Showing 64 items matching "murray river development"
-
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - The Resources and Development of the Murray Valley - Volume 1
... Murray River Development... research and approaches to the development of the Murray River ...This report by the Murray Valley Resources Survey Committee is a detailed analysis of Importance and future the Murray River Valley and Basin for the economic development of Australia. It includes a lengthy Foreword written by Prime Minister, Robert Menzies. A map of Australia with the Murray Valley River and Basin shaded in green, and a fold-out detailed map of the Murray River are featured.A small publication in a bound blue cover with black text. This report by the Murray Valley Resources Survey Committee is a detailed analysis of Importance and future the Murray River Valley and Basin for the economic development of Australia. It includes a lengthy Foreword written by Prime Minister, Robert Menzies. A map of Australia with the Murray Valley River and Basin shaded in green, and a fold-out detailed map of the Murray River are featured.murray river development, murray basin, murray river resources -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Water For the Thirsty Inland, 1945
Water For the Thirsty Inland was published by The Murrumbidgee Valley Water Users Association as a case for diversion of part of the Snowy River waters to the Murrumbidgee. In 1950 The Murrumbidgee Valley Water Users Association and the League established the Murray-Murrumbidgee Development Committee to ensure the Snowy Scheme was completed.This book is a significant research tool for the history of the diversion of the Snowy River.A 44 pp book, titled Water For The Thirsty Inland. On the front cover is a coloured print of a painting of a river (Snowy River?) from the mountains to the flats. The text of the title is white with a black shadow. The book contains b/w photographs and the print is black and green.Some pencilled notes on back.snowy-river murrumbidgee-valley-water-users' irrigation -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaBlack and white rectangular photograph, 1950?
The paddle steamer P. S Pevensy appears to still be a working steamer in this photograph. The boat seems a bit dishevelled and the workers are doing repairs on her, while she is still steaming up the river. If this photograph was taken in 1950, that would have been well before the development of the Tourism Industry in the Murray Darling area. This would explain the number of workers and the fact that they were doing maintenance while the Paddle Steamer was still working. She does not appear to be towing a barge, but a large tarpaulin could be covering a load for transport. This picture holds significance because it shows a paddle steamer in use before the Tourism Industry had developed in the Murray Darling region. The paddle steamer which now carries passengers every day has been renovated to cater for passengers cruising up and down the river. Here is this photograph the P.S Pevensy looks a bit dishevelled and untidy.This is a black and white rectangular photograph of the P.S Pevensey. Four people can be seen painting the wall of the cabins on the upper deck. A person can also be seen kneeling on the back deck working on something lying on the back deck. A wooden boat is nearby, also on the back deck. The boat is steaming and appears to be moving upstream. There is along pole at a 45 degree angle attached to the very front of the paddle steamer.On the front of the photograph written on the paddle steamer can't be seen the words "PEVENSEY. Melbourne." Written on the back of the photograph in lead pencil " M4414-17. K4". p.s pevensey, paddle steamers -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaPhotograph - Black and white photograph, Late 1970s
Relates to a series of 5 photos:P000094-P000098 of the front of the Bridge Hotel on the corner of Murray esplanade and Hopwood gardens. These photos, taken about 1976, were before the Port Restoration Scheme renovated the hotel. The Bridge Hotel was built by Henry Hopwood in 1858. This and the Bond Store were Echuca's first 2 brick buildings. Named from Hopwood's nearby pontoon bridge. The building was bought be The Council in 1970. Restored and reopened in 1975.The Bridge Hotel is an important part of Echuca's settlement and development. It was originally built by Henry Hopwood, the European founder of Echuca, in 1859. Hopwood built the hotel to provide accommodation to people using his punts across the Campaspe and Murray rivers that area central to the landscape of the Port. The hotel was situated on the land between both rivers and punts and provided for a variety of levels of accommodation from grand rooms to very basic rooms. At the time of the photos the hotel was 120 years old and became an important part of the Port of Echuca tourism. Black and white photograph of the Bridge Hotel , showing western wing before restoration.Stamped on the reverse "Gazemore Studio, D. G. Gay, 18 Frances Street Echuca 3625.bridge hotel, echcua, port restoration scheme, bridge hotel restoration, echuca -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaBlack and white photograph
