Showing 69 items matching " human hands"
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Magazine - NORMAN PENROSE COLLECTION: HUMAN HANDS
... NORMAN PENROSE COLLECTION: HUMAN HANDS... Human Hands... with various illustrations of human hands. Blue, green, red and yellow... Human Hands Magazine. Norman Penrose collection: paper cutting ...Magazine. Norman Penrose collection: paper cutting with various illustrations of human hands. Blue, green, red and yellow background of materials and whitish bubbles. Cutting pasted onto a piece of cardboard with an advertisement on the back depicting the Victorian Comforts Fund urging people to give a newspaper to provide comforts for the babies.person, bendigo, norman william penrose, norman penrose collection, human hands -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - X-Rays - Radiographs, Pioneer X-Rays conducted at the Ballarat School of Mines, 1896, 1896
... include human bones, kangaroo hand, steel, bent knee, gold... at the Ballarat School of Mines. X-Rays include human bones, kangaroo hand ...According to 'Salute to the X-Ray Pioneers of Australia' the X-Rays experiments conducted at the Ballarat School of Mines 'played a conspicuous part in the development of the application for x-rays to medicine.' John M. Sutherland conducted most of the experiments with induction coils giving 6 inch, 12 inch and 16 inch sparks respectively. Photograph of a timber frame with 27 original X-Rays conducted by John Sutherland at the Ballarat School of Mines. X-Rays include human bones, kangaroo hand, steel, bent knee, gold in quartz, snake, and others.x-ray, john m. sutherland, ballarat school of mines, john mckenzie sutherland, xray, pioneer xrays -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Poster - Assorted posters
... possum on a human's hand in front of a burnt landscape. 0422... on a human's hand in front of a burnt landscape. 0422 - Poster ...Assorted posters sent to the society. Contains: 0414 - Laminated poster promoting the history of Aboriginal station Coranderrk. 0415 - Poster commemorating the centenary of Federation. 0416 - Poster commemorating the centenary of Australian Federation. 0417 - Double-sided poster promoting the history of Federation in Australia in 1901. Highlights a snapshot of life in Australia in 1901. 0418 - Double-sided poster commemorating the centenary of Australian Federation. One side is a replica of a Federation poster in 1901, and the other side is a timeline of events leading to Federation in 1901. 0419 - Printed poster for the 'Fire Cycle' event held by the Dandenong Ranges Music Council, Inc. at Belgrave Heights Convention Centre on October 8th-9th 2005. Feature possum on a human's hand in front of a burnt landscape. 0422 - Poster of Station Pier. 0423 - Poster focusing on clay pipes from the shipwreck of "Victoria Tower" near Torquay in 1869. 0424 - 2 posters, one green and one blue, about the life of lyrebirds. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Riverina Commercial Press, Griffith, 1963
Albert Jaime Grassby, AM was an Australian politician who served as Minister for Immigration in the Labor Whitlam Government. He completed reforms in immigration and human rights, and is often known as the father of Australian "multiculturalism". Prior to this Grassby worked as a journalist and information officer for the CSIRO in Griffith, New South Wales.This item is a useful reference tool on the history of Griffith in New South Wales.A 46 pp paper back book titled, " Griffith of the Four Faces". on the front cover is a coloured aerial photograph of Griffith, New South Wales. The book contains coloured photographs and a history of the area.on front cover hand-written in blue pen - "M. Gilbert"griffith-new-south-wales griffith-history -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybooks, 1916
These books are part of the Lawless Collection. The Lawless family lived in Orbost from 1907 - c 1920. John Francis Lawless had a saddlery shop. He died at an early age - 47 years - June 7 1912, leaving his wife, Elizabeth and seven children. The eldest son, Victor Rowland lawless volunteered for serv ice in WW1 but did not leave Australia because of illness. The second son, Edward Vincent Lawless (b 1895 d 1917) worked for McCoy & Co. in Orbost, coachbuilding, undertakers, general blacksmiths and farriers, prior to enlisting in WW!. He was trained as a signaller and was sent to France where he was killed in action on 9.10.1917. Elizabeth Lawless worked as a ladies' nurse (midwife) in Orbost prior to leaving the district in 1920. She lived to 6.6.1975 aged 104 years.These personal documents, photographs, medals and books give an insight into the human element of World War 1 ensuring that those who were part of the Orbost community and died while playing a vital role during this time are remembered.Three books used by Edward Vincent Lawless during his service in WW1. 1846.5 has a black cover and contains hand-written notes and diagrams in an exercise book. 1846.6 has a purple cover and contains hand-written notes on bombing. 1846.7 is a small book with a black cover and a ribbon for tying closed. It contains signalling notes1846.5 Edward Lawless 1846.6 E.V. Lawless 1846.7 Ted Lawless A Group Signalling 6th Battalion 22/6 Lark Hill School No 5 Camp No 5 Camp B Coylawless-family ww1 books signalling -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societywoomera
A woomera is a wooden Australian Aboriginal spear-throwing device . It is an extension of the human arm that enables a spear to travel at a greater speed and force than possible with the unaided arm.The necessary tools and equipment for hunting, fishing and warfare were one of the very few items that Aboriginals carried with them from place to place. Most were used for a multiplicity of purposes. Because many were made from raw natural materials, such as wood, generally only partial remains are found today. This woomera is an example of an implement used by early Indigenous people.A flat hand-made dish like wooden spear thrower with curved edges. It has a small spike tied at one end and hardened black gum at the other.woomera aboriginal hunting spear-thrower -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Syringe set, 20th century
