Showing 171 items matching "obstetrics"
-
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyDocument - Certificate, Queen Victoria Hospital, Obstetrics Certificate for Marjorie Jean Burke, 27/02/1947
Obstetrics certificate for Marjorie Jean Burke issued by the Queen Victoria Memorial Hospital for Women and Children in Melbourne.Miss Burke was a nurse, midwife and infant welfare sister. This collection covers her many qualifications throughout Australia and Great Britain, including references both professional and personal. When Miss Burke returned to Australia, she was employed at Diamond Valley Community Hospital as a nurse in 1953 and as Deputy Matron 1954-1971.Certificate typed on cream card.marjorie jean burke, nurses, diamond valley community hospital, queen victoria hospital melbourne -
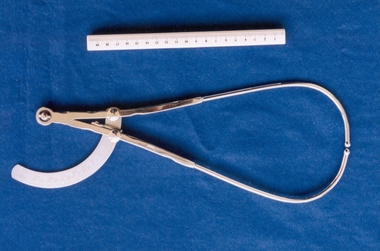 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - 'Ramsay' pelvimeter used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Ramsay
A pelvimeter is used in obstetrics for measurement of the female pelvis, with the aim of attempting to determine whether there will be any potential issues with a vaginal birth. This pelvimeter is similar in style to Martin's pelvimeter (see Aesculapius). This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St Geroge's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pelvimeter, manufactured by Ramsay. Metal device with calibrator graduated to 18 inches/ 45 cms. Inscribed " Ramsay" upper arm."Ramsay"obstetrics -
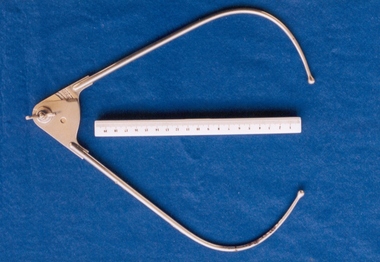 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward
A pelvimeter is used in obstetrics for measurement of the female pelvis, with the aim of attempting to determine whether there will be any potential issues with a vaginal birth. The style of this pelvimeter is similar to Collyer's pelvimeter as depicted in Aesculapius Surgical Instruments p. 2195. This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pelvimeter. Similar in style to Collyer's pelvimeter. Has adjustable arms hinged with a wingnut, and a scale graduated in inches and centimetres.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medal - British Medical Association medal associated with Professor F J Browne, Dublin, 1933, 1933 (approximate)
Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. Collection of objects transferred from the Archives to the Museum collection found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers.Square medal with ribbon. Medal is decorated with blue, green, and red enamel and has silver inserts. Medal design is divided vertically and horizontally by silver lines and carries the text, "B.M.A/DUBLIN/1933". There are three symbols on the upper section of the front of the medal. Top of medal is attached to a green grosgrain ribbon, which in turn is attached to a silver bar inscribed with the words "VICE-PRESIDENT/OBSTETRICS". Small stamp printed on back of medal.numismatics, british medical association -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Medical case used by Dr Reginald Worcester
Reginald George Worcester (1903-1972) was a highly regarded obstetrics and gynaecology specialist. Between 1930 and 1933, Worcester was the Medical Superintendent at the Royal Women's Hospital. He obtained his MRCOG in England in 1935, and on his return to Australia was appointed as a university tutor in obstetrics and gynaecology. In 1939, he was appointed as the honorary gynaecologist to outpatients at the Royal Women's Hospital. Worcester served with the AIF during World War II as C.O. of the 17th Field Ambulance in Darwin and as A.D.M.S., Northern Territory Force, and the 2nd/9th Australian Army Corps from 1942 to 1943. His major war service, however, was undertaken in Borneo and Moratai, commanding the 2nd/1st Australian C.C.S. and the 2nd/9th Australian General Hospital. Worcester acquitted himself admirably during the war, with company commander Hubert Smith praising his contribution in no uncertain terms: " His [Worcester's] success as C.O. of a Field Ambulance resulted from a complete understanding of what the unit should be able to do in the transportation of casualties in the field, as well as of the usual medial functions. He organized both with efficiency and at all times difficult decisions were made with humility and good humour. The personal qualities which made him such a calm and considerate consultant never left him, even in the most dangerous and trying circumstances of war." Worcester's time in the army greatly affected his health, but despite this he was able to build a