Showing 13 items matching "kyle so"
-
 Broadmeadows Historical Society & Museum
Broadmeadows Historical Society & MuseumPhotograph - School Photograph, Classic Studios Victoria, Grade 5/6P Jacana Primary School 1990, 1990
... Kyle So... Bronwyn Robinson Michael Hennessy Andrew Martins Carrie Lewis Kyle ...This 1990 photo shows Grades 5 & 6 at Jacana Primary School, once located in Melbourne’s northern suburbs. The school, now closed and demolished, served the local community for decades. This image offers a nostalgic glimpse into a bygone era of local education and childhood in Jacana.This school photograph of Grades 5 and 6 at Jacana Primary School in 1990 holds enduring historical and emotional value as a visual record of education in a now closed institution. It captures a moment in time that reflects the community spirit, diversity, and educational environment of Jacana during its operational years. As the school has since closed, the image serves as a poignant reminder of the role Jacana Primary played in shaping young lives and fostering local identity. It is a valuable artifact for former students, staff and the broader community, preserving the legacy of a place that once stood as a cornerstone of learning and connection. The image is also a record of the fashion and hairstyles of the era. Colour photograph with blue border on the bottom, on matte paper.jacana primary school, education, class photograph, grade 5/6p, 1990, mark layton, daniel blaney, gunduz tabag, bernadine cilia, joanne verzantvoort, walid hamid, peita anderson, salwa arabi, anthony schewtschuk, matthew maidorn, robert gusak, kasia goray, bronwyn robinson, michael hennessy, andrew martins, carrie lewis, kyle so, andrew jenkins, sandra connell, aaron manson, leo athanasiou, shar-rena fitzgerald, mr brian o'dea, debbie stewart, kelly coates, mr glenn payne, miss karen ringham -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionBalloon Theodolite 1943
Used to measure the rate of rise of helium balloons The telescope is mounted on two movable axes. One axis (vertical) rotates to change elevation, the other (horizontal) azimuth. There are vernier scales and in some cases micrometres that give precise readouts of the relative position of the telescope to each axis. The instrument is set up so that it is level and it is pointed towards true north with both scales reading 0 degrees exactly. A balloon is released in front of the theodolite. It is sighted at timed intervals (usually one minute apart) and the position of the theodolite's telescope (azimuth and elevation) is recorded. It can chart the direction and velocity of winds at various altitudes The rate of ascent of a balloon is mostly dependant on the balloon's drag and its "free lift" (the vertical pull of the balloon). There is some degree of control over these these factors, and as a result, it possible to know approximately how high our balloon will be at any given time after its release. Given a known height and an angular direction (read off the theodolite) to the balloon, a fix is made of the horizontal movement component of the balloon's travel as it moves through different altitudes. The horizontal movement is due to the winds blowing the balloon around at the altitudes that the balloon is traveling throughTheodolite used to measure the rate of rising helium balloons The rate of rise is used in atmospheric calculations such as upper winds and determining inversion layersforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, weather -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionStereoscope
This stereoscope was used to view a pair of separate and overlapping aerial photos as a single three-dimensional image. Smaller units and could be easily used in the field but this larger, mirror stereoscope was used in offices. The aerial images were used to map forest types, timber stands, new roads and tracks, firebreaks, boundaries of timber harvesting, plantations, bushfires, insect and disease attack and so on In 1928, the Forests Commission undertook its first major aerial photography project over 15,000 acres of forest which is said to be the first of its kind in Australia. During the Second World War, large areas of Victoria were photographed by RAAF and used to produce orthophoto maps. By 1945 aerial photography of 13,000 square miles (3.4 M ha) was completed, including much of the inaccessible eastern forests. The Forests Commission started developing its own small format photography in the early 1970s. Simple, cheap and rapid methods of obtaining photographs using 70mm and 35mm cameras were developedFoldable metal stereoscope in wooden box with mirror covers Ex Dept of Defenceforests commission victoria (fcv), surveying, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFoldable Stereoscope
This stereoscope was used to view a pair of separate and overlapping aerial photos as a single three-dimensional image. This smaller foldable unit could be easily used in the field but larger, mirror stereoscope was used in offices. The aerial images were used to map forest types, timber stands, new roads and tracks, firebreaks, boundaries of timber harvesting, plantations, bushfires, insect and disease attack and so on In 1928, the Forests Commission undertook its first major aerial photography project over 15,000 acres of forest which is said to be the first of its kind in Australia. During the Second World War, large areas of Victoria were photographed by RAAF and used to produce orthophoto maps. By 1945 aerial photography of 13,000 square miles (3.4 M ha) was completed, including much of the inaccessible eastern forests. The Forests Commission started developing its own small format photography in the early 1970s. Simple, cheap and rapid methods of obtaining photographs using 70mm and 35mm cameras were developedFoldable plastic stereoscope in box Benallaforests commission victoria (fcv), surveying, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionMcArthur Forest Fire Danger Meter MK5 1973