Macintosh's sawmill was on the banks of the Murray River in Echuca east where the Banyule State forest is now located. A tramway ran out to it from the main rail line near the iron bridge. Macintoshes Sawmill was one of the largest in the area. (Ref. Clare Jackson. )Macintoshes sawmill was set up by James Macintosh in 1868 in Echuca East. His sawmill prospered and in 1878 was "equal to five normal sawmills" (Ref; Coulson, Helen, "Echuca Moama On the Murray." P.158) He also owned 2 paddle steamers and 8 barges. The Macintosh Family contributed substantially to the development of Echuca East, but by 1901 the Family was in severe debt and were forced to sell the sawmill to the Nicholas Family.A black and white photograph of a large group of men outside a sawmill, reputed to be Macintoshes Sawmill in Echuca East.On the back of the photograph written in pencil are the words "Believed to be workmen at McIntosh's mill (Charlie Dowell says)macintosh's sawmill, sawmill industry, echuca east, banyule state forest, macintosh james, dowell, charlie, logging industry, jackson, clare -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionReport, Echuca Moama Tourism Planning and Development Strategy, c1996
Report compiled by three students of 'Tourism Planning and Development' at Ballarat University College (later Federation University Australia).victorian tourism industry, tourism, alumni, echuca, moama, hopwood's ferry, murray river, goulburn river, campaspe river, gaming -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionReport, Echuca Moama Tourism Planning and Development Strategy, 1993, 06/1993
Report compiled by four students of 'Tourism Planning and Development' at Ballarat University College (later Federation University Australia).victorian tourism industry, tourism, alumni, echuca, moama, hopwood's ferry, murray river, goulburn river, campaspe river, gaming, port of echuca -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayDouble Headed Rail, circa 1872 - 1883
Double Headed Rail from Ravenswood Station Siding which was dismantled circa 1987 the two rails were stored for a time at Maldon before being donated to Puffing Billy Museum Bearing makers marks of Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield, North East Derbyshire, England from 1872 - 1883 Double-headed rail In late 1830s Britain, railway lines had a vast range of different patterns. One of the earliest lines to use double-headed rail was the London and Birmingham Railway, which had offered a prize for the best design. This rail was supported by chairs and the head and foot of the rail had the same profile. The supposed advantage was that, when the head became worn, the rail could be turned over and re-used. In practice, this form of recycling was not very successful as the chair caused dents in the lower surface, and double-headed rail evolved into bullhead rail in which the head was more substantial than the foot. Info from Wikipedia - Rail Profile https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rail_profile The first records of double headed rail being used In Victoria by Victorian Railways was in 1859, the rails, chairs, oak and trenails were imported from UK. After the 1870’s the Victorian Railways went over to using flat bottom rails, but they still needed replacement double headed rail for lines already laid and this continued up to at least 1883 Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield England from 1872 - 1883 Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway The Melbourne, Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway Company received parliamentary assent in February 1853 to build Victoria's first inland railway from Melbourne to Williamstown, and Melbourne to Bendigo and Echuca. Construction commenced in January 1854 with work on a pier at Williamstown but lack of funds slowed progress, eventually prompting the company to sell out to the government. The 100-mile (162 km) section to Bendigo opened in October 1862. Its cost of £35,000 per mile made it the most expensive railway ever built in Australia. In 1864, the line was extended to Echuca, tapping into the booming Murray-Darling paddlesteamer trade. info from Museums Victoria - Victorian Railways https://museumsvictoria.com.au/railways/theme.aspx?lvl=3&IRN=450&gall=456 1863 Ravenswood Station open on the 1st Feb 1863 Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Ravenswood Siding When the Victorian Railways were established in 1856 they adopted one of the popular British permanent way standards - heavy 80lb (36.3kg) double-headed rail held up right in cast iron chairs attached to transverse timber sleepers by wooden pegs called trenails. The Ravenswood Railway siding was constructed in 1862 with 12 feet wrought iron double-head rail held in cast iron chairs with Ransom and May patent compressed keys. Trenails held the chairs to the sleepers and the joints were secured in joint chairs. Joints were subsequently joined using fish plates. It formed part of the Melbourne to Echuca rail line, initially known as the Melbourne, Mt Alexander and Murray River Railway. George Christian Derbyshire, the first Engineer-in-Chair of the Victorian Railways was responsible for the design and construction of the works. No new lines were built in Victoria using double-headed rail after 1870. The siding was disconnected from the main line in 1988. The Ravenswood Railway Siding demonstrates the original 1856 philosophy