strong and reputable practice upon his return to Australia. As outlined by Arthur Hill, Worcester " was appointed in turn to the following important posts: Honorary Outpatient Obstetrician and Inpatient Gynaecologist to the Women’s Hospital (1946-1948); Honorary Gynaecologist to Prince Henry’s Hospital (1946-1963); Guest Examiner in London for the R.C.O.G. (1953); Examiner in Obstetrics and Gynaecology for the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (1957-1964); Visiting Gynaecologist to the Repatriation General Hospital, Heidelberg 1963- 1967); and first Victorian Members’ representative (1947-1950) and later Fellows’ Representative (1953-1960) on the Australian (Regional) Council of the R.C.O.G. To these posts he brought the benefits of clear thinking and critical awareness. In 1949 he was elected F.R.C.O.G." In early 1967, Worcester suffered a hemiplegia which left him with an impaired gait and paralysed his right hand. Although unable to do major surgery, he returned to part-time practice by September 1967. His ill-health persisted though, and he was retired from practice in 1970. (Source: (1973), REGINALD GEORGE WORCESTER. Medical Journal of Australia, 1: 770-771.)Brown leather medical case. The case has a solid frame and is rectangular, with a leather handle at top. There are two locks on the top of the case, and a metal clasp on either side to fasten the bag closed. The case is embossed with the text 'R.G. WORCESTER' on top, in a position between the two locks and below the handle at bottom centre. The inside of the case is lined with a canvas bag that is buttoned to the case with press studs. The inside of the case also contains a loose canvas bag on which is handwritten 'BAG No/THREE/ R.G. WORCESTER'. The loose canvas bag has a metal zipper at opening.'R.G.WORCESTER'obstetrics, surgery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Book, Raynalde, Thomas et al, The byrth of mankynde otherwyse named the womans booke, 1560
[26] p., cxxxi leaves, [2] l. of plates : ill ; 20 cm.non-fictionobstetrics, early works to 1800 -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medal - British Medical Association President of Gynaecology and Obstetrics medal associated with Professor F.J. Browne, 1938
Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. A collection of objects found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers were transferred from the Archives to the Museum collections in January 1994.A round metal badge with a green enamelled rim. There is a shield in the centre which is divided into three. In the left hand comer there is a flag, in the right hand comer the medical insignia, and at the bottom of the shield there is a sailing ship. The year 1938 is either side of a central white enamelled plug with the number "106" on it. Attached to the badge is a green grosgrain ribbon, to which is attached an oblong bar with a pin at the back. Inscriptions Around the edge of the badge: "THE BRITISH MEDICAL ASSOCIATION PLYMOUTH"; inscribed on the back of the badge: "BRUFORD, EASTBOURNE AND EXETER"; front lower right hand side ofbadge:"M & W"; front of bar: "PRESIDENT/ GYNAECOLOGY and OBSTETRICS"numismatics, browne fj, rcog -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medal - AOFOG Fellowship medal presented to Dame Ella Macknight, 1993
Ella Macknight was an Australian obstetrician and gynaecologist, who worked at the Queen Victoria Hospital, Melbourne. She was appointed as a Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire on 1 January 1969 for services to medicine. (Wikipedia) Her name has been misspelled on the engraving on this medal.Silver coloured medal with gold coloured decoration on a blue ribbon. The medal is a physical representation of the AOFOG (Asia and Oceania Federation of Obstetrics and Gynaecology) logo, consisting of a translucent central blue circle (possibly made of glass) surrounded by eight abstract torso figures in alternating gold and silver colours. The base of the torso sits adjacent to the central blue circle, and depicts a figure with its arms raised straight up. The torso neighbour each other around the circumference of the central blue circle to form a circular pattern. The figure at the top of the medal has a silver torso and gold head, and these colours interchange from figure to figure (eg. the figure on either side has a gold torso and silver head). The medal is engraved with the text 'Dame Ella McKnight/FELLOW/OF/AOFOG/1993'. The ribbon has two velcro fastenings. The medal is in a protective case, the outside of which is lined with red velvet. Included in the case is a runsheet printed on paper for the ceremony in which Ella MacKnight was presented with this medal. The ceremony was held at PICC Plenary Hall on 14 November, 1993. The velvet case in stored inside a while, rectangular cardboard box, consisting of two parts - lid and base. Sticker attached to top of the cardboard box reads ' DAME ELLA MCKNIGHT/FELLOW/1993'.Dame Ella McKnight/FELLOW/OF/AOFOG/1993'obstetrics, gynaecology, awards -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter, Thom's
