Showing 41 items matching "heating equipment"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Hot water bottle, late 19th - early 20th century
... heating equipment... significance, as an example of personal heating equipment used ...This hot water bottle was designed to lay flat in a bed between the sheets. Its purpose was to warm the bed before use. The bottle was filled with hot water then a stopper was placed in the top to seal it, preventing the water from running out. The inscription on the attached label of this hot water bottle gives both the donor's details and the location of the bottle when it was first displayed at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. the "P.M.O." are the initials for the Port Medical Office. The donor's details are also written in pencil on the base of the bottle. In the 16th-century people warmed their beds with the 'bed warmer', which was a long-handled, metal pan filled with hot coals and embers and covered with a lid. The pan was placed between the bedsheets to warm the bed before the person retired to sleep for the night. In the early 19th-century earthenware bed warmers came began to be used for the same purpose. They would be filled with hot water and sealed then often wrapped in fabric. The ceramic material would hold the heat for quite some time, without being too hot for the person in bed to also warm their feet as they went off to sleep. Hot water bottles were later made from glass, copper, brass or tin. Some manufacturers made them into decorative pieces that still had practical use. In 1903 a patent was taken out for the first rubber hot water bottle, invented by Slavoljub Eduard Penkala, a Croatian engineer. This bottle is of historic significance, as an example of personal heating equipment used in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.Hot water bottle, earthenware, pale colour with brown glaze on top over the shoulder and mouth section and clear glaze on the remainder of the sides. The cylindrical bottle tapers to a slightly narrower base. One side of the bottle, about a sixth of the circumference, is flat. The base of the bottle has a handwritten inscription. An inscription was on the paper label originally attached to the bottle. Inscription hand written on base of bottle "Mrs K. Rob _ / Browns Rd / Offic / 3 _ _ 9" Inscription on paper label " "Mrs K Robinson Browns Rd Officer 3809 - Hot water bottle P.M.O." flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, domestic item, hot water bottle, heating equipment, ceramic bottle, stoneware bottle, potter, earthenware, personal item, bed warmer, foot warmer, flat-sided hot water bottle, household item, stoneware, clay, ceramic -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyHand Warmers, 1923
... Heating equipment.... Heating equipment 2 x Silver metal Hand warmers with ornamentation ...Used for warming hands, the warmth would last for 24 hours. They used methylated spirits or lighter fluid.2 x Silver metal Hand warmers with ornamentation and one with a blue velvet pouch.heating equipment -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Fireplace Crane, Unknown
... Heating equipment... accessories Heating equipment Fireplace crane A black cast iron ...In the late 1800's and early 1900's kitchens were built separate from the main house for safety, as the open fire was used daily for all cooking, washing and heating of water. This very heavy strong fireplace crane could support several items such as cast iron kettles, pans and boilers which were hung on the hinged swing-arm, known as a “crane”. The metal arm was swung out from the fireplace to access the hot water in a kettle relatively safely. A black cast iron fireplace crane with a supporting pole bolted to the wall in the side of the brick open fireplace. It has a swinging handle with a rectangular hand grip at the end to move it over or away from the fire. The metal arm was swung out from the fireplace to access the hot water in a kettle relatively safely. There are holes in the bar for hanging hooks which kitchen cooking pots may be hung. Two small hooks are welded to the bar and there are two small removable hooks and two long ones. architectural elements, fireplaces, fireplace accessories, heating equipment, fireplace crane -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyMantle for Gas Lantern
