Showing 359 items matching "missionaries"
-
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Undated c.1864
Mrs Elizabeth Draper (1808 - 1866). Second wife of the Rev. Daniel James Draper (1810 - 1866). Born Wickham, Hampshire 28 August 1810. In 1830 joined the Methodist Society at Fareham and became a local preacher. Nominated in March 1834 as a candidate for the Wesleyan Methodist ministry. Appointed preacher on probation to the Charteris circuit. Married Sarah Webb in September 1835, ordained 7 October 1835, sailed for Australia on 13 October 1835. Served at Parramatta, where his wife died on 16 February 1838. Married Elizabeth Shelley (1808 - 1866), daughter of William Shelley, formerly a missionary in Tonga and Tahiti in July 1939. Served in N.S.W., Victoria and South Australia. Elected President of the 1859 Conference. Granted leave in 1865 to return to England as the Australian representative to the British Conference. He was returning to Australia on the SS London in January 1866 when he and his wife, along with 244 others, perished when their ship sank during a fierce storm in the Bay of Biscay.Sepia toned, carte de visite studio portrait of Mrs Elizabeth Draper, seated at a table.daniel james draper, sarah webb, elizabeth shelley, ss london, bay of biscay, methodist, wesleyan, minister, president of conference, shipwreck -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, The Inheritance
A novel for young girlsThis is a book of 326 pages. It has a dust cover, partly torn, with an illustration of a man and a woman on a yellow background on the front cover. The spine of the dust cover is yellow with black printing and there is blue printing on the front cover and black printing on the back cover. The hard cover is blue with black printing. The pages contain black printed text. There is a book plate on the inside front coverfictionA novel for young girlswarrnambool baptist church, sacks jewellers warrnambool, audrey sack -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph - Surrey College Cadet Corps, 1899, 1899
Surrey College was opened in early 1892 by Rev. Dr Frederick Darling who had been the first minister of the Presbyterian Church in Canterbury Road. He resigned this position to open the school which operated until 1908 with additional premises at 12 Vincent Street. The school had 40 boarders as well as day boys. Courses included algebra, euclid, history, typewriting, shorthand and drill. In the 1930s, Nethercourt Private Hospital took over the site. Later it became St Jude's Hospital. land in front of the building was subdivided off in the 1970s. The building is still extant as a private dwelling with York Street, Surrey Hills as the address. This is one of 3 photos donated by Susan Hobbs, whose grandfather Rev. George Edward Downton is thought to have been a student at the college. George E. Downton was born in Avoca in 1885. He was later a missionary in New Guinea and Secretary to the Australian Board of Missions in Adelaide. He died in 1926 or 1927. Sepia photo of 26 men and boys dressed in military uniform, many holding rifles. They are standing in front of a brick building with bay windows with blinds and curtains. There is a clump of foliage and grass in front of boys. "Surrey College - Surrey Hills / Principal: Rev Frdk. A. Darling, Melb. Univ./Cadet Corps, 1899." On the mount below the photo. Inscription on bottom right hand corner of photo: "Prepare for cavalry"schools, 1899, surrey hills, surrey college, rev frederick a darling, george edward downton, susan hobbs, union road, nethercourt hospital, st jude's hospital, 219-223 union road, cadet corps, 1890-1899 -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph - Surrey College staff and boarders, 1899, 1899
Surrey College was opened in early 1892 by Rev. Dr Frederick Darling who had been the first minister of the Presbyterian Church in Canterbury Road. He resigned this position to open the school which operated until 1908 with additional premises at 12 Vincent Street. The school had 40 boarders as well as day boys. Courses included algebra, euclid, history, typewriting, shorthand and drill. In the 1930s, Nethercourt Private Hospital took over the site. Later it became St Jude's Hospital. land in front of the building was subdivided off in the 1970s. The building is still extant as a private dwelling with York Street, Surrey Hills as the address. This is one of 3 photos donated by Susan Hobbs, whose grandfather Rev. George Edward Downton is thought to have been a student at the college. George E. Downton was born in Avoca in 1885. He was later a missionary in New Guinea and Secretary to the Australian Board of Missions in Adelaide. He died in 1926 or 1927. Sepia photo of 26 men and boys and one female against a background of a two-storey brick building. This is the rear of the Surrey College. There are 4 additional figures in the background and an additional house can be seen beyond the property boundary. Many of the boys wear or hold caps or boaters. The 2 men in the back row on the right are wearing academic gowns and mortar boards. The gentleman with the beard on the end is Rev. Frederick Darling, the Principal of the college. Sepia photo on cream mount board. Note that the photo is detached from the mount, so the photo is numbered SHP2025.15.1 and the mount as SHP2025.15.2.Front: "Surrey College - Surrey Hills / Principal: Rev. Fredk. A. DARLING, Melb. Univ./STAFF AND BOARDERS, 1899." Back: "York Street, Surrey Hills" in grey lead pencil; possibly Susan John's hand. Back, bottom LH corner: "L. Johnstone" Back, top RH corner: "5621" - this was the registration number used by box Hill historical society Middle back: Purple stamp - "Tennent/Photographer / 110 Johnstone Street / Collingwood" schools, 1899, surrey hills, surrey college, rev frederick a darling, george edward downton, susan hobbs, union road, nethercourt hospital, st jude's hospital, 219-223 union road, 1890-1899, york street -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBadge - Lavington Sports Club Membership 1978 - 1979
The Lavington Sports Ground, former home of the Lavington Sports Club, is now owned and operated by Albury City Council. Over 50 years ago, a group of Lavington locals dreamed of building a new sportsground to encourage more people to play sport, particularly juniors. The original oval opened in 1973. The Sports Ground was developed solely by the Lavington Sports Club, formed by 30 football and cricket players and supporters in 1964. Football and cricket clubs had existed in Lavington since before 1914. In 1964, the football and cricket clubs merged to become the Lavington Sports Club. The new club and facilities were established on land initially leased from the Divine Sword Missionaries on their former seminary and turkey farm. The club expanded its facilities and representative sports throughout the next 20 years, including hosting international events. However the Club's debt worsened and In 2001 the entire Lavington Sports Club operation went into liquidation. It was taken over by Penrith Panthers through the Panthers Entertainment Group. In July 2009 the Albury City Council purchased the Sports Ground and has further redeveloped the ground and its facilities.This badge is representative of the role played by sporting organisations in the local communityA circular blue and silver enamelled badge issued for membership of the Lavington Sports Club.On front of Badge "78 -79/Lavington/Sports/Club/Limited" On reverse "MEMBER/NOT TRANSFERABLE/6114/PERFECTION BADGES/SYDNEY/770775"lavington sports club, recreational facilities albury, sport and recreation -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyLetter - Document, letter