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)"in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.Thom's pelvimeter,internal, stainless steel. Reefer to Down Bros. catalogue 939/4, page 939. Quoted from this source Thom's as used by Whitridge Wuilliams, Obstetrics", pp. 860-906. Thom, "Study of funnel pelvis,"Amereican Journal of Surgery, July 1f915.pelvimetry -
 J. Ward Museum Complex
J. Ward Museum ComplexBook - Medical Book, Tokology: A Book for Every Woman
Originally written in 1885 by Alice Bunker Stockham, an obstetrician and gynaecologist who practiced in the late nineteenth century. “Tokology” refers to the study of childbirth, midwifery, and obstetrics. Stockham wrote Tokology for women to give them knowledge about issues related to childbirth and maintaining their own health. Empowering women by informing them about their own bodies, the book gives women details that they may not have talked to their doctors about considering the lack of female doctors at the time of publication. Wide distribution allowed for women of a variety of socioeconomic backgrounds to have access to information that was often only accessible to those who had access to physicians and the knowledge they possessed. Tokology made progress in helping demonstrate the confidence that comes from being aware of how to maintain one’s own health instead of being subject to the fear that comes from the lack of knowledge. Tokology is more than just a book for every woman; it is an example of the power of education and distributing knowledge to a population to promote the health of a community. In some cultures, though, this book was also seen as taboo – hence the reason the illustrated plates were “hidden” within the inner back cover as is seen with this book.The book is significant is representing the thoughts and concepts surrounding female reproductive and child health in the late 19th century. Leather bound hardcover. Dark brown cover with black embossed print and borders. 386 pages. Pages show wear and ttear through use. Some pages are torn but the majority are good. Foxing on pages. Base of spine is torn away. Illustration plates in excellent condition. Publisher: Pater & Co. Melbourne 1898Inside front cover - T1 (scribbled out) T8 in blue ballpoint ink gynecology, obstetrics, mentalhealth, childbirth, reproductivehealth, womenshealth -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Gynaecological examination chair associated with Dr Robert Zacharin, 1920
This chair belonged to Dr Zacharin from 1970 until he donated it to the College in 2009. Its origins prior to this time are uncertain.Gynaecological examination chair, metal painted white, with two detachable metal stirrups with a back panel, seat panel and leg panel. The leg panel can be adjusted upwards to make a table. The back panel has an upright and two reclining positions. The seat panel has a side mechanism that makes the panel tilt backwards, so that a patient can be positioned head downwards with legs upwardsobstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Auvard-style speculum associated with Dr Kelvin Churches, Ramsay
Auvard's specula were used primarily for douching and operating with continuous irrigation. Some examples had fixed weights, others were detachable. This speculum had belonged to Dr Kelvin Churches who was an honorary at the Royal Women's Hospital, Melbourne. Auvard-style speculum, with detachable weight. Inscribed with initials " C.K.C" (for Kelvin Churches). Stamped "RAMSAY", which is the manufacturer."C.K.C" "RAMSAY"obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Pelvimeter associated with Professor Bruce Mayes, W.M.Bailey & Co, c. 1950-1965
Item originally belonged to Professor Bruce Mayes, University of Sydney c1950-65. According to Professor Warren Jones the items had been in a back room of the medical facility and Professor Mayes gave it to Warren Jones, otherwise it may have been thrown out. Warren Jones took the device with him to Adelaide where he practiced from 1975.Pelvimeter. Device consisting of two thin measuring arms with external, circular measure at base of arms. The arms are curved at the distal (far) end so that the points of the arms face each other. Manufacturers stamp "W.M. Bailey & Co."obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Wooden vaginal speculum with plug, Henry Galante et Fils, c. late 19th century
