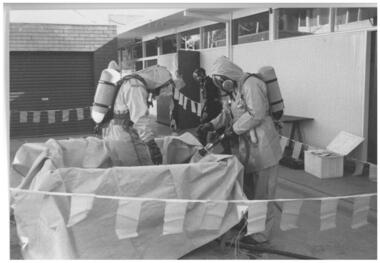 Wangaratta Urban Fire Brigade
Wangaratta Urban Fire Brigadephotographs - hazmat training
HAZMAT training at the back of the fire station in Ely St. 00007.1 - 1 person is in a decontamination tub (a tub to prevent any run off) wearing a gas suit (a fully enclosed suit), being rinsed off by a person using a fire hose and wearing a splash suit (a two piece suit that is open to the enviroment - but will prevent any direct splashing). There is also a person wearing a breathing apparatus (BA) in the background. 00007.2 - showing 2 people after training in gas suits sitting on the concrete with blankets around them. 00007.3 shows 1 person, after gas suit training been comforted by a person in a B.A, 1 in splashsuit tidying up the used gas suit. 00007.4 person removing gas suit with assistance of a person in a splash suit. the person at the rear in BA is about to pick up the blanket to wrap around the person who has been in the gas suit.5 black & white photographs showing HAZMAT (Hazardous materials) training at the fire station in Ely Street.00007.1 - '80%',ely st, hazmat, training -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Sand peg set, Mid-19th to mid-20th Century
This set of Victorian era wooden sand pegs was part of the equipment used by the Rocket Rescue Crew when attending a shipwreck. The broad pegs were designed to give a strong grip on soft sand and soil. The pegs could be used with the sand anchor as well as to give a stronger hold on the tripod holding the hawser. The same design is still available today and is used by the Army and by campers. The rocket rescue crews used a sand anchor at a beach rescue site to weigh down the rescue apparatus. The crew would connect the shackle to the other cable on the anchor and to the loose steel cable to form a triangle with the cable lengths. They would then bury the anchor in about a 0.75-meter trench, keeping the free end of the cable above the surface. This end of the cable was then connected to a block that was attached to the heavy hawser line. The block and a crotch pole were used to keep the hawser line high and taught as the survivors were hauled to shore on a line or in a breeches buoy. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s, the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This set of sand pegs would have been used with sand anchor that is part of the rocket rescue equipment . It is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Peg or spike; set of twelve wooden pegs, painted red. Pages have a long, thick square shank with bevelled side edges, flat top with broad hook on one side of the top and a point at the other end. A small hole goes from one side to the other side near the centre of the shank, on the face without the hook. flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket equipment, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, whip line, endless whip, harbour board, sand anchor, rocket set, anchor backer, beach anchor, backer, steel cable, wire cable, sand peg, wooden tent peg, army peg, military peg -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Technical pamphlet/s, Westinghouse Brake & Saxby Signal Co. Ltd, "Combined Guard's Van Valve and Gauge for Vacuum Brakes", 1924 - 1928
2287.1 - Four page technical pamphlet, titled "Combined Guard's Van Valve and Gauge for Vacuum Brakes", published by Westinghouse Brake and Saxby Signal Co. Ltd. November 1926. Manual No. D.P. 8. 2287.2 - Eight page technical pamphlet, titled "Brake Control Valve for Automatic Vacuum Brake", published by Westinghouse Brake and Saxby Signal Co. Ltd. January 1928, Manual No. D.P. 15. Saddle Stapled. 2287.3 - Twelve page technical pamphlet, titled "Vacuum Brake Apparatus", published by Westinghouse Brake and Saxby Signal Co. May 1924, Manual No. D.P. 3. Saddle Stapled. 2287.4 - Eight page technical pamphlet, titled "Prestal Vacuum Brake Cylinders Combined and Separate Types", published by Westinghouse Brake and Saxby Signal Co. Ltd. January 1928, Manual No. D.P. 14. Saddle Stapled. Two copies held.Each have "Colin Rutledge" stamped on top of page 1.trams, tramways, westinghouse, railway brakes, vacuum brakes, equipment -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Bottle, H London Chemist, Early 1900s
This bottle was made by the Whitall Tatum Glass Company in New Jersey, U.S.A This company operated from 1806 to 1938. The bottle was used by Harry London in his Warrnambool pharmacy. Born in England, Harry London arrived in Victoria in 1883 and worked as a chemist in Ballarat and Euroa. In 1891 he went back to England where he studied dentistry. In 1891 he came to Warrnambool where he bought the pharmacy business of the late William Nettleton. He occupied the Nettleton building in Liebig Street (95 Liebig Street today) until 1896 when he erected new premises at the south west corner of Liebig and Koroit Streets. In 1896 London was the only Warrnambool chemist using a Pasteur filter to make up his prescriptions. In his dentistry business he used gas, chloroform and