Showing 555 items
matching forests commission
-
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFood masher
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)...used at fire camps Forests Commission Victoria (FCV ...used at fire campsMetal food masherforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, camping equipment -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionChief Fire officer Uniform
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)..., in about 2000 Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Bushfire Chief Fire ...Uniforms were not commonly worn by forest and fire staff. This uniform was tailor made for the Chief Fire Officer, Gary Morgan, in about 2000Chief Fire Officer uniform (jacket and tie) belonging to Gary Morganforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV presentation plaque and mould
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... be used. Hand made Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Forest Signs ...The wooden mould was originally made in the early 1980s by one of the crew in his spare time in East Gippsland (Bairnsdale maybe). It was passed it on to Ian Long and then Barrie Marsden at Altona. It was not made for any particular purpose other than just a copy of the iconic FCV logo. It sat in the office at Altona for a little while until one day Barry thought it could be used to cast a solid replica. The wooden mould was taken to a foundry in North Melbourne and three bronze replicas were cast and polished. One was used when the Chief Fire Officer, Bary Johnson, was retiring More were cast in brass and the plaques became a standard presentation item for retiring FCV personnel. The wooden mould eventually cracked and can no longer be used. Hand madeWooden mould and presentation plaqueforests commission victoria (fcv), forest signs -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFire prevention gallows signs (six double sided signs with different messages on each side)
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... to be read from a moving vehicle Forests Commission Victoria (FCV ...Bushfire awareness gallows signs were common features during the summer fire season and hung outside both FCV offices and on major roadways These six large metal signs have different text on each side and the message and lettering is simple enough to be read from a moving vehicle Metal Fire awareness gallows signsforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest signs -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionIncident control desk signs
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... control system Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Bushfire Forest ...Signs used to identify roles at bushfires These roles and titles were used prior to 1984 and the introduction of the AIIMS control system Signs used to identify people and roles as bushfire incidentsforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest signs -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionClock
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... Commission Victoria (FCV) Forest Signs Standard issue Public Service ...Thought to have come from the old Newport workshopsStandard issue Public Service wall clockforests commission victoria (fcv), forest signs -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV measuring band
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... and recalibrating. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) assessment Forest ...Used for measuring distances in the forest. Steel bands (out of tradition were called the chain) were created around 1890. They replaced the traditional Gunter chain. The band could be repaired by soldering slip-on joiners and than and recalibrating.Steel measuring band (50m) on plastic reel with winding handleFCV 281forests commission victoria (fcv), assessment, forest measurement, surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV measuring band
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... and recalibrating. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) assessment Forest ...Used for measuring distances in the forest. Steel bands (out of tradition were called the chain) were created around 1890. They replaced the traditional Gunter chain. The band could be repaired by soldering slip-on joiners and than and recalibrating.Steel measuring band (50m) on plastic reel with winding handle missingFCV 188forests commission victoria (fcv), assessment, forest measurement, surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV measuring band
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... and recalibrating. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) assessment Forest ...Used for measuring distances in the forest. Steel bands (out of tradition were called the chain) were created around 1890. They replaced the traditional Gunter chain. The band could be repaired by soldering slip-on joiners and than and recalibrating.Steel measuring band (1 chain - 66 feet) on metal reelFCV 075forests commission victoria (fcv), assessment, forest measurement, surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionTelescope in wooden box
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)...used for surveying Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Forest ...used for surveyingTelescope used for surveyingStanleyforests commission victoria (fcv), forest measurement, surveying -
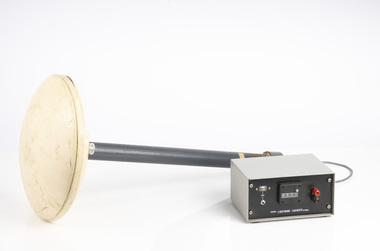 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionLightning Detector
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... position in 10, 20, and 30 minutes Forests Commission Victoria (FCV ...Lightning is one of the major causes of bushfires, particularly in the remote mountains. This lightning detector system was developed by Dr. Peter Kourtz at Canada’s forest fire research institute. By 1977, some 300 were in use across the country. The small mushroom antenna could detect short-range (20-mile) changes in electrostatic field associated with lightning strikes. It needed to be placed out in the open on a hilltop and away from nearby trees. It simply counted the number of "strikes". The detector doesn't seem to have a direction finding capability or be able to distinguish between cloud-to-cloud or cloud-to-ground lightning. It's not sure how this particular unit found its way to Victoria. The Bureau of Meteorology's (BOM) current lightning detector network uses radio waves emitted by lightning to pinpoint the location of lightning strikes. The network is operated by a private company that sends data to the BOM in real time. Lightning detection systems use sensors like antennas, GPS receivers, and processing systems to detect radio waves, also known as sferics. The systems calculate the lightning's location and speed by measuring how long it takes for the radio signal to reach the different antenna stations. The BOM also has a Thunderstorm Tracker that uses weather radar data to identify areas of potential thunderstorm activity. The tracker updates every six minutes and shows the direction thunderstorms are moving, as well as their expected position in 10, 20, and 30 minutesLightning detector 1970sQ-Techforests commission victoria (fcv), weather, bushfire, bushfire aviation -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionRelative Humidity Meter