Application by Mr Frederick R Killey in February 1943 for the position of Manager of the Legacy Club Hostel. It lists his experience as 16 years teaching and missionary work in India in charge of an orphanage. He was rejected from military service in WWI due to defective eyesight and points out he has a badge issued to him at the time stating he was rejected on medical grounds. The note in red ink shows the application was unsuitable. Legacy had a preference for providing positions to ex=servicemen when possible. Holmbush was the first children's residence operated by Melbourne Legacy it was renamed Blamey House when the first Blamey House was sold. Melbourne Legacy ran three residences: Blamey House (purchased 1947) , Stanhope (purchased 1945) and Harelands (purchased 1950), to take care of children whose fathers were servicemen, and who may have been left orphans, or whose mother may have been unable to care for them herself. Harelands accommodated boys and girls under the age of 14, Blamey House looked after boys over 14, and Stanhope looked after girls over 14. The children were cared for until they were old enough to become independent.A record of written correspondence regarding job applications in 1943.Letter written by Mr Killey in 1943 applying for a position at Holmbush on white notepaper, black ink handwriting, two hole punched.Handwritten "Considered by Doug and self. Does not seem suitable. Not a returned man" in red ink.residences, holmbush, holmbush administration -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyBook - St. Mary’s Church, Caulfield
Two copies of St. Mary’s Anglican Church, Glen Eira Road, Caulfield. Souvenir of 50 years 1858-1908. Includes history of the church, home and foreign missions, list of memorials and gifts in the church. Also photos of parishioners the church and interior, the vestry and Rev. A.J.H. Priest and Mrs. Priest, and Rev. H.B. Macartney and Mrs. Macartney. Two copies of St. Mary’s Anglican Church, Glen Eira Road Caulfield. Souvenir record of 60 years 1858-1918. Includes history of the wooden church, names of the early parishioners, the first, third and fourth incumbencies, the jubilee school, Sunday school, choir and organ, daughter churches and St. Mary’s a mission parish, and the last decade from 1908 to 1918. It also has a list of organisations and office bearers. Manila book has all photos omitted. There are twelve photos including St. Mary’s choir, a group of St. Mary’s Sunday school teachers, missionaries, curate, organist and verger, Rev. H.T. Langley and Mrs. Langley. Three leaflets from St. Mary’s Church, the first 100 years of the church building 1871-1971. Leaflets detail the centenary services and functions. It has a list of office bearers and vicars, named windows, the honour roll and some other notable areas in the church and furniture.watts thomas, caulfield, glen huntly road, balaclava, hawthorn road, the black chapel, st. mary’s, park street, porter mrs., pennington mr., pennington mrs., stephen wilberforce, stephen mrs., hart mrs., cox peter, bunton barbara -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph
Rev. Peter Thompson (1847 - 1909) was Superintendent of the East End Wesleyan Mission. Entered the Wesleyan ministry in 1871. Died 1909. The second son of a Lancashire farmer, Peter grew up in a tee-total Methodist household with a rather austere father and a saintly mother. He trained at Didsbury Wesleyan College where he was, by all accounts, a brilliant student. He was stationed in Ulverston and then Huddersfield (by 1876). By 1881 Peter had married and was Minister at Wood Green. He and his wife, Mary, do not appear to have had any children. They spent some years in Redhill and then, following the decision of Conference in 1885 to establish the London Wesleyan Methodist Mission, Peter was sent to the East End of London to take charge of the almost defunct St George’s Wesleyan Chapel. His work as a slum missionary was so successful that soon larger premises were required. In addition the mission took over a ‘most undesirable’ public house (The White Swan on Ratcliffe Highway) and later, in 1891, the Mahogany Bar. In 1898 he was interviewed by Charles Booth as part of Booth’s survey of London. Peter died after a long illness in 1909 having served 24 years in East London, one of the best known and loved Wesleyan ministers of his time. Sepia toned head and shoulders studio portrait of the Rev. Peter Thompson.rev peter williams, methodist, wesleyan, minister, east end mission -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph - Surrey College Cricket Team, 1899, 1899
Surrey College was opened in early 1892 by Reverend Dr Frederick Darling who had been the first minister of the Presbyterian Church in Canterbury Road. He resigned this position to open the school which operated until 1905 with additional premises at 12 Vincent Street. The main building fronted 219-233 Union Road. The school had 40 boarders as well as day boys. Courses included algebra, euclid, history, typewriting, shorthand and drill. In the 1930s, Nethercourt Private Hospital took over the site. Later it became St Jude's Hospital. Land in front of the building was sub-divided off in the 1970s. The building is still extant as a private dwelling with York Street, Surrey Hills as the address. This is one of 3 photos donated by Susan Hobbs, whose grandfather Rev. George Edward Downton is thought to have been a student at the college. George E. Downton was born in Avoca in 1885. He was later a missionary in New Guinea and Secretary to the Australian Board of Missions in Adelaide. He died in 1926 or 1927. This photo is one of two that were originally in the Box Hill Historical Society collection. They were transferred to us in 2024. The third photo could not be located. There was also a rough family tree and notes for the Downton family with correspondence regarding the donation but this was not found.Sepia photograph on grey mount board of 15 men and boys. Eleven of the boys are dressed in whites, 5 wearing ties and 1 a bow tie, one with a boater and one with a cap. The boy seated on the right is holding a cricket bat and the boy seated on left is wearing cricket pads on his legs. There are stumps and bails in the middle of front row. Three young men are in suits and boaters with one in the back row holding items in his hands. On the right hand side of the back row is Reverend Frederick Darling, Principal of the College, who wears a top hat and tails. There is a brick building behind with windows and blinds, and some foliage and plants behind and in front of boys. "Surrey College - Surrey Hills/Principal: Rev Fredk. A Darling, Melb. Unib./Cricket Team, 1899"schools, sport, cricket, 1899, surrey hills, surrey college, rev frederick a darling, george edward downton, susan hobbs, union road, nethercourt hospital, st jude's hospital, 219-223 union road, york street, 1890-1899 -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumFolio, Camp 3
Material collected relating to Camp 3. Material relating to Palestine Group of Internees in Camp 3 Theatre Programs & lists of cast.. Wilhelm Fugmann, Director. Coloured sketch of stage with setting presented to Prompter, Julia Mueller, autographed by the Theatre Group. 1945 Christmas Greetings from the Camp Leaders. "Templers in Israel" by Yossi Ben-Artzi. "Loyalties at Swordpoint - Lutheran Missionaries in Wartime New Guinea" by H.N. Nelson. Records of Resi, Maria, Erich & Friedrich Haering; Rudolf Hoefer, Willy & Else Groezinger, Ruth Stoll, Gisela Stellar. Copies of letters written by Wilhelm Stoll in 1946 seeking employment in S.A. Recollections from Ted Stoll. Obituary of Ruth Stoll. Play (in German) "Prinzess Chiu", written by Fritz Prager for his daughter in Camp 3. Prager, a German businessman in Sydney, Australia, interned with his brother, Hans in Camp 1. Fritz and Hans were later joined by their families in Camp 3. Copy of "FHP Communications", in which Fritz describes how his company, F.H. Prager & Coy. became established. Letter from Ursula Grimsdale describing how the two brothers came to be interned. Prager Company Newsletter from Ursula Grimsdale. Birth certificate of Heidi Wennagel, born in Camp 1 Hospital. Painted backdrop and theatre scene presented to Julia Mueller.Black 3 ring folder with printed material in plastic sleevesdocuments, reports -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMedal - Commemorative, Edward William Cole, Coles Book Arcade, Federation of the World, 1885
