Showing 41 items matching "clothes ironing"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, 1890-1935
... clothes ironing... into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Flat iron cast iron with traces of original black finish on handle. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry, clothes ironing, sad iron, tailors goose -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, 1890-1935
... clothes ironing... into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Flat iron cast iron with stand None item too badly corrodedflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry, clothes ironing, sad iron, tailors goose -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacySlide, Laundry at a residence, 1960s
... A colour slide of two young men ironing clothes...Colour slide of two young men ironing clothes in Kodachrome... A colour slide of two young men ironing clothes in a laundry room ...A colour slide of two young men ironing clothes in a laundry room at a Legacy residence in the 1960s. It is possibly Blamey House in Burke Road or Harelands in Willesmere Road, Kew. It appears to be the same roll of film as 03023 - which is at Harelands dated early 1960s. Legacy ran residences to take care of children whose fathers were deceased servicemen, and who may have been left orphans, or whose mother may have been unable to care for them herself, or they needed to stay in Melbourne for education. Was with many other slides taken in the 1950s and 1960s. The slides have been photographed to make digital images and moved to archive quality sleeves. In many cases the original images were not well focussed and the digital image the best available.A record of a Legacy residence supporting children in their education.Colour slide of two young men ironing clothes in Kodachrome off-white cardboard mount with yellow and red print.Printed on front 'Made in Australia' and '21' in red ink. Faint print mark with slide date 'Se???M' Printed on reverse "Kodachrome Transparency / Processed by Kodak" in red ink.residences, harelands, blamey house -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Ironing board, 1910-1930
... Board Ironing Clothes Wrinkles in Clothes Henry W. Seeley W ...Ironing is the use of a machine, usually a heated tool (an iron), to remove wrinkles from fabric. The heating is around 180–220 °Celsius, depending on the fabric type. Ironing works by loosening the bonds between the long-chain polymer molecules in the fibres of the material. While the molecules are hot, the fibres are straightened by the weight of the iron, and they hold their new shape as they cool. Some fabrics, such as cotton, require the addition of water to loosen the intermolecular bonds. Many modern fabrics developed in or after the mid-twentieth century require little or no ironing. Permanent press clothing was developed to reduce the ironing necessary by combining Wrinkle resistant polymers with cotton. The first known use of the iron for removing wrinkles in clothes is known to have occurred in China, and the electric iron was invented in 1882, by Henry W. Seeley. Seeley patented his "electric flat iron" on June 6, 1882 (U.S. Patent no. 259,054). On 15 February 1858 W. Vandenburg and J. Harvey patented an ironing table that facilitated pressing sleeves and pants legs. A truly portable folding ironing board was first patented in Canada in 1875 by John B. Porter. The invention also included a removable press board used for sleeves. In 1892 Sarah Boone obtained a patent in the United States for improvements to the ironing board, allowing for better quality ironing of shirt sleeves.A domestic item with an interesting history of development, significant as it shows the progress and the evolution of a domestic item designed to make housework more efficient.Wooden Ironing board with press board for sleeves, board is folding.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, domestic item, ironing board, ironing, clothes, wrinkles in clothes, henry w. seeley, w. vandenburg and j. harvey -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Kitchen Equipment, assorted metal pastry cutters 20thC, 20thC
... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones... at the market Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing ...The early settler women of Moorabbin Shire managed the household while their market gardener husbands cultivated the produce to be sold at the market Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones, bread, and pastries. whilst caring for the children and making and mending the family's clothes The early settler women of Moorabbin Shire had to be self sufficient and were skillful cooks providing meals for their familiesAn a assortment of metal pastry, biscuit and scone cutters and tartlet tins with straight and scalloped edges in original condition with no repairs. kitchen equipment, cooking, baking, early settlers, pioneers, moorabbin shire, bentleigh, cheltenham, market gardeners, farmers, -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Biscuit Cutters, Unknown
... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones ...Women in early settler days and 1900's managed the household and had to be self sufficient and were skilful cooks providing meals for their families. Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones, bread, and pastries whilst caring for the children and making and mending the family's clothes. Nine round, one square vintage tin biscuit or pastry cutters: a set of five including a small, medium and large one with curved handles, plus two fluted and one plain cutter and one plain without handles.biscuit cutters, kitchenware, kitchen equipment, pastry cutters -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Container - Bottle