Whether it’s an anaesthetic, blood test, insulin, vitamin shot or vaccination, at a base human level something feels instinctively wrong about having a long thin piece of metal stuck deep into your flesh. And yet, in allowing physicians to administer medicine directly into the bloodstream, the hypodermic needle has been one of the most important inventions of medical science. In the beginning… Typically, it was the Romans. The word ‘syringe’ is derived from Greek mythology. Chased to the edge of a river by the god Pan, a rather chaste nymph by the name of Syrinx magically disguised herself as water reeds. Determined, Pan chopped the hollow reeds off and blew into them to create a musical whistling sound, thereby fashioning the first of his fabled pipes. Taking that concept of ‘hollow tubes’, and having observed how snakes could transmit venom, the practice of administering ointments and unctions via simple piston syringes is originally described in the writings of the first-century Roman scholar Aulus Cornelius Celsus and the equally famous Greek surgeon Galen. It’s unclear if the Egyptian surgeon Ammar bin Ali al-Mawsili was a fan of either of their scribblings, but 800 years later he employed a hollow glass tube and simple suction power to remove cataracts from his patients’ eyes – a technique copied up until the 13th century, but only to extract blood, fluid or poison, not to inject anything. Syringes get modern Then, in 1650, while experimenting with hydrodynamics, the legendary French polymath Blaise Pascal invented the first modern syringe. His device exemplified the law of physics that became known as Pascal’s Law, which proposes “when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container.” But it wasn’t until six years later that a fellow Renaissance man, the English architect Sir Christopher Wren took Pascal’s concept and made the first intravenous experiment. Combining hollow goose quills, pig bladders, a kennel of stray dogs and enough opium to fell a herd of elephants, Wren started injecting the hapless mutts with the ‘milk of the poppy’. By the mid-1660s, thinking this seemed like a great idea, two German doctors, Johann Daniel Major and Johann Sigismund Elsholtz, decided to try their hand at squirting various stuff into human subjects. Things didn’t end well, and people died. Consequently, injections fell out of medical favour for 200 years. Let's try again… Enter the Irish doctor Francis Rynd in 1844. Constructing the first-ever hollow steel needle, he used it to inject medicine subcutaneously and then bragged about it in an issue of the Dublin Medical Press. Then, in 1853, depending on who you believe, it was either a Frenchman or a Scot who invented the first real hypodermic needle. The French physician Charles Pravaz adapted Rynd’s needle to administer a coagulant in order to stem bleeding in a sheep by using a system of measuring screws. However, it was the Scottish surgeon Alexander Wood who first combined a hollow steel needle with a proper syringe to inject morphine into a human. Thus, Wood is usually credited with the invention. Sharp advancements Over the following century, the technology was refined and intravenous injections became commonplace – whether in the administering of pain relief, penicillin, insulin, immunisation and blood transfusions, needles became a staple of medicine. By 1946, the Chance Brothers’ Birmingham glassworks factory began mass-producing the first all-glass syringe with interchangeable parts. Then, a decade later, after sterilisation issues in re-used glass syringes had plagued the industry for years, a Kiwi inventor called Colin Murdoch applied for a patent of a disposable plastic syringe. Several patents followed, and the disposable syringe is now widespread. https://www.medibank.com.au/livebetter/be-magazine/wellbeing/the-history-of-the-hypodermic-needle/ This syringe set was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Syringe set (5 pieces) in container, from W.R. Angus Collection. Rectangular glass container with separate stainless steel lid, syringe cylinder, end piece and angle-ended tweezers. Container is lined with gauze and fabric. Scale on syringe is in "cc". Printed on Syringe "B-D LUER-LOK MULTIFIT, MADE IN U.S.A." Stamped into tweezers "STAINLESS STEEL" and "WEISS LONDON"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, syringe, b d syringe, luer-lok multifit, weiss london, surgical tweezers, hypodermic syringe, injections -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Syringe set, c. 1940s
Whether it’s an anaesthetic, blood test, insulin, vitamin shot or vaccination, at a base human level something feels instinctively wrong about having a long thin piece of metal stuck deep into your flesh. And yet, in allowing physicians to administer medicine directly into the bloodstream, the hypodermic needle has been one of the most important inventions of medical science. In the beginning… Typically, it was the Romans. The word ‘syringe’ is derived from Greek mythology. Chased to the edge of a river by the god Pan, a rather chaste nymph by the name of Syrinx magically disguised herself as water reeds. Determined, Pan chopped the hollow reeds off and blew into them to create a musical whistling sound, thereby fashioning the first of his fabled pipes. Taking that concept of ‘hollow tubes’, and having observed how snakes could transmit venom, the practice of administering ointments and unctions via simple piston syringes is originally described in the writings of the first-century Roman scholar Aulus Cornelius Celsus and the equally famous Greek surgeon Galen. It’s unclear if the Egyptian surgeon Ammar bin Ali al-Mawsili was a fan of either of their scribblings, but 800 years later he employed a hollow glass tube and simple suction power to remove cataracts from his patients’ eyes – a technique copied up until the 13th century, but only to extract blood, fluid