... communities. lighting gas heating camping outdoor equipment lamp ...Originally these mantles where produced to be used in gas street lights in Europe and North America cities.There use started in 1891. These mantles were used before electrical power street lighting was installed. They have been used ever since until safety concerns regarding radiation from their thorium infused particles made alternate mobile lamps more attractive. The age of open flame recreational lighting is fast coming to a close. The greater use of battery and generator powered lighting(ease of operation) has brought the costing of these alternative lighting to an acceptable level. The age of miniaturisation and volatility of the open flame has seen a greater swing to smaller and more stable lighting. These incandescent gas mantles were initially used in the Coleman White Gas LanternsThe Kiewa Valley, with its closeness to the Victorian Alps, allows greater opportunity for the "happy" campers to enjoy the outdoors. The lighting provided by the incandescent gas lamps allow the adventurer at heart to enjoy an alternative lifestyle and still having the comforts of "home" at their finger tips. The numerous camping facilities in the Kiewa Valley and the upper alpine region is testament that those living in the cities need a break from the day to day grind and go to a quieter and more spiritual environment. Artificial lighting, as provided by mobile apparatus, is highly valued by the urban gypsy. The outdoor recreational industry has significantly provided for, if only at holiday time, an industry that has a relatively high employment rate and beneficial to local communities.The gas mantle is in a fabric, pear shaped, of rayon fabric impregnated with cerium. It's appearance is similar to a very small fishing net. The fabric is very ply-able until it is heated by an open flame then it becomes more rigid and lets out an incandescent white light. Its colour is white to off white. It has a draw string fastened a t the bottom (to wrap around the flame source)lighting, gas, heating, camping, outdoor equipment lamp -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Domestic Object - OLA COHN WOODEN BELLOWS
... DOMESTIC EQUIPMENT Heating bellows Wooden bellows belonging to Ola ...Wooden bellows belonging to Ola Cohn. It has a tree design on the handle and on the centre part several metal stud holding the leather to the wooden frame. It has a metal ending. Also in the box, photocopied typed sheet of the resume of Ola Cohn (Carola) M.B.E., A.R.C.A. 'Blossom'. It includes illustrations. Date unknown. (see also 3300.88).domestic equipment, heating, bellows -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Domestic Object - ELECTRIC BED HEATER
... DOMESTIC EQUIPMENT Heating bed heater K78 Tin electric bed heater ...Tin electric bed heater with 2 pin plug.domestic equipment, heating, bed heater, k78 -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Domestic Object - METAL FIRE SCREEN
... DOMESTIC EQUIPMENT Heating fire screen Metal fire screen ...Metal fire screen shaped as a leaf. Painted pcture on the screen of pink roses and green leaves on a green background. Back has three metal vertical supports attached. Two outside supports serve as legs. A fourth metal support is attached as a hinged adjustable third leg.domestic equipment, heating, fire screen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, circa 1900
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top. An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Iron; small flat domestic iron.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, iron, flat iron, domestic iron, laundery, ironing equipment, sad iron -
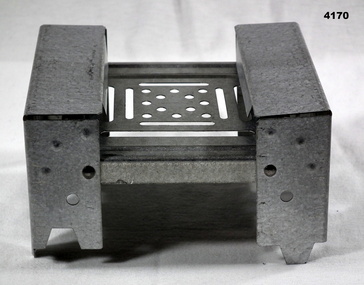 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - HEXAMINE STOVE
... a cooking/heating vessel Equipment HEXAMINE STOVE ...Commonly just called a “Hexy Stove”. When item is closed it can house a packet of HEXAMINE tablets.Made of galvanised coated tin in a box shape that opens out to support a cooking/heating vesselstove, hexamine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyFunctional object - Billy Can, Billy with lid, 1950s
Small billy can used for cooking or heating water when camping.Small metal billy with lid.camping equipment, billies, billy cans -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fire Iron
Fire irons like this one were an essential piece of domestic equipment as hey were used for the open fires.This iron poke is a piece of equipment essential for the open fireplaces used for 19th and early 20th century domestic heating.Fire poker, iron, painted black, shaped from a cylindrical rodflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, fire poker, fire iron, domestic heating -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fire Iron
Fire irons or pokers are essential equipment for people with open fireplaces such as those used for domestic heating in the 19th and early 20th century.This fire iron is significant for representing the type of equipment used in the 19th and early 20th century for used with open heating.Fire poker, iron, painted black, shaped from a steel barflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, fire iron, fire poker, domestic heating, open fireplace -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Stove, Cox and Rizzetti Stove Works, ca. 1918-1930s