... . Used to dampen clothes before ironing.... neck. Used to dampen clothes before ironing. Container Bottle ...Clear glass bottle with silver coloured sprinkler stopper on blue rubber. Bottle has eight sides tapering to narrow neck. Used to dampen clothes before ironing.The property of G.J. Harding & Co Melbourne - 425domestic items, laundering -
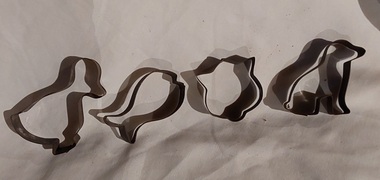 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Biscuit Cutters, Unknown
... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones ...Women in early settler days and 1900's managed the household and had to be self sufficient and were skilful cooks providing meals for their families. Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones, bread, pastries and biscuits whilst caring for the children and making and mending the family's clothes. Animal shapes were fun for the children to help make and eat. Four animal shaped vintage tin biscuit or pastry cutters - a cat, dog, fish and duck. biscuit cutters, kitchenware, kitchen equipment, pastry cutters -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Biscuit Cutters, Unknown
... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones ...Women in early settler days and 1900's managed the household and had to be self sufficient and were skilful cooks providing meals for their families. Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones, bread, and pastries whilst caring for the children and making and mending the family's clothes. Shaped biscuit cutters were fun for children to make and eat. Four aluminium vintage biscuit or pastry cutters, including a star, bell, circle and flower shape with curved handles. Two have fluted edges the other have two have plain edges.biscuit cutters, kitchenware, kitchen equipment, pastry cutters -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyDomestic object - Flatiron, Silvester, Silvester Flatiron, No.7, 1900c
... Used for ironing clothes, heated on stove. These irons came... Plenty Lower Plenty melbourne Used for ironing clothes, heated ...Used for ironing clothes, heated on stove. These irons came in various sizes, this is a number "7".Black cast iron"Silvester Patent Salter". "7"flatirons, laundry equipment -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyiron, c. 1940s, 50s
... connected (early 1960s). Used for ironing clothes.... connected (early 1960s). Used for ironing clothes ...Used in the Orbost district prior to electricity being connected (early 1960s). Used for ironing clothes.This is an example of a domestic appliance commonly used before electricity connection was widespread.A metal iron enamelled in blue colour, with a silver coloured fuel reservoir shaped like a bowl. This most likely stored Shellite which was the fuel to heat the iron. The handle is also blue and made of wood. iron shellite-iron clothes-iron -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron Hand Kerosene, circa 1948
... . This item permitted ironing of clothes to be separate and away from... ironing of clothes to be separate and away from heating stoves ...This item was in use before electricity and was manufactured after the flat stove irons.The weight of the iron base, is heavy, helping in smoothing out crinkly material being ironed. This item permitted ironing of clothes to be separate and away from heating stoves. It permitted greater flexibility for ironing clothes and permitted more control (consistency) of the temperature of the iron.Historically and significantly this item enforces the relative isolation of the Kiewa Valley and period when and where this domestic item was in use(manufactured circa 1950). A rural setting with mining, beef , milk and tobacco production in the early 1900s. Even though the community was in a rural setting, the standards of dress was the same as in the bigger towns and cities. Social and religious mores and values demanded that the personal appearance be clean and crisp no matter where a person was living or working. Heavy laborious work was considered by some religions as virtuous, therefore the heavy and tiring work of ironing during this period had its rewards. Rural areas where the last to be connected to electricity and therefore this item was a domestic necessity far into the 1950's.This iron has a steel base and a metal body coated with green coloured enamel. The wooden hand grip is painted dark green. The kerosene (spirit) container is a chrome metal cylinder with a flat bottom and top. The top has a small filler/air plug is located on the top side. There are two control knobs located next to and under the metal cylinder. The close to the cylinder is a lock which locks the top lid of the iron and the other knob controls the airflow to the heater rodOn the base of the handle "PEERMAN" and below this P/46, C.I. Thomas & Son Pty Ltd household, ironing, domestic kerosene, dry cleaning -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Cookie Press and Icing Set, Unknown
... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones... washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones ...Women in early settler days and 1900's managed the household and had to be self sufficient and were skilful cooks providing meals for their families. Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones, bread, and pastries whilst caring for the children and making and mending the family's clothes. This was the precursor to the current hand held machine for making forcer biscuits. The metal cylinder was filled with biscuit dough and the wooden piece pushed down inside the cylinder to force the dough through different shaped, detachable, apertures to produce various shaped biscuits. The wooden forcer is missing from this set. The tin base has a movable end for cleaning the wooden press. An incomplete rusted long tubular tin cookie or icing press with four pattern attachments. There is no handle or forcer. There are four original shaped profiles which can be interchanged tied together with brown string. The tube was to be filled with biscuit/pastry mixture and a wooden press was used to force the mixture out of it. biscuit cutters, kitchenware, kitchen equipment, pastry cutters -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionDomestic object - Cast Iron Trivet
... ironing clothes. The iron may also have been made from heavy metal.... ironing clothes. The iron may also have been made from heavy metal ...An antique cast iron trivet was primarily used to provide a stable, heat-resistant surface to rest a domestic iron on whilst ironing clothes. The iron may also have been made from heavy metal.The trivet is in the shape of an iron with a pointed top and flat bottom. Raised on 3 legs at each corner and a decorative handle at the flat end. The base of the trivet where the iron would sit is done in a criss cross pattern.ironing, cast iron, decorative pattern, trivet -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Domestic object - Household, Box Silver Star Starch, Probably 1940s-1950s
... for domestic use, mainly for ironing clothes. The box, a product..., as one of its competitions, the Silver Star Starch Ironing ...Robert Harper and Co. Ltd. was an Australian company involved with sugar refining and starch and oatmeal production. Silver Star Starch was a well-known product and starch was used extensively in most households, mainly for shirt collars, aprons, nurses’ uniforms, household linen, tablecloths, doyleys etc. This item is of some interest, both for display and as a good example of housekeeping methods of the past (up to about the 1970s). However, the starching of clothing does continue today, mainly for special purposes – theatre costumes, clerical and ceremonial garb etc. The item can be specifically used by the Warrnambool and District Historical Society in any display connected to the 1896-7 Warrnambool Industrial and Art Exhibition as this exhibition had, as one of its competitions, the Silver Star Starch Ironing Competition (see pages 96-7, book, ‘The Great Warrnambool Exhibition’, by E. O’Callaghan, Collett, Bain and Gaspars, 2002)A box that contained 12 ounces of Silver Star starch for domestic use, mainly for ironing clothes. The box, a product of Robert Harper and Company Limited, Victoria, Australia, has several advertising captions – ‘Won’t Stick to the Iron’, ‘The Best in the World’. ‘Requires no Boiling’, and has directions for use. The front of the box has an illustration of two women from Victorian times using the product,warrnambool, silver star starch, robert harper & co ltd -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionDomestic object - Self-Generating Gas Iron, The "STAR" Self-Generating Gas Iron
... for ironing clothes and other woven material items used by the members... for ironing clothes and other woven material items used by the members ...This iron was given to Isobel and Stan Campbell by another woman in Boort Victoria pre 1999 as per the letter attached with the Donation form. These irons were manufactured in Australia as per the printing on the cardboard box and instruction sheet. These self-generating gas irons used methylated spirits in the small tank at the back of the iron. The irons would have been used prior to electricity being available to be connected to a house and used for ironing clothes and other woven material items used by the members of the household.Brown cardboard box with separate lid with black printing on the front and back of box and lid. A heavy silver iron with 13 holes along each side there is a black handle screwed to top of iron and a small round container attached to the back. An instruction sheet. Box front and back - The "STAR"/Self-Generating Gas iron/(Registered)/Is Made In Australia!/By Australian Workers!/From Australian Material!/ Instruction sheet - MADE IN AUSTRALIA/.../The "STAR' is the most economical Iron ever put on the Market , and/being manufactured of the best materials only, will last a life-time./...social history, domestic appliance, irons, george evans collection, isobel campbell, 1990s -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron Hand, circa 1867 to circa 1871
... in the late 1800s and early 1900s which were used for (press) ironing... as "women's work" house hold ironing domestic pressing clothes ...This is size one of three sizes (Mrs Potts) irons available in the late 1800s and early 1900s which were used for (press) ironing clothes etc. using wood or coal based heaters. The majority of these irons would have been placed on top of wood or coal fuelled stoves. They survived longer in isolated outback regions where electricity had not been connected. The weight of these irons was intentionally heavy so as to press the clothes etc. neatly. These irons were used in an era where stiff collars and creases in particular types of clothing was essentially a social requirementHistorically these irons fulfilled a particular function that was the norm in isolated or semi isolated country locations. Cities and larger towns had professional laundry and pressing shops. In smaller towns and homesteads, wives and relatives would use these heavy irons and required strong arms. In middle and higher levels of society these irons would be used by maids or nannies. Their use was a necessity to conform to the social requirements of acceptable appearances that all clothing worn had been "pressed" clean. In the Kiewa Valley the majority of these irons would have been used by mothers or relatives. Men would hardly have used these irons as society labelled this type of activity as "women's work"This double pointed, heavy and solid cast iron, is a Mrs Potts No. 1 type. It does not have a handle. It was used to iron clothes. Open cavity on top for handle (not included) see KVHS 0369 for No. 3 ironMrs Potts No. 1house hold, ironing, domestic, pressing, clothes appliance -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron Hand, 1867 to 1871