or poison, not to inject anything. Syringes get modern Then, in 1650, while experimenting with hydrodynamics, the legendary French polymath Blaise Pascal invented the first modern syringe. His device exemplified the law of physics that became known as Pascal’s Law, which proposes “when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container.” But it wasn’t until six years later that a fellow Renaissance man, the English architect Sir Christopher Wren took Pascal’s concept and made the first intravenous experiment. Combining hollow goose quills, pig bladders, a kennel of stray dogs and enough opium to fell a herd of elephants, Wren started injecting the hapless mutts with the ‘milk of the poppy’. By the mid-1660s, thinking this seemed like a great idea, two German doctors, Johann Daniel Major and Johann Sigismund Elsholtz, decided to try their hand at squirting various stuff into human subjects. Things didn’t end well, and people died. Consequently, injections fell out of medical favour for 200 years. Let's try again… Enter the Irish doctor Francis Rynd in 1844. Constructing the first-ever hollow steel needle, he used it to inject medicine subcutaneously and then bragged about it in an issue of the Dublin Medical Press. Then, in 1853, depending on who you believe, it was either a Frenchman or a Scot who invented the first real hypodermic needle. The French physician Charles Pravaz adapted Rynd’s needle to administer a coagulant in order to stem bleeding in a sheep by using a system of measuring screws. However, it was the Scottish surgeon Alexander Wood who first combined a hollow steel needle with a proper syringe to inject morphine into a human. Thus, Wood is usually credited with the invention. Sharp advancements Over the following century, the technology was refined and intravenous injections became commonplace – whether in the administering of pain relief, penicillin, insulin, immunisation and blood transfusions, needles became a staple of medicine. By 1946, the Chance Brothers’ Birmingham glassworks factory began mass-producing the first all-glass syringe with interchangeable parts. Then, a decade later, after sterilisation issues in re-used glass syringes had plagued the industry for years, a Kiwi inventor called Colin Murdoch applied for a patent of a disposable plastic syringe. Several patents followed, and the disposable syringe is now widespread. https://www.medibank.com.au/livebetter/be-magazine/wellbeing/the-history-of-the-hypodermic-needle/ This syringe set was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Syringe set (8 pieces),part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Pocket syringe kit in oval stainless steel container with separate lid. Container holds syringe cylinder, plunger, 2 needles, blade and cap. Printed on syringe cylinder "FIVEPOINT BRITISH" and symbol of a red star. One needle stamped "22"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, medical education, medical text book, fivepoint syringe, general surgical co., injections -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionLeisure object - Doll, c. 1920
Displayed at History House.Hand-made fabric doll made from brown velvet (head, torso, arms and feet) and yellow velvet (legs and lower torso-overalls). Glass eyes, brown. Painted eye-brows, eyelashes (black), and lips, nostrils (red and white). Appears to be human hair sewn into head. Body stuffed with wadding, head with a firmer material that crunches.toy, doll, childhood -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionCraft - Rag Doll, c. 1910
Displayed at History HouseHand-made fabric doll. Cotton body (stocking material?), cotton print fabric (red and white flowers and squares on black background) for dress. Embroidered belt (green and gold), bonnet and cuffs. Felt boots with blue and green stitching. Beading at base of skirt in red, white, green, yellow and clear beads (plastic). Stuff with dried plant material. Red ribbon tied around waist. Curly brown hair (human?). Embroidered face.toy, doll, childhood -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle - Castor Oil, Circa 1920's to 1900's
This bottle of castor oil was used during the mid to late 1900's when there was a Hospital in the Kiewa Valley, but regarded as only for serious injuries and near death situation. For this reason many households had a "first aid" box full of items such as this bottle of castor oil. Home based remedies for non life threatening injuries and illnesses were a part of life in a semi remote rural region. True and trusted family "health" remedies were passed from generation to generation.This Castor Oil bottle is very significant to the Kiewa Valley as it demonstrates the self reliance of the early farming and grazing pioneer families. Knowledge of "first aid" was uppermost to the survival of families before the late 1900's. Naturopathic remedies such as connected with the castor oil contained in this bottle, although may not be sanctioned by medical research, does not take into account of the positive "self healing" of the human mind (if you think it is doing you good it creates a positive action). Such preservation techniques were handed down through the generations.Medical Reference material was limited to books available and read and not not from "the internet" in the latter part of the 1900's. The availability of General Practitioners increased because of the boost in the population growth (SEC Vic Hydro Electricity Scheme) in the Kiewa Valley from 1940's onward. This small indigo coloured glass bottle has a narrow neck and a screw on lid.It has an embossed manufacturer's name and contents (Castor Oil) on one side and identification marks embossed on the underside base.medicine bottles, home first aid remedies, indigo glass medicine bottles -
 Burrinja Cultural Centre
Burrinja Cultural CentreIniet Sculpture: Male, hands on hips, Mid 20th Century
Limestone carving of human figure standing on solid base, knees slightly bent, hands resting on hips. Narrow torso with protruding genitals. Facial features clearly defined. Mouth Wide and lips pouted. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyhand drill