of the Victorian Railways to adopt British permanent way technology. The siding demonstrates significant aspects in the development of permanent way technology in England and Victoria over the period from the 1830's to the 1880's. The chairs in the Ravenswood siding are physical evidence of early railway technology rendered obsolete 120 years ago, namely joint chairs at rail joints and trenails to secure the chairs to the sleepers. The double-headed rail demonstrates an important stage in the evolution of British rail technology in the 1830s. The old fish plates, square headed bolts and square nuts demonstrate the success of fishing the rail joins. The Ravenswood siding demonstrates the earliest form of rail joint technology developed in England, and existing in Australia, the joint chair. In part of the siding the sequence of joint and intermediate chairs is consistent with the 1856 specifications, that sequence is rare with the joints secured in joint chairs. The survival of chairs in this sequence is rare and almost certainly demonstrates that they remained in continuous use at the same location from 1862 to 1988. This remnant of the Ravenswood siding has survived 126 years. The siding has proved to be the most significant of extant remnant double-headed sidings in Victoria, containing a rare combination of early permanent way technologies. Construction dates 1862, Info from Ravenswood Railway Siding Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/4693/download-report The remaining section of this siding is significant at the State and National levels in that it demonstrates the use of chaired rail by the Victorian Railways Department for the Trunk Lines and, more particularly, the following stages in the evolution of this long obsolete method of permanent way construction: a) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs at regular intervals inferring that the original wrought iron rail lengths were 12 feet, as is known through documentary sources to have been the case. The survival of chairs in this sequence is unique and almost certainly demonstrates that they have remained in continuous use at the same location and in the same sequence from 1862 to 1988 . b) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs designed for use with trenails. c) The use of later intermediate chairs designed for use with steel pins and the use of fished joints with steel double head chaired rail, representing a second method of constructing the permanent way using chaired rail technology. info from Ravenswood Siding - Melbourne/Echuca Railway Line - Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/70103/download-report Addition to Citation for Melbourne to EchucaRailway Line 1/10/1990 Double Head Rail The surviving lengths of double head rail with chairs on this railway compare with one surviving similar remnant on the Geelong to Ballarat railway and are representative of permanent way construction techniques applied exclusively to the two trunk railways of the 1860's. In this respect they are rare survivors and may be unique at the national level and of technical importance at the international level to the extent that they enhance contemporary understanding of early railway building technology. Surviving lengths of chaired double head rail survive at Kyneton, Ravenswood and Bendigo on this railway and include a number of different types of cast iron intermediate and joint chairs with hardwood keys and metal pins. The Ravenswood siding is of special significance for the diversity of chair types and for the sequence of chairs recalling rail lengths known to be associated with construction of the line in 1862. Construction of the Railway Tenders closed on 24 March 1858 with no less than 133 tenders being received. A contract was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937 to commence work on 1 June 1858 and complete the line by 31 July 1861. Cornish and Bruce made quick early progress with the Melbourne to Sunbury section being officially opened on 13 January 1859. The line was officially opened to Bendigo (Sandhurst) on 20 October 1862 by the Governor of Victoria, Sir Henry Barkly. A great banquet was held for 800 guests and this was followed by a grand ball. The extension of the line to Echuca was a relatively simple matter as that part of the line was across plain country without any significant engineering challenges. Tenders were called for the work in 1863 and the work was completed in 1864 by contractors Collier and Barry Apart from the line contractors, other firms directly involved were J Shire law and Co (sleepers), R Fulton, Langlands Brothers and Co, William Crossley (water supply), B Moreland, Langlands Brothers and Co (platelayers lorries), E Chambers (iron pins, traversers), Miller and McQuinstan (luggage vans and steam engines) and various contractors for building works. Info from Engineers Australia Engineering Heritage Victoria Nomination for Recognition under the Engineering Heritage Australia Heritage Recognition Program for the Goldfields Railways - Melbourne , Bendigo & Echuca Railway Page 25 - .2.9.2 Statement from National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Listing number B5323 for Mt Alexander/Murray Valley Rail Line: Page 69 - Theme 3 