... in the late 1800s and early 1900s which were used for (press) ironing... as "women's work" house hold ironing domestic pressing clothes ...This is size one of three sizes (Mrs Potts) irons available in the late 1800s and early 1900s which were used for (press) ironing clothes etc. using wood or coal based heaters. The majority of these irons would have been placed on top of wood or coal fuelled stoves. They survived longer in isolated outback regions where electricity had not been connected. The weight of these irons was intentionally heavy so as to press the clothes etc. neatly. These irons were used in an era where stiff collars and creases in particular types of clothing was essentially a social requirementHistorically these irons fulfilled a particular function that was the norm in isolated or semi isolated country locations i.e., ironed clothes and linen.The iron was heated by using locally acquired wood in a cast iron stove or "pot Belly". It would be placed on top of the stove but not directly in the flames. Cities and larger towns had professional laundry and pressing shops. In smaller towns and homesteads, wives and relatives would use these heavy irons which required strong arms. In middle and higher levels of society these irons would be used by maids or nannies. Their use was a necessity, to conform to the social requirements of acceptable appearances in that all clothing worn had been "pressed" clean. In the Kiewa Valley the majority of these irons would have been used by mothers or relatives. Men would hardly have used these irons as society labelled this type of activity as "women's work"This double pointed, heavy and solid cast iron, is a Mrs Potts No.3 type. It does not have a handle. It was used to iron clothes. Open cavity on top for handle (not included) Note: one end is pointed up to allow the natural weight of the iron to increase the pressure at any of the "hard to press" spots or emphasizing required creases. see KVHS 0368 for No. 1 ironMrs Potts No. 3house hold, ironing, domestic, pressing, clothes appliance -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, circa 1900
... into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top. An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Iron; small flat domestic iron.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, iron, flat iron, domestic iron, laundery, ironing equipment, sad iron -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron - Charcoal, c1850 - 1920
This iron was used by women, in their domestic role, to press the clothes from the mid 19th century. Coal embers were put inside, heating the base of the iron, to press the family's clothes and linen. Small bellows were used to fire up the embers to keep the iron hot. In the Kiewa Valley the embers would have been from the local hard wood growing on the farms.Ron White worked for the SEC on the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme. The iron belonged to his mother. Ron remembers being a boy of approximately 8 years of age, watching his mother do her ironing with this charcoal iron in the c1920s.This iron is made of cast iron. It has a hinged lid so that coal embers can be put inside for heat. The lid has a curved funnel. Bellows are used to blow air into the iron and keep the coals burning. It has a wooden handle and a lever (also with a wooden handle) to open the lid. There is a 2 and a half centimetre hole at the back of the iron to check the coals. The hole has a swivel cover.There is an embossed "S" on the swivel cover.iron, laudry, household, charcoal, antique, domestic, pressing clothes -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron - Flat
... in their domestic role, ironing the family's clothes and linen. In the Kiewa..., ironing the family's clothes and linen. In the Kiewa Valley ...This iron was used to press clothes prior to the spirit and electrical irons becoming available circa 1930s - 1950s. The main body of the iron was placed on a flat heated surface of a stove (wood, coal or gas fired). It was mainly used by women in their domestic role, ironing the family's clothes and linen. In the Kiewa Valley the supply of coal or gas was not available or too expensive than the locally cut hard wood trees. Ironing was time consuming as the iron had to be heated, used and then reheated to the required level of application. Kiewa Valley farmers' wives used these irons having heated their stoves with local timber from their farms. This iron is made of cast iron. The handle is a hollow cylinder and is 70 mm above the solid 30 mm base. Presumably the handle was wrapped and/or threaded with cloth to protect the hand from the heat of the iron. The iron would have been heated on the top of a stove.6 Metters KFB Victoriairon, laundry, domestic, antique, pressing clothes, household -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
... into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
... into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron - Mrs Potts No. 1