The invention of a hand drill is credited to Arthur James Arnot and William Blanch Brain of Melbourne, Australia who patented the electric drill in 1889. In 1895, the first portable handheld drill was created by brothers Wilhem & Carl Fein of Stuttgart, Germany. Hand-powered devices have been used for millennia. However, during the last quarter of the 19th century a radically improved generation of tools appeared. These tools took advantage of modern mass production machinery and processes (like interchangeable parts) and an increased availability in superior material (metal instead of wood). One of the outcomes included an array of new drilling machines. These human-powered tools were a vast improvement over earlier tools.This item is an example of a commonly used domestic tool - pre power tools.A Stanley hand drill with two wooden handles. The red wheel is painted metal. On red wheel - STANLEY ENGLANDwoodwork tool hand-drill -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Stereoscope, H C White, Late 19th century
The development of stereoscopic photography views or stereographs was immensely popular in the United States and Europe from about the mid-1850s through the early years of the 20th century. First described in 1832 by English physicist Sir Charles Wheatstone, stereoscopy was improved by Sir David Brewster in 1849. The production of the stereograph entailed making two images of the same subject, usually with a camera with two lenses placed 6 cm apart to simulate the position of the human eyes, and then mounting the positive prints side by side laterally on a stiff backing. Brewster devised a stereoscope through which the finished stereograph could be viewed; the stereoscope had two eyepieces through which the laterally mounted images, placed in a holder in front of the lenses, were viewed. The two images were brought together by the effort of the human brain to create an illusion of three-dimensionality. Stereographs were made of a wide range of subjects, the most popular being views of landscapes and monuments and composing narrative scenes of a humorous or slightly suggestive nature. Stereoscopes were manufactured for various price ranges and tastes, from the simple hand-held device introduced by Oliver Wendell Holmes who promoted stereography through articles to elaborate floor models containing large numbers of images that could be flipped into place. The stereograph became especially popular after Queen Victoria expressed interest in it when it was exhibited at the 1851 Crystal Palace Exposition. Like television today, stereography during the second half of the 19th century was both an educational and a recreational device with a considerable impact on public knowledge and taste. The Fine-art Photographers' Publishing Co. published many stereoscopic pictures from many different photographers from around the world under license. They also not only sold these images of various scenes and of famous people of the time but also were retail sellers of the viewers with the subject item having been made in the USA probably by H C White who held the patent for the subject items design from 1895 to 1902.An item that was very popular from the mid 19th century through to the beginning of the Edwardian period. Used for entertainment and also educational purposes and significant as it gives us a snapshot into the Victorian era and its social and domestic societal norms. Stereoscope viewer with adjustable view-finder that has a padded nose rest. The slide holder can move along the channel to suit the viewer. Made in London by the Fine-art Photographers' Publishing Co. Printed on metal plate "THE FINE-ART PHOTOGRAPHERS' PUBLISHING CO. 48 Rydevale Rd, LONDON, S.W." Embossed on viewing cup "U.S.A. PATENT OCT.15.1895" "CANADA / FRANCE / GERMANY / D'R''G'M' NO. 53803" "JUNE 3.1902 / FEBY 1.1896 / B.S.G.D.B. / GREAT BRITAIN / AUSTRIA / BELGIUM"warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, stereoscope, stereographs, stereoscope viewers, home entertainment -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionEquipment - Object, Otto Waschatz, Cast of Hand, Plaster Cast Drawing Prop
The Ballarat Technical Art School boasted a well-stocked Antique Room replete with plaster copies of classical, Renaissance and Gothic sculptural examples, which were used as drawing props by students. The school inherited some casts from its predecessor institutions, and further consignments were purchased during the 1920s, including full length, bust and relief figures, as well as dozens of ornamental and architectural casts. Unfortunately, much of the collection was lost or destroyed in the late 1950s. This is one of the few surviving pieces, with TAFE students reportedly drawing from it into the twenty-first century. This plaster hand is inscribed “Waschatz, Modeller, Melbourne.” Otto Waschatz was a German plasterer who opened a plaster business in the Melbourne suburb of Richmond, and was responsible for the invention of the first true fibrous plaster - using a layer of hemp laid between plaster to create light and strong panels. By 1912 Waschatz's Lottoid Pty Ltd was a thriving and creative business, and possessed over 5,000 moulds for all kinds of plasterwork. The business closed in 1915, as the result of anti-German sentiment during World War One. Plaster cast of a hand used as a teaching aid at the Ballarat Technical Art School. The Victorian Education Department courses required art students to create studies based on ancient sculptures so copies of famous works were purchased as teaching aids. Among these courses were 'Drawing the Human Figure from Cast' and ‘Drawing from the Antique’. Waschatz, Modeller, Melbourneballarat school of mines, art, arts academy, ballarat technical art school, vikki nash, plaster cast, otto waschatz, lattoid pty ltd, school of mines, plaster copy, drawing from the antique, drawing the human figure from cast -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionWork on paper - Artwork, Ballarat East Main Road Joss House Rubbings