The medal was issued by Cole's Book Arcade, with the proverb “Federation of the World, Be Good and Do Good”, circa 1885. This nickel-plated medal is one of a series of medals offering maxims and proverbs issued by E.W. Cole (Edward William Cole), owner of his Book Arcade. He called the medals 'little missionaries for the spread of educative knowledge' According to Sydney Endicott, an employee of Cole, customers were charged three pence for these medals (which he prefers to call tokens) which, when the Arcade was particularly busy, gave them admission to the second-hand books' gallery where the orchestra played. Each medal could be exchanged for thee pence worth of goods, but most were kept. The pierced ones were sometimes worn as pendants or on pocket watch chains. The medals served as perpetual advertisements of the Arcade (Victorian Historical Magazine, February 1962). George Dean suggests that the medals were also given in change at Christmas time, and could be used to operate amusement machines (presumably including the symphonion (clockwork instrument) and hens, although these only required one penny to operate). Cole had his first medal stuck in 1879 and his last one in 1903. The medals were variously gilded, silvered or bronzed, replicating the coinage and then circulating, or plated with nickel or white metal. The metal blanks were usually made of copper or brass, but some might have been bronze; aluminium was also sometimes used. In all, perhaps 300,000 medals were struck, in 97 different types or designs. Only 50 types are known to have circulated according to George Dean's 1988 book "A Handbook on E.W. Cole: His Book Arcade, Tokens and Medals'.The medal is significant for its association with Cole's Book Arcade in Melbourne, established in the 1870s. The unique shop not only had new books, but secondhand books, and many curious and interesting objects and musical treats. Cole's Book Arcade, at the time, was known as one of the wonders of 'marvellous Melbourne. it closed in 1929.Nickle plated bronze medal or token, round, featuring a tree fern and a thought provoking maxim. The medal was issued by E W Cole, Book Arcade, in Melbourne. Obverse: "BE GOOD AND" "DO GOOD" "HINDOO MAXIM" "PURE THOUGHTS" "PURE WORDS" "PURE DEEDS" "PARSES MAXIM" Reverse: "PURE / THOUGHTS / PURE WORDS / PURE DEEDS / PARSEE MAXIM" and below rainbow in tiny letters; "FEDERATION OF THE / WORLD MEDALS / ISSUED / BY E.W. COLE / BOOK ARCADE MELBOURNE"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, medal, maxims, coles arcade melbourne, federation of the world, advertising token, edward william cole, book arcade, e w cole, cole's book arcade -
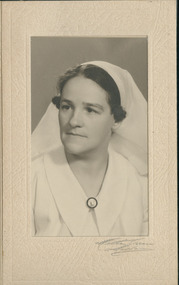 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C1947
Hilda Charlotte Foster, 1902 - 1990, was a Double Certified Nurse when, at the age of 35, she successfully applied to the board of the Australian Inland Mission (AIM) to work at an outback field centre in South Australia. Born and raised in suburban Melbourne, she had been inspired by stories told to her by other missionaries about the fulfilment to be gained working amongst Aboriginal communities. Given her religious faith and nursing skills, she believed she could make a difference. She worked in Oodnadatta in South Australia for two years (1937-1939), followed by a stint in Innamincka in New South Wales in 1940 -1942. Before she became a nurse, Hilda Foster trained to be a Sunday School teacher and was a member of the Sunday School Council of Victoria. She completed first aid courses run through the Presbyterian Deaconesses Institute in Carlton, Victoria, and in 1930 successfully applied to become a trainee nurse at the Austin Hospital for Incurables, in Heidelberg. She commenced her training there in 1931, before moving to the Women's Hospital in 1933. In 1934 she had six months at the Fairfield Infectious Diseases Hospital, before returning to the Austin, where she was employed when she sat her final exams in November 1934. Her combined skills made her a most attractive option for the Australian Inland Mission. As well as being multi-skilled as a nurse, she provided religious instruction and spiritual ministry to members of the community. https://trove.nla.gov.au/people/762093?c=people Sister Foster nursed at Toora Bush Hospital prior to leaving for the Paton Memorial Hospital, Vila, New Hebrides in 1944. She left the New Hebrides in 1946.Matt, black and white, head and shoulders, studio portrait of Sister Hilda Charlotte Foster on card.australian inland mission, presbyterian deaconess, sister hilda charlotte foster, paton memorial hospital vila new hebrides -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Haeusler Collection - Bible and Hymn books, c1890s
The Wodonga Historical Society Haeusler Collection provides invaluable insight into life in late nineteenth and early twentieth century north east Victoria. The collection comprises manuscripts, personal artefacts used by the Haeusler family on their farm in Wodonga, and a set of glass negatives which offer a unique visual snapshot of the domestic and social lives of the Haeusler family and local Wodonga community. The Haeusler family migrated from Prussia (Germany) to South Australia in the 1840s and 1850s, before purchasing 100 acres of Crown Land made available under the Victorian Lands Act 1862 (also known as ‘Duffy’s Land Act’) in 1866 in what is now Wodonga West. The Haeusler family were one of several German families to migrate from South Australia to Wodonga in the 1860s. This Bible belonged to Louis Alfred Haeusler, son of Johann Heinrich Ferdinand Haeusler and Ernestine Wilhelmine nee Rogasch. Louis was born in Wodonga, Victoria on 23 December 1898 and died on 2 February 1960. The other 2 volumes belonged to Louis' sister Eleonora Lydia Haeusler (Nellie), born 14 October 1883 and died 25 November 1979. Louis was the father of John Alfred Lyell (Alf) Haeusler who bequeathed this collection to the Wodonga Historical Society. The Bible was published by Collins' Clear Type Press, a Scottish publishing company founded in 1892.The volume "Church Hymns" was published by the Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge, the oldest Anglican missionary organisation which was originally founded in 1698. This copy was published in London C1885. The Hymnal Companion to the Book of Common Prayer (2nd Edition) was published by Sampson Low, Marston and Company of London C1893.This item is unique and has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It is representative of the religious traditions adopted by this family in Wodonga. A collection of 3 religious books including a Bible, Hymn book and Hymn Book companion. They have different coloured leather covers. Handwritten inside front cover of Bible: L.A. Haeusler/ Wodonga, Vic. Handwritten inside front cover of Hymnal Companion: Eleonora L. Haeusler / St. Lukes, Wodonga Handwritten inside Church Hymns: To Nellie with love from Sister Tilly 20.8.02haeusler family, religious publications, society for promoting christian knowledge, sampson low, marston and company -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Rev. Alexander Sutherland Bremner