The plug (obturator) could be used to apply medication to the mouth of the cervix. Wooden speculums were in use in the second half of the 19th century, before it became commonplace for speculums to be made of metal. Henry Galante was a French instrument maker active from the late 1800s. Speculum consisting of wooden case and introducer. "Galante" inscribed on lower side of case and "2" near the top of the case."Galante"obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Carved wooden figurine of an obstetrician, Germany, Jaschke Pretzl, c. 1950s
This is a German made figurine, attributed to Jaschke Pretzl. Loosely translated, the label text on the figurine says 'Obstetrician', that the birth was happy, and that the father and child are well. Stamp printed on underside of base says that this is a hand-carved figure.Carved wooden figurine. Depicts a man in a white coat and glasses, with a receding hairline, holding a baby. He is holding the baby's legs in his left hand, and supporting the baby's back and neck with his right hand. The figure is atop a small wooden plinth, one side of which carries handwriting that reads 'Geburtshelfer/Geburt glucklich verlan fen,/Vater und Kind wohlanf!' The underside of the plinth is printed with a stamp that reads 'Handgeschnitzte/ Figur'. There is a third word at the centre of the stamp on the underside of the figurine, but it has faded and is illegible. 'Geburtshelfer/Geburt glucklich verlan fen,/Vater und Kind wohlanf!'/'Handgeschnitzte/ Figur'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Carved wooden figurine of a neurologist, Germany, Jaschke Pretzl, c. 1950s
This is a German made figurine, attributed to Jaschke Pretzl. Loosely translated, the label text on the figurine says 'Neurologist' and 'Out! They're getting on my nerves!'. Stamp printed on underside of base says that this is a hand-carved figure.Carved wooden figurine. Depicts a man in a white coat, red tie, and glasses, standing with his hands at his side. He has a receding hairline, and a mohawk-like hair style. The figure is atop a small wooden base, one side of which carries handwriting that reads 'Nervenarzt/Raus! Sie gehen mir/auf die Nerven!' The underside of the plinth is printed with a stamp that reads 'Handgeschnitzte/Pretxl/Figur'. 'Nervenarzt/Raus! Sie gehen mir/auf die Nerven!'/'Handgeschnitzte/Pretxl/Figur'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Carved wooden figurine of a gynaecologist, Germany, Jaschke Pretzl, c. 1950s
This is a German made figurine, attributed to Jaschke Pretzl. Loosely translated, the label text on the figurine says 'Gynaecologist' and 'Commit to the women tenderly!'. Stamp printed on underside of base says that this is a hand-carved figure.Carved wooden figurine. Depicts a man in a white coat, with grey trousers, a red vest, blue tie, and white shirt collar, standing with his right hand in his pocket. He is holding a document in front of his chest in his left hand. The figure is atop a small wooden base, one side of which carries handwriting that reads 'Frauenarzt/Kommit den Frauen zart entgegen! ' The underside of the plinth is printed with a stamp that reads 'Figur/Handgeschnitzt/hand-carved'. 'Frauenarzt/Kommit den Frauen zart entgegen!'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Carved wooden figurine of a doctor holding a baby
The origin of this statue is unknown, but it may possibly be German.Carved wooden figurine of a doctor holding a baby. The doctor is male, and is wearing spectacles and full surgical attire, consisting of a green surgical gown and cap, with a white surgical mask. Brown trouser cuffs and black shoes are visible below the gown. The doctor is holding a baby by its ankles in his left hand, and is holding his right hand as if about to pat hit the baby on the bottom. The baby is facing the doctor, head pointing towards the ground. Sticker on base of figurine bears the handwritten initials 'MW'.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Porcelain figurine of a doctor holding a baby