A number of rubbings of calligraphic carvings thought to be from the Ballarat East Joss House in Main Road. .1) Blue and brown crayon. Translation: Erected on an auspicious day in winter 1859. Think of his loyalty (Quan Yu, now can canonised as the god of war to whom this temple is dedicated) (AD1084) to his sworn lover their sworn botherhood pledged in the peach garden as has been praised for thousands of years. .2) Rubbing in blue crayon of Chinese calligraphy from pole on right hand side of Joss House Door. (Larger) his great graciousness spreads to other (us here in foreign lands) kingdoms, and his virtue guards our gold miners everywhere. (Smaller) Dedicated to his disciples the Chu Pei-Huo family .3) Rubbing on litho paper. translation - One who knows the nature of things (in the world) will thus understand human nature. .4) Rubbing on litho paper. Translation of middle calligraphy - We all behold the wisdom of the gods in the heavens, earth and man. .5) Rubbing on litho paper - translation - The grace of god flows to all corners of the earth. .6) Charcoal rubbing - translation - Temple of the god of war. .7) Crayon rubbing of calligraphy on litho paper. Translation - Dedicated by the Ma Chu-Feng family. Emperor's virtue spreads far and wide. Grace in Abundance. Erected in winter, 1859. .8) Crayon rubbing of calligraphy on litho paper. Translation: Respectfully dedicated by the Ts'Ai Chi-Yang family. Grace in abundance. Erected in winter of 1859. .9) Crayon rubbing .10) Outline of calligraphy on copy paper .11) Rubbings of calligraphy on copy paper. Translation: The Holy God of War. Exhibited in 1862. Your respectful disciples. .12) List of 11 disciples chinese, joss house, keith rash, chu pei-huo, quan yu, ma chu-feng, ts'ai chi-yang, lee chua-yeh, hwong tien-jyue, wa perg-nan, liu chin-chuson, an lee factory, lice hsue-chiere, lee mei-tzy, lee pas-chi, lui lih-nie, wir hon-fu, li hsi-yang -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Scrapbook, Scrap Book Compiled by William Robertson, c1911
Maroon covered minute book that has had handwritten minutes pasted overs with clippings collected by William Robertson. The minutes appear to be of the Budding Rose Juvenile Temple IOGS held in hte Piggoret Public Hall and/or Piggoreet Presbyterian Church Clippings include: Origins of man (Jubilee of Darwin's Theory) Fight Against Evolution (E. Grant Conklin) Neanderthal Man and Grimaldi Man Our First Immigrant Had Human Head, But MOuth Like a Mnkey Darwinism Mutton BurdsThe Missing Link: Supposed Discovery. Man who walked on all-fours Channel tunnel Ernest Haeckel and his work Mr McCabe's Lecture Taungs Skull Jumbo's Trunk Man hand written notes by Roberston are evident, including Heredity, Classification, Fossil Men, Broken Hill Skull (South Africa) budding rose juvenile temple, piggoreet public hall, piggoreet presbyterian church, charlotte leaske, james robertson, nellie robertson, richard webb, bella laidler, john christie, e. prolonseau, charles christie, andrew jamieson, david sinclair, sam webb, origin of man, darwin's theory, darwinism, embyology, origin of creation, sir oliver lodge, missing link, heredity, fossils, pedigree of birds, fourth dimension, joseph mccabe, huxley's reserves, animal intellegence -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooks, H.E. Daw Government Printer, Ballarat School of Mines and Industries Departmental Papers, 1914-1950, 1914-1950
Used at the Ballarat School of Mines and the Ballarat Technical Art SchoolThis collection of examinations is significant because of its completeness with the full range of examinations between 1914 and 1950.Large leather bound books, with leather spine, containing all examinations held at the Ballarat School of Mines (including the Ballarat Technical Art School and Ballarat Junior Technical School). The examination papers were supplied and printed by the Education Department, Victoria. Examinations include: Agriculture, Algebra, Architecture, Arithmetic, Applied Mechanics, Assaying, Biology, Botany, Boilermaking, Building Design, Blacksmithing, Bricklaying, Carpentry and Joinery, Coachbuilding, Cabinet Making, Civil Engineering, Cabinet Making, Commercial, Chemistry, Engineering Drawing, Economics, English, Electrical technology, Electricity and Magnetism, Electric Wiring, Electric Welding, Electrical Fitting, Electrical Trades, Food Analysis, Geology, Geological Mapping, Graphics, Geometry, Heat Engines, Heat Treatment, Hydraulics, Hand Railing, Instrument Making, Millinery, Milling and Gearouting, Machine Shop Practice. Metal Founding, Mining, Metallurgy, Mineralogy, Mathematics, Motor Mechanics, Mine Surveying, Mining Mechanics, Petrology, Physics, Painting and Decorating, Pattern Making, Plastering, Plumbing and Gasfitting, Printing, Refrigeration, Spelling, Science , Shorthand, Surveying. Signwriting. Sheet Metalwork, Toolmaking, Ladies Tailoring, Trigonometry, Typewriting, Welding, Commercial Geography. Millinery, Dressmaking, Needlework, Decorative Needlework, Architecture, Building Design and Construction, Art (Composition in Form and Colour), Art (Casting Clay MOdels) Art (Drapery), Art (Drawing the Human Figure From Casts), Art (Drawing the Antique from Memory), Art (Drawing from Memory); Art (Drawing Plant Forms from Nature, Art (Drawing Plant Forms From Memory), Art (Drawing from Models and Objects), (Drawing From a Flat Example). Art (Drawing in Light and Shade from a Cast of Ornament or Lower Nature), Art (Drawing Ornament from the Cast), Art (Drawing from Models or Objects), Art (Drawing fro Dressmakers' and Milliners' Fashions), Art (Drawing With the Brush), Art (Drawing from a Flat Example); Art (Modelled Design), Art (General Design), Art (Embossed Leatherwork), Art (Practical Plane Geometry), Art (Practical Solid Geometry), Art (Geometrical Drawing), Carpentry and Joinery, Art (Human Anatomy), Art (Historic Ornament), Art (House Decoration), Art (LEttering), Signwriting, Art (Light Metalwork), Art (Modelling), Art (Modelling the Human Figure from a Life), Art (Stencilling); Art (Wood