Alexander Sutherland Bremner was born in Lyster, Scotland in about 1890. He migrated to South Australia and by 1914 was stationed in Mount Gambier as a missionary in connection with St Andrew’s Presbyterian Church. At that stage he was a student of Divinity. He moved to Victoria and served in Beech Forest and Kyabram. After three years in Kyabram, Reverend Bremner transferred to Wodonga in April 1919. Although only in Wodonga for two years, Reverend Bremner quickly became highly regarded in the community for the compassion he brought to his calling. He was particularly concerned about the welfare of boys in Wodonga and became involved in the Scouts as well as establishing the Wodonga Boys’ Club. Although the Boys’ Club had been formed through the Church it was open to all local boys. Tragedy struck on 20th November 1920 when Reverend Bremner was accompanying a group of boys on an outing to the Wodonga Creek. In order to stop the boys from entering a deep water hole he positioned himself on a log between it and the shallower water. Unfortunately he slipped off the log himself and fell into the waterhole. He was unable to swim and despite the best efforts of one of the boys to rescue him, he drowned. To add further to the tragedy, his fiancé was on her way to Wodonga by train to visit Reverend Bremner for the weekend. She could not be advised of his death before arriving at the station where she expected him to be waiting. As a mark of respect, a hall was erected at the back of the Wodonga Presbyterian Church in High Street to serve as a kindergarten and Sunday School. It was officially opened on Sunday 6th November 1921 and named Bremner Hall.This album is significant because it documents the service and untimely death of a highly regarded Minister of the Presbyterian Church in Wodonga.A small brown photo album containing photos and newspaper articles chronicling the drowning of Reverend Alexander Sutherland Bremner in Wodonga.reverend a.s. bremner, presbyterian church, bremner hall -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageArtwork, other - Pen and Wash Painting, Beni Carr Glyn Burnett, The White Ship, circa 1933
Beni Carr Glyn Burnett (also known as B. C. G. Burnett or Beni Burnett) was born in 1889 to missionary parents in Mongolia. When he was 15 years old he began training as an architect with a firm in Shanghai. He worked in Singapore, Japan and China before moving to Australia around 1933. In 1937 he was appointed as the Commonwealth principal architect in the Northern Territory. He went on to design a series of houses for senior public servants and military personnel which became very popular as they were specifically designed for the tropics - incorporating louvres, high ceilings and good ventilation. When Darwin was bombed in February 1942, he was evacuated to Alice Springs where he continued to work as an architect. He also became a Magistrate and Coroner in Alice Springs. In later life he was well known for sketching clientele in public bars. He died in 1955. Beni Burnett was living in Sydney in 1933 when he produced these three artworks. There were several photography firms operating in Sydney at this time who specialised in photographing ships and the shipping trade (e.g. Samuel J. Hood and William James Hall) and whose photographs were used by artists to produce ship portraits. Both of these photographers took photographs of the two ships in B. C. G. Burnett's watercolours This ship depicted by B. C. G. Burnett in his pen and wash sketch labelled "The White Ship" exactly matches a photograph pasted into his personal scrapbook which is in the "Library and Archives N. T.". The name of the ship is unknown and B. C. G. Burnett may have taken some artistic licence with the colouring as in the original photograph, the ship had a dark hull.This artwork (one of a set of three small artworks) is significant as an example of shipping (particularly the use of sailing ships) that were still being used as late as the 1930's in Australia. It is also important as its creator (B. C. G. Burnett) went on to become a well-known public figure in the Northern Territory in the late 1930's due to his innovative approach to designing homes for the tropical climate.An ink sketch of an unknown sailing ship moored to a dock. There are several small boats tied up near the sailing ship and a large steel freighter can be seen in the background. There is a faint wash of colour on parts of the sketch - the bottom of the ship, the masts and booms and the water at the end of the pier. The title (The White Ship) and the artist's name (B. C. G. Burnett) are written in ink in the top left corner. The back of the sketch is black card with faint pencil marks (overwritten in red ink) that appear to read "1842 A". A page from an album belonging to Beni Burnett displays five black and white photos including three photographs of ships. The photograph on the bottom right is an exact match for the pen and wash drawing. front - "THE WHITE SHIP / B. C. G. BURNETT" back - difficult to read "1842 A"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, sailing ships, ships, barque, magdalene vinnen, winterhude, beni carr glyn burnett, b. c. g. burnett, beni burnett, painting, watercolour painting, sketch, ink sketch, sydney harbour, architect, darwin, burnett house, photography, samuel j. hood, william james hall -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Denominational Church and School, Unknown
Presbyterian Church Melton Background: A Combined Denominational Church and School was established in Melton by Protestants from the Presbyterian, Episcopalian, Wesleyan and Baptists denominations. A wooden church was built on the flat area east of the Toolam Toolern Creek. A photo of this church shows the buildings with small houses nearby. In the background the bluestone Presbyterian Church built in 1867 can be seen to the north on Yuille and Sherwin street. The flat area beside the road to Ballarat was subject to flooding and the site was eventually abandoned for a settlement. By the latter part of the 1860s the Church of England and Wesleyan bluestone churches were also being erected in the centre of the township of Melton. The commercial centre developed in High Street from Smith to Palmerston Street. Township of Melton Crown Grants Issued Under Common Law refers to the site of the Combined Denominational Church and School on the east side of Sherwin Street on the corner of Pyke Street. Section 4 Allotments 1 and 10 situated on the corner of Pyke, Bryan and Sherwin Street. The early map has the name of Thomas Cridge on this site. The area known Common (flat) remained open level ground with some cottages and buildings and a milk cooler in the 1930s, Granny Watts house “Lynch Cottage was moved in 1964. Sherwin Street was used until the 1960s with the open area being the used for playing golf. Alterations to the flat occurred when the golf course added to the height and removed the Sherwin Street access. The greens were developed and the height of ground altered the vista across Common. The first Presbyterian Minister in the district was the Reverend Alexander McNicol an advanced student and an experienced missionary from Glasgow, arriving in Melbourne in 1850. He was ordained on the 8th of June and was called to the Bacchus Marsh and Mount Macedon district. On the 1st of May 1851 he was called to Geelong and returned to Bacchus Marsh on February 1856 remaining until July 1859. Group of people in front of the church and school.churches, local identities, education -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Stonleigh, Wodonga