Cast iron stoves burn solid fuel such as wood or coal, and are used for cooking and warmth. The stoves have a firebox with a grate where the fuel is burned. The hot air flows through flues and baffles that heat the stove top and the oven. Before cast iron stoves were invented, cooking and heating were carried out in outdoor open fires, and later, in fireplaces inside the home. In 1642 the first cast iron stove was manufactured in Lynn, Massachusetts, where molten cast iron was poured into a sand mould to make rectangular plates that were then joined together to make a box. Benjamin Franklin invented the more efficient Pennsylvania stove in 1744, and this efficient design is still used today. After the mid-19th century cast iron stoves were produced with burners in different positions, giving varied temperatures, so a wide variety of foods could be cooked at the same time at the most suitable heat, from slow cooking to baking scones. In contemporary times people the new wood-burning stoves had to meet the anti-pollution standards now in place to protect our environment. By the 1920s gas cookers were being introduced for domestic use, and by the 1930s electric home cookers were being offered to householders. PLANET STOVES In August 1925 the firm Cox and Rizzetti, Stove Works, and also Sydney Road, South Melbourne, advertised in the Brunswick and Coburg Leader of November 11, 1925 as "formerly with Harnwell and Sons" and as "specialists in solid cast iron Planet stoves ... which merit an inspection from builders and householders". The firm continued in business and was mentioned as sponsors in the King Island News in 1971. Harnwell and Sons was listed in the Victorian Government Gazette of 1894. It is curious that the firm was mentioned in an article in the Sunrasia Daily of June 14, 1934 titled 'Planet Stoves' as a manufacturer of Planet Stoves. This Planet No 3 stove is an uncommon example of cooking equipment used in kitchens in the early 20th century, as the firebox is above the oven rather than beside it. The cast iron combustion stove is significant as part of the evolution of domestic cooking. Previously cooking was mostly carried out in outdoors in open fires, and later in fireplaces indoors. Cast iron stoves are still used today and have additional features such as thermostats to monitor and maintain temperature, water heating pipes connected, and environmentally approved anti-pollution fittings. Stove; a compact, blackened cast iron combustion cooker, installed within a fireplace and enclosed by bricks on both sides. The upright rectangular stove has a flat top with three round, removable cook plates and a flue connected at the back. The front has three doors with round knob handles; a swing-down firebox door above a sliding ashtray, and two side-hinged oven doors above a sliding opening. Inside on the side walls are two pairs of runners. Behind the pair of doors is an oven with two pairs of rails and two removable metal shelves. The stove has cast inscriptions on the chimney flue and on the front of the right hand side stove door. The model of the stove is The Planet No 3, made in Melbourne.Chimney flue, "[within rectangle] THE / PLANET" Stove door, "(within oval) PLANET / No 3"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, stove, cast iron stove, combustion stove, wood-burning stove, wood stove, wood oven, solid fuel stove, cooker, the planet, planet, planet no. 3, kitchen equipment, baking, domestic cooking, cooking equipment, food preparation, planet stove, planet cooker, cooking range, slow combustion stove, antique, range cooker, cox and rizzetti, harnwell and sons, melbourne manufacturer -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Firedogs
... open fireplace equipment andirons chenets domestic heating ...Firedogs is the common name for andirons and Chenets and have been in use since ancient Greek times. Firedogs are the decorative metal supports or stands that hold logs in a fireplace, allowing air to circulate around the fire to keep it burning, and preventing logs from rolling out of the fireplace. They are usually made of metal, cast iron or steel, but are sometimes ceramic. They have two feet joined across the front and one at the back. Some firedogs, mainly for kitchen use, were plain with forked uprights so that a bar could rest between them on which a cooking pot or a roasting spit could hang. Some firedogs are made in the likeness of animals, shields, crosses, figures and keys. This pair of firedogs are representative of the firedogs that were common to domestic use in previous centuries when home heating and cooking were only possible with open fires. Firedogs or andirons, pair of two decorative cast iron log supports for use in a fireplace hearth. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fire dogs, firedogs, fire grates, log stands, domestic furniture, open fireplace equipment, andirons, chenets, domestic heating -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chest of Drawers, British Imperial Oil Company Ltd, 1905-1927