A clothes iron is used, when heated, to press clothes to remove wrinkles and creases.The early irons were heated over a stove or in a fire. Irons were used very early in time and cast-iron irons during the 18th century. Mrs. Potts invented many irons starting from an early age thus making a difference to the clothing industry. She invented clothes irons with detachable wooden handles. Her first patent was in October 1870.This iron was used in the Kiewa Valley.Vintage cast iron body invented by Mrs Mary Florence Potts 1890s to 1940s. Detachable wooden handle (not attached) was cooler than a metal handle. It is double pointed for ironing in both directions. Body is hollow the top part being held by two screws. It can be filled with a light material. The No. 1 size is for specific ironing task. compared with No. 2 or No. 3. One handle with other bases enabled some to be reheating while using one. This iron has a stand. Formerly KV88B)Mrs Potts / No. 1 / Iron"" embossed on the topmary florence potts iron, cast iron, laundry, mrs potts -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron - Flat, Circa early 1900s
... , ironing the family clothes and linen. In the Kiewa Valley..., ironing the family clothes and linen. In the Kiewa Valley ...Historically this item was used before the spirit and the electrical iron took over Circa 1930s -1950s. The main body of the iron was placed on a flat heated surface of a stove (wood, coal or gas fired). It was mainly used by women in their domestic role, ironing the family clothes and linen. In the Kiewa Valley the supply of coal or gas was not available or too expensive than the locally cut hard wood trees. This particular iron was an improvement on the fixed handled iron because it allowed (by use of its easily detachable handle) to use multiple bases and thereby allowing a constant heat supply to be maintained and not having to waste time for a base to reheat to the required level of application.The significance of this item was that it allowed for a faster method of ironing clothes and linen. It's invention was a progress towards reducing the time it took to undertake a very labour and intensive domestic function. The reduction of time taken for this household duty provided women great flexibility to undertake other activities. These type of improvements to basic domestic tasks liberated housewives not only physically but also mentally from the isolation of the home environment.This flat iron has a removable, clip-on handle. The handle and its release knob are of wood. The base of the handle together with the heavy flat body are made of cast iron. The body of the iron is oval shaped tapered at each end and is 40mm thick.Underneath the handle frame and on the main body, on one side, in raised lettering is "Mrs Potts" and on the other side "Iron". Both are clearly visible when viewed from an aerial position. Under removable handle and on a plate (screwed onto the main body) is "No 2"iron, antique, household, pressing clothes, domestic, laundry -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron Hand Kerosene, mid to late 1900s
The 1950's saw a revolution in small appliances for use in the average household. This hand held self heating(kerosene) iron was introduced as a time saving and more convenient iron for pressing clothes and other cloth fabrics. It replaced irons needing a separate fire source to heat the ironing plate. These irons continued to be in service, even when electricity was available in cities and larger rural towns (domestic electric steam irons were invented in 1938). This item was used before and during the electricity supplies available from the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme. These irons remained in use within regional rural areas that had limited or unreliable electrical reticulation.In the 1950s and later the Kiewa Valley was still a relatively isolated region which was home to rural properties and small settlements. The availability of electricity and or the financial means to afford new types of electric hand irons ensured that older and sometimes less efficient ironing remained for an extended period covering the 1960s to 1970s. Kerosene products, such as this kerosene iron was a cheaper method for farm based domestic and other rural activities requiring a heat source. The use of kerosene as a heat/light source was able to be supplied in bulk and able to be used when floods severed vital roads into this region. The supply of electricity was in summer time subject to interruption from bush fire damaged wooden poles carrying the electrical cables. Self sufficiency by rural populations was the backbone of survival and the ability to store energy sources "on the farm" was a prerequisite of isolated regions, such as the Kiewa Valley, circa 1950s.This Coleman kerosene iron has a solid steel chrome plated(press) base with a painted (blue) wooden handle. The handle is stud fastened onto an oblong shaped rolled steel handle frame and screwed (two screws) onto the base plate. Both the heating plate and the top securing plate are shaped similar to a river boat. The main housing enclosing the heating element is enamel coated(blue in colour) steel and has a half hole for lighting the kerosene at the rear end. Behind the handle and protruding upwards is a stainless steel fully enclosed container (bowl shaped) for the main supply of kerosene to the burner or generator(enclosed within the main body of the iron. The bowl has an air valve and inlet for pressurised air intake (hand pump) On the bottom rear of the fuel bowl there is a screw regulated fuel pump. The fuel heated base plate provides the heat for this advertised "self heating iron(instant lighting). See KVHS 0347B- Instruction sheet; KVHS 0347C- Wrench; and KVHS 0347D Fuel can.Stamped on the base plate of the handle, front region "COLEMAN LAMP & STOVE CO." below this "WICHITA KAN" below this"TORONTO CAN". In the middle of the handle base and in larger print "COLEMAN Instant-Lite" At the rear location in large print "MODEL 4" in smaller print below "MADE IN U.S.A." below this "PAT#1718473"household appliances, alternative non electrical ironing appliances, domestic appliances, kerosene appliances -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyCan Fuel Measuring, circa 1950