Stonleigh is one of Wodonga’s earliest buildings and stands on land granted to Daniel Rhodes in 1854, in one of the first land sales conducted in Wodonga. The building commenced soon after with the stone walls being 18 inches (46cm) thick. It was a four-room granite rubble stone building with central door and a window on either side, with a separate kitchen, as was typical of the worker's cottage of the day. The original roof would have been shingles but it was replaced with corrugated iron. It passed through several owners including Paul Huon in 1858. Peter Tenner, a farmer and vigneron took over in 1866 when it was described as “built of stone and having a cellar and a detached kitchen plus outside toilet, and a shed or two.” In the late 1880’s it was owned by William Smith who had come to Wodonga as a missionary for the Presbyterian Church and who, together with John Whan, storekeeper, was instrumental in building the Presbyterian Church nearby. Between 1890 and 1910 further buildings were added, consisting of double brick walls, two bedrooms, kitchen, laundry with brick and copper, bathroom and side verandah. William Smith established Wodonga Cordage Works in the Stonleigh buildings. The front room of the house was the display room for the business which manufactured and sold fishing lines, various types of cordage and water bags, the latter being of hand-sewn canvas. After 1954 Stonleigh became a bottle depot and bottle museum under ownership of Ramon Porta. At one stage he had over 50,000 bottles on display. In 1991 it was purchased by Mark Fraser, a cabinet maker, who made extensive renovations at the rear of the premises and internally, but left the façade untouched. Over recent times, Stonleigh was the home of several business including a florist, a patchwork maker and a café. Stonleigh was sold in 2021 and is now a private residence.These images capture one of Wodonga's oldest buildings.A series of photos, both colour and black and white, showing the building "Stonleigh' at different periodsstonleigh wodonga, old buildings wodonga, wodonga businesses, wodonga pioneers -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesConference proceedings, Jon Reyhner, Nurturing native languages, 2003
Section I: Language and Culture Immersion 1. Native Language Immersion /? Jon Reyhner 2. Assessing the Impact of Total Immersion on Cherokee Language Revitalization: A Culturally Responsive, Participatory Approach /? Lizette Peter with Ella Christie, Marilyn Cochran, Dora Dunn, Lula Elk, Ed Fields, JoAnn Fields, Tracy Hirata-Edds, Anna Huckaby, Margaret Raymond, Deputy Chief Hastings Shade, Gloria Sly, George Wickliffe, Akira Yamamoto 3. Situational Navajo: A School-Based, Verb-Centered Way of Teaching Navajo /? Wayne Holm, Irene Silentman, Laura Wallace Section II: Technology Sustaining Indigenous Languages in Cyberspace /? Courtney B. Cazden 5. Saving a Language with Computers, Tape Recorders, and Radio /? Ruth Bennett Section III: Other Issues 6. How To Teach When the Teacher Isn't Fluent /? Leanne Hinton 7. Preparing Indigenous Language Advocates, Teachers, and Researchers in Western Canada /? Heather A. Blair, Donna Paskemin, Barbara Laderoute 8. Whaia Te Reo: Pursuing the Language': How Metaphors Describe - Our Relationships with Indigenous Languages /? Jeanette King 9. Honoring the Elders /? Evangeline Parsons-Yazzie, Robert N. St. Clair 10.Spanish: A Language of Indigenous Peoples of the Americas /? Florencia Riegelhaupt, Roberto Carrasco, Elizabeth Brandt 11. Keresan Pueblo Indian Sign Language /? Walter P. Kelley, Tony L. McGregor 12. Oral History Shares the Wealth of a Navajo Community /? Sara L. Begay, Mary Jimmie, Louise Lockard 13. Mothertongue: Incorporating Theatre of the Oppressed into Language Restoration Movements /? Qwo-Li Driskill 14. Missionaries and American Indian Languages /? Evangeline Parsons Yazzie Biographical Information on the Authors.tables, b&w illustrationsnavajo, cherokee, indian sign language, bilingual education, indigenous language teaching, native language immersion, language and technology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - CAPITOL THEATRE PROGRAM '' YOU'RE IN LOVE''MARCH 24-25-26-27 1958
Bendigo Operatic Society ''You're in Love'' Capitol Theatre - Mon., Tues., Wed., Thurs., March 24th,25th,26th,27th, 1958. Programme, 1/- Bendigo Operatic Society President: Mr. John Cannon - Vice-President: Mr C. Bubb - Secretary: Mr. E.B.Thomas - Treasurer: Mr. Bruce Ralph - Hon. Auditor: Mr. Frank Iredale - Committee: Messrs L. Spencely, J. Smyth, W. Kelly, Mesdames J. Cannon, N. McCarthy, J. McGrergor, J. Smyth and Miss M. Welch. Our Producer: Norman Lee - Our Musical Director: Max O'Loghlen Gertrude Perry Plays Georgiana - Bert Donovan Plays Hobby Douglas - Alfred Annison Plays Mr. Wix - Celia Douglas Plays Mrs.Payton - Barbara McGregor Plays Dorothy - Brian Brewer Plays Lacey Hart. Synopsis of ''You're in Love'' The action of this story takes place prior to and during a pleasure cruise of the Hawaiian Islands and centres around Hobby Douglas and Georgianawho both wish to marry, but are unable to do so without the consent of georgiana aunt, Mrs. Payton. Mr. wix a missionary worker and Hobby's Guardian is also against marriage. Dorothy and Lacey are a young married couple on the honeymoon cruise. What happens to this assortment of people will have to be seen. Cast in order of appearance: Judge Brewster: Max Beckwith - Lacey Hart: Brian Brewer - Dorothy: Barbara McGregor - Mrs.Payton: Celai Douglas - Georgiana: Gertrude Perry - Hobby Douglas: Bert Donovan - Mr. Wix: Alfred Annison - The Captain: Mervyn Penno - The Steward: Joseph Quigg - Specialty Dancers; Ann Stone, Rosalie Spencely. Costunmes and Scenery by J.C. Williamsons Ltd. Music by Rudolf Friml. Book and Lyrics by Otto Hauerbach and Edward Clarck.program, theatre, bendigo operatic society -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoriaphotograph, May 10th or 11th 1935
Kagawa, Toyohiko (1888-1960) Japanese evangelist and social movement leader Kagawa was born in Kobe to Kame and Junichi Kagawa. In lonely years following the death of his parents at age four, he met Harry W. Myers and Charles A. Logan, missionaries of the (Southern) Presbyterian Church, U.S., and was baptized by Myers on February 14, 1904, at the Tokushima church. He pursued theological study at Meiji Gakuin in Tokyo and Kobe Theological Seminary. During his student days in Kobe he moved into the Shinkawa slum to serve the physical and spiritual needs of some 7,500 people. Between August 1914 and May 1917 Kagawa studied in the United States at Princeton Theological Seminary and then became involved in labor and peasants movements in Japan and in organizing religious programs, with the Jesus Band of Kobe as the base of his work. In 1921 Kagawa organized the Friends of Jesus. This Franciscan-like band of young people strove for spiritual discipline, compassion for the poor, and an evangelical life of witness. When Tokyo suffered a massive earthquake in 1923, he shifted the main emphasis of his work to that city. He promoted economic cooperatives in Japan and peace and social reform programs before and after World War II. Kagawa was a prolific writer. Most of his writings are collected in the twenty-four volume Kagawa Toyohiko Zenshu (The work of Kagawa Toyohiko) (1964). His theological focus was on the redemptive love of God, manifest in the life of Jesus Christ, to whom people can commit themselves through a mystical experience of faith and intellectual creativity. Kagawa was known more as a Christian social reformer than as a religious leader both in and out of Japan, but he was fundamentally an evangelist throughout his life. Robert M. Fukada, “Kagawa, Toyohiko” in Biographical Dictionary of Christian Missions, ed. Gerald H. Anderson (New York: Macmillan Reference USA, 1998), 350. This article is reprinted from Biographical Dictionary of Christian Missions, Macmillan Reference USA, copyright © 1998 Gerald H. Anderson, by permission of Macmillan Reference USA, New York, NY. All rights reserved. B & W informal photograph of the Rev. H.C. Matthew and Toyohiko Kagawa standing in front of the door to Captain Cook's Cottage in the Fitzroy Gardens, Melbourne. "Melbourne May 19th or 11th 1935. H.C. Matthew & Toyohiko Kagawa standing by the cottage recently removed to Australia & re-erected in Melbourne Botanical Gardens in which Captain Cook was born."toyohiko kagawa, h.c. matthews, captain cook's cottage, friends of jesus, christian missions. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePainting - Watercolour Painting, Beni Carr Glyn Burnett, The Winterhude, 1933