The Forest Fire Danger Index (FFDI) was originally invented by the grandfather of Australian bushfire science, Alan Grant McArthur, during the 1950s and ‘60s. Alan published his landmark paper, “Controlled burning in eucalypt forests” in 1962. Leaflet No. 80, as it was known, proved a turning point for forest and fire managers across Australia. More importantly, Alan was very practical forester and wanted his work to be useful to people in the field, so after several iterations he came up with the now familiar circular slide rule called the Forest Fire Danger Meter (FFDM). The Mk 4 version first appeared in operational use in 1967. This is the Mark 5 from 1973Alan McAthur's scientific legacy with the FFDI meter is unquestionably huge and has served forest firefighters very well over the decades.Cardboard fire danger meter Series of circular slide rules to calculate Forest Fire Danger Index (FFDI)forests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPacific Marine pump Type Y
The Pacific Marine company was based in Seattle on the west coast of America and manufactured its first satisfactory portable fire pump 1925. These early Type N pumps were replaced in 1933 by the more familiar Type Y pumps. The updated pumps proved popular with the US Forest Service, and a large number were purchased by the Forests Commission as part of the equipment upgrade program in the wake of the 1939 bushfires. The Pacific Marine had a 9.8 Hp, two-cylinder, two-stroke petrol motor running with a high oil mix ratio of 16:1, so it blew vast clouds of blue smoke as the motor screamed at 4500 rpm. Part of its unique design was the water-cooled engine and muffler. But if the flow of water was interrupted the engine would quickly overheat and seize, so it needed constant monitoring and attention. Water was driven through a pair of bronze impeller gears which also needed a constant flow of water otherwise they would also self-destruct. When running properly, a Pacific Marine could pump 63 US gallons per minute, or about enough to fill a 200-litre drum. But its main feature was its high pressure of up to 225 psi. Pacific Marine pumps were often mounted on top of departmental fire tankers and used to spray water into the tops of burning trees. Compared to other pumps of the era it was light weight at only 70 pounds and was often mounted on a wooden stretcher frame. But they were cantankerous things to start with the rope pull and many exasperated novices came away with skinned knuckles. Modern Honda motors, which were more reliable and smoother running, replaced the Pacific Marines as the pump of choice for forest firefighters in the 1980s.High pressure Pacific marine Pumpforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, fire pump -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPacific Marine pump Type Y with wooden carry frame
The Pacific Marine company was based in Seattle on the west coast of America and manufactured its first satisfactory portable fire pump 1925. These early Type N pumps were replaced in 1933 by the more familiar Type Y pumps. The updated pumps proved popular with the US Forest Service, and a large number were purchased by the Forests Commission as part of the equipment upgrade program in the wake of the 1939 bushfires. The Pacific Marine had a 9.8 Hp, two-cylinder, two-stroke petrol motor running with a high oil mix ratio of 16:1, so it blew vast clouds of blue smoke as the motor screamed at 4500 rpm. Part of its unique design was the water-cooled engine and muffler. But if the flow of water was interrupted the engine would quickly overheat and seize, so it needed constant monitoring and attention. Water was driven through a pair of bronze impeller gears which also needed a constant flow of water otherwise they would also self-destruct. When running properly, a Pacific Marine could pump 63 US gallons per minute, or about enough to fill a 200-litre drum. But its main feature was its high pressure of up to 225 psi. Pacific Marine pumps were often mounted on top of departmental fire tankers and used to spray water into the tops of burning trees. Compared to other pumps of the era it was light weight at only 70 pounds and was often mounted on a wooden stretcher frame. But they were cantankerous things to start with the rope pull and many exasperated novices came away with skinned knuckles. Modern Honda motors, which were more reliable and smoother running, replaced the Pacific Marines as the pump of choice for forest firefighters in the 1980s.High pressure Pacific marine Pumpforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, fire pump -
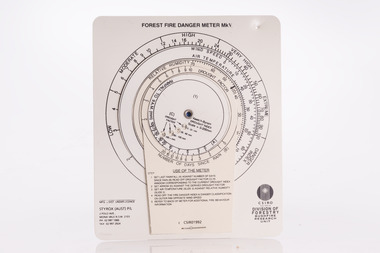 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionMcArthur Forest Fire Danger Meter - Mk 5, 1992