cocaine as anaesthetics. The making of dentures was his speciality. In 1904 London was the owner of the only set of Rontgen X Ray apparatus in Warrnambool. In 1905 his shop was the first in Warrnambool to establish electric lighting. This bottle is of importance as it is one of the few items we have associated with the prominent Warrnambool chemist, Harry London. It is comparatively rare so it is of some local significance. This is a glass bottle with a rectangular base with curved ledges, a circular neck and a circular moulded top. There is no stopper and the top is badly chipped. The name of the chemist is embossed on the front in an indent in the glass. ‘H. London, Chemist and Dentist, Warrnambool’ On Base: ‘W.T.Co, T, U.S.A.’ harry london, chemist, chemists in warrnambool, history of warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Bell, Probably second half of 19th Century or first half of the 20th Century for this particular item
The school bell has been used in various forms for several centuries. In Australia and the UK it was often a hand bell, located on the teacher's desk in a small school. In larger schools it was positioned in a central area, and one bell was used to signal to all classrooms. In North America it was more usual to find a large bell on a stand located in a central area of the school where it could be heard by everyone throughout the premises. More recently, the school bell has become wall located, and electrically activated, using a mechanical timing apparatus. Now the same bell is computer programmed and activated, although there are many older bells still in operation. The school bell was rung at the beginning at the school day, often to summon students to the morning assembly in larger schools. It was then rung throughout the day to signal the start and end of specific lesson periods, the beginning and end of school morning and afternoon breaks, the lunch period, and the end of the school day, no doubt eagerly awaited by many students! The school bell was used as a timing device in schools to signal the start and end of specific activities.Bell brass with heavy metal square shaped base and wooden handle-hand held, Kel(?)her Melbourne on the topInscribed on the metal at the top of the bell are the letters "Kel(?)her Melbourne" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, bell, school, lessons -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photography, Camera Kodak Flash 11 with leather case c1940, c1940
Kodak was founded by George Eastman and Henry A. Strong on September 4, 1888 in New York USA. During most of the 20th century, Kodak held a dominant position in photographic film. Kodak began to struggle financially in the late 1990s, as a result of the decline in sales of photographic film and its slowness in transitioning to digital photography, despite developing the first self-contained digital camera. The first model of the Kodak camera appeared in 1888. It took round pictures 6.4 cm (2.5 in) in diameter, was of the fixed focus type, and carried a roll of film enough for 100 exposures. Its invention practically marked the advent of amateur photography, as before that time both apparatus and processes were too burdensome to classify photography as recreation. The first films had to be loaded into the camera and unloaded in the dark room, but the film cartridge system with its protecting strip of opaque paper made it possible to load and unload the camera in ordinary light. The Brownie camera was introduced in 1900, creating a new mass market for photography. This Kodak Brownie Box Camera is typical of the cameras used by amateur photographers c 1940A metal Kodak Brownie Box camera with a leather case, and an empty folder for negatives and prints Front ; KODAK / 'KODET' LENS / Brownie Flash 11 / CAMERA / MADE IN ENGLAND BY KODAK LTD LONDON Folder The Pleasures of PHOTOGRAPHY / Make Photography Your Hobby kodak ltd, eastman george, strong henry, photography. brownie box camera, digital photography, -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryInhaler, Probyn Williams, Mayer & Meltzer, c. 1900
Hurley, Sir Thomas Ernest Victor (1888-1958) was gifted this Probyn Williams inhaler in 1914. After studying at Melbourne University, Victorian-born Hurley was a Medical Officer at the Royal Melbourne Hospital until he commenced private practice in Collins Street. He was appointed Captain Australian Army Medical Corps, AIF and served in Gallipoli with the 2nd Field Ambulance. He served in Enypt, London, and the Western Front during World War 1. He gained a Companion of the Order of St George and St Michael in 1917. Upon return to Melbourne he held positions such as surgeon to Victoria Police (1928-1956), elected to Council of the Victorian branch of the British Medical Association, member of the Charities Board of Victoria and foundation member of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons and chaired the Flying Personnel Research Committee m a consulting surgeon at the Royal Melbourne Hospital. This apparatus is transitional between Clover's and Hewitt's having Clover's narrow "ways" and compact size, but using Hewitt's ether-control lever.Black round topped box with brass hooks [missing] at front and brass hinges at rear. The initials T.E.V.H. are printed in gold leaf on the front. There is a black fabric handle on the top. Inside the box is black padding with the manufacturer's logo printed in gold leaf. There is a square section in the base of the box for holding the square clear glass bottle for ether. The pear-shaped mask is made of metal. There is also a metal ether measure for pouring the ether. The metal inhaler is ovoid shaped. The rotating gauge has a series of numbers engraved onto the inhaler for measurement. There is an elbow joint attaching a re-breather bag, with a small amount of waxy paper remaining attached with a thin ribbon. There is a small glass bulb encased in a metal housing. Printed in gold leaf on front of box: T.E.V.H. •Printed in gold leaf on inside lid of box: MAYER & MELTZER / LONDON / MELBOURNE & CAPE TOWN •Engraved on side of inhaler: PRESENTED / TO / T.E.V. Hurley Esq.,M.D.M.S. / by / THE M.S.S. / 15.6.14. •Engraved on reverse side of inhaler: PROBYN WILLIAMS / ETHER INHALER •Moulded into connector on elbow joint: MAYER & MELTZER •Stamped into base of metal pourer: MAYER & MELTZER / LONDON •Blue sticker with white printed text on front of inhaler: O.2.21.hurley, thomas ernest victor, probyn williams, university of melbourne, world war 1, wwi, gallipoli, australian army medical corps, medical student society, mayer & meltzer, clover, joseph, hewitt, fredrick william -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumFunctional object - Bottle
Recovered from the wreck site of the Fiji. The barque Fiji left Hamburg on 22nd of May 1891. The vessel went ashore at 3 am on the morning of the 6th of September 1891in squally and boisterous weather soon after sighting Cape Otway. The wind had suddenly veered, and the vessel missed stays after attempting to wear ship and was driven onto the rocks. Attempts were made to launch the boats but they were swamped and dashed to pieces. Delays in getting the lifeboat and rocket apparatus to the scene resulted in 12 of the 25 crew drowning after 10 hours trapped on board. A local resident, Arthur Wilkinson, lost his life trying to save one of the crew who was struggling in the surf. Coffins were made out of the wreck timbers and the men buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The deaths precipitated critical comment in the press over the lack of prompt action. Other news items appeared claiming drunk and disorderly behaviour by plunderers amongst the corpses and wreckage on the beach. The controversy reached parliament.Brown bottleWarner's, Safe, Cure, Melbourne Aust, London Eng, Toronto Can, Rochester NY USAwrecks, salvage, bottle, barque fiji -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomTraining Set, Universal, Wireless, No 1, about 1948
The kit is packed in 2 wooden transit boxes. The Training Set is a semi-portable instrument for training operators in morse reading and sending and R.T. communication. The set comprises audio oscillators for morse reading, morse interference and background noise interference, power supply for microphones, an audio amplifier, and a switch board for group working with up to six independent, contained in the instructor's set. The instructor and each operator under training has a receiver-head gear, a hand microphone and a morse key. The instructor has an additional morse key used for providing morse interference. In the case of each operator, the microphones and headphones plug into an "operator's control unit" fitted to the table in front of each operator. The units also house a morse key, and are connected to the instructor's set by four-core cable. Plug and socket connections are used. The apparatus may be used for a class of up to 36 operators. Working Instructions - filed on Object Data Record radio, wireless, training set -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - OFFICIAL PROGRAMME VICTORIAN 1851-1901 GOLDEN JUBILEE
Six page Official Victorian Golden Jubilee Program dated April 24th 1902. Cover depicts a lithograph scene of a kneeling 'digger' panning for gold in the centre of a scrolled heading reading 'Victorian Gold Jubilee 1851-1901 Exhibition Official Programme Bendigo. Advertisements for 23 Bendigo business houses enclosed. Victoria Brewery, E Owen, Wertheims Depot, Stapleton's Arcade, Bartlett's Bros, Bosito's, W Sanderson, Morley Johnston & Co, D'Arc's Marionettes, Waxwork & Cyclorama, 'The Favourite Shop', Henderson & Goodisson, T R Jones, Mr J H Knight, Bush's Stores, George H Bush & Co, Faul's Acetylene Apparatus, X L Gas Engines, G Sallaway, J Carr's Hopetoun Hotel, Hartley Cycles, Kandy Koola Tea, Dessaux Fils Vinegar. Covering letter to Jim Evans from Winsome Menadue via John Messer.bendigo, business, gold jubliee 18561 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBottle Corker, late 1800's to early 1900's