Beni Carr Glyn Burnett (also known as B. C. G. Burnett or Beni Burnett) was born in 1889 to missionary parents in Mongolia. When he was 15 years old he began training as an architect with a firm in Shanghai. He worked in Singapore, Japan and China before moving to Australia around 1933. In 1937 he was appointed as the Commonwealth principal architect in the Northern Territory. He went on to design a series of houses for senior public servants and military personnel which became very popular as they were specifically designed for the tropics - incorporating louvres, high ceilings and good ventilation. When Darwin was bombed in February 1942, he was evacuated to Alice Springs where he continued to work as an architect. He also became a Magistrate and Coroner in Alice Springs. In later life he was well known for sketching clientele in public bars. He died in 1955. Beni Burnett was living in Sydney in 1933 when he produced these three artworks. There were several photography firms operating in Sydney at this time who specialised in photographing ships and the shipping trade (e.g. Samuel J. Hood and William James Hall) and whose photographs were used by artists to produce ship portraits. Both of these photographers took photographs of the two ships in B. C. G. Burnett's watercolours. The "Winterhude" (originally called "Mabel Rickmers) was a three masted Finnish barque built in 1898 by Rickers - Werft Bremerhaven for use on the East India rice trade and later the South American nitrate trade. After WW1 it came under French control as war compensation. It was also sold several times and at one stage was called "Selma Hemsoth" but in 1925 it was bought by Gustaf Erikson who restored the name "Winterhude" and the vessel became a regular transport in the Australian wheat trade. In 1944 it was sold to the German navy before being taken over by the British at the end of WW2. It was photographed in Sydney by William James Hall in1931 on its way to Port Lincoln, South Australia to load wheat for Europe.This painting (one of a set of three small artworks) is significant as an example of shipping (particularly the use of sailing ships) that were still being used as late as the 1930's in Australia. It is also important because its creator (B. C. G. Burnett) went on to become a well-known public figure in the Northern Territory in the late 1930's due to his innovative approach to designing homes for the tropical climate.A watercolour painting of a sailing ship called "Winterhude". It shows a 3 masted barque with a blue and red steel hull in full sail heading away from the viewer. A small figure can be seen at the wheel at the rear of the ship. The painter's name (B. C. G. Burnett) and date (1933) are written on the bottom left-hand corner of the painting. The name of the ship is written in faded pencil on the back of the painting.front - "B. C. G. BURNETT. 1933" back - in faded pencil - "the Winterhude"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, sailing ships, ships, barque, winterhude, beni carr glyn burnett, b. c. g. burnett, beni burnett, painting, watercolour painting, sketch, ink sketch, sydney harbour, architect, darwin, burnett house, photography, samuel j. hood, william james hall, mabel rickmers -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook with CD, Doreen Mellor et al, Many voices : reflections on experiences of Indigenous child separation, 2002
This book bring together voices of children who were separated from their families, people who cared for them, families who took them into their homes and Government officers who carried out official directions. Contents of CD: Track 1. Jim Hart, b.1927, Queensland, separated from family as a child. See ch. 5. Interviewer: David Woodgate (3m 02s) track 2. Clara Coulthard, b.1929, South Australia, separated from family as a child. See ch. 3. Interviewer: Sue Anderson (4m 06s) track 3. John Moriarty, AM, b.1938, New South Wales, South Australia, Northern Territory, separated from family as a child. See ch. 4. Interviewer: Frank Heimans (4m 12s) track 4. Sandra Hill, b.1951, Western Australia, separated from family as a child. See ch. 11. Interviewer: John Bannister (4m 11s) track 5. Trevor Deshong, b.1965, Queensland, separated from family as a child. See ch .6. Interviewer: Colleen Hattersley (4m 45s) track 6. Julie Wilson, b.1958, New South Wales, adopted as an infant. See ch. 6. Interviewer: Frank Heimans (4m 04s) track 7. Dorothy Pyatt, b.1918, South Australia, police officer in remote South Australia, 1950s and 1960s. See ch. 8. Interviewer: Karen George (4m 18s) track 8. Margaret Somerville, MBE, b.1912, New South Wales, Northern Territory, missionary and cottage mother. See ch. 7. Interviewer: Frank Heimans (3m 15s) track 9. Reg Worthy, OAM, b.1920, Queensland, Northern Territory, Victoria, welfare officer, senior administrator, Departmental Head. See ch. 8. Interviewer: Barbara Erskine (4m 55s)D?.b&w photographs, b&w illustrations, CDstolen generations, child welfare, bringing them home, oral histories -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Head & Shoulders of Chris Eldridgest. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Head & Shoulders of Chris Tudor.st. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Tudor and Eldridge in conversation with the College in the background.st. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePainting - Watercolour painting, Beni Carr Glyn Burnett, Magdalene Vinnen, 1933
Beni Carr Glyn Burnett (also known as B. C. G. Burnett or Beni Burnett) was born in 1889 to missionary parents in Mongolia. When he was 15 years old he began training as an architect with a firm in Shanghai. He worked in Singapore, Japan and China before moving to Australia around 1933. In 1937 he was appointed as the Commonwealth principal architect in the Northern Territory. He went on to design a series of houses for senior public servants and military personnel which became very popular as they were specifically designed for the tropics - incorporating louvres, high ceilings and good ventilation. When Darwin was bombed in February 1942, he was evacuated to Alice Springs where he continued to work as an architect. He also became a Magistrate and Coroner in Alice Springs. In later life he was well known for sketching clientele in public bars. He died in 1955. Beni Burnett was living in Sydney in 1933 when he produced these three artworks. There were several photography firms operating in Sydney at this time who specialised in photographing ships and the shipping trade (e.g. Samuel J. Hood and William James Hall) and whose photographs were used by artists to produce ship portraits. Both of these photographers took photographs of the two ships in B. C. G. Burnett's watercolours. The "Magdalene Vinnen" was photographed by Samuel J Hood in a series of photos taken in March 1933. It was a 4 masted steel barque, built in 1921 in Kiel, Germany and for almost 80 years was the largest traditional sailing ship in operation. She was used extensively as a cargo ship. She sailed into Sydney Harbour on 27th Feb 1933, loaded with almost 16,000 bales of wool destined for Falmouth, England. In March 1933 (whilst in Sydney) the German Republic flag (on orders from Adolph Hitler) was lowered and replaced with the old monarchist flag which was then to be the official flag and beside it the Nazi flag was to be flown on all ceremonial occasions. It visited Australia again in 1935 with its cargo being wheat from Port Broughton, S. A. In 1936 it was renamed "Kommodore Johnsen" and in 1945 (after WW2) the ship was awarded to the Soviet Union as war compensation and renamed "STS Sedov". This painting (one of a set of 3 small artworks) is significant as an example of shipping (particularly the use of sailing ships) that were still being used as late as the 1930's in Australia. It is also important because its creator (B. C. G. Burnett) went on to become a well-known public figure in the Northern Territory in the late 1930's due to his innovative approach to designing homes for the tropical climate. A watercolour painting of a sailing ship called "Magdalene Vinnen". It shows a 4 masted barque with a blue and red steel hull in full sail heading towards the viewer. The painter's name (B. C. G. Burnett) and date (1933) are written on the bottom left-hand corner of the painting. The location and name of the ship is written in ink on the back of the painting.front - "B. C. G. BURNETT. 