Porcelain bisque figurine of a doctor holding a baby. The doctor is male, with brown hair and a moustache. He is wearing a white surgical gown and cap, with brown trouser cuffs and black shoes visible below the gown. The doctor is holding a baby by its ankles in his left hand, and is holding his right hand with the palm facing towards the baby. The baby is facing the doctor, head pointing towards the ground. The figure is supported by a plinth behind the right leg, and is standing on a flat, sandy coloured base.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Porcelain figurine of a doctor holding a monkey
The writing is unclear, but the name of the artist for this piece may be Bessi.Colourful porcelain figurine of a doctor holding a monkey. The doctorhas yellow hair and is wearing a white coat, with a white substance on their hands resembling gloves. They are wearing bright green and orange striped pants below the gown, and green high heeled shoes. The doctor is holding a monkey by its ankles in their left hand, and is holding the palm of his right hand on the monkey's bottom. The doctor is standing behind a small white crib, which is covered with a blue and white patterned blanket. The maker's name 'BESSI'(?) and the word 'ITALY' are hand painted on the underside of the crib.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Porcelain figurine of an obstetrician holding a baby, Abbott, 1972
Enduron (methylclothiazide) was a diuretic used to treat high blood pressure and fluid retention. Its use has been discontinued. This object was likely produced as a promotional item by the manufacturers of Enduron.Porcelain figurine of a doctor holding a baby. The doctor has brown hair, is of male appearance, and is dressed in surgical attire, consisting of a white surgical gown and cap. There are some areas of blue detailing on the gown. Blue trouser cuffs and black shoes are visible below the gown. The doctor is holding a baby by its ankles in his left hand, and is holding his right hand against the baby's bottom. The baby is facing to the side, head pointing towards the ground. The figure is standing on a square plinth. Writing printed on the front of the plinth reads 'OBSTETRICIAN/"I just delivered/a president." Writing printed on either side of the plinth reads 'ENDURON/methylclothiazide'. Writing printed on the back of the plinth reads 'ABBOTT 1972'. Sticker attached to underside of statue reads 'THE COBID CORP'.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Porcelain figurine of an obstetrician holding a baby
George Zoltan Lefton, a Hungarian immigrant who came to the United States in 1939, was the driving force behind Lefton China. Although he began his career in clothing and sportswear, his porcelain collecting interest led to the formation of the Lefton Company in 1940. Headquartered in Chicago, the company was a wholesale and marketer of ceramic goods. After the bombing of Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, Lefton helped his friend Nunome, a Japanese American, board up his business to avoid looting. When the war ended, Nunome introduced Lefton to Japanese ceramic manufacturers during the Japanese occupation. Lefton was one of the first American businessmen to work with these manufacturers. (WorthPoint)Porcelain figurine of a doctor holding a baby. The doctor has black hair, is of male appearance, and is dressed in surgical attire, consisting of a short sleeved white surgical gown and cap, brown trousers and black and white shoes. There is a glove protruding from the pocket of the gown at the left hip. The doctor is holding a baby by its ankles in his left hand, and is holding his right hand against the baby's bottom. The baby is crying. The figure is seated on the edge of a stool, and standing on a brown coloured base. There is a copyright symbol (a c inside a circle) printed on the underside of the base of the statue, along with the text 'geo.z.Lefton/THE O.B.' Sticker attached to underside of base reads 'Lefton/TRADE MARK/EXCLUSIVES/JAPAN'.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sculpture - Pewter vignette of an obstetrician observing an antenatal patient, Michael Ricker Pewter
Michael Ricker was a renowned American pewter artist. His most famous piece, entitled 'Park City', was a 30 foot by 10 foot miniature town depicting life at the turn of the 19th century. It was completed in 1986 and presented to former President Gerald Ford. Ford graciously accepted the "key" to Park City and promised a home for the masterpiece in the Smithsonian Institute. (foundantique.com)Pewter sculpture featuring an obstetrician and an antenatal patient. A pregnant woman is lying on a low bench, with her left hand resting on her stomach, and her right arm by her side. She is wearing a dress and shoes, and has her eyes closed. To her right stands the figure of on obstetrician, wearing trousers, a short sleeved shirt, stethoscope and gloves. He is standing straight with his arms at his sides. The entire sculpture is silver in colour.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Collin's-type pelvimeter used by Dr Fritz Duras