This early 20th-century chest of drawers is unique. It was made from recycled timber kerosene boxes and metal tins. The case was made in South Australia between 1905 and 1927 by the British Imperial Oil Company Ltd, which was the first business to import bulk petroleum products into Australia. Before this, ships carried crates of kerosene as cargo. Items salvaged from the 1880 wreck of the vessel Eric the Red included kerosene boxes. Kerosene replaced plant and animal-based fuel, such as whale oil, for lighting in homes and for the lamps in lighthouses and on marine vessels. It was also used for cooking and heating and as engine fuel. The last kerosene-fueled lighthouse lamp was transferred to solar power in 1985. The chest of drawers is one-of-a-kind. The original uses for the components of the chest of drawers, the wooden box and metal tins were for containing and transporting kerosene. Kerosene was used from the late 19th century for fuel in lamps, heating, and cooling. Previously whale oil was used for the lamps in lighthouses. The company providing the kerosene was the first to import it into Australia in bulk quantities. The set of drawers is one of the many ways that inventive Australians were able to repurpose materials.Chest of drawers; wooden frame and rails, metal drawers with vertical metal handles. The frame has been constructed from the wooden panels of a vintage oil and kerosene box. The three drawers have been created from empty kerosene cans that were cut in half from top to bottom, some with the round opening closed over. Inscriptions from the original box and cams are stencilled on the top and base of the frame and impressed or painted on the metal cans. The frame has provision for a further drawer. The wooden case and metal tins were made in Australia.Top and base of frame; "THE BRITISH IMPERIAL OIL CO. LTD." "OIL ENGINE KEROSENE" "CASE ANDTINS AUSTRALIAN MADE" On tin; "POWIRIN" "BIOCO LTD" Logo [cross} with inscription on horizontal bar "CROSS" Impressed in timber drawer dividers (indecipherable text) Side of drawer, painted in orange on black; "TY -, REG U S - TIDE - "flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, antique, domestic equipment, chest of drawers, tool box, furniture, storage, recycled tin, recycled box, kerosene, fossil fuel, lighthouse lamp fuel, british imperial oil company ltd. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Booklet, The Institute of Physics Handbook: Exhibition of Scientific Instruments and Apparatus, 08/1960
The Exhibition of Scientific Instruments and apparatus was set up to show the professional scientist the latest tools of trade and glimpses of future developments in the field of instrumentation .Cream soft covered book of 198 pages relating to an exhibition of scientific instruments and apparatus held at the School of Chemistry, University of Sydney. Exhibitors in the exhibition include: Advance components, Airmec, Akashi, Aladdin Industries, Amalgamated Wireless, Applied Physics Corporation, Ardente, Austral Engineering Supplies Pty Ltd, Avo Limited, Baird Atomic, Baker, Baldwin Instrument Co., B. and Relays, Barnstead Still and Steriliser Co., Beckman, Bender, Boonton Radio Corporation, Bosch, British Electric Resistence, British Physical Laboratories, Buccho, Bundenberg, Buehler, Bureau of Analysed Samples Ltd, Business Equipment Pty Ltd, Cambridge Instrument Co, Casella, Chamberlain and Hookham, Cossar, Cooke Troughton, Counting Instruments Co, CSIRO, Dawe Instruments, Difco, Duff and Macintosh, Dumont, Dupree, Dynatron Rodio Ltd, East Lancashire Chemical Co., Edwards High Vacuum Ltd, Eletircal Equipment Australia, Electronic Industries, Electroscientific Industries, Electrothermal Heating, Elema Schonanda, EMI, Englehard, Epprect, ERD Engineering, Ericsson Telephones, Esdaile, Ether Ltd, Evershed and Vignoles, Faraday Electronic Instruments, Federal Products, Filtron, Fischer, Fluke, Foot, Fortiphone, PX Fox, Foxall Instruments, Gambrell Bros, Gardener and Salmon, Garlick, Gelman , Gossen, Griffen and george, Gurr, Guthrie. Hasler, Headland Engineering Developments, Heraeus, Hersey Sparling Meter Co, Hewlett Packard, Heyneco, Hilger and Watts, Instron Engineering, Institute of Physics, Intermetal, Internation Resistance Corporation, Jacoby Mitchell and Co, Janke and Kinkel, JENA-er Glasswerke Schott and Gen, Keithly Instruments, Kelvin and Hughes, Kent, Kipp and Zonene, Kovo, Krautkramer, Kruss, Lambrecht, Land Pyrometers Leeds and Northrup, Leeds Meter Co, Leybold, Liddle and Epstein, Long Industrial Equipment, macdougall, McKinlay Fletcher, McLellan, Marconi Instruments, Masruements, Metrimpex, Metrohn, Metron, Mettler, Mica Corporation, Minneapolis