1933 back - "off Sydney" / "Magdalene Vinnen"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, sailing ships, ships, barque, magdalene vinnen, beni carr glyn burnett, b. c. g. burnett, beni burnett, painting, watercolour painting, sketch, sydney harbour, architect, darwin, burnett house, photography, samuel j. hood, william james hall, sedov, kommodore johnsen -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaJournal (item) - Periodicals-Annual, Shiplovers' Society of Victoria, The Annual Dog Watch
This journal provides the reader with glimpses of the adventures and hardships of a seaman's life. Many of the stories are of sailing ships.Contributes to our knowledge of the importance of shipping and places on record those stories of the sea which would otherwise be lost.Contents Foreword - 13 Editorial - 15 “Tyburnia” — London - R. W. Glassford - 19 Australian Reminiscences - Captain Carl Meyer - 30 By Tug from England - Geo. W. Torry - 40 New Year Revels in Honolulu - Richard Lunn - 44 Yuletide on the High Seas - Sir James Bisset, C.B.E., R.D., R.N.R., LL.D., Cantab. - 50 My Last Voyage in Sail - Captain Harry Daniel, M.B.E, D.S.C. - 54 “Emma,” Annie Larsen” and “Maverick” - Winston Langdon - 62 Hell’s Gates — Macquarie Harbour - Captain W. E. Eglen - 80 Jack of All Trades - J. H. Barr - 86 A Centenary Missionary Cruise - Captain E. Moodie-Heddie, O.B.E. - 92 The Steamship — “Sir John Harvey” Erik Heyl - 96 Memories of Childhood on Board the “Carlisle Castle” - J. M. Bruce Robertson - 101 Jorgen Jorgensen - George R. Leggett, B.A. - 109 Survivors of Sail - Captain H. R. Watson - 114 “Hard Over” - W. A. Thomson - 119 Intrepid South Sea Pioineers - Captain Harry O’May - 124 Memories of the “Strathdon” - Taken from Papers of the Late Captain W. Philip - 127 The Story of the “Rip” - E. M. Christie - 134 Postscript, “Superb” — London - R.W.G. - 137 Book Reviews - 139sailing ships, steamships, shipping, seafaring life, shiplovers' society of victoria, dog watch -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Reproduction, Jay Miller, 6 June 2019
This photograph was published in the Geelong Advertiser on Friday 23 November 1906, page 4 with this article: "Owing to the generosity of an anonymous donor, the Victorian Missions to Seamen has been supplied with a long felt want in the shape of a modern motor launch to facilitate and render more efficient the work among the vessels in the Yarra and Hobson's Bay. The order for the construction of the boat, was placed with Mr. Chas. Blunt, of the Eastern Beach, and complimentary references were made to her graceful line- as she rode in light .trim after the launching on Wednesday afternoon. She is 31ft. long. Oft. beam, and has a depth of 3ft. The frame is of jarrah and ben* blackwood. and inch kauri planking has been used in building Iter. A neat deck-house with Oft. headroom is situat ed-umidsliip*. and a short mast is pro vided to carry the well-known blue flag of the -.fission. The launch motors will develop a speed of between nine and ten miles an hour: The finishing touches have yet to be given her. and she will afterwards be row«l to have her engines fitted in. -The launch will he ready for service for the busy wheat season com mencing at- the end of the year. The launching ceremony took place at 6 p.m. on Wednesday at the builder's yards, in the .presence of njarge gather ing of spectators. The Archdeacon of Geelong. the Rev. O. P. C'ros-.ley. ecu ducted a short dedication service, and the other clergymen who took part in the service were the Primate of Aus tralia. the Right Rev. Dr. Sauiuarcz Smith: the Rev. A. Giirney Goldsmith, the Missions chaplain: and the Rev. H. Kelly. The Bishop of Newcastle, Dr. Stretch, and the chaplain of the New castle Mission, the Rev. AYnddy. and Canon Nash were also present. The Primpte. addressing the gar boring as "My good friends of Geelong." said be had never been in sight of the hay before. bill had'gladly accepted the in vitation to say a few words in connec tion with the dedication of tiro launch. He had always been interested in mis sions of all sorts, as they ali as Christian men and women 110 doubt- were, and lie was particularly interested in Missions to Seamen, because in the Society at' borne, with which this Society was con nected, he had a son-in-law who was mission chaplain in the Medway. He therefore know something about a launch for the purpose of a mission like this, and also knew 'something about missions to seamen. In Sydney for some time past it had been doing good work—work which he was sure they would all feel was of the widest possible value. This year he was at the annual meeting of the Missions to Seamen in London presided over by the Bishop o-f Stcphney. -He (the Primate) at that meeting remarked that the Mission in it, value was personal, local and Im perial. It was of personal value to thee who came under the ministra tions of the church, and in the social as pect : it was local because where the Mission existed the feelings of the lo cality were thrown out. in sympathy with j tlie -Mission, and the people themselves thus benefited. It was also a matter of Imperial interest because it- was really i a world-wide Mission, inasmuch as the | sailors as they" went from one part of the world to another were in themselves j missionaries either for evil or for good, i Thev might he missionaries with a mcs i sago which might degrade and "work ail I evil influence amongst, men, and with i conduct which might reflect a reproach !' upon Christian profession. On the other hand, they might be Chrisian men endeavoring more and more to show the .example of the Christian life in the J midst of very big difficulties and tempta tions. • -Ho came to show liis sympathy with tlio appropriately-named '"'Southern Cross," and from what lie had boon told he believed she was a good boat, a good gift, and launched for a good purpose. They should be thankful that it was a good boat and .thankful because it was a good gift by an anonymous donor, whom he congratulated on doing such a useful thing." The idea of the launch ing ceremony was to ask the blessing of God because ".Except the Lord hless'the house their labor is hut lost'that build it." The Archdeacon expressed thanks to the Primate for attending the cere mony, and regretted that the Arch bishop was unable to attend. They dc- | sired that the boat- should always be as sociated with the.Church Congress 1906. I The opening hymn was "For those in j peril on the sea," followed hv Psalm I 107, "'They'that, go down to the sea in 1 Ships." Tlio prayers included an ap peal foiUDirine blessing on .the launch, and for tho preservation of those who may travel in her. ' Xlio Benediction was pronounced by the Primate, and the christening cere mony performed by Hiss Connibere. From the bow there was suspended a bottle of pure water covered with red, white and blue streamers and roses. Dashing the bottle in,fragments against the launch's bow. Miss Connibere named her the "Southern Cross." Cheers were given for the launch/and as she travell ed down the slip further cheers were given. She carried the Mission flag at tho masthead, and between Union Jacks at tho bow and stern, a long string of flags fluttered gaily* in the breeze. The collection was in aid of the Mis sions to Seamen and the Geelong Sailors' Rest.Reproduction of a photograph from a newspaper.Fujifilm / Quality Dry Photo papersouthern cross, motor boat, mission to seamen, seamen's mission, charles blunt, blunt boatbuilders, geelong -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, Yielima, 31 Erasmus Street, Surrey Hills