The 1950's saw a revolution in small appliances for use in the average household. The hand held self heating(kerosene) iron for which this filling can was provided ,was introduced as a time saving and more convenient iron for pressing clothes and other cloth fabrics. It replaced irons needing an external fire source to heat the ironing plate. These irons continued to be in service, even when electricity was available in cities and larger rural towns. This item was used before and during the electricity supplies available from the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme. These irons remained in use within regional rural areas that had limited or unreliable electrical reticulation and the ability to service them from this filling can was an essential part.n the 1950s and later the Kiewa Valley was still a relatively isolated region which was home to rural properties and small settlements. The availability of electricity and or the financial means to afford new types of electric hand irons ensured that older and sometimes less efficient ironing appliances remained for an extended period covering the 1960s to 1970s. Kerosene products, such as the kerosene self heating (KVHS 0347A) iron and this kerosene filling item, was a cheaper method for farm based domestic and other rural activities requiring a heat source. The use of kerosene as a heat/light source was able to be supplied in bulk and able to be used when floods severed vital roads into this region. The supply of electricity was in summer time subject to interruption from bush fire damaged wooden poles carrying the electrical cables. Self sufficiency by rural populations was the backbone of survival and the ability to store energy sources "on the farm" was a prerequisite of isolated regions, such as the Kiewa Valley, circa 1950s.This specially spout fitted can was provided with the Coleman self heating kerosene iron (see KVHS 0347A). On one side of the half enclosed top of the can there is a small spout(for poring the appropriate liquid into the egg shaped fount container) at the rear end of the hand iron. The can is made from tin. See KVHS 0347B- Instruction sheet; KVHS 0347C- Wrench.On one side of the can in black print on yellow background is "FUEL MEASURING CAN" underneath is "For Coleman Instant-Lite Iron" underneath are four numbered paragraphs detailing the use of this can. Below this is the name and places of manufacture. On the other side of the can is printed "BE SURE" with filling and maintenance instructionskerosene can, ironing, domestic appliances, household appliances -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
... into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Iron, Mrs Florence Potts, Late 19th to early 20th century
Sad irons of the 19th century were so named because of the weight 1.8Kg that was needed to press wrinkled clothes and sheets. They were made of solid metal, including the handle. When the iron was heated, this meant that the handle would also heat up. The user would have to use a thick cloth or a mitt of some sort before they could pick up the iron. Even so, burns and blisters, as well as strained, tired arms, were a normal part of the “ironing day.” Mrs Mary Florence Potts of Ottumwa, Iowa, brought a change to the world of ironing. At the age of 19, in 1870, she invented her first sad iron. It had a hollow metal body that could be filled with a non-conducting material such as plaster of Paris. In 1871, Mary invented the removable wood handle, so that it could be changed from the cool iron to one that was hot and ready to use. A final improvement was the shape: Mary made both ends pointed so its user could iron in either direction. All of these inventions were patented under her name, a rarity for the time. Mary, with the help of her husband, tried unsuccessfully to market her invention on her own. It wasn't until she sold the sales rights to the American Manufacturing Company that sales took off. Advertised as "Mrs Potts' sad iron," it became a sensation. The company manufactured the iron from about 1876 to 1951. Mrs Potts' sad iron became a household word and a standard for future inventors to have to surpass. This didn't happen until 1882 when Henry W. Seely patented the first electric iron. The item is significant not only as a usable domestic tool, but it was, at the time of its creation, a revolutionary labour-saving device. Mrs Potts invention remains associated with a housewife's answer to the domestic drudgery of ironing.Iron,"Mrs Potts" pattern iron. Semi-circular or 'D' shaped wood handle and wood knob.Mrs Pottsflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, clothes iron, flat iron, laundry, sad iron, mrs potts -
 Blacksmith's Cottage and Forge
Blacksmith's Cottage and ForgeIron-flat, Iron, 19th. century
Domestic item, well used. Heated on the stove top and used to iron clothes.Interesting domestic item that shows how ironing was done prior to electricity.Black, heavy, triangular shaped with handle attached. Handle rounded smoothed metal.domestic, iron, cast iron, iron flat