The Forest Fire Danger Index (FFDI) was originally invented by the grandfather of Australian bushfire science, Alan Grant McArthur, during the 1950s and ‘60s. Alan published his landmark paper, “Controlled burning in eucalypt forests” in 1962. Leaflet No. 80, as it was known, proved a turning point for forest and fire managers across Australia. More importantly, Alan was very practical forester and wanted his work to be useful to people in the field, so after several iterations he came up with the now familiar circular slide rule called the Forest Fire Danger Meter (FFDM). The Mk 4 version first appeared in operational use in 1967. This is the Mark 5 from 1992Alan McAthur's scientific legacy with the FFDI meter is unquestionably huge and has served forest firefighters very well over the decades.Control burning meter Series of circular slide rules to calculate Forest Fire Danger Index (FFDI)bushfire, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
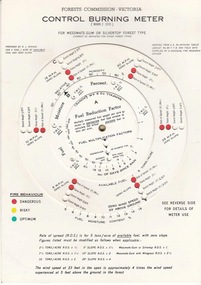 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV Control burning meter, 1970
The Forest Fire Danger Index (FFDI) was originally invented by the grandfather of Australian bushfire science, Alan Grant McArthur, during the 1950s and ‘60s. Alan published his landmark paper, “Controlled burning in eucalypt forests” in 1962. Leaflet No. 80, as it was known, proved a turning point for forest and fire managers across Australia. More importantly, Alan was very practical forester and wanted his work to be useful to people in the field, so after several iterations he came up with the now familiar circular slide rule called the Forest Fire Danger Meter (FFDM). The Mk 4 version first appeared in operational use in 1967. Two Forests Commission staff, Athol Hodgson and Rus Ritchie, built on McArthur’s pioneering work and by applying their own practical experience, developed a modified version in the late 1960s called the Control Burning Meter which was better suited to Victorian forest conditions.Introduced to the FCV in 1970Control burning meterbushfire, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV Benalla Forest District office sign
This sign is believed to have hung outside the Benalla Forest District Office. The sign features a pine tree (so probably made before the 1956 restructure). In 1956, the new Chairman of the Forests Commission, Alf Lawrence, introduced a major restructure of the organisation to create 56 Forest Districts. The process included amalgamating the plantations and hardwood divisions, which had been separate and rival entities up to that time. Things remained largely unchanged for the next three decades until the early 1980s. The iconic Forests Commission Victoria (FCV) “two-tree” logo was designed in the early 1960s by graphic artist, Alan Rawady.Benalla Forest District Office Sign -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPocket Stereoscope
This pocket stereoscope was used to view a pair of separate and overlapping aerial photos as a single three-dimensional image. It was small and could be easily used in the field. Larger, mirror stereoscope were also available in some offices. The aerial images were used to map forest types, timber stands, new roads and tracks, firebreaks, boundaries of timber harvesting, plantations, bushfires, insect and disease attack and so on In 1928, the Forests Commission undertook its first major aerial photography project over 15,000 acres of forest which is said to be the first of its kind in Australia. During the Second World War, large areas of Victoria were photographed by RAAF and used to produce orthophoto maps. By 1945 aerial photography of 13,000 square miles (3.4 M ha) was completed, including much of the inaccessible eastern forests. The Forests Commission started developing its own small format photography in the early 1970s. Simple, cheap and rapid methods of obtaining photographs using 70mm and 35mm cameras were developed Small pocket stereoscope to interprete aerial photographs in the field Adjustable lenses on foldaway wire legsSokkisha Tokyoforest measurement, surveying, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionY Valve
Y valves were used to split water supplies so it could be directed to a number of locations on a fire. In this case four outlets with two controlling valves. Canvas 1.5 inch hose was normally attached Screw connections rather than twist-camm locksY ValveYarrawonga Forests Commissionbushfire, fire pump, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPitney Bowes Fax Machine
In the late 1970s, the must-have gadget in every forest office could be best characterised by the fax machine. Millions of people bought them because they represented a miracle. With a fax machine, you could send a sheet of paper to someone, anywhere in the country, or anywhere in the world, complete with a signature, in seconds. E-mail really didn't exist yet (except in military and university environments), so the fax machine was simply amazing. During the "golden age" of the fax machine, people faxed everything. Office lunch orders went to the local Chinese takeaway by fax rather than being phoned in, while fire maps, timesheets and other urgent documents, could all be sent out straight away. Nearly every legal document got faxed once it was signed. People also traded recipes, jokes, funny pictures and personal letters by fax rather than sending them in the snail mail. With the early machines, the output was printed onto a roll of thermal paper that regularly spewed out coils onto the floor if you weren’t watching. All this technology quickly faded, only to be superceded by the pervasive e-mail in the 1990s. But the humble fax machine gave us an early glimpse of what the office of the future would be like.Facsimile machinePitney Bowes 8050communications, forests commission victoria (fcv)