https://www.engineersaustralia.org.au/portal/system/files/engineering-heritage-australia/nomination-title/Melbourne_%20Bendigo_Echuca%20Railway%20Nomination.pdf The Melbourne, Mount Alexander and Murray River Railway Company was a railway company in Victoria, Australia. It was established on 8 February 1853 to build a railway from Melbourne to Echuca on the Victorian-NSW border and a branch railway to Williamstown. The company struggled to make any progress and on 23 May 1856, the colonial Government took over the Company and it became part of the newly established Department of Railways, part of the Board of Land and Works. The Department of Railways became Victorian Railways in 1859. Construction of the Bendigo line commenced in 1858, but this private consortium also met with financial difficulties when it was unable to raise sufficient funds, and was bought out by the Victorian colonial government. The design work was then taken over by Captain Andrew Clarke, R. E., Surveyor-General of Victoria, with bridge designs completed by Bryson and O'Hara The contract for the first stage of the line from Footscray to Sandhurst (now Bendigo), was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937.2s.2d ($6.714 million) with work commencing on 1 June 1858. Completion of the permanent way was to be by 31 July 1861 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melbourne,_Mount_Alexander_and_Murray_River_Railway_Company Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Victorian Railways : report of the Board of Land and Works November 1862 GP V 1862/63 no. 21 (2.8 MB) https://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1862-63No21.pdfHistoric - Victorian Railways - Double Headed rail Ravenswood Railway Station and Siding Victorian Heritage Database Reports Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1100 Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1786 National Trust VHR H1100 Mount Alexander and Murray River Rail way Line National Trust2 rail lengths of Double Headed Rail made of Iron makers marks : Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel and 20 joint chairs with metal rail pins Makers mark Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel (possible date 187? very hard to read ) puffing billy, double headed rail, wilson & cammell - dronfield - steel works, ravenswood station siding, melbourne to echuca rail line, initially known as the melbourne, mt alexander and murray river railway. -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook, The Story of Melbourne, 1934
Cream, pale green cover. Brown lettering. Sketches of early discovery scene and Yarra river, Flinders Street, Station and St. Paul's Cathedralthe story of melbourne, kenyon af, stewart f, tatura, victorian history, sir gengoult-smith -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook, Irrigation and Water Supply Development in Victoria, 1954
History of irrigaton in Victoria. Reference to Eildon Reservoir, Goulburn Weir, Waranga Reservoir, River Murray irrigation systemsBuff and blue covered book, showing farmhouse, dairy cattle on front cover, cattle, trees and channel on backirrigation, water supply, goulburn river, books, history, local -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Education Department of South Australia, The Ngarrindjeri people : Aboriginal people of the River Murray, Lakes and Coorong : an Aboriginal studies course for secondary students in Years 8-10, 1990
An Aboriginal studies course detailing the history, culture and life experiences of the original peoples of the areas along the River Murray, Lakes and Coorong. It is part of the 8-12 Aboriginal studies program developed to meet the needs of students, teachers and Aboriginal people.maps, b&w illustrations, b&w photographs, oral histories, suggested class activitiesngarrindjeri, river murray, coorong, aboriginal studies, secondary school education, oral history, curriculum development -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Printmaking - Silkscreen, Lin Onus, 'Walawala Garrkman' by Lin Onus, 2001
Lin ONUS (1948-1996) Language: Wiradjuri / Yorta Yorta Lin Onus played a pivotal role in the recognition of Aboriginal art as an expression of a contemporary and dynamic living culture. Prior to his premature death at just 47 years of age he was a prominent, strident, yet non-confrontational agent in renegotiating the history of colonial and Aboriginal Australia. His father, Bill Onus, was the founder of the Aboriginal Advancement League in Victoria and a prominent maker of artefacts in Melbourne. As a young Koori growing up, Lin lived in a cultural environment that included exposure to visiting Aboriginal artists, including Albert Namatjira. He began his artistic life assisting his father in decorating artifacts, went on to develop skills working with metal and painting with air brush as a panel beater; and by 1974 he was painting watercolors and photo-realist landscapes. In the 1970's he completed a set of paintings on the first Aboriginal guerrilla fighter Mosquito, which holds pride of place on the walls of the Advancement League in Melbourne, to this day. Lin Onus was a largely self-taught artist. Particularly important in his development was his visits to Garmedi (Arnhem Land) starting in 1986. Jack Wunuwun, the Yolngu artist, introduced him into the Murrungun-Djinang clan and gave him permission to use some of traditional images in