Known as ‘Yielima’ 1888-1922 and ‘St. Aubins’ 1922-1956, this ‘modernized’ mansion was built about 1887 for Edward Kellett. He was born in Chorley, Lancashire, England. Edward Kellett married Selina Wells in 1852 at St Peters, Eastern Hill. She was born in c1827 in Aston Clinton, Buckinghamshire, daughter of William Wells and Elizabeth Allan. The family arrived from Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire on the 'Osprey' on 22 March 1849. The couple had 8 children - 5 girls and 3 boys; 3 died in infancy. All were born in Collingwood before the family came to Surrey Hills. Edward's funeral notice in The Argus of 11 July 1893 states that he was a corn merchant of Exhibition Street. His property was sworn at 1512 pounds, 1232 in realty and 280 pounds personally. He was buried in Melbourne General Cemetery (CofE Compartment K, No 306). Selina is listed in Erasmus Street in the 1903, 1905 and 1908 electoral rolls as a boarding house keeper. She died at Surrey Hills on 22/10/1911. In her will she left realty valued at 900 pounds and personally at 220 pounds. She was buried with her husband. 'Yielima' was sold on 19 Febraury 1919 with a sale of contents on 18 March 1919. From 1922-1947 Thomas Daniel O’Callaghan (c1871-1962), a police magistrate, made his home here. He is remembered as being of ‘soldierly demeanour, with a flowing mane of hair’. He always carried a walking stick and wore a flower in his buttonhole. His wife was Florence (nee Harling, c1873-1933) pre-deceased him. They had previously lived in Essendon, Moonee Ponds and Stawell before coming to Erasmus Street. After moving out of Erasmus Street he is listed in the 1949 and 1954 electoral rolls at 90 Durham Road, Surrey Hills. In 1952 the property was purchased by Father Timothy Fitzpatrick, Parish Priest of Our Holy Redeemer Parish, Surrey Hills. It consisted of a large two storey house, a coach house and stable, and an acre and a half of land. In 1954 the coach house and stable were converted into the Church of Our Lady of Perpetual Succour and the following year Father John Kelly was appointed parish priest. and resided in the house. At this time the house was not in good repair. "The gentleman who had lived there alone since his wife died many years before, lived in the servants quarters and the rest of the house had been badly neglected. (REF: https://ourholyredeemer.cam.org.au/history) At the beginning of 1957 the Missionary Sisters of the Sacred Heart opened a school next door. As they travelled from Balwyn on a daily basis, the property at 301 Elgar Road was purchased as a presbytery and 'Yielima' became a convent. The stables continued to be used as a church until 1964 when a new church was completed and opened by His Grace Archbishop Simmonds on the 20th of March. There were never large numbers of double-storey Victorian mansions in Surrey Hills. 'Yielma' is significant as one of the few remaining ones. It is also significant for its association with the Catholic Church.A black and white photograph of an Italianate style home with a weatherboard building with a cross on it in front of the main building and to the left of the photograph. There are some well established trees in the garden, a car parked in the parking area and a picket fence along the front.yielima, st aubins, house names, erasmus street, surrey hills, 1887, (mr) edward kellett, (mr) thomas daniel o'callaghan, corn merchant, police, italianate style, wattle park roman catholic church, (mrs) florence o'callaghan, mrs selina kellett, miss selina wells, convent, presbytery, our lady of perpetual succour -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Undated c.1880s
Born 1823 West Indies, commenced ministry 1847, died 1890 in Rookwood, NSW. Joseph Horner Fletcher (1823-1890), Wesleyan minister, was born at St Vincent, Windward Islands, the eldest son of Rev. Joseph Fletcher, Wesleyan missionary, and his wife Mary, née Horner. In 1830-37 he attended a Methodist school in Kingswood, England, and then his uncle's school in Bath. He entered business but in July 1842 became a local preacher. He was accepted for the Wesleyan ministry in 1845 and after training at Richmond College, Surrey, he married Kate Green in December 1848. He was sent to Auckland, New Zealand, where he became the founding principal of Wesley College. In 1856 poor health obliged him to take up circuit work in Auckland and New Plymouth, where he witnessed the Maori war. He moved to Queensland and in 1861-64 was on circuit in Brisbane. In 1863 he became the first chairman of the Queensland Wesleyan District. In 1865 Fletcher was serving at Ipswich when invited to succeed Rev. John Manton as president of Newington College, Sydney. He acknowledged that the main business of the school was secular education in a Christian atmosphere and believed that education could help to overcome sectarianism. He invited distinguished academics to examine Newington students and strongly supported (Sir) Henry Parkes's education policies. He opposed the formation of a Methodist university college until a strong secondary school was established. He believed that boys should be taught to appreciate orderly conduct rather than to fear punishment and that corporal punishment was degrading and to be used only in extreme circumstances. Under Fletcher Newington developed a high moral tone and a tradition of order and respect. After he retired in 1887 the old boys gave him an address of appreciation and a portrait in oils to be hung in the hall. In addition to his normal duties from 1883 he had taught resident theological students. From 1887 he was an effective and progressive full-time theological tutor. As a preacher Fletcher had exceptional power: he expressed his thoughts in a fresh way with sparkling illustrations and characteristic humour. He combined humility with great spiritual power, prophetic vision and administrative ability. He encouraged the development of institutional church work which grew into the Central Methodist Mission in Sydney. Fletcher was elected as the first president of the New South Wales and Queensland Wesleyan Methodist Conference in 1874 and again in 1884, when he was also president of the General Conference of the Australasian Wesleyan Methodist Church. As conference editor in 1868, 1871 and 1873, Fletcher contributed more than fifty articles, numerous essays and reviews of books to the Weekly Advocate. He read widely, deeply and with discrimination. Never robust in health, he suffered months of illness before he died aged 66 at Stanmore, Sydney, on 30 June 1890. He was survived by three sons and two daughters, and buried in the Wesleyan section of Rookwood cemetery. In 1892 his eldest son, Joseph, edited a memorial edition of his Sermons, Addresses & Essays. Information from Australian Dictionary of Biography, Vol. 4, 1972. Sepia toned carte de visite. Seated studio portrait of the Rev. Joseph Fletcher.Rev Joseph Fletcherrev. joseph fletcher, joseph horner, wesleyan minister, newington college sydney, new zealand, queensland, president general conference, wesleyan methodist church, central methodist mission