Honeywell Regulator Company, Moisture Regulator, Morganite, Morris, Moseley, Muirhead, Mullard- Australia, Nagard, National Instrument Co, National Standards Laboratory, Negretti and Zamba, Nira, Northeastern Engineering, Nuclear Equipment Ltd, Ronald payne, Philbrick, Philips, Physik Instruments, Pincombe, Precision Tools and Instrument Co., Printed Electronics, Pye, Quicfit, Radion Corporation of Amerixa, Radio Frequency Laboratories, Radiometer, Rank Cintel, record Electric Co., Reichert Optische Werke, Rhode and Schwarz, Ridsdales and Co, Rocol, Rotameter, Rototherm, Rowe, George Sample, Santon, Sanders, Sartorious-Werke, Sauter August, Schneider, Scruttons, SEFRAM, Selby, Sensitive Research, Servomax Controls, shckman, Shimadzu, Siemens, Simpson, Sodeco, Soiltest, Solartorn, Southern Instruments, Albert Speck, Stanford X-Ray, Sunvic Controls, Sweda, Sydney County Council, Tamson, techne Cambridge, Tektronix, Telefunken, Telequipment, Andrew Thom, Thompson J, Langha,, Thronethwaite, Tinsley, Tokyo Opptical co., Townsen and Mercer, Treacerlab, Tylors, Unicam, Union OPtical Co, Varian Associated, Venner Electronics, Vidler Thornethwaite Engineering, Crosweller, Wandel and Golterman, Watson Victor Limited, Wayne Kerr Laboratories, waveforms, West Instruments, Herman Wetzer, Wild Instrument Supply Co, Yokagawa Electrical Works, Carl Seiss, Zwick.science, instruments, apparatus, scientific objects -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Boiler, ca 1880
This little steam boiler has been beautifully built. It could have been used to drive an engine in a small workshop, a boat or launch, or even farming equipment. It is an example of the steam technology and mechanisation of the 19th century. William Cook introduced steam heating in England in the 18th century. Steam combined with pressure was used for powering transport, such as steam engines for trains, and manufacturing, such as steam engines driving manufacturing machines. Steam boilers are still used today as an energy-efficient means of power.This steam boiler would have been suitable to drive a small engine, possibly that of a small boat. Coal was added to the firebox for fuel to heat water in the boiler. It is an example of the power used to drive machinery and equipment in the mid-to-late 19th century. Steam boilers like this one have played a part in the evolution of steam power. Steam engine boiler; vertical cylindrical coal-fired boiler with a black firebox at its base and a dome top. The cylinder's sides and top have brass fittings, inlet and outlet taps. A round opening near the base is covered by an adjustable metal plate that controls the boiler's temperature. The front door of the firebox has two hinges at the base and when the side clips are opened. A shiny brass collar tops the tall chimney. Oak wood planks around the sides of the boiler, and held in place by brass bands with nut and screw fixtures. The boiler stands on a metal and wood frame with a looped handle at the back. An inscription has been noted. Circa 1880. "1948 D/430" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, boiler, steam engine, steam boiler, coal fired boiler, vertical boiler, boat boiler, power source, steam driven, engine boiler, steam machine, firebox, steam engine boiler -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Functional object - Kitchen equipment, fire bellows, c1900
... for cooking and heating purposes. Preservation of meat entailed curing ...Early settlers had to daily maintain a fire in their kitchen hearth for cooking and heating purposes. Preservation of meat entailed curing by smoking in the kitchen hearth, hence domestic bellows were an important item of kitchen equipment. These domestic fire bellows were used to maintain the fire in the kitchen hearth for cooking,preserving and heating purposes by an early settler family in Moorabbin Shire.A small, domestic, fire bellows for maintaining a fire in the kitchen hearth for cooking and heating. brighton, moorabbin, cooking, pioneers, market gardeners, early settlers, kitchen equipment, bellows, meat, betleigh, fireplaces, farm equipment -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Equipment, Army, Stove Hexamine
Small folding hinged metal portable stove with unopened packet of Hexamine tablets inside stove. used by one man for heating food or waterDetailed directions on tablet packagehexamine stove, cooking, sas -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - BOOK - MAY 1937. VICTORIA TELEPHONE DIRECTORY