his paintings. His cultural education on the Aboriginal side was also provided by visits to Cummeragunja with his father, and stories told by his uncle Aaron Briggs, known as 'the old man of the forest' who gave him his Koori name - Burrinja, meaning 'star'. They would sit on the banks of the Murray River within view of the Barmah Forest, Lin's spiritual home, the subject of many of his later paintings and his final resting place. Lin's father had been of the Yorta Yorta people from the Barmah Forest country, and Lin also used images from this area in his paintings. The images in his works include haunting photorealist portrayals of the Barmah red gum forests of his father's ancestral country, and the use of rarrk cross-hatching-based based painting style that he learned (and was given permission to use when in Arnhemland). His painting Barmah Forest won Canberra's national Aboriginal Heritage Award in 1994. (http://www.cooeeart.com.au/aboriginal_artist/lin_onus/A, accessed 18 May 2015) This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Framed limited edition silkscreen.Signed 'Onus' lower right (posthumously by Tiriki Onus) Edition 68/80art, artwork, lin onus, onus, printmaking, screenprint, aboriginal, dreaming, frogs, available -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBooklet - Albury Show Society Biography of Committee Members 1901 & 1918, Jan Hunter and Helen Livsey, 2012
The Albury Show Society is one of the oldest organisations in Albury, NSW. In 1857, forty people attended a meeting in Albury called by Robert Brown. From that meeting, 150 years ago, the Albury and Murray River Agricultural and Horticultural Society was born. It was eventually to evolve into the Albury Show Society through the work of many dedicated members. This publication includes a brief history of the Society and biographies of key people in its development.non-fictionThe Albury Show Society is one of the oldest organisations in Albury, NSW. In 1857, forty people attended a meeting in Albury called by Robert Brown. From that meeting, 150 years ago, the Albury and Murray River Agricultural and Horticultural Society was born. It was eventually to evolve into the Albury Show Society through the work of many dedicated members. This publication includes a brief history of the Society and biographies of key people in its development.albury show society, agricultural shows new south wales, biographies -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - The River Port of Red Bank
THE RIVER PORT OF REDBANK During the 1870s, Red Bank would have been one of the busiest ports on the Murray River. When the railway line was being built from Melbourne to Wodonga all the railway material was brought up river from Echuca by paddle steamer and barge and unloaded at Red Bank. The material was loaded onto horse teams or bullock wagons and taken along the route of the spur line. During the 187 MacCulloch & Co. handled 3000 tons of railway material here' The port was operational from approximately 1870 until 1874. THE FIG TREES The fig trees and a small bank of gravel are the only visible reminders of where the spur line from the wharf at Red Bank met the main line. It was at this point that all the material for the mainline was transferred from the small locomotives and wagons from Red Bank. It would have been carried by bullock wagons and horse teams and unloaded at different places as the line progressed. After the line was completed in 1873 the fettlers from Wodonga would patrol this length of the line.These images are significant because they document an important stage in the development of transportation in North East Victoria.Images of the River Port of Red bank near Wodonga on the Murray River. 1. The wharf 2. All that remainsred bank port, historic wharf wodonga, river transport -
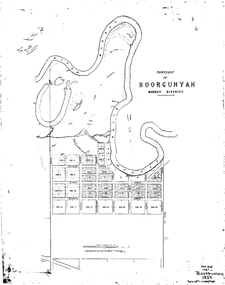 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncMap - Boorgunyah - "The Town that never was"
At the height of the river trade, there was a town surveyed and laid out, and streets were named. This town was to house the workers at the river port of Red Bank when the paddle steamers plied the Murray River as far as Albury, carrying produce such as wool and wheat to the various towns along the river in the 1800s. As the river trade died away, this town never went ahead – one might say, “The town that never was.” A lone gum tree stands on the site today.This item is significant because it documents plans which were made for the early development of Wodonga.A black an white map depicting the proposed location of the township. The map is based on a sketch and is not to scale,early wodonga, boorgunyah - "the town that never was", wodonga heritage -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - The Murray, Norman Mackay and David Eastburn, 1990