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... to the adiabatic saturation temperature. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV ...Bushfire behaviour is influenced by many factors including temperature, relative humidity (RH), forest type, fuel quantity and fuel dryness, topography and even slope. Wind has a dominant effect on the Rate of Spread (ROS), as well as fire size, shape and direction. Temperature and relative humidity have major impacts on fuel dryness and therefore upon the availability of fuel for combustion. The amount of fine fuel available can increase rapidly from nearly zero when fuel moisture content is more than 16% after rain or a heavy morning dew, to many tonnes per hectare as fuel dries out later in the day and the moisture content drops below 9%. This explosive escalation in the amount of available fuel can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. This device is used for determining air temperature and relative humidity. It contains two thermometers, one of which is covered with a wick saturated with ambient temperature liquid water. These two thermometers are called dry bulb and wet bulb. Once the thermometers to reach equilibrium temperatures the two thermometers are quickly read. The figures are then used to convert the dry bulb temperature TDB and the wet bulb temperature TWB into humidity information. The wet bulb temperature is approximately equal to the adiabatic saturation temperature. Relative humidity meter in wooden box two stainless steel tubes contain wet and dry thermometers A small clock drives a fan motor in the base to circulate airforests commission victoria (fcv), weather, bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionChadwick-Miller Office Calculator
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... to that number. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Forest measurement ...Used for adding and inventory work The Speedie was a manual adding machine that could not perform subtraction. It consisted of eight columns and five rows of keys in both maroon and ivory. It had a nine digit display that could add up. It could perform multiplication by using repeat action. If you examine the keyboard you’ll note that it only shows numbers 1 through 5. If you want to use numbers 6 through 9 then what you do is hit two keys that add up to that number. Simple office adding machine Made from Bakelite Chadwick-Miller Inc (CMI) was a Boston based importer of low-cost gift items and stationery products sourced mostly from Japan. These products were branded as Chadwick-Miller although CMI was not a manufacturer. It is known that Chadwick-Miller was in business in 1960, although its founding year is unknown. The company dissolved in 2007.Speedie add-a-maticforests commission victoria (fcv), forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionLong Range Signal Lamp
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... World War 1 and also through to World War 2 Forests Commission ...These lamps were used for military communications during World War 1 and also through to World War 2A portable, electric morse signalling lamp, used for daylight communications The lamp design was patented in 1916 by Oliver Lucas. This unit was manufactured in 1918 This signalling lamp used an external battery as a power source. An adjustable screen is provided (used with a coloured lens) for night time signalling Includes sight tube Lucas Birmingham 1918forests commission victoria (fcv), communications -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionSpotting telescope
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)...Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Communications Surveying ...Telescope mounted on tripodL McKenzieforests commission victoria (fcv), communications, surveying -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionArmstrong Rapid Log Calculator
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... Commission Victoria (FCV) Forest Harvesting Forest measurement ...Logs were sold to sawmillers from State forest from 1 July 1974 in cubic metres (true volume). Previously sawlogs had been sold on the basis of Hoppus volume. This simple device with two rotating wheels enabled staff in FCV offices to rapidly calculate log volumes from measurements taken in the bush of log girth and length and recorded on paper log dockets. From the early 1980s automated systems became available with the advent of cheap electronic office calculators and simple computers.An early manual device that was superseded by electronic calculatorsOffice Device Twin rollers used to quickly and simply calculate true log volumes using measurements of girth and length. An allowance could also be made for pipe defects. The top roller was for larger diameter logs.Imperial measurement of logs (pre 1976)forests commission victoria (fcv), forest harvesting, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPlanimeter (fixed arm)
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... were taken to ensure accuracy and precision Forests Commission ...The heavy weight is pinned onto the map and the tracing arm is used to follow the boundary to be measured Reading the number of revolutions from the two the scale wheels the area in square inches could be measured. Knowing the scale of the mapsheet the figure was converted to areas or hectares Generally at least three measurements were taken to ensure accuracy and precisionPlanimeter used to measure areas from scale maps. Includes wooden box One revolution of the main wheel equaled 10 square inches. A smaller rotating scale on the side was used to subdivide the area.Benallaforests commission victoria (fcv), forest measurement, surveying -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPlanimeter (Digital)
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... taken to ensure accuracy and precision Forests Commission ...The heavy weight is pinned onto the map and the tracing arm is used to follow the boundary to be measured. Reading from the digital scale the area in square centimetres could be measured. Knowing the scale of the mapsheet the figure was converted to areas or hectares Generally at least three measurements were taken to ensure accuracy and precisionPlanimeter used to measure areas from scale maps. Kent Planitron UP103forests commission victoria (fcv), forest measurement, surveying -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPlanimeter (roller digital)
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... taken to ensure accuracy and precision Forests Commission ...The rollers move over the map as the tracing arm is used to follow the boundary to be measured. The wheels allow unlimited horizontal travel and vertical travel within the limits of the arm movement. They measure in the X and Y directions Reading from the digital scale the area in square centimetres could be measured. Knowing the scale of the mapsheet the figure was converted to areas or hectares Generally at least three measurements were taken to ensure accuracy and precisionPlanimeter used to measure areas from scale maps. Includes box but no charger Plancom KP90forests commission victoria (fcv), forest measurement, surveying -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionMapping dividers