This hand held, wooden bottle corker would have been used by soft drink or wine producers to insert corks into their bottles to seal the drink inside. It seems it may have had a metal tip on the end of the plunger, as do other similar bottle corkers, because this plunger has a compressed end and a ring shape impressed into the wood a little way up from the tip. How to use the bottle corker … - soak a long, bullet shaped cork in water to soften it - place the bottle corker over the bottle’s neck - insert the cork through the side opening and place onto the metal funnel - push the plunger down onto the cork, forcing it into the tapered, which will squeeze the cork to size as it enters the bottle. Use a mallet or hammer if necessary The design of this bottle corker is very similar to “"Redlich's Apparatus for Corking Bottles", which was invented and patented by Henry Redlich of Chicago, USA, in 1862, US patent #35,325. H. Redlich’s gave the following instructions for the use of the bottle corker: “DIRECTIONS: SOAK THE CORK, DROP INTO THE OPENING AND TAP THE PLUNGER WITH A MALLET OR HAMMER.” This hand held, wooden bottle corker would have been used by soft drink or wine producers to insert corks into their bottles to seal the drink inside. It seems it may have had a metal tip on the end of the plunger, as do other similar bottle corkers, because this plunger has a compressed end and a ring shape impressed into the wood a little way up from the tip. How to use the bottle corker … - soak a long, bullet shaped cork in water to soften it - place the bottle corker over the bottle’s neck - insert the cork through the side opening and place onto the metal funnel - push the plunger down onto the cork, forcing it into the tapered, which will squeeze the cork to size as it enters the bottle. Use a mallet or hammer if necessary The design of this bottle corker is very similar to “"Redlich's Apparatus for Corking Bottles", which was invented and patented by Henry Redlich of Chicago, USA, in 1862, US patent #35,325. H. Redlich’s gave the following instructions for the use of the bottle corker: “DIRECTIONS: SOAK THE CORK, DROP INTO THE OPENING AND TAP THE PLUNGER WITH A MALLET OR HAMMER.” Bottle corker, a hand operated wooden corking device for sealing bottles. Bottle corker has two parts comprising a wooden plunger rod with knob handle, and wooden cylinder containing a metal tube that is flared to a funnel shape on the top. The cylinder has a hole the diameter of the rod at both ends and an oval insertion slot in one side. The tip of the plunger rod is slightly compressed and it has an indented line around the circumference as though it has had something attached to it. Manufactured in the late 1899s to early 1900s in Melbourne.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, cork -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet - Annual Report, The Ballarat School of Mines, Industries and Science, Annual Report 1891, 1891
The Ballarat School of Mines Annual Report 1891. Annual Report, Crown Grant, Affiliation Statute, Constitution, Examination Statutes, Associateship of The School, Certificates Granted by the Council, Clunes Branch Report, Departmental Expenditure, Fees, Form of Bequest, Gauge-Testing Apparatus, General Balance Sheet and Liabilities and Assets, Honorary Correspondents, Life Governors, Meteorological Observations, Number of Students attended The School of Mines, Office Bearers, Practical Treatment of Ores, Report of the Professor of Mineralogy and Geology and Curator of the Museum, Report of the Superintendent of Laboratories, Report of the Lecturer on Engineering and Surveying, Report of the Lecturer on Mathematics, Report of the Lecturer on Electrical Engineering and Telegraphy, Report of the Lecturer on Botany, Report of the Lecturer on Geometrical and Freehand Drawing, Report of the Lecturer on Materia Medica and Physiology, Report of University Classes, Report on Mining Laboratory, Examinations Held, Scale of Charges for Assays and Analyses, Statement of Receipts and Expenditure for the year 1891 and Special Trust Funds, Statistics - Students attending Lectures, Subjects and Lecturers, Subjects and Examiners, Subscriptions and Donations from 1st January to 31st December 1891, Syllabus of Lecture CoursesThe Ballarat School of Mines Industries and Science Annual Report, 1891. Cover is browning around the edges, front cover has small tear on bottom of cover, 132 pages. ballarat school of mines, annual report, andrew anderson j.p. - president, f. j. martell - vice president, r. denham pinnock - vice president, rivett henry bland - trustee, the hon. sir w. j. clarke - trustee, the hon. john warrington rogers - trustee, james oddie - trustee, the hon. henry cuthbert - honorary solicitor, c. eyres - honorary treasurer, charles kent - auditor, andrew berry - registrar, f. m. krause - professor of mineralogy and geology, and curator of the museum, alf. mica. smith - chemistry, metallurgy, natural philosophy, f. m. krause - geology, mineralogy, geological surveying, j. h. horwood - lecturer on engineering and surveying, h. j. hall - lecturer free-hand and model