A study of the Murray River system, commissioned by the Murray Darling Basin Commission and published in 1990. This book provided a starting point for the understanding needed to make sustainable development og the Murray-Darling system an achievable goal. It provides a basis for action to halt futher degradation of the River and to rehabilitate its damaged environment. The picture that emerges from this volume is of a river in decline but not yet beyond saving. It covers topics such as groundwater and salinity, the associated fauna and flora, the surrounding environment, and the human impact. Illustrated with maps, diagrams and colour photographs. Includes a glossary and an index.non-fictionA study of the Murray River system, commissioned by the Murray Darling Basin Commission and published in 1990. This book provided a starting point for the understanding needed to make sustainable development og the Murray-Darling system an achievable goal. It provides a basis for action to halt futher degradation of the River and to rehabilitate its damaged environment. The picture that emerges from this volume is of a river in decline but not yet beyond saving. It covers topics such as groundwater and salinity, the associated fauna and flora, the surrounding environment, and the human impact. Illustrated with maps, diagrams and colour photographs. Includes a glossary and an index.upper murray region, murray river ecology, stream ecology murray river -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Union of Vic. and N.S.W. Rail System at Albury 1883
The final linking of the railway systems of Victoria and NSW at Albury-Wodonga was finally achieved in June 1883 when a temporary railway bridge across the Murray River was opened. A grand celebration was held in Albury to mark the occasion. This book details the significance of the railway and the celebrations of 1883.A photocopy of the original publication with annotations.non-fictionThe final linking of the railway systems of Victoria and NSW at Albury-Wodonga was finally achieved in June 1883 when a temporary railway bridge across the Murray River was opened. A grand celebration was held in Albury to mark the occasion. This book details the significance of the railway and the celebrations of 1883.railways australia, railway albury wodonga, history railways -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Water Resources of the Murray Valley, Department of Water Resources New South Wales, 1992
... -- murray river region murray river A study of the Murray River ...A study of the Murray River water management and resources, including illustrations and maps.non-fictionA study of the Murray River water management and resources, including illustrations and maps.water resources development, water quality management -- murray river region, murray river -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Introduction - Part 2, Department of Public Works, N.S.W, 1927
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. (continued from previous image). have been completed, Locks Nos. 2, 4 and 6, also in South Australia, are under construction. In the description of the Hume Dam the following emendations have to be made. The total length will be 5,300 feet of which 4,258 feet will consist of an earthen embankment. The maximum depth of water conserved will be 24 feet more than originally intended with an additional allowance of 9 feet for surcharge, the total capacity will be 2,000,000 acre feet, the water surface at full supply level 44,000 acres, and provision is being made for a flood discharge of 182,000 cusecs. For handy reference, the main dimensions and figures and comparisons with other dams throughout the world are given in a tabulated statement attached. The Hume Reservoir will be the largest in the British Empire. Photographs showing the work at various stages of construction are appended. The Resident Engineer for New South Wales from the start of the work until his recent promotion to the position of Inspecting Engineer was Mr J. Keith Ross, M.A., B.Sc., A.M.Inst.C.E., who has been succeeded by Mr S.W. Jones, B.E., A.M.Inst.C.E. The Resident Engineer for Victoria is Mr A.W. Johnson, B.E. (Signed) M. Inst.C.E. Chief Engineer New South Wales Constructing Authority 27th October 1927. hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Mud Sweat and Snow: Memories of Snowy Workers 1949-1959, Noel Gough, 1994
This book tells the human story of the first decade of building the great Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Scheme, with adventures and anecdotes told by the workers themselves, and illustrated with unusual photographs. Appendices give further information about the project and list the workers named in Snowy records. The author began his 10 years with the Electrical and Mechanical Division at the age of 20. The construction of the Snowy Mountains Hydro-electric Scheme is a well-documented part of our nation’s history and a leading example of Australian innovation and ingenuity. As far back as the 1880s, Australians had been considering diverting water from some of Australia’s best-known rivers – the Murray, Murrumbidgee, Snowy and Tumut – to drought-proof parts of NSW and Victoria. It was not until 1944 that Commonwealth and State governments formed a committee to examine the development of water resources in the Snowy Mountains area. As a result of their work, on 7 July 1949, the Commonwealth Parliament passed legislation to establish a Statutory Authority and start construction of the Snowy Scheme. NSW. Construction was completed in 1974 at a total cost of $820 million. On completion, the Scheme consisted of seven power stations, 16 major dams, 80 kilometres of aqueducts and 145 kilometres of interconnected tunnels.non-fictionThis book tells the human story of the first decade of building the great Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Scheme, with adventures and anecdotes told by the workers themselves, and illustrated with unusual photographs. Appendices give further information about the project and list the workers named in Snowy records. The author began his 10 years with the Electrical and Mechanical Division at the age of 20. The construction of the Snowy Mountains Hydro-electric Scheme is a well-documented part of our nation’s history and a leading example of Australian innovation and ingenuity. As far back as the 1880s, Australians had been considering diverting water from some of Australia’s best-known rivers – the Murray, Murrumbidgee, Snowy and Tumut – to drought-proof parts of NSW and Victoria. It was not until 1944 that Commonwealth and State governments formed a committee to examine the development of water resources in the Snowy Mountains area. As a result of their work, on 7 July 1949, the Commonwealth Parliament passed legislation to establish a Statutory Authority and start construction of the Snowy Scheme. NSW. Construction was completed in 1974 at a total cost of $820 million. On completion, the Scheme consisted of seven power stations, 16 major dams, 80 kilometres of aqueducts and 145 kilometres of interconnected tunnels.snowy mountains hydro-electric scheme, hydroelectric power plants, snowy mountains -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - A Tale of Twin Cities Part 1 The Founding Years, Desmond Martin, 1981
A detailed history covering the founding development, commerce, pioneers and personalities of the Wodonga-Albury area, and the constant influence of the river.non-fictionA detailed history covering the founding development, commerce, pioneers and personalities of the Wodonga-Albury area, and the constant influence of the river.wodonga, albury, murray river -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Dimensions of Hume Reservoir, Department of Public Works, N.S.W, 1927
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.Table outlining the Dimensions of the Hume Weir and comparisons with MAKWAR and BURRINJUCK DAMS, and some other comparisons. MAKWAR Dam is located on the Blue Nile about five miles south of Sennar and 175 miles south of Khartoum in Sudan. The construction of this dam started in 1922 and was completed in May 1925, while the British Empire colonised Sudan. It was officially opened on 21st January 1926. The BURRINJUCK DAM is situated in the upper catchment of the Murrumbidgee River, approximately 60 kms from Yass, N.S.W. It was built from 1907 to 1927 The stated purpose of the Hume Reservoir is to get storage to ensure regulated output for:- 1. Irrigation 2. Navigation 3. Hydro-electric Generation.hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume dimensions -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncArticle - Festivities for arrival of North-Eastern Railway in Wodonga, The Illustrated Australian News, 1873
The arrival of the railway from Melbourne to Wodonga was celebrated on 21st November 1873. The railway line between Melbourne and Wodonga was constructed in three sections. The first section from Essendon to Seymour was fifty-six miles. It was constructed by Messrs. O'Grady, Leggatt and Noonan at a cost of £305,558. The second section from Seymour to Benalla was sixty miles under contract to Messrs. Styles, Murray and Co. for £314,994. The final section of sixty six miles to Wodonga was constructed by Messrs. Cain, Dalrymple and Holton for £350,100. The Illustrated Australian News for Home Readers 4 December 1873 reported extensively on the event. The Victorian Government was determined to celebrate the event with a banquet, to which twelve hundred guests were invited. Four special trains had departed Melbourne to bring dignitaries to Wodonga. The Governor Sir George Bowen, Lady Bowen and, two Misses Bowen, were among the guests. Sir George Bowen proposed a toast to the “Prosperity to the North-eastern railway”. The banquet was held in marquees erected for the event, although the facilities struggled to cater adequately for the more than 5,000 people who arrived to celebrate. The estimated population of Wodonga was 500 only people. That evening a ball was held in the goods' shed, which was handsomely decorated with flags, evergreens and flowers. About five hundred guests were present. It would be another decade before New South Wales completed the line from Sydney to Albury and a connecting rail bridge was built over the Murray River.This item is significant because it documents the festivities celebrating the arrival of the railway line in Wodonga.A colourised version of a newspaper article documenting the celebrations for the arrival of the North Eastern Railway to Wodonga. It depicts crowds of people congregated near the railway line area. Large tents have been erected to house visitors and special activities. The railway goods shed can be seen in the background and a steam locomotive is on the track. The image was accompanied by a lengthy article which detailed the development of the railway line.northeast railway line, wodonga transport -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - General View of Works from New South Wales end, Looking Upstream, August 1927