A copy of the Victoria Telephone Directory which is dated in May 1937. It features the telephone numbers for Bendigo, Castlemaine, Echuca, St. Arnaud, Sea Lakes, Swan hill Districts. The front cover also features an ad for the Bendigo moving Business Buckell and Jeffry which has a picture of a black truck with its back open and has the text "Buckell and Jeffry PTY. LTD BENDIGO Local & Interstate FURNITURE, BRICK REMOVALS, STORAGE, Office Railway Place PHONE 17 Bendigo, Special Equipment available also for MOVING HOUSES and HEAVY MACHINERY" The back cover also features two ads, one for the Hotel Ritz which details "Country Visitors to Melbourne will find the HOTEL RITZ, FITZROY STREET ST. KILDA, Conveniently situated to Beaches (3 minutes) and City (10 minutes). Electric Trams pass the door. equipped with Central heating. Hot and Cold water and House Phone in every Bedroom. Luxuriously Furnished. Execellent Cuisine. The Ritz offers the Finest in Hotel Accommodation." and the other ad for the Colonial Scale Repair Co. in Melbournebook, rural -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayEquipment - Victorian Railways Carriage Foot Warmer
During prestige, long distance train journeys some carriages had air-conditioning, and the majority of passengers had to brave unheated carriages. To offer some comfort during the winter months, the non-air-conditioned carriages were provided with footwarmers. These were metal containers roughly 100 mm thick and 300 mm wide, and about 750 mm long, which were filled with salt crystals (concentrated crystalline hydrated sodium acetate). The footwarmers were covered by sleeves of thick canvas, and two footwarmers were usually placed in each compartment of non-air-conditioned carriages. To activate the chemicals, the footwarmers were heated almost to boiling point. This was done by removing the canvas sleeves and placing the footwarmers in a large bath of very hot water. After they had been heated, they were removed from the bath and the sleeves refitted. They were then ready to be placed in the carriages. The McLaren patent foot warmer was used on railways in New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria and South Australia as well as South Africa and New Zealand. It was during the 1901 royal visit by the Duke and Duchess of Cornwall that these foot warmers were first used in New Zealand in the royal carriage. Before railway carriage heating was introduced, McLaren patent foot warmers were placed on the floor of New South Wales government railway carriages from 1891 to provide a little passenger comfort. The rectangular steel container worked a bit like a hot water bottle but instead of water contained six and a half kilograms of loosely-packed salt crystals, (concentrated crystalline hydrated sodium acetate). This was permanently sealed inside the container with a soldered cap. After the foot warmer was heated in vat of boiling water for about one and a quarter hours the crystals became a hot liquid. (The melting point for sodium acetate is 58 degrees). There was a whole infrastructure of special furnaces set up at stations for the daily heating of foot warmers. By 1914 the Victorian railways had 4,000 foot warmers in service and by 1935 there were 33 furnaces at principal stations to heat them. After about 10 hours the container was picked up by the handle and given a good vertical shake which helped the cooled liquid reform into a solid mass of hot crystals. Staff or sometimes passengers shook them en route when the foot warmers began to get cold. However, as they were heavy this was only possible by fit and agile passengers. At the end of the journey the containers were boiled again for reuse on the next trip. Sodium acetate railway foot warmers were introduced in Victoria in 1889, Adelaide to Melbourne express in 1899. "Shaking up" on this service took place at Murray Bridge and Stawell on the tip to Melbourne and at Ballarat and Serviceton on the trip to Adelaide. The use of foot warmers began to decline in New South Wales from the 1930s with the first trial of carriage air-conditioning in 1936, steam heating from 1948 ad LP gas heating from 1961. By the early 1960s the main services using foot warmers were the overnight mail trains. info from : http://www.powerhousemuseum.com/collection/database/?irn=67564#ixzz4UBNzVf6t Under Creative Commons License: Attribution Non-Commercial There was a whole infrastructure set up at stations for the daily heating of foot warmers in special furnaces. In Victoria alone in 1935 there were 33 heating works.Historic - Victorian Railways - Carriage Heater - Foot warmerA rectangular-shaped stainless steel casing with a welded seam down the back and welded ends. There is a handle at one end for carrying and shaking. Inside the foot warmer are two baffle plates and three trays to contain the sodium acetate. There was a cast-iron ball in each internal compartment. puffing billy, victorian railways, carriage haeter, foot warmer, passenger comfort, station furnace, railway ephemera, early heating methods -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumHeating Unit