Carving) Refrigeration, Teaching, Boilermaking, Blacksmithing, Carpentry and Joinery, Coachbuilding and Carriage Drafting, Electric Wiring, Electrical Fitting, Graining and Marbling, Instrument Making , Machine Shop Practice, Metal Founding, Milling and Gear Cutting, Motor Mechanics, Painting and Decorating, Sheet Metalwork, Toolmaking, Printing, Pattern Making, Plumbing and gasfitting, examinations, ballarat school of mines, ballarat technical art school, trades, education department victoria, agriculture, algebra, architecture, arithmetic, applied mechanics, assaying, biology, botany, boilermaking, building design, blacksmithing, bricklaying, carpentry and joinery, coachbuilding, cabinet making, civil engineering, commercial, chemistry, engineering drawing, economics, english, electrical technology, electricity and magnetism, electric wiring, electric welding, electrical fitting, electrical trades, food analysis, geology, geological mapping, graphics, geometry, heat engines, heat treatment, hydraulics, hand railing, instrument making, millinery, milling and gearouting, machine shop practice, metal founding, mining, metallurgy, mineralogy, mathematics, motor mechanics, mine surveying, mining mechanics, petrology, physics, painting and decorating, pattern making, plastering, plumbing and gasfitting, printing, refrigeration, spelling, science, shorthand, surveying, signwriting, sheet metalwork, toolmaking, ladies tailoring, trigonometry, typewriting, welding., dressmaking, needlework, decorative needlework, architecture, building design and construction, art (composition in form and colour), art (casting clay models), art (drapery), art (drawing the human figure from casts), art (drawing the antique from memory), art (drawing from memory), art (drawing plant forms from nature, art (drawing plant forms from memory), art (drawing from models and objects), (drawing from a flat example), art (drawing in light and shade from a cast of ornament or lower nature), art (drawing ornament from the cast), art (drawing from models or objects), art (drawing for dressmakers' and milliners' fashions), art (drawing with the brush), art (drawing from a flat example), art (modelled design), art (general design), art (embossed leatherwork), art (practical plane geometry), art (practical solid geometry), art (geometrical drawing), art (human anatomy), art (historic ornament), art (house decoration), art (lettering), art (light metalwork), art (modelling), art (modelling the human figure from a life, art (stencilling), art (wood carving), teaching, coachbuilding and carriage drafting, graining and marbling, milling and gear cutting, commercial geography, exams, examination book -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph - Plateway (Wheelway) Steel, circa 1885
By the later 1800s the dirt roads in the then out-lying areas of the City of Moorabbin became dangerous, and almost impassable due to huge potholes and muddy swampy areas. The heavily laden market gardener’s carts regularly broke axles and wheels, and horses foundered on their way to the Melbourne markets. Even worse, the heavier “iron maidens”, carrying their malodorous loads of sewage from Melbourne’s inner suburbs for dumping in the outlying areas of the City of Moorabbin, also got bogged in the mire. It was decided that a practical solution to this problem was to install a metal plateway on the side of the problematic roads. In about 1887 the Moorabbin Shire Centre Road, in the Brighton East area, two parallel metal rails were installed so that the wheels of carts could run along smoothly, the horse travelled in the filled, middle area between the rails. Point Nepean Road plateway was removed in 1930 and Centre Dandenong Road plateway was removed in 1934-35. The worn plateway along Centre Road, East Brighton (now known as Bentleigh), was gradually taken up in several pieces, commencing in the the1920s, when its condition deteriorated and it caused a hazard to bikes, pedestrians, motor-cycles and the few early cars. The early steel plateway, constructed by David Munro, and opened on 23rd March 1885 by Thomas Bent, was built along Nepean Highway, between Asling St. and Bay St. The Point Nepean Track was subsequently extended into Moorabbin with branches along Centre, Cumins, South, Wickham, and Keys Roads, the total length was 13 miles. In 1908-1909 plates were laid along Centre Dandenong Road to Ross Street Bentleigh This innovative solution proved successful and was used until gradually the main roads were upgraded, and motorised vehicles started to appear. Two parallel metal rails were installed in the right hand side of a few main roads in the Shire of Moorabbin so that the wheels of heavily-loaded market gardener's carts on their way to markets in Melbourne could run along smoothly. The horse pulling the carts travelled in the filled, middle area between the rails. The Steel Plateway was constructed by David Munro, and opened on 23rd March 1885 by Thomas Bent. The wheelway first only ran along Nepean Highway, but it soon extended from Centre Dandenong Road, along Nepean road to its junction with Chapel Street, St Kilda. Later branch lines were built along Centre Road, Bentleigh as far as Warrigal Road and, according to early photographs, along Wickham Road Moorabbin as well. This innovative solution proved successful and was used until gradually the main roads were upgraded, and motorised vehicles started to appear. There was a problem with the wheelway : there was only a single set of rails and this was established on the right-hand side of the Nepean Road, travelling towards the city. Traffic FROM the city travelled on the correct or left-hand side of the road. The exception to this rule was the malodorous iron-clads, heavily riveted iron carts, generally travelling in convoy, carrying several tons of human effluent out of Melbourne to be trenched-in in the sandy soil of the Moorabbin district. Moorabbin City Council donated and installed a small section of Plateway at Box Cottage Museum in 1984melbourne, brighton, moorabbin, roads, plateway, wheelway, transport, st kilda, bent thomas, munro david, market gardens, steelway, carts horse-drawn, iron maidens, point nepean track -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - COHEN'S MODERN SELF INSTRUCTOR IN PHRENOLOGY
... in Phrenology, Physiognomy and physiology or The Peoples Hand book... Hand book of Human Nature. Red in colour with gold print.The ...271 page hardcover titled 'The Modern Self Instructor in Phrenology, Physiognomy and physiology or The Peoples Hand book of Human Nature. Red in colour with gold print.The first page is yellow paper which has a hand written note in black ink which reads: 'Presented to Henry Gough by his teacher A. Hampson for obtaining the highest number of marks during 1887 in his class at St. Paul's Sunday School dated 1/04/88. The book is Cohen's view into the mind, body, and sole of human beings.Gustavus Cohen. George Whitehead & Sons, Printers, New Street & Kings Street, Huddersfield.medicine, mental health, phrenology, henry gough, a. hampton -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Crecy Publishing, No moon tonight, 2000
Don Charlwood was born in Melbourne in 1915. Accepted as a RAF navigator in 1940, he was posted to 103 Squadron at Elsham Wolds in the winter of 1942. There he crewed up with a pilot from Western Australia and a British crew to fly a Lancaster bomber. In No Moon Tonight he gives a profound insight into the inner lives of the men of Bomber Command and their hopes and fears in the face of mounting losses. He depicts the appalling human cost of the air war in an account which has been favorably compared to other enduring memoirs of the 1st World War, namely Sassoon's Memoirs of an Infantry Officer and Remarque's All Quiet on the Western Front. A memorable first hand account of the air war over Germany.Ill, p.244.non-fictionDon Charlwood was born in Melbourne in 1915. Accepted as a RAF navigator in 1940, he was posted to 103 Squadron at Elsham Wolds in the winter of 1942. There he crewed up with a pilot from Western Australia and a British crew to fly a Lancaster bomber. In No Moon Tonight he gives a profound insight into the inner lives of the men of Bomber Command and their hopes and fears in the face of mounting losses. He depicts the appalling human cost of the air war in an account which has been favorably compared to other enduring memoirs of the 1st World War, namely Sassoon's Memoirs of an Infantry Officer and Remarque's All Quiet on the Western Front. A memorable first hand account of the air war over Germany.world war 1939-1945 - aerial operations - britain, world war 1939-1945 - personal narratives - australia -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, M. Joseph, The Korean war, 1987
On 25 June 1950 the invasion of South Korea by the Communist North launched one of the bloodiest conflicts of the last century. The seemingly limitless power of the Chinese-backed North was thrown against the ferocious firepower of the UN-backed South in a war that can be seen today as the stark prelude to Vietnam. Max Hastings has drawn on first-hand accounts of those who fought on both sides to produce this vivid and incisive reassessment of the Korean War, bringing the military and human dimensions into sharp focus.Index, bib, ill, maps, p.476.On 25 June 1950 the invasion of South Korea by the Communist North launched one of the bloodiest conflicts of the last century. The seemingly limitless power of the Chinese-backed North was thrown against the ferocious firepower of the UN-backed South in a war that can be seen today as the stark prelude to Vietnam. Max Hastings has drawn on first-hand accounts of those who fought on both sides to produce this vivid and incisive reassessment of the Korean War, bringing the military and human dimensions into sharp focus.korean war 1950-1953 - history, korea - history -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Angela NAGEL, Angela Nagel, How to Explain Genetics to a Thylacine, 2009
Entry into the 2009 Nillumbik Prize. Angela holds a Masters of Fine Art and has worked with clay for over 20 years. Her work is held in collections around Australia.Angela Nagel's creative practice is informed by an interest in the human condition, universal symbols, mythology and Jung's theory on the 'collective unconscious'. Her hybrid part human/animal creatures reference introduced species and indigenous Australian animals as a way for her to explore a personal mythology, and narrative, of home and environment. Recent work is developing around the relationship of ceramics to other materials such as glass, printmaking and found objects. Angela holds a Masters of Fine Art and has worked with clay for over 20 years. Her work is held in collections around Australia.Human and animal like figure in the stance reminiscent of classical sculpture. Hand built ceramics with engobes, oxides, glaze and gold leaf Medium: Porcelain, oxide, underglazeangela nagel, nillumbik shire council collection, victoria, nillumbik prize, ceramic -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilPrint (etching & acquatint): George BALDESSIN (b.1939 ITA – d.1978 AUS), George Baldessin, ‘Portrait II’ from 'The Baldessin & Friends' commemorative folio, 1966 (printed 2017)