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 22. General View of Works from New South Wales end, Looking Upstream. Features: At the left, part of the North Wing Wall, the highest part of which is 26 feet below its ultimate height. Below in the foreground is the portion of the dam where provision is to be made for hydro-electric generation. The tubes, three in number, 13 feet in diameter, will be laid on the level shown and an early start will be made in laying them. The level for the other four regulating outlets, 9 feet in diameter, together with a part of the spillway section of the dam, is underwater at this stage and it may be remarked that at one point, about half way across the channel where the water is now flowing, the concrete foundations are about 80 feet below the level of the water. The broken surface of the water is due to the large “plums” in the concrete. The still water in the right foreground is the stilling pool over the concrete floor of which there is now more than 20 feet of water and by means of which the discharge from the outlet pipes will be quelled. The trestlework on the upstream side of the dam carries the concrete belt conveyor. It extends from the concrete mixer house, which is out of the picture, behind the wing wall, along almost the entire length of the concrete portion of the dam. The concrete is discharged from the belt at any desired point by means of trippers, one of which may be seen over the second trestle. On the other side of the flowing water is the coffer dam. A channel 300 feet wide involving about 140,000 cubic yards of excavation and dug for the temporary diversion of the river as it is flowing now. To the right top of the view beyond the Coffer Dam is the earth embankment being thrown across the major part of the valley by the Victorian Constructing Authority. The Mitta Mitta River flows into the Murray at the far end of the reach of water on the left. August 1927.hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Section of completed coffer dam, January 1927
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 20. Section of completed coffer dam with river diverted over the concrete foundations of dam that were placed during the first stage of operations. New South Wales. January 1927. Cofferdams are temporary structures used where construction is being carried out in areas submerged in water. They are most commonly used to facilitate the construction or repair of dams, piers and bridges. To divert the river, a Coffer Dam was built across the old bed above and below the Dam site and tying into the end of the concrete wall built inside the levee bank. This completely surrounded the remainder of the site of the Dam and south wing wall, including an area of 12½ acres. hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Driving first row of piles for coffer dam across the river, December 1925
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 19. Driving first row of piles for coffer dam across the river. New South Wales. December 1925. Cofferdams are temporary structures used where construction is being carried out in areas submerged in water. They are most commonly used to facilitate the construction or repair of dams, piers and bridges. To divert the river, a Coffer Dam was built across the old bed above and below the Dam site and tying into the end of the concrete wall built inside the levee bank. This completely surrounded the remainder of the site of the Dam and south wing wall, including an area of 12½ acres. hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Excavations for foundations inside coffer dam, January 1927
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 21. Excavations for foundations inside coffer dam. New South Wales. January 1927. Cofferdams are temporary structures used where construction is being carried out in areas submerged in water. They are most commonly used to facilitate the construction or repair of dams, piers and bridges. To divert the river, a Coffer Dam was built across the old bed above and below the Dam site and tying into the end of the concrete wall built inside the levee bank. This completely surrounded the remainder of the site of the Dam and south wing wall, including an area of 12½ acres. hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction, coffer dam -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Stilling pool opposite outlet section of dam, December 1925
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 18. Stilling pool opposite outlet section of dam. New South Wales. December 1925 A stilling pool is a structure at the downstream side of a dam, designed to take away some of the energy from overtopping water flowing down the spillway, to reduce the risk of erosion of the ground near the dam and the dam itself.hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Gravity incline for transport of rocks
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 16. Gravity incline for transport of "plums" from Quarry, New South Wales. "Plums" were larger rocks which could be re-used for other construction purposes.hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - General view of earth embankment in Victoria, October 1924
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 17. General view of earth embankment in Victoria. New South Wales section of work and Township beyond. October 1924.hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction