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)...used to measure distances on maps Forests Commission ...used to measure distances on mapsAdjustable stainless steel mapping dividers with wooden boxforests commission victoria (fcv), forest measurement, surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionParallel ruler
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)...Used to draw parallel lines on maps Forests Commission ...Used to draw parallel lines on mapsHeavy metal ruler on brass rollers with a wooden boxforests commission victoria (fcv), surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionDumpy level
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... and contours Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Surveying mapping SCA ...Engineers level used to lay out construction sites, roads and contoursMetal dumpy with box level SCAforests commission victoria (fcv), surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Actionmap measuring wheels
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV).... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Surveying mapping Map scales ...The map wheel is a simple, fast and accurate way to measure distances on maps, whether in straight lines or along curves. Hold the device from the tip and trace with the small wheel at the bottom along the line to be measured Measures distances in miles, kilometres or nautical miles depending on the scale on the side.Two metal map measuring wheel sMap scales on each side of wheelforests commission victoria (fcv), surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionMapping scale ruler
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)...Used to measure distance on scale maps Forests Commission ...Used to measure distance on scale mapsScale rulerW&G forests commission victoria (fcv), surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPrototype fuel moisture meter
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... Commission Victoria (FCV) Bushfire Forest measurement T-H Fine Fuel ...Bushfire behaviour is influenced by many things including temperature, relative humidity, forest type, fuel quantity and fuel dryness, topography and even slope. Wind has a dominant effect on the Rate of Spread (ROS), and also bushfire size, shape and direction. Fuel arrangement is as important as fuel quantity (tonnes/ha). Fibrous and ribbon bark, together with elevated and near-surface scrub fuels act as ladders which lead flames into the tree canopy. But the availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Since the 1930s foresters, firefighters and researchers have been working to develop quick and reliable techniques for measuring fuel moisture content. One of the most accurate methods is slowly drying a sample of fuel in a conventional oven for 24-48 hours to remove all the moisture and measuring the weight difference, but this takes time and is not practical in the field when rapid measurements are needed. But oven drying is often used as a benchmark to compare other methods. Microwave ovens are faster but can cause uneven drying and even char the fuel. They are also not very practical for use in the field. Some mathematical models rely on weather records such as rainfall, wind speed, evaporation, cloud cover, shading, relative humidity, slope, aspect and season of the year to predict soil and fuel moisture. The Keetch-Byram Drought Index of soil dryness is the most common. But complex fuels with leaves, twigs, grass etc make the predictive models often inadequate for fine fuels. The most common technique in Victorian forests until recently was the trusty Speedy Moisture Meter. Originally developed in England during the 1920s for measuring moisture in wheat and other grains it was adapted for Australian forest fuels in the 1950s (I think). Fuel was first ground using a spong mincer, often attached to the bullbar of a vehicle, and a small sample placed into the Speedy together with a measure of calcium carbide and then sealed. A chemical reaction created gas pressure which was read on the external dial. There were important techniques with cleaning, mincing and using the chemicals with the Speedy to give reliable readings, but it was quick, inexpensive, robust, portable and practical in the field. It was used routinely before igniting a fuel reduction burn or measuring fuel moisture differentials on slash burns. But in about 1996, Karen Chatto and Kevin Tolhurst from the Department’s Creswick Research Station developed the Wiltronics Fuel Moisture meter which measured electrical resistance. Wiltronics is an Australian owned company operating from Ballarat. The final result was a kit that was portable, accurate and could reliably measure fuel moisture contents between 3% and 200%. Although expensive, it is now widely used by fire agencies around the world which has virtually relegated the Speedy to the back cupboard.Prototype Fuel moisture meterT-H Fine Fuel Meterforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFuel sampling ring
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... was pushed into the litter to sample 0.1m2 Forests Commission ...Used to sample fine fuels on the forest floor. The ring was pushed into the litter to sample 0.1m2Heavy metal ring with sharpened bottom edgeforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionSpeedy Moisture meter test kit
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... meters Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Bushfire Forest ...Used for pressure testing and recalibrating Speedy Moisture metersKit used pressure test Speedy Moisture metersforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFuel Mincer
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... out. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Bushfire Forest ...Used to mince fuel samples to measure moisture content Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Fuel mincer Made at Altona as an alternative design to the commercial Spong Mincer With wooden plug to push fuel into the mincer and glass jar to collect sampleforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionSpong Fuel Mincer
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... out. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Bushfire Forest ...Used to mince fuel samples to measure moisture content Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Spong No 10 food mincerforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionElectric Fuel Mincer
... Forests Commission Victoria (FCV)... out. Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) Bushfire Forest ...Used to mince fuel samples to measure moisture content Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Battery operated Fuel mincer. Plugs into 12 volt car cigarette lighter socket Adaption using parts from commercial food processor Made at Altona as an alternative design to the commercial Spong Mincer Glass jar to collect sampleforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement