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany , and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. Metal pelvimeter. Consists of a device with two arms, which curve into rounded points at their ends. A semi-circular measuring gauge is attached to the end of the pelvimeter.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Uterine catheter used by Dr Fritz Duras
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany , and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. Metal catheter with internal wire. Catheter is in a vague 's' shape, with a thinner and thicker section. A loop at one end it attached to a wire which can be slid in and out of the device. There are two small round attachments at the thinner end of the device which function as grips. obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Tissue forceps used by Dr Michael Kloss
This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss, who was an obstetrician. Dr Kloss used this item in his own practice, before donating the item to the College. Dr Kloss is the son-in-law of Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), a doctor who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany, and Dr Duras came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University.Set of tissue forceps. Made of metal, the forceps resemble long tweezers, with a grip section and a small set of teeth at the end of each arm of the forceps. The proximal end of the forceps is engraved with the word 'Kloss'.'Kloss'obstetrics -
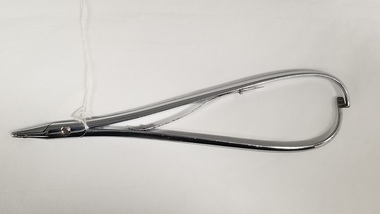 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Needle holder used by Dr Fritz Duras
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany, and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments given to his son-in-law, Dr Michael Kloss, who was an obstetrician. Dr Kloss donated these items to the College. Metal needle holder. The needle holder's overall shape is that of a teardrop, with a rounded handle section narrowing to serrated grip points at one end. The needle holder appears to be made of a plated metal.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Uterine catheter used by Dr Fritz Duras and Dr Michael Kloss
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany, and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments given to his son-in-law, Dr Michael Kloss, who was an obstetrician. Dr Kloss subsequently had it engraved and used it in his own practice, before donating the item to the College. Metal uterine catheter. Thin, curved instrument with two oval shaped fittings attached to the sides of the instrument at the proximal end for grip. There is a seam roughly halfway down the instrument indicating that the halves of the instrument can be separated. One side of the instrument is engraved with the word 'Kloss'.'Kloss'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Uterine catheter used by Dr Fritz Duras
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany, and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments given to his son-in-law, Dr Michael Kloss, who was an obstetrician. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this item to the College. Small metal uterine catheter. Thin, curved instrument with a brass coloured, bell shaped attachment at one end, curving to a hollow tip at the other end. There is a oval shaped fitting attached to the side of the bell attachment.obstetrics -
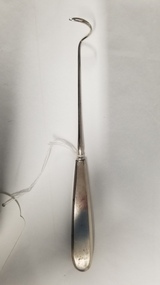 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Cervical suture needle used by Dr Fritz Duras and Dr Michael Kloss
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany, and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments given to his son-in-law, Dr Michael Kloss, who was an obstetrician. Dr Kloss subsequently had it engraved and used it in his own practice, before donating the item to the College. Metal instrument used for cervical sutures. Instrument consists of a handle and shaft. The end of the shaft is curved so as the tip of the instrument is almost perpendicular to the handle. The end of the shaft is in the shape of a loop to allow for sutures to be passed through it. The handle of the instrument is engraved with the word 'KLOSS'.'KLOSS'obstetrics