drawing, george day - botany, j. f. usher - materia medica and physiology, c. w. wilson - university classes, isaac jaques jones j.p., mr e. wattis - manager, mining laboratory, j. a. dawson - electrical engineering and telegraphy, elder gray, harry e. sando, charles matthews - auditor, j. h. daley - auditor, henry crone - assistant registrar of titles, henry b. loch, isaac jacques jones, charles eyres, j.a, j.a. dawson, statistics, university classes, bella guerin, c.w. wilson, clunes branch of the ballarat school of mines, w.e. burbridge, h.j. hall, museum, state school students, daniel walker, a.j. higgins, state school science classes -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionCorrespondence, Letters from A. Gallenkamp & Co to the Ballarat School of Mines, 1898, 1898
Two hand written letters relating to orders from the Ballarat School of Mines .1) 31 March 1898 Dear Sir, In reply to your favor of 23 February we have nearly all the apparatus now ready you were good enough to order. I've [illegible] here 12 cases [illegible] fomr Robinson's goods we likely had to wait about 5 months for supply from works, the demand having been quite extraordinary this year. Ou people [illegible] are so busy with Rontgen ray tubes that we cannot get crokes ad Uranium tubes as quickly as we should like. Yours are not yet to hand, have however a promise of delivery very shortly when all goods will be ready for dispatch. Now we have [illegible] in our very large new warehouses in Sun Street, we are importing [illegible] and other glass goods in four or five times the quantity, we could store in our old place, so that we shall hold presently the August stock of glass apparatus in London, enabling us to fill orders of every size in much shorter issue. We shall not loose a day or a book so soon as we are ready with the order early in April. We beg to call your attention to fene glass listed by the [illegible] book post. Your esteemed further orders will oblige. Yours truly [Illegible] .2) 09 September 1898 Dear Sir We thank you for the favor of your order of August just received and give [illegible] attention. arriving to our ... For Reagent bottle 1757 you state no size, we will give you 250cm as the size usually order here. ... We beg to confirm our letter of 2nd inst and enclose two circulars of interest. Yours Faithfully [illegible]a. gallenkamp and co., letterhead, ballarat school of mines, frederick martell, x-ray, xray, rontgen tubes, crooks tubes, uranium tubes -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaArticle, Herald, Gymnasium of novel design to be lighted from dome, 23 October 1919
"GYMNASIUM OF NOVEL DESIGN TO BE LIGHTED FROM DOME Trafalgar Day (October 21) was selected as a fittlng occasion for the laying of the foundation stone of the "Norla" gymnasium In connection with the Missions to Seamen new building in Flinders street extension. The ceremony was performed by Lady Fraser. The design of the gymnasium is an entirely novel one. The building is of reinforced concrete, with a dome having a span of 40 feet. The design is based on that of the Pantheon at Rome, and like the Pantheon has no windows. The entire lighting is from an opening In the centre of the dome. Through this aperture the light radiates equally throughout tho gymnasium; and the necessary ventilation is also secured. Between the gymnasium and the main building there is an ambulatory 12ft. wide, from which onlookers may watch the games and exercises. The floor Is to be laid with a fall to the centre for rlnking purposes. The gymnasium will complete the buildings connected with the Missions to Seamen In Melbourne, and the claim Is made that the society has not anywhere a flner or more complete set of buildings than the seamen are favored with here. The ladies who take an active interest in the Mission are inviting subscriptions to furnish the gymnasium with trapeze, punch balls, and other exercising apparatus. Messrs Walter and Richard Butler are the architects."norla dome, lady fraser, 1919, foundation stone, walter richmond butler (1864–1949), richard butler, gymnasium, trafalgar day, simon fraser (1832-1919), pantheon -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Hand Barrow, 1860s
This hand barrow, sometimes called a Welsh hand barrow, was used to transport a load of marine rescue equipment from the beach cart to the rescue site, particularly over hilly, uneven or rough terrain. Hand barrows were in common use in the 19th century. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This hand barrow is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Hand barrow; a transporting device carried between two people walking one in front of the other. A wooden ladder-like frame with two handles at each end, blue painted body with unpainted handles. Seven equal-length slats are joined at equal distance between two parallel poles, and two longer slats are attached diagonally between the first and last slats as a brace. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, hand barrow, manual transport, welsh hand barrow