George Baldessin (1939-1978) was born in San Biagio di Callalta, in the Veneto in Northern Italy and arrived in Australia ten years later. A printmaker and sculptor he built his bluestone studio at St Andrews (Nillumbik) in 1971 with his partner Tess and the three Hails brothers, Rob, Doug and Don. Made of recycled materials the studio today contains all of George’s equipment including the large press, which he modelled himself with the help of Neil Jeffrey (Enjay Presses). George won many prizes throughout his career and is represented in many of Australia's public art collections including his famous 'Pears' sculpture in front of the National Gallery of Australia, Canberra. In 1975 he represented Australia in the Sao Paulo Biennale, before living and working in Paris until his return to St Andrews in 1977. In 1978 George was killed in a car accident aged 39 years. In 2001 Tess returned to St Andrews to reclaim the run-down studio and reconstitute it as The Baldessin Press & Studio - a printmaking retreat. It operates in George’s memory, so that artists may continue to create, perpetuating the generous spirit of George. This work chosen for the folio is from an incomplete edition from 1966. It has been printed on Baldessin's original 1974 cast aluminium Enjay press (designed and made in collaboration with Neil Jeffreys) and restored specifically for this project by Dan Jones. In addition Deanna Hitti has used Baldessin's original Japanese Torinoko paper, stored safely in his studio for over forty years. ‘Portrait II’ is one of eight prints in the 'Baldessin & Friends commemorative folio. The folio was conceived by Tess Edwards as a fundraising initiative in celebration of the The Baldessin Press & Studio's fifteen year anniversary, and as a way to honour George Baldessin's memory. The Baldessin Press & Studio is a not-for-profit organisation created in memory of the late George Baldessin (1939-1978), whose original studio is now open to the public for creative use and as a practical legacy to living artists. The Studio is located in St Andrews, Nillumbik. The folio is a unique coming together of seven very different and acclaimed artists who are connected by their friendship to the missing eighth member, George Baldessin. This print is a fine example of Baldessin's primary interest of the figure, which displays great sensitivity to and observation of the human condition. Distortion, exaggeration and fragmentation were employed by Baldessin as tools to animate and scrutinize the displaced, dispossessed and alienated figure, flattened against the picture plane. Black and white distorted and exaggerated figure (head and shoulders), with hands raised to the face and the figure's right eye. acquatint, etching, baldessin, ekphrasis2018, figure -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Bennett, M. M, The Australian Aboriginal as a human being, 1930
" The problem of what to do with the race, the most interesting at present on earth, and the least deserving to be exterminated by us, and the most wronged at our hands, is not a difficult one to solve were a solution really desired." - Dr. Ramsay Smith, Commonwealth Year Book for 1909.146 p. ; index; 19 cm." The problem of what to do with the race, the most interesting at present on earth, and the least deserving to be exterminated by us, and the most wronged at our hands, is not a difficult one to solve were a solution really desired." - Dr. Ramsay Smith, Commonwealth Year Book for 1909.aboriginal australians. | aboriginal australians -- government relations. -
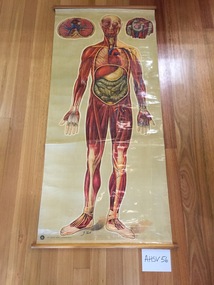 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumChart, medical, human body, muscles and organs
Rectangular medical chart showing the human body, muscles and organs.The chart is made from coated and printed paper on a fabric (?cotton) backing and is attached with metal tacks to timber batons at each end . A strip of red cotton tape is attached to the mid-part of the upper baton and has been used to secure the chart when it is rolled up. Metal ring eyelets are screwed into either end of the upper baton and were probably used to assist when hanging the chart.The artists name 'J.Teck' is included on the lower edge on the front of the chart. The logo of the St John's Ambulance Association and the words 'ST JOHN'S GATE, LONDON E.C. 1' are printed on the lower edge of the chart (left hand side on the front of the chart). The words 'FULL BODY INC LIMBS' is written in black texter pen on the upper baton. The words 'ORGANS, MUSCLES' have been written on the top margin of the chart on the reverse side.medical chart, human body, j.teck -
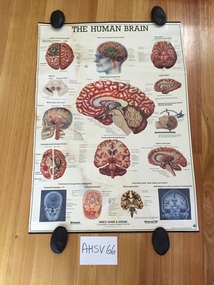 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumChart, medical, human body, brain, Merck Sharpe and Dohme, The Human Brain
Rectangular chart made from glossy paper with colour printing. The chart is mounted at either end on black metal strips. The strip on the upper edge has a loop used for hanging the chart.The word 'BRAIN' is hand written on the reverse of the chart in black texter pen.merck, merck sharpe and dohme, human brain, medical chart -
 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumPhotograph, ambulance, human powered
Possibly some sort of military ambulance (suggested) by white red cross flag). Possibly used in First World War. Possibly some sort of gear mechanism on right hand wheel.Black and white photograph of hand drawn ambulance something like an Ashford Litter. Ambulance has red cross flag and canvas patient cover fitted (also with re cross symbol). -
 Wonthaggi RSL
Wonthaggi RSLTrench shovel
A trenching tool used in Vietnam war, carried by soldiers with their kit. This tool had multiple uses including digging in-field trenches, disposal of human waste, and an an improptu weapon in hand-to-hand combat.This trenching tool is representative of filed kits issued to Australian soldiers in the Vietnam War. Length of handle suggests it was used by Sappers or Artillary.A portable folding shovel with a rivetted lip attached to a wooden handle. A metal tube is atached to the end of the handle. The metal blade is hinged by rivet to the metal tube on the end of the handle. A circular steel tube is on the metal tube.trenching tool, field shovel, vietnam war, military kit, shovel -
 Department of Health and Human Services
Department of Health and Human ServicesA dignitary handing the pledge - A Message of Loyalty to Queen Elizabeth II - to 2 high school students from Northam High School in Western Australia on 04/05/1958 - 1 of 3 photos - Department of Health – National Fitness Office (Sports & Recreation) – Historical Press Release Photo Collection
Department of Health – National Fitness Office (Sports & Recreation) – Historical Press Release Photo - Empire Youth Day & Royals on Tour CollectionDepartment of Health – National Fitness Office (Sports & Recreation) – Historical Press Release Photo - Empire Youth Day & Royals on Tour Collection