Heating unit.Labec Selbys Scientific Instruments Chemicals Laboratory Apparatus Melbourne-Sydney-Brisbane-Perth-Adelaide Made by Lsboratory Equipment Pty. Ltd. Sydney Volts 240 Serial 4798 Watts 1200 -
 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumHumidicrib, CIG, Port-O-Cot, The Commonwealth Industrial Gases Limited
Humidicribs are used to transport sick babies from small hospitals to major hospitals for specialist care. They work by maintaining normal body temperature and provide oxygen if needed during ambulance transit. Known by a variety of commercial names, earlier humidicribs were ones heated with water bottles. Not part of an ambulances standard equipment, humidicribs are kept in ambulance stations and carried if babies needed to be transported. In the early days before humidicribs came into use and when air ambulances did not exist, many more babies died during emergency transits than do today Manufactured by the Commonwealth Industrial Gases Limited (better known as CIG), Australian-made Port-O-Cot brand humidicribs came replaced timber home-made humidicribs. They had electrical heating and easy to control oxygen flow and humidity control equipment. CIG also noted that noted that: Once the baby has been placed inside, the cot need not be opened, all nursing operations being carried out through the iris armholes. Even though the baby is in complete isolation nursing is a straight forward matter… The iris armholes allow nurses to feed, weigh, take temperatures, change napkins or, in fact, carry out any procedures without changing or disturbing the atmosphere within the cot. Happily for ambulance officers and nurses, the new Port-O-Cots were also much lighter and easy to carry than their old timber ones! metal box with carry handles and Perspex opening top. Carry handles at each end.PORT-O-COTinfant -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook - Dynamo operations and machinery, I.C.S. Reference LIbrary Dynamos & Motors, Operation of Dynanmos & Motors, Dynamo-Electric Machnery, Geometrical Drawings, Mechanical Drawing, Steam Heating. Steam Turbines
... & equipment & steam turbines/heating circa 1897 to 190-4 Red covered ...Non Fiction. Technical overview of dynamo motors & equipment & steam turbines/heating circa 1897 to 190-4Red covered bookNon Fiction. Technical overview of dynamo motors & equipment & steam turbines/heating circa 1897 to 190-4dsynamo operatios and machinery -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncEquipment, Hotpoint, Electric Iron, 1930s
Hotpoint Irons were first developed in 1903 in California. The invention was named Hotpoint, after the heating elements that converged in the iron's tip, allowing it to be used to press around buttonholes and in and around ruffles and pleats on clothing and curtains.Early electric iron manufactured under license by Hotpoint Australia. The iron has a metal base into which a separate power cord is plugged. The iron has a wooden handle.Label: " Hotpoint. Made in Australia. Licensed by Edison Elelectric Appliance Co. Inc. Chicago, U.S.A. Cat.915 F61. W.575, W200."hotpoint -- australia, electric irons -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncEquipment, Hotpoint, Electric Iron, 1930s
Hotpoint Irons were first developed in 1903 in California. The invention was named Hotpoint, after the heating elements that converged in the iron's tip, allowing it to be used to press around buttonholes and in and around ruffles and pleats on clothing and curtains.Early electric iron manufactured under license by Hotpoint Australia. The iron has a metal base into which a separate power cord is plugged. The iron has a wooden handle. Missing cord.Label: " Hotpoint. Made in Australia. Licensed by Edison Elelectric Appliance Co. Inc. Chicago, U.S.A. Cat.915 F61. W.575, W230."electric irons, hotpoint australia -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record - Text, 72nd Annual Report 1965 - 1966 Braille Library of Victoria, 1966
Articles include the production of Christmas cards for purchase, a visit by the Chief Secretary Hon. A. Rylah who advised that the Free Library Scheme was for municipal councils and that instead a State Library Council (which was being formed) would be a better source of relief, offers of help to contact potential overseas suppliers for electronic and braille equipment, the organisation of the Reservoir auxiliary, establishment of a Machines Committee to look at mechanized forms of Braille production and the possibility of entering into talking book production, improvements to heating, cooking and lighting, needing to use discretion when hiring hall due to an unfortunate incident, donations of Perkins Braillers, brailling of Decimal conversion charts, agreement in prinicipal to a National Braille Reference Library in Canberra, and purchase of Perkins and Stainsby Braillers to improve output of Braille books.32 pages of text with drawingsbraille library of victoria, corporation records
